Submitted:
07 February 2024
Posted:
08 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
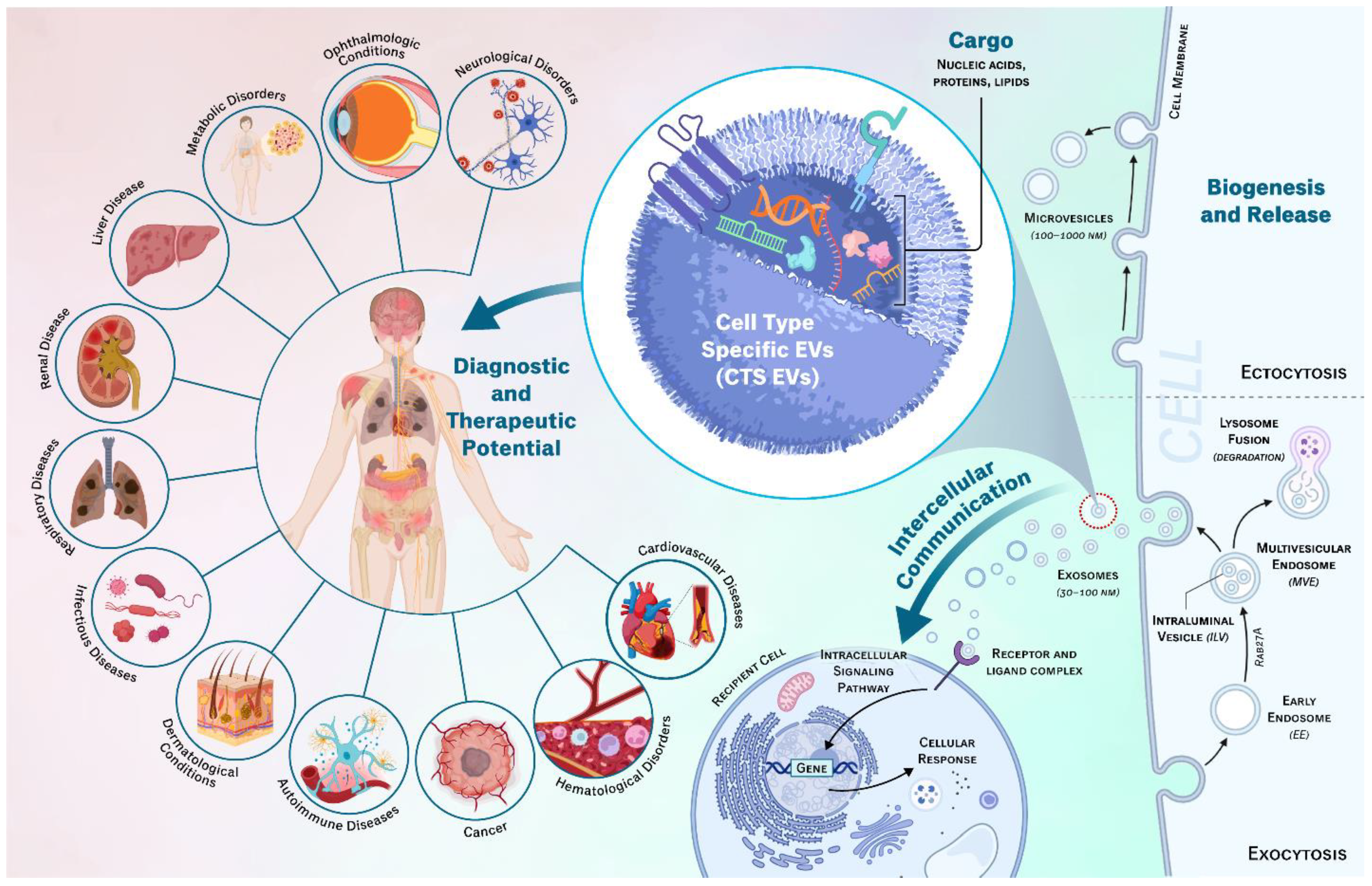
1. Introduction
2. EV Origins and Intercellular Communication
2.1. Biogenesis and Release
2.2. Molecular Composition
2.3. CTS-EVs in Intercellular Communication
3. CTS-EVs in Physiology and Pathology
3.1. Normal Physiological Function
3.2. Cancer
3.3. Neurological Disorders
3.4. Ophthalmic Conditions
3.5. Infectious Disease:
3.6. Autoimmune Diseases:
3.7. Cardiovascular Diseases
3.8. Hematologic Disorders
3.9. Reproductive Disorders
3.10. Metabolic Diseases
3.11. Liver Disease
3.12. Renal Diseases
3.13. Respiratory Diseases
3.14. Dermatological Diseases
3.14. Challenges and Emerging Trends
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massoumi, H.; Amin, S.; Soleimani, M.; Momenaei, B.; Ashraf, M.J.; Guaiquil, V.H.; Hematti, P.; Rosenblatt, M.I.; Djalilian, A.R.; Jalilian, E. Extracellular-Vesicle-Based Therapeutics in Neuro-Ophthalmic Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.E.; de Jong, O.G.; Brouwer, M.; Wood, M.J.; Lavieu, G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Vader, P. Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics: Natural versus Engineered Targeting and Trafficking. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, E.; Bigit, B.; Amin, S.; Massoumi, H.; Katz, E.; Guaiquil, V.H.; Rosenblatt, M.; Djalilian, A.R. Exosomes from 3D Cultures of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell (BM-MSCs) Have Higher Neuro-Regenerative Potential than Those Generated from 2D Conditions. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 1209-A0209-1209-A0209.
- Jalilian, E.; Massoumi, H.; Bigit, B.; Amin, S.; Katz, E.A.; Guaiquil, V.H.; Anwar, K.N.; Hematti, P.; Rosenblatt, M.I.; Djalilian, A.R. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in a 3D System Produce Higher Concentration of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) with Increased Complexity and Enhanced Neuronal Growth Properties. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 425. [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Jalilian, E.; Katz, E.; Frank, C.; Yazdanpanah, G.; Guaiquil, V.H.; Rosenblatt, M.I.; Djalilian, A.R. The Limbal Niche and Regenerative Strategies. Vision 2021, 5, 43. [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, E.; Putra, I.; Katz, E.; Yazdanpanah, G.; Guaiquil, V.H.; Shen, X.; Anwar, K.; An, S.; Rosenblatt, M.; Djalilian, A.R. Interactions between Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) and Trigeminal Ganglion (TGs) Improve Neurite Growth and Elongation. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 892.
- Massoumi, H.; Katz, E.; Nguyen, T.T.; Zhou, Q.; Jazayerli, C.; Anwar, K.; Ashraf, M.; Soleimani, M.; Guaiquil, V.H.; Rosenblatt, M.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) from 3D Cultured Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hBM-MSC) Demonstrated Increased Complexity and Neurite Elongation in an in-Vivo Corneal Injury Model. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 2350.
- Carnino, J.M.; Lee, H.; Jin, Y. Isolation and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles from Broncho-Alveolar Lavage Fluid: A Review and Comparison of Different Methods. Respir Res 2019, 20, 240. [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles 2018, 7, 153575. [CrossRef]
- Consortium, E.-T. EV-TRACK: Transparent Reporting and Centralizing Knowledge in Extracellular Vesicle Research. Nat Methods 2017, 14, 228–232. [CrossRef]
- Boukouris, S.; Mathivanan, S. Exosomes in Bodily Fluids Are a Highly Stable Resource of Disease Biomarkers. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2015, 9, 358–367. [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Rai, A.; Chen, M.; Suwakulsiri, W.; Greening, D.W.; Simpson, R.J. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer — Implications for Future Improvements in Cancer Care. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 617–638. [CrossRef]
- Akbar, A.; Malekian, F.; Baghban, N.; Kodam, S.P.; Ullah, M. Methodologies to Isolate and Purify Clinical Grade Extracellular Vesicles for Medical Applications. Cells 2022, 11, 186. [CrossRef]
- Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Immunomodulation and Regeneration: A next Generation Therapeutic Tool? | Cell Death & Disease Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41419-022-05034-x (accessed on 26 January 2024).
