Submitted:
12 February 2024
Posted:
14 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. The Effects of Gaming Skills on Cognitive and Affective Functioning
1.2. The Gaming Skill Questionnaire (GSQ)
1.3. Aims of This Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Gaming Skills Questionnaire
2.2.2. Edinburgh Cognitive & Behavioural ALS Screen (ECAS)
2.2.3. Trail Making Test (TMT)
2.2.4. Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test (RMET)
2.2.5. The Adolescent Empathy Spectrum Quotient (EQ)
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analyses
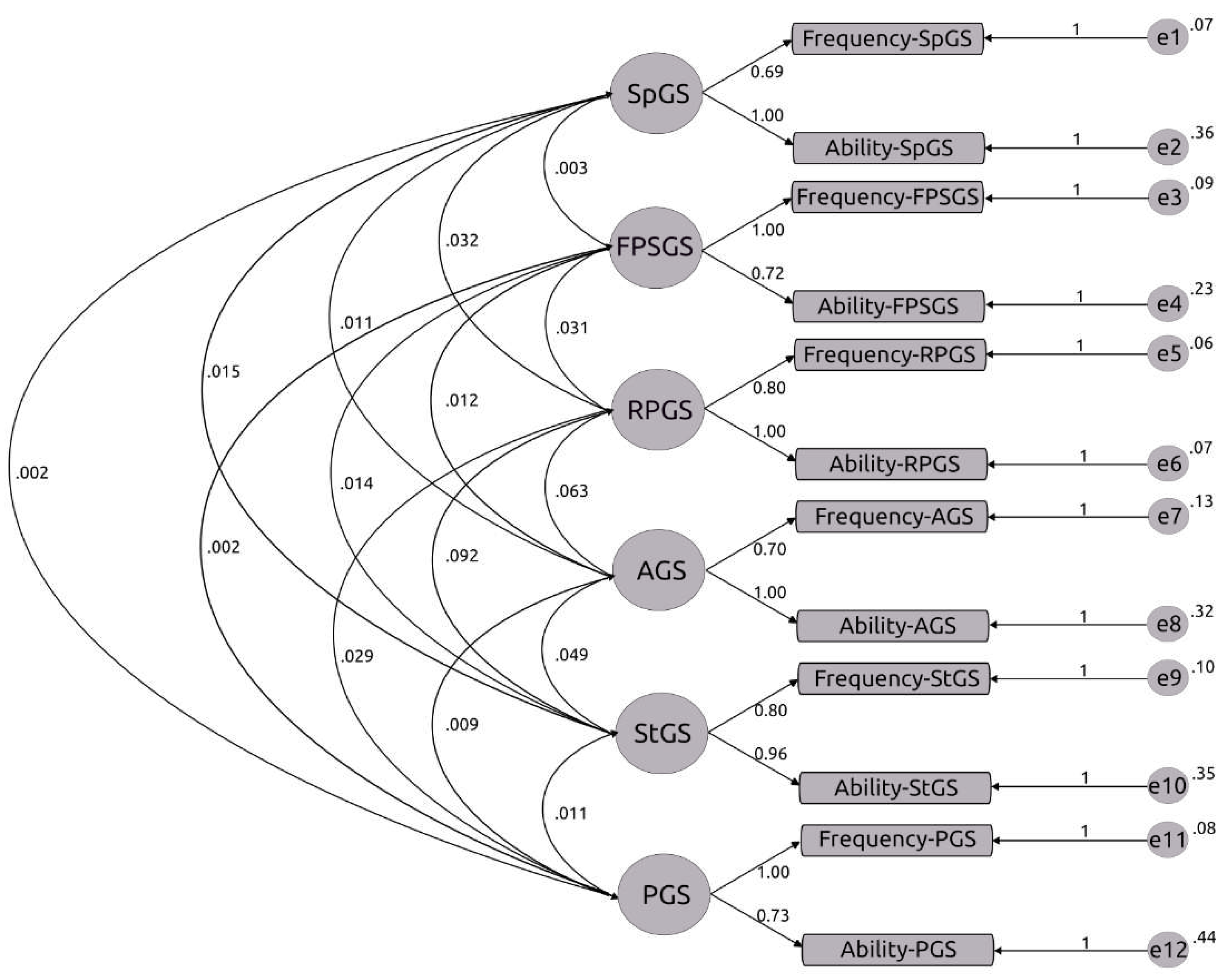
2.4.1. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
2.4.2. Regression Analysis Process
2.4.3. Two-Way ANOVA Analyses
3. Results
3.1. GSQ Internal Reliability, Goodness of Fit, and CFA
3.2. Correlations
| ECAS-L | ECAS-VF | ECAS-EF | ECAS-M | ECAS-TS | TMT-A | TMT-B | RMET | EQ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | .69*** | .71*** | .18*** | .23*** | .68*** | -.79*** | -.76*** | -.01 | -.14* |
| Residence Location^ | -.09 | .05 | .15** | .26*** | .14** | .02 | .09 | .12* | -.27*** |
| Parent Age | .18*** | .15** | .12* | .08 | .23*** | -.25*** | .-.20*** | .04 | -.07 |
| Parent Education^ | .19*** | .07 | .09 | .12* | .14* | -.06 | -.10 | .01 | -.03 |
| Family Income | .08 | .03 | .01 | -.01 | .05 | -.10 | -.17** | .01 | -.07 |
| Sport Games Skill | .07 | -.07 | -.05 | .07 | .01 | -.06 | -.04 | -.12* | -.13* |
| FPS Games Skill | .05 | .05 | .12* | .18* | .11* | -.06 | -.05 | .07 | -.21*** |
| RPG Skill | .07 | .02 | .23*** | .19*** | .17** | .03 | -.08 | .08 | -.19*** |
| Action-Adventure Games Skill | .11* | .08 | .33*** | .21*** | .25*** | -.13* | -.15** | .21*** | -.37*** |
| Strategy Games Skill | .09 | .07 | .17** | .16** | .17** | -.09 | -.11* | -.08 | -.14** |
| Puzzle Games Skill | .18*** | .16*** | .35*** | .23*** | .33*** | -.18*** | -.28*** | .17** | -.26*** |
| Total Gaming Skill | .19*** | .10 | .38*** | .35*** | .35*** | -.19*** | -.24*** | .11* | -.48*** |
3.3. Best Regression Models
| Predicted | Predictors | β coefficient | p-value(β) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECAS – Language | Age | 0.68 | <.001*** | .50 |
| Parent Education | 0.13 | <.001*** | ||
| ECAS – Verbal Fluency | Age | 0.72 | <.001*** | .52 |
| Residence Location | 0.08 | .026* | ||
| Sport Games Skills | -0.11 | .004** | ||
| ECAS – Executive Functions | Action Games Skill | 0.29 | <.001*** | |
| Strategy Games Skill | 0.16 | .002** | .21 | |
| Puzzle Games Skill | 0.24 | <.001*** | ||
| ECAS – Memory | Age | 0.19 | <.001*** | .20 |
| Residence Location | 0.23 | <.001*** | ||
| Total Gaming Skill | 0.28 | <.001*** | ||
| ECAS – Total Score | Age | 0.66 | <.001*** | .54 |
| Residence Location | 0.15 | <.001*** | ||
| Total Gaming Skill | 0.21 | <.001*** | ||
| Trail Making Test – A | Age | -0.79 | <.001*** | .63 |
| Trail Making Test – B | Age | -0.74 | <.001*** | .60 |
