Introduction
The incidence of bacterial STIs in general, but syphilis in particular, has recently increased dramatically in a number of countries, including Belgium [
1]. These increases have led to calls for novel measures to reverse this trend. One of the most promising interventions is the ingestion of doxycycline after condomless sex (Doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis or doxy-PEP), which has been shown to reduce the incidence of syphilis, chlamydia and possibly gonorrhoea in men who have sex with men (MSM) [
2,
3,
4]. These findings have led a number of organizations, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the European AIDS Clinicians Society (EACS), to promote the use of doxy-PEP in sub-populations of MSM [
5]. We have calculated that the introduction of doxy-PEP in Belgian HIV-pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) cohorts would increase the consumption of doxycycline by up to 88-fold [
6]. This intense consumption of doxycycline could induce and select for antimicrobial resistance (AMR) to tetracyclines and other antimicrobials in a range of bacterial species [
7,
8,
9]. Doxycycline is a vital backup medication for individuals who cannot receive intramuscular penicillin due to frequent stock-outs, silicone implants or penicillin allergy [
10]. If doxy-PEP were to induce tetracycline resistance in
Treponema pallidum subsp.
pallidum, the causative agent of syphilis, this would have far-reaching consequences.
Previous genotypic assessments of
T. pallidum have not found mutations that have been predicted to cause tetracycline resistance [11, 12]. One exception is a study from China that detected the
tetB gene directly from 15/171 syphilitic lesions via PCR amplification [
13]. Concerns have, however, been raised that the
tetB genes detected represented contamination from other bacteria present in these clinical samples [
14]. Because
T. pallidum is not known to contain any mobile elements, point mutations in specific regions of the gene encoding the 16S rRNA or specific ribosomal proteins would be the most plausible pathway to tetracycline resistance [12, 15]. Furthermore, A2058G and A2059G mutations in
T. pallidum's 23S rRNA that confer resistance to macrolides have arisen independently in multiple lineages of
T. pallidum and spread to attain prevalences close to 100% [16, 17]. The 16S and 23S rRNA are part of the same single-copy operon in
T. pallidum, and thus, point mutations are possible in the 16S rRNA gene.
T. pallidum is challenging to culture
in vitro, and thus far, a single study has established that the doxycycline MICs of the four strains assessed were between 0.06mg/L to 0.1mg/L [
18]. No study has attempted to induce tetracycline resistance
in vitro or
