Submitted:
25 January 2024
Posted:
26 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures and Technology
2.2.1. Positive and Negative Affect Scale (PANAS)
2.2.2. Perceived Stress Scale (PSS)
2.2.3. Internet Gaming Disorder Scale 9 - Short form (IGDS9-SF)
2.2.4. Instantaneous Pulse Rate (Photoplethysmography; PPG)
2.2.5. Video Game Conditions
2.3. Procedure
2.3.1. Ethical approval
2.4. Research Design
3. Results
3.2. Demographic Results
3.3. Normality Testing
3.4. Hypothesis Testing
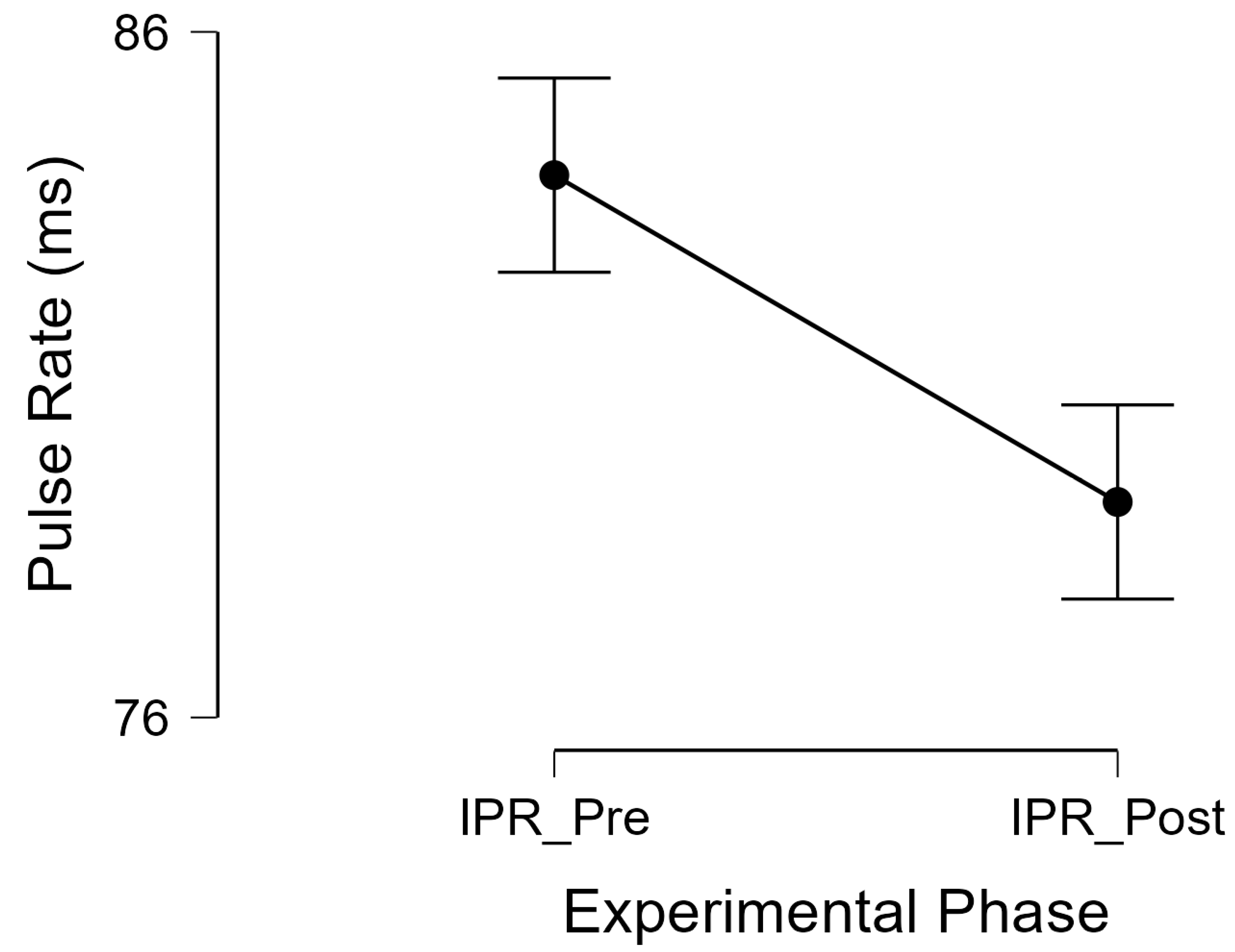
3.4.1. Instantaneous Pulse Rate
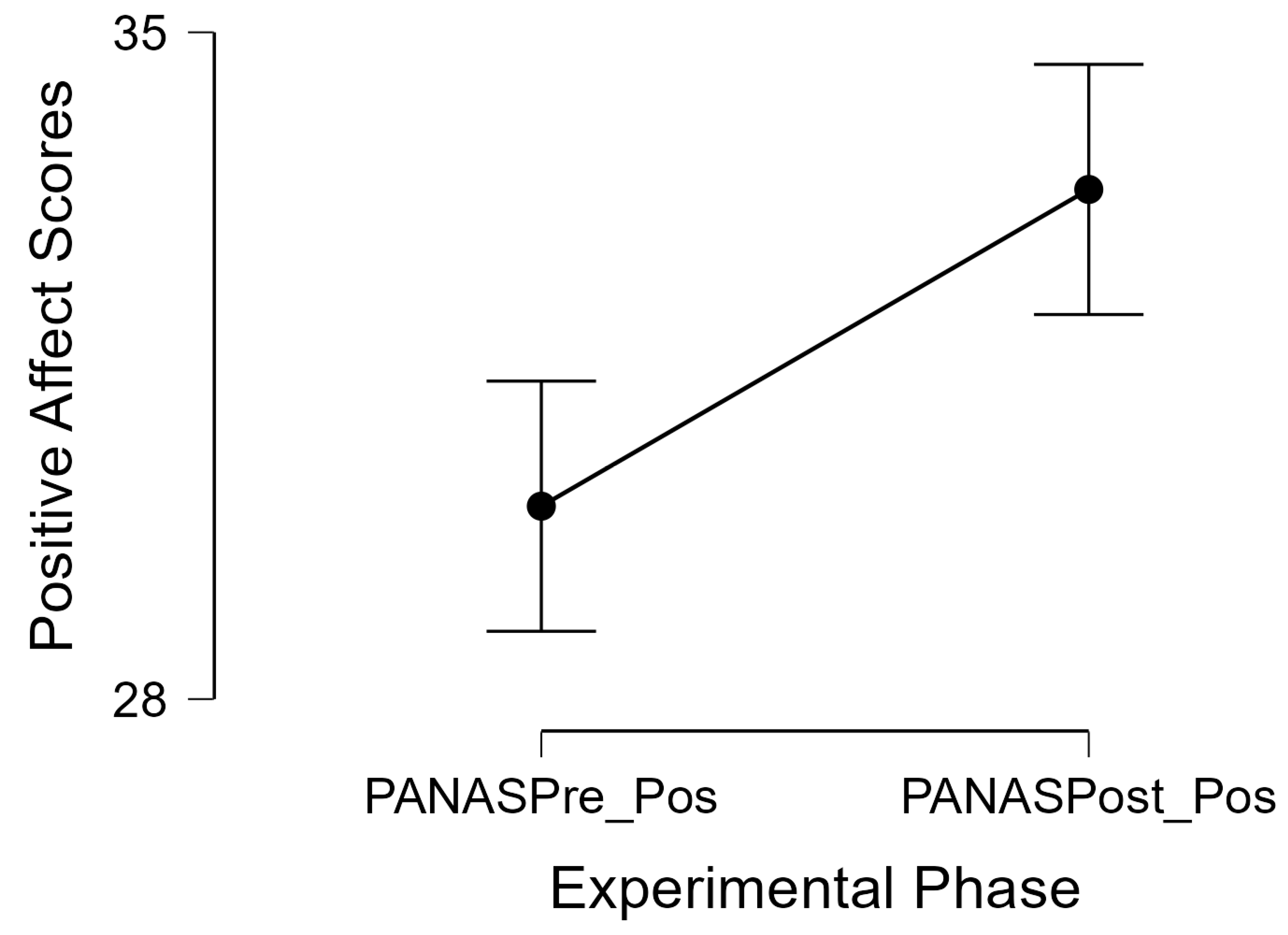
3.4.2. Positive Affect
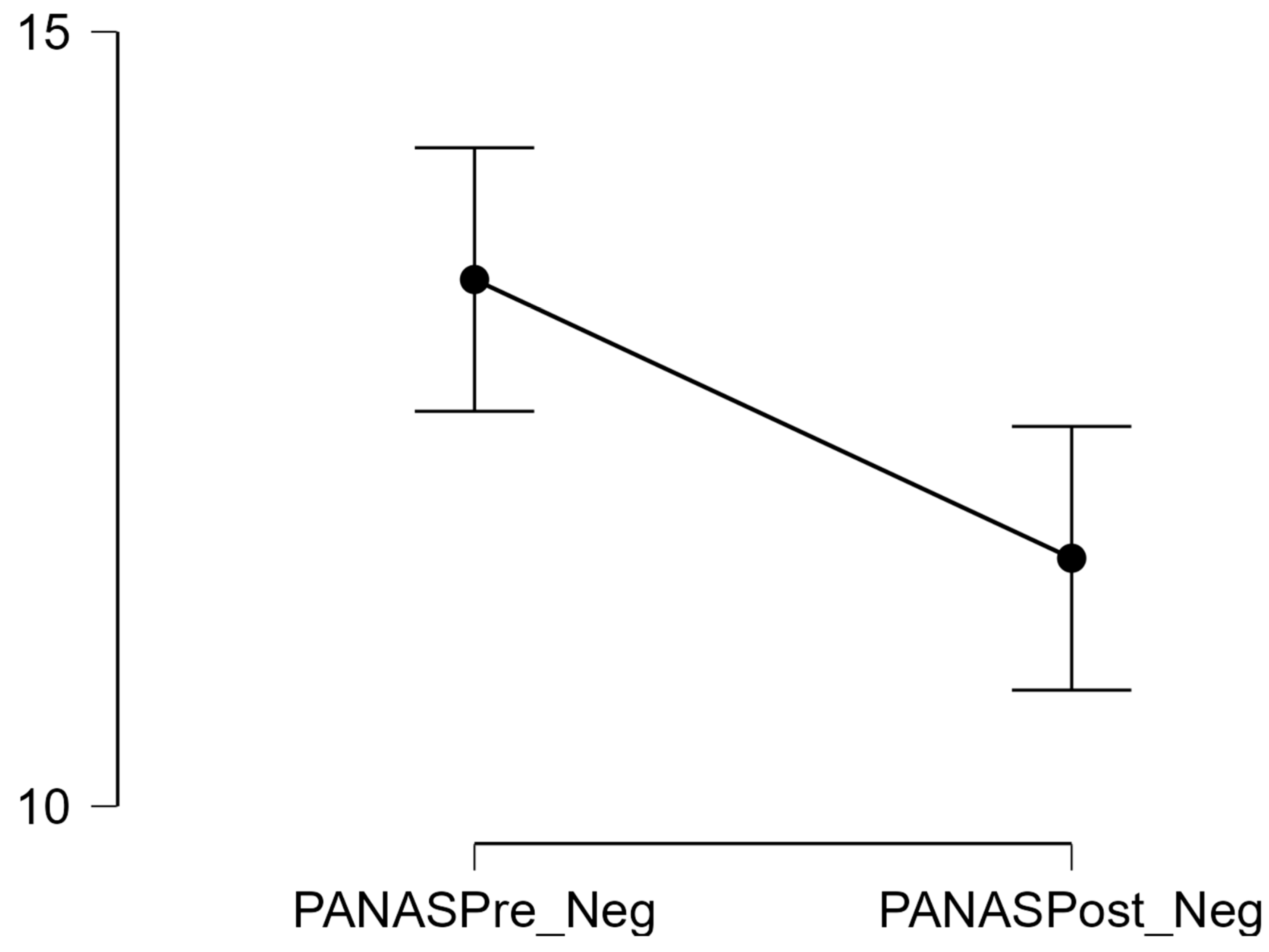
3.4.3. Negative Affect
3.4.4. Positive Affect and Problematic Gaming
3.4.5. Instantaneous Pulse Rate and Problematic Gaming
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpretations of Results
4.2. Limitations & Considerations
4.3. Conclusion
References
- Allen, J. J., & Anderson, C. A. (2018). Satisfaction and frustration of basic psychological needs in the real world and in video games predict internet gaming disorder scores and well-being. Computers in Human Behavior, 84, 220–229. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C. A., & Bushman, B. J. (2001). Effects of Violent Video Games on Aggressive Behavior, Aggressive Cognition, Aggressive Affect, Physiological Arousal, and Prosocial Behavior: A Meta-Analytic Review of the Scientific Literature. Psychological Science, 12(5), 353–359. [CrossRef]