- Fuloria, S.; Subramaniyan, V.; Dahiya, R.; Dahiya, S.; Sudhakar, K.; Kumari, U.; Sathasivam, K.; Meenakshi, D.U.; Wu, Y.S.; Sekar, M.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Regenerative Potential and Challenges. Biology 2021, 10, 172. [CrossRef]
- Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Exosomes in Cardiac Repair - PMC Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9885380/ (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Zargar, M.J.; Kaviani, S.; Vasei, M.; Soufi Zomorrod, M.; Heidari Keshel, S.; Soleimani, M. Therapeutic Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Respiratory Disease. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 194. [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, L. The Roles of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Diabetes Mellitus and Its Related Complications. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1027686. [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.Y.; Ahmad, H.; Lin, G.; Carbonneau, M.; Tran, S.D. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Ophthalmology: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1167. [CrossRef]
- Samsonraj, R.M.; Raghunath, M.; Nurcombe, V.; Hui, J.H.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Cool, S.M. Concise Review: Multifaceted Characterization of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Use in Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 2173–2185. [CrossRef]
- Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Cancer Therapy Resistance: Recent Advances and Therapeutic Potential | Molecular Cancer | Full Text Available online: https://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12943-022-01650-5 (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Fafián-Labora, J.A.; O’Loghlen, A. Classical and Nonclassical Intercellular Communication in Senescence and Ageing. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 628–639. [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Kogure, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Urabe, F.; Usuba, W.; Prieto-Vila, M.; Ochiya, T. Exploiting the Message from Cancer: The Diagnostic Value of Extracellular Vesicles for Clinical Applications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jin, M.; Chen, Q.; Li, Q.; Xing, X.; Luo, Y.; Sun, X. Insight into Extracellular Vesicles in Vascular Diseases: Intercellular Communication Role and Clinical Application Potential. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 310. [CrossRef]
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [CrossRef]
- Hristov, M.; Erl, W.; Linder, S.; Weber, P.C. Apoptotic Bodies from Endothelial Cells Enhance the Number and Initiate the Differentiation of Human Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Vitro. Blood 2004, 104, 2761–2766. [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.F.; Wyllie, A.H.; Currie, A.R. Apoptosis: A Basic Biological Phenomenon with Wide-Ranging Implications in Tissue Kinetics. Br. J. Cancer 1972, 26, 239–257. [CrossRef]
- Akers, J.C.; Gonda, D.; Kim, R.; Carter, B.S.; Chen, C.C. Biogenesis of Extracellular Vesicles (EV): Exosomes, Microvesicles, Retrovirus-like Vesicles, and Apoptotic Bodies. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 113, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The Exosome Journey: From Biogenesis to Uptake and Intracellular Signalling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 47. [CrossRef]
- Pols, M.S.; Klumperman, J. Trafficking and Function of the Tetraspanin CD63. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 1584–1592. [CrossRef]
- Molecular Mechanism of Multivesicular Body Biogenesis by ESCRT Complexes - PubMed Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20305637/ (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Morishita, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Takakura, Y. Pharmacokinetics of Exosomes—An Important Factor for Elucidating the Biological Roles of Exosomes and for the Development of Exosome-Based Therapeutics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 2265–2269. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K.; Kang, B.; Kim, O.Y.; Choi, D.-S.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.R.; Go, G.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, S.C.; et al. EVpedia: An Integrated Database of High-Throughput Data for Systemic Analyses of Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, W.H. Exosomes: Biogenesis, Biologic Function and Clinical Potential. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 19. [CrossRef]
- Waldenström, A.; Ronquist, G. Role of Exosomes in Myocardial Remodeling. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 315–324. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tan, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q. MicroRNA in Extracellular Vesicles Regulates Inflammation through Macrophages under Hypoxia. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Vlassov, A.V.; Magdaleno, S.; Setterquist, R.; Conrad, R. Exosomes: Current Knowledge of Their Composition, Biological Functions, and Diagnostic and Therapeutic Potentials. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA - Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 940–948. [CrossRef]
- Mashouri, L.; Yousefi, H.; Aref, A.R.; Ahadi, A. mohammad; Molaei, F.; Alahari, S.K. Exosomes: Composition, Biogenesis, and Mechanisms in Cancer Metastasis and Drug Resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 75. [CrossRef]
- G, N.; Gundogan, B.; Tan, A.; Farhatnia, Y.; Wu, W.; Rajadas, J.; Seifalian, A.M. Exosomes as Immunotheranostic Nanoparticles. Clin. Ther. 2014, 36, 820–829. [CrossRef]
- Skotland, T.; Hessvik, N.P.; Sandvig, K.; Llorente, A. Exosomal Lipid Composition and the Role of Ether Lipids and Phosphoinositides in Exosome Biology. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 9–18. [CrossRef]
- Sunshine, H.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. Membrane Lipids and Cell Signaling. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2017, 28, 408–413. [CrossRef]
- Subra, C.; Grand, D.; Laulagnier, K.; Stella, A.; Lambeau, G.; Paillasse, M.; Medina, P.D.; Monsarrat, B.; Perret, B.; Silvente-Poirot, S.; et al. Exosomes Account for Vesicle-Mediated Transcellular Transport of Activatable Phospholipases and Prostaglandins [S]. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2105–2120. [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.; Royo, F.; Aizpurua-Olaizola, O.; Pazos, R.; Boons, G.-J.; Reichardt, N.-C.; Falcon-Perez, J.M. Glycosylation of Extracellular Vesicles: Current Knowledge, Tools and Clinical Perspectives. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1442985. [CrossRef]
- Yokose, T.; Kabe, Y.; Matsuda, A.; Kitago, M.; Matsuda, S.; Hirai, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Masugi, Y.; Hishiki, T.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. O-Glycan-Altered Extracellular Vesicles: A Specific Serum Marker Elevated in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2469. [CrossRef]
- Chernomordik, L.V.; Melikyan, G.B.; Chizmadzhev, Y.A. Biomembrane Fusion: A New Concept Derived from Model Studies Using Two Interacting Planar Lipid Bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA - Rev. Biomembr. 1987, 906, 309–352. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-B.; Dammer, E.B.; Ren, R.-J.; Wang, G. The Endosomal-Lysosomal System: From Acidification and Cargo Sorting to Neurodegeneration. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 18. [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular Vesicles: Exosomes, Microvesicles, and Friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xie, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Fang, M.; Zhou, F. The Function and Clinical Application of Extracellular Vesicles in Innate Immune Regulation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 323–334. [CrossRef]
- Saliba, D.G.; Céspedes-Donoso, P.F.; Bálint, Š.; Compeer, E.B.; Korobchevskaya, K.; Valvo, S.; Mayya, V.; Kvalvaag, A.; Peng, Y.; Dong, T.; et al. Composition and Structure of Synaptic Ectosomes Exporting Antigen Receptor Linked to Functional CD40 Ligand from Helper T Cells. eLife 2019, 8, e47528. [CrossRef]
- Buzas, E.I. The Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in the Immune System. Nat Rev Immunol 2023, 23, 236–250. [CrossRef]
- Boilard, E. Thematic Review Series: Exosomes and Microvesicles: Lipids as Key Components of Their Biogenesis and Functions Extracellular Vesicles and Their Content in Bioactive Lipid Mediators: More than a Sack of microRNA. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 2037–2046. [CrossRef]
- Skogberg, G.; Lundberg, V.; Berglund, M.; Gudmundsdottir, J.; Telemo, E.; Lindgren, S.; Ekwall, O. Human Thymic Epithelial Primary Cells Produce Exosomes Carrying Tissue-restricted Antigens. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 727–734. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Brown, B.A.; Siegel, A.P.; El Masry, M.S.; Zeng, X.; Song, W.; Das, A.; Khandelwal, P.; Clark, A.; Singh, K.; et al. Exosome-Mediated Crosstalk between Keratinocytes and Macrophages in Cutaneous Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12732–12748. [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; DiPietro, L.A. Factors Affecting Wound Healing. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 219–229. [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wu, P.; Li, L.; Sahal, H.M.; Ji, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qian, H.; Shi, H.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Autologous Dermal Fibroblasts Promote Diabetic Cutaneous Wound Healing through the Akt/β-Catenin Pathway. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 616–622. [CrossRef]
- Glady, A.; Vandebroek, A.; Yasui, M. Human Keratinocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Activate the MAPKinase Pathway and Promote Cell Migration and Proliferation in Vitro. Inflamm. Regen. 2021, 41, 4. [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.-C.; Tao, S.-C.; Yin, W.-J.; Qi, X.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, C.-Q. Exosomes Derived from Platelet-Rich Plasma Promote the Re-Epithelization of Chronic Cutaneous Wounds via Activation of YAP in a Diabetic Rat Model. Theranostics 2017, 7, 81–96. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, Z.; He, L.; Qu, Y.; Liu, O.; Han, Y.; Xu, C.; Duan, D. Platelet Rich Plasma-Derived Exosomal USP15 Promotes Cutaneous Wound Healing via Deubiquitinating EIF4A1; In Review, 2021.
