Submitted:
15 November 2023
Posted:
16 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
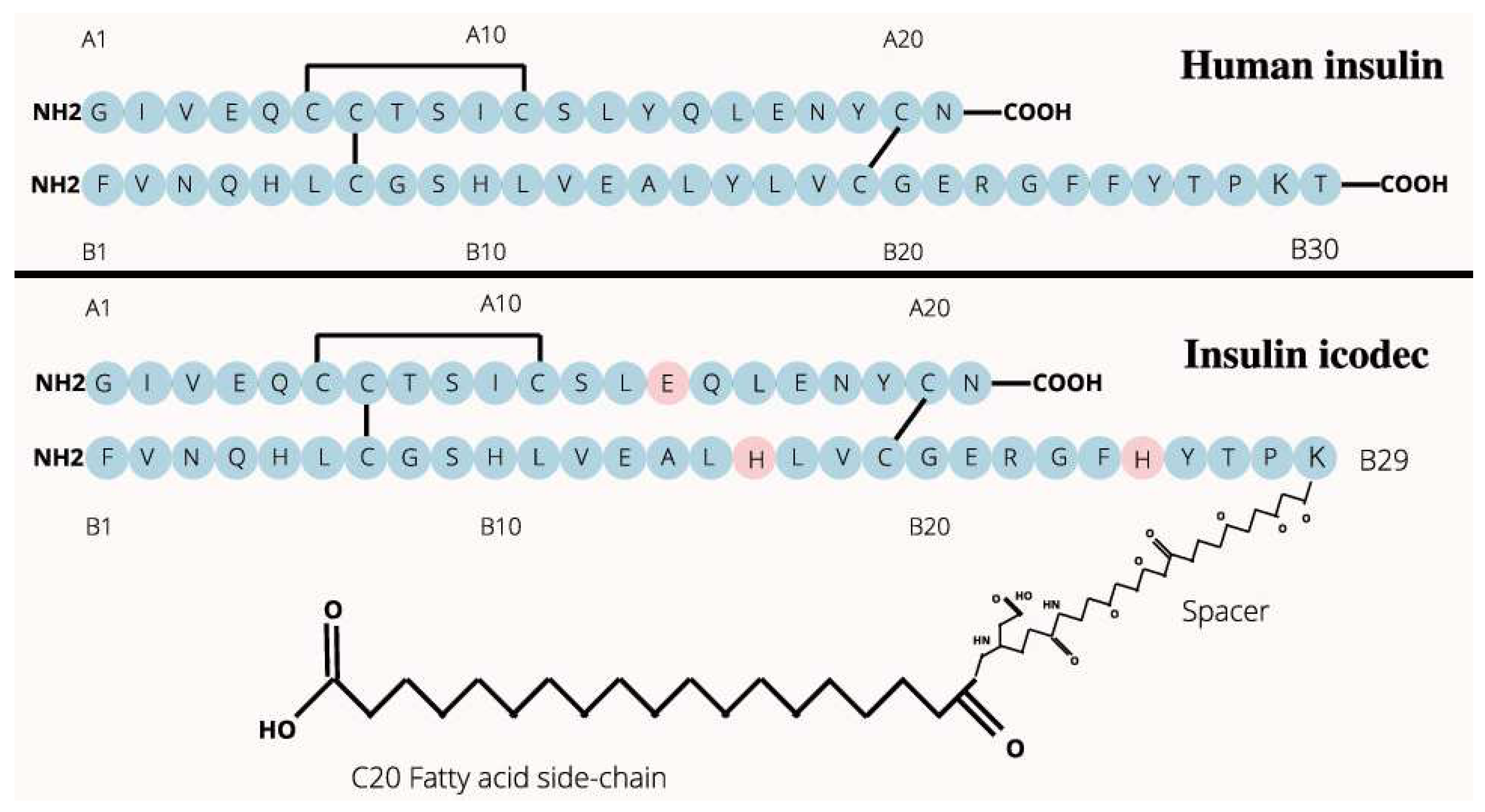
- insulin icodec is able to form aggregates or clusters at the subcutaneous injection site, gradually releasing into the bloodstream over an extended period.
- insulin icodec undergoes structural modifications that increases its stability and solubility and preventing enzyme-mediated degradation and rapid clearance [36].