- Bean, A. M., Nielsen, R. K. L., van Rooij, A. J., & Ferguson, C. J. (2017). Video game addiction: The push to pathologize video games. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 48, 378–389. [CrossRef]
- Bosboom, J., Demaine, E. D., Hesterberg, A., Lynch, J., & Waingarten, E. (2016). Mario Kart Is Hard. In J. Akiyama, H. Ito, T. Sakai, & Y. Uno (Eds.), Discrete and Computational Geometry and Graphs (Vol. 9943, pp. 49–59). Springer International Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Bowman, N. D., & Tamborini, R. (2012). Task demand and mood repair: The intervention potential of computer games. New Media & Society, 14(8), 1339–1357. [CrossRef]
- Canale, N., Marino, C., Griffiths, M. D., Scacchi, L., Monaci, M. G., & Vieno, A. (2019). The association between problematic online gaming and perceived stress: The moderating effect of psychological resilience. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 8(1), 174–180. [CrossRef]
- Cheikh-Ammar, M. (2020). The bittersweet escape to information technology: An investigation of the stress paradox of social network sites. Information & Management, 57(8), 103368. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S., Kamarck, T., & Mermelstein, R. (1994). Perceived stress scale. Measuring Stress: A Guide for Health and Social Scientists, 10(2), 1–2.