- Schnatz, A.; Müller, C.; Brahmer, A.; Krämer-Albers, E. Extracellular Vesicles in Neural Cell Interaction and CNS Homeostasis. FASEB BioAdvances 2021, 3, 577–592. [CrossRef]
- Holm, M.M.; Kaiser, J.; Schwab, M.E. Extracellular Vesicles: Multimodal Envoys in Neural Maintenance and Repair. Trends Neurosci. 2018, 41, 360–372. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Zheng, J.C. Exosomes Released from Neural Progenitor Cells and Induced Neural Progenitor Cells Regulate Neurogenesis through miR-21a. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 96. [CrossRef]
- Zappulli, V.; Friis, K.P.; Fitzpatrick, Z.; Maguire, C.A.; Breakefield, X.O. Extracellular Vesicles and Intercellular Communication within the Nervous System. J. Clin. Invest. 2016, 126, 1198–1207. [CrossRef]
- Herrera Lopez, M.; Bertone Arolfo, M.; Remedi, M.; Gastaldi, L.; Wilson, C.; Guendulain, G.; Ceschin, D.; Cardozo Gizzi, A.; Caceres, A.; Moyano, A.L. Human Neural Rosettes Secrete Bioactive Extracellular Vesicles Enriched in Neuronal and Glial Cellular Component 2024.
- Jalilian, E.; Shin, S.R. Novel Model of Cortical-Meningeal Organoid Co-Culture System Improves Human Cortical Brain Organoid Cytoarchitecture. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7809. [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.; Romero, J.A.A.; Iglesia, R.P.; Lopes, M.H. Extracellular Vesicles: Decoding a New Language for Cellular Communication in Early Embryonic Development. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 94. [CrossRef]
- Huang-Doran, I.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Vidal-Puig, A. Extracellular Vesicles: Novel Mediators of Cell Communication In Metabolic Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 3–18. [CrossRef]
- Kranendonk, M.E.G.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Van Herwaarden, J.A.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.M.; De Jager, W.; Wauben, M.H.M.; Kalkhoven, E. Effect of Extracellular Vesicles of Human Adipose Tissue on Insulin Signaling in Liver and Muscle Cells: Adipose Tissue Vesicles and Insulin Signaling. Obesity 2014, 22, 2216–2223. [CrossRef]
- Kranendonk, M.E.G.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Van Balkom, B.W.M.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.M.; Van Herwaarden, J.A.; De Jager, W.; Schipper, H.S.; Brenkman, A.B.; Verhaar, M.C.; Wauben, M.H.M.; et al. Human Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicles in Reciprocal Signaling between Adipocytes and Macrophages. Obesity 2014, 22, 1296–1308. [CrossRef]
- Gesmundo, I.; Pardini, B.; Gargantini, E.; Gamba, G.; Birolo, G.; Fanciulli, A.; Banfi, D.; Congiusta, N.; Favaro, E.; Deregibus, M.C.; et al. Adipocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Regulate Survival and Function of Pancreatic β Cells. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e141962. [CrossRef]
- Zaborowski, M.P.; Balaj, L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lai, C.P. Extracellular Vesicles: Composition, Biological Relevance, and Methods of Study. BioScience 2015, 65, 783–797. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, T.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Shi, H. Adipose Tissue-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Promising Biomarker and Therapeutic Strategy for Metabolic Disorders. Stem Cells Int. 2023, 2023, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Bylicky, M.A.; Mueller, G.P.; Day, R.M. Mechanisms of Endogenous Neuroprotective Effects of Astrocytes in Brain Injury. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 6501031. [CrossRef]
- Bahram Sangani, N.; Gomes, A.R.; Curfs, L.M.G.; Reutelingsperger, C.P. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles during CNS Development. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 205, 102124. [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, A.; Radoszkiewicz, K.; Rybkowska, P.; Wedzinska, A.; Sarnowska, A. Interaction of Neural Stem Cells (NSCs) and Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) as a Promising Approach in Brain Study and Nerve Regeneration. Cells 2022, 11, 1464. [CrossRef]
- Oncogenic H-Ras Reprograms Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) Cell-Derived Exosomal Proteins Following Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition* - Molecular & Cellular Proteomics Available online: https://www.mcponline.org/article/S1535-9476(20)32528-7/fulltext (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Hu, T.; Hu, J. Melanoma-Derived Exosomes Induce Reprogramming Fibroblasts into Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts via Gm26809 Delivery. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 3085–3094. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhu, L.; Song, J.; Wang, G.; Li, P.; Li, W.; Luo, P.; Sun, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Liquid Biopsy at the Frontier of Detection, Prognosis and Progression Monitoring in Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 86. [CrossRef]
- Clayton, A.; Mitchell, J.P.; Court, J.; Linnane, S.; Mason, M.D.; Tabi, Z. Human Tumor-Derived Exosomes Down-Modulate NKG2D Expression1. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 7249–7258. [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Lei, J. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Circulating Tumor Cell-Mediated Distant Metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22. [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.J.; James, V. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Development of a Cancer Stem Cell Microenvironment Niche and Potential Therapeutic Targets: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 2435. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, J.; Hu, H.; Tu, L.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, F. Lung CSC-derived Exosomal miR-210-3p Contributes to a Pro-metastatic Phenotype in Lung Cancer by Targeting FGFRL1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6324–6339. [CrossRef]
- Irmer, B.; Chandrabalan, S.; Maas, L.; Bleckmann, A.; Menck, K. Extracellular Vesicles in Liquid Biopsies as Biomarkers for Solid Tumors. Cancers 2023, 15, 1307. [CrossRef]
- Alegre, E.; Zubiri, L.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; González-Cao, M.; Soria, L.; Martín-Algarra, S.; González, A. Circulating Melanoma Exosomes as Diagnostic and Prognosis Biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2016, 454, 28–32. [CrossRef]
- Osti, D.; Del Bene, M.; Rappa, G.; Santos, M.; Matafora, V.; Richichi, C.; Faletti, S.; Beznoussenko, G.V.; Mironov, A.; Bachi, A.; et al. Clinical Significance of Extracellular Vesicles in Plasma from Glioblastoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 266–276. [CrossRef]
- Duijvesz, D.; Versluis, C.Y.L.; van der Fels, C.A.M.; Vredenbregt-van den Berg, M.S.; Leivo, J.; Peltola, M.T.; Bangma, C.H.; Pettersson, K.S.I.; Jenster, G. Immuno-Based Detection of Extracellular Vesicles in Urine as Diagnostic Marker for Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 2869–2878. [CrossRef]
- König, L.; Kasimir-Bauer, S.; Bittner, A.-K.; Hoffmann, O.; Wagner, B.; Santos Manvailer, L.F.; Kimmig, R.; Horn, P.A.; Rebmann, V. Elevated Levels of Extracellular Vesicles Are Associated with Therapy Failure and Disease Progression in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2017, 7, e1376153. [CrossRef]
- Ghoroghi, S.; Mary, B.; Asokan, N.; Goetz, J.G.; Hyenne, V. Tumor Extracellular Vesicles Drive Metastasis (It’s a Long Way from Home). FASEB BioAdvances 2021, 3, 930–943. [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Garrastacho, M.; Bajo-Santos, C.; Line, A.; Martens-Uzunova, E.S.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Moros, M.; Soekmadji, C.; Tasken, K.A.; Llorente, A. Extracellular Vesicles as a Source of Prostate Cancer Biomarkers in Liquid Biopsies: A Decade of Research. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 331–350. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Use of a Liquid Biopsy Signature as Blood Biomarker for Early Detection and Monitoring Early-Onset Gastric Cancer; clinicaltrials.gov, 2023.
