Submitted:
01 February 2024
Posted:
01 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Motivation
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
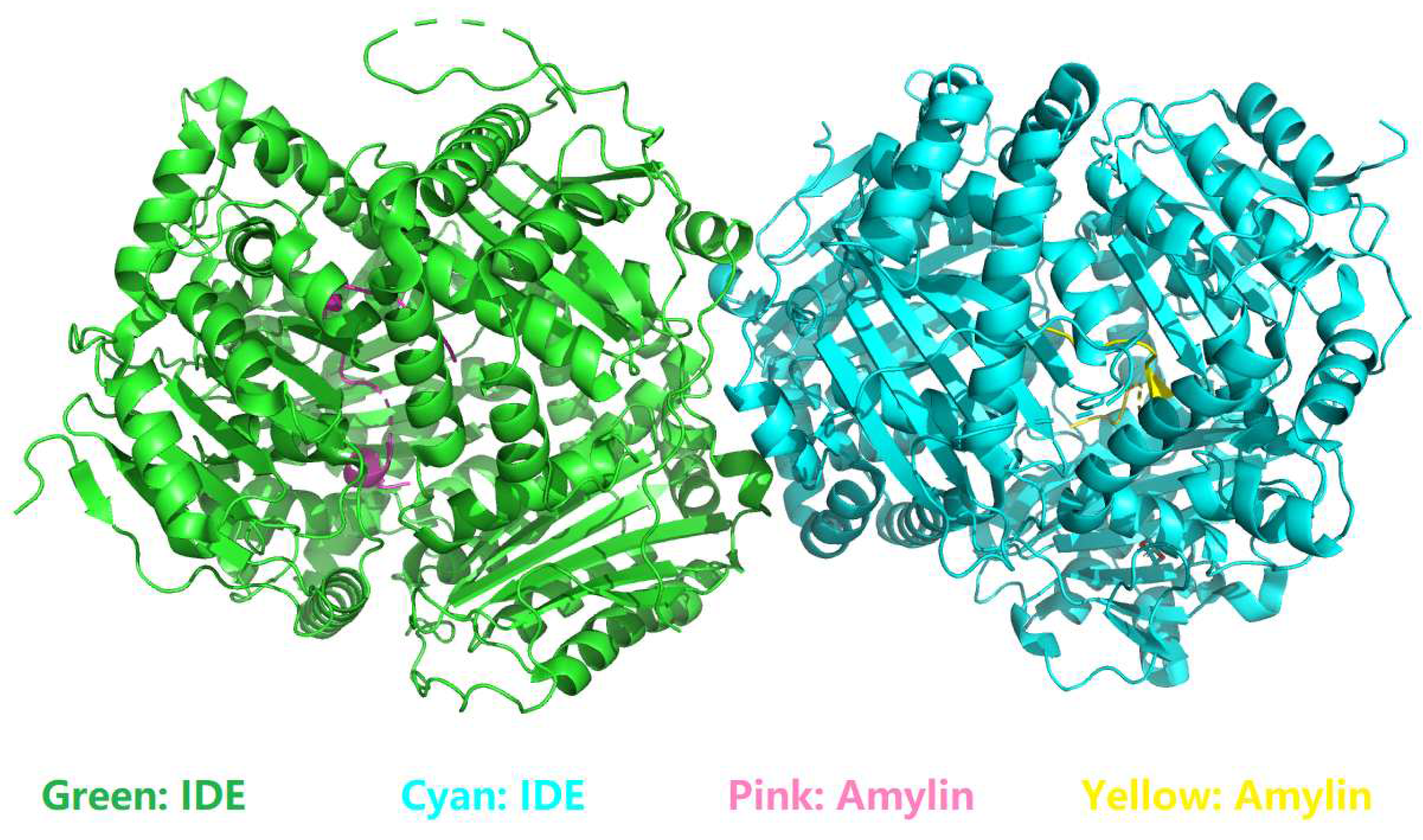
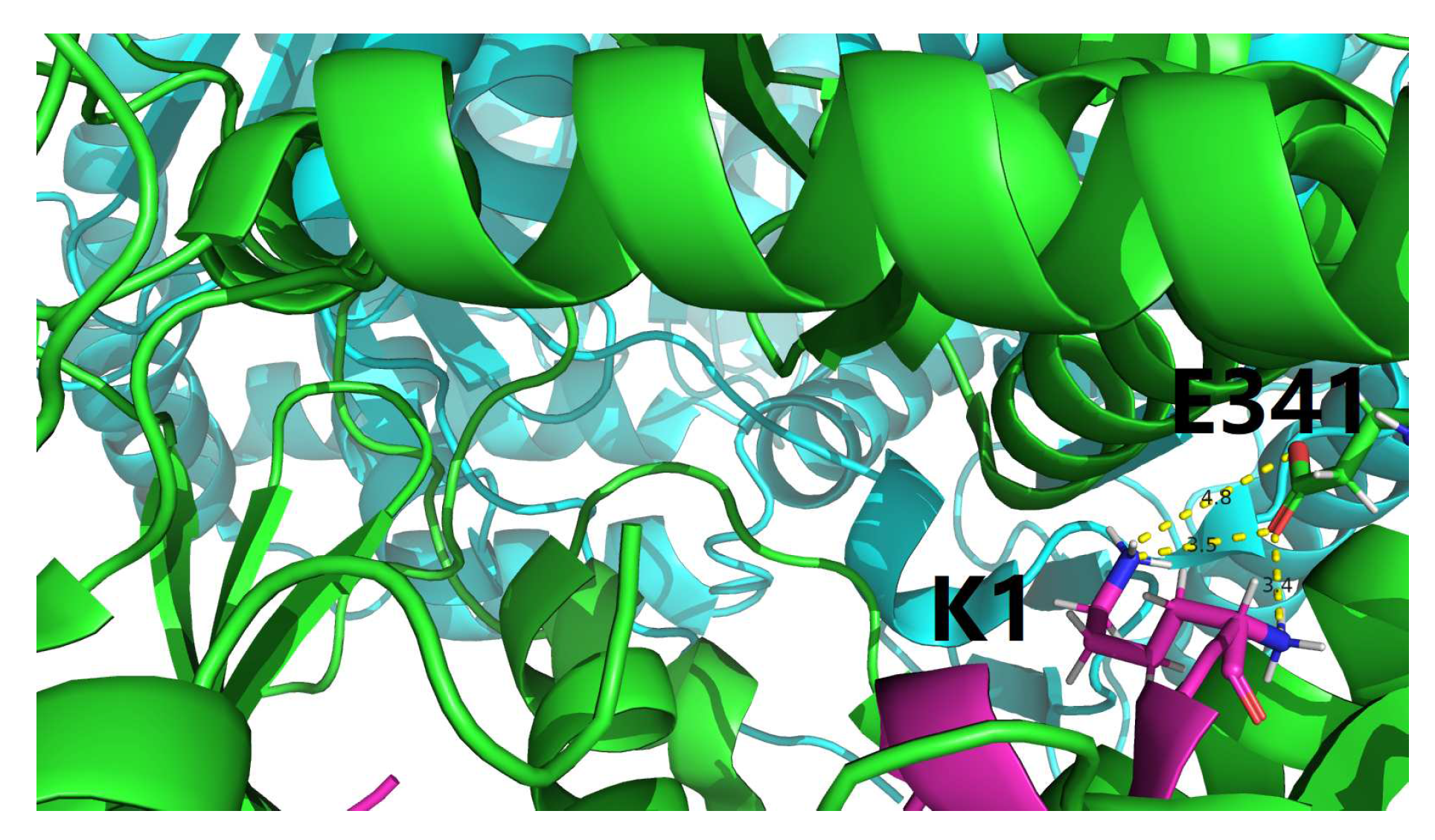
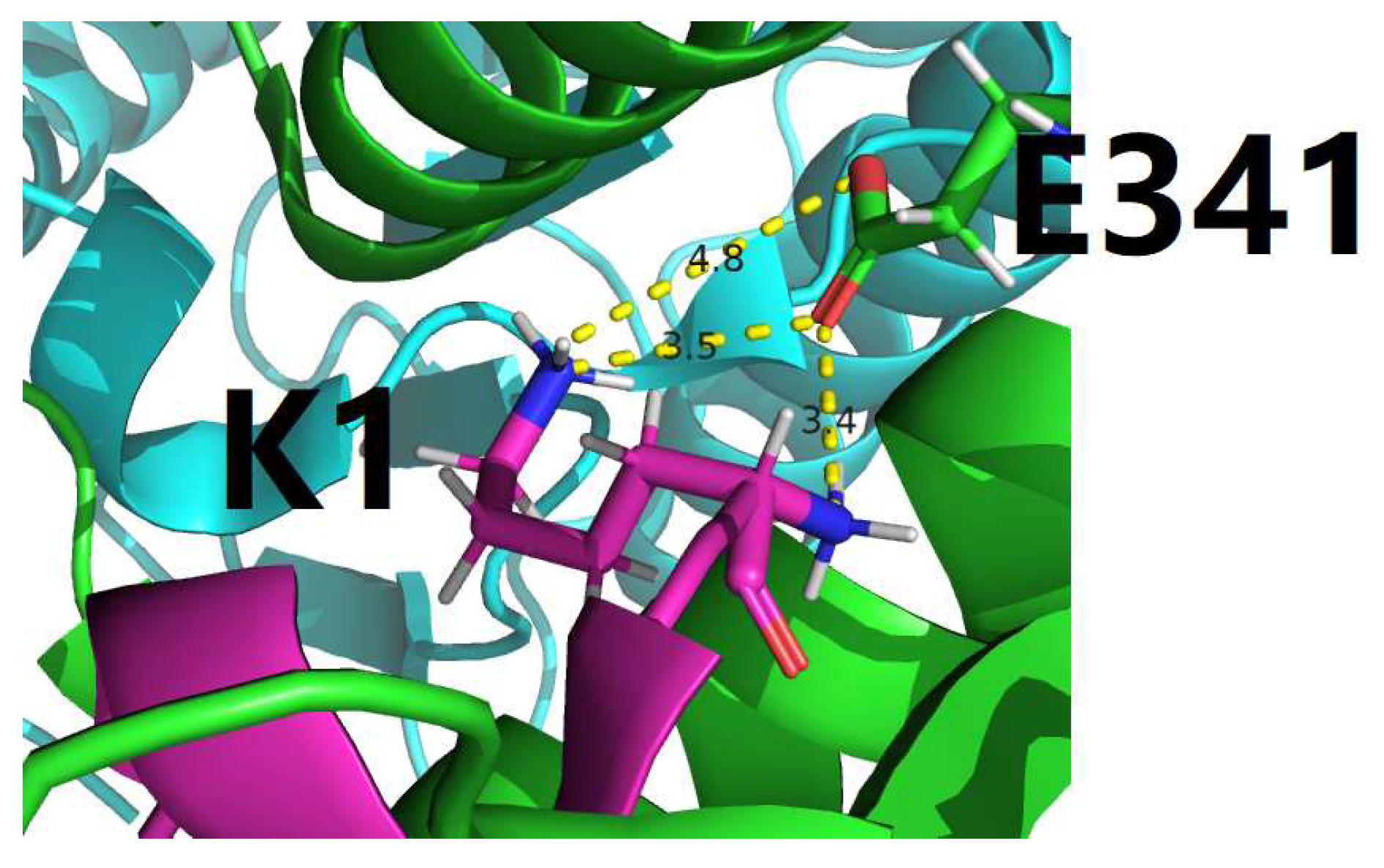
4.1. Characterization of residue-specific electrostatic interactions at the amylin-IDE binding interface
- among the 22, only 3 interfacial salt bridges (Table 5) were structurally identified between Lys1 and Glu341 (Figure 2 and Figure 3) at the binding interface of IDE and amylin for the amylin-IDE complex structure PDB ID 2G48 [45,46], according to a new set of criteria [33] as defined in the section of Materials and Methods.
- among the 16, only 4 interfacial salt bridges (Table 5) were structurally identified between Lys1 and Glu341 (Figure 2 and Figure 3) at the binding interface of IDE and amylin for the amylin-IDE complex structure PDB ID 3HGZ [47,48], according to a new set of criteria [33] as defined in the section of Materials and Methods.
4.2. Structural identification of an electrostatic hotspot at amylin-IDE binding interface
5. Conclusion
- This finding also contributes to the growing body of knowledge aimed at unraveling the intricacies of protein–protein interactions and provides a foundation for future research endeavors in the development of targeted therapeutics for metabolic disorders, particularly diabetes (T2DM) and obesity [57,58].
- The rationale for targeting electrostatic hotspots in the amylin-IDE interaction lies in the role of such sites as preferred binding locations for drug-like small molecules. By pinpointing these hotspots, we aim to provide a precise target for the development of small molecules capable of disrupting the amylin-IDE interaction. The potential therapeutic implications of such disruptors extend to modulating glucose homeostasis and mitigating the risk of amyloid formation, which is particularly relevant in the context of type 2 diabetes.