| Family Income | -0.10 | .003** | ||
| Total Gaming Skill | -0.11 | .002** | ||
| Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test | Residence Location | 0.11 | .046* | .10 |
| Sport Games Skills | -0.14 | .007** | ||
| Action-Adventure Games Skill | 0.14 | .014* | ||
| Strategy Games Skill | -0.13 | .021* | ||
| Puzzle Games Skill | 0.17 | .003** | ||
| Empathy Quotient | Total Gaming Skill | -0.45 | <.001*** | .27 |
| Residence Location | -0.21 | <.001*** |
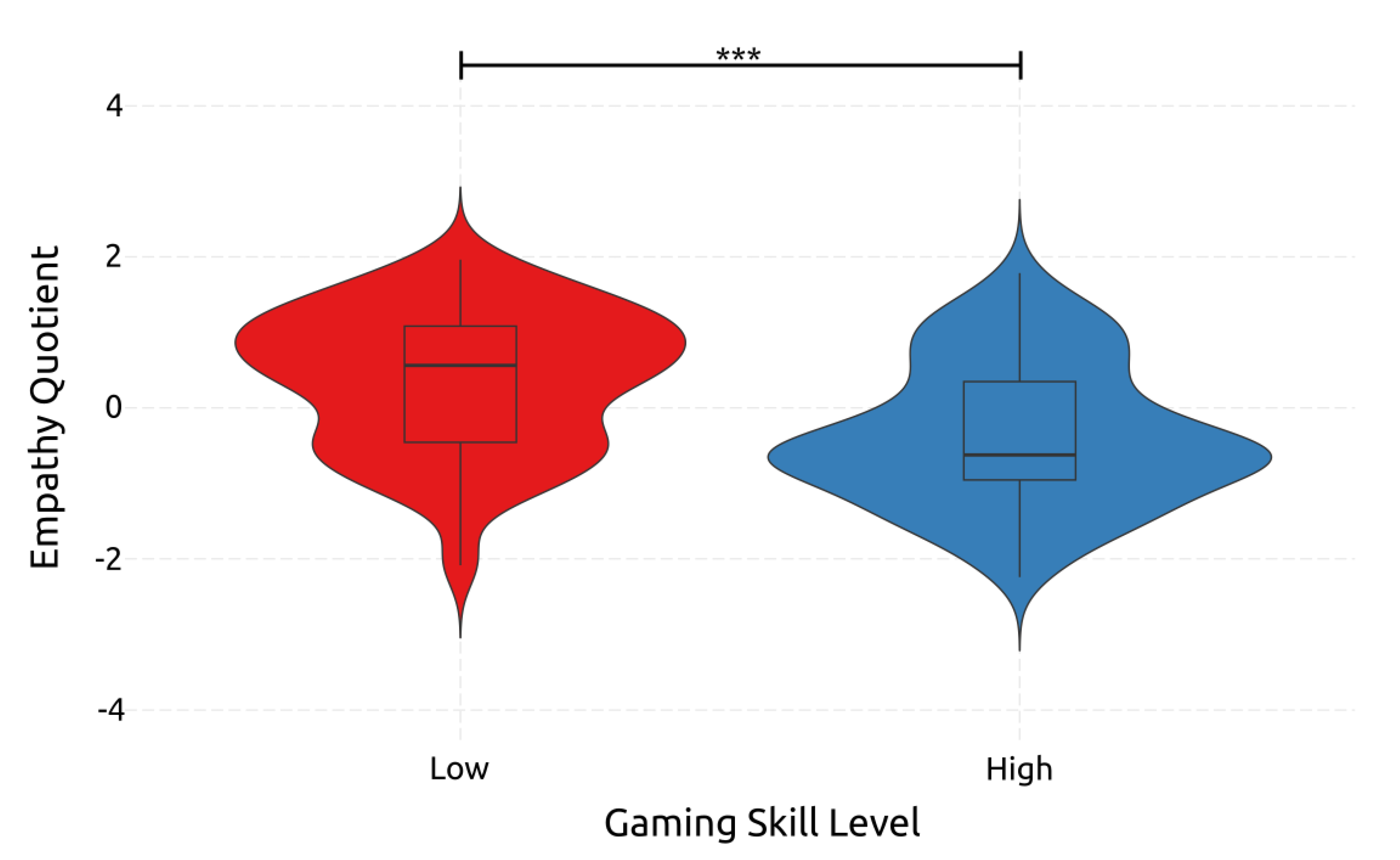
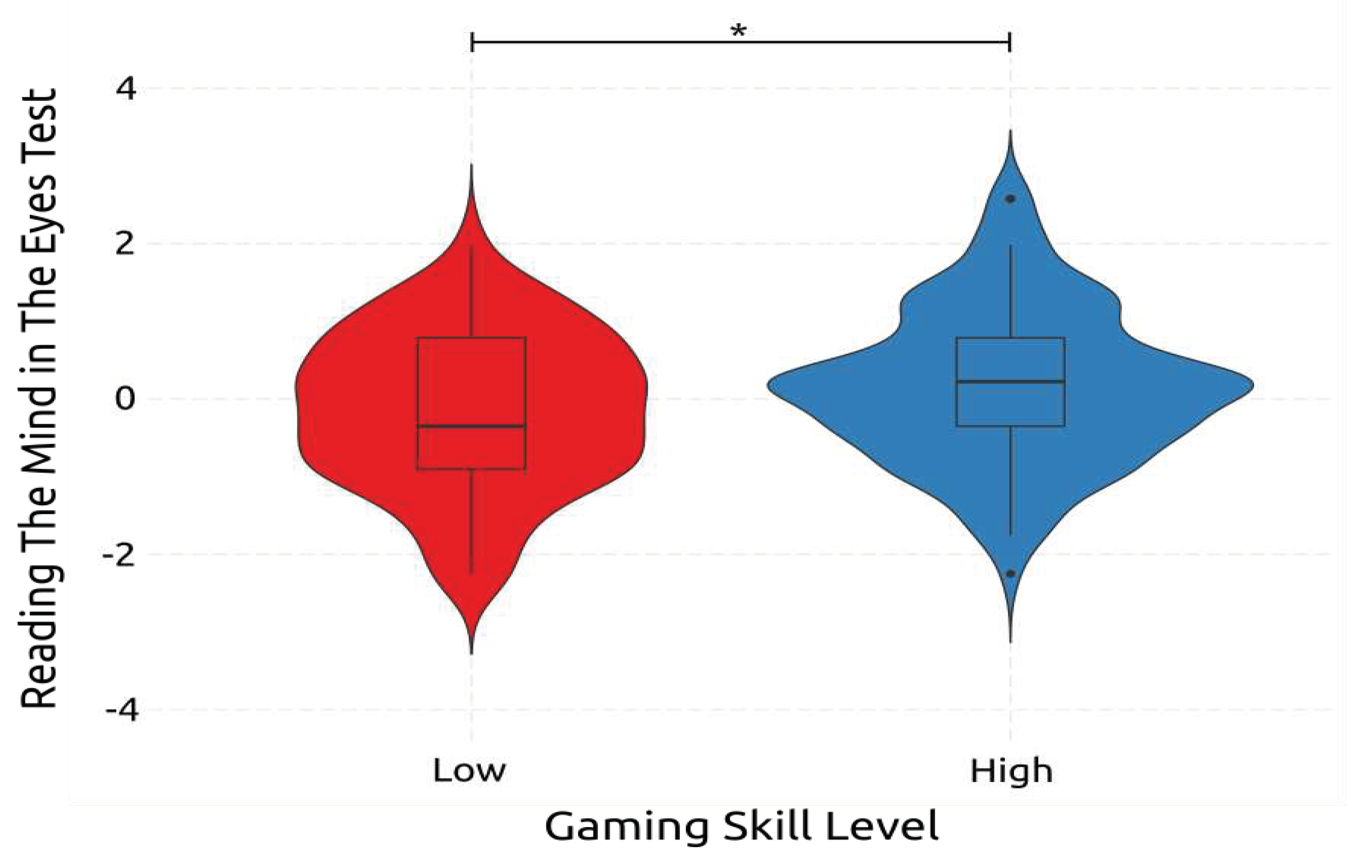
3.4. ANOVA Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Validatity and Relialibility of the Gaming Skills Questionnaire
4.2. Gaming Skills Effects on Cognitive and Affective Functioning in Adolescence
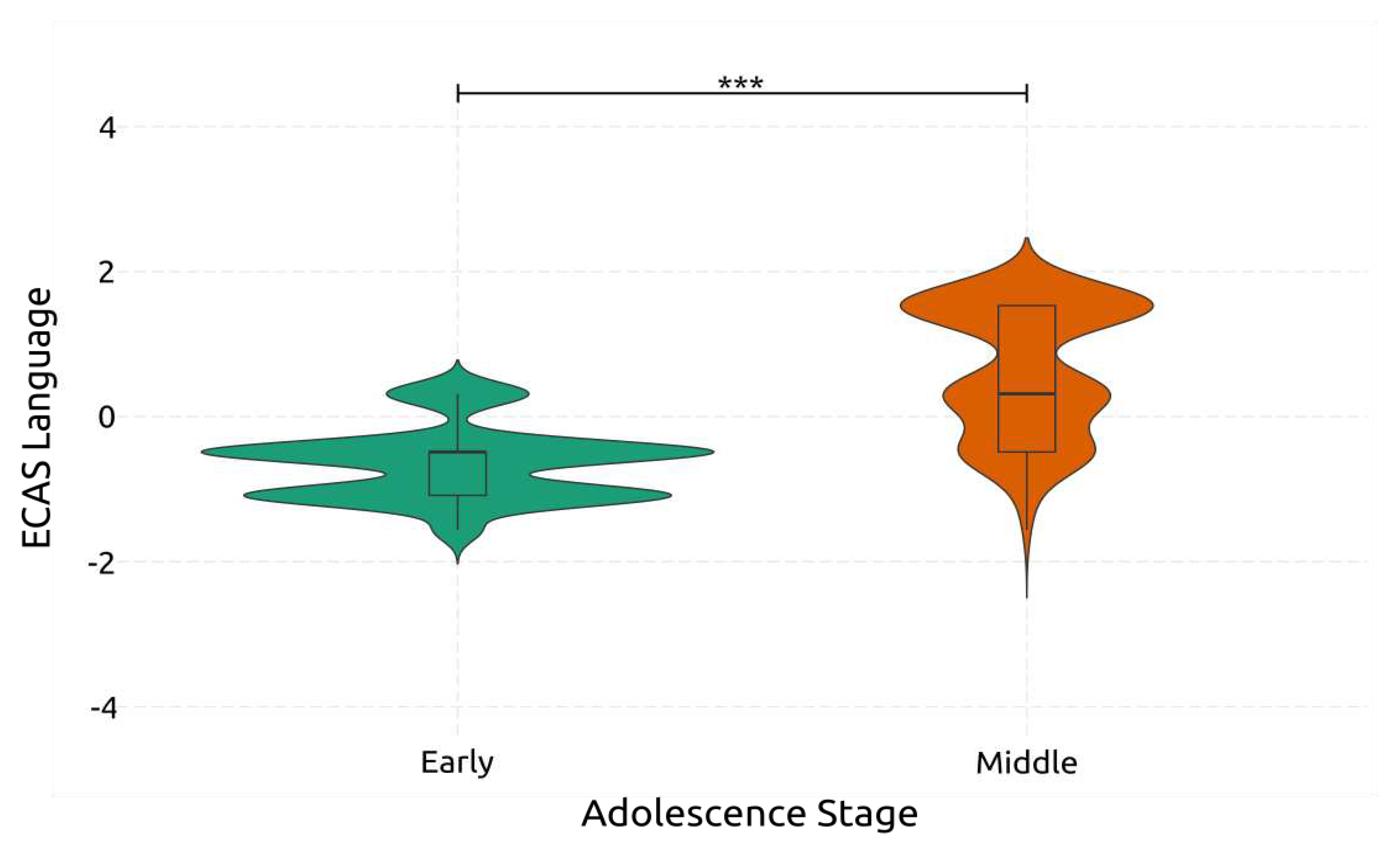
4.2.1. Language
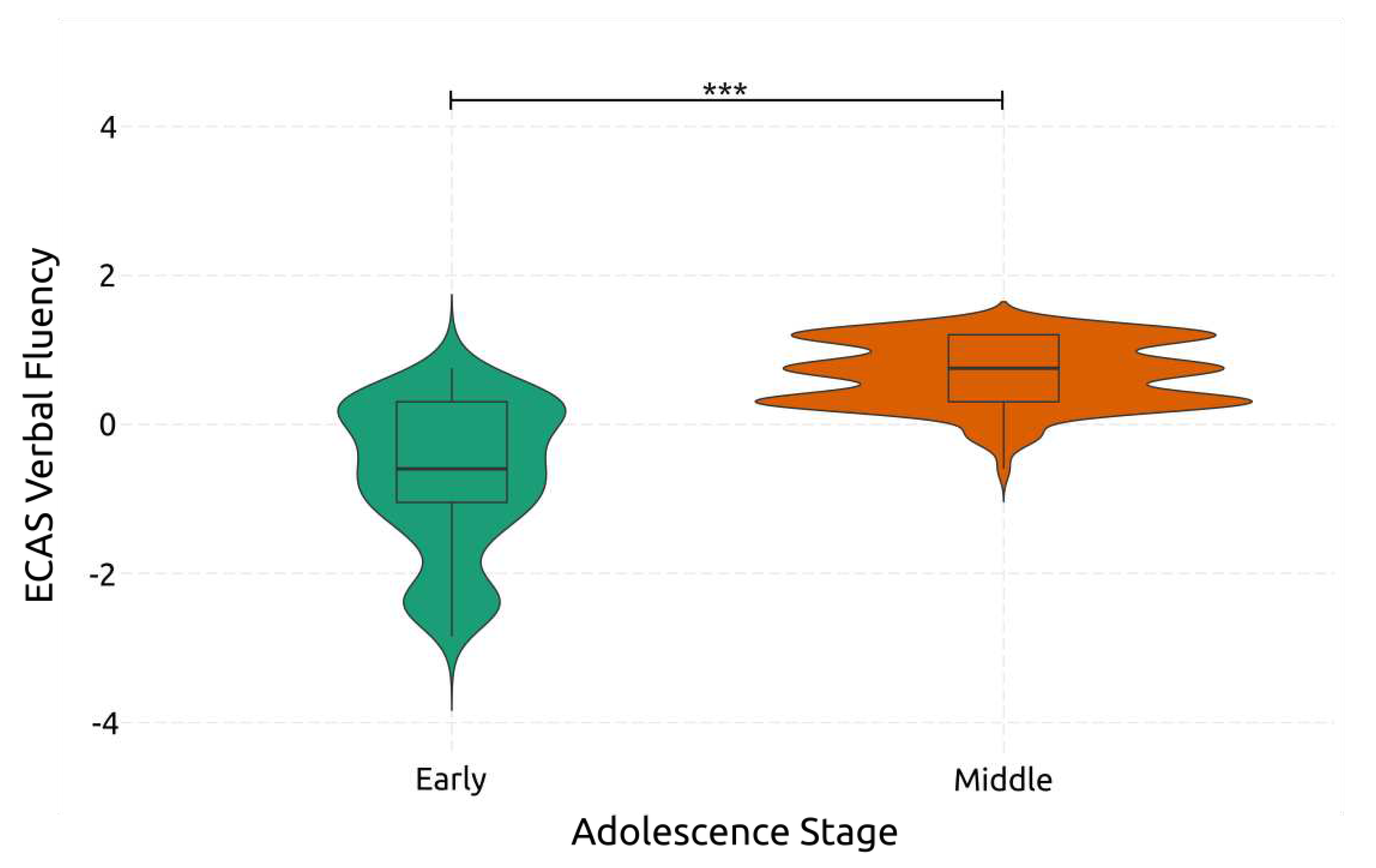
4.3.2. Verbal Fluency
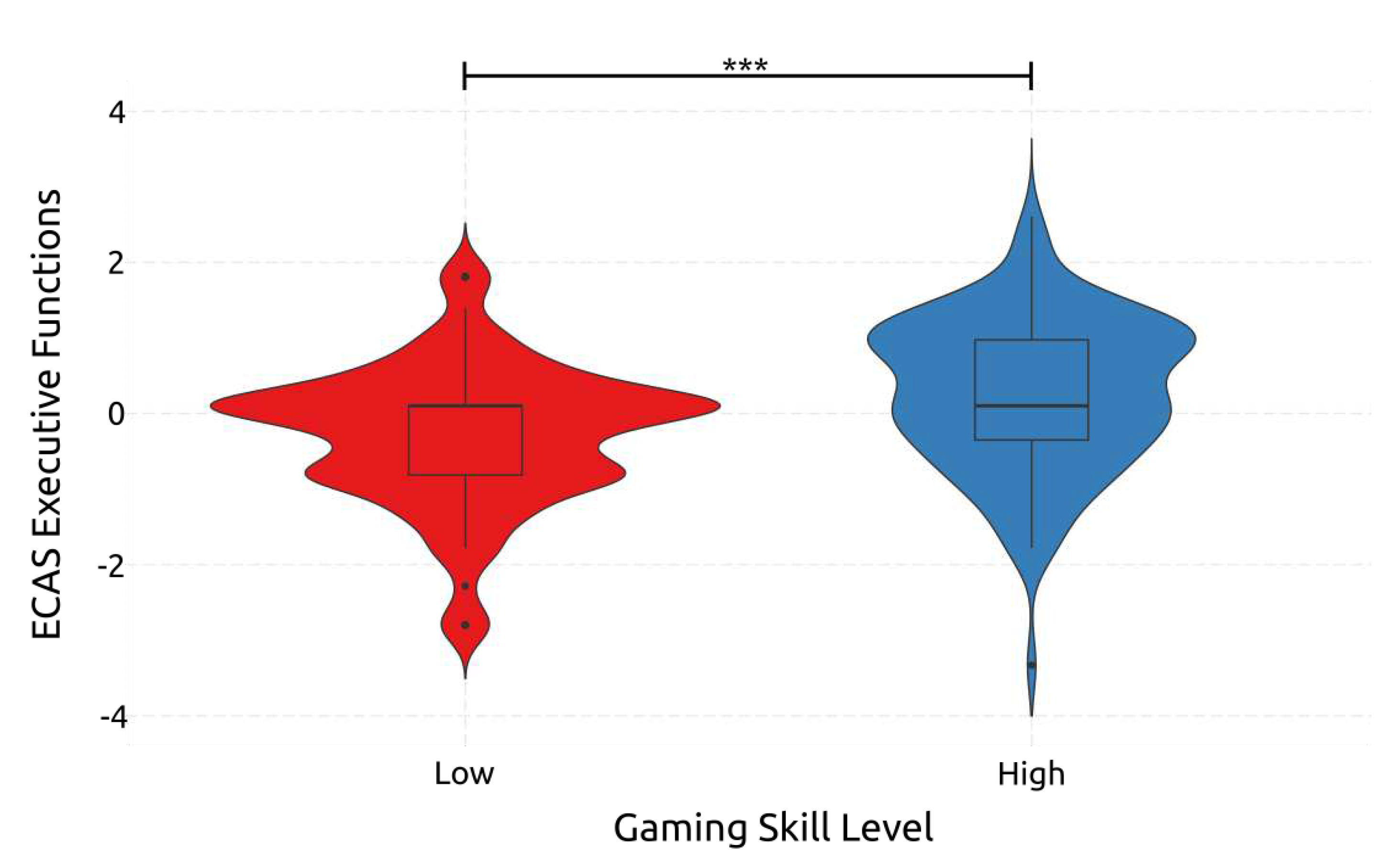
4.2.3. Executive Functioning
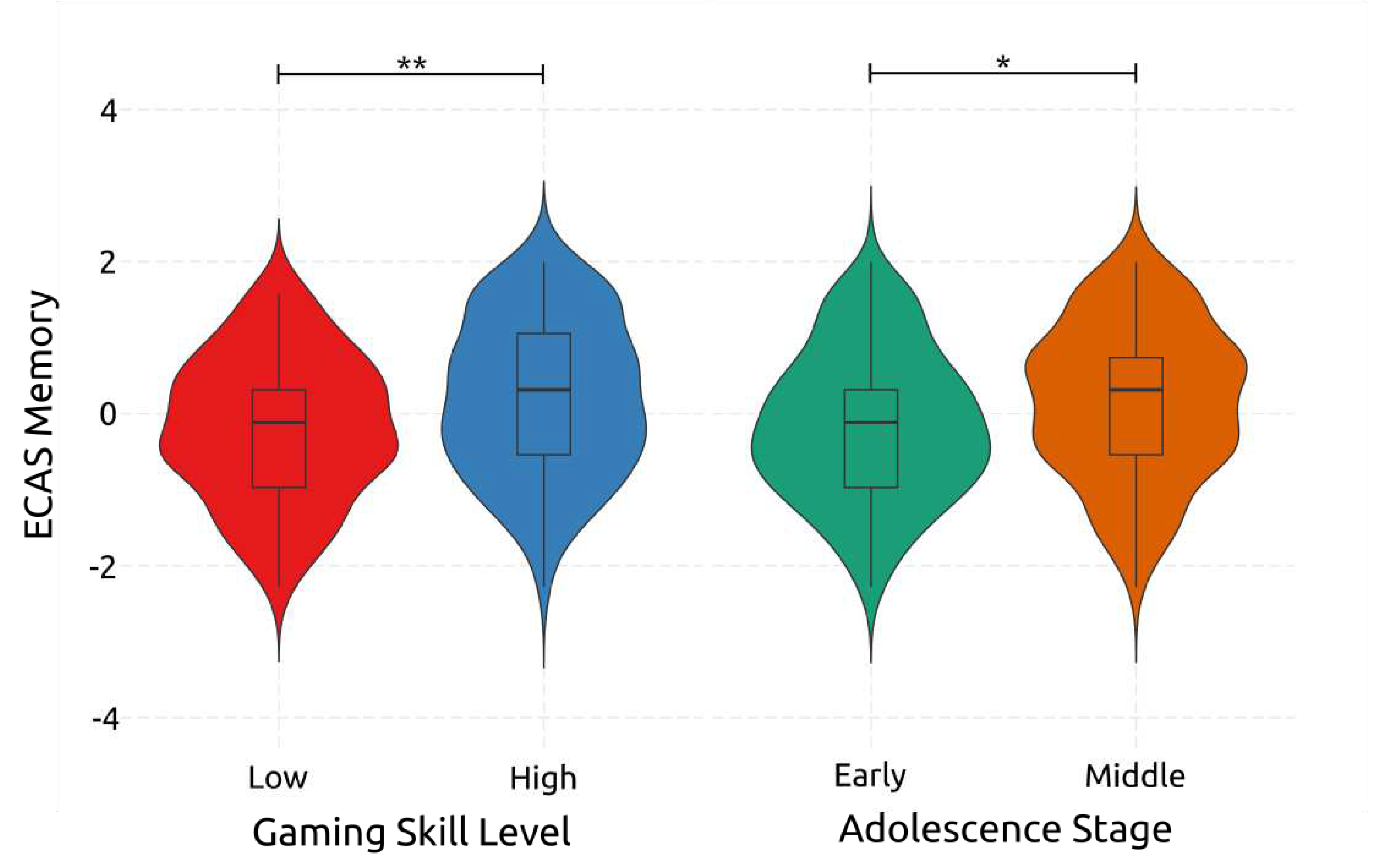
4.2.4. Memory
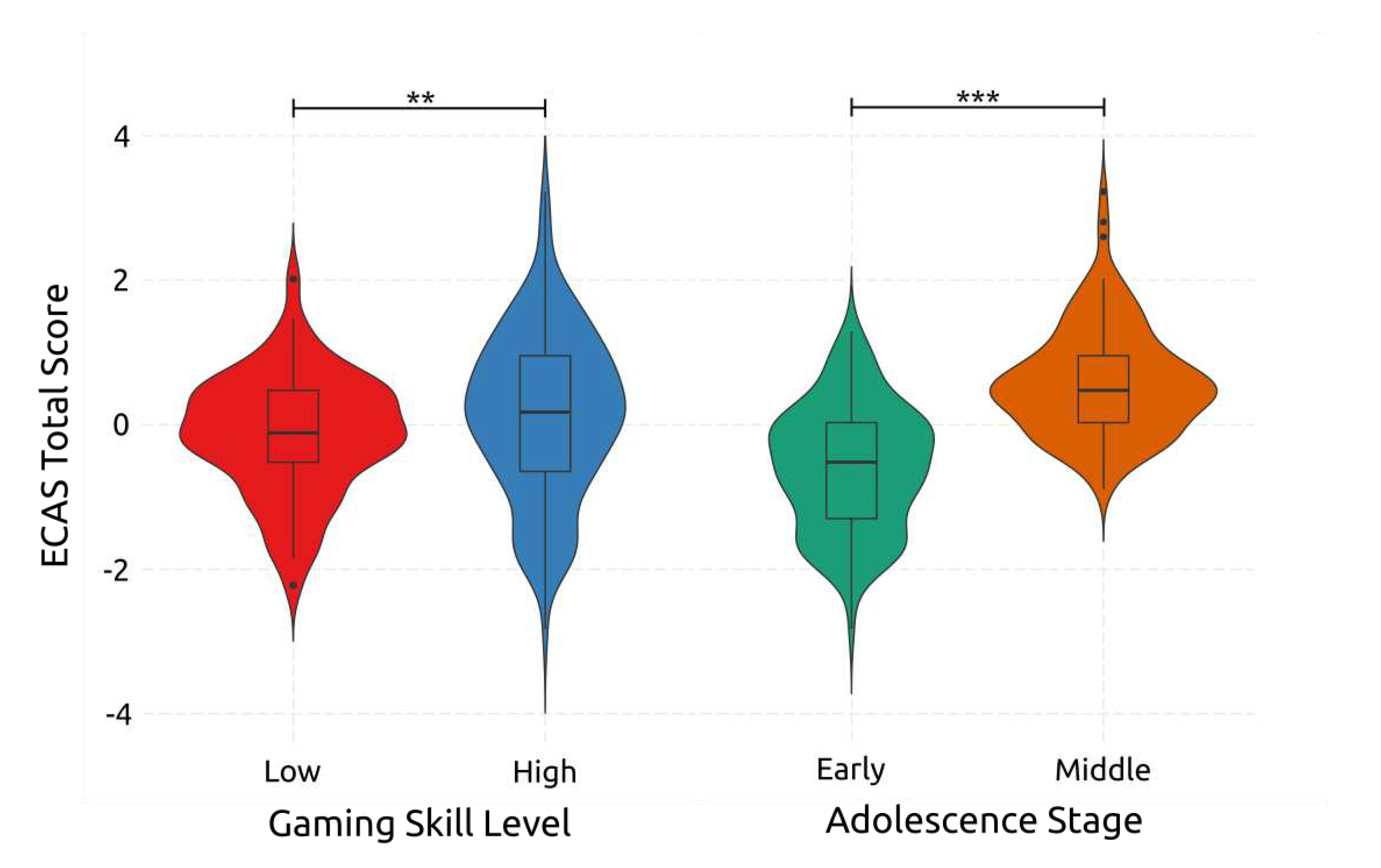
4.2.5. Overall Cognition
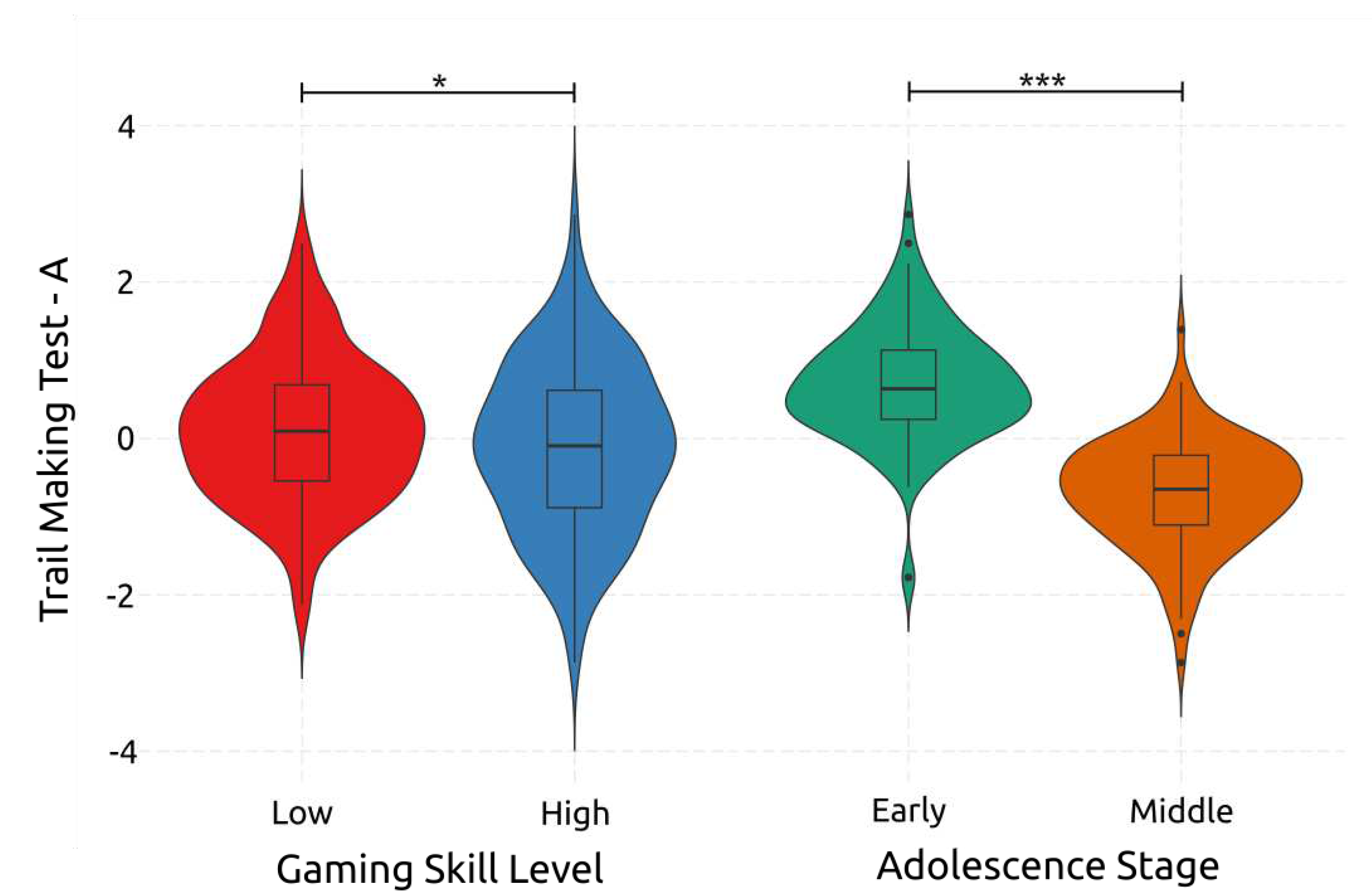
4.2.6. Attentional Processing Speed
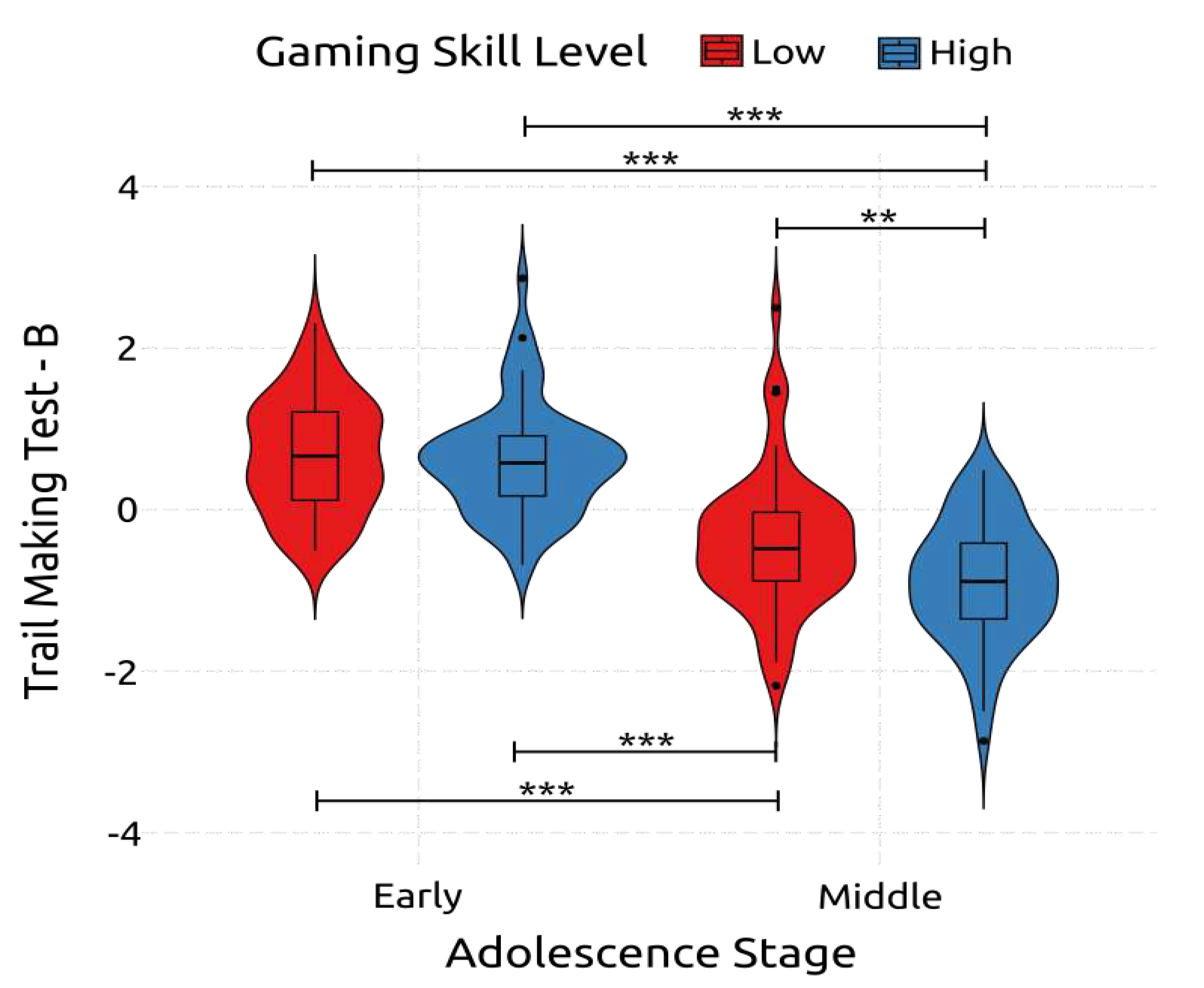
4.2.7. Cognitive Flexibility
4.2.8. Emotion Recognition
4.2.9. Empathy
4.3. Limitations & Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine., The promise of adolescence: Realizing opportunity for all youth. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Christie, D.; Viner, R. Adolescent development. BMJ 2005, 330, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. Salmela-Aro, “Stages of Adolescence,” in Encyclopedia of Adolescence, Elsevier, 2011, pp. 360–368. [CrossRef]
- Swider-Cios, E.; Vermeij, A.; Sitskoorn, M.M. Young children and screen-based media: The impact on cognitive and socioemotional development and the importance of parental mediation. Cogn. Dev. 2023, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Moreno, M.; Binger, K.; Zhao, Q.; Eickhoff, J.; Minich, M.; Uhls, Y.T. Digital Technology and Media Use by Adolescents: Latent Class Analysis. JMIR Pediatr. Parent. 2022, 5, e35540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.; Wang, Y. The Relation of Violent Video Games to Adolescent Aggression: An Examination of Moderated Mediation Effect. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, M.L.; Denmark, N.; Harden, B.J.; Stapleton, L.M. The Role of Parent Education and Parenting Knowledge in Children's Language and Literacy Skills among White, Black, and Latino Families. Infant Child Dev. 2015, 25, 198–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. N. Nikmah, “Understanding Pro-Social Behavior: The Impact of Empathy on Adolescents in Rural and Urban Areas,” in Proceedings of the 4th ASEAN Conference on Psychology, Counselling, and Humanities (ACPCH 2018), Surat Thani, Thaland: Atlantis Press, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Noppert, G.A.; Martin, C.L.; Zivich, P.N.; Aiello, A.E.; Harris, K.M.; O'Rand, A. Adolescent neighborhood disadvantage and memory performance in young adulthood. Heal. Place 2022, 75, 102793–102793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.J.; Jensen, M.R.; Russell, M.A.; Gassman-Pines, A.; Copeland, W.E.; Hoyle, R.H.; Odgers, C.L. Young Adolescents' Digital Technology Use, Perceived Impairments, and Well-Being in a Representative Sample. J. Pediatr. 