- Moon, P.-G.; Lee, J.-E.; Cho, Y.-E.; Lee, S.J.; Chae, Y.S.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, I.-S.; Park, H.Y.; Baek, M.-C. Fibronectin on Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as a Liquid Biopsy to Detect Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40189–40199. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Bu, J.; Ai, F.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhu, X. Extracellular Vesicles in the Treatment and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer: A Status Update. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1202493. [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, M.; Villa, A.; Rizzi, N.; Kuryk, L.; Rinner, B.; Cerullo, V.; Yliperttula, M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Ciana, P. Extracellular Vesicles Enhance the Targeted Delivery of Immunogenic Oncolytic Adenovirus and Paclitaxel in Immunocompetent Mice. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2019, 294, 165–175. [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, M.; Jia, H.; Wu, P. Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Anti-Cancer Drugs and Advanced Functionalization Platforms for Cancer Therapy. Drug Deliv. 29, 2513–253. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gao, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Bao, J.; Li, Y. The CRISPR/Cas9 System Delivered by Extracellular Vesicles. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 984. [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, M.; Jia, H.; Wu, P. Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Anti-Cancer Drugs and Advanced Functionalization Platforms for Cancer Therapy. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2513–2538. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Su, D.; Li, S.; Guan, L.; Shi, C.; Li, D.; Hu, S.; Ma, X. The Connexin 46 Mutant (V44M) Impairs Gap Junction Function Causing Congenital Cataract. J. Genet. 2017, 96, 969–976. [CrossRef]
- Acuña, R.A.; Varas-Godoy, M.; Berthoud, V.M.; Alfaro, I.E.; Retamal, M.A. Connexin-46 Contained in Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Malignancy Features in Breast Cancer Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 676. [CrossRef]
- Faldoni, F.L.C.; Villacis, R.A.R.; Canto, L.M.; Fonseca-Alves, C.E.; Cury, S.S.; Larsen, S.J.; Aagaard, M.M.; Souza, C.P.; Scapulatempo-Neto, C.; Osório, C.A.B.T.; et al. Inflammatory Breast Cancer: Clinical Implications of Genomic Alterations and Mutational Profiling. Cancers 2020, 12, 2816. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Ni, J.; Beretov, J.; Wasinger, V.C.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Recent Advances of Small Extracellular Vesicle Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 33. [CrossRef]
- Moon, P.-G.; Lee, J.-E.; Cho, Y.-E.; Lee, S.J.; Jung, J.H.; Chae, Y.S.; Bae, H.-I.; Kim, Y.-B.; Kim, I.-S.; Park, H.Y.; et al. Identification of Developmental Endothelial Locus-1 on Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Biomarker for Early Breast Cancer Detection. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1757–1766. [CrossRef]
- Eubanks, S.E. A Pilot Study of Tumor-Derived Exosomes as Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy; clinicaltrials.gov, 2017.
- Armstrong, J.P.; Holme, M.N.; Stevens, M.M. Re-Engineering Extracellular Vesicles as Smart Nanoscale Therapeutics. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 69–83. [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Janke, F.; Dietz, S.; Sültmann, H. Circulating MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Lung Cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. Fortschritte Krebsforsch. Progres Dans Rech. Sur Cancer 2020, 215, 299–318. [CrossRef]
- 104. Sun, J. Clinical Study of ctDNA and Exosome Combined Detection to Identify Benign and Malignant Pulmonary Nodules; clinicaltrials.gov, 2019.
- Li, X.-Q.; Liu, J.-T.; Fan, L.-L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wang, F.; Yu, H.-Q.; Gao, J.; Wei, W.; Wang, H.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Gefitinib-Treated EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer Cells Alter Cisplatin Sensitivity via up-Regulating Autophagy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 24585–24595. [CrossRef]
- Saviana, M.; Romano, G.; Le, P.; Acunzo, M.; Nana-Sinkam, P. Extracellular Vesicles in Lung Cancer Metastasis and Their Clinical Applications. Cancers 2021, 13, 5633. [CrossRef]
- Urine Exosomes for Non-Invasive Assessment of Gene Expression and Mutations of Prostate Cancer | PLOS ONE Available online: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0154507 (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Del Re, M.; Crucitta, S.; Sbrana, A.; Rofi, E.; Paolieri, F.; Gianfilippo, G.; Galli, L.; Falcone, A.; Morganti, R.; Porta, C.; et al. Androgen Receptor (AR) Splice Variant 7 and Full-Length AR Expression Is Associated with Clinical Outcome: A Translational Study in Patients with Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer. BJU Int. 2019, 124, 693–700. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Shi, C.; Xu, W.; Yang, H.-L.; Xia, B.; Tian, C. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Inhibit Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via miR-34a-5p. Endocr. J. 2021, 68, 1197–1208. [CrossRef]
- Izadirad, M.; Huang, Z.; Jafari, F.; Hamidieh, A.A.; Gharehbaghian, A.; Li, Y.-D.; Jafari, L.; Chen, Z.-S. Extracellular Vesicles in Acute Leukemia: A Mesmerizing Journey With a Focus on Transferred microRNAs. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 766371. [CrossRef]
- Hornick, N.I.; Huan, J.; Doron, B.; Goloviznina, N.A.; Lapidus, J.; Chang, B.H.; Kurre, P. Serum Exosome MicroRNA as a Minimally-Invasive Early Biomarker of AML. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11295. [CrossRef]
- Ruiss, R.; Jochum, S.; Mocikat, R.; Hammerschmidt, W.; Zeidler, R. EBV-Gp350 Confers B-Cell Tropism to Tailored Exosomes and Is a Neo-Antigen in Normal and Malignant B Cells—A New Option for the Treatment of B-CLL. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25294. [CrossRef]
- Gärtner, K.; Luckner, M.; Wanner, G.; Zeidler, R. Engineering Extracellular Vesicles as Novel Treatment Options: Exploiting Herpesviral Immunity in CLL. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1573051. [CrossRef]
- Dubois, K.; Tannoury, M.; Bauvois, B.; Susin, S.A.; Garnier, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Tumor Microenvironment Messengers as a Basis for New Targeted Therapies? Cancers 2023, 15, 2307. [CrossRef]
- Runz, S.; Keller, S.; Rupp, C.; Stoeck, A.; Issa, Y.; Koensgen, D.; Mustea, A.; Sehouli, J.; Kristiansen, G.; Altevogt, P. Malignant Ascites-Derived Exosomes of Ovarian Carcinoma Patients Contain CD24 and EpCAM. Gynecol. Oncol. 2007, 107, 563–571. [CrossRef]
- Keserű, J.S.; Soltész, B.; Lukács, J.; Márton, É.; Szilágyi-Bónizs, M.; Penyige, A.; Póka, R.; Nagy, B. Detection of Cell-Free, Exosomal and Whole Blood Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number in Plasma or Whole Blood of Patients with Serous Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 298, 76–81. [CrossRef]
- McAlarnen, L.A.; Gupta, P.; Singh, R.; Pradeep, S.; Chaluvally-Raghavan, P. Extracellular Vesicle Contents as Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Ovarian Malignancies. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 26, 347–359. [CrossRef]
- Pisano, S.; Pierini, I.; Gu, J.; Gazze, A.; Francis, L.W.; Gonzalez, D.; Conlan, R.S.; Corradetti, B. Immune (Cell) Derived Exosome Mimetics (IDEM) as a Treatment for Ovarian Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 553576. [CrossRef]
- Hallal, S.M.; Tűzesi, Á.; Sida, L.A.; Xian, E.; Madani, D.; Muralidharan, K.; Shivalingam, B.; Buckland, M.E.; Satgunaseelan, L.; Alexander, K.L. Glioblastoma Biomarkers in Urinary Extracellular Vesicles Reveal the Potential for a ‘Liquid Gold’ Biopsy. Br. J. Cancer 2024. [CrossRef]
- University Hospital, Limoges Clinical Relevance of Detecting Molecular Abnormalities in Glial Tumor Exosomes; clinicaltrials.gov, 2023.
- Lovinger, D.M. Communication Networks in the Brain. Alcohol Res. Health 2008, 31, 196–214.