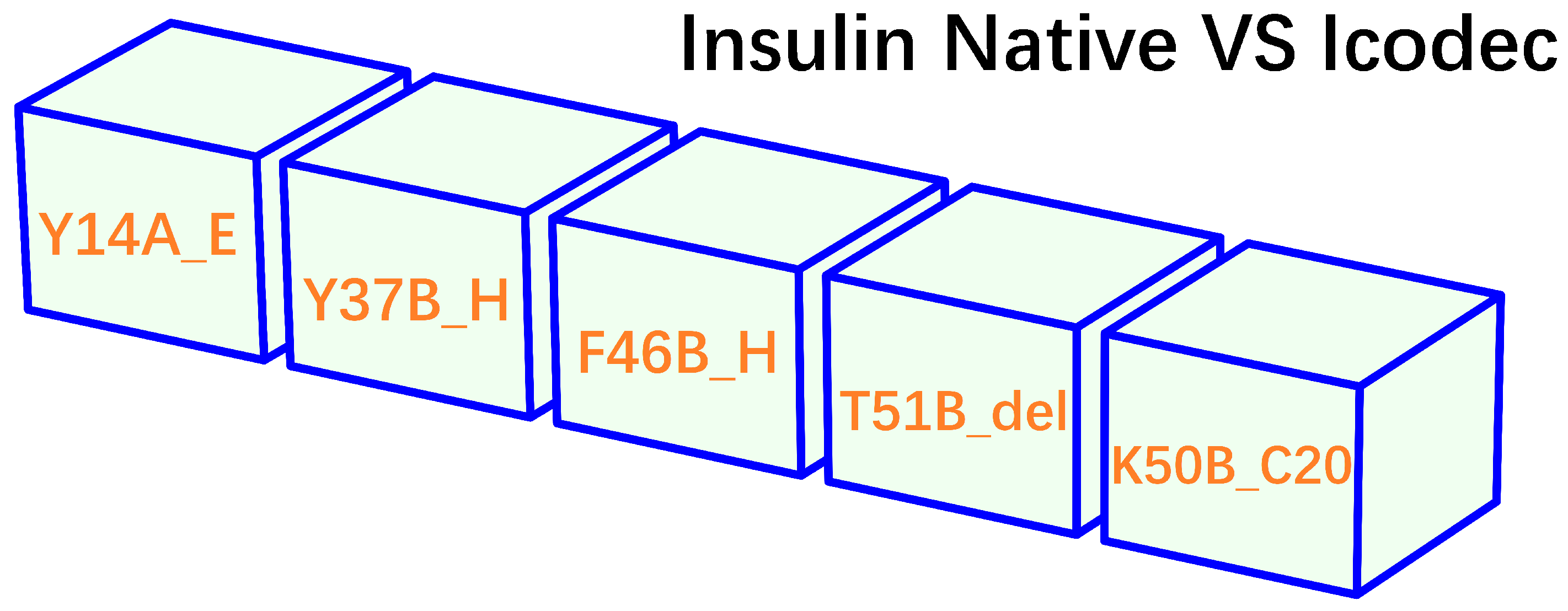
- insulin icodec is conjugated with a fatty acid at position B30 (K50B_C20, Figure 2). After injection, the fatty acid chain in insulin icodec interacts with albumin in the subcutaneous tissue, forming reversible albumin-insulin complexes. These complexes act as a reservoir, gradually releasing insulin icodec into the bloodstream, increasing its fat solubility and allowing it to bind to fatty acid-binding proteins, forming a depot of the insulin icodec reversibly bound to albumin.
- the incorporation of fatty acid chains facilitate the formation of stable hexameric structures, thereby delaying insulin absorption and promoting sustained release.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. A summary of insulin receptor-related structures in PDB
2.2. Construction of a complex structural model of insulin icodec bound to IR
2.3. A comprehensive structural and biophysical analysis of insulin icodec bound to IR
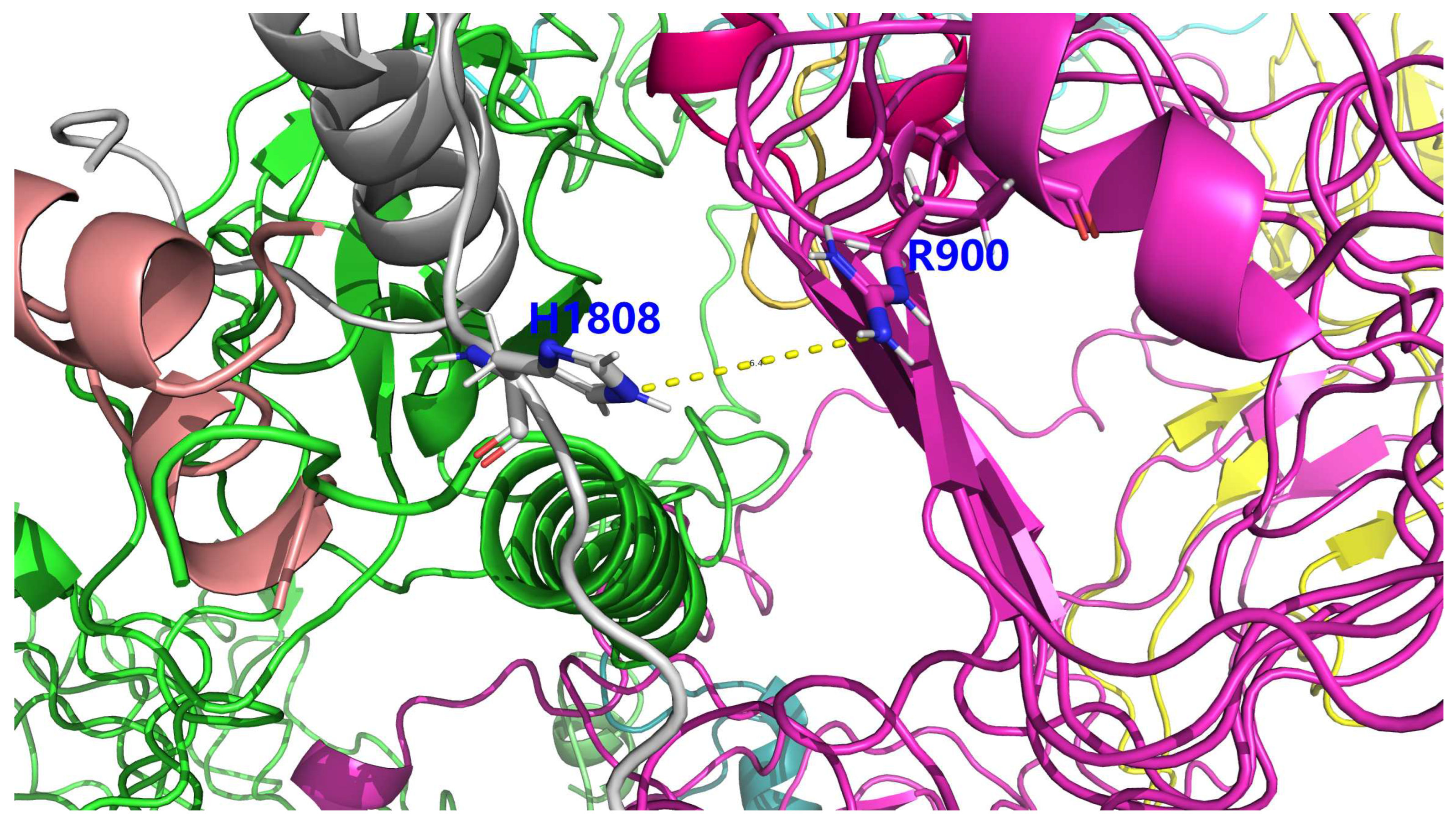
3. Results
4. Conclusion and Discussion
5. Ethical statement
6. Declaration of generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuji, H.; Qi, F.; Qu, L.; Takaesu, Y.; Hoshino, T. Prediction of Ligand Binding Affinity to Target Proteins by Molecular Mechanics Theoretical Calculation. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2017, 65, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.; Henrick, K.; Nakamura, H. Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 2003, 10, 980–980. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Half-a-century Burial of ρ, θ and φ in PDB 2021.
- Li, W. How do SMA-linked mutations of SMN1 lead to structural/functional deficiency of the SMA protein? PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0178519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, E.; Pridal, L.; Glendorf, T.; Hansen, B.F.; Hubálek, F.; Kjeldsen, T.; Kristensen, N.R.; Lützen, A.; Lyby, K.; Madsen, P.; Pedersen, T.Å.; Ribel-Madsen, R.; Stidsen, C.E.; Haahr, H. Molecular and pharmacological characterization of insulin icodec: a new basal insulin analog designed for once-weekly dosing. BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care 2021, 9, e002301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, A.; Singh, R.; Misra, A. Once-weekly basal insulin icodec: Looking ONWARDS from pharmacology to clinical trials. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews 2022, 16, 102615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, H.S.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Christoffersen, A.; Davies, M.J.; Gowda, A.; Isendahl, J.; Lingvay, I.; Senior, P.A.; Silver, R.J.; Trevisan, R.; Rosenstock, J. Switching to Once-Weekly Insulin Icodec Versus Once-Daily Insulin Glargine U100 in Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled on Daily Basal Insulin: A Phase 2 Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstock, J.; Bain, S.C.; Gowda, A.; Jódar, E.; Liang, B.; Lingvay, I.; Nishida, T.; Trevisan, R.; Mosenzon, O. Weekly Icodec versus Daily Glargine U100 in Type 2 Diabetes without Previous Insulin. New England Journal of Medicine 2023, 389, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philis-Tsimikas, A.; Bajaj, H.S.; Begtrup, K.; Cailleteau, R.; Gowda, A.; Lingvay, I.; Mathieu, C.; Russell-Jones, D.; Rosenstock, J. Rationale and design of the phase 3a development programme (ONWARDS 1–6 trials) investigating once-weekly insulin icodec in diabetes. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2022, 25, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philis-Tsimikas, A.; Asong, M.; Franek, E.; Jia, T.; Rosenstock, J.; Stachlewska, K.; Watada, H.; Kellerer, M. Switching to once-weekly insulin icodec versus once-daily insulin degludec in individuals with basal insulin-treated type 2 diabetes (ONWARDS 2): a phase 3a, randomised, open label, multicentre, treat-to-target trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2023, 11, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, C.; Ásbjörnsdóttir, B.; Bajaj, H.S.; Lane, W.; Matos, A.L.S.A.; Murthy, S.; Stachlewska, K.; Rosenstock, J. Switching to once-weekly insulin icodec versus once-daily insulin glargine U100 in individuals with basal-bolus insulin-treated type 2 diabetes (ONWARDS 4): a phase 3a, randomised, open-label, multicentre, treat-to-target, non-inferiority trial. The Lancet 2023, 401, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingvay, I.; Asong, M.; Desouza, C.; Gourdy, P.; Kar, S.; Vianna, A.; Vilsbøll, T.; Vinther, S.; Mu, Y. Once-Weekly Insulin Icodec vs Once-Daily Insulin Degludec in Adults With Insulin-Naive Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA 2023, 330, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingvay, I.; Buse, J.B.; Franek, E.; Hansen, M.V.; Koefoed, M.M.; Mathieu, C.; Pettus, J.; Stachlewska, K.; Rosenstock, J. A Randomized, Open-Label Comparison of Once-Weekly Insulin Icodec Titration Strategies Versus Once-Daily Insulin Glargine U100. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldsen, T.B.; Hubálek, F.; Hjørringgaard, C.U.; Tagmose, T.M.; Nishimura, E.; Stidsen, C.E.; Porsgaard, T.; Fledelius, C.; Refsgaard, H.H.F.; Gram-Nielsen, S.; Naver, H.; Pridal, L.; Hoeg-Jensen, T.; Jeppesen, C.B.; Manfè, V.; Ludvigsen, S.; Lautrup-Larsen, I.; Madsen, P. Molecular Engineering of Insulin Icodec, the First Acylated Insulin Analog for Once-Weekly Administration in Humans. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2021, 64, 8942–8950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstock, J.; Bajaj, H.S.; Janež, A.; Silver, R.; Begtrup, K.; Hansen, M.V.; Jia, T.; Goldenberg, R. Once-Weekly Insulin for Type 2 Diabetes without Previous Insulin Treatment. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 383, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, H.S.; Goldenberg, R.M. Insulin Icodec Weekly: A Basal Insulin Analogue for Type 2 Diabetes. European Endocrinology 2023, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMarchi, R.D.; Mayer, J.P. Icodec Advances the Prospect of Once-Weekly Insulin Injection. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2021, 64, 8939–8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstock, J.; Prato, S.D. Basal weekly insulins: the way of the future! Metabolism 2022, 126, 154924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Kapoor, N. Contemporary Classification of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists (GLP1RAs). Diabetes Therapy 2021, 12, 2133–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratley, R.; Amod, A.; Hoff, S.T.; Kadowaki, T.; Lingvay, I.; Nauck, M.; Pedersen, K.B.; Saugstrup, T.; Meier, J.J. Oral semaglutide versus subcutaneous liraglutide and placebo in type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 4): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3a trial. The Lancet 2019, 394, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.L.; Beutel, T.R.; Trujillo, J.M. Oral semaglutide in type 2 diabetes. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications 2020, 34, 107520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. Strengthening Semaglutide-GLP-1R Binding Affinity via a Val27-Arg28 Exchange in the Peptide Backbone of Semaglutide: A Computational Structural Approach. Journal of Computational Biophysics and Chemistry 2021, 20, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, P.; Chepurny, O.G.; Holz, G.G. Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis by GLP-1. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Elsevier, 2014; pp. 23–65.
- Lau, J.; Bloch, P.; Schäffer, L.; Pettersson, I.; Spetzler, J.; Kofoed, J.; Madsen, K.; Knudsen, L.B.; McGuire, J.; Steensgaard, D.B.; Strauss, H.M.; Gram, D.X.; Knudsen, S.M.; Nielsen, F.S.; Thygesen, P.; Reedtz-Runge, S.; Kruse, T. Discovery of the Once-Weekly Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Analogue Semaglutide. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2015, 58, 7370–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabery, S.; Salinas, C.G.; Paulsen, S.J.; Ahnfelt-Rønne, J.; Alanentalo, T.; Baquero, A.F.; Buckley, S.T.; Farkas, E.; Fekete, C.; Frederiksen, K.S.; Helms, H.C.C.; Jeppesen, J.F.; John, L.M.; Pyke, C.; Nøhr, J.; Lu, T.T.; Polex-Wolf, J.; Prevot, V.; Raun, K.; Simonsen, L.; Sun, G.; Szilvásy-Szabó, A.; Willenbrock, H.; Secher, A.; Knudsen, L.B. Semaglutide lowers body weight in rodents via distributed neural pathways. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plum-Mörschel, L.; Andersen, L.R.; Hansen, S.; Hövelmann, U.; Krawietz, P.; Kristensen, N.R.; Lehrskov, L.L.; Haahr, H. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Characteristics of Insulin Icodec After Subcutaneous Administration in the Thigh, Abdomen or Upper Arm in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clinical Drug Investigation 2023, 43, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belal, H.; Gandhi, G.Y. In uncontrolled T2DM treated with a basal-bolus insulin regimen, weekly icodec was noninferior to daily glargine for HbA1c at 26 wk. Annals of Internal Medicine 2023, 176, JC94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.L.; Bassetti, M.; Mangoni, A.A. Drugs in Context Editorial: Review of 2020 and what lies ahead in therapeutic interventions. Drugs in Context 2021, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, T.P.; Dinneen, S.F. In T2DM, weekly insulin icodec did not differ from daily glargine for reducing HbA1c or significant/severe hypoglycemia. Annals of Internal Medicine 2021, 174, JC34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieber, T.R.; Arfelt, K.N.; Cailleteau, R.; Hart, M.; Kar, S.; Mursic, I.; Svehlikova, E.; Urschitz, M.; Haahr, H. Hypoglycaemia frequency and physiological response after double or triple doses of once-weekly insulin icodec vs once-daily insulin glargine U100 in type 2 diabetes: a randomised crossover trial. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1413–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerihun, K.; Mhanna, M.; Ayesh, H.; Ghazaleh, S.; Khader, Y.; Beran, A.; Aldhafeeri, A.; Sharma, S.; Iqbal, A.; Legesse, H.; Jaume, J. Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Icodec Versus Glargine U100: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. American Journal of Therapeutics 2022, 30, e480–e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellary, S.; Barnett, A.H. Insulin icodec: evolution or revolution in diabetes therapy? The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2023, 11, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- e Silva, R.R.; de Miranda Gauza, M.; Guisso, M.E.S.; da Silva, J.O.N.; Kohara, S.K. Once-Weekly Insulin Icodec vs. Once-Daily Insulin Glargine U100 for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of phase 2 randomized controlled trials. Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism 2023, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieber, T.R.; Asong, M.; Fluhr, G.; Höller, V.; Kristensen, N.R.; Larsen, J.H.; Ribel-Madsen, R.; Svehlikova, E.; Vinther, S.; Voortman, M.; Haahr, H. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of once-weekly insulin icodec in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell-Jones, D.; Babazono, T.; Cailleteau, R.; Engberg, S.; Irace, C.; Kjaersgaard, M.I.S.; Mathieu, C.; Rosenstock, J.; Woo, V.; Klonoff, D.C. Once-weekly insulin icodec versus once-daily insulin degludec as part of a basal-bolus regimen in individuals with type 1 diabetes (ONWARDS 6): a phase 3a, randomised, open-label, treat-to-target trial. The Lancet 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feher, J. Digestion and Absorption of the Macronutrients. In Quantitative Human Physiology; Elsevier, 2017; pp. 821–833. [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, T.; Schäfer, I.B.; Poojari, C.; Brankatschk, B.; Vattulainen, I.; Strauss, M.; Ünal Coskun. Cryo-EM structure of the complete and ligand-saturated insulin receptor ectodomain. Journal of Cell Biology 2019, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; Lepore, R.; Schwede, T. SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Research 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasini, M.; Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; Arnold, K.; Studer, G.; Schmidt, T.; Kiefer, F.; Cassarino, T.G.; Bertoni, M.; Bordoli, L.; Schwede, T. SWISS-MODEL: modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Research 2014, 42, W252–W258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Protein Structure Modeling with MODELLER. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer US, 2020; pp. 239–255.
- DeLano, W.L. Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsletter On Protein Crystallography 2002, 40, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
| PDB ID | Structure Title (release date from newest to oldest) |
|---|---|
| 8DWN | Crystal structure of bis-phosphorylated insulin receptor kinase domain |
| 7YQ3 | human insulin receptor bound with A43 DNA aptamer and insulin |
| 7YQ4 | human insulin receptor bound with A62 DNA aptamer and insulin - locally refined |
| 7YQ5 | human insulin receptor bound with A62 DNA aptamer and insulin |