2020, 219, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looi, J.C.; A Wilkes, F.; Bastiampillai, T.; Allison, S. Practical psychiatry: Taking gaming seriously – a primer for psychiatrists on gamers and gaming culture. Australas. Psychiatry 2023, 32, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granic, I.; Lobel, A.; Engels, R.C.M.E. The benefits of playing video games. Am. Psychol. 2014, 69, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derevensky, J.L.; Hayman, V.; Gilbeau, L. Behavioral Addictions : Excessive Gambling, Gaming, Internet, and Smartphone Use Among Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 2019, 66, 1163–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Fernandez, O.; Williams, A.J.; Griffiths, M.D.; Kuss, D.J. Female Gaming, Gaming Addiction, and the Role of Women Within Gaming Culture: A Narrative Literature Review. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolari, C.; Contreras-Espinosa, R. How do teens learn to play video games?: Informal learning strategies and video game literacy. J. Inf. Lit. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Won, J. The Effects of Adolescents’ Participation in Video Games on Cognitive Function and Motor Control Skills. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavelier, D.; Achtman, R.; Mani, M.; Föcker, J. Neural bases of selective attention in action video game players. Vis. Res. 2012, 61, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelantado-Renau, M.; Moliner-Urdiales, D.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Beltran-Valls, M.R.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Álvarez-Bueno, C. Association Between Screen Media Use and Academic Performance Among Children and Adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgonovi, F. Video gaming and gender differences in digital and printed reading performance among 15-year-olds students in 26 countries. J. Adolesc. 2016, 48, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.A.; Carnagey, N.L. Causal effects of violent sports video games on aggression: Is it competitiveness or violent content? J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2009, 45, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, J.; Lenhard, W. A Meta-Analysis on the Longitudinal, Age-Dependent Effects of Violent Video Games on Aggression. Media Psychol. 2021, 25, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, S.M.; Warburton, W.A.; Essig, L.W.; Stockdale, L.A. Violent video games, externalizing behavior, and prosocial behavior: A five-year longitudinal study during adolescence. Dev. Psychol. 