- Cheng, L.; Hill, A.F. Therapeutically Harnessing Extracellular Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 379–399. [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.; Avila, J.; Hernández, F. Propagation of Tau via Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13. [CrossRef]
- Gomes, P.; Tzouanou, F.; Skolariki, K.; Vamvaka-Iakovou, A.; Noguera-Ortiz, C.; Tsirtsaki, K.; Waites, C.L.; Vlamos, P.; Sousa, N.; Costa-Silva, B.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles and Alzheimer’s Disease in the Novel Era of Precision Medicine: Implications for Disease Progression, Diagnosis and Treatment. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 358, 114183. [CrossRef]
- Si, Q.; Wu, L.; Pang, D.; Jiang, P. Exosomes in Brain Diseases: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Targets. MedComm 2023, 4, e287. [CrossRef]
- Xian, X.; Cai, L.-L.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.-C.; Xu, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Xie, Y.-H.; Zhu, X.-L.; Li, Y.-F. Neuron Secrete Exosomes Containing miR-9-5p to Promote Polarization of M1 Microglia in Depression. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 122. [CrossRef]
- Riancho, J.; Vázquez-Higuera, J.L.; Pozueta, A.; Lage, C.; Kazimierczak, M.; Bravo, M.; Calero, M.; Gonalezález, A.; Rodríguez, E.; Lleó, A.; et al. MicroRNA Profile in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: Analysis of miR-9-5p and miR-598 in Raw and Exosome Enriched Cerebrospinal Fluid Samples. J. Alzheimers Dis. JAD 2017, 57, 483–491. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, Q.; Ping, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Lin, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, A. The Role of Exosomal microRNAs and Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 3232869. [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Muraoka, S.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Hu, J.; McQuade, A.K.; Young-Pearse, T.; Aslebagh, R.; Shaffer, S.A.; Gygi, S.P.; Blurton-Jones, M.; et al. Human Neural Cell Type-Specific Extracellular Vesicle Proteome Defines Disease-Related Molecules Associated with Activated Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. J Extracell Vesicles 2022, 11, e12183. [CrossRef]
- 130. John van Geest Centre for Brain Repair, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Cambridge, UK; Kouli, A.; Torsney, K.M.; Department of Medicine for the Elderly, Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, UK; Clinical Gerontology Unit, Department of Public Health and Primary Care, University of Cambridge, UK; Kuan, W.-L.; John van Geest Centre for Brain Repair, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Cambridge, UK Parkinson’s Disease: Etiology, Neuropathology, and Pathogenesis. In Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects; John Van Geest Centre for Brain Repair, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Cambridge, UK, Stoker, T.B., Greenland, J.C., John Van Geest Centre for Brain Repair, Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Cambridge, UK, Eds.; Codon Publications, 2018; pp. 3–26 ISBN 978-0-9944381-6-4.
- Yu, H.; Sun, T.; An, J.; Wen, L.; Liu, F.; Bu, Z.; Cui, Y.; Feng, J. Potential Roles of Exosomes in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment to Prognosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 86. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; He, X.; Yang, X.; Shan, F.; Feng, J. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Inflammation and Demyelination of the Central Nervous System in EAE Rats by Regulating the Polarization of Microglia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 268–280. [CrossRef]
- Pinnell, J.R.; Cui, M.; Tieu, K. Exosomes in Parkinson Disease. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 413–428. [CrossRef]
- Agliardi, C.; Guerini, F.R.; Zanzottera, M.; Bolognesi, E.; Picciolini, S.; Caputo, D.; Rovaris, M.; Pasanisi, M.B.; Clerici, M. Myelin Basic Protein in Oligodendrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Multiple Sclerosis: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 894. [CrossRef]
- Karnas, E.; Dudek, P.; Zuba-Surma, E.K. Stem Cell- Derived Extracellular Vesicles as New Tools in Regenerative Medicine - Immunomodulatory Role and Future Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1120175. [CrossRef]
- Ollen-Bittle, N.; Roseborough, A.D.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.D.; Whitehead, S.N. Mechanisms and Biomarker Potential of Extracellular Vesicles in Stroke. Biology 2022, 11, 1231. [CrossRef]
- Kawata, K.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Aldret, R. A Preliminary Report on Brain-Derived Extracellular Vesicle as Novel Blood Biomarkers for Sport-Related Concussions. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 239. [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, D.; Kuo, W.P.; Frühbeis, C.; Sun, J.-J.; Zehendner, C.M.; Luhmann, H.J.; Pinto, S.; Toedling, J.; Trotter, J.; Krämer-Albers, E.-M. Multifaceted Effects of Oligodendroglial Exosomes on Neurons: Impact on Neuronal Firing Rate, Signal Transduction and Gene Regulation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130510. [CrossRef]
- Ollen-Bittle, N.; Roseborough, A.D.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.D.; Whitehead, S.N. Mechanisms and Biomarker Potential of Extracellular Vesicles in Stroke. Biology 2022, 11, 1231. [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.A.; Asim, M.; El-Menyar, A.; Biswas, K.H.; Rizoli, S.; Al-Thani, H. The Evolving Role of Extracellular Vesicles (Exosomes) as Biomarkers in Traumatic Brain Injury: Clinical Perspectives and Therapeutic Implications. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 933434. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.-X.; Xie, G.-J.; Mao, X.; Zou, X.-P.; Liao, Y.-J.; Liu, Q.-S.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y. Exosomes from Patients with Major Depression Cause Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice with Involvement of miR-139-5p-Regulated Neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 1050–1058. [CrossRef]
- Lafourcade, C.A.; Fernández, A.; Ramírez, J.P.; Corvalán, K.; Carrasco, M.Á.; Iturriaga, A.; Bátiz, L.F.; Luarte, A.; Wyneken, U. A Role for Mir-26a in Stress: A Potential sEV Biomarker and Modulator of Excitatory Neurotransmission. Cells 2020, 9, 1364. [CrossRef]
- Couch, Y. Challenges Associated with Using Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Disease. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 23, 1091–1105. [CrossRef]
- Khadka, A.; Spiers, J.G.; Cheng, L.; Hill, A.F. Extracellular Vesicles with Diagnostic and Therapeutic Potential for Prion Diseases. Cell Tissue Res. 2023, 392, 247–267. [CrossRef]
- Ugalde, C.L.; Finkelstein, D.I.; Lawson, V.A.; Hill, A.F. Pathogenic Mechanisms of Prion Protein, Amyloid-β and A-synuclein Misfolding: The Prion Concept and Neurotoxicity of Protein Oligomers. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 162–180. [CrossRef]
- Ananbeh, H.; Vodicka, P.; Kupcova Skalnikova, H. Emerging Roles of Exosomes in Huntington’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4085. [CrossRef]
- Klingeborn, M.; Skiba, N.P.; Stamer, W.D.; Bowes Rickman, C. Isolation of Retinal Exosome Biomarkers from Blood by Targeted Immunocapture. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1185, 21–25. [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.-Y.; Bang, J.Y.; Choi, A.J.; Yoon, J.; Lee, W.-C.; Choi, S.; Yoon, S.; Kim, H.C.; Baek, J.-H.; Park, H.S.; et al. Exosomal Proteins in the Aqueous Humor as Novel Biomarkers in Patients with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 581–595. [CrossRef]
- Mighty, J.; Rubio-Navarro, A.; Shi, C.; Zhou, J.; Flores-Bellver, M.; Heissel, S.; Onwumere, O.; Einbond, L.; Gharbaran, R.; Casper, D.S.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles of Human Diabetic Retinopathy Retinal Tissue and Urine of Diabetic Retinopathy Patients Are Enriched for the Junction Plakoglo Bin Protein. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1077644. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, C.; Deng, Y.; Yu, Q.; Meng, X.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Q.; Fu, Y. Effect of Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Angiogenesis and the Ensuing Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy through a miR-30b-Dependent Mechanism. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 188. [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Shin, H.A.; Duong, V.-A.; Lee, H.; Lew, H. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Optic Nerve Injury: Neuroprotection and Mitochondrial Homeostasis. Cells 2022, 11, 3720. [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, F.S.; Riddick, B.J.; Roberts, H.; Skiba, N.; Stamer, W.D. Comparison of the Extracellular Vesicle Proteome between Glaucoma and Non-Glaucoma Trabecular Meshwork Cells. Front. Ophthalmol. 2023, 3, 1257737. [CrossRef]
- Cells | Free Full-Text | Extracellular Vesicles from Ocular Melanoma Have Pro-Fibrotic and Pro-Angiogenic Properties on the Tumor Microenvironment Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/11/23/3828 (accessed on 16 January 2024).
- Pucker, A.D.; Ngo, W.; Postnikoff, C.K.; Fortinberry, H.; Nichols, J.J. Tear Film miRNAs and Their Association With Human Dry Eye Disease. Curr. Eye Res. 2022, 47, 1479–1487. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, D.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Promote Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Lens Epithelial Cells under Oxidative Stress. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 398, 112362. [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhou, L.; An, J.; Shao, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, G.; Chen, S.; Cui, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Comprehensive Profiling of Extracellular Vesicles in Uveitis and Scleritis Enables Biomarker Discovery and Mechanism Exploration. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 388. [CrossRef]
- McKay, T.B.; Yeung, V.; Hutcheon, A.E.K.; Guo, X.; Zieske, J.D.; Ciolino, J.B. Extracellular Vesicles in the Cornea: Insights from Other Tissues. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2021, 2021, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Yeung, V.; Boychev, N.; Farhat, W.; Ntentakis, D.P.; Hutcheon, A.E.K.; Ross, A.E.; Ciolino, J.B. Extracellular Vesicles in Corneal Fibrosis/Scarring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5921. [CrossRef]
- Hindman, H.B.; DeMagistris, M.; Callan, C.; McDaniel, T.; Bubel, T.; Huxlin, K.R. Impact of Topical Anti-Fibrotics on Corneal Nerve Regeneration in Vivo. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 181, 49–60. [CrossRef]
- Katz, E.; Guaiquil, V.H.; Ivakhnitskaia, E.; Lara, D.; Anwar, K.; Jalilian, E.; Rosenblatt, M.; Djalilian, A.R. Exosomes as a Novel Multitarget Approach to Promote Growth of Corneal Sensory Neurons. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 749.
