Submitted:
28 January 2024
Posted:
29 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test materials
2.2. Preparation method of the RM adsorbent
2.3. Establishment and application of the BP neural network model
2.3.1. Determination of input and output training datasets
2.3.2. Establishment of a BP network optimization model
2.3.3. Training data preprocessing and parameter setting
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Network training and verification
| Name of component | RM/g | FA/g | W:H | A2C/% | HPMC/% | Na2SiO4/% |
| Range | 275–300 | 1.7–8.5 | 1:3 | 2–10 | 0.05–0.25 | 2 |
| Name of component | KH-602/% | H2O2/% | MnO2/% | HCl/% | SDBS/% | |
| Range | 0.1 | 0.4–2 | 0.08–0.4 | 0.25–1.25 | 0.05–0.25 |
3.2. Performance analysis of RM particle adsorbents
3.2.1. Effect of FA on adsorbent properties
3.2.2. Effect of enhanced and anti-chalking agents on the adsorbent properties
3.2.3. The effect of non-thermal pore-forming agent H2O2 on adsorbent properties
3.2.4. Effect of HCl on adsorbent properties
3.2.5. Effect of the surfactant on the adsorbent properties
3.2.6. The influence of adsorbent dose on adsorption
3.2.7. The influence of adsorption time on adsorption
3.3. Preparation and test of the active RM adsorbent with the optimal formula
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Declaration of Competing Interest
Table of Abbreviations
| BP | Back-propagation neural networks |
| FA | Fly ash |
| RM | Red mud |
| SDBS | Sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate |
| A2C | aluminate cement |
References