6. Discussion
6.1. Disrupting the amylin-IDE interaction: a drug discovery and design perspective
6.2. High-throughput comprehensive structural biophysical analysis: a methological perspective
7. Ethical statement
8. Declaration of generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathiesen, D.S.; Bagger, J.I.; Knop, F.K. Long-acting amylin analogues for the management of obesity. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2022, 29, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, D.L.; Chen, S.; Lutz, T.A.; Parkes, D.G.; Roth, J.D. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 564–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghrably, M.; Czaban, I.; Jaremko, L.; Jaremko, M. Interaction of amylin species with transition metals and membranes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 191, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moracci, L.; Crotti, S.; Traldi, P.; Agostini, M.; Cosma, C.; Lapolla, A. Role of mass spectrometry in the study of interactions between amylin and metal ions. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2021, 42, 984–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, R.G.; Duckworth, W.C.; Hamel, F.G. Degradation of Amylin by Insulin-degrading Enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36621–36625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.J. Targeting Insulin-Degrading Enzyme to Treat Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamek, R.N.; Suire, C.N.; Stokes, R.W.; Brizuela, M.K.; Cohen, S.M.; Leissring, M.A. Hydroxypyridinethione Inhibitors of Human Insulin-Degrading Enzyme. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 1776–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, W.; Huang, Y.M.; Qiao, Y.C.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhao, H.L. Human Amylin: From Pathology to Physiology and Pharmacology. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, W. Molecular links between Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes mellitus. Neuroscience 2013, 250, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, L.; Guarda, M.; Meneses, M.J.; Macedo, M.P.; Vicente Miranda, H. Insulin-degrading enzyme: An ally against metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. J. Pathol. 2021, 255, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tundo, G.R.; Sbardella, D.; Ciaccio, C.; Grasso, G.; Gioia, M.; Coletta, A.; Polticelli, F.; Di Pierro, D.; Milardi, D.; Van Endert, P.; Marini, S.; Coletta, M. Multiple functions of insulin-degrading enzyme: A metabolic crosslight? Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 52, 554–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.K.; Chorell, E.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Insulin-degrading enzyme is activated by the C-terminus of -synuclein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 466, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elseweidy, M.M.; Amin, R.S.; Atteia, H.H.; Ali, M.A. Vitamin D3 intake as regulator of insulin degrading enzyme and insulin receptor phosphorylation in diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maianti, J.P.; McFedries, A.; Foda, Z.H.; Kleiner, R.E.; Du, X.Q.; Leissring, M.A.; Tang, W.J.; Charron, M.J.; Seeliger, M.A.; Saghatelian, A.; Liu, D.R. Anti-diabetic activity of insulin-degrading enzyme inhibitors mediated by multiple hormones. Nature 2014, 511, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Manolopoulou, M.; Bian, Y.; Schilling, A.B.; Tang, W.J. Molecular Basis for the Recognition and Cleavages of IGF-II, TGF-α, and Amylin by Human Insulin-Degrading Enzyme. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 395, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, M.A. Unraveling Alzheimer’s: Making Sense of the Relationship between Diabetes and Alzheimer’s Disease1. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 51, 961–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.G.; Hamel, F.G.; Duckworth, W.C. An Insulin-Degrading Enzyme Inhibitor Decreases Amylin Degradation, Increases Amylin-Induced Cytotoxicity, and Increases Amyloid Formation in Insulinoma Cell Cultures. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2315–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QIU, W.; FOLSTEIN, M. Insulin, insulin-degrading enzyme and amyloid- peptide in Alzheimer’s disease: Review and hypothesis. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, T.B.; Toth, J.L.; Klimkowski, V.J.; Cao, J.X.; Siesky, A.M.; Alexander-Chacko, J.; Wu, G.Y.; Dixon, J.T.; McGee, J.E.; Wang, Y.; Guo, S.Y.; Cavitt, R.N.; Schindler, J.; Thibodeaux, S.J.; Calvert, N.A.; Coghlan, M.J.; Sindelar, D.K.; Christe, M.; Kiselyov, V.V.; Michael, M.D.; Sloop, K.W. Dual Exosite-binding Inhibitors of Insulin-degrading Enzyme Challenge Its Role as the Primary Mediator of Insulin Clearance in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 20044–20059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.S.; Ozbil, M.; Zhang, T.; Sheetz, M.; Lee, D.; Tran, D.; Li, S.; Prabhakar, R.; Hersh, L.B.; Rodgers, D.W. An Extended Polyanion Activation Surface in Insulin Degrading Enzyme. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costes, S.; Butler, P. Insulin-Degrading Enzyme Inhibition, a Novel Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes? Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellia, F.; Grasso, G. The role of copper(II) and zinc(II) in the degradation of human and murine IAPP by insulin-degrading enzyme: Metal ion modulation of IAPP degradation by IDE. J. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 49, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Geniposide protects pancreatic INS-1E cells from hIAPP-induced cell damage: Potential involvement of insulin degrading-enzyme. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 39, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suire, C.N.; Brizuela, M.K.; Leissring, M.A. Quantitative, High-Throughput Assays for Proteolytic Degradation of Amylin. Methods Protoc. 2020, 3, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, M.F.; Meier, D.T.; Zraika, S.; Templin, A.T.; Mellati, M.; Hull, R.L.; Leissring, M.A.; Kahn, S.E. Inhibition of Insulin-Degrading Enzyme Does Not Increase Islet Amyloid Deposition in Vitro. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3462–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.S.; Jang, H.; Guo, H.F.; Juliano, M.A.; Juliano, L.; Morris, A.J.; Galperin, E.; Rodgers, D.W.; Hersh, L.B. Inositol phosphates and phosphoinositides activate insulin-degrading enzyme, while phosphoinositides also mediate binding to endosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Fang, G.G.; Walsh, K.; Mwamburi, M.; Wolozin, B.; Abdul-Hay, S.O.; Ikezu, T.; Leissring, M.A.; Qiu, W.Q. Characterization of Insulin Degrading Enzyme and Other Amyloid-β Degrading Proteases in Human Serum: A Role in Alzheimer’s Disease? J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 29, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Joachimiak, A.; Rich Rosner, M.; Tang, W.J. Structures of human insulin-degrading enzyme reveal a new substrate recognition mechanism. Nature 2006, 443, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J. Drugs on the horizon for diabesity. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2005, 5, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gamba, A.; Leal, M.; Morelli, L.; Castano, E. Insulin-Degrading Enzyme: Structure-Function Relationship and its Possible Roles in Health and Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 3644–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.; Henrick, K.; Nakamura, H. Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nat. Struct. & Mol. Biol. 2003, 10, 980–980. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Half-a-century Burial of ρ, and φ in PDB. Preprint 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. How do SMA-linked mutations of SMN1 lead to structural/functional deficiency of the SMA protein? PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0178519. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Delving deep into the structural aspects of a furin cleavage site inserted into the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2: A structural biophysical perspective. Biophys. Chem. 2020, 264, 106420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortemme, T.; Kim, D.E.; Baker, D. Computational Alanine Scanning of Protein-Protein Interfaces. Sci. Signal. 2004, 2004, pl2–pl2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. A: Structural Modifications of Insulin Icodec Contributes to Its Prolonged Duration of Action: A Structural and Biophysical Perspective 2023, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Cai, W.; Weng, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Bao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zeng, S.; Bei, C.; Li, Y. High-affinity PD-1 molecules deliver improved interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. Delving Deep into the Structural Aspects of the BPro28-BLys29 Exchange in Insulin Lispro: A Structural Biophysical Lesson 2020.
- Li, W. Extracting the Interfacial Electrostatic Features from Experimentally Determined Antigen and/or Antibody-Related Structures inside Protein Data Bank for Machine Learning-Based Antibody Design. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.K.; Li, W.; Moore, M.J.; Choe, H.; Farzan, M. A 193-Amino Acid Fragment of the SARS Coronavirus S Protein Efficiently Binds Angiotensin-converting Enzyme 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 279, 3197–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.W.; O’Brien, J.S. Gaucher’s Disease: Deficiency of CID β-Glucosidase and Reconstitution of Enzyme Activity In Vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 2810–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.P.; Chain, E. An enzyme from bacteria able to destroy penicillin. Nature 1940, 146, 837–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Strengthening Semaglutide-GLP-1R Binding Affinity Via a Val27-Arg28 Exchange in the Peptide Backbone of Semaglutide: A Computational Structural Approach. Journal of Computational Biophysics and Chemistry.