- Soleimani, M.; Mirshahi, R.; Cheraqpour, K.; Baharnoori, S.M.; Massoumi, H.; Chow, C.; Shahjahan, S.; Momenaei, B.; Ashraf, M.J.; Koganti, R.; et al. Intrastromal versus Subconjunctival Injection of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells for Promoting Corneal Repair. Ocul. Surf. 2023, 30, 187–195. [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.; Parekh, M.; Kaye, S.B.; Ahmad, S. Epithelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Trigger the Differentiation of Two Epithelial Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1718. [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Khare, D.; Poe, A.J.; Amador, C.; Ghiam, S.; Fealy, A.; Ebrahimi, S.; Shadrokh, O.; Song, X.-Y.; Santiskulvong, C.; et al. MicroRNA and Protein Cargos of Human Limbal Epithelial Cell-Derived Exosomes and Their Regulatory Roles in Limbal Stromal Cells of Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Corneas. Cells 2023, 12, 2524. [CrossRef]
- Poe, A.J.; Shah, R.; Khare, D.; Kulkarni, M.; Phan, H.; Ghiam, S.; Punj, V.; Ljubimov, A.V.; Saghizadeh, M. Regulatory Role of miR-146a in Corneal Epithelial Wound Healing via Its Inflammatory Targets in Human Diabetic Cornea. Ocul. Surf. 2022, 25, 92–100. [CrossRef]
- Barberis, E.; Vanella, V.V.; Falasca, M.; Caneapero, V.; Cappellano, G.; Raineri, D.; Ghirimoldi, M.; De Giorgis, V.; Puricelli, C.; Vaschetto, R.; et al. Circulating Exosomes Are Strongly Involved in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 632290. [CrossRef]
- Kakizaki, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yabuta, S.; Kurosaki, N.; Kagawa, T.; Kotani, A. The Immunological Function of Extracellular Vesicles in Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Hepatocytes. PloS One 2018, 13, e0205886. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H. The Complex Role of Extracellular Vesicles in HIV Infection. BMB Rep. 2023, 56, 335–340. [CrossRef]
- Arakelyan, A.; Fitzgerald, W.; Zicari, S.; Vanpouille, C.; Margolis, L. Extracellular Vesicles Carry HIV Env and Facilitate Hiv Infection of Human Lymphoid Tissue. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1695. [CrossRef]
- Sims, B.; Farrow, A.L.; Williams, S.D.; Bansal, A.; Krendelchtchikov, A.; Gu, L.; Matthews, Q.L. Role of TIM-4 in Exosome-Dependent Entry of HIV-1 into Human Immune Cells. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 4823–4833. [CrossRef]
- Tumne, A.; Prasad, V.S.; Chen, Y.; Stolz, D.B.; Saha, K.; Ratner, D.M.; Ding, M.; Watkins, S.C.; Gupta, P. Noncytotoxic Suppression of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Transcription by Exosomes Secreted from CD8+ T Cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4354–4364. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, R.-H.; Ho, W.-Z.; Li, J.-L. Exosomes Contribute to the Transmission of Anti-HIV Activity from TLR3-Activated Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells to Macrophages. Antiviral Res. 2016, 134, 167–171. [CrossRef]
- Haghighitalab, A.; Dominici, M.; Matin, M.M.; Shekari, F.; Ebrahimi Warkiani, M.; Lim, R.; Ahmadiankia, N.; Mirahmadi, M.; Bahrami, A.R.; Bidkhori, H.R. Extracellular Vesicles and Their Cells of Origin: Open Issues in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1090416. [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.-T.; Wang, B.; Lv, L.-L.; Liu, B.-C. Extracellular Vesicle-Based Nanotherapeutics: Emerging Frontiers in Anti-Inflammatory Therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8111–8129. [CrossRef]
- Schioppo, T.; Ubiali, T.; Ingegnoli, F.; Bollati, V.; Caporali, R. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 3481–3497. [CrossRef]
- Testa, U.; Pelosi, E.; Castelli, G.; Labbaye, C. miR-146 and miR-155: Two Key Modulators of Immune Response and Tumor Development. Non-Coding RNA 2017, 3, 22. [CrossRef]
- Ciesielski, O.; Biesiekierska, M.; Panthu, B.; Soszyński, M.; Pirola, L.; Balcerczyk, A. Citrullination in the Pathology of Inflammatory and Autoimmune Disorders: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 94. [CrossRef]
- González-González, A.; García-Sánchez, D.; Dotta, M.; Rodríguez-Rey, J.C.; Pérez-Campo, F.M. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Secretome: The Cornerstone of Cell-Free Regenerative Medicine. World J. Stem Cells 2020, 12, 1529–1552. [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, M.; Khokha, R. Metalloproteinases in Extracellular Vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA - Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 1989–2000. [CrossRef]
- Admou, B.; Eddehbi, F.; Elmoumou, L.; Elmojadili, S.; Salami, A.; Oujidi, M.; Brahim, I.; Hazime, R. Anti-Double Stranded DNA Antibodies: A Rational Diagnostic Approach in Limited-Resource Settings. Pract. Lab. Med. 2022, 31, e00285. [CrossRef]
- Ohl, K.; Tenbrock, K. Inflammatory Cytokines in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, R.; Ye, S.; Lin, S.; Yin, G.; Xie, Q. Recent Advances in the Use of Exosomes in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1509. [CrossRef]
- Roescher, N.; Tak, P.; Illei, G. Cytokines in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Oral Dis. 2009, 15, 519–526. [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.L. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Clinical Review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12144. [CrossRef]
- Uranga, J.A.; Martínez, V.; Abalo, R. Mast Cell Regulation and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Effects of Food Components with Potential Nutraceutical Use. Molecules 2020, 25, 4314. [CrossRef]
- Weaver, K.R.; Mustapic, M.; Kapogiannis, D.; Henderson, W.A. Neuronal-enriched Extracellular Vesicles in Individuals with IBS: A Pilot Study of COMT and BDNF. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2022, 34, e14257. [CrossRef]
- Langhorst, J.; Elsenbruch, S.; Koelzer, J.; Rueffer, A.; Michalsen, A.; Dobos, G.J. Noninvasive Markers in the Assessment of Intestinal Inflammation in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Performance of Fecal Lactoferrin, Calprotectin, and PMN-Elastase, CRP, and Clinical Indices. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 162–169. [CrossRef]
- Maggio, S.; Ceccaroli, P.; Polidori, E.; Cioccoloni, A.; Stocchi, V.; Guescini, M. Signal Exchange through Extracellular Vesicles in Neuromuscular Junction Establishment and Maintenance: From Physiology to Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2804. [CrossRef]
- Sabre, L.; Punga, T.; Punga, A.R. Circulating miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Myasthenia Gravis: Tools for Personalized Medicine. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 213. [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; De Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135. [CrossRef]
- Sarlon-Bartoli, G.; Bennis, Y.; Lacroix, R.; Piercecchi-Marti, M.D.; Bartoli, M.A.; Arnaud, L.; Mancini, J.; Boudes, A.; Sarlon, E.; Thevenin, B.; et al. Plasmatic Level of Leukocyte-Derived Microparticles Is Associated With Unstable Plaque in Asymptomatic Patients With High-Grade Carotid Stenosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1436–1441. [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y. Extracellular Vesicles in Cardiovascular Diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 68. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Hosen, M.R.; Zietzer, A.; Flender, A.; Levermann, P.; Schmitz, T.; Frühwald, D.; Goody, P.; Nickenig, G.; et al. Atherosclerotic Conditions Promote the Packaging of Functional MicroRNA-92a-3p Into Endothelial Microvesicles. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 575–587. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liao, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhuang, T.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Ge, J. Coronary Serum Exosomes Derived from Patients with Myocardial Ischemia Regulate Angiogenesis through the miR-939-Mediated Nitric Oxide Signaling Pathway. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2079–2093. [CrossRef]
- Jansen, F.; Yang, X.; Proebsting, S.; Hoelscher, M.; Przybilla, D.; Baumann, K.; Schmitz, T.; Dolf, A.; Endl, E.; Franklin, B.S.; et al. MicroRNA Expression in Circulating Microvesicles Predicts Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e001249. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Rodrigues, T.M.; Laundos, T.L.; Pereira-Carvalho, R.; Batista-Almeida, D.; Pereira, R.; Coelho-Santos, V.; Silva, A.P.; Fernandes, R.; Zuzarte, M.; Enguita, F.J.; et al. Exosomes Secreted by Cardiomyocytes Subjected to Ischaemia Promote Cardiac Angiogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 1338–1350. [CrossRef]
- Pantaleão, L.C.; Loche, E.; Fernandez-Twinn, D.S.; Dearden, L.; Córdova-Casanova, A.; Osmond, C.; Salonen, M.; Kajantie, E.; Niu, Y.; de Almeida-Faria, J.; et al. Programming of Cardiac Metabolism by miR-15b-5p, a miRNA Released in Cardiac Extracellular Vesicles Following Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Mol. Metab. 2024, 101875. [CrossRef]