- Joseph, C.G., Taufiq-Yap, Y.H., Krishnan, V., Li Puma, G., 2020. Application of modified red mud in environmentally-benign applications: A review paper. Environ. Eng. Res. 25. 795–806. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., Sun, N., Tang, H., Sun, W., 2019. A review on comprehensive utilization of red mud and prospect analysis. Minerals. 9. [CrossRef]
- Hegedűs, M., Tóth-Bodrogi, E., Jónás, J., Somlai, J., Kovács, T., 2018. Mobility of 232Th and 210Po in red mud. J. Environ. Radioact. 184–185. [CrossRef]
- Papatheodorou, G., Papaefthymiou, H., Maratou, A., Ferentinos, G., 2005. Natural radionuclides in bauxitic tailings (red-mud) in the Gulf of Corinth. Greece, Radioprotection. 40. S549–S555. [CrossRef]
- Rai, S., Bahadure, S., Chaddha, M.J., Agnihotri, A., 2020. Disposal Practices and Utilization of Red Mud (Bauxite Residue): A Review in Indian Context and Abroad. J. Sustain. Metall. 6. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Qi, X., Wang, H., Zhang, L., Xu, B., Shi, Q., Li, F., 2020. Removal of Cr (Ⅲ) from aqueous solution by using bauxite residue (red mud): Identification of active components and column tests. Chemosphere. 245. 125560. [CrossRef]
- Cusack, P.B., Callery, O., Courtney, R., Ujaczki, É., O’Donoghue, L.M.T., Healy, M.G., 2019. The use of rapid, small-scale column tests to determine the efficiency of bauxite residue as a low-cost adsorbent in the removal of dissolved reactive phosphorus from agricultural waters. J. Environ. Manage. 241. 273–283. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X., Niu, Z., Li, W., Zhao, H., Tang, Q., 2020. A novel process for recovery of aluminum, iron, vanadium, scandium, titanium and silicon from red mud. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8. 103528. [CrossRef]
