1. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD)
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) represent a spectrum of lifelong, debilitating conditions that result from prenatal exposure to alcohol [
1,
2,
3,
4]. This diverse range of disorders encompasses a continuum of physical, cognitive, behavioral, and developmental impairments, which can have profound and lasting effects on individuals throughout their lives [
5,
6,
7]. The term "spectrum" reflects the wide variability in the impact of alcohol exposure on fetal development, with some individuals experiencing more severe manifestations than others. The critical period of vulnerability is during pregnancy, particularly during the first trimester when organ systems are rapidly developing [
8]. The main risk factors for FASD are increased fetal exposure to alcohol and sustained alcohol intake during any trimester of pregnancy, genetic predisposition, maternal lower socioeconomic statuses and smoking, and paternal chronic alcohol use [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14].
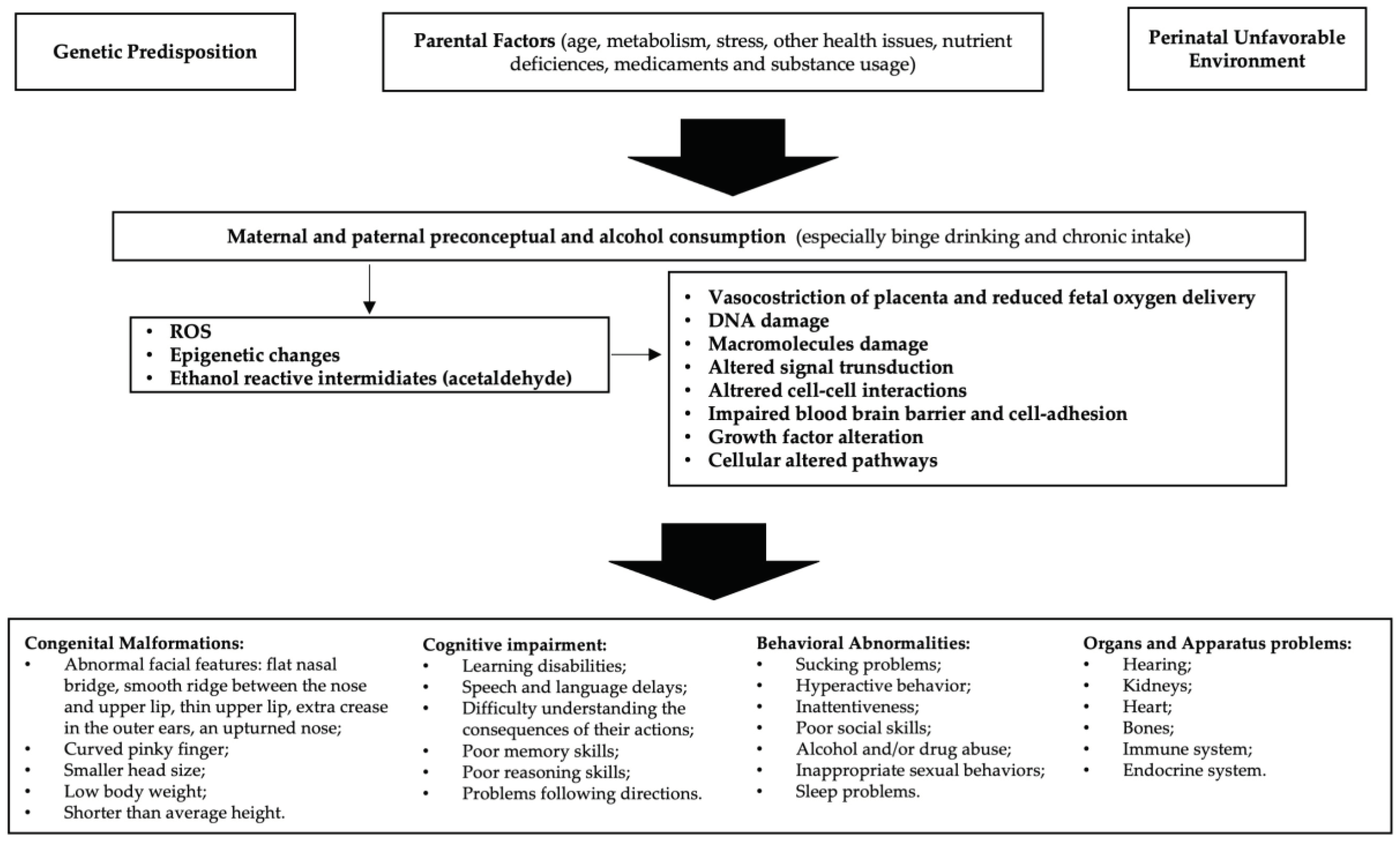
Alcohol is able to freely cross the placenta during pregnancy and enter the growing fetus through the umbilical cord, the different quantity, defense efficiency and excretion of maternal and fetal enzymes allow for alcohol to have a lengthy effect on the fetus [
15]. Alcohol is a teratogen substance acting through various methods including direct damage of its metabolites, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated as byproducts of CYP2E1, decreased endogenous antioxidant levels, mitochondrial damage, lipid peroxidation, disrupted neuronal cell-cell adhesion, placental vasoconstriction, inhibition of cofactors required for fetal growth and development and epigenetic changes (
Figure 1. Alcohol interferes with the development of cells and tissues in the fetus [
16]. It disrupts the process of cell division and differentiation, leading to abnormal growth and development of various organs, especially the brain. Early observations supported alcohol, rather than acetaldehyde, being the more important teratogen and specific genetic susceptibility differences to alcohol-related birth defects were found (e.g. alcohol dehydrogenase-2*3 allele protects against alcohol-related birth defects) [
17].
So, prenatal exposure to alcohol can interfere with the normal growth and development of the fetus, leading to a myriad of challenges that may manifest in infancy, childhood, adolescence, and adulthood. The severity of FASD can be influenced by factors such as the timing, amount, and pattern of alcohol consumption. Individual genetic and environmental factors also play a significant role [
18]. The hallmark features of FASD include physical anomalies, cognitive deficits, and behavioral issues [
19]. Physical characteristics may include facial abnormalities, growth deficiencies, and organ malformations [
20]. Cognitive impairments often encompass difficulties in learning, memory, attention, and problem-solving skills [
21]. Behavioral challenges can range from hyperactivity and impulsivity to social and emotional difficulties [
22]. The intricate interplay of these components makes the diagnosis and management of FASD a complex and multidisciplinary task. Prevention is paramount, and education about the risks of alcohol consumption during pregnancy is crucial [
23]. Unfortunately, FASD remain a significant public health concern globally, affecting individuals from all walks of life [
19].
