1. Introduction
In the frame of bio-circular economy [
1,
2] the replacement of petroleum-based plastics on the eco-friendly biodegradable polymers such as polylactides (PLAs), polyalkanoates (PHAs), poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL), and others, as well the assessment of their decomposition mechanism and exploitation lifetime [
3] are the important ecology and medical tasks. As it known PLA is a linear aliphatic polyester produced from the L and D isomers of lactic acid formed during the fermentation of the natural raw [
4,
5]. This biopolyesters family, as the main commercial product on the market of the biodegradable polymers, is broadly implemented in many areas such as packaging, environmental safety, eco-friendly constructional materials design, biomedicine and others [
6,
7].
Polylactides with diverse chemical structures, crystallinity, and morphology are used as biodegradable, biocompatible, and sustainable plastics. They are successfully acceptable for biomedical implants engineering [
8], drug delivery platforms’ elaboration [
9], separation/filtration membranes design [
10], active packaging implementation [
11], eco-friendly safety providing [
12] and for many others. The PLA mechanical behavior can be compared with conventional synthetic polymers like PP (polypropylene), PS (polystyrene), PVC (polyvinylchloride) that is suitably summarized in a comprehensive work [
13]. And furthermore, tensile and flexural strengths for PLA have the higher values than PVC and PP. Additionally under low and ambient temperatures the bio-polyester given shows an appropriate thermal destruction stability with a wide melt-processing window [
14] and efficient oil/water separation capability [
15]. As the basic factor of climatic change the CO
2 gas emission during PLA biodegradation is approximately 1.60 kg/kg, that is less than for PP (~1.85 kg/kg) and essentially less than for PS (~2.74 kg/kg), PET (~4.15 kg/kg), and nylon (~7.15 kg/kg) biodegradation [
13]. Besides, the substitution of above synthetic polymers with PLA produced on the base of agricultural substrates can potentially lead to the significant decrease in the emission of greenhouse gases [
13]. And finally, concerning the environmental advances of PLA, Vink et al. have very recently reported [
16], that the amount of fossil energy being spent on the PLA fabrication is 25-55% less than the energy required for producing petrol-based plastics.
It is widely recognized that under environmental or exploitation conditions PLA degradability is significantly enhanced when it exposed to UV-light and atmospheric oxygen simultaneously. In this connection the need of careful study of the mechanism of photo oxidation arises with the object to estimate the lifetime of PLA items and to determine the intermediate and terminal products of degradation in term of their toxicity and pollution ability. A significant number of works are presented in the literature that have explored the impact of UV radiation on kinetics and the mechanism of PLA photodegradation where the polyester occurs as the homopolymer, blends, and composites [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21]. Monitoring of molecular mass evolution, analytical evaluation of chemical compositions for intermediate and terminal products of photodegradation, physical-chemical analysis of polymer crystallinity and morphology changes, the test of mechanical behavior deterioration, and others see e. g. [
17,
21,
22]. However, a number of previous studies devoted to photodegradation in the spectral wavelength range above 300 nm where the irradiation energy is too small to disrupt the covalent bonds in PLA backbone [
23]. As is widely acknowledged, PLA items are generally applicable in biomedicine, packaging, and environmental exposition where UV emission occurs at 254 nm for sterilization [
24] and weathering explorations via European standard ISO 4892-2:2013 [
25].
The principal drawbacks of the PLA use in biomedicine comprise its hydrophobicity that can promote inflammation, low number of functional groups participated in cell adhesion that constrains the elaboration of scaffolds and conduits, and weak resistance to hydrolysis [
26]. The biodegradation PLA occurs at relatively harsh conditions when the samples are composted or exposed in sea water [
27]. Therefore, the polyester utilization is challenging the certain problems. One of the ways for tailoring this concern is the blending of PLA with the natural polysaccharides which are lightly released in aqueous media, for example such as cellulose and starch [
28,
29]. After the transition of the polysaccharide from the blend matrix into soil or see water, the integrity of the blends is sufficiently impaired, the inherent surface of PLA being available for enzymatic attack is increased and the rate of biodegradation for the polyester is accelerated essentially. Alternative way to initiate PLA decomposition is its photodegradation under UV irradiation that was explored in a series of pioneer works of Ikada and Ashida [
30,
31]. Here the authors have shown the high efficacy of UV action on polymer wastes processing and the design of plastics with the controlled service live.
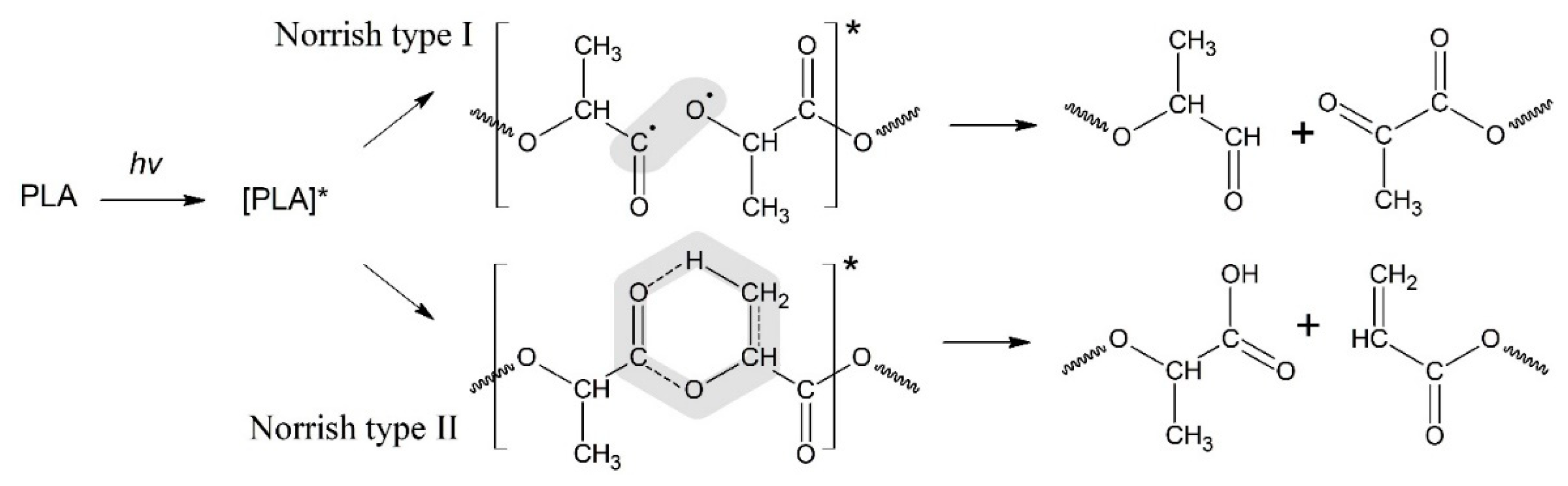
In a series of previous comprehensive publications, the experts have advanced the basic mechanism of photodegradation for polyesters and especially for PLA determined the Norrish I and Norrish II types of polymer chain scission [
17,
32]. The scheme the PLA photodegradation process according to the Norrish I and Norrish II mechanisms is presented in
Figure 1. Meanwhile, the realistic way of PLA decomposition is still under consideration. So, in the above publications, Ikada has claimed that the exposition of PLA to UV irradiation leads to Norrish II-type mechanism mostly, namely that the PLA backbone absorbs an UV photon with a sufficient energy to provide breaking the C-O bonds [
30]. Alternatively, Olewnik-Kruszkowska and coauthor [
23] have proposed another way of degradation where acetic anhydride is involved into the set of radical reactions.
For the Norrish I mechanism of PLA photodegradation is realized through homolytic breaking of the bond C-OR belonging to the carboxylic group that results in the aldehyde and diketone derivatives, while a Norrish II type degradation (
Figure 1) occurs via the formation of six-membered intermediate cycle. However, the attempt of description for the PLA decay in the framework of only one type mechanism does not allow experts to interpret quantitatively the kinetics of polyester photodegradation. The analysis of given situation allows to the authors to suggest that chemical evolution of PLA exposed to UV radiation proceeds more complicative with involving initiating study for the Norrish reactions. Besides, it is appropriate to consider the role of intermolecular interaction of the macro-radicals, leading to branched and cross-linked structures formation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
The polylactide (PLA) grade PLA 4043D (Nature Works, Minnetonka, MN, USA (Mw = 1.3 × 105 g/mol, Tm = 163oC) was used in the work.
2.2. Preparation of Samples
Films were prepared by dissolving PLA in chloroform, which was mixed with mechanical stirring. The solutions were poured onto Petri dishes. The solvent was removed by slow evaporation at room temperature and then at 50 °C until constant weight. The thickness of the films was 0.2–0.3 mm.