- Li, W. Designing rt-PA Analogs to Release its Trapped Thrombolytic Activity. J. Comput. Biophys. Chem. 2021, 20, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Joachimiak, A.; Rich Rosner, M.; Tang, W.J. Structures of human insulin-degrading enzyme reveal a new substrate recognition mechanism. Nature 2006, 443, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tang, W.J. crystal structure of human insulin-degrading enzyme in complex with amylin. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Bian, Y.; Tang, W. Crystal structure of human insulin-degrading enzyme in complex with amylin. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Manolopoulou, M.; Bian, Y.; Schilling, A.B.; Tang, W.J. Molecular Basis for the Recognition and Cleavages of IGF-II, TGF-α, and Amylin by Human Insulin-Degrading Enzyme. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 395, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera: A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Cao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Qi, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, G.; Wu, Y.; Yan, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, G.F. Cryo-EM structures of MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV spike glycoproteins reveal the dynamic receptor binding domains. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. Structural and Functional Consequences of the SMA-Linked Missense Mutations of the Survival Motor Neuron Protein: A Brief Update. In Novel Aspects on Motor Neuron Disease; IntechOpen, 2019.
- Deciphering critical amino acid residues to modify and enhance the binding affinity of ankyrin scaffold specific to capsid protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology 2017.
- DeLano, W.L. Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsl. Protein Crystallogr. 2002, 40, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Marmentini, C.; Guimarães, D.S.P.; de Lima, T.I.; Teófilo, F.B.S.; da Silva, N.S.; Soares, G.M.; Boschero, A.C.; Kurauti, M.A. Rosiglitazone protects INS-1E cells from human islet amyloid polypeptide toxicity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 928, 175122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.Q.; Zhu, H. Amylin and its analogs: A friend or foe for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Kuo, W.L.; Yousef, M.; Rosner, M.R.; Tang, W.J. The C-terminal domain of human insulin degrading enzyme is required for dimerization and substrate recognition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 343, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, V.K.L.; Ma, R.C.W.; Lee, H.M.; Hu, C.; Park, K.S.; Furuta, H.; Wang, Y.; Tam, C.H.T.; Sim, X.; Ng, D.P.K.; Liu, J.; Wong, T.Y.; Tai, E.S.; Morris, A.P.; Tang, N.L.S.; Woo, J.; Leung, P.C.; Kong, A.P.S.; Ozaki, R.; Jia, W.P.; Lee, H.K.; Nanjo, K.; Xu, G.; Ng, M.C.Y.; So, W.Y.; Chan, J.C.N. Genetic Associations of Type 2 Diabetes with Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Processing and Degrading Pathways in Asian Populations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston-Mourney, K.; Zraika, S.; Udayasankar, J.; Subramanian, S.L.; Green, P.S.; Kahn, S.E.; Hull, R.L. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Reduces Islet Amyloid Formation by Degrading Islet Amyloid Polypeptide. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3553–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.J. Targeting Insulin-Degrading Enzyme to Treat Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebokova, E.; Christ, A.; Boehringer, M.; Mizrahi, J. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitors: The Next Generation of New Promising Therapies for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alafuzoff, I.; Aho, L.; Helisalmi, S.; Mannermaa, A.; Soininen, H. -Amyloid deposition in brains of subjects with diabetes. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2009, 35, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zraika, S.; Hull, R.L.; Udayasankar, J.; Clark, A.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Tong, J.; Gerchman, F.; Kahn, S.E. Identification of the Amyloid-Degrading Enzyme Neprilysin in Mouse Islets and Potential Role in Islet Amyloidogenesis. Diabetes 2007, 56, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. A Local Spherical Coordinate System Approach to Protein 3D Structure Description 2020.
- Li, W. Calcium Channel Trafficking Blocker Gabapentin Bound to the -2–1 Subunit of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel: A Computational Structural Investigation 2020.
- Li, W.; Vottevor, G. Towards a Truly General Intermolecular Binding Affinity Calculator for Drug Discovery & Design. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crunkhorn, S. Role of the Protein Data Bank. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 98–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, J.D.; Burley, S.K. How Structural Biologists and the Protein Data Bank Contributed to Recent FDA New Drug Approvals. Structure 2019, 27, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. Visualising the Experimentally Uncharted Territories of Membrane Protein Structures inside Protein Data Bank 2020.
- Wu, J.; Yan, Z.; Li, Z.; Qian, X.; Lu, S.; Dong, M.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, N. Structure of the voltage-gated calcium channel CaV1.1 at 3.6 Å resolution. Nature 2016, 537, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, G. How CaV1.2-bound verapamil blocks Ca2+ influx into cardiomyocyte: Atomic level views. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PDB ID | Structure Title |
|---|---|
| 8AZ7 | IAPP S20G plateau-phase fibril polymorph 4PF-LJ |
| 8AZ6 | IAPP S20G plateau-phase fibril polymorph 4PF-LU |
| 8AZ5 | IAPP S20G plateau-phase fibril polymorph 4PF-CU |
| 8AZ4 | IAPP S20G plateau-phase fibril polymorph 2PF-L |
| 8AZ3 | IAPP S20G growth-phase fibril polymorph 4PF-CU |
| 8AZ2 | IAPP S20G growth-phase fibril polymorph 3PF-CU |
| 8AZ1 | IAPP S20G growth-phase fibril polymorph 2PF-C |
| 8AZ0 | IAPP S20G growth-phase fibril polymorph 2PF-L |
| 8AWT | IAPP S20G lag-phase fibril polymorph 2PF-P |