To address the complexities of FASD, a comprehensive approach is required. This involves collaboration among healthcare professionals, educators, policymakers, and community support systems. Early intervention and appropriate support services can enhance the quality of life for individuals with FASD, providing them with the tools they need to navigate the challenges associated with their unique conditions. As our understanding of FASD continues to evolve, ongoing research and advocacy efforts are essential to raise awareness, improve diagnostic methods, and develop effective interventions to mitigate the impact of prenatal alcohol exposure on individuals and their families.
2. FASD Epigenetics
Epigenetics, a captivating and rapidly advancing field within the realm of genetics, unveils the intricate dance between genes and the environment, fundamentally shaping the destiny of living organisms [
24]. At its core, epigenetics explores the heritable changes in gene activity that occur without alterations to the underlying DNA sequence. This field revolutionizes our understanding of how external factors, spanning from lifestyle choices to environmental exposures, can imprint molecular marks on the genome, influencing gene expression and, consequently, the phenotype.
The term ‘epigenetics’ itself underscores the pivotal role of these processes. It translates to ‘above’ or ‘on top of’ genetics [
25]. Unlike the unalterable DNA code, epigenetic modifications act as dynamic regulators, orchestrating the symphony of gene expression in response to various internal and external cues. These modifications include DNA methylation, histone modification, and non-coding RNA molecules, collectively influencing the accessibility of genes to the cellular machinery responsible for transcription [
26,
27]. The impact of epigenetics extends far beyond the individual organism, as these marks can be passed down through generations, heralding the era of transgenerational inheritance [
4,
28]. This phenomenon challenges the conventional view that genetic information flows strictly through the DNA sequence, introducing a dynamic layer of complexity to our understanding of heredity.
Consequently, the study of epigenetics not only elucidates the molecular intricacies governing development and cellular function but also sheds light on the potential intergenerational consequences of environmental exposures. In this expansive landscape, researchers delve into the epigenetic mechanisms underpinning health and disease. From the early stages of embryonic development to the intricate regulation of tissue-specific gene expression, epigenetic processes play a pivotal role in determining cellular identity and function [
29]. Moreover, aberrations in epigenetic regulation have been implicated in a myriad of diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic conditions, providing a new avenue for therapeutic exploration. As scientists continue to unravel the epigenetic tapestry, they grapple with the ethical implications and societal ramifications of this knowledge.
The dynamic nature of epigenetic modifications prompts questions about the potential reversibility of epigenetic changes and the development of interventions to modulate these processes for therapeutic purposes [
30,
31]. The intersection of science, ethics, and medicine in the realm of epigenetics underscores the need for careful consideration and responsible stewardship as we navigate the uncharted territories of this revolutionary field.
The epigenetics of FASD represents a compelling area of research that delves into the molecular mechanisms underlying the long-term effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on gene regulation [
32,
33]. Furthermore, FASD, resulting from maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy, encompass a range of developmental, cognitive, and behavioral abnormalities. Understanding how alcohol-induced epigenetic changes contribute to the varied and often severe phenotypic outcomes is crucial for developing targeted interventions and therapies [
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. Most of the studies on FASD epigenetics have been published in the last decades and the majority have been conducted on animal models [
40]. One of the key epigenetic modifications associated with FASD is DNA methylation [
15,
40,
41,
42]. Studies have revealed alterations in the methylation patterns of specific genes involved in neural development and function in individuals with FASD.
For instance, genes related to neuronal migration, synaptogenesis, and neurotransmitter regulation may undergo abnormal DNA methylation, leading to disruptions in neural circuitry and function [
43,
44]. The dynamic nature of DNA methylation makes it a potential biomarker for assessing the severity and persistence of FASD-related impairments. Histone modifications, another critical facet of epigenetics, play a role in orchestrating the three-dimensional structure of chromatin and regulating gene accessibility [
45]. Prenatal alcohol exposure has been linked to changes in histone acetylation and methylation patterns, particularly in genes associated with neurodevelopment [
46].
Altered histone modifications can influence the expression of genes involved in learning, memory, and behavioral regulation, contributing to the cognitive and behavioral deficits observed in individuals with FASD. Non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs, also emerge as key players in the epigenetic landscape of FASD [
47,
48]. These small RNA molecules can post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression, and their dysregulation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of neurodevelopmental disorders. Studies suggest that alcohol exposure during pregnancy can disrupt the expression of specific microRNAs, potentially contributing to the aberrant gene expression patterns associated with FASD [
47].
The transgenerational aspect of epigenetics adds an additional layer of complexity to the study of FASD [
11,
27]. Emerging evidence suggests that prenatal alcohol exposure can induce epigenetic changes that persist across generations, influencing the susceptibility of offspring to FASD-related outcomes [
4]. This transgenerational epigenetic inheritance underscores the importance of considering not only the immediate consequences of prenatal alcohol exposure but also its potential impact on future generations.
Understanding the epigenetic landscape of FASD holds promise for the development of targeted interventions and therapeutic strategies. By unraveling the molecular mechanisms through which alcohol exposure induces lasting epigenetic changes, researchers aim to identify potential targets for intervention and prevention, ultimately improving the quality of life for individuals affected by FASD and potentially mitigating the risk of FASD in future generations.
3. Oxidative Stress and FASD
Alcohol causes FASD by interfering during fetal development with molecular pathways associated with increased oxidative stress, altered organ development, and change of epigenetic gene expression control [
49]. Oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s ability to neutralize them, plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of FASD leading to potential damage to key cellular components during the development phase of the fetus [
50,
51]. When alcohol is metabolized in the liver, it generates ROS as byproducts (including superoxide radicals and hydrogen peroxide), leading to elevated levels of ROS that can overwhelm the body’s antioxidant defense systems and result in oxidative stress [
52,
53]. ROS can cause damage to cellular structures such as lipids, proteins, and DNA of developing fetal tissues, including the brain, which is particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress because of the rich lipid composition and the high metabolic rate. Furthermore, oxidative stress can impact mitochondrial function, trigger inflammatory responses and disrupt normal cellular processes, including neuronal migration, synaptogenesis, and myelination [
54,
55].