- Milenković, A.S., Smičiklas, I.D., Šljivić-Ivanović, M.Z., Živković, L.S., Vukelić, N.S., 2016. Effect of experimental variables onto Co2+ and Sr2+ sorption behavior in red mud-water suspensions. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst. Environ. Eng. 51. 679–690. [CrossRef]
- Tsamo, C., Djomou Djonga, P.N., Dangwang Dikdim, J.M., Kamga, R., Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of Cr(VI), Cu(II) and Pb(II) Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Red Mud, a Low-Cost Adsorbent. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43. 2353–2368. [CrossRef]
- ]Lin, J.Y., Kim, M., Li, D., Kim, H., pao Huang, C., 2020. The removal of phosphate by thermally treated red mud from water: The effect of surface chemistry on phosphate immobilization. Chemosphere. 247. 125867. [CrossRef]
- López-García, M., Martínez-Cabanas, M., Vilariño, T., Lodeiro, P., Rodríguez-Barro, P., Herrero, R., Barriada, J.L., 2017. New polymeric/inorganic hybrid sorbents based on red mud and nanosized magnetite for large scale applications in As(V) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 311. 117–125. [CrossRef]
- Ribas, M.C., Adebayo, M.A., Prola, L.D.T., Lima, E.C., Cataluña, R., Feris, L.A., Puchana-Rosero, M.J., Machado, F.M., Pavan, F.A., Calvete, T., 2014. Comparison of a homemade cocoa shell activated carbon with commercial activated carbon for the removal of reactive violet 5 dye from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 248. 315–326. [CrossRef]