| 8T89 | Racemic mixture of amyloid beta segment 16-KLVFFA-21 forms heterochiral rippled beta-sheet |
| 8T86 | Racemic mixture of amylin segment 25-AILSS-29 forms heterochiral rippled beta-sheet |
| 8T84 | Racemic mixture of amyloid beta segment 35-MVGGVV-40 forms heterochiral rippled beta-sheet, includes hexafluoroisopropanol |
| 8T82 | Racemic mixture of amyloid beta segment 35-MVGGVV-40 forms heterochiral rippled beta-sheet, includes pentafluoropropionic acid |
| 8F2B | Amylin 3 Receptor in complex with Gs and Pramlintide analogue peptide San45 |
| 8F2A | Human Amylin3 Receptor in complex with Gs and Pramlintide analogue peptide San385 (Cluster 5 conformation) |
| 8F0K | Human Amylin3 Receptor in complex with Gs and Pramlintide analogue peptide San385 |
| 8F0J | Calcitonin Receptor in complex with Gs and Pramlintide analogue peptide San45 |
| 7YKW | Structure of hIAPP fibril at 3.6 Angstroms resolution |
| 7YL7 | Structure of hIAPP-TF-type3 |
| 7YL3 | Structure of hIAPP-TF-type1 |
| 7YL0 | Structure of hIAPP-TF-type2 |
| 8AX7 | Crystal structure of a CGRP receptor ectodomain heterodimer bound to macrocyclic inhibitor HTL0031448 |
| 8AX6 | Crystal structure of a CGRP receptor ectodomain heterodimer bound to macrocyclic inhibitor HTL0029882 |
| 8AX5 | Crystal structure of a CGRP receptor ectodomain heterodimer bound to macrocyclic inhibitor HTL0029881 |
| 7P0I | Crystal structure of a CGRP receptor ectodomain heterodimer bound to macrocyclic inhibitor Compound 13 |
| 7P0F | Crystal structure of a CGRP receptor ectodomain heterodimer bound to macrocyclic inhibitor HTL0028125 |
| 7TYX | Human Amylin2 Receptor in complex with Gs and rat amylin peptide |
| 7TYN | Calcitonin Receptor in complex with Gs and salmon calcitonin peptide |
| 7TYI | Calcitonin Receptor in complex with Gs and rat amylin peptide, CT-like state |
| 7TZF | Human Amylin3 Receptor in complex with Gs and rat amylin peptide |
| 7TYY | Human Amylin2 Receptor in complex with Gs and salmon calcitonin peptide |
| 7TYW | Human Amylin1 Receptor in complex with Gs and salmon calcitonin peptide |
| 7TYO | Calcitonin receptor in complex with Gs and human calcitonin peptide |
| 7TYL | Calcitonin Receptor in complex with Gs and rat amylin peptide, bypass motif |
| 7TYH | Human Amylin2 Receptor in complex with Gs and human calcitonin peptide |
| 7TYF | Human Amylin1 Receptor in complex with Gs and rat amylin peptide |
| 7VV0 | Cryo-EM structure of pseudoallergen receptor MRGPRX2 complex with PAMP-12, local |
| 7M65 | Cryo-EM structure of human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP, or amylin) fibrils seeded by patient extracted fibrils, polymorph 4 |
| 7M64 | Cryo-EM structure of human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP, or amylin) fibrils seeded by patient extracted fibrils, polymorph 3 |
| 7M62 | Cryo-EM structure of human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP, or amylin) fibrils seeded by patient extracted fibrils, polymorph 2 |
| 7M61 | Cryo-EM structure of human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP, or amylin) fibrils seeded by patient extracted fibrils, polymorph 1 |
| 7BG0 | Fusion of MBP and the backbone of the long-acting amylin analog AM833. |
| 7KNU | CryoEM structure of the CGRP receptor with bound CGRP peptide in a detergent micelle |
| 7KNT | CryoEM structure of the apo-CGRP receptor in a detergent micelle |
| 6ZRR | three-protofilament amyloid structure of S20G variant of human amylin (IAPP - Islet Amyloid Polypeptide) |
| 6ZRQ | two-protofilament amyloid structure of S20G variant of human amylin (IAPP - islet amyloid polypeptide) |
| 6ZRF | amyloid structure of amylin (IAPP - islet amyloid polypeptide) |
| 6V2E | Crystal structure of the human CLR:RAMP2 extracellular domain heterodimer with bound high-affinity adrenomedullin S45R/K46L/S48G/Q50W variant |
| 6ZIS | Crystal structure of a CGRP receptor ectodomain heterodimer with bound high affinity inhibitor |
| 6ZHO | Crystal structure of a CGRP receptor ectodomain heterodimer with bound high affinity inhibitor |
| 6VW2 | Cryo-EM structure of human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP, or amylin) fibrils |
| 6UVA | CryoEM Structure of the active Adrenomedullin 2 receptor G protein complex with adrenomedullin 2 peptide |
| 6UUS | CryoEM Structure of the active Adrenomedullin 2 receptor G protein complex with adrenomedullin peptide |
| 6UUN | CryoEM Structure of the active Adrenomedullin 1 receptor G protein complex with adrenomedullin peptide |
| 6Y1A | Amyloid fibril structure of islet amyloid polypeptide |
| 6UCK | proIAPP in DPC Micelles - Two-Conformer Ensemble Refinement, Bent Conformer |
| 6UCJ | proIAPP in DPC Micelles - Two-Conformer Ensemble Refinement, Open Conformer |
| 6UMG | Crystal structure of erenumab Fab bound to the extracellular domain of CGRP receptor |
| 6PGQ | Crystal structure of N-glycosylated human calcitonin receptor extracellular domain in complex with salmon calcitonin (22-32) |
| 6PFO | Crystal structure of N-glycosylated human calcitonin receptor extracellular domain in complex with salmon calcitonin (16-32) |
| 6NIY | A high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of a calcitonin receptor-heterotrimeric Gs protein complex |
| 6E3Y | Cryo-EM structure of the active, Gs-protein complexed, human CGRP receptor |
| 6D1U | Crystal structure of the human CLR:RAMP1 extracellular domain heterodimer in complex with adrenomedullin 2/intermedin |
| 5V6Y | Crystal structure of the human CLR:RAMP1 extracellular domain heterodimer with bound high-affinity and altered selectivity adrenomedullin variant |
| 5UZ7 | Volta phase plate cryo-electron microscopy structure of a calcitonin receptor-heterotrimeric Gs protein complex |
| 5MGQ | Solution structure of oxidized and amidated human IAPP (1-37), the diabetes II peptide. |
| 5KO0 | Human Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Segment 15-FLVHSSNNFGA-25 Determined by MicroED |
| 5KNZ | Human Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Segment 19-SGNNFGAILSS-29 with Early Onset S20G Mutation Determined by MicroED |
| 5K5G | Structure of human islet amyloid polypeptide in complex with an engineered binding protein |