2.3. UV Irradiation
The effect of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on PLA films was studied at a wavelength of 253.7 nm, the lamp power (4 Philips TUV lamps) was 11 W. During irradiation, film samples were placed in a chamber where they were exposed to UV radiation. In order to maintain uniform exposure, the samples mounted on the holder rotated uniformly inside the chamber at a speed of 6 rpm. The exposure time was 2, 5, 24 and 144 hours.
2.4. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
The molecular mass characteristics of the samples were determined by means of Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) on a liquid chromatograph by Waters (USA) equipped with refractometric and UV detectors. Eluent - tetrahydrofuran, elution rate 1 ml/min, column temperature 35oC, refractometer temperature 45oC. Polymer samples were dissolved in THF, the solution was filtered through a PTFE filter Anatop 25 (Whatman) 0.2 µm. For measurements, two PL-gel columns connected in series, MIXED-C 5 µm were used. The average molecular weight (Mw) of the PLA samples was calculated using a calibration curve, obtained by means of polystyrene standards with MW from 589 to 3.7 x 106 Da.
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
The thermophysical characteristics of PLA samples exposed to UV irradiation were studied using DSC method on a DSC-204 F1 (NETZSCH-Gerätebau GmbH, Germany) calorimeter at the heating rate of 10 K/min in an inert atmosphere of Ar in the temperature range of 25–200oC. The use of a repeating heating–cooling mode in DSC studies of polymers in order to remove the “prehistory” of their production is generally accepted. However, in this work DSC studies were carried out in one stage mode without a reheating, since we intended to characterize the primary morphology of UV-irradiated PLA samples, rather than “erase their thermal memory” or “thermodynamically balance” their initial structure.
The degree of crystallinity of PLA samples, χ%, was calculated by equation
where
- enthalpy of melting,
- enthalpy of crystallization (enthalpy of "cold" crystallization) and
- the theoretical value of the of 100%-crystalline poly(L-lactide) melting enthalpy (93.6 J/g) [
35].
2.5. NMR Spectrometry
1H NMR spectra (500.18 MHz) were recorded on an Avance III 500 spectrometer (Bruker) in CDCl3.
2.6. FTIR Spectrometry
The infrared spectra of the polyester PLA before and after the UV-radiation has acted on it were acquired with the aid of Bruker Tensor 27 IR Fourier spectrometer with ATR PIKE Miracles™ accessory (PIKE Technologies, Madison, WI, USA) equipped with a germanium (Ge) crystal. IR spectra were recorded in the range of 4000–700 cm−1 with a resolution of 4 cm−1 and averaging over 32 successive scans.
3. Results and Discussion
Our study was aimed to investigate the accelerated aging process of PLA thin films under 253.7 nm UV-C irradiation for an initial 24 hours and continuous irradiation for 144 hours with the use of GPC, NMR, FTIR and DSC methods. The results of analyzes using GPC and DSC methods indicated a significant degree of destructive changes in PLA macromolecules, while spectroscopic methods NMR and FTIR showed maintenance of PLA main structural elements even after a long time of UV exposure. In addition to that, the GPC method displayed the formation of a high-molecular fraction starting from 24 hours of irradiation, and an increase in its content after 144 hours of experiment.
3.1. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
GPC method was used in order to determine the molecular weight distribution (M
w) of oligomers formed during the photodegradation of PLA. The results obtained are presented in
Figure 2 and
Table 1.
From the data presented in
Table 2 it is clearly seen a sharp decrease in M
w just after 2 hours of UV irradiation. However, after 5 hours of UV-exposure, there is a distinct slowdown of the process. Furthermore, PLA samples exposed to irradiation for 24 and 144 hours, in addition to the main photodegradation fractions M
w = 12590 and 2818, contain also the fractions with larger values of M
w* = 120 220 and 48 980, respectively (
Table 1). In order to calculate the percentage of the main fractions obtained after 24 and 144 hours of UV irradiation, the deconvolution of asymmetric peaks (M
w and M
w*) presented in the curves (
Figure 2b) was carried by Fraser-Suzuki algorithm using NETZSCH Peak Separation 2006.01 software [
36,
37,
38] (
Supplementary S1, Figure S1).
Araujo at al. [
39] had reported previously similar results in the GPC study of PLA 4042D photodegradation under UV with λ= 365 nm. Two peaks on chromatograms corresponding to the low and high molecular mass fractions of PLA were detected. We suggested that the accumulation of high molecular fractions under long-term UV irradiation can be explained by intermolecular reactions of PLA macroradicals recombination.
Thus, the GPC results of the PLA photodegradation products suggest a more complex mechanism of photolysis than the mechanism presented previously in the works of Ikada [
30,
31] (
Figure 1).
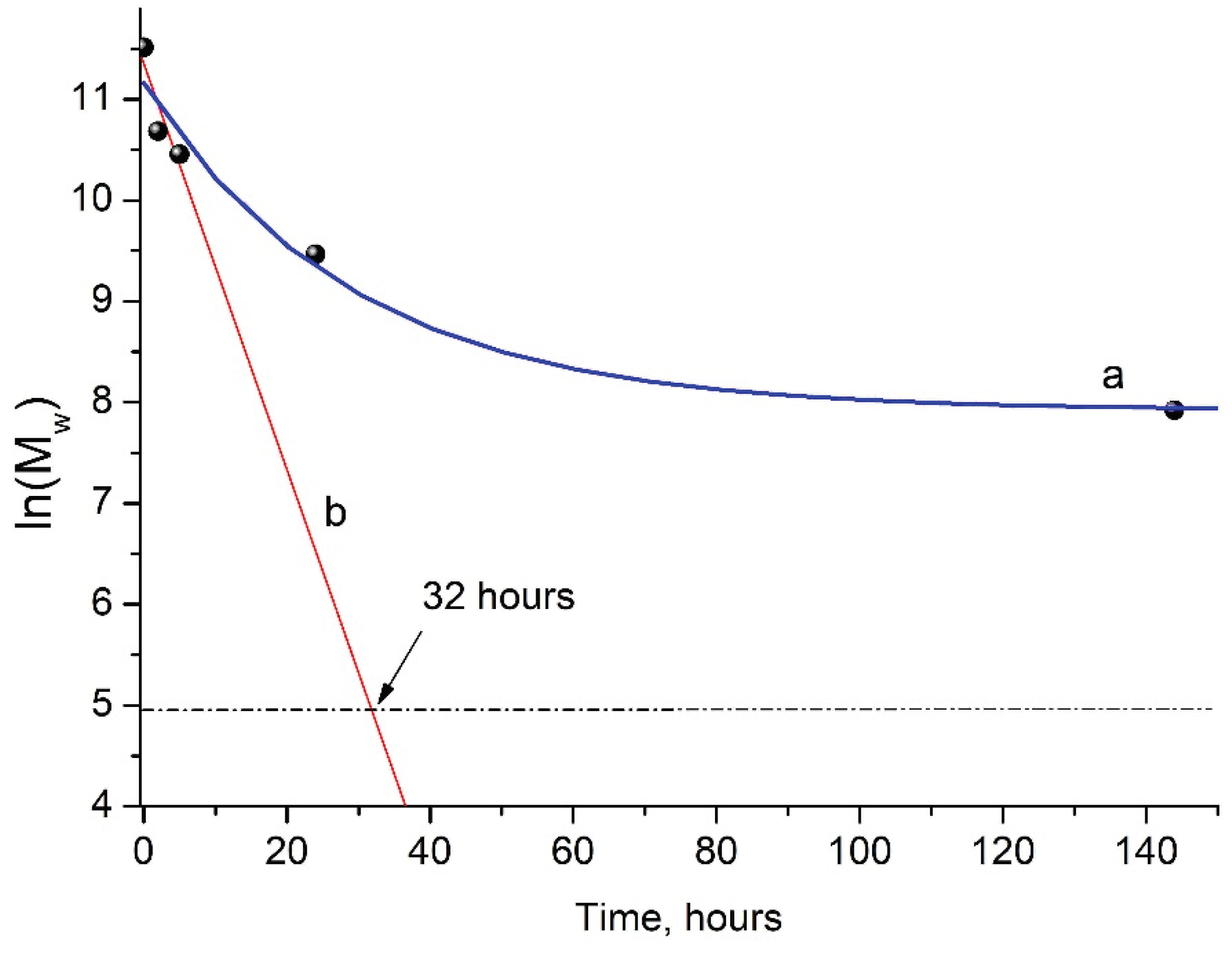
3.2. Kinetics of PLA Photodegradation
As mentioned above, the GPC results showed a steady decrease in M
w of PLA samples under UV irradiation (
Figure 2b), which made it possible to provide a formal kinetic analysis of the process. Data presented on
Figure 3 (kinetic curve a) clearly shows the nonlinear dependence of ln(Mw) on PLA photodegradation time.