- Cole, H., & Griffiths, M. D. (2007). Social Interactions in Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Gamers. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 10(4), 575–583. [CrossRef]
- Desai, V., Gupta, A., Andersen, L., Ronnestrand, B., & Wong, M. (2021). Stress-Reducing Effects of Playing a Casual Video Game among Undergraduate Students. Trends in Psychology, 29(3), 563–579. [CrossRef]
- Dutcher, J. M., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). The role of brain reward pathways in stress resilience and health. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 95, 559–567. [CrossRef]
- Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Buchner, A., & Lang, A.-G. (2009). Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behavior Research Methods, 41(4), 1149–1160. [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Aranda, F., Jiménez-Murcia, S., Santamaría, J. J., Gunnard, K., Soto, A., Kalapanidas, E., Bults, R. G. A., Davarakis, C., Ganchev, T., Granero, R., Konstantas, D., Kostoulas, T. P., Lam, T., Lucas, M., Masuet-Aumatell, C., Moussa, M. H., Nielsen, J., & Penelo, E. (2012). Video games as a complementary therapy tool in mental disorders: PlayMancer, a European multicentre study. Journal of Mental Health, 21(4), 364–374. [CrossRef]
- Gaetan, S., Bréjard, V., & Bonnet, A. (2016). Video games in adolescence and emotional functioning: Emotion regulation, emotion intensity, emotion expression, and alexithymia. Computers in Human Behavior, 61, 344–349. [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J. E. (1991). Can the Mario Bros. help? Nintendo games as an adjunct in psychotherapy with children. Psychotherapy: Theory, Research, Practice, Training, 28, 667–670. [CrossRef]
- Giardina, A., Blasi, M. D., Schimmenti, A., King, D. L., Starcevic, V., & Billieux, J. (2021). ONLINE GAMING AND PROLONGED SELF-ISOLATION: EVIDENCE FROM ITALIAN GAMERS DURING THE COVID-19 OUTBREAK. 10.
- Gil, E., Orini, M., Bailón, R., Vergara, J. M., Mainardi, L., & Laguna, P. (2010). Photoplethysmography pulse rate variability as a surrogate measurement of heart rate variability during non-stationary conditions. Physiological Measurement, 31(9), 1271. [CrossRef]
- Govender, M., Bowen, R. C., German, M. L., Bulaj, G., & Bruggers, C. S. (2015). Clinical and Neurobiological Perspectives of Empowering Pediatric Cancer Patients Using Videogames. Games for Health Journal, 4(5), 362–374. [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, D., & Long, C. (2009). Mood specific media use and emotion regulation: Patterns and individual differences | Elsevier Enhanced Reader. [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M. (1999). Internet addiction: Fact or fiction? The Psychologist, 12, 246–250.