in vivo. For such studies and for the evaluation of suspected tetracycline resistance in human infections, it would be useful to know which resistance mutations are possible based on what resistance-associated mutations occur in related bacterial species. This study assesses the occurrence and prevalence of tetracycline resistance associated with chromosomal mutations in
Spirochetales. The
Spirochetales order contains three families:
Spirochaetaceae, Brachyspiraceae, and
Leptospiraceae. Previous studies have found that mutations in 16S,
rpsC and
rpsJ have been shown to be associated with tetracycline susceptibility in several other spirochaetes, such as
Borrelia spp., and
Leptospira spp. [
19,
20,
21].
Materials and Methods
Dataset for Analysis
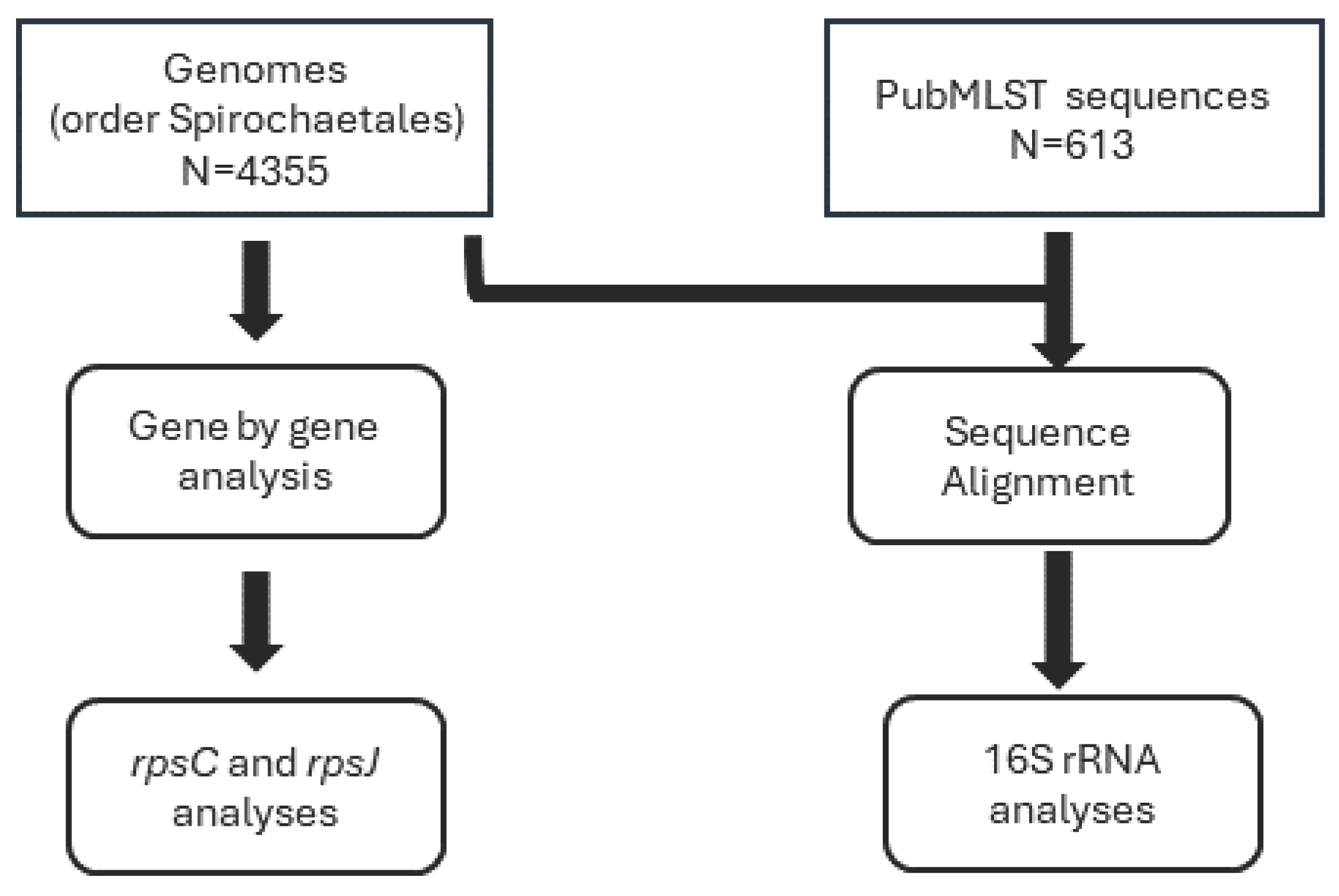
The whole genome sequence (WGS) used in this study was acquired from GenBank®. This collection included 4,355 genomes from the order Spirochaetales (NCBI Taxonomy ID: 136). Additionally, the study incorporated 16S sequence data from PubMLST Treponema pallidum isolate collection. This collection included 613 sequences.
Detection of genetic resistance to tetracycline
WGS were screened for tetracycline resistance, and the analysis was carried out as described [
22]. In brief, WGS (n = 4355) was analyzed using chewBBACA version 2.8.5 [
23]. Firstly, a training file was created from the complete genome of
T. pallidum (AE000520.1) using Prodigal and used in subsequent steps [
24]. Secondly, a study-specific
T. pallidum schema was created, and a FASTA file for each coding sequence (CDS) was generated. Thirdly, a BLAST database was created using the study-specific schema, herein referred to as the schema database. This was followed by a BLASTN search against the schema database using the
rpsC and
rpsJ genes from
T. pallidum (AE000520.1) as queries. The multiple sequence alignment files were imported into CLC Genomics Workbench (v20), and the CDSs were translated. The presence of non-synonymous substitutions in the following proteins was further evaluated: rpsC (Lys4; His175) and rpsJ (Val57).
For 16S analysis, a BLASTN search using the 16S rRNA T. pallidum (AE000520.1) sequence was queried against the BLAST database that was created using all 4,355 genomes. A BLASTN search was also performed against T. pallidum isolate collection in PubMLST. Thus, for the 16S analysis, the dataset included the genomes and sequences from Genbank and PubMLST, respectively.
Results
Mutations in the 16S rRNA gene
Our analyses revealed a transition mutation from TGA to TGG at positions 965 to 967 (
Escherichia coli 16S rRNA numbering) observed among Treponema (5.6% occurrence) and Spirochaeta spp. (3.97% occurrence) genomes. Additional mutations at the same positions, including CGC, GGT, CGA, TGR(A/G), TGC and AGC, were detected less frequently (
Table 1).