2018, 54, 1868–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummer, T.A.; Wang, Y.; Kronenberger, W.G.; Mosier, K.M.; Kalnin, A.J.; Dunn, D.W.; Mathews, V.P. Short-Term Violent Video Game Play by Adolescents Alters Prefrontal Activity During Cognitive Inhibition. Media Psychol. 2010, 13, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, S.M.; Stockdale, L. Growing Up with Grand Theft Auto: A 10-Year Study of Longitudinal Growth of Violent Video Game Play in Adolescents. Cyberpsychology, Behav. Soc. Netw. 2021, 24, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, S.; Eshet-Alkalai, Y. The Effect of Digital Games and Game Strategies on Young Adolescents' Aggression. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2014, 50, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.; Porter-Armstrong, A.P. Impact of Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games upon the Psychosocial Well-Being of Adolescents and Young Adults: Reviewing the Evidence. Psychiatry J. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirni, D.; Garufo, E.; Di Falco, L.; Lavanco, G. The Playing Brain. The Impact of Video Games on Cognition and Behavior in Pediatric Age at the Time of Lockdown: A Systematic Review. Pediatr. Rep. 2021, 13, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Violent Video Game Exposure and Problem Behaviors among Children and Adolescents: The Mediating Role of Deviant Peer Affiliation for Gender and Grade Differences. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2022, 19, 15400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiroglu, A.Y.; Celik, G.G.; Avci, A.; Seydaoglu, G.; Uzel, M.; Altunbas, H. Short-Term Effects of Playing Computer Games on Attention. J. Atten. Disord. 2009, 13, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karle, J.W.; Watter, S.; Shedden, J.M. Task switching in video game players: Benefits of selective attention but not resistance to proactive interference. Acta Psychol. 2010, 134, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, S.; Gallinat, J.; Mascherek, A. Effects of computer gaming on cognition, brain structure, and function: a critical reflection on existing literature. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 21, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, S.; Lorenz, R.; Banaschewski, T.; Barker, G.J.; Büchel, C.; Conrod, P.J.; Flor, H.; Garavan, H.; Ittermann, B.; Loth, E.; et al. Positive Association of Video Game Playing with Left Frontal Cortical Thickness in Adolescents. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e91506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, K.H.; Hwang, H.C.; Kim, S.M.; Han, D.H. Comparison of Behavioral Changes and Brain Activity between Adolescents with Internet Gaming Disorder and Student Pro-Gamers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2020, 17, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.; Shin, S.