- Griffiths, M. D., Kuss, D. J., & King, D. L. (2012). Video game addiction: Past, present and future. Current Psychiatry Reviews, 8(4), 308–318. [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M. D., Kuss, D. J., Lopez-Fernandez, O., & Pontes, H. M. (2017). Problematic gaming exists and is an example of disordered gaming: Commentary on: Scholars’ open debate paper on the World Health Organization ICD-11 Gaming Disorder proposal (Aarseth et al.). Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 6(3), 296–301. [CrossRef]
- Halbrook, Y. J., O’Donnell, A. T., & Msetfi, R. M. (2019). When and How Video Games Can Be Good: A Review of the Positive Effects of Video Games on Well-Being. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 14(6), 1096–1104. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Y., Bègue, L., & Bushman, B. J. (2013). Violent Video Games Stress People Out and Make Them More Aggressive. Aggressive Behavior, 39(1), 64–70. [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-H., & Hsiao, T.-C. (2022). Very Short-Term Photoplethysmography-Based Heart Rate Variability for Continuous Autoregulation Assessment. Applied Sciences, 12(13), Article 13. [CrossRef]
- Hull, K. (2009). Computer/Video Games as a Play Therapy Tool in Reducing Emotional Disturbances in Children. Doctoral Dissertations and Projects. https://digitalcommons.liberty.edu/doctoral/263.
- Hussain, U., Jabarkhail, S., Cunningham, G. B., & Madsen, J. A. (2021). The dual nature of escapism in video gaming: A meta-analytic approach. Computers in Human Behavior Reports, 3, 100081. [CrossRef]
- JASP Team. (2022). JASP - A Fresh Way to Do Statistics. https://jasp-stats.org/.
- Jenny, S. E., & Thompson, R. M. (2016). Pokémon Go: Encouraging Recreation through Augmented Reality Gaming. International Journal of Technology in Teaching and Learning, 12(2), 112–122.
- Jo, Y. S., Bhang, S. Y., Choi, J. S., Lee, H. K., Lee, S. Y., & Kweon, Y.-S. (2019). Clinical Characteristics of Diagnosis for Internet Gaming Disorder: Comparison of DSM-5 IGD and ICD-11 GD Diagnosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(7), Article 7. [CrossRef]
- Johannes, N., Vuorre, M., & Przybylski, A. K. (2020). Video game play is positively correlated with well-being [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. [CrossRef]
- Johannes, N., Vuorre, M., & Przybylski, A. K. (2021). Video game play is positively correlated with well-being [Preprint]. PsyArXiv. [CrossRef]
- Kardefelt-Winther, D. (2014). The moderating role of psychosocial well-being on the relationship between escapism and excessive online gaming. Computers in Human Behavior, 38, 68–74. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-G., Cheon, E.-J., Bai, D.-S., Lee, Y. H., & Koo, B.-H. (2018). Stress and Heart Rate Variability: A Meta-Analysis and Review of the Literature. Psychiatry Investigation, 15(3), 235–245. [CrossRef]
- King, D. L., & Delfabbro, P. H. (2014). The cognitive psychology of Internet gaming disorder. Clinical Psychology Review, 34(4), 298–308. [CrossRef]
- King, D. L., Herd, M. C. E., & Delfabbro, P. H. (2017). Tolerance in Internet gaming disorder: A need for increasing gaming time or something else? Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 6(4), 525–533. https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.6.2017.072. [CrossRef]
- Király, O., Sleczka, P., Pontes, H. M., Urbán, R., Griffiths, M. D., & Demetrovics, Z. (2017). Validation of the Ten-Item Internet Gaming Disorder Test (IGDT-10) and evaluation of the nine DSM-5 Internet Gaming Disorder criteria. Addictive Behaviors, 64, 253–260. [CrossRef]
- Kiran kumar, C., Manaswini, M., Maruthy, K. N., Siva Kumar, A. V., & Mahesh kumar, K. (2021). Association of Heart rate variability measured by RR interval from ECG and pulse to pulse interval from Photoplethysmography. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, 10, 100698. [CrossRef]