- Wu, W., Chen, Z., Huang, Y., Li, J., Chen, D., Chen, N., Su, M., 2021. Red mud for the efficient adsorption of U(VI) from aqueous solution: Influence of calcination on performance and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 409. 124925. [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F., Niu, S., Wang, L., Liu, R., Sun, W., He, D., 2021. Efficient removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution by modified red mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 406. [CrossRef]
- Pu, X., Luo, A., Su, H., Zhang, K., Tian, C., Chen, B., Chai, P., Xia, X., 2020. Optimization and mechanism of postponing aging of polysaccharides from Chinese herbal medicine formula. Toxicol. Res. (Camb). 9. 239–248. [CrossRef]
- Madani-Tonekaboni, M., Kamankesh, M., Mohammadi, A., 2015. Determination of furfural and hydroxymethyl furfural from baby formula using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography and method optimization by response surface methodology. J. Food Compos. Anal. 40. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- He, Y., Meng, Z., Xu, H., Zou, Y., 2020. A dynamic model of evaluating differential automatic method for solving plane problems based on BP neural network algorithm. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 556. 124845. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Huang, H., Xu, Z., Ma, H., Guo, Y., 2020. Mechanism study on manganese(II) removal from acid mine wastewater using red mud and its application to a lab-scale column. J. Clean. Prod. 253. 119955. [CrossRef]
- Deihimi, N., Irannajad, M., Rezai, B., 2018. Prediction of removal percentage and adsorption capacity of activated red mud for removal of cyanide by artificial neural network. Geosystem Eng. 21, 273–281. [CrossRef]