At the same time, during the first 5 hours of UV exposure, a quasi-linear dependence of ln(M
w) values on time is observed (
Figure 3, straight line b).
This allowed us to assume the formal first-order kinetic mechanism of PLA photodegradation:
The value of the PLA photodegradation rate constant k
fd= 0.20117 h
-1 = 5.6×10
-5 c
-1 was calculated by the use of linear regression analysis (
Supplementary Figure S2).
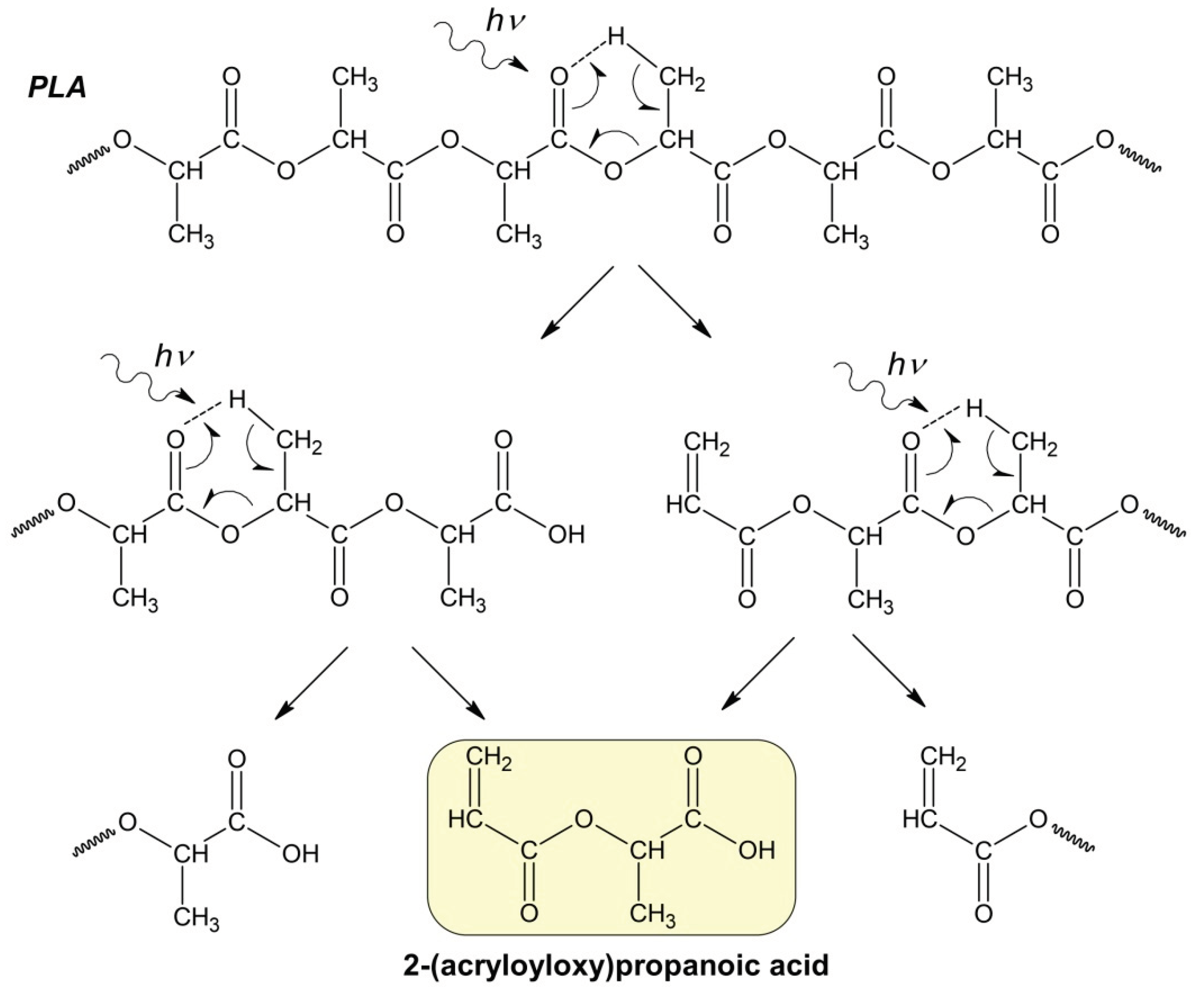
Apparently, at the initial stage of photodegradation (first 5 hours), the PLA macromolecules break up along ester bonds according to the Norrish II mechanism forming oligomeric fractions containing terminal carboxyl and vinyl groups (
Figure 4).
One can suppose that PLA photodegradation proceeds in one stage (first order) according to the Norrish II mechanism while maintaining the flexibility of PLA macromolecules and the equiprobable formation of intermediate six-membered transition states in the monomer units (
Figure 1) throughout the entire interval of UV irradiation time.
In this case, the PLA photodegradation according to Norrish II mechanism will eventually results in a low molecular ultimate product of 2 (acryloyloxy)propanoic acid with M
w = 144 g/mol (ln(M
w) = 4.96). Taking into account the calculated value of reaction rate constant k
fd = 5.6×10
-5 c
-1, it can be determined that the initial PLA with M
w = 13.27×10
5 will decompose completely to the ultimate product of 2-(acryloyloxyloide) with M
w = 144 in 32 hours (
Figure 3b).
Similar data were obtained when studying the degradation of amorphous PLA under the UV irradiation at 300 and 365 nm, where the almost complete destruction of the polymer in 12 hours was explained by the absence of PLA crystalline phase [
30]. This is probably why, with longer UV irradiation of PLA, a decline in the rate of photodegradation was observed (
Figure 3, curve a). This fact may be associated with the increasing role of recombination reactions of primary PLA macroradicals by restoring the original bonds, as well as with the simultaneous occurrence of intermolecular recombination reactions of macroradicals of neighboring chains, which is confirmed by GPC data (
Table 1). These reactions reduce the overall rate of the PLA photodegradation process, as a result of which a nonlinear dependence of ln(M
w) vs. time is observed (
Figure 3a). An additional factor slowing down the process is the presence of a hard crystalline phase in the PLA matrix.
It can be assumed that the crystalline fragments of PLA macrochains are under various strains preventing the formation of six-membered transition states necessary for the implementation of photodegradation by the Norrish II mechanism. That is why, the decomposition of PLA under the influence of UV irradiation by the Norrish I mechanism becomes preferable.
In order to determine the content of crystalline phase in PLA samples exposed to UV radiation, we conducted DSC experiments.