- Koban, K., Biehl, J., Bornemeier, J., & Ohler, P. (2021). Compensatory video gaming. Gaming behaviours and adverse outcomes and the moderating role of stress, social interaction anxiety, and loneliness. Behaviour & Information Technology, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Kriz, W. C. (2020). Gaming in the Time of COVID-19. Simulation & Gaming, 51(4), 403–41. [CrossRef]
- Kuss, D. J., & Griffiths, M. D. (2012). Internet gaming addiction: A systematic review of empirical research. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 10(2), 278–296. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H. E., So, H., Han, S. P., & Oh, W. (2016). Excessive Dependence on Mobile Social Apps: A Rational Addiction Perspective. Information Systems Research, 27(4), 919–939. [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, J. S., Valkenburg, P. M., & Gentile, D. A. (2015). The Internet Gaming Disorder Scale. Psychological Assessment, 27(2), 567–582. https://doi.org/10.1037/pas0000062. [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, J. S., Valkenburg, P. M., & Peter, J. (2011). Psychosocial causes and consequences of pathological gaming. Computers in Human Behavior, 27(1), 144–152. [CrossRef]
- Leung, L. (2007). Stressful Life Events, Motives for Internet Use, and Social Support Among Digital Kids. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 10(2), 204–214. [CrossRef]
- Loton, D., Borkoles, E., Lubman, D., & Polman, R. (2016). Video Game Addiction, Engagement and Symptoms of Stress, Depression and Anxiety: The Mediating Role of Coping. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 14(4), 565–578. [CrossRef]
- Maroney, N., Williams, B. J., Thomas, A., Skues, J., & Moulding, R. (2019). A Stress-Coping Model of Problem Online Video Game Use. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 17(4), 845–858. [CrossRef]
- McMahan, R. P., Alon, A. J. D., Lazem, S., Beaton, R. J., Machaj, D., Schaefer, M., Silva, M. G., Leal, A., Hagan, R., & Bowman, D. A. (2010). Evaluating natural interaction techniques in video games. 2010 IEEE Symposium on 3D User Interfaces (3DUI), 11–14. [CrossRef]
- Nahum, M., & Bavelier, D. (2020). Chapter 10—Video games as rich environments to foster brain plasticity. In N. F. Ramsey & J. del R. Millán (Eds.), Handbook of Clinical Neurology (Vol. 168, pp. 117–136). Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- Oe, H. (2020). Discussion of digital gaming’s impact on players’ well-being during the COVID-19 lockdown. arXiv:2005.00594 [Cs]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2005.00594.
- Pallavicini, F., Pepe, A., & Mantovani, F. (2021). Commercial Off-The-Shelf Video Games for Reducing Stress and Anxiety: Systematic Review. JMIR Mental Health, 8(8), e28150. https://doi.org/10.2196/28150. [CrossRef]
- Pallavicini, F., Pepe, A., & Mantovani, F. (2022). The Effects of Playing Video Games on Stress, Anxiety, Depression, Loneliness, and Gaming Disorder During the Early Stages of the COVID-19 Pandemic: PRISMA Systematic Review. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 25(6), 334–354. [CrossRef]
- Paschke, K., Austermann, M. I., Simon-Kutscher, K., & Thomasius, R. (2021). Adolescent gaming and social media usage before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. SUCHT, 67(1), 13–22. [CrossRef]
- Pine, R., Fleming, T., McCallum, S., & Sutcliffe, K. (2020). The Effects of Casual Videogames on Anxiety, Depression, Stress, and Low Mood: A Systematic Review. Games for Health Journal, 9(4), 255–264. [CrossRef]
- Poisson, C. L., Engel, L., & Saunders, B. T. (2021). Dopamine Circuit Mechanisms of Addiction-Like Behaviors. Frontiers in Neural Circuits, 15. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fncir.2021.752420.
- Porter, A. M., & Goolkasian, P. (2019). Video Games and Stress: How Stress Appraisals and Game Content Affect Cardiovascular and Emotion Outcomes. Frontiers in Psychology, 10. https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00967.