- Genç-Fuhrman, H., Tjell, J.C., McConchie, D., 2004. Adsorption of Arsenic from Water Using Activated Neutralized Red Mud. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38. 2428–2434. [CrossRef]
- Ye, J., Zhang, P., Hoffmann, E., Zeng, G., Tang, Y., Dresely, J., Liu, Y.,2014. Comparison of response surface methodology and artificial neural network in optimization and prediction of acid activation of bauxsol for phosphorus adsorption. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 225. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., Xu, G., Gu, X., Gao, Y., Zhao, P., 2021. High value-added applications of coal fly ash in the form of porous materials: A review. Ceram. Int. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P., Yan, Y., Cao, J., Feng, J., Qi, J., 2021. Surface activation towards manganese dioxide nanosheet arrays via plasma engineering as cathode and anode for efficient water splitting. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 586. 95–102. [CrossRef]
- Li, T., Wang, Z., Zhou, T., He, Y., Huang, F., 2019. Preparation and properties of magnesium phosphate cement foam concrete with H2O2 as foaming agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 205. 566–573. [CrossRef]
- Bacioiu, I.G., Stoica, L., Constantin, C., Stanescu, A.M., 2017. Removal of Tartrazine from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption on Activated Red Mud. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 228. [CrossRef]
- Wołowicz, A., Staszak, K., Hubicki, Z., 2019. Static sorption of heavy metal ions on ion exchanger in the presence of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate. Adsorption. 25. 393–404. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.P., Tao, D.L., 2020. Improved green strength of ceramic bodies through extrusion using hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as binder. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 17. 1249–1254. [CrossRef]
- Ba, M., Gao, Q., Ma, Y., Zhu, J., Du, Y., 2021. Improved hydration and properties of magnesium oxysulfate (MOS) cement using sodium silicate as an additive. Constr. Build. Mater. 267. [CrossRef]
- Ye, J., Cong, X., Zhang, P., Hoffmann, E., Zeng, G., Wu, Y., Zhang, H., Fan, W., 2015. Phosphate Adsorption onto Granular-Acid-Activated-Neutralized Red Mud: Parameter Optimization, Kinetics, Isotherms, and Mechanism Analysis. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 226. [CrossRef]
- Kaewmee, P., Song, M., Iwanami, M., Tsutsumi, H., Takahashi, F., 2020. Porous and reusable potassium-activated geopolymer adsorbent with high compressive strength fabricated from coal fly ash wastes. J. Clean. Prod. 272. 122617. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S., Xie, F., Chen, S., Fu, B., 2020. The removal of Pb (II) and Cd (II) with hydrous manganese dioxide: mechanism on zeta potential and adsorption behavior. Environ. Technol. (United Kingdom). 41. 3219–3232. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., Liu, F., Qin, X., 2017. Adsorption of diclofenac onto goethite: Adsorption kinetics and effects of pH. Chemosphere. 180. 373–378. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Liu, S., 2017. Wettability Modification of Lignite by Adsorption of Dodecyl Based Surfactants for Inhibition of Moisture Re-adsorption. J. Surfactants Deterg. 20. 707–716. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C., Jeremias, F., Ernst, S.J., Henninger, S.K., 2017. Synthesis, functionalization and evaluation of ethylene-bridged PMOs as adsorbents for sorption dehumidification and cooling systems. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 244. 151–157. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Dan, H., Bukasa, O.T., Song, L., Liu, Y., Wang, L., Li, J., 2020. Low-Cost Efficient Magnetic Adsorbent for Phosphorus Removal from Water. ACS Omega. 5. 25326–25333. [CrossRef]
- Jin, J., Li, M., Jin, L., 2015. Data Normalization to Accelerate Training for Linear Neural Net to Predict Tropical Cyclone Tracks. Math. Probl. Eng. 21.18-29. [CrossRef]
- Chingono, K.E., Sanganyado, E., Bere, E., Yalala, B., 2018. Adsorption of sugarcane vinasse effluent on bagasse fly ash: A parametric and kinetic study. J. Environ. Manage. 224. 182–190. [CrossRef]
- Boczkaj, G., Gągol, M., Klein, M., Przyjazny, A., 2017. Effective method of treatment of effluents from production of bitumens under basic pH conditions using hydrodynamic cavitation aided by external oxidants. Ultrason. Sonochem. 40. 969–979. [CrossRef]
- Gu, G., Xu, F., Ruan, S., Huang, X., Zhu, J., Peng, C., 2020. Influence of precast foam on the pore structure and properties of fly ash-based geopolymer foams. Constr. Build. Mater. 256. 119410. [CrossRef]