| 7YQ6 | human insulin receptor bound with A62 DNA aptamer |
| 8EYX | Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant with physically decoupled alpha CTs (C684S/C685S/C687S; denoted as IR-3CS) Asymmetric conformation 1 |
| 8EYY | Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant with physically decoupled alpha CTs (C684S/C685S/C687S, denoted as IR-3CS) Asymmetric conformation 2 |
| 8EZ0 | Cryo-EM structure of 4 insulins bound full-length mouse IR mutant with physically decoupled alpha CTs (C684S/C685S/C687S; denoted as IR-3CS) Symmetric conformation |
| 8GUY | human insulin receptor bound with two insulin molecules |
| 7U6D | Head region of insulin receptor ectodomain (A-isoform) bound to the non-insulin agonist IM459 |
| 7U6E | Head region of insulin receptor ectodomain (A-isoform) bound to the non-insulin agonist IM462 |
| 7PHT | Structure of Insulin receptor’s transmembrane domain |
| 8DTL | Cryo-EM structure of insulin receptor (IR) bound with S597 peptide |
| 8DTM | Cryo-EM structure of insulin receptor (IR) bound with S597 component 2 |
| 7S0Q | Head region of a complex of IGF-I with the ectodomain of a hybrid insulin receptor / type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor |
| 7S8V | Leg region of a complex of IGF-I with the ectodomain of a hybrid insulin receptor / type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor |
| 7SL1 | Full-length insulin receptor bound with site 1 binding deficient mutant insulin (A-V3E) |
| 7SL2 | Full-length insulin receptor bound with site 2 binding deficient mutant insulin (A-L13R) – asymmetric conformation |
| 7SL3 | Full-length insulin receptor bound with site 2 binding deficient mutant insulin (A-L13R) – symmetric conformation |
| 7SL4 | Full-length insulin receptor bound with site 2 binding deficient mutant insulin (B-L17R) – asymmetric conformation |
| 7SL6 | Full-length insulin receptor bound with site 2 binding deficient mutant insulin (B-L17R) – symmetric conformation |
| 7SL7 | Full-length insulin receptor bound with both site 1 binding deficient mutant insulin (A-V3E) and site 2 binding deficient mutant insulin (A-L13R) |
| 7STH | Full-length insulin receptor bound with unsaturated insulin WT (2 insulin bound) symmetric conformation |
| 7STI | Full-length insulin receptor bound with unsaturated insulin WT (1 insulin bound) asymmetric conformation |
| 7STJ | Full-length insulin receptor bound with unsaturated insulin WT (2 insulins bound) asymmetric conformation (Conformation 1) |
| 7STK | Full-length insulin receptor bound with unsaturated insulin WT (2 insulins bound) asymmetric conformation (Conformation 2) |
| 7MQO | The insulin receptor ectodomain in complex with a venom hybrid insulin analogue - "head" region |
| 7MQR | The insulin receptor ectodomain in complex with four venom hybrid insulins - symmetric conformation |
| 7MQS | The insulin receptor ectodomain in complex with three venom hybrid insulin molecules - asymmetric conformation |
| 7MD4 | Insulin receptor ectodomain dimer complexed with two IRPA-3 partial agonists |
| 7MD5 | Insulin receptor ectodomain dimer complexed with two IRPA-9 partial agonists |
| 7PG0 | Low resolution Cryo-EM structure of full-length insulin receptor bound to 3 insulin with visible ddm micelle, conf 1 |