-H.; Ryu, J.-K.; Jung, K.-I.; Hyun, Y.; Kim, J.; Park, M.-H. Association of Extensive Video Gaming and Cognitive Function Changes in Brain-Imaging Studies of Pro Gamers and Individuals With Gaming Disorder: Systematic Literature Review. JMIR Serious Games 2021, 9, e25793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenbergen, L.; Sellaro, R.; Stock, A.-K.; Beste, C.; Colzato, L.S. Action Video Gaming and Cognitive Control: Playing First Person Shooter Games Is Associated with Improved Action Cascading but Not Inhibition. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0144364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bediou, B.; Adams, D.M.; Mayer, R.E.; Tipton, E.; Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. Meta-analysis of action video game impact on perceptual, attentional, and cognitive skills. Psychol. Bull. 2018, 144, 77–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso-Leite, P.; Kludt, R.; Vignola, G.; Ma, W.J.; Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. Technology consumption and cognitive control: Contrasting action video game experience with media multitasking. Attention, Perception, Psychophys. 2015, 78, 218–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, G.; Kattner, F.; Bavelier, D.; Green, C.S. Cognitive abilities of action video game and role-playing video game players: Data from a massive open online course. Psychol. Popul. Media 2020, 9, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Zinni, M.; Bavelier, D.; Hillyard, S.A. Neural Basis of Superior Performance of Action Videogame Players in an Attention-Demanding Task. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torner, H.P.; Carbonell, X.; Castejón, M. A comparative analysis of the processing speed between video game players and non-players. 2019, 37. [CrossRef]
- Spence, I.; Feng, J. Video Games and Spatial Cognition. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2010, 14, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, S.E.; Woldorff, M.G.; Mitroff, S.R. Video game players show more precise multisensory temporal processing abilities. Attention, Perception, Psychophys. 2010, 72, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisolini, D.C.; Petilli, M.A.; Daini, R. Is action video gaming related to sustained attention of adolescents? Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2018, 71, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, D.A.; Swing, E.L.; Lim, C.G.; Khoo, A. Video game playing, attention problems, and impulsiveness: Evidence of bidirectional causality. Psychol. Popul. Media Cult. 2012, 1, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaldo, C.; Christian, R.; Hosea, H.; Gunawan, A.A.S. Using Video Games to Improve Capabilities in Decision Making and Cognitive Skill: A Literature Review. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 179, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Woo, M. False accusation of online games: Internet gaming can enhance the cognitive flexibility of adolescents. Asian J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2021, 1, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colzato, L.S.; Wildenberg, W.P.M.v.D.; Zmigrod, S.; Hommel, B. Action video gaming and cognitive control: playing first person shooter games is associated with improvement in working memory but not action inhibition. Psychol. Res. 2012, 77, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colzato, L.S.; van Leeuwen, P.J.; Wildenberg, W.P.v.D.; Hommel, B. DOOM'd to switch: superior cognitive flexibility in players of first person shooter games. Front. Psychol. 2010, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sungur, H.; Boduroglu, A. Action video game players form more detailed representation of objects. Acta Psychol. 2012, 139, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbet, D.J.; Sergio, L.E. Move faster, think later: Women who play action video games have quicker visually-guided responses with later onset visuomotor-related brain activity. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0189110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alho, K.; Moisala, M.; Salmela-Aro, K. Effects of Media Multitasking and Video Gaming on Cognitive Functions and Their Neural Bases in Adolescents and Young Adults. Eur. Psychol. 2022, 27, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacker, K.J.; Curby, K.M.; Klobusicky, E.; Chein, J.M. Effects of action video game training on visual working memory. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2014, 40, 1992–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaarani, B.; Chaarani, B.; Ortigara, J.; Ortigara, J.; Yuan, D.; Yuan, D.; Loso, H.; Loso, H.; Potter, A.; Potter, A.; et al. Association of Video Gaming With Cognitive Performance Among Children. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2235721–e2235721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, A.F.; Bavelier, D.; Green, C.S. Memory abilities in action video game players. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 34, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzing, V.; Heinks, T.; Eggenberger, N.; Schmidt, M. Acute Cognitively Engaging Exergame-Based Physical Activity Enhances Executive Functions in Adolescents. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0167501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buelow, M.T.; Okdie, B.M.; Cooper, A.B. The influence of video games on executive functions in college students. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 45, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Choudhury, K. Buge, and S. Nighute, “Cognitive Optimisation or Decline ? : Impact Analysis of Playing Video Games on the Cognitive Functions of Adolescents,” May 2022. 20 May.