- Cusack, P.B., Healy, M.G., Ryan, P.C., Burke, I.T., O’ Donoghue, L.M.T., Ujaczki, É., Courtney, R., 2018. Enhancement of bauxite residue as a low-cost adsorbent for phosphorus in aqueous solution, using seawater and gypsum treatments. J. Clean. Prod. 179. 217–224. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H., Li, Q.F., Wang, J.W., Kang, M.Q. Wang, X.K., 2014. Preparation and properties of carbon fiber/polyether polyurethane composites. Xinxing Tan Cailiao/New Carbon Mater. 29 .454–460. [CrossRef]
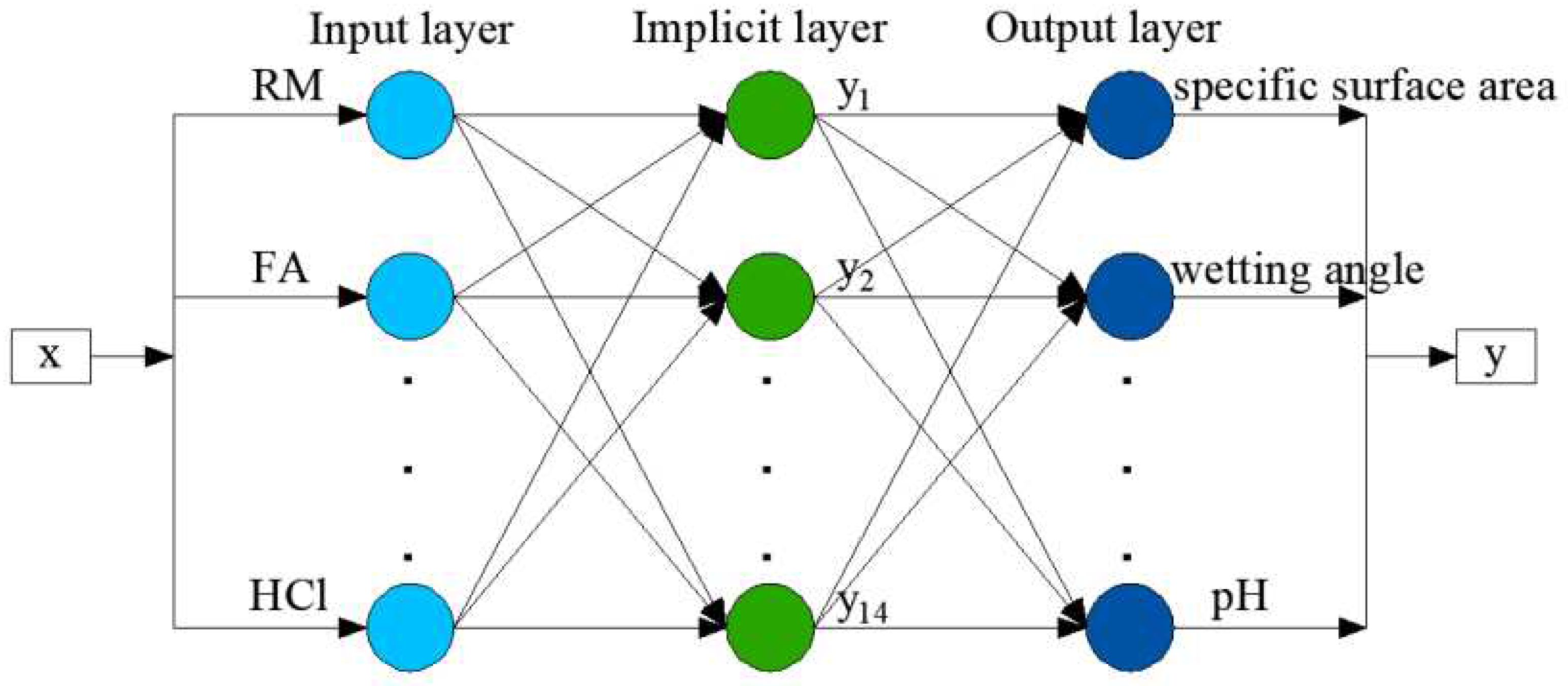
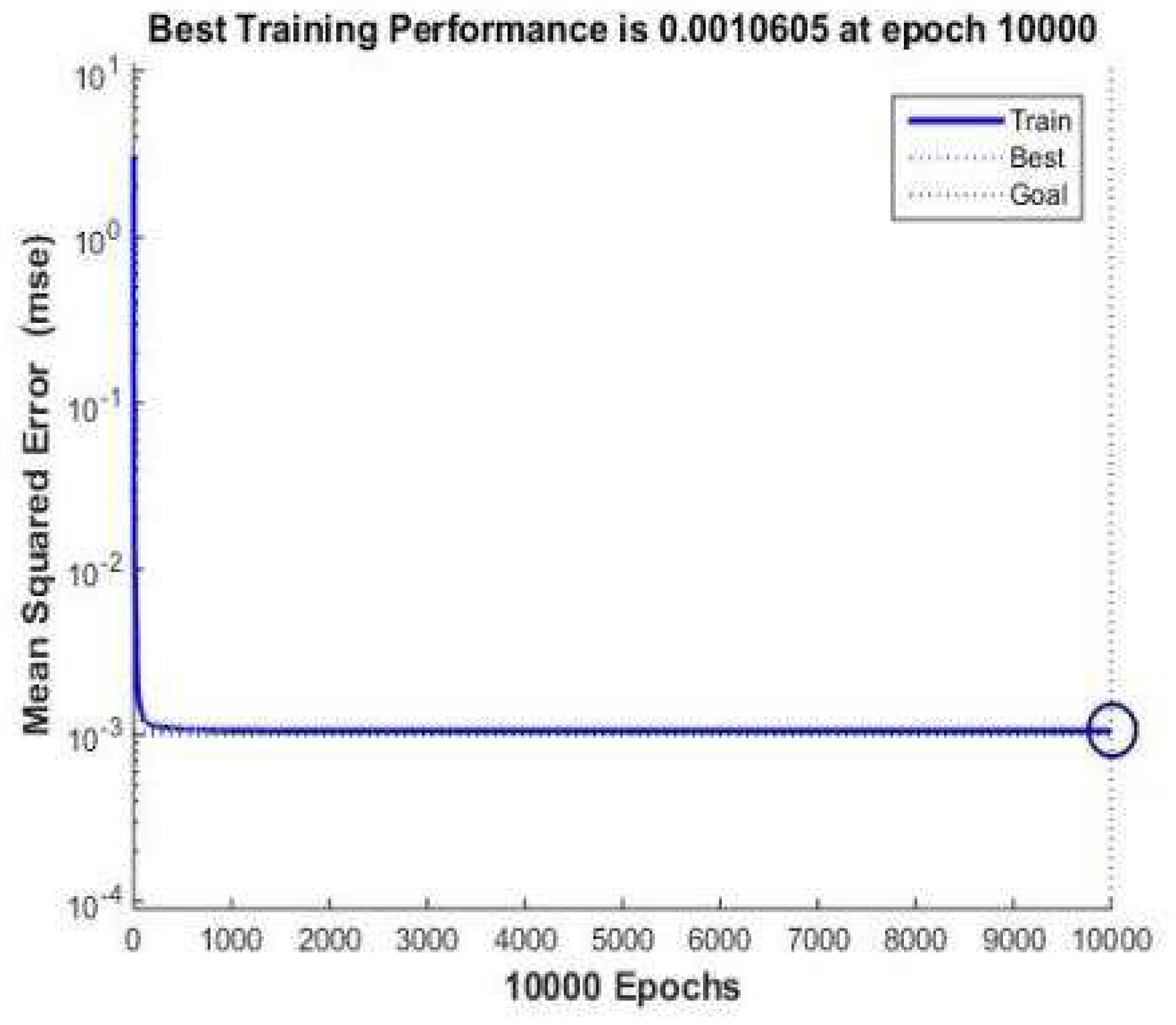
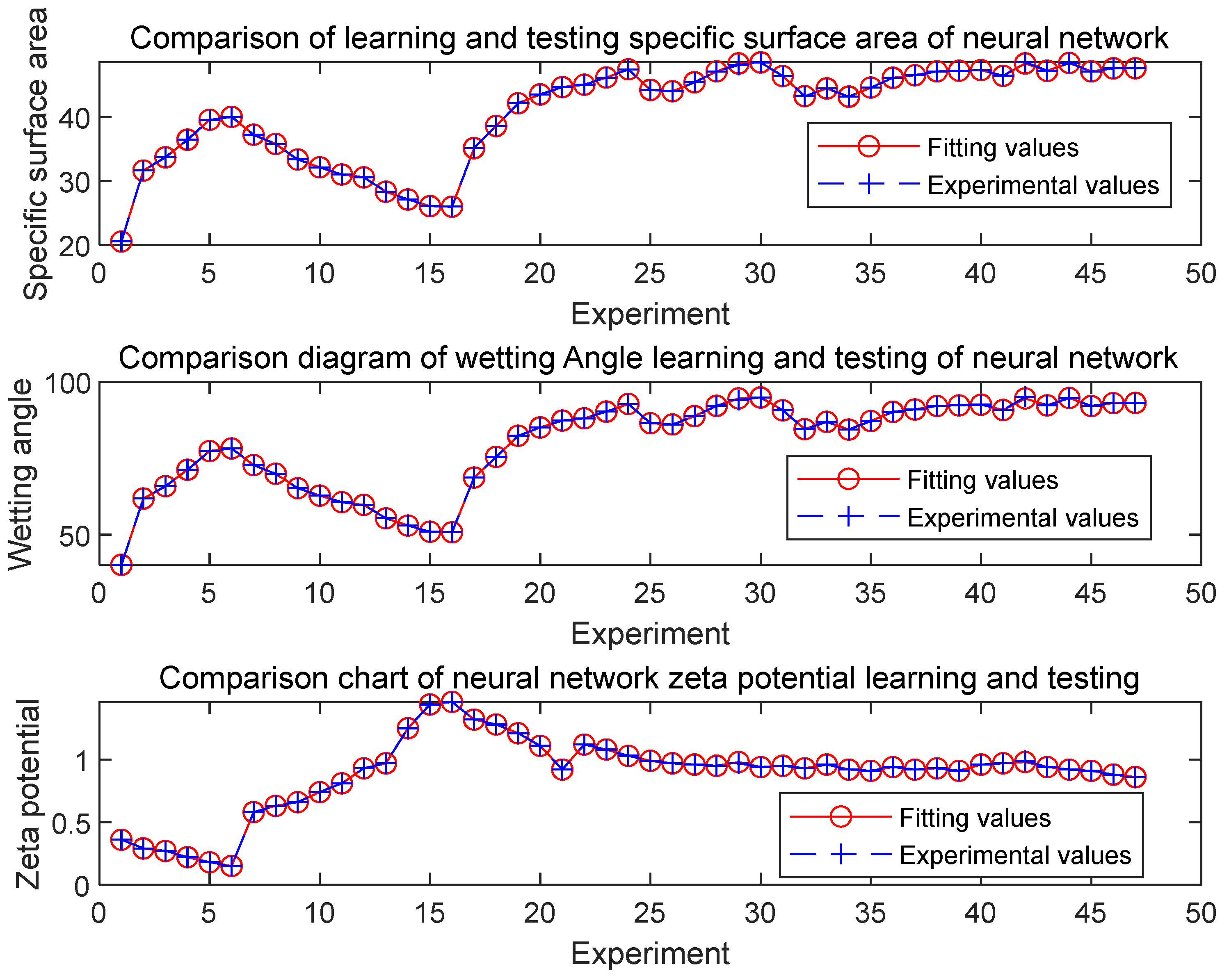
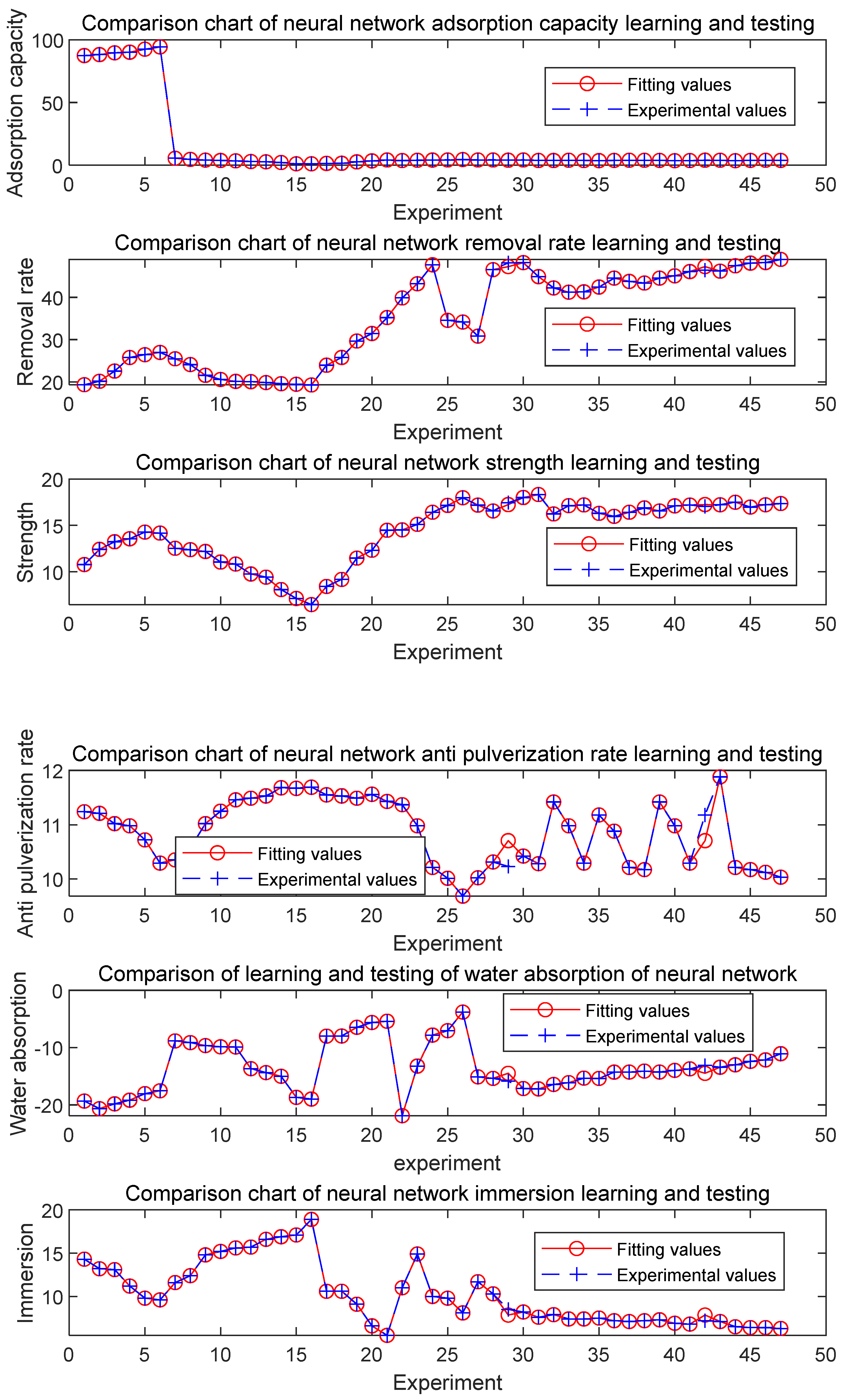
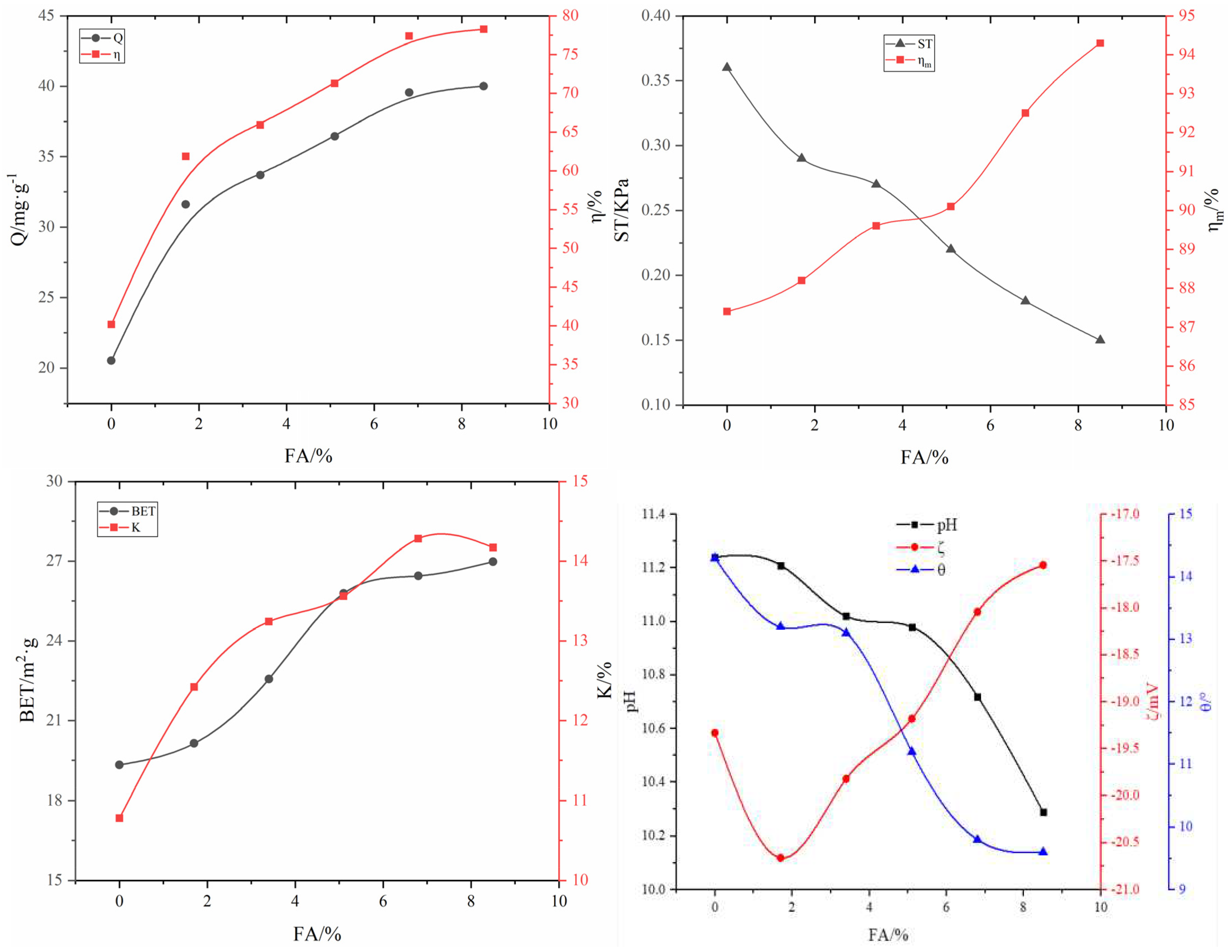
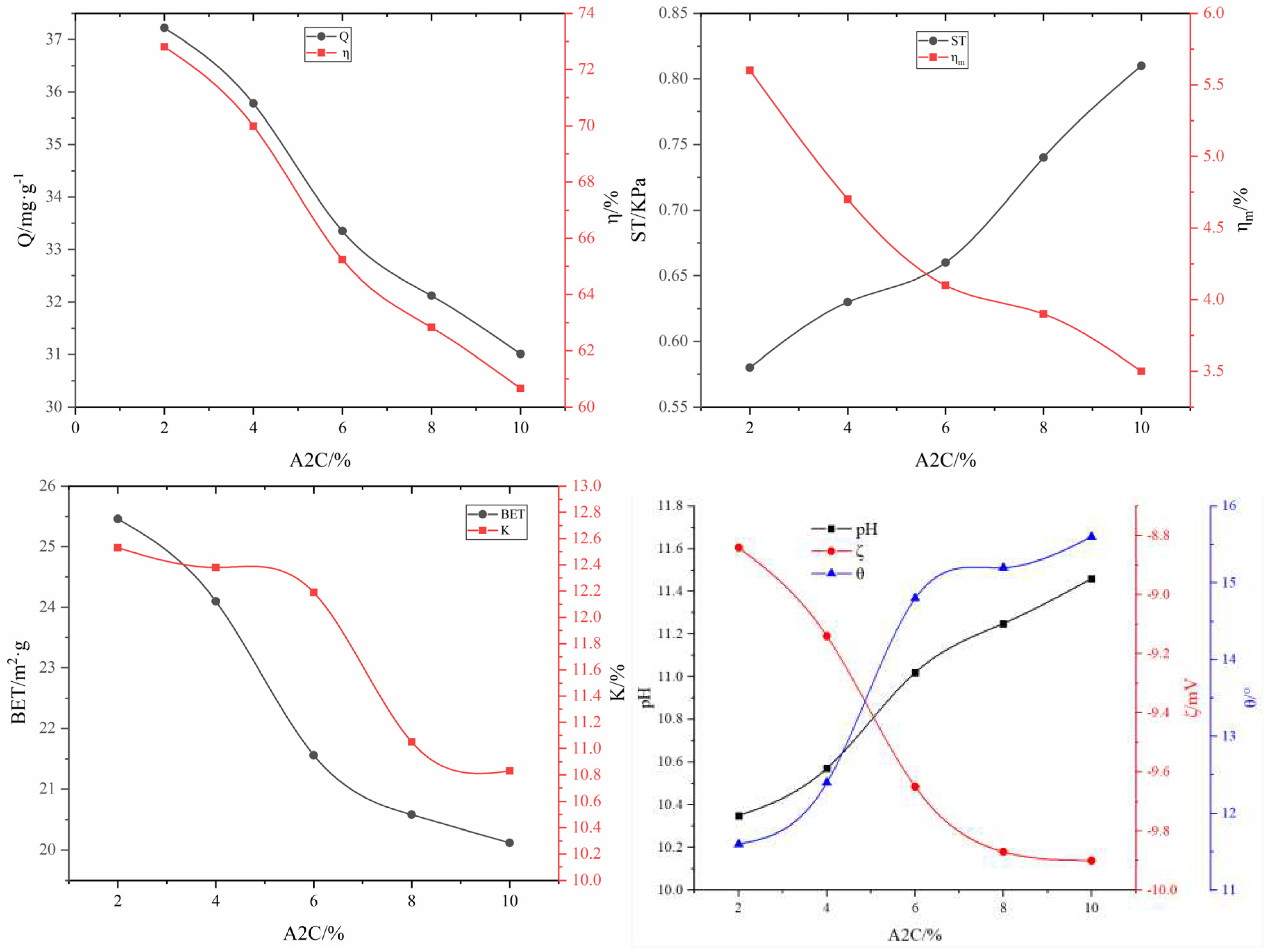
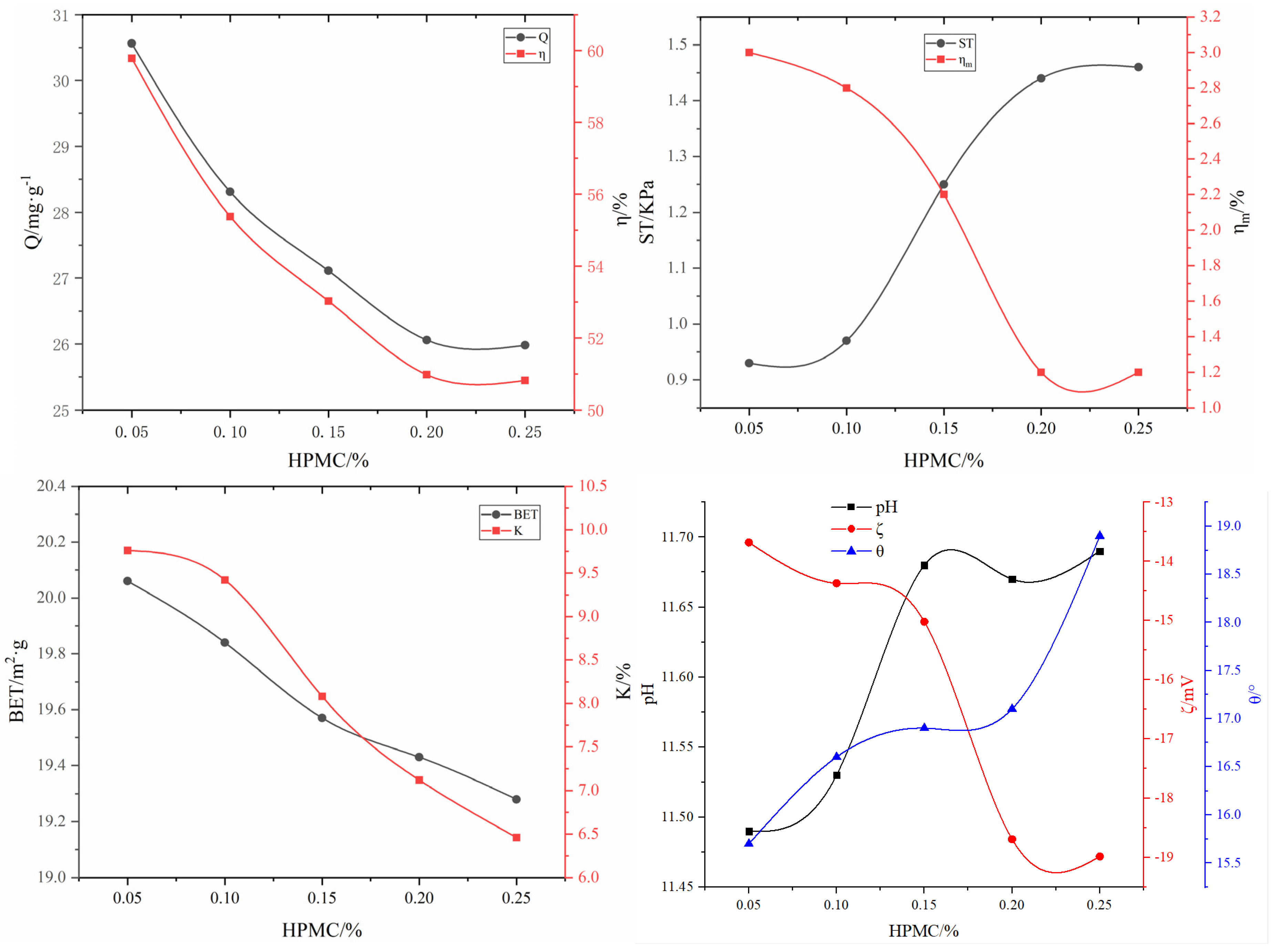
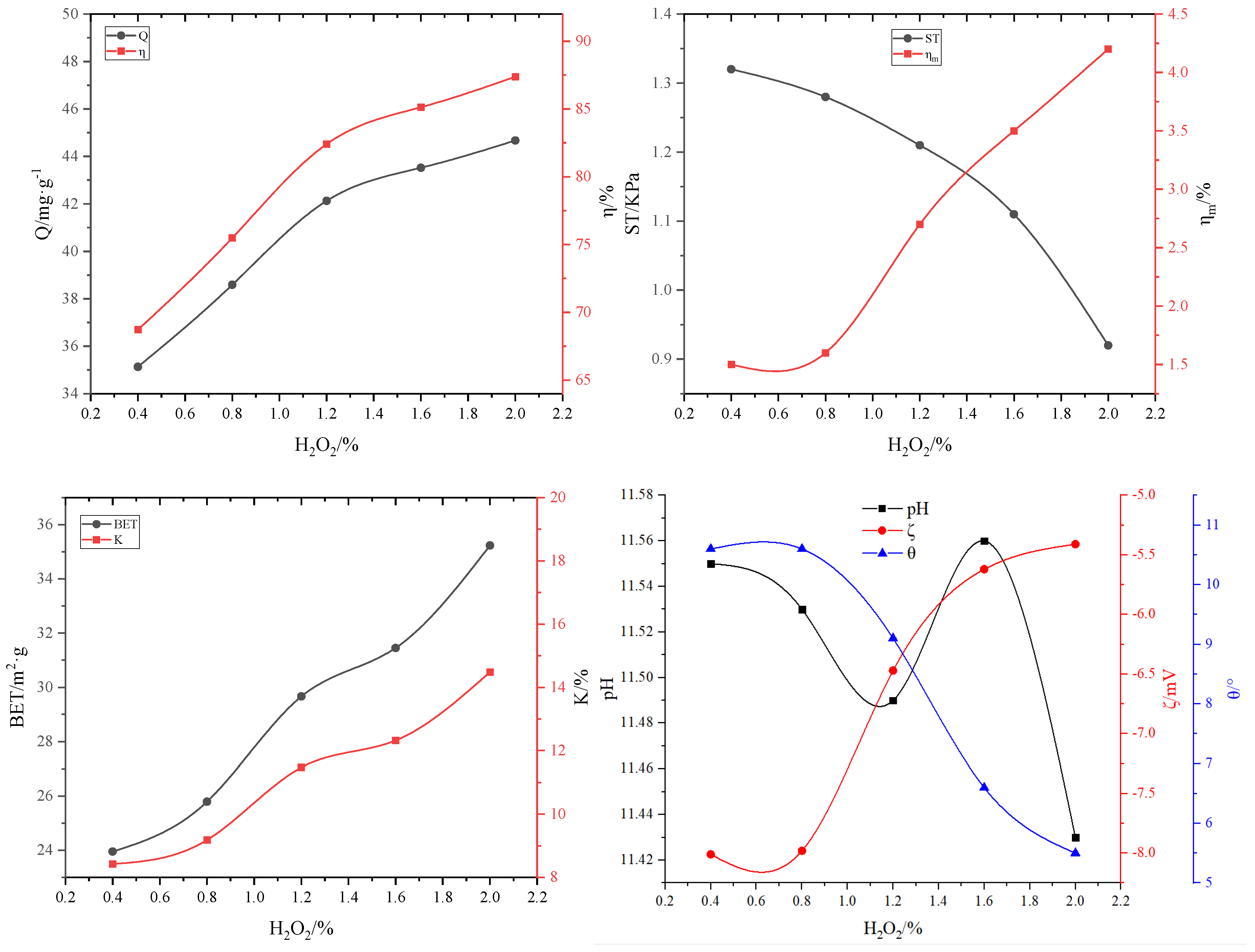
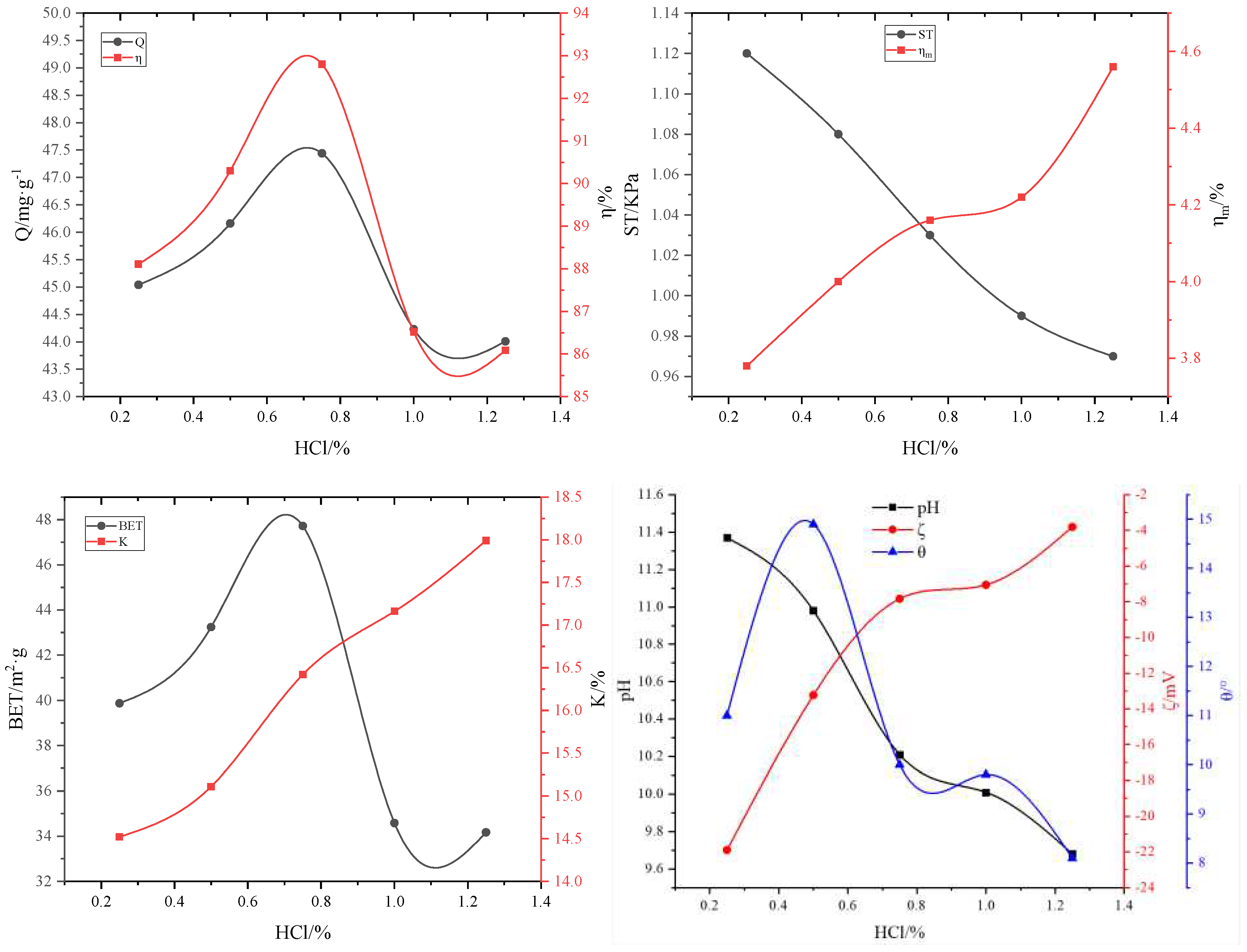
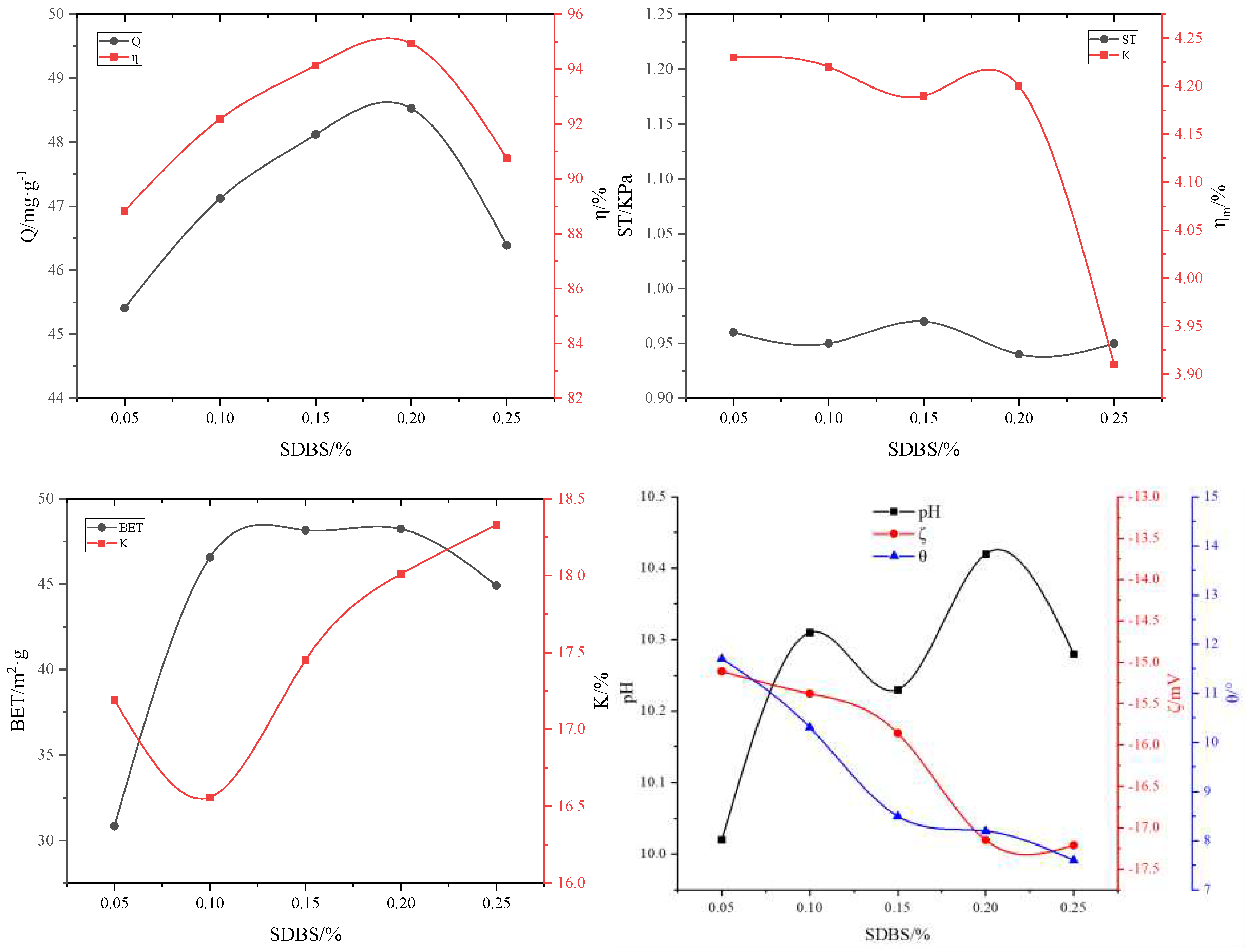
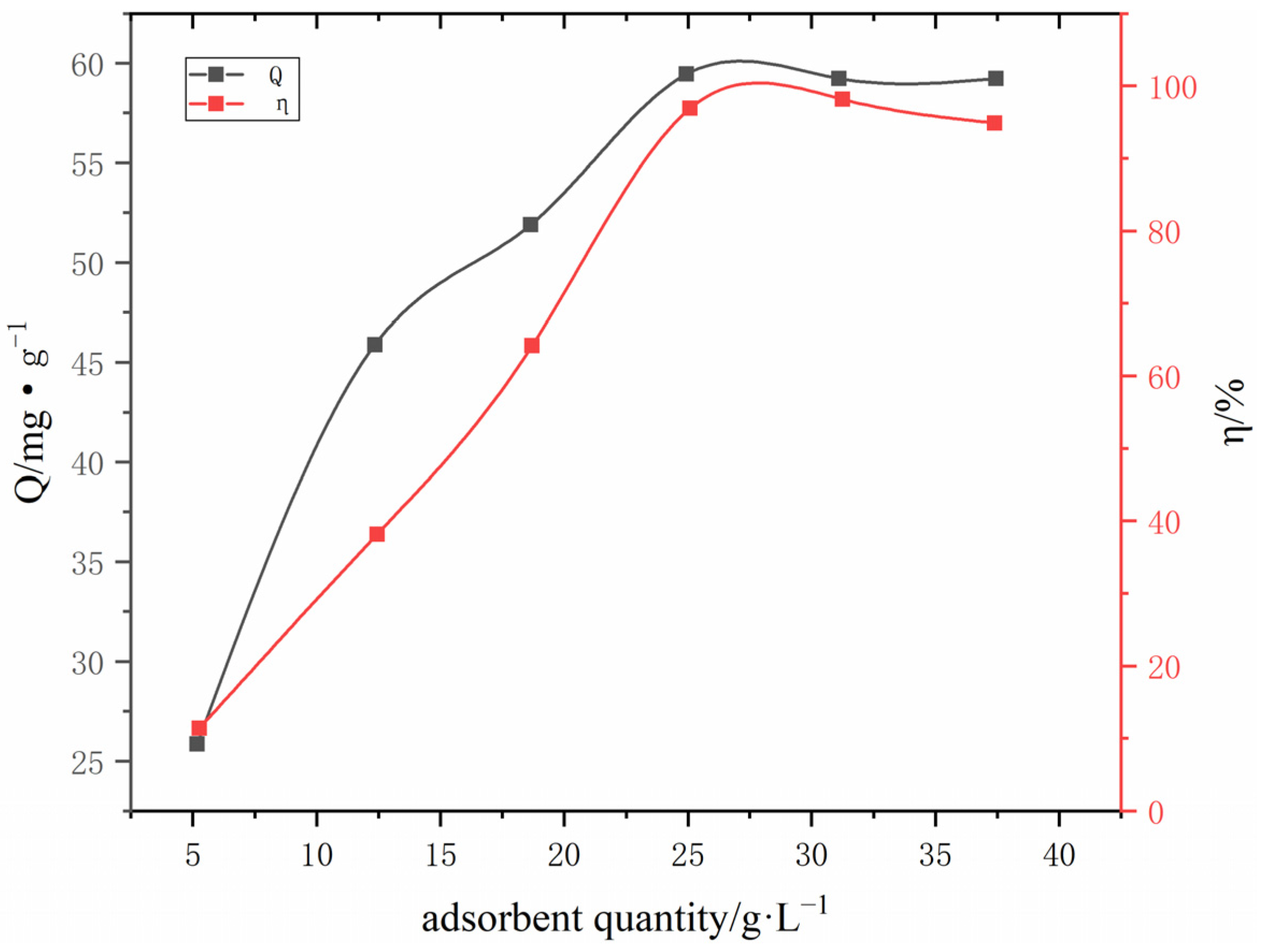
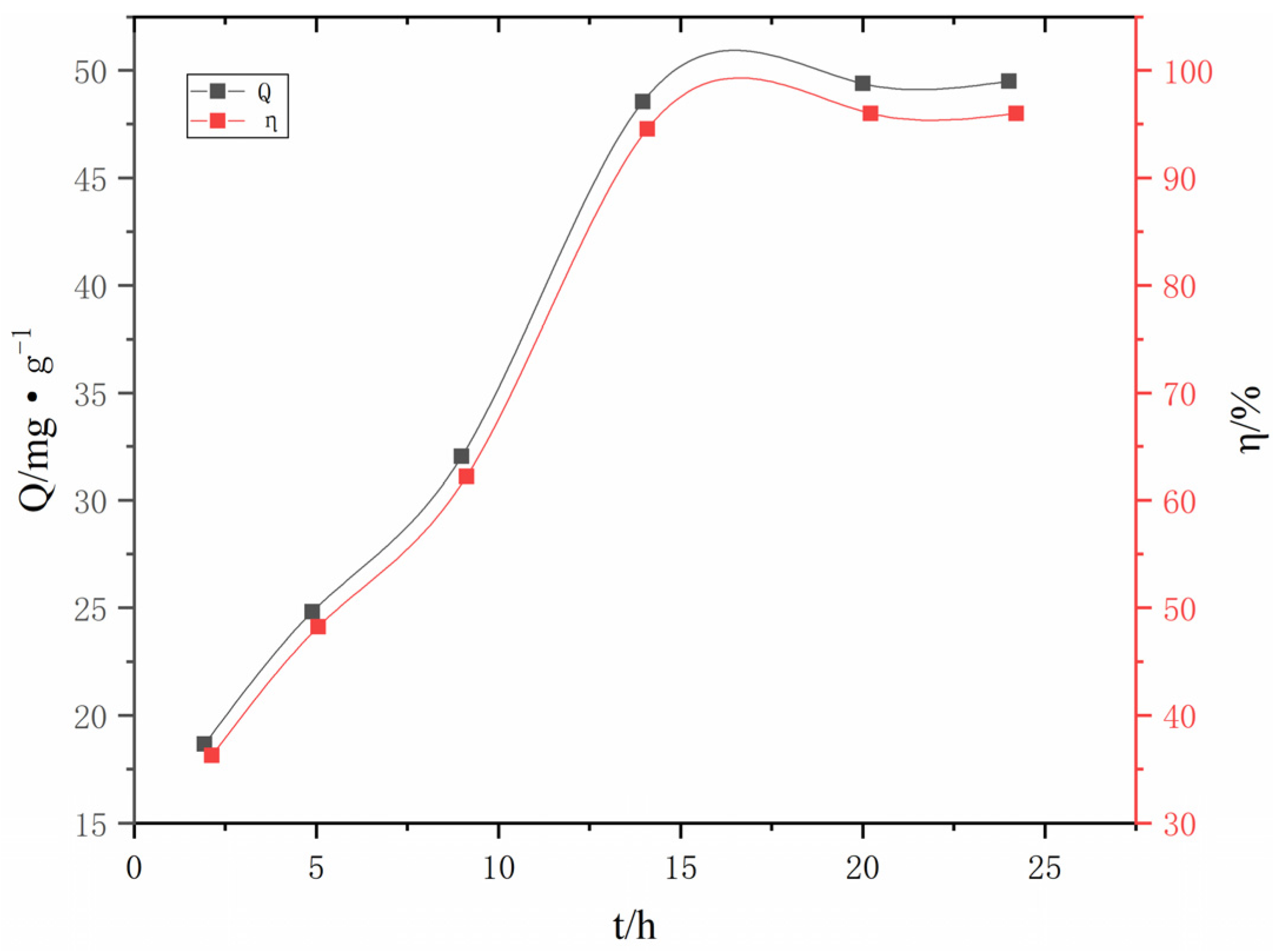
| #02-#06 | #07-#11 | #12-#16 | #17-#21 | #22-#26 | #27-#31 | ||
| RM/g | FA/% | A2C/% | HPMC/% | H2O2/% | MnO2/% | HCl/% | SDBS/% |
| 295 | 1.7 | 2 | 0.05 | 0.4 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.05 |
| 290 | 3.4 | 4 | 0.10 | 0.8 | 0.16 | 0.5 | 0.1 |
| 285 | 5.1 | 6 | 0.15 | 1.2 | 0.24 | 0.75 | 0.15 |
| 280 | 6.8 | 8 | 0.20 | 1.6 | 0.32 | 1.00 | 0.2 |
| 275 | 8.5 | 10 | 0.25 | 2.0 | 0.4 | 1.25 | 0.25 |
| BET/m2·g−1 | Zeta potential/mV | Wetting angle/° | Immersion pulverization rate/% | pH |
| 48.92 | −8.23 | 6.1 | 3.79 | 10.16 |
| Adsorption capacity of phosphorus/mg·g−1 | Removal rate of phosphorus/% | Compressive strength/KPa | Water absorption/% | |
| 48.63 | 95.13 | 1.12 | 16.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