- Vélez, P.; Parguiña, A.; Ocaranza-Sánchez, R.; Grigorian-Shamagian, L.; Rosa, I.; Alonso-Orgaz, S.; Cuesta, F.D.L.; Guitián, E.; Moreu, J.; Barderas, M.; et al. Identification of a Circulating Microvesicle Protein Network Involved in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 112, 716–726. [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Kwon, K.; Park, J.; Ryu, D.-R.; Shin, J.-A.; Lee Kang, J.; Choi, J.H.; Park, E.-M.; Lee, K.E.; Woo, M.; et al. Extracellular Matrix-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Cardiomyocyte Growth and Electrical Activity in Engineered Cardiac Atria. Biomaterials 2017, 146, 49–59. [CrossRef]
- Halkein, J.; Tabruyn, S.P.; Ricke-Hoch, M.; Haghikia, A.; Nguyen, N.-Q.-N.; Scherr, M.; Castermans, K.; Malvaux, L.; Lambert, V.; Thiry, M.; et al. MicroRNA-146a Is a Therapeutic Target and Biomarker for Peripartum Cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 2143–2154. [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.G.; Watanabe, S.; Lee, A.; Gorski, P.A.; Lee, P.; Jeong, D.; Liang, L.; Liang, Y.; Baccarini, A.; Sahoo, S.; et al. miR-146a Suppresses SUMO1 Expression and Induces Cardiac Dysfunction in Maladaptive Hypertrophy. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 673–685. [CrossRef]
- Eustes, A.S.; Dayal, S. The Role of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Immune-Mediated Thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7837. [CrossRef]
- Bordin, A.; Chirivì, M.; Pagano, F.; Milan, M.; Iuliano, M.; Scaccia, E.; Fortunato, O.; Mangino, G.; Dhori, X.; De Marinis, E.; et al. Human Platelet Lysate-derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Angiogenesis through miR-126. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13312. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Law, S.Q.K.; Shojaee, M.; Hall, A.S.; Bhuiyan, S.; Lim, M.B.L.; Silva, A.; Kong, K.J.W.; Schoppet, M.; Blyth, C.; et al. First-in-human Clinical Trial of Allogeneic, Platelet-derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Potential Therapeutic for Delayed Wound Healing. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, 12332. [CrossRef]
- Gardin, C.; Ferroni, L.; Leo, S.; Tremoli, E.; Zavan, B. Platelet-Derived Exosomes in Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12546. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, Q. The Effect of Extracellular Vesicles on Thrombosis. J Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2023, 16, 682–697. [CrossRef]
- Thangaraju, K.; Neerukonda, S.N.; Katneni, U.; Buehler, P.W. Extracellular Vesicles from Red Blood Cells and Their Evolving Roles in Health, Coagulopathy and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 153. [CrossRef]
- Georgatzakou, H.T.; Fortis, S.P.; Papageorgiou, E.G.; Antonelou, M.H.; Kriebardis, A.G. Blood Cell-Derived Microvesicles in Hematological Diseases and Beyond. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 803. [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.; Greening, D.W.; Bolumar, D.; Balaguer, N.; Salamonsen, L.A.; Vilella, F. Extracellular Vesicles in Human Reproduction in Health and Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 292–332. [CrossRef]
- Sang, Q.; Yao, Z.; Wang, H.; Feng, R.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Xing, Q.; Jin, L.; He, L.; Wu, L.; et al. Identification of microRNAs in Human Follicular Fluid: Characterization of microRNAs That Govern Steroidogenesis in Vitro and Are Associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Vivo. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 3068–3079. [CrossRef]
- Harp, D.; Driss, A.; Mehrabi, S.; Chowdhury, I.; Xu, W.; Liu, D.; Garcia-Barrio, M.; Taylor, R.N.; Gold, B.; Jefferson, S.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Endometriotic Stromal Cells Have Enhanced Angiogenic Effects in Vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 187–196. [CrossRef]
- Berezin, A.E.; Kremzer, A.A.; Berezina, T.A.; Martovitskaya, Y.V. The Pattern of Circulating Microparticles in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus with Asymptomatic Atherosclerosis. Acta Clin. Belg. 2016, 71, 38–45. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wei, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Meng, W.; Mo, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Ren, K.; Du, R.; et al. Cell-Derived Microparticles in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 39, 2439–2450. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Eguchi, A.; Tempaku, M.; Honda, T.; Togashi, K.; Iwasa, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Takei, Y.; Sumida, Y.; Taguchi, O. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles Are Associated with Lipid and Insulin Metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E574–E582. [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, A.; Lazic, M.; Armando, A.M.; Phillips, S.A.; Katebian, R.; Maraka, S.; Quehenberger, O.; Sears, D.D.; Feldstein, A.E. Circulating Adipocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Are Novel Markers of Metabolic Stress. J. Mol. Med. Berl. Ger. 2016, 94, 1241–1253. [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Horigome, H.; Tanaka, K.; Nakata, Y.; Ohkawara, K.; Katayama, Y.; Matsui, A. Impact of Weight Reduction on Production of Platelet-Derived Microparticles and Fibrinolytic Parameters in Obesity. Thromb. Res. 2007, 119, 45–53. [CrossRef]
- Pardo, F.; Villalobos-Labra, R.; Sobrevia, B.; Toledo, F.; Sobrevia, L. Extracellular Vesicles in Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus. Mol. Aspects Med. 2018, 60, 81–91. [CrossRef]
- Stepanian, A.; Bourguignat, L.; Hennou, S.; Coupaye, M.; Hajage, D.; Salomon, L.; Alessi, M.-C.; Msika, S.; de Prost, D. Microparticle Increase in Severe Obesity: Not Related to Metabolic Syndrome and Unchanged after Massive Weight Loss. Obes. Silver Spring Md 2013, 21, 2236–2243. [CrossRef]
- Campello, E.; Zabeo, E.; Radu, C.M.; Spiezia, L.; Foletto, M.; Prevedello, L.; Gavasso, S.; Bulato, C.; Vettor, R.; Simioni, P. Dynamics of Circulating Microparticles in Obesity after Weight Loss. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2016, 11, 695–702. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yin, X.-M. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Liver Pathogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2022, 192, 1358–1367. [CrossRef]
- Azparren-Angulo, M.; Royo, F.; Gonzalez, E.; Liebana, M.; Brotons, B.; Berganza, J.; Goñi-de-Cerio, F.; Manicardi, N.; Abad-Jordà, L.; Gracia-Sancho, J.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles in Hepatology: Physiological Role, Involvement in Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic Opportunities. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 218, 107683. [CrossRef]
- Povero, D.; Panera, N.; Eguchi, A.; Johnson, C.D.; Papouchado, B.G.; de Araujo Horcel, L.; Pinatel, E.M.; Alisi, A.; Nobili, V.; Feldstein, A.E. Lipid-Induced Hepatocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Regulate Hepatic Stellate Cells via MicroRNA Targeting Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 646-663.e4. [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, T.; Amo-Shiinoki, K.; Ishikura, S.; Takahara, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Kaneto, H.; Kuroda, A.; Matsuhisa, M.; Hashida, S. Sequential Cleavage of Insulin Receptor by Calpain 2 and γ-Secretase Impairs Insulin Signalling. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2711–2721. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Dai, B.; Li, J.; Shang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, X. Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Derived Exosomal miRNA-21 Contributes to Tumor Progression by Converting Hepatocyte Stellate Cells to Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 324. [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Hou, X. MiR-223 as a Regulator and Therapeutic Target in Liver Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 860661. [CrossRef]
- Liver Cancer: Your Chances for Recovery (Prognosis) | Saint Luke’s Health System Available online: https://www.saintlukeskc.org/health-library/liver-cancer-your-chances-recovery-prognosis (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Grange, C.; Bussolati, B. Extracellular Vesicles in Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 499–513. [CrossRef]
- Korecka, K.; Gawin, M.; Pastuszka, A.; Partyka, M.; Koszutski, T.; Pietrowska, M.; Hyla-Klekot, L. Proteomics of Urinary Small Extracellular Vesicles in Early Diagnosis of Kidney Diseases in Children-Expectations and Limitations. PROTEOMICS n/a, 2300168. [CrossRef]
- Barutta, F.; Tricarico, M.; Corbelli, A.; Annaratone, L.; Pinach, S.; Grimaldi, S.; Bruno, G.; Cimino, D.; Taverna, D.; Deregibus, M.C.; et al. Urinary Exosomal microRNAs in Incipient Diabetic Nephropathy. PloS One 2013, 8, e73798. [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.-L.; Cao, Y.-H.; Ni, H.-F.; Xu, M.; Liu, D.; Liu, H.; Chen, P.-S.; Liu, B.-C. MicroRNA-29c in Urinary Exosome/Microvesicle as a Biomarker of Renal Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2013, 305, F1220–F1227. [CrossRef]