In fact, the fetal body has defenses against ROS. Specifically, it can produce endocrine antioxidative enzymes, such as catalase, providing critical protection. It can also activate mechanisms to repair damaged cellular and genetic components, such as oxoguanine glycosylase 1 (OGG1) activated in the case of DNA. Additionally, the fetal body can reduce the risk of damage by producing products like the fetal nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a ROS-sensing protein that upregulates an array of proteins, including antioxidative enzymes and DNA repair proteins [
53].
In particular, oxidative stress plays a major role in the epigenetic changes associated with FASDs [
53,
56]. In fact, it has been associated with alterations in DNA methylation patterns and miRNAs expression, as well as histone modifications shifting gene accessibility and expression in patients affected by FASD and neurodevelopmental disorders. Furthermore, as stated before, oxidative stress can directly cause damage to DNA and its components leading to mutations potentially affecting the expression of genes critical for brain development and function. Mitochondrial dysfunction also may contribute to epigenetic changes, as mitochondria play a key role in providing the intermediate metabolites necessary to generate and modify epigenetic marks in the nucleus, which in turn can regulate the expression of mitochondrial proteins [
57]. In the context of FASD, neuroinflammation may contribute to epigenetic changes that modulate the expression of genes involved in neurodevelopment.
Studying the impact of oxidative stress on FASD epigenetics holds great potential for advancing our understanding of the disorder, identifying diagnostic markers, and improving the management of this incurable disease.
4. Epigenetics and Oxidative Stress
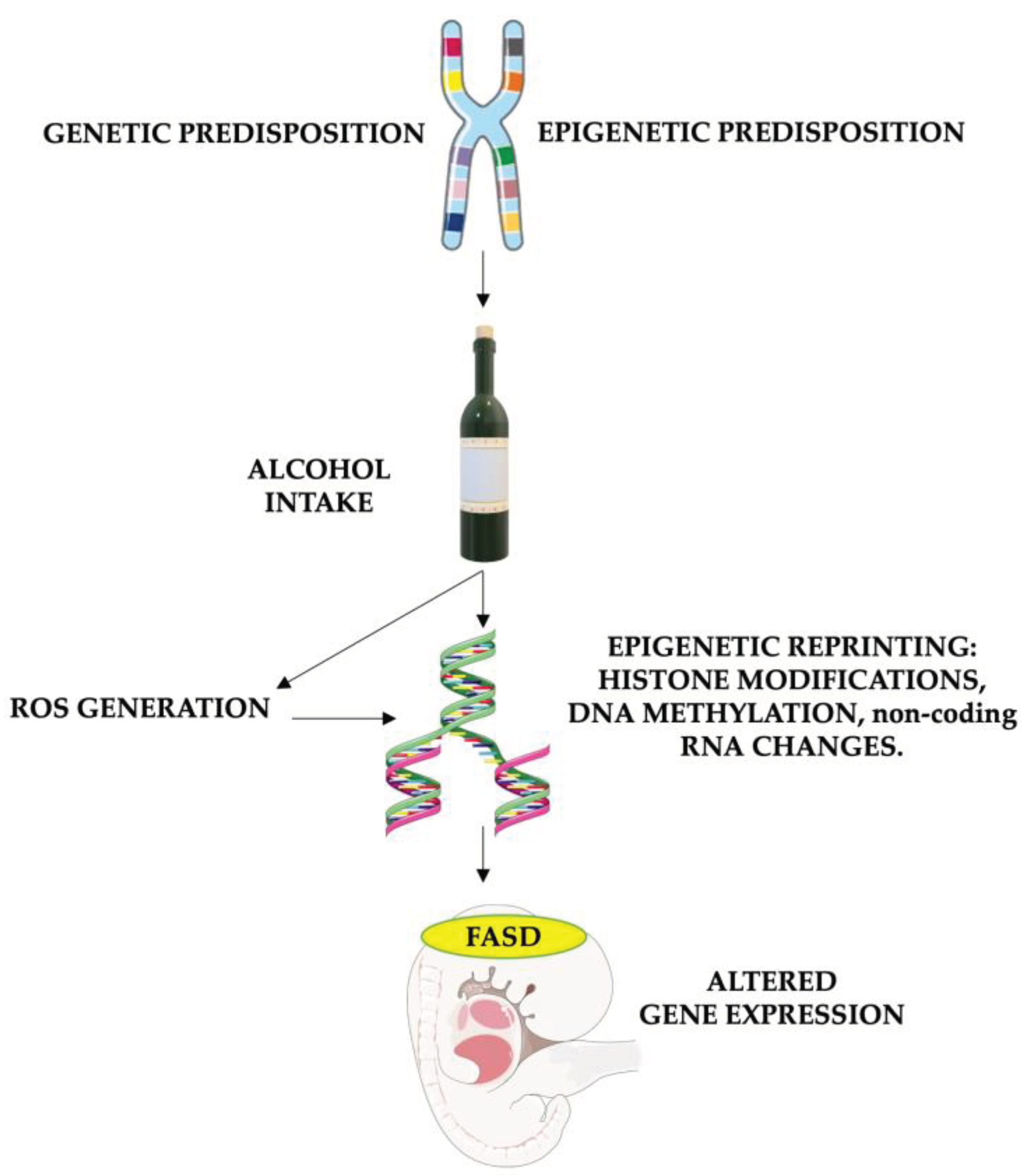
FASD risk is likely increased in children who are genetically and environmentally predisposed, especially in the case of enhanced pathways for ROS formation and/or deficient pathways for ROS detoxification or DNA repair [
58].
As stated before, alcohol has the potential to alter gene expression by impacting DNA methylation processes [
59,
60]. This occurs by enhancing the breakdown and reduction of methyl groups, leading to the disruption of subsequent SAM-dependent transmethylation reactions in the folate pathway, which are crucial for DNA methylation [
8]. Additionally, alcohol influences nucleosomal remodeling by initiating histone modifications. It also impacts the expression of microRNA. Furthermore, both maternal and paternal preconceptual alcohol exposures induce mitochondrial dysfunction and a heightened response to oxidative stress in developing organs. This is achieved by metabolizing ethanol into acetaldehyde, facilitated by enzymes like alcohol dehydrogenase, cytochrome P450-CYP2E1, or catalase [
50,
53,
61]. This process generates ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), altering the cell’s internal redox balance, leading to neuronal cell death and modified gene expression due to DNA oxidation. Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage, which are also hallmarks of aging, are key events in FASD [
62,
63].