- Przybylski, A. K., Rigby, C. S., & Ryan, R. M. (2010). A Motivational Model of Video Game Engagement. Review of General Psychology, 14(2), 154–166. [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, L. (2009). Games and Recovery: The Use of Video and Computer Games to Recuperate from Stress and Strain. Journal of Media Psychology: Theories, Methods, and Applications, 21, 126–142. [CrossRef]
- Roy, A., & Ferguson, C. J. (2016). Competitively versus cooperatively? An analysis of the effect of game play on levels of stress. Computers in Human Behavior, 56, 14–20. [CrossRef]
- Russoniello, C., O’Brien, K., & Parks, J. M. (2009a). The effectiveness of casual video games in improving mood and decreasing stress. Journal of Cyber Therapy and Rehabilitation, 2, 53–66.
- Russoniello, C., O’Brien, K., & Parks, J. M. (2009b). The effectiveness of casual video games in improving mood and decreasing stress. Journal of Cyber Therapy and Rehabilitation, 2, 53–66.
- Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being. American Psychologist, 67.
- 63. Schäfer, A., & Vagedes, J. (2013). How accurate is pulse rate variability as an estimate of heart rate variability?: A review on studies comparing photoplethysmographic technology with an electrocardiogram. International Journal of Cardiology, 166(1), 15–29. [CrossRef]
- Stanhope, J., Owens, C., & Elliott, L. (2016). Stress Reduction: Casual Gaming versus Guided Relaxation. Human Factors and Applied Psychology Student Conference. https://commons.erau.edu/hfap/hfap-2015/papers/9.
- Ting, C., Mondragon, J., Almirante, J., Ramolete, G., Cohen, M., & Custodio, B. (2020). Usability and Gaming Experience Assessment of the Nintendo Switch User Interface by Filipino Users (pp. 777–783). [CrossRef]
- Tyack, A., Wyeth, P., & Johnson, D. (2016). The Appeal of MOBA Games: What Makes People Start, Stay, and Stop. Proceedings of the 2016 Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction in Play, 313–325. [CrossRef]
- van Doorn, J., van den Bergh, D., Böhm, U., Dablander, F., Derks, K., Draws, T., Etz, A., Evans, N. J., Gronau, Q. F., Haaf, J. M., Hinne, M., Kucharský, Š., Ly, A., Marsman, M., Matzke, D., Gupta, A. R. K. N., Sarafoglou, A., Stefan, A., Voelkel, J. G., & Wagenmakers, E.-J. (2021). The JASP guidelines for conducting and reporting a Bayesian analysis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 28(3), 813–826. [CrossRef]
- Villani, D., Carissoli, C., Triberti, S., Marchetti, A., Gilli, G., & Riva, G. (2018). Videogames for Emotion Regulation: A Systematic Review. Games for Health Journal, 7(2), 85–99. [CrossRef]
- Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063–1070. [CrossRef]
- Webster, J. G. (1997). Design of Pulse Oximeters. CRC Press.
- Wolfers, L. N., & Schneider, F. M. (2021). Using Media for Coping: A Scoping Review. Communication Research, 48(8), 1210–1234. [CrossRef]
- Wood, R. T. A. (2008). Problems with the Concept of Video Game “Addiction”: Some Case Study Examples. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 6(2), 169–178. [CrossRef]
- Yee, N. (2006). Motivations for Play in Online Games. 6.
- Yoon, S., Yang, Y., Ro, E., Ahn, W.-Y., Kim, J., Shin, S.-H., Chey, J., & Choi, K.-H. (2021). Reliability, and Convergent and Discriminant Validity of Gaming Disorder Scales: A Meta-Analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 12. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.764209.
- Young, K. S., & Abreu, C. N. de. (2010). Internet Addiction: A Handbook and Guide to Evaluation and Treatment. John Wiley & Sons.
- Yu, J. J., Kim, H., & Hay, I. (2013). Understanding adolescents’ problematic Internet use from a social/cognitive and addiction research framework. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(6), 2682–2689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.06.045. [CrossRef]
- Zemestani, M., Niakan, F., Shafeizadeh, K., & Griffiths, M. D. (2023). The relationship between psychobiological dimensions of personality and internet gaming disorder: The role of positive and negative affects. Current Psychology, 42(6), 4744–4753. [CrossRef]
- Zendle, D., Ballou, N., Cutting, J., & Petrovskaya, E. (2023). Four grand challenges for video game effects scholars: How digital trace data can improve the way we study games. PsyArXiv. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