Figure 1.
Flowchart describing genomes and sequences used in the analyses.
Figure 1.
Flowchart describing genomes and sequences used in the analyses.
Mutations in the rpsJ gene
Analysis of the
rpsJ gene, which encodes the 30S ribosomal subunit protein S10, showed the presence of the V57G substitution that was observed in both the
Treponema porcinum genomes and 20% of
Treponema sp. genomes (
Table 1). The presence of additional variants, V57I and V57K, was also observed at a lower incidence (
Table 1). The substitution V57K (169 GTG-AAG 171) frequently appeared in the Spirochaeta spp. (1.69% of genomes) and other Treponema spp. (1.12% of genomes) (
Table 1).
Mutations in the rpsC gene
An H178Q substitution in the
rpsC gene, associated with the 30S ribosomal subunit protein S3, was found in 80% of the genomes of the Spirochaetales bacterium (
Table 1).
Discussion
The emergence and dissemination of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) are of utmost concern in infectious disease management, particularly in the context of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as syphilis. The resurgence of syphilis incidence in various countries, including Belgium, necessitates innovative interventions to curb this trend [
1]. One such intervention is the administration of doxycycline as post-exposure prophylaxis (doxy-PEP), which has demonstrated efficacy in reducing the incidence of syphilis and other STIs among men who have sex with men (MSM) [
5]. However, the extensive use of doxycycline raises concerns about the potential induction of AMR, especially considering its critical role as an alternative to penicillin, the first-line treatment [
10].
Our study focused on the potential chromosomal mutations associated with tetracycline resistance within the Spirochetales order. The genomic data from this order, including 4,355 whole genome sequences and an additional 613 16S rRNA sequences, were systematically analyzed for the presence of mutations in 16S rRNA and non-synonymous mutations in the rpsC and rpsJ genes, which encode the 30S ribosomal subunit proteins S3 and S10, respectively.
Our analysis revealed the transition mutation TGA to TGG at positions 965 to 967 (
Escherichia coli 16S rRNA numbering) in the 16S rRNA gene of
Treponema and
Spirochaeta spp. genomes. The identification of this mutation across these species suggests a potential mechanism of resistance that might become more prevalent under selective pressure from increased doxycycline use [
25]. Although less frequent, other mutations in this gene point to the potential for diverse resistance mechanisms within these genera.
In the
rpsJ gene, the V57G amino acid substitution was present in both the genomes of
Treponema porcinum and a significant subset of
Treponema spp., and this mutation could confer a fitness advantage in the presence of tetracycline. The V57I and V57K substitutions were also observed but at lower frequencies. Notably, the GTG-AAG (V57K) mutation at nucleotide positions 169-171 was relatively common in Spirochaeta spp. and other
Treponema spp.. The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of
E. coli to tetracycline with V57K substitution was found to be 0.75 μg/ml, and
Escherichia coli with V57I substitution showed a slightly increased MICs to tigecycline and tetracycline [
26]. Substitutions in V57 amino acid positions that confer resistance to tetracycline or tigecycline have been observed in both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, namely
E. coli, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Bacillus subtilis,
Enterococcus faecium, Enterococcus faecalis and
Staphyloccus aureus [
26,
27,
28,
29].
The
rpsC gene analysis uncovered an H178Q (corresponding to the H175 position in
Streptococcus pneumoniae) substitution in a substantial majority of the Spirochaetales bacterium genomes, highlighting the critical nature of this mutation within this specific bacterial group [
30].
In light of the widespread use of doxy-PEP, the putative mutations associated with tetracycline resistance reported in this study provide a prerequisite for developing molecular methods for the rapid detection and surveillance of antibiotic-resistant
T. pallidum in clinical specimens [
31]. Our study contributes to the foundational knowledge necessary for guiding future studies and public health strategies to mitigate the spread of AMR in the context of STI management.