| 5II0 | Crystal structure of the human calcitonin receptor ectodomain in complex with a truncated salmon calcitonin analogue |
| 4RWG | Crystal structure of the CLR:RAMP1 extracellular domain heterodimer with bound high affinity CGRP analog |
| 4RWF | Crystal structure of the CLR:RAMP2 extracellular domain heterodimer with bound adrenomedullin |
| 3AQE | Crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human RAMP2 |
| 3AQF | Crystal structure of the human CRLR/RAMP2 extracellular complex |
| 2L7S | Determination of the three-dimensional structure of adrenomedullin, a first step towards the analysis of its interactions with receptors and small molecules |
| 2L86 | Solution NMR structure of human amylin in SDS micelles at pH 7.3 |
| 2XVT | Structure of the extracellular domain of human RAMP2 |
| 3N7S | Crystal structure of the ectodomain complex of the CGRP receptor, a Class-B GPCR, reveals the site of drug antagonism |
| 3N7R | Crystal structure of the ectodomain complex of the CGRP receptor, a Class-B GPCR, reveals the site of drug antagonism |
| 3N7P | Crystal structure of the ectodomain complex of the CGRP receptor, a Class-B GPCR, reveals the site of drug antagonism |
| 3HGZ | Crystal structure of human insulin-degrading enzyme in complex with amylin |
| 2WK3 | Crystal structure of human insulin-degrading enzyme in complex with amyloid-beta (1-42) |
| 2KIB | Protein Fibril |
| 3E50 | Crystal structure of human insulin degrading enzyme in complex with transforming growth factor-alpha |
| 3E4Z | Crystal structure of human insulin degrading enzyme in complex with insulin-like growth factor II |
| 3FTR | Structure of an amyloid forming peptide SSTNVG from IAPP (alternate polymorph) |
| 3FTL | NVGSNTY segment from Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (IAPP or Amylin), dehydrated crystal form |
| 3FTK | NVGSNTY segment from Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (IAPP or Amylin), hydrated crystal form |
| 3FTH | NFLVHSS segment from Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (IAPP or Amylin) |
| 3FR1 | NFLVHS segment from Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (IAPP or Amylin) |
| 3FPO | HSSNNF segment from Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (IAPP or Amylin) |
| 3G7W | Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (IAPP or Amylin) Residues 1 to 22 fused to Maltose Binding Protein |
| 3G7V | Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (IAPP or Amylin) fused to Maltose Binding Protein |
| 2KJ7 | Three-Dimensional NMR Structure of Rat Islet Amyloid Polypeptide in DPC micelles |
| 2KB8 | The dynamic alpha-helix structure of micelle-bound human amylin. |
| 3DGJ | NNFGAIL segment from Islet Amyloid Polypeptide (IAPP or amylin) |
| 3DG1 | Segment SSTNVG derived from IAPP |
| 2YX8 | Crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human RAMP1 |
| 2G48 | crystal structure of human insulin-degrading enzyme in complex with amylin |
| 2FLY | Proadrenomedullin N-Terminal 20 Peptide |
| 1KUW | High-Resolution Structure and Localization of Amylin Nucleation Site in Detergent Micelle |
| PDB ID | Residue A | Atom A | Residue B | Atom B | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2G48 | A_ARG_722 | NH1 | B_ASP_706 | OD1 | 2.987 |
| 2G48 | A_ARG_722 | NH1 | B_ASP_706 | OD2 | 2.560 |
| 2G48 | A_ARG_722 | NH2 | B_GLU_702 | OE2 | 3.255 |
| 2G48 | A_LYS_756 | NZ | B_ASP_706 | OD1 | 3.852 |
| 2G48 | B_ARG_722 | NH1 | A_ASP_706 | OD1 | 2.728 |
| 2G48 | B_ARG_722 | NH1 | A_ASP_706 | OD2 | 3.524 |
| 2G48 | B_ARG_722 | NH2 | A_ASP_706 | OD1 | 3.653 |
| 2G48 | B_LYS_756 | NZ | A_ASP_706 | OD1 | 3.253 |
| 2G48 | B_LYS_756 | NZ | A_ASP_706 | OD2 | 2.575 |
| 2G48 | C_LYS_1 | NZ | A_GLU_341 | OE1 | 3.514 |
| 3HGZ | A_ARG_164 | NH1 | B_GLU_408 | OE1 | 3.083 |
| 3HGZ | A_ARG_164 | NH1 | B_GLU_408 | OE2 | 3.662 |
| 3HGZ | A_ARG_164 | NH2 | B_GLU_408 | OE1 | 3.032 |
| 3HGZ | B_LYS_327 | NZ | A_GLU_880 | OE1 | 3.476 |
| 3HGZ | D_LYS_1 | NZ | A_GLU_341 | OE1 | 2.441 |
| 3HGZ | E_LYS_1 | NZ | B_GLU_341 | OE1 | 3.179 |
| PDB ID | Acceptor (A) | Donor (D) | Hydrogen (H) | D-A (Å) | H-A (Å) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2G48 | O, C_LYS_1 | N, A_GLY_361 | H, A_GLY_361 | 2.72 | 1.72 | 5.66 |
| 2G48 | OE2, B_GLU_699 | OG, A_SER_761 | HG, A_SER_761 | 2.52 | 1.67 | 22.41 |
| 2G48 | O, C_LEU_16 | NH2, A_ARG_824 | HH21, A_ARG_824 | 2.98 | 2.09 | 22.98 |
| 2G48 | O, D_ASN_14 | N, B_THR_142 | H, B_THR_142 | 2.89 | 1.99 | 21.69 |
| 2G48 | O, D_LYS_1 | N, B_GLY_361 | H, B_GLY_361 | 2.89 | 1.89 | 5.77 |
| 2G48 | OD1, A_ASP_706 | NH1, B_ARG_722 | HH12, B_ARG_722 | 2.73 | 1.91 | 29.32 |
| 2G48 | OD2, A_ASP_706 | NZ, B_LYS_756 | HZ1, B_LYS_756 | 2.57 | 1.59 | 10.38 |
| 2G48 | OE2, A_GLU_699 | OG, B_SER_761 | HG, B_SER_761 | 2.51 | 1.64 | 19.94 |
| 2G48 | O, A_GLY_361 | N, C_ASN_3 | H, C_ASN_3 | 2.65 | 1.76 | 22.83 |
| 2G48 | O, A_ALA_140 | N, C_LEU_16 | H, C_LEU_16 | 2.97 | 2.01 | 15.18 |
| 2G48 | OE1, B_GLU_341 | N, D_LYS_1 | H2, D_LYS_1 | 2.85 | 1.85 | 6.72 |
| 2G48 | O, B_GLY_361 | N, D_ASN_3 | H, D_ASN_3 | 2.67 | 1.76 | 20.40 |
| 2G48 | O, B_GLN_363 | ND2, D_ASN_3 | HD22, D_ASN_3 | 2.73 | 1.89 | 26.92 |
| 2G48 | O, B_ALA_140 | N, D_LEU_16 | H, D_LEU_16 | 2.83 | 1.95 | 23.79 |
| PDB ID | Acceptor (A) | Donor (D) | Hydrogen (H) | D-A (Å) | H-A (Å) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2G48 | OE2, B_GLU_699 | OG, A_SER_761 | HG, A_SER_761 | 2.52 | 1.67 | 22.41 |
| 2G48 | OD1, A_ASP_706 | NH1, B_ARG_722 | HH12, B_ARG_722 | 2.73 | 1.91 | 29.32 |
| 2G48 | OD2, A_ASP_706 | NZ, B_LYS_756 | HZ1, B_LYS_756 | 2.57 | 1.59 | 10.38 |
| 2G48 | OE2, A_GLU_699 | OG, B_SER_761 | HG, B_SER_761 | 2.51 | 1.64 | 19.94 |
| PDB ID | Residue A | Atom A | Residue B | Atom B | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2G48 | A_ARG_722 | NH1 | B_GLU_702 | OE2 | 4.700 |
| 2G48 | A_ARG_722 | NH1 | B_ASP_706 | OD1 | 2.987 |
| 2G48 | A_ARG_722 | NH1 | B_ASP_706 | OD2 | 2.560 |
| 2G48 | A_ARG_722 | NH2 | B_GLU_702 | OE1 | 5.134 |
| 2G48 | A_ARG_722 | NH2 | B_GLU_702 | OE2 | 3.255 |
| 2G48 | A_ARG_722 | NH2 | B_ASP_706 | OD1 | 4.711 |
| 2G48 | A_ARG_722 | NH2 | B_ASP_706 | OD2 | 4.433 |
| 2G48 | A_LYS_756 | NZ | B_GLU_702 | OE2 | 5.525 |
| 2G48 | A_LYS_756 | NZ | B_ASP_706 | OD1 | 3.852 |