| 7PG2 | Low resolution Cryo-EM structure of full-length insulin receptor bound to 3 insulin, conf 1 |
| 7PG3 | Low resolution Cryo-EM structure of the full-length insulin receptor bound to 3 insulin, conf 2 |
| 7PG4 | Low resolution Cryo-EM structure of the full-length insulin receptor bound to 2 insulin, conf 3 |
| 7QID | tentative model of the human insulin receptor ectodomain bound by three insulin |
| 7KD6 | Insulin Receptor L1-CR plus alphaCT fragment in co-complex with Fv 83-7 and single-chain insulin SCI-b |
| 7BW7 | Cryo-EM Structure for the Ectodomain of the Full-length Human Insulin Receptor in Complex with 1 Insulin. |
| 7BW8 | Cryo-EM Structure for the Insulin Binding Region in the Ectodomain of the Full-length Human Insulin Receptor in Complex with 1 Insulin |
| 7BWA | Cryo-EM Structure for the Ectodomain of the Full-length Human Insulin Receptor in Complex with 2 Insulin |
| 6VEP | Human insulin in complex with the human insulin microreceptor in turn in complex with Fv 83-7 |
| 6VEQ | Con-Ins G1 in complex with the human insulin microreceptor in turn in complex with Fv 83-7 |
| 6SOF | human insulin receptor ectodomain bound by 4 insulin |
| 6PXV | Cryo-EM structure of full-length insulin receptor bound to 4 insulin. 3D refinement was focused on the extracellular region. |
| 6PXW | Cryo-EM structure of full-length insulin receptor bound to 4 insulin. 3D refinement was focused on the top part of the receptor complex. |
| 6HN4 | Leucine-zippered human insulin receptor ectodomain with single bound insulin - "lower" membrane-proximal part |
| 6HN5 | Leucine-zippered human insulin receptor ectodomain with single bound insulin - "upper" membrane-distal part |
| 6CE7 | Insulin Receptor ectodomain in complex with one insulin molecule |
| 6CE9 | Insulin Receptor ectodomain in complex with two insulin molecules |
| 6CEB | Insulin Receptor ectodomain in complex with two insulin molecules - C1 symmetry |
| 5U1M | Structure of the IRS-1 PTB Domain Bound to the Juxtamembrane Region of the Insulin Receptor |
| 5KQV | Insulin receptor ectodomain construct comprising domains L1,CR,L2, FnIII-1 and alphaCT peptide in complex with bovine insulin and FAB 83-14 (REVISED STRUCTURE) |
| 5TQ1 | Phospholipase C gamma-1 C-terminal SH2 domain bound to a phosphopeptide derived from the insulin receptor |
| 5J3H | Human insulin receptor domains L1-CR in complex with peptide S519C16 and 83-7 Fv |
| 5HHW | Crystal structure of insulin receptor kinase domain in complex with cis-(R)-7-(3-(azetidin-1-ylmethyl)cyclobutyl)-5-(3-((tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methoxy)phenyl)-7H -pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-amine. |
| 4ZXB | Structure of the human insulin receptor ectodomain, IRDeltabeta construct, in complex with four Fab molecules |
| 5E1S | The Crystal structure of INSR Tyrosine Kinase in complex with the Inhibitor BI 885578 |
| 4XSS | Insulin-like growth factor I in complex with site 1 of a hybrid insulin receptor / Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor |
| 4XST | Structure of the endoglycosidase-H treated L1-CR domains of the human insulin receptor in complex with residues 697-719 of the human insulin receptor (A-isoform) |
| 4XLV | Crystal structure of the activated insulin receptor tyrosine kinase dimer |