Indeed, alcohol can induce mtDNA damage, resulting in increased oxidative stress and alterations in the mtDNA repair protein 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase-1 (OGG1) [
64]. Therefore, pregnancy inherently heightens susceptibility to oxidative stress, and this risk is further increased by alcohol consumption, leading to various adverse outcomes. These include impaired development, abnormal placental function, and several complications such as pre-eclampsia, recurrent pregnancy loss, fetal anomalies, intrauterine growth restriction, and, in severe cases, fetal demise [
65]. In response to the uncontrolled rise in RNS/ROS levels, the body relies on trace elements involved in both non-enzymatic and enzymatic defense mechanisms.
These elements, namely copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), and selenium (Se), play a crucial role. Assessing ROS may benefit from the use of marker proteins like malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GR), catalase (CAT), and glutathione (GSH) [
66]. These markers serve as indirect indicators of the intensity of oxidative stress and can provide insights into potential pregnancy complications. Prenatal alcohol exposure can alter the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway resulting in increased oxidative stress [
67]. mTOR plays a major role in modulating protein synthesis and autophagy necessary for proper fetal development. In fact, mTOR alterations have recently been implicated in FASD etiology as long-lasting effects following alcohol exposure include impaired hippocampal and synapse formation, reduced brain size, as well as cognitive, behavioral, and memory impairments [
68].
The brain is particularly susceptible to generating ROS, including superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals [
69]. This susceptibility arises due to the brain’s elevated metabolic rate for oxygen consumption. Its cells utilize about 20% of the oxygen consumed by the entire organism. Additionally, brain tissues contain high levels of unsaturated fatty acids, which serve as substrates for the production of ROS. Moreover, certain brain regions contain elevated levels of iron, and various neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, levodopa, serotonin, and norepinephrine, have a tendency to react spontaneously with oxygen [
70].
It’s important to note that antioxidant enzyme activity, including superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, is generally lower in the brain than in organs like the liver or kidney [
71,
72]. Furthermore, even though oxidative stress plays a role in normal fetal development, its imbalance caused by alcohol consumption and the higher susceptibility of fetal cells leads to neurotoxic effects. Hence, antioxidants such as vitamin E, vitamin C, and glutathione play a crucial role in FASD treatment. Their ability to counteract the harmful effects of oxidative stress has the potential to mitigate or prevent some of the neurological and developmental issues caused by prenatal alcohol exposure. (
Figure 2).
Ethanol-induced oxidative stress can also cause damage to DNA, resulting in genetic mutations within individual cells [
58]. This damage can lead to the immortalization and multiplication of cells, potentially resulting in cancer development after birth. Alternatively, ethanol-induced oxidative stress can lead to direct or indirect alterations in the epigenetic makeup of DNA, histones, or RNA across multiple cells
These modifications can influence the expression of genes and contribute to teratogenesis, leading to birth defects and abnormalities in neurodevelopment after birth. Moreover, paternal consumption of alcohol before conception triggers epigenetic alterations in male sperm. This is facilitated by ROS generation and accelerated breakdown of substances, leading to the loss of methyl groups. These changes disrupt SAM-dependent transmethylation reactions in the folate pathway, crucial for DNA methylation. Additionally, there is restructuring of nucleosomes via modifications to histones and abnormal expression of microRNAs [
4].
Research has specifically focused on several neurotransmitters, insulin resistance, alterations of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, abnormal glycosylation of several proteins, oxidative stress, nutritional antioxidants, and various epigenetic factors [
73]. Prenatal alcohol consumption is also associated with a widespread increase in the neuroendocrine stress response, regulated by the HPA axis [
74,
75]. This response influences drinking behavior and is linked to epigenetic changes in neurotrophins and POMC genes, impacting pathways that regulate mood, emotion, and serotonergic function. Recent studies found a correlation between mtDNA damage and phenotypical abnormalities associated with FASD. This suggests that the amount of damaged mtDNA in fetal brain-derived exosomes may serve as a marker to predict FASD risk in fetuses [
64]. Moreover, IGF-1 might reduce alcohol-caused mtDNA damage and neuronal apoptosis.
4. Therapeutic Implications
Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by FASD but a cure is not available for this disease [
76,
77]. Antioxidants are commonly employed to protect the fetus against ethanol teratogenicity [
78,
79]. Indeed, while the optimal therapeutic strategy is complete abstinence from alcohol during pregnancy, various substances have been shown to reduce the production of ROS in these patients and lessen the frequency of severe FASD manifestations[
61,
80,
81,
82,
83,
84]. On the other hand, considering that epigenetic changes are potentially reversible through pharmaceutical interventions, there is an opportunity to develop drugs targeting specific epigenetic mechanisms involved in regulating gene expression. This could have significant clinical relevance [
85].
Mitigating oxidative stress through strategies like antioxidant supplementation or lifestyle modifications may potentially modulate FASD-associated epigenetic modifications, improving clinical outcomes. In a recent study, glutathione supplementation was shown to inhibit the effects of prenatal alcohol exposure. This led to improved survival, reduced incidence of morphological defects (especially congenital heart abnormalities), and prevention of global hypomethylation of DNA in heart tissues [
86]. Moreover, targeting the effects of oxidative stress on epigenetics, along with the ROS-generating pathways, may offer new avenues for therapeutic interventions in FASD [
87].
However, currently, the best therapeutic approach for patients affected by FASD remains unclear. It often involves prenatal administration of antioxidants, food supplements, folic acid, choline, neuroactive peptides, and neurotrophic growth factors. Studies have shown that avoiding comorbidities and addressing the family system can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with FASD [
15,
88]. Moreover, many other products with antioxidant activity have been effectively tested. Particularly, those that act on the methionine metabolic cycle have taken the spotlight in recent years [
89,
90].