| 2G48 | A_LYS_756 | NZ | B_ASP_706 | OD2 | 5.449 |
| 2G48 | A_LYS_1009 | NZ | B_GLU_990 | OE1 | 5.840 |
| 2G48 | B_ARG_722 | NH1 | A_ASP_706 | OD1 | 2.728 |
| 2G48 | B_ARG_722 | NH1 | A_ASP_706 | OD2 | 3.524 |
| 2G48 | B_ARG_722 | NH2 | A_GLU_702 | OE1 | 5.354 |
| 2G48 | B_ARG_722 | NH2 | A_ASP_706 | OD1 | 3.653 |
| 2G48 | B_ARG_722 | NH2 | A_ASP_706 | OD2 | 5.078 |
| 2G48 | B_LYS_756 | NZ | A_ASP_706 | OD1 | 3.253 |
| 2G48 | B_LYS_756 | NZ | A_ASP_706 | OD2 | 2.575 |
| 2G48 | B_LYS_1009 | NZ | A_GLU_997 | OE1 | 5.095 |
| 2G48 | C_LYS_1 | NZ | A_GLU_341 | OE1 | 3.514 |
| 2G48 | C_LYS_1 | NZ | A_GLU_341 | OE2 | 4.876 |
| 2G48 | C_LYS_1 | NZ | A_GLU_612 | OE2 | 5.297 |
| 3HGZ | A_LYS_123 | NZ | B_ASP_416 | OD1 | 4.754 |
| 3HGZ | A_ARG_164 | NH1 | B_GLU_408 | OE1 | 3.083 |
| 3HGZ | A_ARG_164 | NH1 | B_GLU_408 | OE2 | 3.662 |
| 3HGZ | A_ARG_164 | NH2 | B_GLU_408 | OE1 | 3.032 |
| 3HGZ | A_ARG_164 | NH2 | B_GLU_408 | OE2 | 4.613 |
| 3HGZ | A_LYS_884 | NZ | B_GLU_457 | OE1 | 4.680 |
| 3HGZ | B_HIS_53 | ND1 | A_GLU_875 | OE1 | 4.690 |
| 3HGZ | B_HIS_53 | NE2 | A_GLU_875 | OE1 | 4.274 |
| 3HGZ | B_LYS_327 | NZ | A_GLU_880 | OE1 | 3.476 |
| 3HGZ | B_LYS_327 | NZ | A_GLU_880 | OE2 | 5.083 |
| 3HGZ | B_LYS_415 | NZ | A_GLU_133 | OE1 | 5.186 |
| 3HGZ | D_LYS_1 | NZ | A_GLU_341 | OE1 | 2.441 |
| 3HGZ | D_LYS_1 | NZ | A_GLU_341 | OE2 | 4.468 |
| 3HGZ | E_LYS_1 | NZ | B_GLU_341 | OE1 | 3.179 |
| 3HGZ | E_LYS_1 | NZ | B_GLU_341 | OE2 | 5.147 |
| PDB ID | Acceptor (A) | Donor (D) | Hydrogen (H) | D-A (Å) | H-A (Å) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2G48 | NE2, C_HIS_18 | NZ, A_LYS_192 | HZ3, A_LYS_192 | 4.89 | 4.23 | 44.36 |
| 2G48 | OD1, C_ASN_14 | OG1, A_THR_220 | HG1, A_THR_220 | 3.22 | 2.28 | 9.48 |
| 2G48 | ND2, C_ASN_14 | OG1, A_THR_220 | HG1, A_THR_220 | 3.21 | 2.65 | 47.15 |
| 2G48 | OE1, B_GLN_718 | NE2, A_HIS_589 | HE2, A_HIS_589 | 4.14 | 3.18 | 16.40 |
| 2G48 | NE2, B_GLN_718 | NE2, A_HIS_589 | HE2, A_HIS_589 | 4.55 | 3.58 | 13.52 |
| 2G48 | OG, B_SER_721 | NH1, A_ARG_711 | HH12, A_ARG_711 | 4.90 | 3.97 | 20.43 |
| 2G48 | NE2, B_GLN_718 | NH2, A_ARG_711 | HH21, A_ARG_711 | 3.92 | 3.14 | 33.89 |
| 2G48 | OG, B_SER_721 | NH2, A_ARG_711 | HH21, A_ARG_711 | 4.86 | 3.92 | 19.33 |
| 2G48 | NE2, B_HIS_589 | NE2, A_GLN_718 | HE22, A_GLN_718 | 3.40 | 2.61 | 32.75 |
| 2G48 | OD1, B_ASP_706 | NH1, A_ARG_722 | HH12, A_ARG_722 | 2.99 | 2.41 | 46.66 |
| 2G48 | OE2, B_GLU_702 | NH2, A_ARG_722 | HH22, A_ARG_722 | 3.25 | 2.43 | 29.82 |
| 2G48 | OE1, B_GLU_699 | OG, A_SER_761 | HG, A_SER_761 | 3.84 | 2.92 | 13.96 |
| 2G48 | OE2, B_GLU_699 | OG, A_SER_761 | HG, A_SER_761 | 2.52 | 1.67 | 22.41 |
| 2G48 | OD2, B_ASP_586 | NE2, A_GLN_762 | HE22, A_GLN_762 | 3.64 | 3.02 | 45.51 |
| 2G48 | NE2, B_GLN_770 | NE2, A_GLN_770 | HE21, A_GLN_770 | 4.30 | 3.39 | 22.59 |
| 2G48 | OG, D_SER_19 | ND2, B_ASN_139 | HD22, B_ASN_139 | 4.49 | 3.91 | 48.99 |
| 2G48 | OD1, D_ASN_14 | OG1, B_THR_220 | HG1, B_THR_220 | 3.09 | 2.14 | 8.07 |
| 2G48 | ND2, D_ASN_14 | OG1, B_THR_220 | HG1, B_THR_220 | 3.42 | 2.85 | 46.81 |
| 2G48 | OE1, A_GLN_718 | NE, B_ARG_711 | HE, B_ARG_711 | 4.89 | 3.96 | 20.15 |
| 2G48 | OG, A_SER_721 | NE, B_ARG_711 | HE, B_ARG_711 | 4.94 | 4.15 | 34.49 |
| 2G48 | OG, A_SER_721 | NH1, B_ARG_711 | HH12, B_ARG_711 | 4.28 | 3.36 | 20.95 |
| 2G48 | OD1, A_ASP_706 | NH1, B_ARG_722 | HH12, B_ARG_722 | 2.73 | 1.91 | 29.32 |
| 2G48 | OD2, A_ASP_706 | NH1, B_ARG_722 | HH12, B_ARG_722 | 3.52 | 2.69 | 29.77 |
| 2G48 | OD1, A_ASP_706 | NH2, B_ARG_722 | HH21, B_ARG_722 | 3.65 | 3.09 | 49.48 |
| 2G48 | OD2, A_ASP_706 | NZ, B_LYS_756 | HZ1, B_LYS_756 | 2.57 | 1.59 | 10.38 |
| 2G48 | OE1, A_GLU_699 | OG, B_SER_761 | HG, B_SER_761 | 4.00 | 3.07 | 11.68 |
| 2G48 | OE2, A_GLU_699 | OG, B_SER_761 | HG, B_SER_761 | 2.51 | 1.64 | 19.94 |
| 2G48 | OD2, A_ASP_586 | NE2, B_GLN_762 | HE22, B_GLN_762 | 4.17 | 3.60 | 49.58 |
| 2G48 | NE2, A_GLN_770 | NE2, B_GLN_770 | HE21, B_GLN_770 | 4.30 | 3.46 | 30.40 |
| 2G48 | OD1, D_ASN_22 | NH2, B_ARG_847 | HH22, B_ARG_847 | 4.10 | 3.14 | 17.00 |
| 2G48 | ND2, D_ASN_22 | NH2, B_ARG_847 | HH22, B_ARG_847 | 4.95 | 3.97 | 13.60 |
| 2G48 | OE1, A_GLU_341 | NZ, C_LYS_1 | HZ3, C_LYS_1 | 3.51 | 2.72 | 32.95 |
| 2G48 | OE2, A_GLU_341 | NZ, C_LYS_1 | HZ3, C_LYS_1 | 4.88 | 4.20 | 43.27 |
| 2G48 | ND1, A_HIS_332 | OG1, C_THR_4 | HG1, C_THR_4 | 3.10 | 2.41 | 37.40 |
| 2G48 | OG1, A_THR_220 | ND2, C_ASN_14 | HD22, C_ASN_14 | 3.21 | 2.37 | 28.58 |
| 2G48 | NE2, A_HIS_679 | NE2, C_HIS_18 | HE2, C_HIS_18 | 4.27 | 3.60 | 43.28 |
| 2G48 | OG1, B_THR_220 | ND2, D_ASN_14 | HD22, D_ASN_14 | 3.42 | 2.67 | 36.00 |
| 2G48 | NE2, B_HIS_679 | NE2, D_HIS_18 | HE2, D_HIS_18 | 4.32 | 3.75 | 49.86 |
| PDB ID | Acceptor (A) | Donor (D) | Hydrogen (H) | D-A (Å) | H-A (Å) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3HGZ | NE2, B_GLN_407 | NZ, A_LYS_120 | HZ3, A_LYS_120 | 4.83 | 4.00 | 31.04 |
| 3HGZ | OE1, B_GLU_408 | NH1, A_ARG_164 | HH11, A_ARG_164 | 3.08 | 2.20 | 24.18 |
| 3HGZ | OE2, B_GLU_408 | NH1, A_ARG_164 | HH11, A_ARG_164 | 3.66 | 2.70 | 14.52 |
| 3HGZ | OE1, B_GLU_408 | NH2, A_ARG_164 | HH21, A_ARG_164 | 3.03 | 2.13 | 21.99 |
| 3HGZ | OE2, B_GLU_408 | NH2, A_ARG_164 | HH21, A_ARG_164 | 4.61 | 3.89 | 39.58 |
| 3HGZ | OE1, B_GLN_412 | NH2, A_ARG_164 | HH22, A_ARG_164 | 3.72 | 2.94 | 34.36 |
| 3HGZ | OE1, B_GLU_457 | OG1, A_THR_878 | HG1, A_THR_878 | 2.79 | 2.15 | 40.71 |
| 3HGZ | OE2, B_GLU_457 | OG1, A_THR_878 | HG1, A_THR_878 | 3.07 | 2.47 | 43.72 |
| 3HGZ | OE1, B_GLU_457 | NZ, A_LYS_884 | HZ3, A_LYS_884 | 4.68 | 3.74 | 18.88 |
| 3HGZ | OG1, B_THR_55 | NZ, A_LYS_933 | HZ2, A_LYS_933 | 3.39 | 2.77 | 44.49 |
| 3HGZ | OE1, A_GLU_880 | NZ, B_LYS_327 | HZ1, B_LYS_327 | 3.48 | 2.53 | 17.30 |
| 3HGZ | OE1, A_GLU_341 | NZ, D_LYS_1 | HZ1, D_LYS_1 | 2.44 | 1.85 | 44.11 |
| 3HGZ | OH, A_TYR_609 | NZ, D_LYS_1 | HZ2, D_LYS_1 | 3.91 | 3.25 | 43.14 |
| 3HGZ | OE1, B_GLU_341 | NZ, E_LYS_1 | HZ2, E_LYS_1 | 3.18 | 2.42 | 34.86 |
| 3HGZ | OH, B_TYR_609 | NZ, E_LYS_1 | HZ3, E_LYS_1 | 3.97 | 3.23 | 37.37 |
