Submitted:
31 January 2024
Posted:
01 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
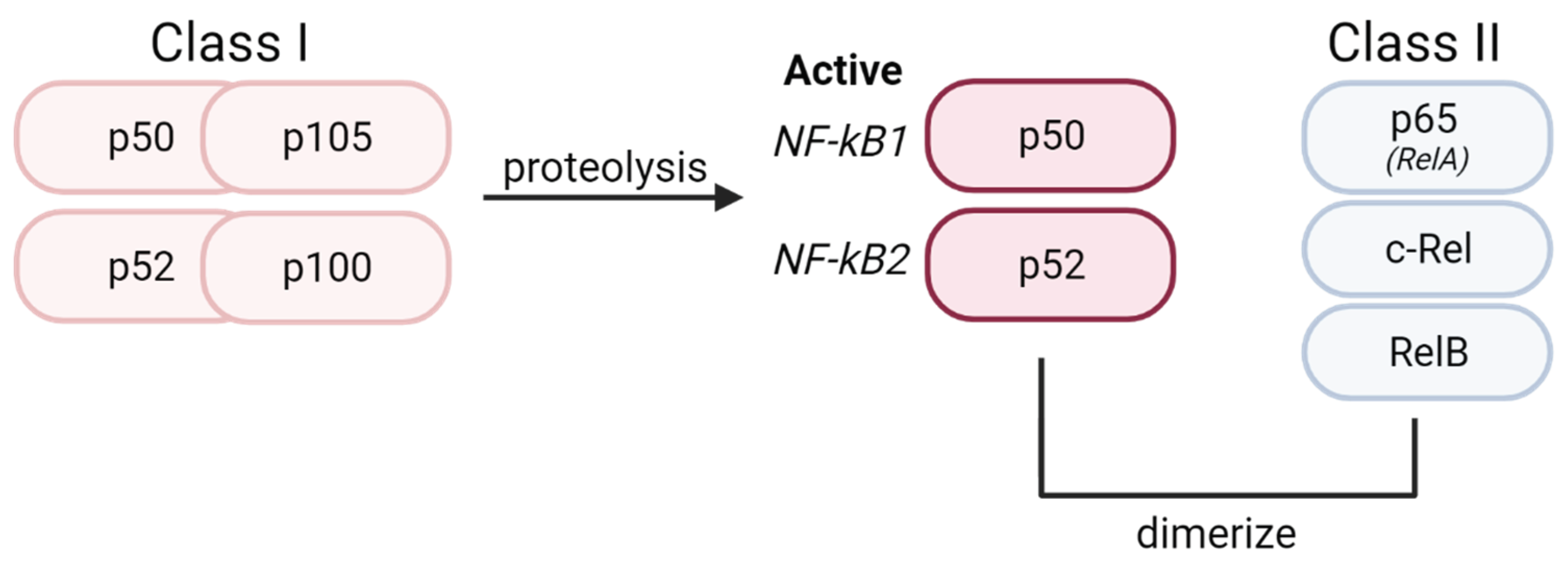
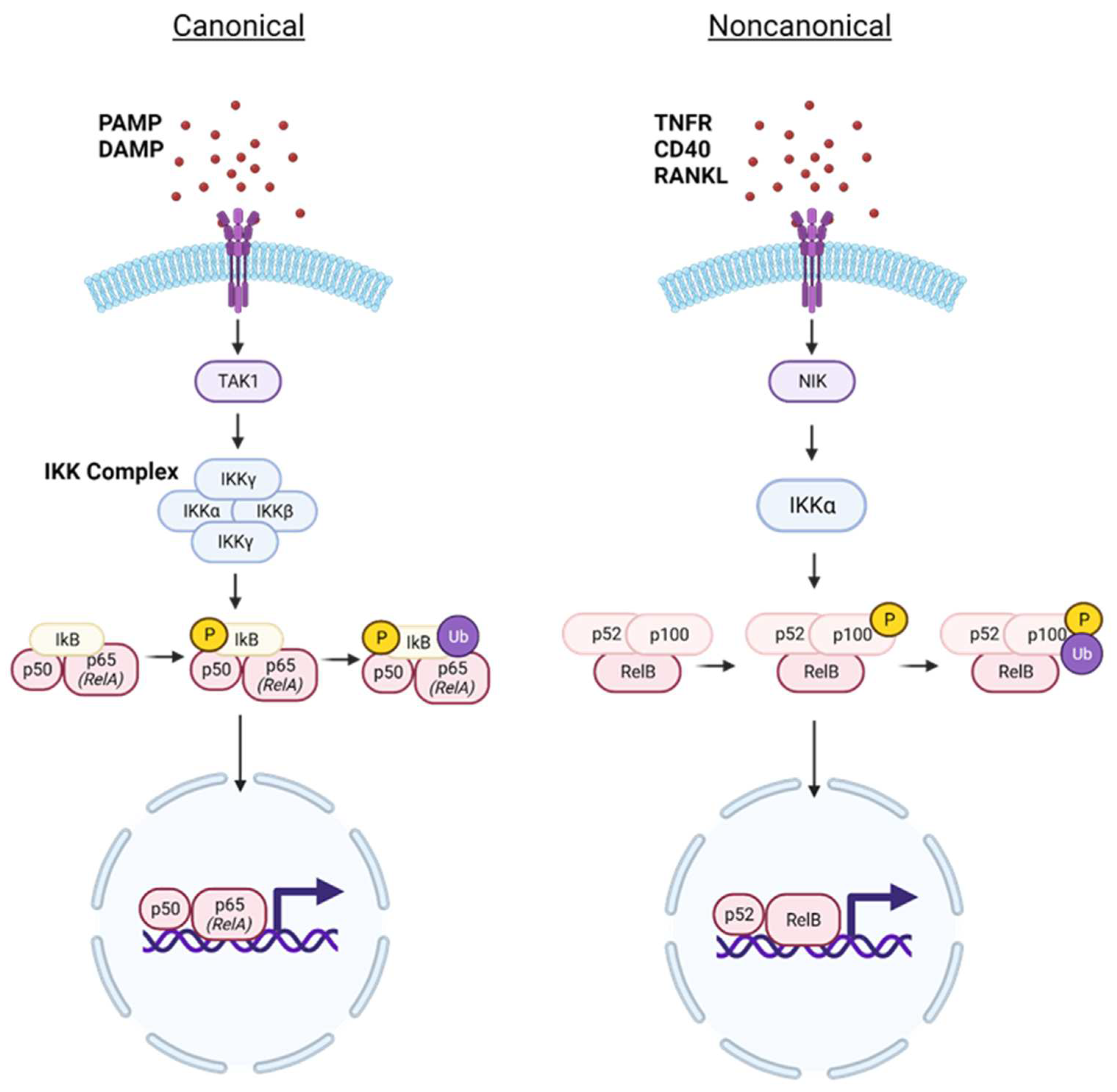
1. NF-κB Signaling Pathway
2. NF-κB in the Central Nervous System
2.1. Neurons
2.2. Glia
2.2.1. Oligodendrocytes
2.2.2. Astrocytes
2.2.3. Microglia
3. Role of Microglial NF-κB in CNS Disease
3.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
3.2. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
3.3. Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, H.L. Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6853–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, F.; Smith, E.L.; Carmody, R.J. The Regulation of NF-κB Subunits by Phosphorylation. Cells 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, M.J.; Ghosh, S. Rel/NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: an overview. Semin Cancer Biol 1997, 8, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Molecular Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Yin, Q.; Wu, H. Structural studies of NF-κB signaling. Cell Res 2011, 21, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.C. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Res 2011, 21, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin Microbiol Rev 2009, 22, 240–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, O.; Vayttaden, S.J.; Fraser, I.D.C. Measurement of NF-κB Activation in TLR-Activated Macrophages. Methods Mol Biol 2018, 1714, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Coyne, C.B.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T. PAMPs and DAMPs: signal 0s that spur autophagy and immunity. Immunol Rev 2012, 249, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S. Danger-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs): the Derivatives and Triggers of Inflammation. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2018, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussbacher, M.; Derler, M.; Basílio, J.; Schmid, J.A. NF-κB in monocytes and macrophages - an inflammatory master regulator in multitalented immune cells. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1134661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussbacher, M.; Salzmann, M.; Brostjan, C.; Hoesel, B.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Datler, H.; Hohensinner, P.; Basílio, J.; Petzelbauer, P.; Assinger, A.; et al. Cell Type-Specific Roles of NF-κB Linking Inflammation and Thrombosis. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresselhaus, E.C.; Meffert, M.K. Cellular Specificity of NF-κB Function in the Nervous System. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-C. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Research 2011, 21, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cildir, G.; Low, K.C.; Tergaonkar, V. Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling in Health and Disease. Trends Mol Med 2016, 22, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-C. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nature Reviews Immunology 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Goodman, Y.; Luo, H.; Fu, W.; Furukawa, K. Activation of NF-kappaB protects hippocampal neurons against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis: evidence for induction of manganese superoxide dismutase and suppression of peroxynitrite production and protein tyrosine nitration. Journal of neuroscience research 1997, 49, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridmacher, V.