- Flynn, R.M.; Richert, R.A. Cognitive, not physical, engagement in video gaming influences executive functioning. J. Cogn. Dev. 2018, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oei, A.C.; Patterson, M.D. Playing a puzzle video game with changing requirements improves executive functions. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 37, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.E.; Parong, J.; Bainbridge, K. Young adults learning executive function skills by playing focused video games. Cogn. Dev. 2018, 49, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Anguera, J.; Gazzaley, A. Video games, cognitive exercises, and the enhancement of cognitive abilities. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2015, 4, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homer, B.D.; Plass, J.L.; Raffaele, C.; Ober, T.M.; Ali, A. Improving high school students' executive functions through digital game play. Comput. Educ. 2018, 117, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.S.; Seitz, A.R. The Impacts of Video Games on Cognition (and How the Government Can Guide the Industry). Policy Insights Behav. Brain Sci. 2015, 2, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Shin, S.-H.; Ryu, J.-K.; Jung, K.-I.; Kim, S.-Y.; Park, M.-H. Commercial video games and cognitive functions: video game genres and modulating factors of cognitive enhancement. Behav. Brain Funct. 2020, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnambs, T.; Appel, M. Is computer gaming associated with cognitive abilities? A population study among German adolescents. Intelligence 2017, 61, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özçetin, M.; Gümüştaş, F.; Çağ, Y.; Gökbay, I.Z.; Özmel, A. The relationships between video game experience and cognitive abilities in adolescents. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, ume 15, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, S.; Bediou, B.; Antico, L.; Jack, R.; Garrod, O.; Sims, C.; Green, C.S.; Schyns, P.; Bavelier, D. Emotion perception in habitual players of action video games. Emotion 2021, 21, 1324–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarsenbayeva, Z.; Tag, B.; Yan, S.; Kostakos, V.; Goncalves, J. Using Video Games to Regulate Emotions. OzCHI '20: 32nd Australian Conference on Human-Computer-Interaction. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, AustraliaDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Villani, D.; Carissoli, C.; Triberti, S.; Marchetti, A.; Gilli, G.; Riva, G. Videogames for Emotion Regulation: A Systematic Review. Games Heal. J. 2018, 7, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaetan, S.; Bréjard, V.; Bonnet, A. Video games in adolescence and emotional functioning: Emotion regulation, emotion intensity, emotion expression, and alexithymia. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemenover, S.H.; Bowman, N.D. Video games, emotion, and emotion regulation: expanding the scope. Ann. Int. Commun. Assoc. 2018, 42, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahood, C.; Hanus, M. Role-playing video games and emotion: How transportation into the narrative mediates the relationship between immoral actions and feelings of guilt. Psychol. Popul. Media Cult. 2017, 6, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Blasi, M.; Giardina, A.; Giordano, C.; Coco, G.L.; Tosto, C.; Billieux, J.; Schimmenti, A. Problematic video game use as an emotional coping strategy: Evidence from a sample of MMORPG gamers. J. Behav. Addict. 2019, 8, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, A.K.; Choo, H.; Li, D.; Gentile, D.A.; Sim, T.; Khoo, A. Pathological video-gaming among youth: A prospective study examining dynamic protective factors. Addict. Res. Theory 2014, 23, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montag, C.; Weber, B.; Trautner, P.; Newport, B.; Markett, S.; Walter, N.T.; Felten, A.; Reuter, M. Does excessive play of violent first-person-shooter-video-games dampen brain activity in response to emotional stimuli? Biol. Psychol. 2012, 89, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.; Ferguson, C.J.; Wang, C.K.J. Prosocial Video Game Content, Empathy and Cognitive Ability in a Large Sample of Youth. J. Youth Adolesc. 2021, 51, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.-H.; Ahn, D. Associations Between Game Use and Cognitive Empathy: A Cross-Generational Study. Cyberpsychology, Behav. Soc. Netw. 2013, 16, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, M.E. ; Agri Ibrahim Cecen University Empathy and Video Game Addiction in Adolescents: Serial Mediation by Psychological Resilience and Life satisfaction. Int. J. Progress. Educ. 2021, 17, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.M.; Padilla-Walker, L.M.; Coyne, S.M.; Nelson, L.J.; Stockdale, L.A. Associations Between Violent Video Gaming, Empathic Concern, and Prosocial Behavior Toward Strangers, Friends, and Family Members. J. Youth Adolesc. 2012, 41, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greitemeyer, T.; Osswald, S.; Brauer, M. Playing prosocial video games increases empathy and decreases schadenfreude. Emotion 2010, 10, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, B.; O’connell, M. Video games as virtual teachers: Prosocial video game use by children and adolescents from different socioeconomic groups is associated with increased empathy and prosocial behaviour. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 63, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Deng, T.; Kanske, P. Affective empathy mediates the positive effect of prosocial video games on young children’s sharing behavior. Cogn. Dev. 2023, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.A.; Shibuya, A.; Ihori, N.; Swing, E.L.; Bushman, B.J.; Sakamoto, A.; Rothstein, H.R.; Saleem, M. Violent video game effects on aggression, empathy, and prosocial behavior in Eastern and Western countries: A meta-analytic review. Psychol. Bull. 2010, 136, 151–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.S.; Pouget, A.; Bavelier, D. Improved Probabilistic Inference as a General Learning Mechanism with Action Video Games. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanyam, K.; Renukarya, B. Digital Games and Learning: Identifying Pathways of Influence. Educ. Psychol. 2015, 50, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, E.C.; Karas, T.L.; Winsler, A.; Way, E.; Madigan, A.; Tyler, S. Young Children's Video/Computer Game Use: Relations with School Performance and Behavior. Issues Ment. Heal. Nurs. 2009, 30, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinovic, D.; Burgess, G.H.; Pomerleau, C.M.; Marin, C. Computer games that exercise cognitive skills: What makes them engaging for children? Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 60, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, L.; Grumi, S.; Di Blasio, P. Positive Effects of Videogame Use on Visuospatial Competencies: The Impact of Visualization Style in Preadolescents and Adolescents. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oei, A.C.; Patterson, M.D. Enhancing Cognition with Video Games: A Multiple Game Training Study. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e58546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deleuze, J.; Christiaens, M.; Nuyens, F.; Billieux, J. Shoot at first sight! First person shooter players display reduced reaction time and compromised inhibitory control in comparison to other video game players. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 72, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuyens, F.M.; Kuss, D.J.; Lopez-Fernandez, O.; Griffiths, M.D. The Empirical Analysis of Non-problematic Video Gaming and Cognitive Skills: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Ment. Heal. Addict. 2018, 17, 389–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.T.; Basak, C. A game-factors approach to cognitive benefits from video-game training: A meta-analysis. PLOS ONE 2023, 18, e0285925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greitemeyer, T.; Mügge, D.O. Video Games Do Affect Social Outcomes. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2014, 40, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.; Bavelier, D. Learning, Attentional Control, and Action Video Games. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R197–R206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Qu, W.; Fan, H.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, S. Association between video gaming time and cognitive functions: A cross-sectional study of Chinese children and adolescents. Asian J. Psychiatry 2023, 84, 103584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieury, A.; Lorant, S.; Trosseille, B.; Champault, F.; Vourc’h, R. Video games vs. reading and school/cognitive performances: a study on 27000 middle school teenagers. Educ. Psychol. 2014, 36, 1560–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallavicini, F.; Ferrari, A.; Mantovani, F. Video Games for Well-Being: A Systematic Review on the Application of Computer Games for Cognitive and Emotional Training in the Adult Population. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartanto, A.; Toh, W.X.; Yang, H. Age matters: The effect of onset age of video game play on task-switching abilities. Attention, Perception, Psychophys. 2016, 78, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.P.; Du'Mont, S. Measuring the effect of gaming experience on virtual environment navigation tasks. 2009 IEEE Symposium on 3D User Interfaces. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, USADATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 3–10. [CrossRef]
- Kourtesis, P.; MacPherson, S.E. How immersive virtual reality methods may meet the criteria of the National Academy of Neuropsychology and American Academy of Clinical Neuropsychology: A software review of the Virtual Reality Everyday Assessment Lab (VR-EAL). Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep. 2021, 4, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtesis, P.; Vizcay, S.; Marchal, M.; Pacchierotti, C.; Argelaguet, F. Action-Specific Perception & Performance on a Fitts's Law Task in Virtual Reality: The Role of Haptic Feedback. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2022, 28, 3715–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtesis, P.; Amir, R.; Linnell, J.; Argelaguet, F.; MacPherson, S.E. Cybersickness, Cognition, & Motor Skills: The Effects of Music, Gender, and Gaming Experience. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2023, 29, 2326–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtesis, P.; Kouklari, E.-C.; Roussos, P.; Mantas, V.; Papanikolaou, K.; Skaloumbakas, C.; Pehlivanidis, A. Virtual Reality Training of Social Skills in Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Examination of Acceptability, Usability, User Experience, Social Skills, and Executive Functions. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiwal, S.; Jain, P.; Jain, A.K. Impact of Playing Action and Puzzle Video-games on Attention and Executive Function: A Comparative Study. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 63, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, L.; Gimenes, M.; Lambert, E. Video games and board games: Effects of playing practice on cognition. PLOS ONE 2023, 18, e0283654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciano, L.; Camerini, A.-L.; Morese, R. The Developing Brain in the Digital Era: A Scoping Review of Structural and Functional Correlates of Screen Time in Adolescence. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niven, E.; Newton, J.; Foley, J.; Colville, S.; Swingler, R.; Chandran, S.; Bak, T.H.; Abrahams, S. Validation of the Edinburgh Cognitive and Behavioural Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Screen (ECAS): A cognitive tool for motor disorders. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2015, 16, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourtesis, P.; Christidi, F.; Margioti, E.; Demenega, C.; Rentzos, M.; Evdokimidis, I.; Abrahams, S. The Edinburgh cognitive and behavioral amyotrophic lateral sclerosis screen (ECAS): sensitivity in differentiating between ALS and Alzheimer’s disease in a Greek population. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2019, 21, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourtesis, P.; Margioti, E.; Demenega, C.; Christidi, F.; Abrahams, S. A Comparison of the Greek ACE-III, M-ACE, ACE-R, MMSE, and ECAS in the Assessment and Identification of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2020, 26, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitan, R.M. Validity of the Trail Making Test as an Indicator of Organic Brain Damage. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1958, 8, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalonis, I.; Kararizou, E.; Triantafyllou, N.I.; Kapaki, E.; Papageorgiou, S.; Sgouropoulos, P.; Vassilopoulos, D. A Normative Study of the Trail Making Test A and B in Greek Adults. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2008, 22, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Wheelwright, S.; Hill, J.; Raste, Y.; Plumb, I. The “Reading the Mind in the Eyes” Test Revised Version: A Study with Normal Adults, and Adults with Asperger Syndrome or High-functioning Autism. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2001, 42, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogindroukas, I.; Chelas, E.-N.; Petridis, N.E. Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test (Children's Version): A Comparison Study between Children with Typical Development, Children with High-Functioning Autism and Typically Developed Adults. Folia Phoniatr. et Logop. 2014, 66, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auyeung, B.; Allison, C.; Wheelwright, S.; Baron-Cohen, S. Brief Report: Development of the Adolescent Empathy and Systemizing Quotients. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2012, 42, 2225–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivanidis, A.; Tasios, K.; Papanikolaou, K.; Douzenis, A.; Michopoulos, I. Validation of the Empathy Quotient (EQ) - Greek version. Psychiatriki 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, C.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Wheelwright, S.; Stone, M.; Muncer, S. Psychometric analysis of the Empathy Quotient (EQ). Pers. Individ. Differ. 2011, 51, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team (2023). _R: A Language and Environment for Statistical computing_. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on June 2023).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio, PBC; Boston, MA, USA, 2020. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/.
- Revelle, W. psych: Procedures for Psychological, Psychometric, and Personality Research; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 2018; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=psych (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org.