| PDB ID | REMARK | REMARK ID | ResName | Chain ID | ResID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ASN | D | 3 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | THR | D | 4 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ALA | D | 5 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | THR | D | 6 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | CYS | D | 7 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ALA | D | 8 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | THR | D | 9 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | GLN | D | 10 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ARG | D | 11 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | VAL | D | 17 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | HIS | D | 18 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | SER | D | 19 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | SER | D | 20 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ASN | D | 21 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ASN | D | 22 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | PHE | D | 23 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | GLY | D | 24 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ALA | D | 25 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ILE | D | 26 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | LEU | D | 27 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | SER | D | 28 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | SER | D | 29 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | THR | D | 30 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ASN | D | 31 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | VAL | D | 32 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | GLY | D | 33 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | SER | D | 34 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ASN | D | 35 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | THR | D | 36 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | TYR | D | 37 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | THR | E | 4 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ALA | E | 5 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | THR | E | 6 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | THR | E | 9 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | GLN | E | 10 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ARG | E | 11 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | VAL | E | 17 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | HIS | E | 18 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | SER | E | 19 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | SER | E | 20 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ASN | E | 21 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ASN | E | 22 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | PHE | E | 23 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | GLY | E | 24 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ALA | E | 25 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ILE | E | 26 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | LEU | E | 27 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | SER | E | 28 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | SER | E | 29 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | THR | E | 30 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ASN | E | 31 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | VAL | E | 32 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | GLY | E | 33 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | SER | E | 34 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | ASN | E | 35 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | THR | E | 36 |
| 3HGZ | REMARK | 465 | TYR | E | 37 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | CYS | C | 7 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ALA | C | 8 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | THR | C | 9 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ASN | C | 22 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | PHE | C | 23 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | GLY | C | 24 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ALA | C | 25 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ILE | C | 26 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | LEU | C | 27 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | SER | C | 28 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | SER | C | 29 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | THR | C | 30 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ASN | C | 31 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | VAL | C | 32 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | GLY | C | 33 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | SER | C | 34 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ASN | C | 35 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | THR | C | 36 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | TYR | C | 37 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ALA | D | 5 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | THR | D | 6 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | CYS | D | 7 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ALA | D | 8 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | THR | D | 9 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | GLN | D | 10 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | GLY | D | 24 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ALA | D | 25 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ILE | D | 26 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | LEU | D | 27 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | SER | D | 28 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | SER | D | 29 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | THR | D | 30 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ASN | D | 31 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | VAL | D | 32 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | GLY | D | 33 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | SER | D | 34 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | ASN | D | 35 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | THR | D | 36 |
| 2G48 | REMARK | 465 | TYR | D | 37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