References
- Mitjà O, Padovese V, Folch C, et al (2023) Epidemiology and determinants of reemerging bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and emerging STIs in Europe. Lancet Reg Heal - Eur 34:100742. [CrossRef]
- Molina J-M, Charreau I, Chidiac C, et al (2018) Post-exposure prophylaxis with doxycycline to prevent sexually transmitted infections in men who have sex with men: an open-label randomized substudy of the ANRS IPERGAY trial. Lancet Infect Dis 18:308–317. [CrossRef]
- Luetkemeyer AF, Donnell D, Dombrowski JC, et al (2023) Postexposure Doxycycline to Prevent Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections. N Engl J Med 388:1296–1306. [CrossRef]
- Molina JM, Bercot B, Assoumou L, et al (2023) ANRS 174 DOXYVAC: an open-label randomized trial to prevent STIs in MSM on PrEP. In: 30th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI).
- Mårdh O, Plachouras D (2023) Using doxycycline for prophylaxis of bacterial sexually transmitted infections: considerations for the European Union and European Economic Area. Eurosurveillance 28:. [CrossRef]
- Vanbaelen T, Tsoumanis A, Kenyon C (2023) Total Antimicrobial Consumption in Doxycycline Postexposure Prophylaxis Cohorts and the Intensity of Screening for Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections. Clin Infect Dis ciad553. [CrossRef]
- Vanbaelen T, Manoharan-Basil SS, Kenyon C (2023) Doxycycline Postexposure Prophylaxis Could Induce Cross-Resistance to Other Classes of Antimicrobials in Neisseria gonorrhoeae : An In Silico Analysis. Sex Transm Dis 50:490–493. [CrossRef]
- Gestels Z, Manoharan-Basil SS, Kenyon C (2023) Doxycycline post exposure prophylaxis could select for cross-resistance to other antimicrobials in various pathogens: An in silico analysis. Int J STD AIDS 34:962–968. [CrossRef]
- Kenyon C (2024) Doxycycline post exposure prophylaxis could theoretically select for resistance to various antimicrobials in 19 pathobionts: an in silico analysis. Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis. [CrossRef]
- Nurse-Findlay S, Taylor MM, Savage M, et al (2017) Shortages of benzathine penicillin for prevention of mother-to-child transmission of syphilis: An evaluation from multi-country surveys and stakeholder interviews. PLoS Med 14:e1002473. [CrossRef]
- Wu B-R, Liu W-C, Wu P-Y, et al (2014) Surveillance study of Treponema pallidum harbouring tetracycline resistance mutations in patients with syphilis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 44:370–372.
- Sanchez A, Mayslich C, Malet I, et al (2020) Surveillance of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Treponema Pallidum Subspecies Pallidum from Patients with Early Syphilis in France. Acta Derm Venereol 100:adv00221. [CrossRef]
- Xiao H, Li Z, Li F, et al (2017) Preliminary study of tetracycline resistance genes in Treponema pallidum. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 9:1–2.
- Lukehart, S. (2022) Could doxycycline PEP induce tetracycline resistance in Treponema pallidum?
- Xiao Y, Liu S, Liu Z, et al (2016) Molecular Subtyping and Surveillance of Resistance Genes In Treponema pallidum DNA From Patients With Secondary and Latent Syphilis in Hunan, China. Sex Transm Dis 43:310–316. [CrossRef]
- Beale MA, Marks M, Cole MJ, et al (2021) Global phylogeny of Treponema pallidum lineages reveals recent expansion and spread of contemporary syphilis. Nat Microbiol 6:1549–1560. [CrossRef]
- Mikalová L, Grillová L, Osbak K, et al (2017) Molecular Typing of Syphilis-Causing Strains Among Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Patients in Antwerp, Belgium. Sex Transm Dis 44:376–379. [CrossRef]
- Edmondson DG, Wormser GP, Norris SJ (2020) In Vitro Susceptibility of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum to Doxycycline. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 64:. [CrossRef]
- Hunfeld K-P, Kraiczy P, Kekoukh E, et al (2002) Standardized in vitro susceptibility testing of Borrelia burgdorferi against well-known and newly developed antimicrobial agents--possible implications for new therapeutic approaches to Lyme disease. Int J Med Microbiol 291 Suppl:125–137. [CrossRef]
- Sicklinger M, Wienecke R, Neubert U (2003) In vitro susceptibility testing of four antibiotics against Borrelia burgdorferi: a comparison of results for the three genospecies Borrelia afzelii, Borrelia garinii, and Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto. J Clin Microbiol 41:1791–1793. [CrossRef]
- Moreno LZ, Miraglia F, Lilenbaum W, et al (2016) Profiling of Leptospira interrogans, L. santarosai, L. meyeri and L. borgpetersenii by SE-AFLP, PFGE and susceptibility testing--a continuous attempt at species and serovar differentiation. Emerg Microbes Infect 5:e17. [CrossRef]
- Manoharan-Basil SS, Laumen JGE, Van Dijck C, et al (2021) Evidence of Horizontal Gene Transfer of 50S Ribosomal Genes rplB, rplD, and rplY in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Front. Microbiol. 12:1263.