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Goudeau, B.; Ndiaye, D.; Rossi, F.M.; Pfeiffer, J.; Kaltschmidt, C.; Israël, A.; Mémet, S. Forebrain-specific neuronal inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activity leads to loss of neuroprotection. J Neurosci 2003, 23, 9403–9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.S.; Wenzel, H.J.; Kinoshita, Y.; Robbins, C.A.; Donehower, L.A.; Schwartzkroin, P.A. Loss of the p53 tumor suppressor gene protects neurons from kainate-induced cell death. J Neurosci 1996, 16, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Koo, S.Y.; Riessland, M.; Cho, H.; Chaudhry, F.; Kolisnyk, B.; Russo, M.V.; Saurat, N.; Mehta, S.; Garippa, R.; et al. TNF-NFkB-p53 axis restricts in vivo survival of hPSC-derived dopamine neuron. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jamison, S.; Lin, W. Interferon-γ activates nuclear factor-κ B in oligodendrocytes through a process mediated by the unfolded protein response. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanoue, M.; Yoshioka, A.; Ohashi, T.; Eto, Y.; Takamatsu, K. NF-kappaB prevents TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in an oligodendrocyte cell line. Neurochem Res 2004, 29, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.; Jamison, S.; Yue, Y.; Durose, W.; Schmidt-Ullrich, R.; Lin, W. NF-κB Activation Protects Oligodendrocytes against Inflammation. J Neurosci 2017, 37, 9332–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Kaltschmidt, C. NF-kappaB in the nervous system. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2009, 1, a001271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P.; Meffert, M.K. Roles for NF-κB in nerve cell survival, plasticity, and disease. Cell Death & Differentiation 2006, 13, 852–860. [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti, L.; Klein, M.; Schlett, K.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Eisel, U.L. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated neuroprotection against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity is enhanced by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation. Essential role of a TNF receptor 2-mediated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent NF-kappa B pathway. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 32869–32881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamatani, M.; Che, Y.H.; Matsuzaki, H.; Ogawa, S.; Okado, H.; Miyake, S.; Mizuno, T.; Tohyama, M. Tumor necrosis factor induces Bcl-2 and Bcl-x expression through NFkappaB activation in primary hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 1999, 274, 8531–8538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Mayo, M.W.; Korneluk, R.G.; Goeddel, D.V.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 1998, 281, 1680–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhan, M.; Guo, M.