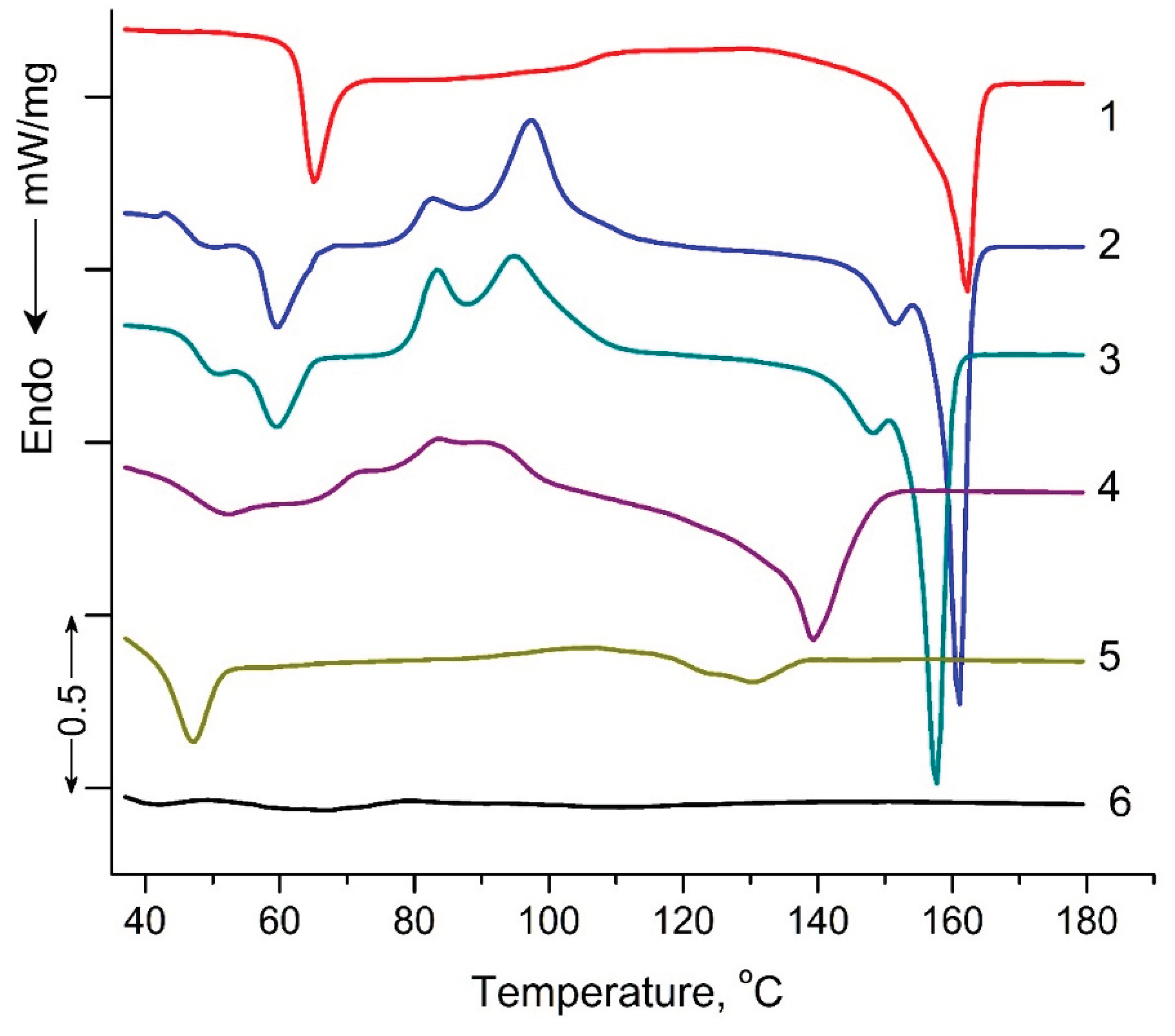
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
Figure 5 shows DSC thermograms of PLA samples exposed to UV-irradiation. Characteristic DSC parameters: glass transition
Tg, peak temperatures for cold crystallization
Tcc and melting
Tm, peak temperature of enthalpy relaxation
Tr, characteristic enthalpies associated with cold crystallization Δ
Hcc and melting Δ
Hm, degree of crystallization (χ) and are summarized in
Table 2. Small "relaxation" effects in PLA samples (except of PLA exposed to UV irradiation for 144 hours) illustrated by endothermic heat capacity peaks (
Tr) can be seen at temperature above the
Tg (
Figure 5). These peaks characterize the phenomenon of enthalpy relaxation, which is associated with the mobility and the recovery of PLA chains to their thermodynamic equilibrium status at a temperature above
Tg. As can be seen from the figure 5, а transition from a glassy to a highly elastic state was observed for all PLA samples in the temperature range of 63.5 - 35.6°C. At the same time, the glass transition temperature (T
g) values decrease as the UV exposure time of the samples increases from 63.5°C for the original PLA sample to 35.6°C for the PLA sample UV-irradiated for 144 hours (
Table 2). At temperatures above 90°C, for all PLA compositions exposed to UV-irradiation, except of the PLA sample UV-irradiated for 48 and 144 hours, the exothermic effect of “cold crystallization” was observed (
Table 2). It is noteworthy that for PLA samples exposed to UV irradiation for 2, 5 and 24 hours, a double exo-peak of cold crystallization is observed in
Figure 5, which is characteristic of the formation of two different crystalline PLA forms.
The most interesting research results are the data on the melting temperatures and degrees of PLA samples crystallinity (
Table 2). For the PLA samples exposed to 2, 5, 24, and 48 hours of UV irradiation, similar to cold crystallization, double melting endo-peaks are observed. These peaks are characterized of
α - ordered (orthorhombic) and
α′ – limit disordered (hexagonal) crystalline forms of PLA. At the same time, the degree of crystallinity for PLA samples exposed to 2, 5, 24 and 48 hours of UV irradiation decreases from 20.4 to 5.1%, and the sample exposed to UV irradiation for 144 hours becomes completely amorphous (
Table 2).
DSC results showed significant structural changes in UV-irradiated PLA samples compared to the original polylactide. The most pronounced changes in thermodynamic parameters were observed at the maximum time of UV exposure of PLA (144 hours), which suggests qualitative structural transformations of the sample. In order to specify the structural changes in the irradiated PLA samples, NMR and FTIR methods were used in the work.
3.4. NMR Analysis
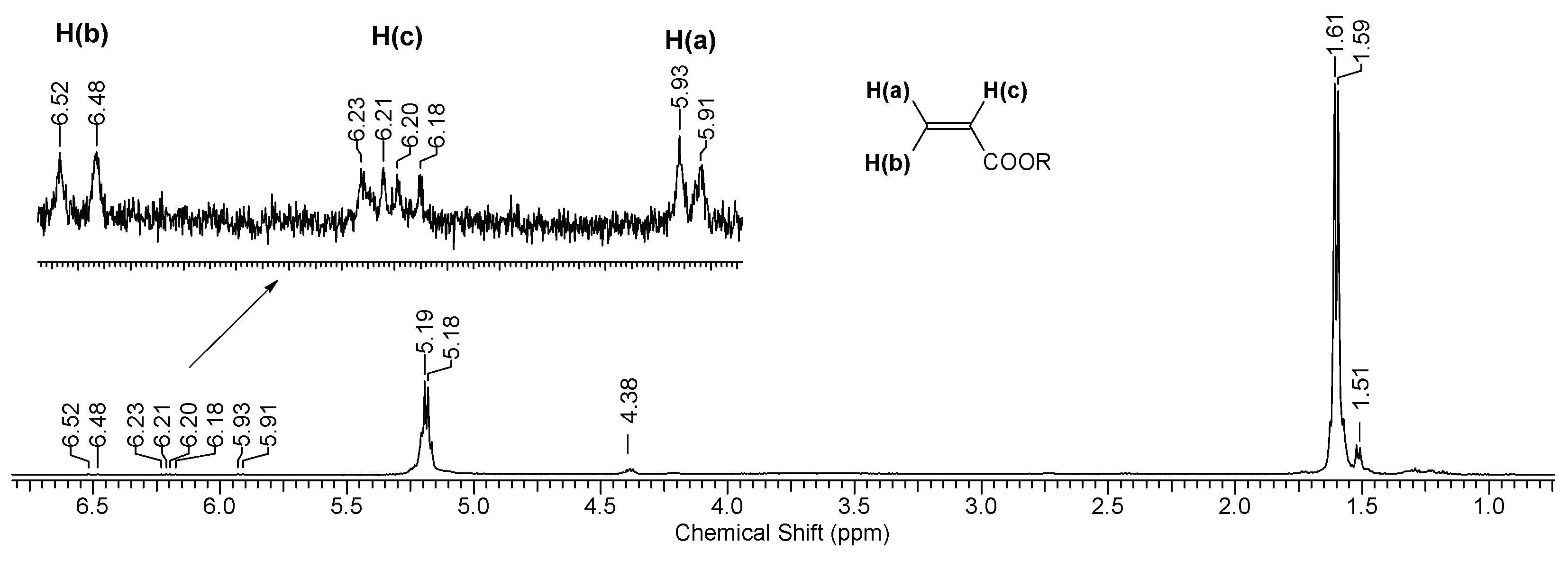
Figure 6 shows the (
1H) NMR spectrum of a PLA sample after 144 hours of UV irradiation. As can be seen from the spectral data the main signals are the multiplets corresponding to the protons of the initial PLA: (
δ, ppm) 1.60 (3H, CH
3) and 5.19 (1H, CH) (
Supplementary S3, Figure S3). Moreover, the spectrum also contains minor signals of the terminal group of lactic acid (-CH(OH)CH
3): (
δ, ppm) 1.51 (3H, CH
3) and 4.38 (1H, CH) (
Supplementary S4, Figure S4). Also, in the spectrum one can observe weak signals that relate to the double bond of the C=C-C(O)O- group (
2JH(a)H(b)=1.5 Hz,
3JH(b)H(c)=17,0 Hz and
3JH(a)H(c) =10.0 Hz) (
Supplementary S5, Figure S5). However, their intensity indicates an insignificant concentration of double bonds in the sample.
Fragments of the NMR spectrum of pristine PLA and PLA after 144 hours of UV irradiation show an increase in the number of -CH(OH)CH
3 end groups (
Figure 7b). This is evidenced by the ratio of the integral intensities of protons belonging to the polymer chain (5.19 ppm) and terminal groups (4.38 ppm).
