Submitted:
04 March 2024
Posted:
05 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Extraction
2.2. Synthesis of MnOx NPs
2.3. Photocatalytic degradation of MnO NPs
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
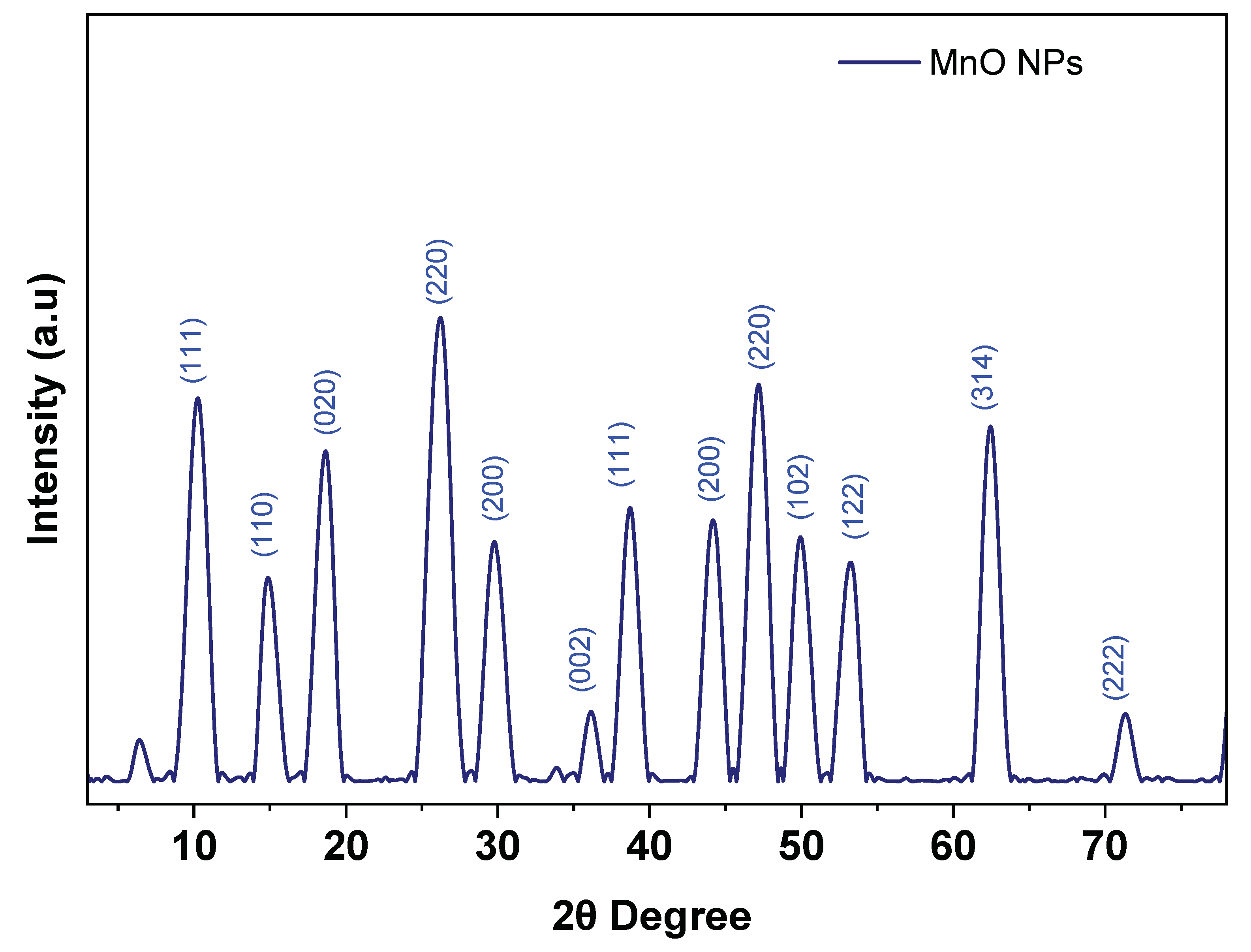
3.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
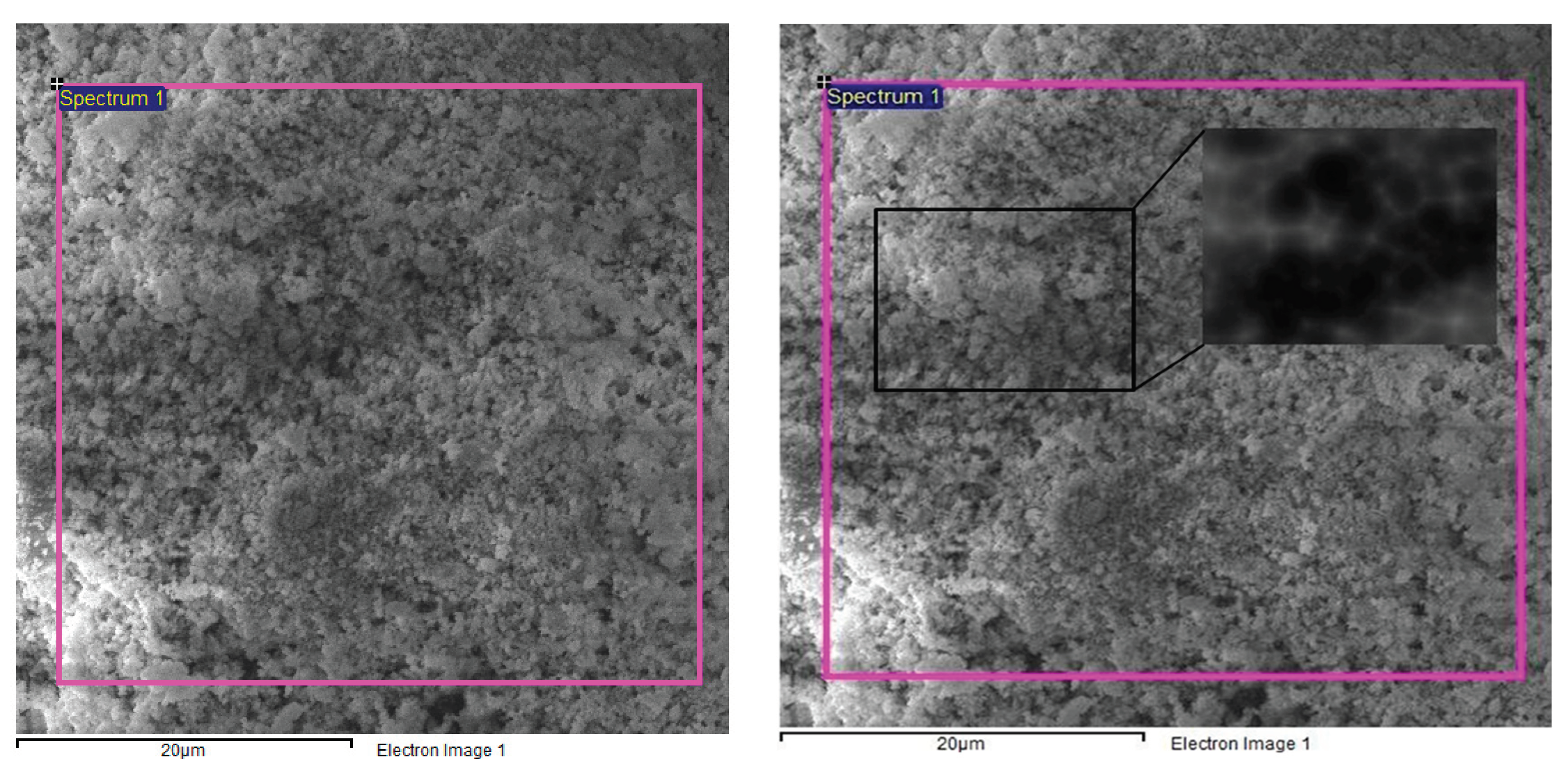
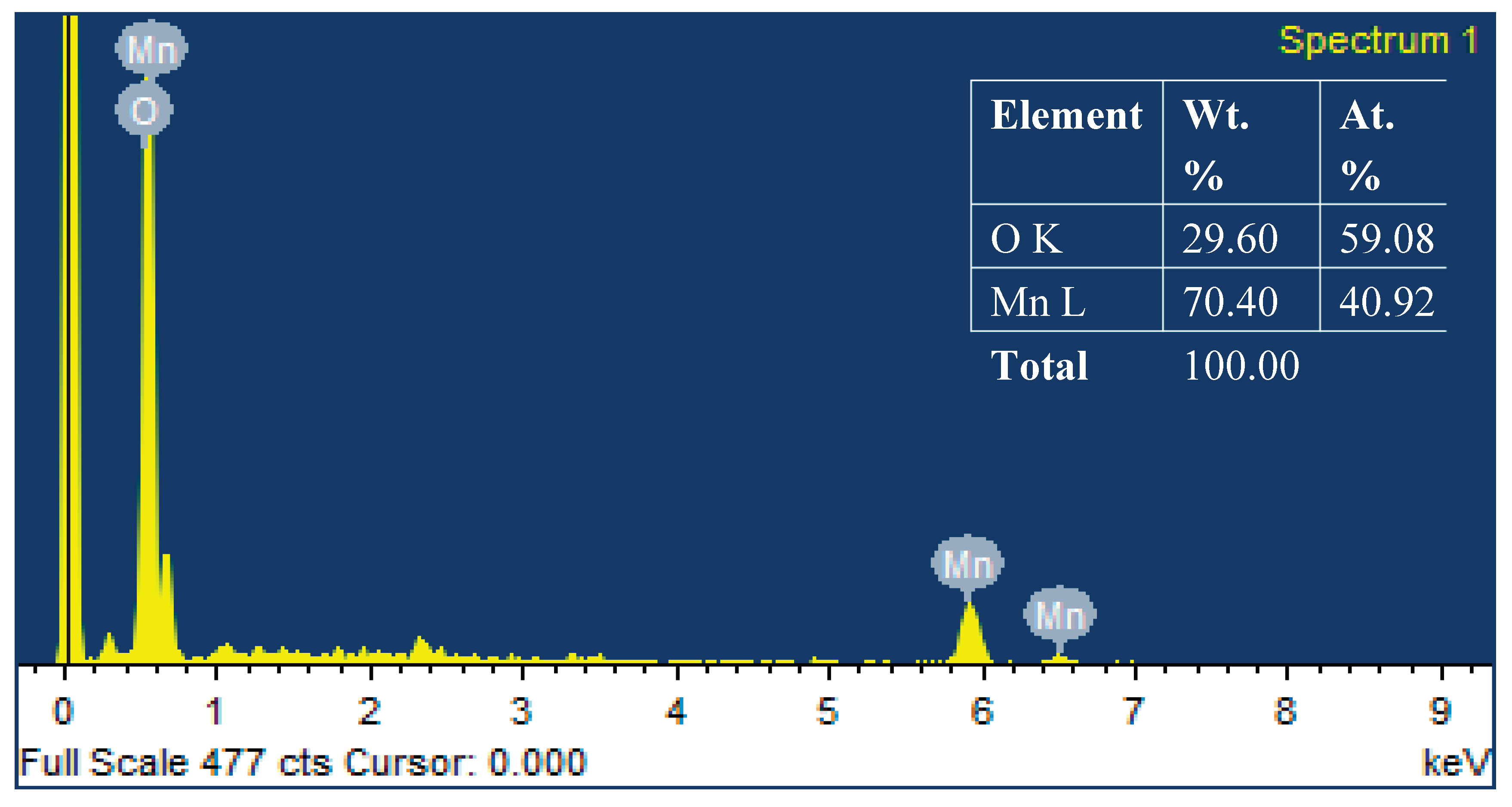
3.2. SEM and EDX Analysis
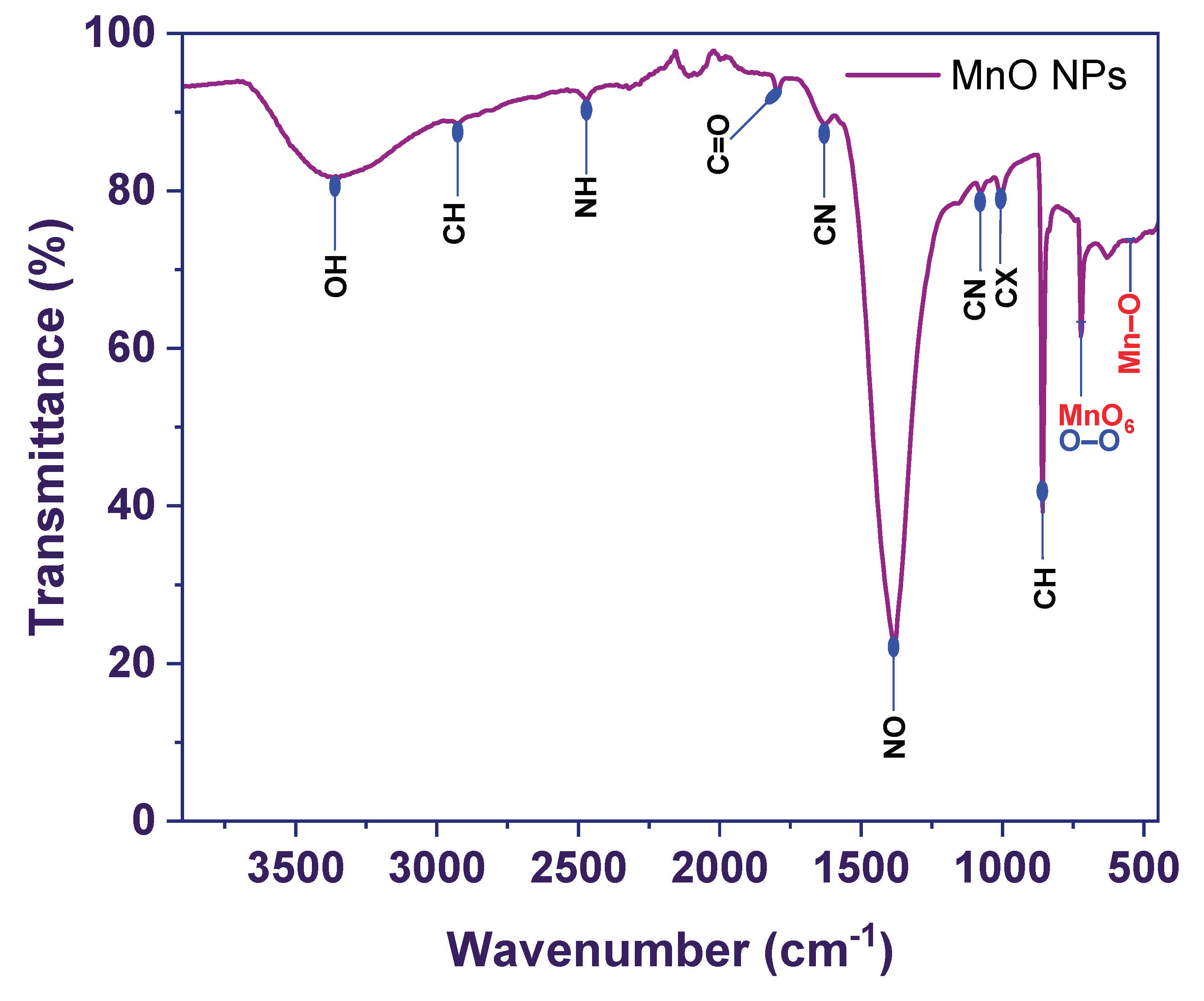
3.3. FTIR Analysis
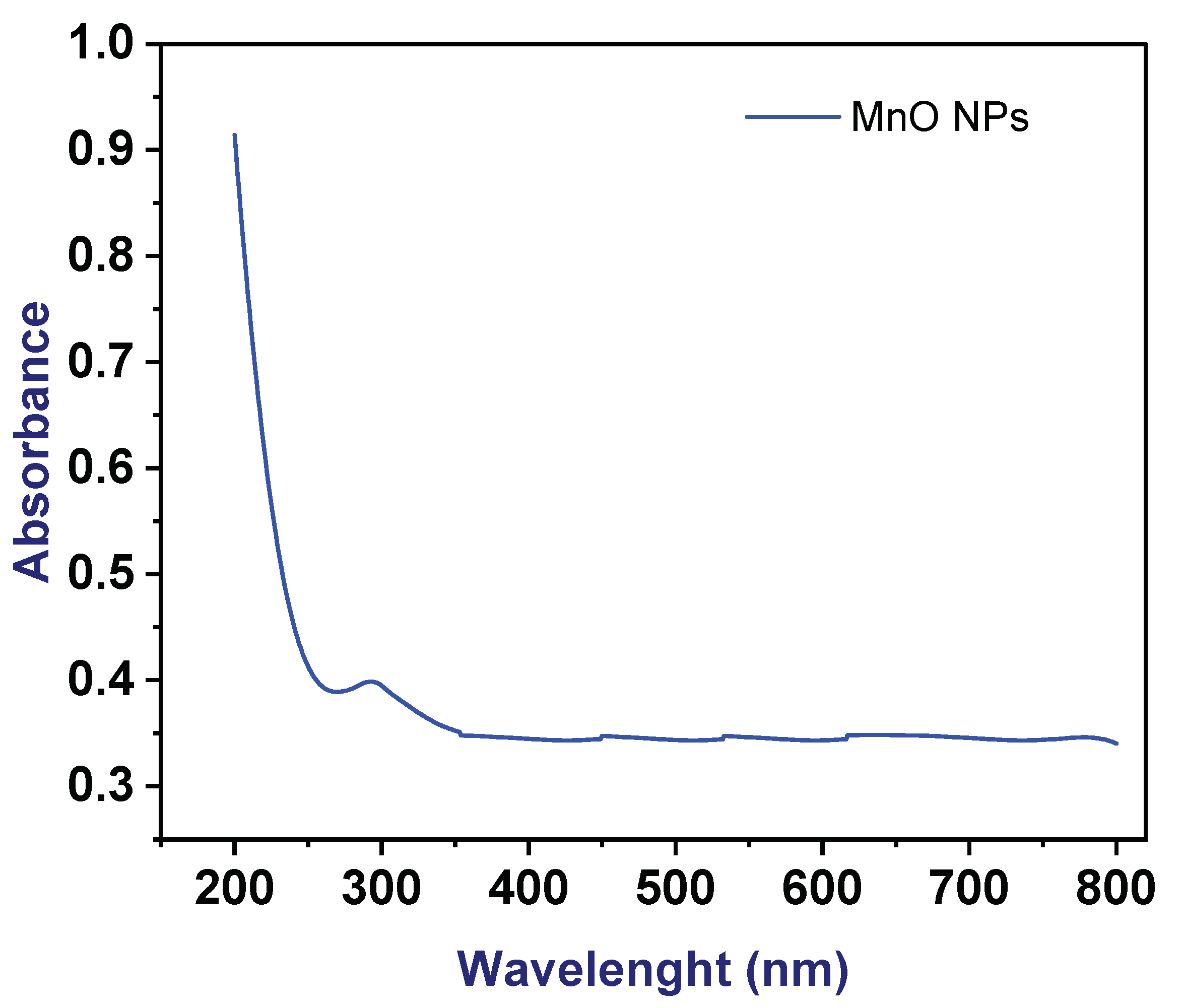
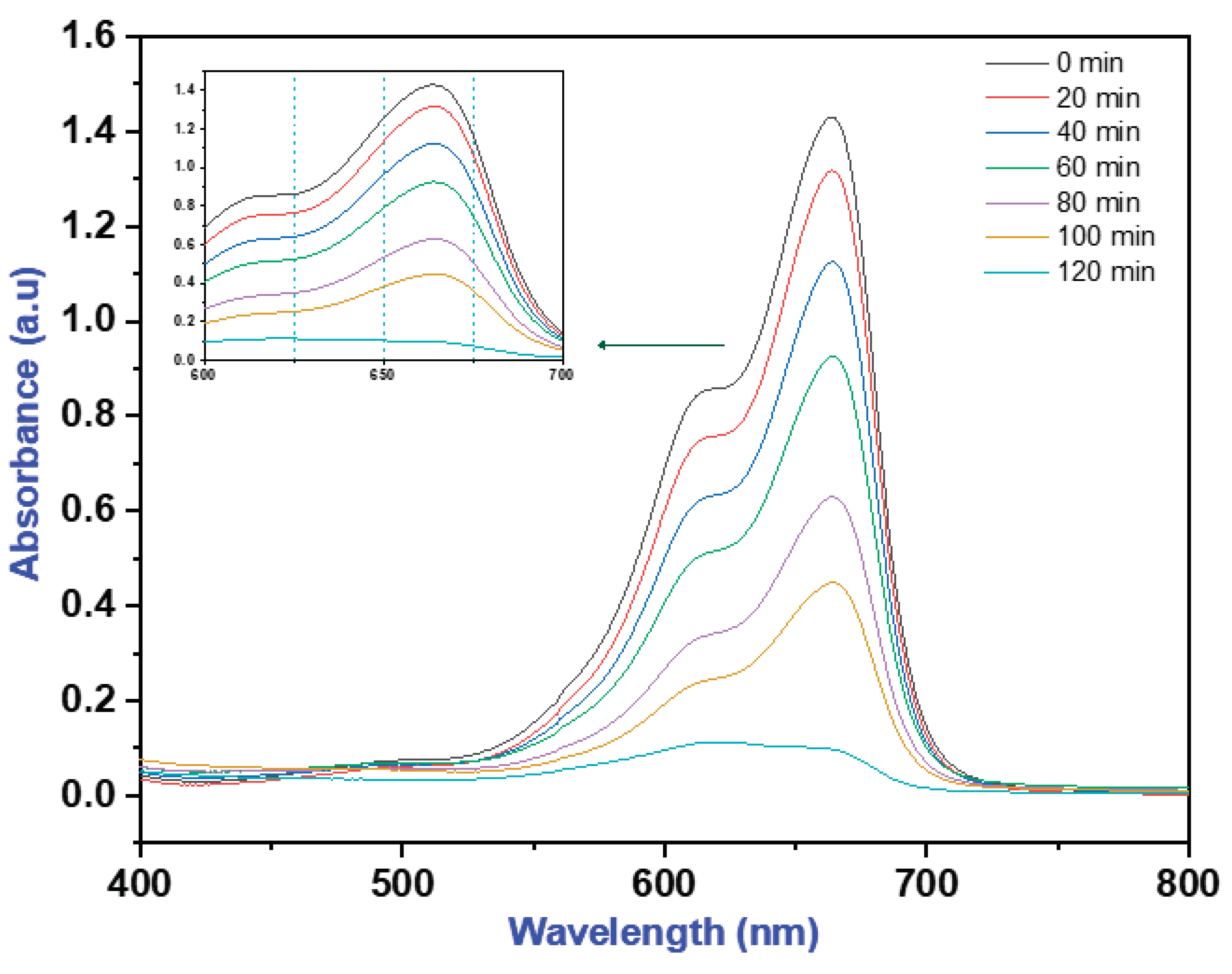
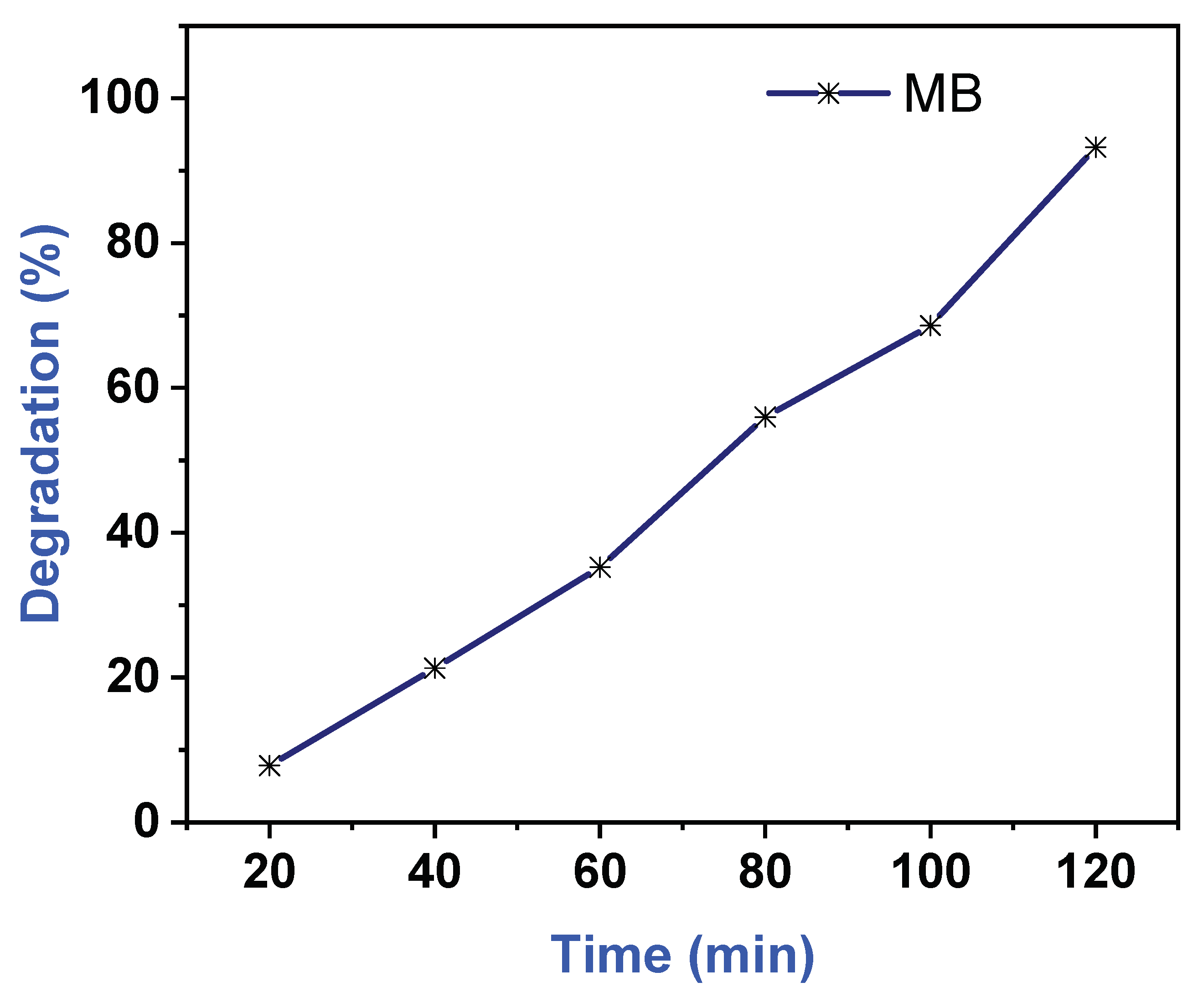
3.4. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue (MB) Dye
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgment
Conflict of Interest
References
- Khan, S.A.; Arshad, Z.; Shahid, S.; Arshad, I.; Rizwan, K.; Sher, M.; Fatima, U. Synthesis of TiO2/Graphene oxide nanocomposites for their enhanced photocatalytic activity against methylene blue dye and ciprofloxacin. Composites Part B: Engineering 2019, 175, 107120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Sajadi, S.M.S.; Amiri, O.; Hamadanian, M.; Moayedi, H.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Beigi, M.M. MgCr2O4 and MgCr2O4/Ag nanostructures: Facile size-controlled synthesis and their photocatalytic performance for destruction of organic contaminants. Composites Part B: Engineering 2019, 175, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirpara, D.G.; Gajera, H.P. Green synthesis and antifungal mechanism of silver nanoparticles derived from chitin-induced exometabolites of Trichoderma interfusant. Applied Organometallic Chemistry 2020, 34, e5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangeneh, M.M.; Zangeneh, A. Novel green synthesis of Hibiscus sabdariffa flower extract conjugated gold nanoparticles with excellent anti-acute myeloid leukemia effect in comparison to daunorubicin in a leukemic rodent model. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Radadi, N.S. Green synthesis of platinum nanoparticles using Saudi’s Dates extract and their usage on the cancer cell treatment. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 330–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahvilian, R.; Zangeneh, M.M.; Falahi, H.; Sadrjavadi, K.; Jalalvand, A.R.; Zangeneh, A. Green synthesis and chemical characterization of copper nanoparticles using Allium saralicum leaves and assessment of their cytotoxicity, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and cutaneous wound healing properties. Applied organometallic chemistry 2019, 33, e5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, B.; Saneei, S.; Qorbani, M.; Zhaleh, M.; Zangeneh, A.; Zangeneh, M.M.; Ghaneialvar, H. Ziziphora clinopodioides Lam leaves aqueous extract mediated synthesis of zinc nanoparticles and their antibacterial, antifungal, cytotoxicity, antioxidant, and cutaneous wound healing properties under in vitro and in vivo conditions. Applied Organometallic Chemistry 2019, 33, e5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharfar, R.; Zareyee, D.; Allahgholipour, S.L. Synthesis and characterization of MgO nanoparticles supported on ionic liquid-based periodic mesoporous organosilica (MgO@PMO-IL) as a highly efficient and reusable nanocatalyst for the synthesis of novel spirooxindole-furan derivatives. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Abbasi, B.A.; Mahmood, T.; Hameed, S.; Munir, A.; Kanwal, S. Green synthesis and characterizations of Nickel oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Rhamnus virgata and their potential biological applications. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, F.; Shahid, S.; Khan, S.A.; Ahmad, W.; Zaman, S. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Abutilon indicum leaf extract: Antimicrobial, antioxidant and photocatalytic dye degradation activitie. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Noreen, F.; Kanwal, S.; Iqbal, A.; Hussain, G. Green synthesis of ZnO and Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles from leaf extracts of Abutilon indicum, Clerodendrum infortunatum, Clerodendrum inerme and investigation of their biological and photocatalytic activities. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2018, 82, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, S.; Rehman, W.; Waseem, M.; Shah, A.; Khan, A.R.; Rehman, M.U.; Ahmad, P.; Khan, B.; Ali, G. Green synthesis and characterization of tin dioxide nanoparticles for photocatalytic and antimicrobial studies. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 025012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeramani, H.; Aruguete, D.; Monsegue, N.; Murayama, M.; Dippon, U.; Kappler, A.; Hochella, M.F. Low-Temperature Green Synthesis of Multivalent Manganese Oxide Nanowires. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Kanwal, S.; Rizwan, K.; Shahid, S. Enhanced antimicrobial, antioxidant, in vivo antitumor and in vitro anticancer effects against breast cancer cell line by green synthesized un-doped SnO2 and Co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles from Clerodendrum inerme. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 366–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, S.; Fatima, U.; Sajjad, R.; Khan, S.A. Bioinspired nanotheranostic agent: Zinc oxide; green synthesis and biomedical potential. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct 2019, 14, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Mohmand, N.Z.K.; Hassan, A.; Ullah, H.; Shah, Y. Rumax dentatus Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles, Antimicrobial Activity and Characterization. 2023.
- Hassan, A.; Mohmand, N.Z.K.; Ullah, H.; Hussain, A. ; Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, and Antihypertension Inhibitory Potentials of Phenolic Rich Medicinal Plants. J. Chem. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Ullah, I.; Ahmad, W. Isolation and Evaluation of Antibacterial Potential Test of Plant Carthamus oxycantha. J. Trop. Pharm. Chem. 2021, 5, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, H.; Shahzeb, M.W.; Nawaz, K. Extraction and antibacterial potential of traditional medicinal plant Cypreus compressus. TMR Modern Herbal Medicine 2021, 4, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A.; Ullah, H.; Israr, M. The Antioxidant Activity and Phytochemical Analysis of Medicinal Plant Veronica Biloba. J. Trop. Pharm. Chem. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Du, J.; Singh, P.; Yi, T.H. Ecofriendly synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by Euphrasia officinalis leaf extract and its biomedical applications. Artif. Cells, Nanomedicine, Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Shahid, S.; Shahid, B.; Fatima, U.; Abbasi, S.A. Green synthesis of MnO nanoparticles using abutilon indicum leaf extract for biological, photocatalytic, and adsorption activities. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoor, S.; Nabi, G.A.K.; Hussain, S.; Javid, Z.; Jan, F.A. Synthesis, Characterization, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Study of Photocatalytic Degradation of Malachite Green Dye Using MnO2 Nanoparticles as Catalyst. Chem. Afr. 2023, 7, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.; Jan, F.A.; Saleem, S.; Ullah, R.; Wajidullah, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Ullah, N. Salman Juglans regia L. mediated synthesis of cobalt oxide and zinc-doped cobalt oxide nanoparticles: characterization and evaluation for environmental, antibacterial and cytotoxic potential. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2022, 7, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjula, R.; Thenmozhi, M.; Thilagavathi, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Kathirvel, A. Green synthesis and characterization of manganese oxide nanoparticles from Gardenia resinifera leaves. Mater. Today: Proc. 2020, 26, 3559–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Hasan, M.M. Exploring globally used antiurolithiatic plants of M to R families: Including Myrtaceae, Phyllanthaceae, Piperaceae, Polygonaceae, Rubiaceae and Rutaceae. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry 2017, 6, 325–335. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Deng, D.; Jiang, L.; Shu, C.; Wang, C. Facile Synthesis of Porous Mn2O3 Nanoplates and Their Electrochemical Behavior as Anode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries. Chem. – A Eur. J. 2014, 20, 6126–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, H.; Gong, X.; Xu, R.; Xiao, Y.; Dong, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y. A simple additive-free approach for the synthesis of uniform manganese monoxide nanorods with large specific surface area. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 166–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labhane, P.K.; Sonawane, G.H.; Sonawane, S.H. Influence of rare-earth metal on the zinc oxide nanostructures: application in the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and p-nitro phenol. Green Process. Synth. 2017, 7, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganyi, D.; Altaf, M.; Wekesa, I. Synthesis and characterization of whisker-shaped MnO2 nanostructure at room temperature. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 3, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Yang, G.F.; Li, Q.Y.; Zhong, X.X.; Wang, F.P.; Li, Z.S.; Li, Y.H. Porous nano-MnO2: large scale synthesis via a facile quick-redox procedure and application in a supercapacitor. New Journal of Chemistry 2011, 35, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.A.; Salunke, B.K.; Alkotaini, B.; Sathiyamoorthi, E.; Kim, B.S. Biological synthesis of manganese dioxide nanoparticles by Kalopanax pictus plant extract. IET Nanobiotechnology 2015, 9, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Ja, A.; Subramanian, A.; Subramanian, S.A.N.G.E.E.T.H.A. Synthesis and characterization of manganese dioxide using brassica oleracea (cabbage). J. Ind. Pollut. Control 2017, 33, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar]
- Rajabathar, J.R.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Arunachalam, P.; Issa, Z.A.; Gnanamani, M.K.; Appaturi, J.N.; Ibrahim, S.N.; Dahan, W.M. Synthesis and characterization of metal chalcogenide modified graphene oxide sandwiched manganese oxide nanofibers on nickel foam electrodes for high performance supercapacitor applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 850, 156346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Banis, M.N.; Liu, J.; Geng, D.; Li, R.; Sun, X. Facile controlled synthesis and growth mechanisms of flower-like and tubular MnO2 nanostructures by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 369, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Yu, L.; Chen, G.Z. Capacitive and non-capacitive faradaic charge storage. Electrochimica Acta 2016, 206, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Ahmadi, N.; Rezaei, B. Electrochemical preparation and characterization of a polypyrrole/nickel-cobalt hexacyanoferrate nanocomposite for supercapacitor applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 91448–91456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouda, E.; Yousf, N.; Magar, H.S.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; Duraia, E.-S.M. Electrochemical properties of MnO2-based carbon nanomaterials for energy storage and electrochemical sensing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dong, X.; Shi, J.; Zhao, J.; Hua, Z.; Gao, J.; Ruan, M.; Yan, D. Templated synthesis of hierarchically porous manganese oxide with a crystalline nanorod framework and its high electrochemical performance. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; He, J. Facile Synthesis of Monodisperse Manganese Oxide Nanostructures and Their Application in Water Treatment. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 17540–17545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estelrich, J.; Sanchez-Martin, M.J.; Busquets, M.A. Nanoparticles in magnetic resonance imaging: from simple to dual contrast agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1727–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Xiao, Y.; Yuan, D. Alcohol-assisted hydrothermal carbonization to fabricate spheroidal carbons with a tunable shape and aspect ratio. Carbon 2010, 48, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A.B. Chemical and Structural Properties of Carbonaceous Products Obtained by Hydrothermal Carbonization of Saccharides. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2009, 15, 4195–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Carmona, A.J.; Mora, E.S.; Flores, J.I.P.; Márquez-Beltrán, C.; Castañeda-Antonio, M.D.; González-Reyna, M.A.; Barrera, M.C.; Misaghian, K.; Lugo, J.E.; Toledo-Solano, M. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue by Magnetic Opal/Fe3O4 Colloidal Crystals under Visible Light Irradiation. Photochem 2023, 3, 390–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Synthesis of Magnetic Fe3O4@hierarchical Hollow Silica Nanospheres for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 10629–10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkannan, M.; Karthikeyan, C.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, D.J. One-pot green synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (RGO)/Fe3O4 nanocomposites and its catalytic activity toward methylene blue dye degradation. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2015, 136, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaast, S.; Grewal, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles, characterization and evaluation of their photocatalytic dye degradation activity. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