- Silva M, Machado MP, Silva DN, et al (2018) chewBBACA: A complete suite for gene-by-gene schema creation and strain identification. Microb genomics. [CrossRef]
- Hyatt D, Chen GL, LoCascio PF, et al (2010) Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinformatics. [CrossRef]
- Pringle M, Fellström C, Johansson K-E (2007) Decreased susceptibility to doxycycline associated with a 16S rRNA gene mutation in Brachyspira hyodysenteriae. Vet Microbiol 123:245–248. [CrossRef]
- Izghirean N, Waidacher C, Kittinger C, et al (2021) Effects of Ribosomal Protein S10 Flexible Loop Mutations on Tetracycline and Tigecycline Susceptibility of Escherichia coli. Front Microbiol 12:663835. [CrossRef]
- Williams G, Smith I (1979) Chromosomal mutations causing resistance to tetracycline in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet 177:23–29. [CrossRef]
- Villa L, Feudi C, Fortini D, et al (2014) Genomics of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 512 clone highlights the role of RamR and ribosomal S10 protein mutations in conferring tigecycline resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:1707–1712. [CrossRef]
- Cattoir V, Isnard C, Cosquer T, et al (2015) Genomic analysis of reduced susceptibility to tigecycline in Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:239–244. [CrossRef]
- Lupien A, Gingras H, Leprohon P, Ouellette M (2015) Induced tigecycline resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae mutants reveals mutations in ribosomal proteins and rRNA. J Antimicrob Chemother 70:2973–2980. [CrossRef]
- Stamm L V (2010) Global challenge of antibiotic-resistant Treponema pallidum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:583–589. [CrossRef]
Table 1.
List of the tetracycline resistance associated mutations.
Table 1.
List of the tetracycline resistance associated mutations.
| Ribosomal genes |
Source of genomes |
Organism |
Total no of genomes |
Mutations |
No of genomes with mutations |
No of genomes with 2 copies |
No of genomes with >2 copies |
Copy number |
| 16S rRNA |
Genbank |
Treponema parvum |
5 |
TGA 965-967 TGG |
2 |
2 |
|
1-2 copies |
| TGA 965-967 GGT |
1 |
0 |
|
1 copy |
| Treponema brennaborense |
4 |
TGA 965-967 TGG |
1 |
1 |
|
4 copies |
| Treponema peruense |
4 |
TGA 965-967 TGG |
1 |
1 |
|
4 copies |
| Treponema bryantii |
5 |
TGA 965-967 TGG |
2 |
0 |
3 |
1-4 copies |
| Treponema sp. |
60 |
TGA 965-967 CGC |
1 |
0 |
|
1 copy |
| Other Treponema spp. |
1341 |
TGA 965-967 TGG |
71 |
24 |
9 |
1-3 copies |
| Spirochaeta spp. |
1006 |
TGA 965-967 CGA |
8 |
0 |
|
1 copy |
| TGA 965-967 TGG |
40 |
18 |
|
1 to 5 copies |
| PubMLST |
Treponema pallidum |
544 |
TGA 965-967 TGG |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
| TGA 965-967 TGR(A/G) |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
| TGA 965-967 TGC |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
| TGA 965-967 AGC |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
| rpsJ (30S ribosomal subunit protein S10) |
Genbank |
Candidatus Borreliella tachyglossi |
1 |
V57A |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
| Treponema porcinum |
2 |
V57G |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
| Treponema sp. |
60 |
V57G |
12 |
- |
- |
- |
| V57I |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
| V57K |
3 |
- |
- |
- |
| Borrelia persica |
1 |
V57I |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
| Spirochaeta spp. |
1006 |
V57G |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
| V57I |
4 |
- |
- |
- |
| V57K |
17 |
- |
- |
- |
| Other Treponema spp. |
1341 |
V57K |
15 |
- |
- |
- |
| rpsC (30S ribosomal subunit protein S3) |
Genbank |
Spirochaetales bacterium |
5 |
H178Q |
4 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).