Thus, based on the NMR data (
Figure 6 and
Figure 7), we can conclude that PLA macromolecules decompose in at least two directions under UV exposure. As a result of one of them, double C=C bonds are formed with the participation of CH
3 groups, which may be associated with photodissociation of PLA according to the Norrish II mechanism (
Figure 1). However, the very low intensity of signals from vinyl protons in the NMR spectrum (
Figure 6) indicates the weakly expressed nature of this mechanism. Another direction of PLA photolysis is the destruction of the ester bond without the participation of the CH
3 group, which can be explained by hydrolytic processes involving traces of atmospheric water. This direction was studied in the work of Copinet
et.
al. [
40], when UV irradiation of PLA was carried out under conditions of high humidity. It was shown that in this case hydrolytic processes are significantly intensified. NMR analysis also showed that the main structural fragments of PLA are preserved even in the case of the formation of oligomers identified using GPC. Similar characteristics of structural changes in PLA were found by FTIR analysis.
3.5. FTIR Analysis
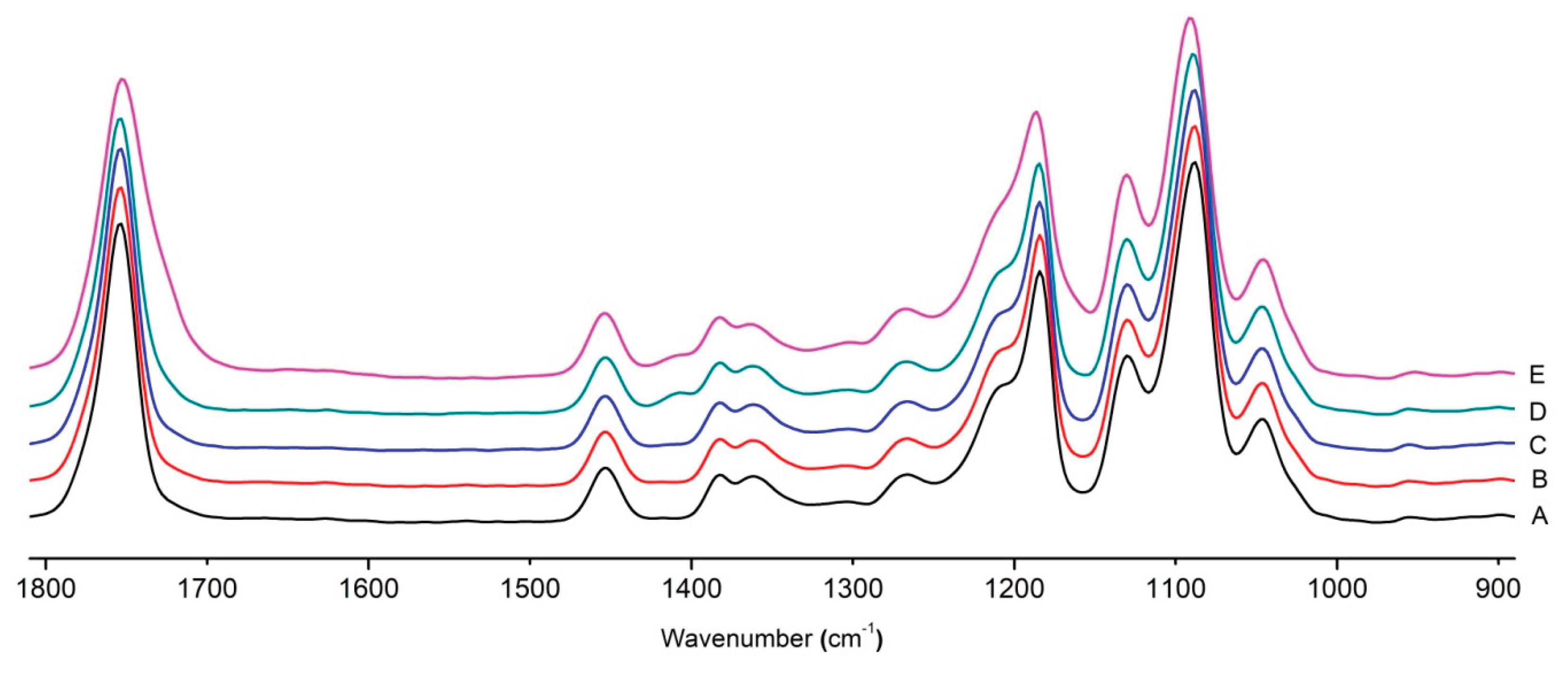
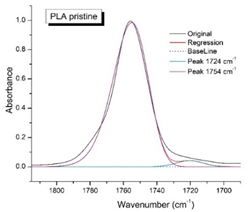
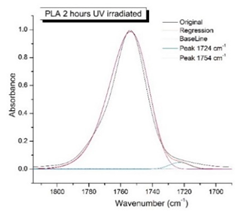
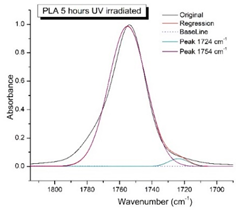
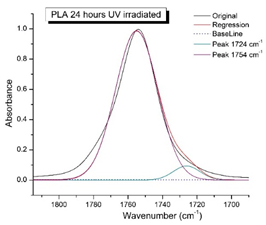
Figure 8 shows the IR spectra of PLA samples at different times of UV irradiation. The main characteristic frequencies of the PLA spectra of exposed to UV irradiation are given in
Table 3.
Significant changes can be observed in the 1235-1160 cm-1 area of asymmetric vibrations of the C-C(O)-O group [
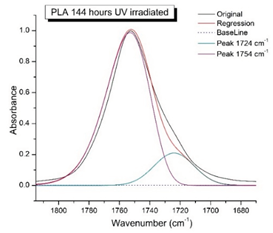
41]. In this region, a broadening of the absorption bands is observed, which is especially noticeable for the sample exposed to UV irradiation for 144 hours. One can also note the broadening of the band at 1754 cm
-1 related to the carbonyl group C=O [
41,
42,
44] due to the formation of a poorly resolved peak at 1724 cm
-1. Apparently, this peak belongs to the carbonyl of the ester group, the spatial configuration and environment of which differs from the carbonyl in the original
L-PLA. Meanwhile the intensity of this peak increases with time of UV irradiation. To quantify the obtained FTIR data, peak separation (deconvolution) of the peaks in the region of 1850-1680 cm
-1 belonging to the C=O stretching vibrations of ester groups was carried out. Deconvolution of the overlapping FTIR peaks at 1724 and 1754 cm
-1 was performed using NETZSCH Peak Separation 2006.01 program employing the GAUSS algorithm for symmetric signals [
38] (
Table 4).
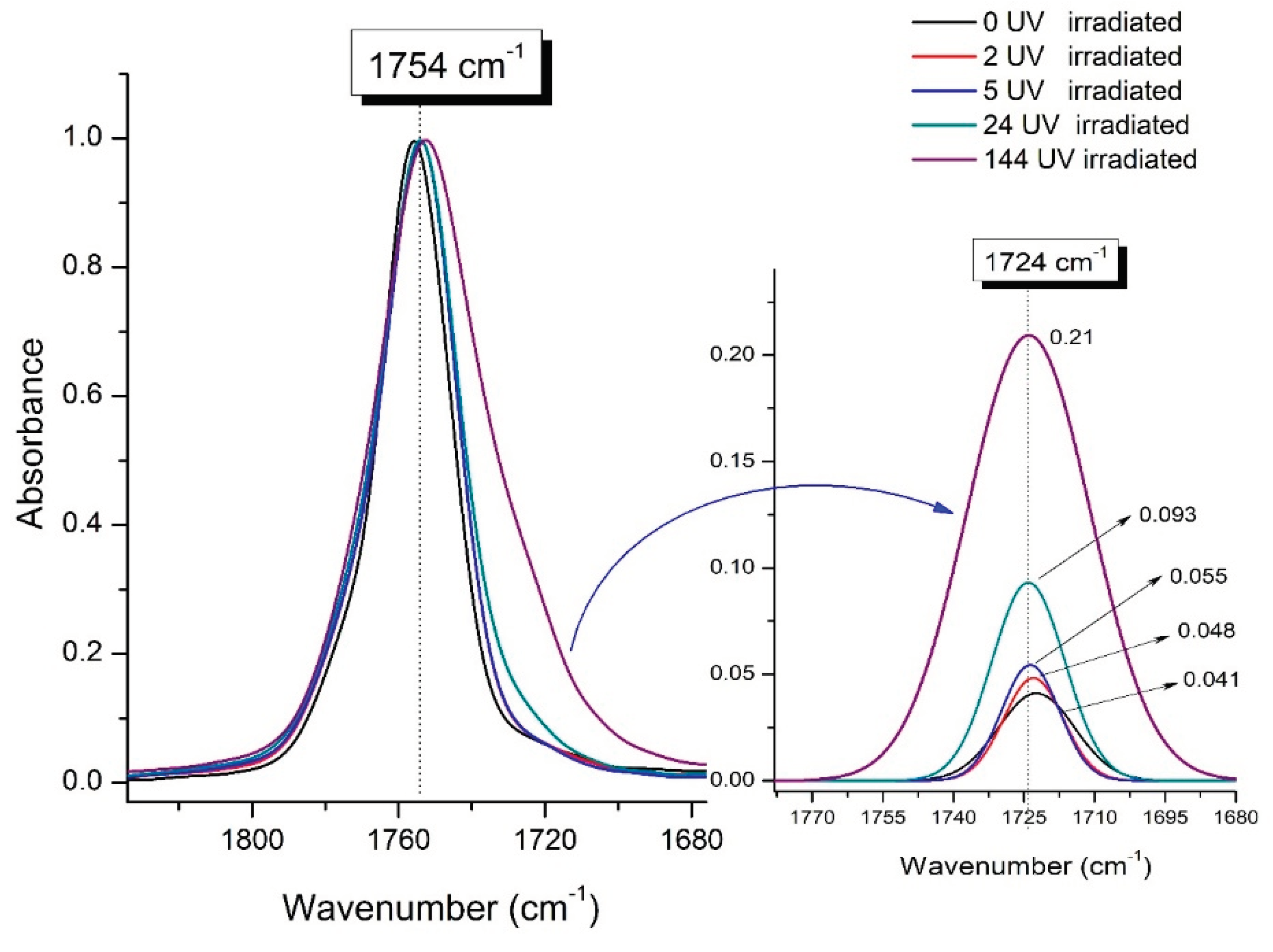
Figure 9 presents evolution of the broadening of the main C=O peak at 1754 cm
-1 (left graph), as well as the change in intensity of the peak at 1724 cm
-1 (right graph). The data of peaks intensity at 1724 cm
-1 presented in
Table 4.