- Eirin, A.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Puranik, A.S.; Tang, H.; McGurren, K.A.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Lerman, A.; Lerman, L.O. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Kidney Inflammation. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 114–124. [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, F.; Morosi, L.; Corbetta, S.; Chinello, C.; Brambilla, P.; Mina, P.D.; Villa, A.; Albo, G.; Battaglia, C.; Bosari, S.; et al. Differential Protein Profiling of Renal Cell Carcinoma Urinary Exosomes. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 1220–1233. [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Akamatsu, S.; Kita, Y.; Goto, T.; Kobayashi, T. The Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in the Progression of Renal Cell Carcinoma and Their Potential for Future Clinical Application. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1611. [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Shi, L.; Li, K.; Liu, W.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Q. Mechanism of Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Regulating Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression by the Delivery of MALAT1. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 187. [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, J.; Lee, H. Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Respiratory System. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 887–895. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Zhang, D.; Laskin, D.L.; Jin, Y. Functional Evidence of Pulmonary Extracellular Vesicles in Infectious and Noninfectious Lung Inflammation. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2018, 201, 1500–1509. [CrossRef]
- Nagano, T.; Katsurada, M.; Dokuni, R.; Hazama, D.; Kiriu, T.; Umezawa, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishimura, Y. Crucial Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Bronchial Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2589. [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Kadota, T.; Araya, J.; Ochiya, T.; Kuwano, K. Clinical Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics for Inflammatory Lung Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 355. [CrossRef]
- O’Farrell, H.E.; Yang, I.A. Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, S2141–S2154. [CrossRef]
- Hough, K.P.; Chanda, D.; Duncan, S.R.; Thannickal, V.J.; Deshane, J.S. Exosomes in Immunoregulation of Chronic Lung Diseases. Allergy 2017, 72, 534–544. [CrossRef]
- Carnino, J.M.; Lee, H.; Jin, Y. Isolation and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles from Broncho-Alveolar Lavage Fluid: A Review and Comparison of Different Methods. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 240. [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Araya, J.; Ito, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Kosaka, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kadota, T.; Hara, H.; Kuwano, K.; Ochiya, T. Suppression of Autophagy by Extracellular Vesicles Promotes Myofibroblast Differentiation in COPD Pathogenesis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 28388. [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.S.D.; Shen, H.-M.; Wong, W.S.F. Dysregulated Autophagy in COPD: A Pathogenic Process to Be Deciphered. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Perera, G.K.; Di Meglio, P.; Nestle, F.O. Psoriasis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2012, 7, 385–422. [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Fang, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, G. Extracellular Vesicles in Inflammatory Skin Disorders: From Pathophysiology to Treatment. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9937–9955. [CrossRef]
- Tamagawa-Mineoka, R.; Katoh, N.; Kishimoto, S. Platelet Activation in Patients with Psoriasis: Increased Plasma Levels of Platelet-Derived Microparticles and Soluble P-Selectin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 621–626. [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, J.; Mohler, E.R.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Moore, J.; Rogers, W.T.; Zhang, L.; Gelfand, J.M.; Mehta, N.N. Endothelial Cell-, Platelet-, and Monocyte/Macrophage-Derived Microparticles Are Elevated in Psoriasis beyond Cardiometabolic Risk Factors. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000507. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sales, V.; Vila, V.; Ricart, J.M.; Vayá, A.; Todolí, J.; Nńñez, C.; Contreras, T.; Ballester, C.; Reganon, E. Increased Circulating Endothelial Cells and Microparticles in Patients with Psoriasis. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2015, 60, 283–290. [CrossRef]
- Ovcina-Kurtovic, N.; Kasumagic-Halilovic, E. Serum Levels of Tumor Necrosis Factor - Alpha in Patients With Psoriasis. Mater. Socio-Medica 2022, 34, 40–43. [CrossRef]
- Dainichi, T.; Kitoh, A.; Otsuka, A.; Nakajima, S.; Nomura, T.; Kaplan, D.H.; Kabashima, K. The Epithelial Immune Microenvironment (EIME) in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1286–1298. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tan, X.; Chen, G.; Liu, X.; Feng, A.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Extracellular Vesicles of Commensal Skin Microbiota Alleviate Cutaneous Inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis Mouse Model by Re-Establishing Skin Homeostasis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2023, S0022-202X(23)00169-0. [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-W.; Kim, M.-R.; Lee, E.-Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Jeon, S.G.; Yang, J.-M.; Lee, B.-J.; Pyun, B.-Y.; Gho, Y.S.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Staphylococcus Aureus Induce Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Inflammation. Allergy 2011, 66, 351–359. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, C.; Lohcharoenkal, W.; Ali, M.M.; Xing, P.; Zheng, W.; Görgens, A.; Gustafsson, M.O.; EL Andaloussi, S.; Sonkoly, E.; et al. Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Exert an Oncogenic Role by Activating Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 1–12. [CrossRef]
| Disease Type | Specific Diseases | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.2 | Cancer | Breast, Lung, Prostate, Leukemia, Ovarian, Glioblastoma, Pancreatic, Colorectal, Bladder, Oropharyngeal, Gastric | [75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120] |
| 3.3 | Neurological Disorders | Alzheimer’s, Parkinson, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke, Epilepsy, Depression, Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI), Multiple sclerosis, Huntington, ALS, Prion disease | [121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146] |
| 3.4 | Ophthalmologic Conditions | Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD), Diabetic Retinopathy, Glaucoma, Uveitis, Retinal dystrophies, Dry Eye Disease, Corneal trauma, Posterior Capsular Opacification, Ocular Melanoma | [1,5,6,7,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164] |
| 3.5 | Infectious Diseases | Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Hepatitis Viruses, COVID-19, Tuberculosis | [50,165,166,167,168,169,170,171] |
| 3.6 | Autoimmune Diseases | Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren’s Syndrome, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD), Myasthenia Gravis, Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases, Celiac Disease, Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma), Antiphospholipid Syndrome | [172,173,174,175,176,177,178,179,180,181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188] |
| 3.7 | Cardiovascular diseases | Myocardial infarction, Coronary artery disease, Atrial fibrillation, Cardiomyopathy | [189,190,191,192,193,194,195,196,197,198,199,200] |
| 3.8 | Hematological Disorders | Thrombosis, Sickle Cell anemia, Hemophilia, Anemia, Thrombocytopenia, Immunodeficiency | [50,201,202,203,204,205,206,207] |
| 3.9 | Reproductive Disorders | Endometriosis, Infertility, Genetic Testing, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) | [208,209,210] |
| 3.10 | Metabolic Disorders | Diabetes, Metabolic syndrome, Obesity | [211,212,213,214,215,216,217,218] |
| Liver Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma, Liver fibrosis and cirrhosis | [219,220,221,222,223,224,225] | |
| 3.11 | Renal Diseases | Chronic kidney disease, Renal artery stenosis, Renal cell Carcinoma | [226,227,228,229,230,231,232,233] |
| 3.12 | Respiratory Diseases | Acute Lung Injury (ARI), Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), Asthma | [234,235,236,237,238,239,240,241,242] |
| 3.13 | Dermatological Conditions | Psoriasis, Atopic dermatitis, Skin Cancer | [243,244,245,246,247,248,249,250,251,252] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