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; de The, H.; Chen, Z.; et al. Yolk sac-derived Pdcd11-positive cells modulate zebrafish microglia differentiation through the NF-κB-Tgfβ1 pathway. Cell Death Differ 2021, 28, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhakar, A.L.; Tannis, L.L.; Zeindler, C.; Russo, M.P.; Jobin, C.; Park, D.S.; MacPherson, S.; Barker, P.A. Constitutive nuclear factor-kappa B activity is required for central neuron survival. J Neurosci 2002, 22, 8466–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mincheva, S.; Garcera, A.; Gou-Fabregas, M.; Encinas, M.; Dolcet, X.; Soler, R.M. The canonical nuclear factor-κB pathway regulates cell survival in a developmental model of spinal cord motoneurons. J Neurosci 2011, 31, 6493–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, G.; Hamanoue, M.; Enokido, Y.; Wyatt, S.; Pennica, D.; Jaffray, E.; Hay, R.T.; Davies, A.M. Cytokine-induced nuclear factor kappa B activation promotes the survival of developing neurons. J Cell Biol 2000, 148, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilli, M.; Memo, M. Possible role of NF-kappaB and p53 in the glutamate-induced pro-apoptotic neuronal pathway. Cell Death Differ 1999, 6, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Lozano, G. NF-kappa B activation of p53. A potential mechanism for suppressing cell growth in response to stress. J Biol Chem 1994, 269, 20067–20074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, J.A.; Stephenson, D.T.; Smalstig, E.B.; Dixon, E.P.; Little, S.P. Global ischemia activates nuclear factor-kappa B in forebrain neurons of rats. Stroke 1997, 28, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, A.; Lindsberg, P.J.; Koistinaho, M.; Zhang, W.; Juettler, E.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.L.; Weih, F.; Frank, N.; Schwaninger, M.; Koistinaho, J. Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke 2004, 35, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, E.A.; Butler, T.; Collier, L.; Collier, S.; Pennypacker, K.R. NF-kappaB protects neurons from ischemic injury after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Brain Res 2006, 1088, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Martin-Villalba, A.; Weih, F.; Vogel, J.; Wirth, T.; Schwaninger, M. NF-κB is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Nature Medicine 1999, 5, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, M.; Goffi, F.; Boroni, F.; Benarese, M.; Perkins, S.E.; Liou, H.C.; Spano, P. Opposing roles for NF-kappa B/Rel factors p65 and c-Rel in the modulation of neuron survival elicited by glutamate and interleukin-1beta. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 20717–20723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, R.S.; Wing, M.G.; Compston, A. Nonactivated microglia promote oligodendrocyte precursor survival and maturation through the transcription factor NF-kappa B. Eur J Neurosci 2001, 13, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretz, A.; Herrmann, K.H.; Fischer, S.; Engelmann, C.; Witte, O.W.; Reichenbach, J.R.; Weih, F.; Haenold, R. Dysfunctional NF-κB and brain myelin formation. Eur J Hum Genet 2014, 22, 724–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlett, J.S.; Mettang, M.; Skaf, A.; Schweizer, P.; Errerd, A.; Mulugeta, E.A.; Hein, T.M.; Tsesmelis, K.; Tsesmelis, M.; Büttner, U.F.G.; et al. NF-κB is a critical mediator of post-mitotic senescence in oligodendrocytes and subsequent white matter loss. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2023, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raasch, J.; Zeller, N.; van Loo, G.; Merkler, D.; Mildner, A.; Erny, D.; Knobeloch, K.P.; Bethea, J.R.; Waisman, A.; Knust, M.; et al. IkappaB kinase 2 determines oligodendrocyte loss by non-cell-autonomous activation of NF-kappaB in the central nervous system. Brain 2011, 134, 1184–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Yue, Y.; Stone, S.; Wu, S.; Lin, W. NF-κB Activation Accounts for the Cytoprotective Effects of PERK Activation on Oligodendrocytes during EAE. J Neurosci 2020, 40, 6444–6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, G.; Jamison, S.; Li, J.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D.; Lin, W. PERK activation preserves the viability and function of remyelinating oligodendrocytes in immune-mediated demyelinating diseases. Am J Pathol 2014, 184, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, D. Factoring in astrocytes. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2015, 16, 67–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomoto, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Fukushima, T.; Kimura, H.; Ohshima, K.; Tomonaga, M. Expression of Nuclear Factor κB and Tumor Necrosis Factor α in the Mouse Brain after Experimental Thermal Ablation Injury. Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla, R.; Bracchi-Ricard, V.; Hu, W.H.; Frydel, B.; Bramwell, A.; Karmally, S.; Green, E.J.; Bethea, J.R. Inhibition of astroglial nuclear factor kappaB reduces inflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Exp Med 2005, 202, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, R.; Hurtado, A.; Persaud, T.; Esham, K.; Pearse, D.D.; Oudega, M.; Bethea, J.R. Transgenic inhibition of astroglial NF-κB leads to increased axonal sparing and sprouting following spinal cord injury. Journal of Neurochemistry 2009, 110, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Krabbe, G.; Du, F.; Jones, I.; Reichert, M.C.; Telpoukhovskaia, M.; Kodama, L.; Wang, C.; Cho, S.H.; Sayed, F.; et al. Proximal recolonization by self-renewing microglia re-establishes microglial homeostasis in the adult mouse brain. PLoS Biol 2019, 17, e3000134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Long, J.; He, T.; Belshaw, R.; Scott, J. Integrated genomic approaches identify major pathways and upstream regulators in late onset Alzheimer's disease. Scientific reports 2015, 5, 12393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Uherek, M.; Volk, B.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Kaltschmidt, C. Transcription factor NF-kappaB is activated in primary neurons by amyloid beta peptides and in neurons surrounding early plaques from patients with Alzheimer disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1997, 94, 2642–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, S.; Deng, Y.; Cai, F.; Tone, M.; Tone, Y.; Tong, Y.; Song, W. Increased NF-κB signalling up-regulates BACE1 expression and its therapeutic potential in Alzheimer's disease. The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 15, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Fan, L.; Khawaja, R.R.; Liu, B.; Zhan, L.; Kodama, L.; Chin, M.; Li, Y.; Le, D.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Microglial NF-κB drives tau spreading and toxicity in a mouse model of tauopathy. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masrori, P.; Van Damme, P. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a clinical review. Eur J Neurol 2020, 27, 1918–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boillée, S.; Vande Velde, C.; Cleveland, D.W. ALS: a disease of motor neurons and their nonneuronal neighbors. Neuron 2006, 52, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, A.M.; Nguyen, M.D.; Roberts, E.A.; Garcia, M.L.; Boillée, S.; Rule, M.; McMahon, A.P.; Doucette, W.; Siwek, D.; Ferrante, R.J.; et al. Wild-type nonneuronal cells extend survival of SOD1 mutant motor neurons in ALS mice. Science 2003, 302, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarup, V.; Phaneuf, D.; Dupré, N.; Petri, S.; Strong, M.; Kriz, J.; Julien, J.P. Deregulation of TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis triggers nuclear factor κB-mediated pathogenic pathways. J Exp Med 2011, 208, 2429–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frakes, A.E.; Ferraiuolo, L.; Haidet-Phillips, A.M.; Schmelzer, L.; Braun, L.; Miranda, C.J.; Ladner, K.J.; Bevan, A.K.; Foust, K.D.; Godbout, J.P.; et al. Microglia induce motor neuron death via the classical NF-κB pathway in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuron 2014, 81, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosio, C.; Valle, C.; Casciati, A.; Iaccarino, C.; Carrì, M.T. Astroglial inhibition of NF-κB does not ameliorate disease onset and progression in a mouse model for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). PLoS One 2011, 6, e17187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.C.; Yang, S.N. Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011, 2011, 609813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; McCullough, L.D. Inflammatory responses in hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2013, 34, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, S.; Perego, C.; Pischiutta, F.; Zanier, E.R.; De Simoni, M.G. The ischemic environment drives microglia and macrophage function. Front Neurol 2015, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Ignazio, L.; Rocha, S. Hypoxia Induced NF-κB. Cells 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Kan, E.M.; Lu, J.; Hao, A.; Dheen, S.T.; Kaur, C.; Ling, E.-A. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates microglial activation and production of inflammatory mediators in neonatal rat brain following hypoxia: role of TLR4 in hypoxic microglia. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2013, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghloul, N.; Kurepa, D.; Bader, M.Y.; Nagy, N.; Ahmed, M.N. Prophylactic inhibition of NF-κB expression in microglia leads to attenuation of hypoxic ischemic injury of the immature brain. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cell Type | NF-κB | ||
| Protective (Against) | Detrimental (In) |
Constitutively Active |
|
| Neuron | Oxidative Stress | Ischemia | In survival |
| In development | |||
| Oligodendrocyte | Inflammatory Cytokines | In survival (possible) | |
| Multiple Sclerosis (EAE) | |||
| Astrocyte | Spinal Cord Injury | ||
| Microglia | Alzheimer’s Disease | ||
| Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (SOD1 mutant) Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy |
|||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