- Peterson, R.A.; Cavanaugh, J.E. Ordered quantile normalization: a semiparametric transformation built for the cross-validation era. J. Appl. Stat. 2019, 47, 2312–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavelier, D.; Green, C.S.; Dye, M.W. Children, Wired: For Better and for Worse. Neuron 2010, 67, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedechkina, M.; Borgonovi, F. A Review of Evidence on the Role of Digital Technology in Shaping Attention and Cognitive Control in Children. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summaka, M.; Jebahi, F.; Al-Thalaya, Z.; Assaf, S.; Al-Kammouni, Z.; Al Zein, H.; Haidar, R.; Kresht, J.; Hassan, F.E.Z.; Matar, W.; et al. Verbal fluency in Lebanese children: Preliminary normative data, sociodemographic determinants, and patterns of clustering and switching. Appl. Neuropsychol. Child 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, P.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Lin, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Neural substrates of the executive function construct, age-related changes, and task materials in adolescents and adults: ALE meta-analyses of 408 fMRI studies. Dev. Sci. 2021, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirni, P.; Villardita, C.; Zappala, G. Spatial Memory Span in Adolescents: Cultural and Sex Differences. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1983, 57, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Molloy, K. The Changes of Cognition in Teenagers after Playing Video Games. J. Stud. Res. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, N.; Redick, T.S.; McMillan, B.D.; Hambrick, D.Z.; Kane, M.J.; Engle, R.W. Is Playing Video Games Related to Cognitive Abilities? Psychol. Sci. 2015, 26, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crone, E.A.; Konijn, E.A. Media use and brain development during adolescence. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, W.R.; Kramer, A.F.; Simons, D.J.; Fabiani, M.; Gratton, G. The effects of video game playing on attention, memory, and executive control. Acta Psychol. 2008, 129, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaus, M.; Marron, E.M.; Viejo-Sobera, R.; Redolar-Ripoll, D. Neural Basis of Video Gaming: A Systematic Review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 248. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00248. [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, J.D.; Hickey, C.; Theeuwes, J.; Kingstone, A. Reduced attentional capture in action video game players. Attention, Perception, Psychophys. 2010, 72, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dye, M.W.G.; Green, C.S.; Bavelier, D. The development of attention skills in action video game players. Neuropsychologia 2009, 47, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousignant, B.; Sirois, K.; Achim, A.M.; Massicotte, E.; Jackson, P.L. A comprehensive assessment of social cognition from adolescence to adulthood. Cogn. Dev. 2017, 43, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniqued, P.L.; Lee, H.; Voss, M.W.; Basak, C.; Cosman, J.D.; DeSouza, S.; Severson, J.; Salthouse, T.A.; Kramer, A.F. Selling points: What cognitive abilities are tapped by casual video games? Acta Psychol. 2012, 142, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, G.; Joessel, A.; Bavelier, D.; Green, C.S. A new look at the cognitive neuroscience of video game play. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2020, 1464, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, G.P.; Stoltz, S.E.; Berg, Y.H.v.D.; Cillessen, A.H. The influence of competitive and cooperative video games on behavior during play and friendship quality in adolescence. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 91, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.R.; Subrahmanyam, K.; on behalf of the Cognitive Impacts of Digital Media Workgroup. Digital Screen Media and Cognitive Development. PEDIATRICS 2017, 140, S57–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greitemeyer, T. Playing Video Games Cooperatively Increases Empathic Concern. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 44, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Polat, U.; Makous, W.; Bavelier, D. Enhancing the contrast sensitivity function through action video game training. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mean | SD | Minimum | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 13.63 | 1.43 | 12 | 16 |
| Residence Location(Median/Mode) | 2/2 | - | 1 | 4 |
| Parent Age | 43.89 | 4.49 | 36 | 55 |
| Parent Education | 15.31 | 1.78 | 12 | 18 |
| Family Income(Median/Mode) | 3/3 | - | 3 | 4 |
| Sport Games Skill | 3.13 | 1.69 | 2 | 8 |
| FPS Games Skill | 2.99 | 1.55 | 2 | 9 |
| RPG Skill | 2.71 | 1.46 | 2 | 11 |
| Action-Adventure Games Skill | 3.35 | 1.85 | 2 | 10 |
| Strategy Games Skill | 2.48 | 1.49 | 2 | 10 |
| Puzzle Games Skill | 3.38 | 1.72 | 2 | 9 |
| Total Gaming Skill | 18.05 | 4.52 | 12 | 33 |
| ECAS – Language | 25.54 | 1.15 | 22 | 28 |
| ECAS – Verbal Fluency | 19.11 | 4.38 | 6 | 24 |
| ECAS – Executive Functions | 40.89 | 2.25 | 34 | 47 |
| ECAS – Memory | 19.19 | 2.47 | 13 | 24 |
| ECAS – Visuospatial | 12.00 | 0.00 | 12 | 12 |
| ECAS – Total Score | 116.73 | 7.52 | 89 | 135 |
| TMT – A – Reaction Time | 36.34 | 6.85 | 22.70 | 49.30 |
| TMT – B – Reaction Time | 96.90 | 40.78 | 30.70 | 180.50 |
| RMET | 20.59 | 1.81 | 16 | 25 |
| Empathy Quotient | 41.46 | 6.00 | 28 | 53 |
| Statistic | Threshold | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Cronbach’s α | ≥ .70 | SpGS = .80 |
| FPSGS = .86 | ||
| RPGS = .91 | ||
| AGS = .82 | ||
| StGS = .83 | ||
| PGS = .81 | ||
| χ2/df | ≤ 2.00 | 1.97 |
| CFI | ≥ .90 | .959 |
| TLI | ≥ .90 | .906 |
| SRMR | ≤ .08 | .079 |
| RMSEA | ≤ .08 | .078 |
| Adolescence Stage | Gaming Skill | Mean | SD | Minimum | Maximum | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Early | High | 12.4 | 0.50 | 12 | 13 | |||||||
| Low | 12.3 | 0.48 | 12 | 13 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 15.1 | 0.84 | 14 | 16 | ||||||||
| Low | 14.8 | 0.78 | 14 | 16 | |||||||||
| Total Gaming Skill | Early | High | 21.1 | 3.93 | 17 | 32 | |||||||
| Low | 14.5 | 1.48 | 12 | 16 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 21.6 | 4.15 | 17 | 33 | ||||||||
| Low | 14.5 | 1.54 | 12 | 16 | |||||||||
| ECAS – Language | Early | High | 24.6 | 0.67 | 23 | 26 | |||||||
| Low | 24.7 | 0.82 | 23 | 26 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 26.3 | 0.98 | 23 | 28 | ||||||||
| Low | 26.1 | 0.88 | 24 | 27 | |||||||||
| ECAS – Verbal Fluency | Early | High | 15.2 | 4.57 | 6 | 22 | |||||||
| Low | 16.1 | 3.86 | 8 | 20 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 21.5 | 1.91 | 16 | 24 | ||||||||
| Low | 21.8 | 1.88 | 18 | 24 | |||||||||
| ECAS – Executive Functions | Early | High | 41.2 | 2.03 | 34 | 44 | |||||||
| Low | 40.1 | 2.29 | 35 | 45 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 41.7 | 2.42 | 37 | 47 | ||||||||
| Low | 40.3 | 1.67 | 36 | 45 | |||||||||
| ECAS – Memory | Early | High | 19.2 | 2.41 | 14 | 24 | |||||||
| Low | 18.6 | 2.11 | 14 | 23 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 20.3 | 2.27 | 15 | 24 | ||||||||
| Low | 19.0 | 2.30 | 14 | 23 | |||||||||
| ECAS – Visuospatial | Early | High | 12.0 | 0.00 | 12 | 12 | |||||||
| Low | 12.0 | 0.00 | 12 | 12 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 12.0 | 0.00 | 12 | 12 | ||||||||
| Low | 12.0 | 0.00 | 12 | 12 | |||||||||
| ECAS – Total Score | Early | High | 112.2 | 7.85 | 89 | 125 | |||||||
| Low | 111.6 | 5.98 | 97 | 122 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 121.8 | 5.19 | 111 | 135 | ||||||||
| Low | 119.2 | 3.78 | 110 | 129 | |||||||||
| TMT – A – Reaction Time | Early | High | 42.0 | 4.93 | 24.5 | 49.30 | |||||||
| Low | 42.5 | 3.90 | 31.8 | 48.00 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 31.0 | 4.88 | 22.7 | 46.40 | ||||||||
| Low | 33.3 | 4.63 | 24.0 | 43.70 | |||||||||
| TMT – B – Reaction Time | Early | High | 129.2 | 25.05 | 66.80 | 180.50 | |||||||
| Low | 131.9 | 27.11 | 76.10 | 172.90 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 66.5 | 28.46 | 30.70 | 130.70 | ||||||||
| Low | 84.4 | 34.52 | 31.40 | 176.00 | |||||||||
| RMET | Early | High | 21.0 | 1.51 | 18 | 25 | |||||||
| Low | 20.1 | 1.90 | 16 | 23 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 20.7 | 2.00 | 16 | 25 | ||||||||
| Low | 20.5 | 1.83 | 16 | 24 | |||||||||
| Empathy Quotient | Early | High | 39.5 | 5.09 | 32 | 51 | |||||||
| Low | 43.8 | 5.34 | 34 | 53 | |||||||||
| Middle | High | 39.3 | 6.03 | 28 | 52 | ||||||||
| Low | 43.8 | 5.60 | 29 | 52 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