Figure 9 (right graph) shows that the intensity of the peak at 1724 cm
-1 rises as the UV exposure time of PLA increases. At the same time, according to NMR (
Figure 6,
Supplementary S3, Figure S3, Supplementary S4, Figure S4), the basic structure of polyester skeleton is preserved. In addition, the DSC results show complete amortization of PLA sample after 144 hours of UV exposure, (
Figure 5, curve 6). Since NMR and FTIR data of this sample don’t indicate qualitative chemical changes in the basic structure of polymer, this phenomenon may be due to the tautomeric transformations in PLA macromolecules under the UV influence. As a result, some of the units transform from
L- to the
D-configuration. Previously, Yasuda
et al. [
45] with the use of
13C NMR analysis, discovered racemization mainly at the terminal units of PLA macromolecules upon UV irradiation.
At the same time, the spatial environment of the carbonyl groups of the ester’s changes, which is reflected in the FTIR spectrum of the irradiated PLA samples by increasing the peak intensity at 1724 cm
-1 (
Figure 9).
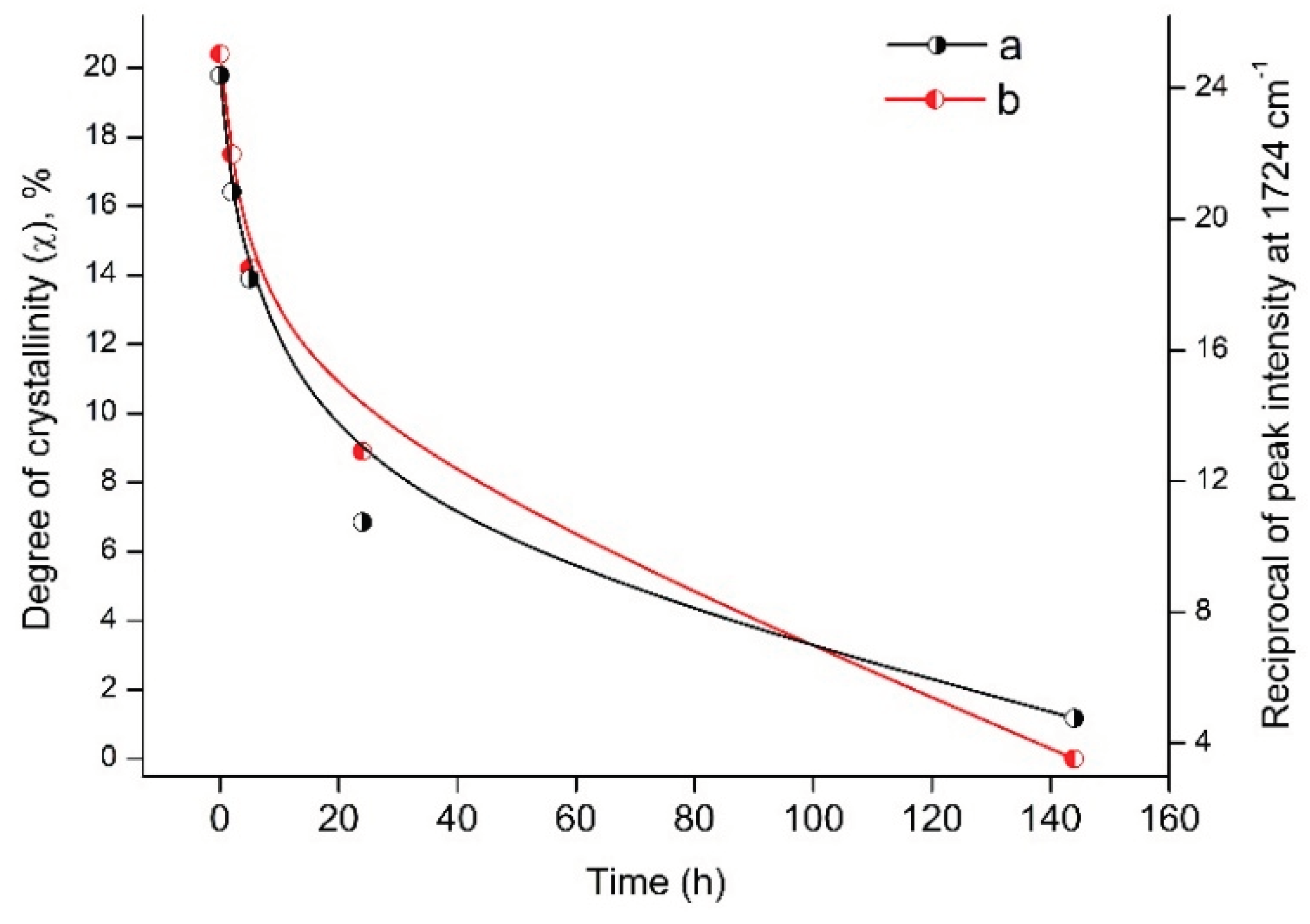
Analysis of DSC and FTIR data indicates a similar behavior of the degree of crystallinity (χ) and the reciprocal value of intensity peak at 1724 cm
-1 depending on the time of UV irradiation of PLA samples (
Figure 10).
This correlation between DSC and FTIR results indicates significant morphological changes in PLA structure under UV exposure.
4. Conclusions
Summarizing all findings obtained by the combination of GPC, NMR, FTIR and DSC techniques, a significant impact of PLA morphology on its photodegradation has been indicated.
At the initial stage, during the first 5 hours, the photolysis of PLA develops intensively in accordance to the Norrish II mechanism of the ester bond cleavage that was supported with GPC data. After this time period, the rate of PLA photodegradation slowed down remarkably. For the first time, this study showed that a distinctive feature of prolonged UV exposure is the emergence of intra- and intermolecular radical recombination reactions, leading to the formation of a high-molecular fraction of PLA decomposition products.
Along with that, it was found that long-term UV irradiation leads to an increase in the intensity of the absorption stretching vibration band for the carbonyl of the ester groups, the spatial configuration and environment of which differs from the C=O in the original L-PLA. Apparently, its formation is associated with tautomeric transformations in individual polymer units, resulting in accumulation of D-isomeric groups which impede PLA crystallization.
This conclusion was confirmed by DSC results of a PLA sample irradiated for 144 hours, demonstrating its complete amorphization due to the accumulation of D-lactide units preventing the polymer crystallization. Analysis of NMR data enables the authors to suggest that PLA molecules can be decomposed to form the double bonds C=C according to the Norrish II mechanism. Besides, the very low intensity of vinyl protons in the NMR spectrum after 144 h of UV irradiation indicates a Norrish I photodegradation pathway. Moreover, under prolonged UV exposure, the photodegradation of PLA is accompanied by intra- and intermolecular recombination reactions, which depend on the polymer morphology changes.