| 4OGA | Insulin in complex with Site 1 of the human insulin receptor |
| 2MFR | Solution structure of the transmembrane domain of the insulin receptor in micelles |
| 4IBM | Crystal structure of insulin receptor kinase domain in complex with an inhibitor Irfin-1 |
| 3W11 | Insulin receptor ectodomain construct comprising domains L1-CR in complex with human insulin, Alpha-CT peptide(704-719) and FAB 83-7 |
| 3W12 | Insulin receptor ectodomain construct comprising domains L1-CR in complex with high-affinity insulin analogue [D-PRO-B26]-DTI-NH2, alpha-CT peptide(704-719) and FAB 83-7 |
| 3W13 | Insulin receptor ectodomain construct comprising domains L1-CR in complex with high-affinity insulin analogue [D-PRO-B26]-DTI-NH2, alphact peptide(693-719) and FAB 83-7 |
| 3ETA | Kinase domain of insulin receptor complexed with a pyrrolo pyridine inhibitor |
| 3EKN | Insulin receptor kinase complexed with an inhibitor |
| 3EKK | Insulin receptor kinase complexed with an inhibitor |
| 2Z8C | Phosphorylated insulin receptor tyrosine kinase in complex with (4-[5-carbamoyl-4-(3-methylanilino)pyrimidin-2-yl]aminophenyl)acetic acid |
| 3BU3 | Crystal structure of the insulin receptor kinase in complex with IRS2 KRLB peptide |
| 3BU5 | Crystal structure of the insulin receptor kinase in complex with IRS2 KRLB peptide and ATP |
| 3BU6 | Crystal structure of the insulin receptor kinase in complex with IRS2 KRLB phosphopeptide |
| 2HR7 | Insulin receptor (domains 1-3) |
| 2B4S | Crystal structure of a complex between PTP1B and the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase |
| 2AUH | Crystal structure of the Grb14 BPS region in complex with the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase |
| 1RQQ | Crystal Structure of the Insulin Receptor Kinase in Complex with the SH2 Domain of APS |
| 1LK2 | 1.35A crystal structure of H-2Kb complexed with the GNYSFYAL peptide |
| 1P14 | Crystal structure of a catalytic-loop mutant of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase |
| 1I44 | CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC STUDIES OF AN ACTIVATION LOOP MUTANT OF THE INSULIN RECEPTOR TYROSINE KINASE |
| 1GAG | CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE INSULIN RECEPTOR KINASE IN COMPLEX WITH A BISUBSTRATE INHIBITOR |
| 1IR3 | PHOSPHORYLATED INSULIN RECEPTOR TYROSINE KINASE IN COMPLEX WITH PEPTIDE SUBSTRATE AND ATP ANALOG |
| 1IRK | CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE TYROSINE KINASE DOMAIN OF THE HUMAN INSULIN RECEPTOR |
| PDB file name | Residue A | Atom A | Residue B | Atom B | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
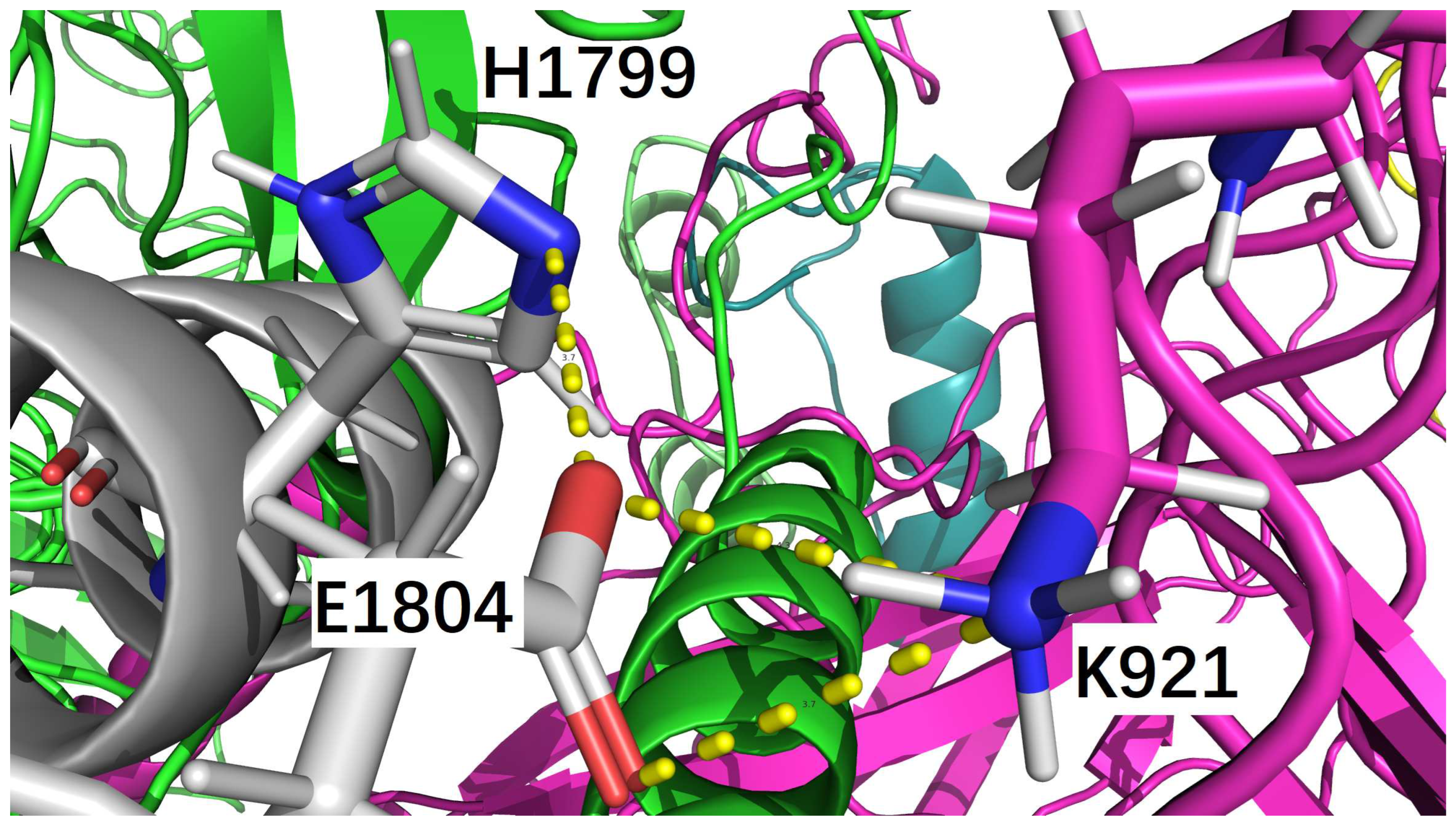
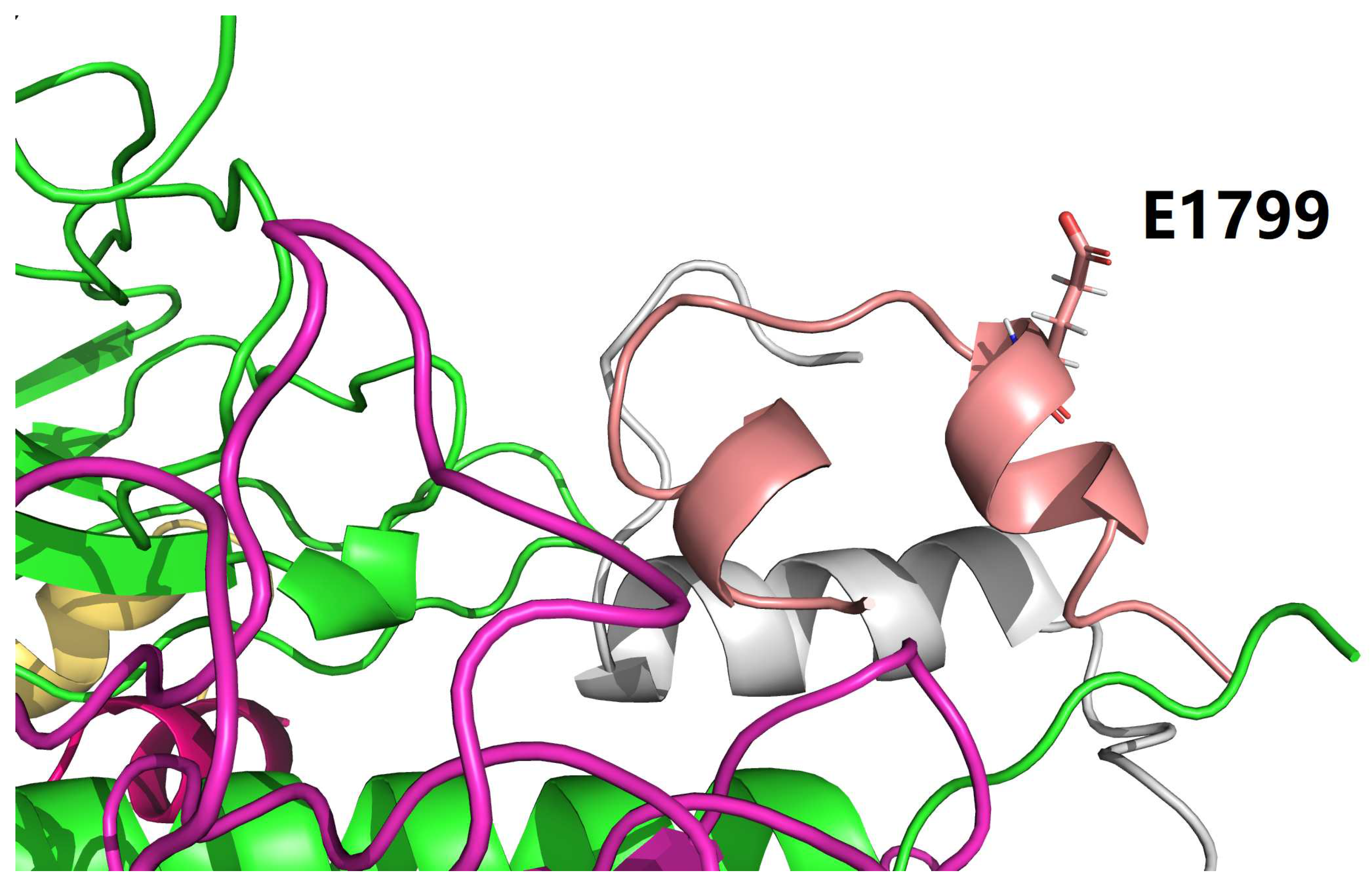
| icod.pdb | C_LYS_921 | NZ | F_GLU_1804 | OE1 | 3.659 |
| icod.pdb | F_HIS_1799 | NE2 | F_GLU_1804 | OE2 | 3.669 |
| nati.pdb | C_LYS_921 | NZ | F_GLU_1804 | OE2 | 3.204 |
| PDB file name | Residue A | Atom A | Residue B | Atom B | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nati.pdb | C_LYS_921 | NZ | F_GLU_1804 | OE2 | 3.204 |
| PDB file name | Residue A | Atom A | Residue B | Atom B | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| icod.pdb | C_LYS_921 | NZ | F_GLU_1804 | OE1 | 3.659 |
| icod.pdb | F_HIS_1799 | NE2 | F_GLU_1804 | OE2 | 3.669 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