Therapies targeting specific epigenetic pathways affected by prenatal alcohol exposure may also help alleviate FASD-related impairments. Unfortunately, most evidence supporting the beneficial effects of therapeutic approaches acting on both ROS and epigenetic pathways comes from murine models, with human clinical trials still being notably scarce. Additional clinical trials are needed to determine the extent to which antioxidants contribute to mitigating FASD damage and to assess the actual impact of their epigenetic modulatory effects on the management and efficacy of treating these patients [
81].
The role of oxidative stress on epigenetics in FASD underscores the complex interplay between environmental exposures, genetic predisposition, molecular mechanisms, and clinical outcomes. Further research in this area is necessary to fully comprehend the implications for the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of FASD.
5. Discussion
The primary objective of the study discussed in this paper was to explore the intricate relationship between oxidative stress and epigenetics in the pathogenesis of FASD and its therapeutic implications. FASD represents a spectrum of lifelong impairments resulting from prenatal exposure to alcohol, presenting significant challenges due to their diverse manifestations, ranging from physical abnormalities to cognitive and behavioral deficits [
91]. Prenatal exposure to alcohol disrupts normal fetal development, leading to a myriad of health problems, including facial abnormalities, growth deficiencies, and organ malformations [
92].
Additionally, cognitive impairments, such as difficulties in learning, memory, attention, and problem-solving skills, are common among individuals with FASD [
20,
93]. Behavioral challenges may include hyperactivity, impulsivity, and social/emotional difficulties. These issues not only affect the individuals with FASD but also have broader implications for their families and communities, highlighting the urgent need for effective prevention and intervention strategies. The projected lifespan for individuals with FAS is approximately 34 years (with a 95% confidence range of 31 to 37 years), with external causes contributing significantly (44%) to mortality. These external causes encompass suicide (15%), accidents (14%), and substance-related fatalities involving illegal drugs or alcohol poisoning (7%), among other factors [
94].
As a safe dose of alcohol use during pregnancy has not been established, it is recommended that pregnant women abstain completely from alcohol to prevent FASD. Unfortunately, identifying women at risk remains challenging, and the diagnosis tends to be overlooked or delayed, lacking adequate public acknowledgment [
51,
95]. This oversight in diagnosing has substantial social and economic repercussions, escalating challenges in education, employment, and social interactions and leading to increased dependency on social services and healthcare systems [
96].
Fetal cellular epigenetic mutations and susceptibility to reactive oxygen species (ROS) appear to play a major role in causing fetal changes. The molecular bases of FASD involve oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between ROS and antioxidant defense systems induced by alcohol metabolism. This oxidative stress leads to cellular damage, particularly in the vulnerable fetal brain, resulting in disruptions in development. Moreover, oxidative stress is implicated in epigenetic changes, including alterations in DNA methylation, histone modifications, and microRNA expression, influencing gene regulation in individuals with FASD [
53,
58].
These epigenetic changes can influence gene regulation, contributing to the varied phenotypic outcomes observed in individuals with FASD. It has been suggested that the risk of FASD is increased in genetically predisposed progeny, particularly in cases of heightened oxidative stress [
58].
Prevention should be the primary focus to reduce this preventable disease. Unfortunately, deterrence and educational campaigns appear to have failed in definitively reducing alcohol use during pregnancy [
97]. The role of oxidative stress on epigenetics in FASD has significant implications for prevention and treatment.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment significantly enhance the quality of life for FASD patients [
15]. Current treatment options for FASD involve supportive approaches such as motivational interviewing and the community-reinforcement approach. There is potential for proactive maternal nutritional intervention, including prenatal administration of antioxidant supplements, folic acid, choline, neuroactive peptides, and neurotrophic growth factors [
20,
98,
99]. Recent suggestions indicate that targeting specific epigenetic mechanisms involved in regulating gene expression could hold significant clinical relevance for individuals with FASD [
85]. Additionally, emerging epigenetic tools might be utilized as preventive, diagnostic, and therapeutic markers.
Understanding these mechanisms presents opportunities for targeted therapeutic interventions, such as antioxidant supplementation and lifestyle modifications, to alleviate the detrimental impact of alcohol on fetal development and mitigate FASD-related impairments [
86]. Further clinical trials are essential to validate the efficacy of these interventions in humans and assess their impact on epigenetic modifications associated with FASD.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of oxidative stress and epigenetics in FASD provides valuable insights into the intricate interplay between environmental exposures, genetic predisposition, molecular mechanisms, and clinical outcomes. By unraveling these mechanisms, researchers aim to develop targeted interventions and therapeutic strategies to mitigate the impact of prenatal alcohol exposure on individuals and their families. Continued research in this field is essential for advancing our understanding of FASD and for developing effective prevention and treatment approaches to address this global health challenge.
Future approaches to FASD prevention and treatment may involve multidisciplinary strategies targeting both oxidative stress and epigenetic pathways. Therapeutic interventions aimed at modulating epigenetic changes associated with prenatal alcohol exposure hold promise for improving clinical outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for individuals affected by FASD. Additionally, efforts to raise awareness, improve diagnostic methods, and develop effective interventions are essential for addressing this significant public health concern on a global scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.T.; G.F.; and M.F.; methodology, S.T.; M.V.; L.V., M.L.; S.F.; G.F.; and M.F.; validation, S.T.; G.F.; and M.F.; formal analysis, S.T.; G.F.; M.V.; L.V., M.L.; S.F.; L.T.; M.C.; and M.F.; investigation, X.X.; resources, X.X.; data curation, S.T.; G.F.; L.V., M.V.; M.L.; S.F.; L.T.; M.C.; and M.F.; writing—original draft preparation, S.T.; G.F.; and M.F.; writing—review and editing, S.T.; G.F.; L.T.; M.C.; and M.F.; supervision, S.T.; G.F.; L.T.; M.C.; and M.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable for review papers.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable for review papers.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable for review papers.
Acknowledgments
We thank SITAC, Società Italiana per il Trattamento dell’Alcolismo e le sue Complicanze, Rome, Italy, Sapienza University of Rome, Italy and IBBC-CNR, Rome, Italy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mattson, S.N.; Crocker, N.; Nguyen, T.T. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: neuropsychological and behavioral features. Neuropsychol Rev 2011, 21, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenmyer, J.R.; Popova, S.; Klug, M.G.; Burd, L. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: a systematic review of the cost of and savings from prevention in the United States and Canada. Addiction 2020, 115, 409–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorgias, D.; Bernstein, B. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome., Treasure Island (FL), Treasure Island (FL): 2021.