As a result of the aforementioned, it is reasonable to conclude that PLA photolysis is a complex set of physicochemical processes comprising the combination of Norrish I and II mechanisms as well as the formation of high molecular fraction of PLA decomposition products.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1: Deconvolution results of the ln(Mw) curves for PLA-24 (a) and PLA-144 (b); Figure S2: Kinetic analysis of PLA photodegradation; Figure S3: 1H NMR spectrum of neat PLA (500.18 MHz, CDCl3). δ ,ppm: 1,60 (3H, CH3); 5,19 (1H, CH); 4,38 (1H, CH); Figure S4. 1H NMR spectrum of PLA after 144 hours of UV irradiation (500.18 MHz, CDCl3). δ , ppm: 1.60 (3H, CH3); 5.19 (1H, CH); 4.38 (1H, CH); 5.91, 6.21, 6.52 (CH2=CH-); Figure S5. COZY (H, H) spectrum of PLA after 144 hours of UV irradiation. 2JH(a)H(b)=1.5 Hz, 3JH(b)H(c)=17,0 Hz and 3JH(a)H(c) =10.0 Hz.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L.; Data curation, S.R.; Funding acquisition, A.I.; Investigation, L.Z., S.U., E.P., I.L. and N.S., Methodology, Yu.M.; Project administration, A.B.; Supervision, A.B.; Validation, O.K.; Visualization, L.Z.; Writing—original draft, L.Z., O.K.; Writing—review and editing, S.L., S.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was performed under financial support of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (contracts no. 122041300207-2, 122040400099-5 and АААА-А19-119041090087-4).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Marshall, D.; O’Dochartaigh, A.; Prothero, A.; Reynolds, O.; Secchi, E. Are you ready for the sustainable, biocircular economy? Business Horizons 2023, 66, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, N. M. A readiness level framework for sustainable circular bioeconomy. EFB Bioeconomy Journal 2022, 2, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laycocka, B.; Nikolic, M.; Colwell, J.M.; Gauthier, E.; Halley, P.; Bottle, S.; George, G. Lifetime prediction of biodegradable polymers. Progress in Polymer Science 2017, 71, 144–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalidas, V.K.; Pavendhan, R.; Sudhakar, K.; Sumanth, T.P.; Sharvesh, R.A.; Santhosh, K.S.; Kumar, K.Y. Study of synthesis and analysis of bio-inspired polymers-review. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021, 44, Part–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.; Loong-Tak, L.; Susan, E.M.; Selke, H.T. Poly(lactic acid): Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Applications. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2010, 499 p. [CrossRef]
- Fahim, S.; Chbib, H.; Mahmoud, H.M. The synthesis, production & economic feasibility of manufacturing PLA from agricultural waste. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy 2019, 12, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaei, D.; Alvarez, C.; Mullen, A. M. Biodegradable Packaging Materials from Animal Processing Co-Products and Wastes: An Overview. Polymers (Basel) 2021, 13, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaw, M. Recent advances in bio-medical implants; mechanical properties, surface modifications and applications. Eng. Res. Express 2022, 4, 032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachopoulos, A.; Karlioti, G.; Balla, E.; Daniilidis, V.; Kalamas, N.; Stefanidou, M.; Bikiaris, N.; Christodoulou, E.; Koumentakou, I.; Karavas, E.; Bikiaris, D. Poly(Lactic Acid)-Based Microparticles for Drug Delivery Applications: An Overview of Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, N.; Avhad, M.; Utekar, S.; More, A. Polylactic acid (PLA) membrane—significance, synthesis, and applications: a review. Polymer Bullet. 2023, 80, 1117–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahap, H.; Julianti, E.; Safitri, A.; Jaafar, M. Smart Packaging Based on Polylactic Acid: The Effects of Antibacterial and Antioxidant Agents from Natural Extracts on Physical–Mechanical Properties, Colony Reduction, Perishable Food Shelf Life, and Future Prospective. Polymers 2023, 15, 4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, M.R.; Barlow, C.Y. Life cycle assessments of biodegradable, commercial biopolymers—A critical review. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 2013, 78, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, A.K.; Gupta, M.K.; Singh, H. PLA based biocomposites for sustainable products: A review. Advanced Industrial and Engineering Polymer Research 2023, 6, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Gong, R.H.; Zhou, F.; Li, Y.; Deng, B. Polylactide single-polymer composites with a wide melt-processing window based on core-sheath PLA fiber. Materials and Design 2018, 139, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianchi, C.; Jie, G.; Hao, X.; Jialu, Z.; Hu, N.; Liu, H. One-step fabrication of biodegradable superhydrophobic PLA fabric for continuous oil/water separation. Applied Surface Science 2022, 576, 151766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, E.T.H.; Glassner, D.A.; Kolstad, J.J.; Wooley, R.J.; O'Connor, R.P. The ecoprofiles for current and near-future NatureWorks® polylactide (PLA) production, Ind. Biotechnol. 2007, 58, 58–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ye, G.; Fan, D.; Lu, Y.; Shi, P.; Wang, X.; Bateer, B. Photo-oxidative resistance and adjustable degradation of poly-lactic acid (PLA) obtained by biomass addition and interfacial construction. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2021, 194, 109762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, P.; Lv, P.; Lemstra, P.J.; Cai, X.; Yang, W.; Dong, W.; Chen, M.; Liu, T.; Du, M.; Ma, P. Excellent UV resistance of polylactide by interfacial stereocomplexation with double-shell-structured TiO2 nanohybrids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 49090–49100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Tobias, H.; Morales, G.; Maldonado-Textle, H.; Grande, D. Photo-degradation of electrospun composite mats based on poly(D,L-lactide) submicron fibers and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2018, 152, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchini, S; Fukushima, K. ; Di Blasio, A.; Fina, A.; Frache, A.; Geobaldo, F. Polylactic Acid and Polylactic Acid-Based Nanocomposite Photooxidation. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2919–2926. [CrossRef]
- Gardette, M.; Therias, S.; Gardette, J.-L.; Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. Photooxidation of polylactide/calcium sulphate composites. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2011, 96, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virag, A.D.; Toth, C.; Molnar, K. Photodegradation of polylactic acid: Characterisation of glassy and melt behaviour as a function of molecular weight. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2023, 252, 126336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E.; Koter, I.; Skopinska-Wisniewska, J.; Richert, J. Degradation of polylactide composites under UV irradiation at 254 nm. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry 2015, 311, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, B.M.; Banrud, H.; Boe, E.; Bjordal, O.; Drangsholt, F. Comparison of UV C light and Chemicals for Disinfection of surfaces in hospital isolation units. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2006, 27, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litauszki, K.; Kovacs, Z.; Meszaros, L.; Kmetty, A. Accelerated photodegradation of poly(lactic acid) with weathering test chamber and laser exposure – A comparative study. Polymer Testing 2019, 76, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limsukon, W.; Rubino, M.; Rabnawaz, M.; Lim, L.-T.; Auras, R. Hydrolytic degradation of poly(lactic acid): Unraveling correlations between temperature and the three phase structures. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2023, 217, 110537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, H.; Tao, X. Evaluating and Modeling the Degradation of PLA/PHB Fabrics in Marine Water. Polymers 2023, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogovina, S.Z; Aleksanyan, K.V.; Kosarev, A.A.; Ivanushkina, N.E.; Prut, E.V.; Berlin, A.A. Biodegradable Polymer Composited Based on Polylactide and Cellulose. Polym. Sci. B 2016, 58, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogovina, S.; Prut, E.; Aleksanyan, K.; Krashininnikov, V.; Perepelitsyna, E.; Shaskin, D.; Berlin, A. Сompositions based on starch and Polylactide. Polym. Sci. B 2019, 61, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikada, E. Photo- and bio-degradable polyesters. Photodegradation behaviors of aliphatic polyesters. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol., 1997, 10, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikada, Е.; Ashida, М. Promotion of photodegradation of polymers for plastic waste treatment. Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology 1991, 4, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzarelli, P.; Piredda, G.; La Carta, S.; Mirabella, E.F.; Valenti, G.; Bernet, R.; Impallomen, G. Characterization and laser-induced degradation of a medical grade polylactide. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2019, 169, 108991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyi, V.A.; Kuzivanov, I.M.; Fedorova, I.V.; Shumova, O.A.; Tropnikov, E.M.; Istomina, E.I.; Chukicheva, I.Y.; Kuchin, A.V. Tailoring Photoprotection of Polylactide with New Isobornyl Derivatives of Phenol and Aniline. Polymers 2023, 15, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Echizen, Y.; Nishimura, Y. Photodegradation of biodegradable polyesters: A comprehensive study on poly (l-lactide) and poly(l-caprolactone). Polymer Degradation and Stability 2006, 91, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.; Sterzel, H.; Wegner, G. Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reactions. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 1973, 521, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.D.; Suzuki, E. Resolution of overlapping bands. Functions for simulating band shapes Analytical Chem. 1969, 41, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexeeva, O.; Olkhov, A.; Konstantinova, M.; Lomakin, S.; Podmasterev, V.; Siracusa, V.; Iordanskii, A. Improvement of the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Polylactic Acid Films by Addition of Glycero-(9,10-trioxolane)-Trialeate. Polymers 2022, 14, 3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opfermann, J. Rechentechnik/Datenverarbeitung 1985, 22, 26–27.
- Araujo, S.; Sainlaud, C.; Delpouve, N.; Richaud, E.; Delbreilh, L.; Dargent, E. Segmental Relaxation Dynamics in Amorphous Polylactide Exposed to UV Light. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2022, 223, 2200085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copinet, A.; Bertrand, C.; Govindin, S.; Coma, V.; Couturier, Y. Effects of ultraviolet light (315 nm), temperature and relative humidity on the degradation of polylactic acid plastic films. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kister, G.; Cassanas, G.; Vert, M. Effects of morphology, conformation and configuration on the IR and Raman spectra of various poly(lactic acid)s. Polymer 1998, 39, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuniarto, K.; Purwanto, Y.A.; Purwanto, S.; Welt, B.A.; Purwadaria, H.K.; Sunarti, T.C. Infrared and Raman studies on polylactide acid and polyethylene glycol-400 blend. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2016, 1725, 020101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaurio, E. , Lopez-Rodriguez, N., Sarasua, J. R. Infrared Spectrum of Poly(l-lactide): Application to Crystallinity Studies. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 9291–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogovina, S.; Lomakin, S.; Usachev, S.; Yakhina, A.; Zhorina, L.; Berlin, A. Thermal Behavior of Biodegradable Compositions of Polylactide and Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) with Chitosan and the Effect of UV Radiation on Their Structure. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, N.; Tsukegi, T.; Shirai, Y.; Nishida, H. Characteristic Chain-End Racemization Behavior during Photolysis of Poly(L-lactic acid). Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3299–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Schemes of the PLA photodegradation process according to the Norrish I and Norrish II mechanisms.
Figure 1.
Schemes of the PLA photodegradation process according to the Norrish I and Norrish II mechanisms.
Figure 2.
Chromatograms (a) and Mw curves (b) of samples of initial PLA (1) and PLA after 2 (2), 5 (3), 24 (4) and 144 (5) hours of UV irradiation.
Figure 2.
Chromatograms (a) and Mw curves (b) of samples of initial PLA (1) and PLA after 2 (2), 5 (3), 24 (4) and 144 (5) hours of UV irradiation.
Figure 3.
Kinetic curve of PLA photodegradation (a); linear dependence of ln(M
w) vs. time (b) according to regression analysis data (
Supplementary Figure S2).
Figure 3.
Kinetic curve of PLA photodegradation (a); linear dependence of ln(M
w) vs. time (b) according to regression analysis data (
Supplementary Figure S2).
Figure 4.
Hypothetical mechanism of PLA photodegradation (Norrish II) according to the formal first-order kinetic equation.
Figure 4.
Hypothetical mechanism of PLA photodegradation (Norrish II) according to the formal first-order kinetic equation.
Figure 5.
DSC heat flow curves of pristine PLA (1), PLA UV irradiated for: 2 (2), 5 (3), 24 (4), 48 (5), 144 (6) hours.
Figure 5.
DSC heat flow curves of pristine PLA (1), PLA UV irradiated for: 2 (2), 5 (3), 24 (4), 48 (5), 144 (6) hours.
Figure 6.
1H NMR spectrum of PLA after 144 hours of UV irradiation.
Figure 6.
1H NMR spectrum of PLA after 144 hours of UV irradiation.
Figure 7.
Fragments of NMR spectra related to the chemical shifts of protons (5.19 ppm) of the PLA polymer chain at the tertiary carbon atom and terminal CH3 groups (4.38 ppm): (a) initial PLA, (b) PLA after UV irradiation (144 h).
Figure 7.
Fragments of NMR spectra related to the chemical shifts of protons (5.19 ppm) of the PLA polymer chain at the tertiary carbon atom and terminal CH3 groups (4.38 ppm): (a) initial PLA, (b) PLA after UV irradiation (144 h).
Figure 8.
FTIR spectra of pristine PLA (A) and after UV irradiation: B (2), C (5), D, (24), E (144) hours.
Figure 8.
FTIR spectra of pristine PLA (A) and after UV irradiation: B (2), C (5), D, (24), E (144) hours.
Figure 9.
Evolution of the spectral band at 1754 cm-1, attributed to the carbonyl group C=O in PLA (left graph); changes in intensity peak at 1724 cm-1, belonging to the carbonyl ester group obtained using the regression analysis procedure (right graph).
Figure 9.
Evolution of the spectral band at 1754 cm-1, attributed to the carbonyl group C=O in PLA (left graph); changes in intensity peak at 1724 cm-1, belonging to the carbonyl ester group obtained using the regression analysis procedure (right graph).
Figure 10.
Dependence of the degree of crystallinity (χ) and the reciprocal value of the peak intensity at 1724 cm-1 on the time of UV irradiation of PLA samples.
Figure 10.
Dependence of the degree of crystallinity (χ) and the reciprocal value of the peak intensity at 1724 cm-1 on the time of UV irradiation of PLA samples.
Table 1.
Values of the weight average mass Mw, polydispersity PD (Mw/Mn) and percentage of the main photodegradation fraction for PLA samples at different UV irradiation time.
Table 1.
Values of the weight average mass Mw, polydispersity PD (Mw/Mn) and percentage of the main photodegradation fraction for PLA samples at different UV irradiation time.
| UV irradiation time for PLA films (h) |
Mw/ Mw* |
PD |
Percentage of main fractions (Mw and Mw*) |
| 0 |
132700 |
2.4 |
100 |
| 2 |
46770 |
3.3 |
100 |
| 5 |
34670 |
2.3 |
100 |
| 24 |
12590/120220* |
2.1 |
83.2/16.8* |
| 144 |
2818/48980* |
1.9 |
76/24* |
Table 2.
DSC parameters of thermal transitions observed in PLA samples exposed to UV irradiation.
Table 2.
DSC parameters of thermal transitions observed in PLA samples exposed to UV irradiation.
| Sample |
Tg (oC) |
Tr (oC) |
Tcc (oC) |
Tm (oC) |
ΔHcc (J/g)
|
ΔHm (J/g)
|
χ (%) |
| PLA |
63.5 |
65.1 |
n/a |
162.0 − n/a |
n/a |
-19.1 |
20.4 |
| PLA UV irradiated for 2 hours |
57.9 |
59.7 |
97.3 – 82.9* |
161.0 − 154.2* |
21.2 |
-37.5 |
17.5 |
| PLA UV irradiated for 5 hours |
57.3 |
59.6 |
94.7 − 83.1* |
157.3 − 148.3* |
28.3 |
-41.6 |
14.2 |
| PLA UV irradiated for 24 hours |
49.4 |
54.2 |
92.1 − 83.5* |
139.3 − n/a |
11.0 |
-19.4 |
8.9 |
| PLA UV irradiated for 48 hours |
45.0 |
47.5 |
n/a |
130.5 − 129.3* |
n/a |
-4.8 |
5.1 |
| PLA UV irradiated for 144 hours |
35.6 |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
n/a |
− |
Table 3.
Assignment of bands in the IR spectra of PLA samples after UV irradiation.
Table 3.
Assignment of bands in the IR spectra of PLA samples after UV irradiation.
| Wavenumber (cm-1) |
Spectral assignment |
Literature |
| 1454 |
CH3 asymmetric oscillatory mode |
[41,42] |
| 1410 |
This band appears as a result of UV irradiation (OC-OH) |
|
| 1382 |
CH3 symmetric strain vibration |
[41] |
| 1361 |
CH deformation and asymmetric bands |
[42] |
| 1269 |
mixed band; CH bending vibrations and C-CO-C stretching asymmetric vibrations |
[41,43] |
| 1211 - 1184 |
asymmetric vibrations of the C-CO-O group and bending vibrations of CH3
|
[41] |
| 1130 |
CH3 asymmetric rocking vibration |
[41] |
| 1087 |
C-O-C symmetric vibrations |
[41] |
| 1047 |
C-CH3 stretching vibrations |
[41] |
Table 4.
The deconvolution results of peaks in the 1850-1680 cm-1 region.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).