- Terracina, S.; Ferraguti, G.; Tarani, L.; Messina, M.P.; Lucarelli, M.; Vitali, M.; et al. Transgenerational Abnormalities Induced by Paternal Preconceptual Alcohol Drinking. Findings from Humans and Animal Models. Curr Neuropharmacol 2021, 19, 1158–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalberg, W.O.; Buckley, D. FASD: what types of intervention and rehabilitation are useful? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2007, 31, 278–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Data & Statistics: Prevalence of FASDs. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Haycock, P.C. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: the epigenetic perspective. Biol Reprod 2009, 81, 607–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciafrè, S.; Ferraguti, G.; Greco, A.; Polimeni, A.; Ralli, M.; Ceci, F.M.; et al. Alcohol as an early life stressor: epigenetics, metabolic, neuroendocrine and neurobehavioral implications. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2020, 118, 654–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, S.; Lange, S.; Shield, K.; Mihic, A.; Chudley, A.E.; Mukherjee, R.A.S.; et al. Comorbidity of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2016, 387, 978–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.; Andrew, G.; Zwaigenbaum, L.; Tough, S. Neurobehavioural outcomes of children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: A Canadian perspective. Paediatr Child Heal 2008, 13, 185–91. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, E.A.; Sarkar, D.K. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders and their transmission through genetic and epigenetic mechanisms. Front Genet 2014, 5, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burd, L.; Blair, J.; Dropps, K. Prenatal alcohol exposure, blood alcohol concentrations and alcohol elimination rates for the mother, fetus and newborn. J Perinatol 2012, 32, 652–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keen, C.L.; Uriu-Adams, J.Y.; Skalny, A.; Grabeklis, A.; Grabeklis, S.; Green, K.; et al. The plausibility of maternal nutritional status being a contributing factor to the risk for fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: The potential influence of zinc status as an example. BioFactors 2010, 36, 125–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.C.; Fabro, S. Alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking: effect on pregnancy. Clin Obstet Gynecol 1983, 26, 437–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Shirasaka, T. An Update on Fetal Alcohol Syndrome—Pathogenesis, Risks, and Treatment. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2016, 40, 1594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.; Shapiro, A.M.; Wells, P.G. Embryonic catalase protects against ethanol-initiated DNA oxidation and teratogenesis in acatalasemic and transgenic human catalase-expressing mice. Toxicol Sci 2013, 134, 400–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarver, D.G.; Thomasson, H.R.; Martier, S.S.; Sokol, R.J.; Li, T. Alcohol dehydrogenase-2*3 allele protects against alcohol-related birth defects among African Americans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997, 283, 1095–101. [Google Scholar]
- Tunc-Ozcan, E.; Sittig, L.J.; Harper, K.M.; Graf, E.N.; Redei, E.E. Hypothesis: Genetic and epigenetic risk factors interact to modulate vulnerability and resilience to FASD. Front Genet 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, S.; Charness, M.E.; Burd, L.; Crawford, A.; Hoyme, H.E.; Mukherjee, R.A.S.; et al. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Nat Rev Dis Prim 2023, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton-Larrivée, M.; Elder, E.; Legault, L.; Langford-Avelar, A.; MacFarlane, A.J.; McGraw, S. Mitigating the detrimental developmental impact of early fetal alcohol exposure using a maternal methyl donor-enriched diet. FASEB J 2023, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccanti, M.; Hamilton, D.; Coriale, G.; Carito, V.; Aloe, L.; Chaldakov, G.; et al. Spatial learning in men undergoing alcohol detoxification. Physiol Behav 2015, 149, 324–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coriale, G.; Battagliese, G.; Pisciotta, F.; Attilia, M.L.; Porrari, R.; De Rosa, F.; et al. Behavioral responses in people affected by alcohol use disorder and psychiatric comorbidity: Correlations with addiction severity. Ann Ist Super Sanita 2019, 55, 131–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.; Buckley, S.; Budacki, R.; Jabbar, A.; Gallicano, G.I. Screening, Diagnosing and Prevention of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: Is This Syndrome Treatable. Dev Neurosci 2010, 32, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, J.; Shvedova, M.; Thanapaul, R.J.R.S.; Botchkarev, V.; Roh, D. Epigenetic Regulation of Cellular Senescence. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitro, N.; Verdeguer, F.; Perissi, V. Editorial: Epigenetics and metabolism. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, I.M.; Mydlarz, W.K.; Mithani, S.K.; Califano, J.A. DNA global hypomethylation in squamous cell head and neck cancer associated with smoking, alcohol consumption and stage. Int J Cancer 2007, 121, 1724–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finegersh, A.; Rompala, G.R.; David, I.K.; Martin, G.E.H. Drinking beyond a lifetime: New and emerging insights into paternal alcohol exposure on subsequent generations. Alcohol 2015, 49, 461–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, D.K. Male germline transmits fetal alcohol epigenetic marks for multiple generations: A review. Addict Biol 2016, 21, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-M.; Johnson, A.; Tarapore, P.; Janakiram, V.; Zhang, X.; Leung, Y.-K. Environmental Epigenetics and Its Implication on Disease Risk and Health Outcomes. ILAR J 2012, 53, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomberk, G.A.; Iovanna, J.; Urrutia, R. The promise of epigenomic therapeutics in pancreatic cancer. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 831–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaló, J.; Berdasco, M. Ethical implications of epigenetics in the era of personalized medicine. Clin Epigenetics 2022, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, M. Genetic and epigenetic insights into fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Genome Med 2010, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavarajappa, B.S. Epigenetics in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 2023, 197, 211–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legault, L.M.; Bertrand-Lehouillier, V.; McGraw, S. Pre-implantation alcohol exposure and developmental programming of FASD: An epigenetic perspective. Biochem Cell Biol 2018, 96, 117–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavarajappa, B.S.; Subbanna, S. Epigenetic mechanisms in developmental alcohol-induced neurobehavioral deficits. Brain Sci 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminen-Ahola, N. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms. Prenat Diagn 2020, 40, 1185–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnke, A.H.; Miranda, R.C.; Homanics, G.E. Epigenetic mediators and consequences of excessive alcohol consumption. Alcohol 2017, 60, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, S.; Otsuka, I.; Shinko, Y.; Horai, T.; Hirata, T.; Yamaki, N.; et al. Epigenetic Clock Analysis in Children With Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2021, 45, 329–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, V.; Curtis, K.; Zachariah, R.; Chudley, A.; Rastegar, M. Overview of the Genetic Basis and Epigenetic Mechanisms that Contribute to FASD Pathobiology. Curr Top Med Chem 2016, 17, 808–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungerer, M.; Knezovich, J.; Ramsay, M. In utero alcohol exposure, epigenetic changes, and their consequences. Alcohol Res Curr Rev 2013, 35, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Oei, J.L. Alcohol use in pregnancy and its impact on the mother and child. Addiction 2020, 115, 2148–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouko, L.A.; Shantikumar, K.; Knezovich, J.; Haycock, P.; Schnugh, D.J.; Ramsay, M. Effect of alcohol consumption on CpG methylation in the differentially methylated regions of H19 and IG-DMR in male gametes - Implications for fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2009, 33, 1615–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.C.; Skiles, W.M.; Chronister, S.S.; Wang, H.; Sutton, G.I.; Bedi, Y.S.; et al. DNA methylation-independent growth restriction and altered developmental programming in a mouse model of preconception male alcohol exposure. Epigenetics 2017, 12, 841–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haycock, P.C.; Ramsay, M. Exposure of mouse embryos to ethanol during preimplantation development: effect on DNA methylation in the h19 imprinting control region. Biol Reprod 2009, 81, 618–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiulionis, M.G. Abnormal epigenetic regulation of immune system during aging. Front Immunol 018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussier, A.A.; Bodnar, T.S.; Weinberg, J. Intersection of Epigenetic and Immune Alterations: Implications for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder and Mental Health. Front Neurosci 2021, 15, 788630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompala, G.R.; Mounier, A.; Wolfe, C.M.; Lin, Q.; Lefterov, I.; Homanics, G.E. Heavy chronic intermittent ethanol exposure alters small noncoding RNAs in mouse sperm and epididymosomes. Front Genet 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedi, Y.; Chang, R.C.; Gibbs, R.; Clement, T.M.; Golding, M.C. Alterations in sperm-inherited noncoding RNAs associate with late-term fetal growth restriction induced by preconception paternal alcohol use. Reprod Toxicol 2019, 87, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roozen, S.; Ehrhart, F. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders and the risk of crime. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2023, 197, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentzel, P.; Rydberg, U.; Eriksson, U.J. Antioxidative treatment diminishes ethanol-induced congenital malformations in the rat. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2006, 30, 1752–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derme, M.; Piccioni, M.G.; Brunelli, R.; Crognale, A.; Denotti, M.; Ciolli, P.; et al. Oxidative Stress in a Mother Consuming Alcohol during Pregnancy and in Her Newborn: A Case Report. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, C.; Marchi, S.; Simoes, I.C.M.; Ren, Z.; Morciano, G.; Perrone, M.; et al. Mitochondria and Reactive Oxygen Species in Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 2018, 340, 209–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, P.G.; Bhatia, S.; Drake, D.M.; Miller-Pinsler, L. Fetal oxidative stress mechanisms of neurodevelopmental deficits and exacerbation by ethanol and methamphetamine. Birth Defects Res Part C - Embryo Today Rev 2016, 108, 108–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.C. A mitochondrial paradigm of metabolic and degenerative diseases, aging, and cancer: A dawn for evolutionary medicine. Annu Rev Genet 2005, 39, 359–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, F.; Ramnath, N.; Nagrath, D. Reactive oxygen species in the tumor microenvironment: An overview. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, H.K.; Mueller, S. Alcohol and cancer: An overview with special emphasis on the role of acetaldehyde and cytochrome P450 2E1. Adv Exp Med Biol 2015, 815, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matilainen, O.; Quirós, P.M.; Auwerx, J. Mitochondria and Epigenetics – Crosstalk in Homeostasis and Stress. Trends Cell Biol 2017, 27, 453–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Drake, D.M.; Miller, L.; Wells, P.G. Oxidative stress and DNA damage in the mechanism of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Birth Defects Res 2019, 111, 714–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkman, B.G.; Sakharkar, A.J.; Pandey, S.C. Epigenetics-beyond the genome in alcoholism. Alcohol Res 2012, 34, 293–305. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, D.K.; Gangisetty, O.; Wozniak, J.R.; Eckerle, J.K.; Georgieff, M.K.; Foroud, T.M.; et al. Persistent Changes in Stress-Regulatory Genes in Pregnant Women or Children Exposed Prenatally to Alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2019, 43, 1887–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Márquez, J.M.; Navarro-Hortal, M.D.; Jiménez-Trigo, V.; Muñoz-Ollero, P.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Esteban-Muñoz, A.; et al. An Olive-Derived Extract 20% Rich in Hydroxytyrosol Prevents β-Amyloid Aggregation and Oxidative Stress, Two Features of Alzheimer Disease, via SKN-1/NRF2 and HSP-16.2 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxidants 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Tong, M.; Monte, S.M. Chronic ethanol exposure causes mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in immature central nervous system neurons. Acta Neuropathol 2007, 113, 659–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, S.; Matsushita, S.; Murayama, M.; Takagi, S.; Hayashida, M. Alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase polymorphisms and the risk for alcoholism. Am J Psychiatry 1995, 152, 1219–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbinian, N.; Darbinyan, A.; Merabova, N.; Kassem, M.; Tatevosian, G.; Amini, S.; et al. In utero ethanol exposure induces mitochondrial DNA damage and inhibits mtDNA repair in developing brain. Front Neurosci 2023, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzeszczak, K.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Malinowski, W.; Ziętek, P.; Kosik-Bogacka, D. Oxidative Stress in Pregnancy. Biomolecules 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Verma, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Ahmad, M.K.; Nischal, A.; Singh, S.K.; et al. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Status in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Scand J Immunol 2017, 85, 130–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutala, R.; Wang, J.; Kadapakkam, S.; Hwang, Y.; Ticku, M.; Li, M.D. Microarray analysis of ethanol-treated cortical neurons reveals disruption of genes related to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and protein synthesis. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2004, 28, 1779–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabulea, A.L.; Janeski, J.D.; Naik, V.D.; Chen, K.; Mor, G.; Ramadoss, J. A multi-organ analysis of the role of mTOR in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. FASEB J 2023, 37, e22897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokoloff, L. Energetics of functional activation in neural tissues. Neurochem Res 1999, 24, 321–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, M.; Ben-Shachar, D.; Riederer, P.; Youdim, M.B.H. Altered brain metabolism of iron as a cause of neurodegenerative diseases? J Neurochem 1994, 63, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floyd, R.A.; Carney, J.M. Free radical damage to protein and DNA: Mechanisms involved and relevant observations on brain undergoing oxidative stress. Ann Neurol 1992, 32, S22–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamini, C.; Gambetti, S.; Dondi, A.; Cervellati, C. Oxygen, Reactive Oxygen Species and Tissue Damage. Curr Pharm Des 2005, 10, 1611–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakoyiannis, I.; Gkioka, E.; Pergialiotis, V.; Mastroleon, I.; Prodromidou, A.; Vlachos, G.D.; et al. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders and cognitive functions of young children. Rev Neurosci 2014, 25, 631–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rompala, G.R.; Finegersh, A.; Homanics, G.E. Paternal preconception ethanol exposure blunts hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis responsivity and stress-induced excessive fluid intake in male mice. Alcohol 2016, 53, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.; Tarabulsy, G.M.; Bussières, E.-L. Foetal programming and cortisol secretion in early childhood: A meta-analysis of different programming variables. Infant Behav Dev 2015, 40, 204–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coriale, G.; Fiorentino, D.; Lauro, F.D.I.; Marchitelli, R.; Scalese, B.; Fiore, M.; et al. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD): Neurobehavioral profile, indications for diagnosis and treatment. Riv Psichiatr 2013, 48, 359–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.; Condon, C.; Hamilton, S.; Mutch, R.C.; Bower, C.; Watkins, R.E. Challenges in Accurately Assessing Prenatal Alcohol Exposure in a Study of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder in a Youth Detention Center. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2019, 43, 309–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Kerem, R.; Koren, G. Antioxidants and fetal protection against ethanol teratogenicity. Neurotoxicol Teratol 2003, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micangeli, G.; Menghi, M.; Profeta, G.; Tarani, F.; Mariani, A.; Petrella, C.; et al. The Impact of Oxidative Stress on Pediatrics Syndromes. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, C.; Carito, V.; Carere, C.; Ferraguti, G.; Ciafrè, S.; Natella, F.; et al. Oxidative stress inhibition by resveratrol in alcohol-dependent mice. Nutrition 2020, 79–80, 10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y. A review of interventions against fetal alcohol spectrum disorder targeting oxidative stress. Int J Dev Neurosci 2018, 71, 140–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, Q.; et al. The protective effect of astaxanthin on fetal alcohol spectrum disorder in mice. Neuropharmacology 2014, 84, 13–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.; Desrocher, M.; Moore, T. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder: A Review of Neurodevelopmental Findings and Interventions. J Dev Phys Disabil 2011, 23, 143–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carito, V.; Ceccanti, M.; Cestari, V.; Natella, F.; Bello, C.; Coccurello, R.; et al. Olive polyphenol effects in a mouse model of chronic ethanol addiction. Nutrition 2017, 33, 65–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraguti, G.; Terracina, S.; Micangeli, G.; Lucarelli, M.; Tarani, L.; Ceccanti, M.; et al. NGF and BDNF in pediatrics syndromes. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2023, 145, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawaid, S.; Strainic, J.P.; Kim, J.; Ford, M.R.; Thrane, L.; Karunamuni, G.H.; et al. Glutathione Protects the Developing Heart from Defects and Global DNA Hypomethylation Induced by Prenatal Alcohol Exposure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2021, 45, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciafrè, S.; Carito, V.; Ferraguti, G.; Greco, A.; Chaldakov, G.N.; Fiore, M.; et al. How alcohol drinking affects our genes: An epigenetic point of view. Biochem Cell Biol 2019, 97, 345–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, L.A.; Coles, S.; Blitz, R. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Am Fam Physician 2017, 96, 515–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, L.; Nogales, F.; Murillo, L.; Carreras, O. The role of folic acid and selenium against oxidative damage from ethanol in early life programming: A review. Biochem Cell Biol 2018, 96, 178–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunamuni, G.; Sheehan, M.M.; Doughman, Y.Q.; Gu, S.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Supplementation with the Methyl Donor Betaine Prevents Congenital Defects Induced by Prenatal Alcohol Exposure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2017, 41, 1917–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyme, H.E.; Kalberg, W.O.; Elliott, A.J.; Blankenship, J.; Buckley, D.; Marais, A.S.; et al. Updated clinical guidelines for diagnosing fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20154256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainsod, A.; Bendelac-Kapon, L.; Shabtai, Y. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder: Embryogenesis Under Reduced Retinoic Acid Signaling Conditions. Subcell Biochem 2020, 95, 197–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceci, F.M.; Ferraguti, G.; Petrella, C.; Greco, A.; Ralli, M.; Iannitelli, A.; et al. Nerve Growth Factor in Alcohol Use Disorders. Curr Neuropharmacol 2020, 19, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.X.; Jonsson, E. Life expectancy of people with fetal alcohol syndrome. J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol 2016, 23, e53–9. [Google Scholar]
- May, P.A.; Gossage, J.P. Maternal risk factors for fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: not as simple as it might seem. Alcohol Res Health 2011, 34, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, N.X.; Jonsson, E.; Salmon, A.; Sebastianski, M. Incidence and prevalence of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder by sex and age group in Alberta, Canada. J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol 2014, 21, e395–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Popova, S.; Lange, L.; Probst, C.; Gmel, G.; Rehm, J. Estimation of national, regional, and global prevalence of alcohol use during pregnancy and fetal alcohol syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2017, 5, 290–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steane, S.E.; Cuffe, J.S.M.; Moritz, K.M. The role of maternal choline, folate and one-carbon metabolism in mediating the impact of prenatal alcohol exposure on placental and fetal development. J Physiol 2023, 601, 1061–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, P.A.; Marais, A.-S.; Kalberg, W.O.; de Vries, M.M.; Buckley, D.; Hasken, J.M.; et al. Multifaceted case management during pregnancy is associated with better child outcomes and less fetal alcohol syndrome. Ann Med 2023, 55, 926–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).