Submitted:
26 January 2024
Posted:
29 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
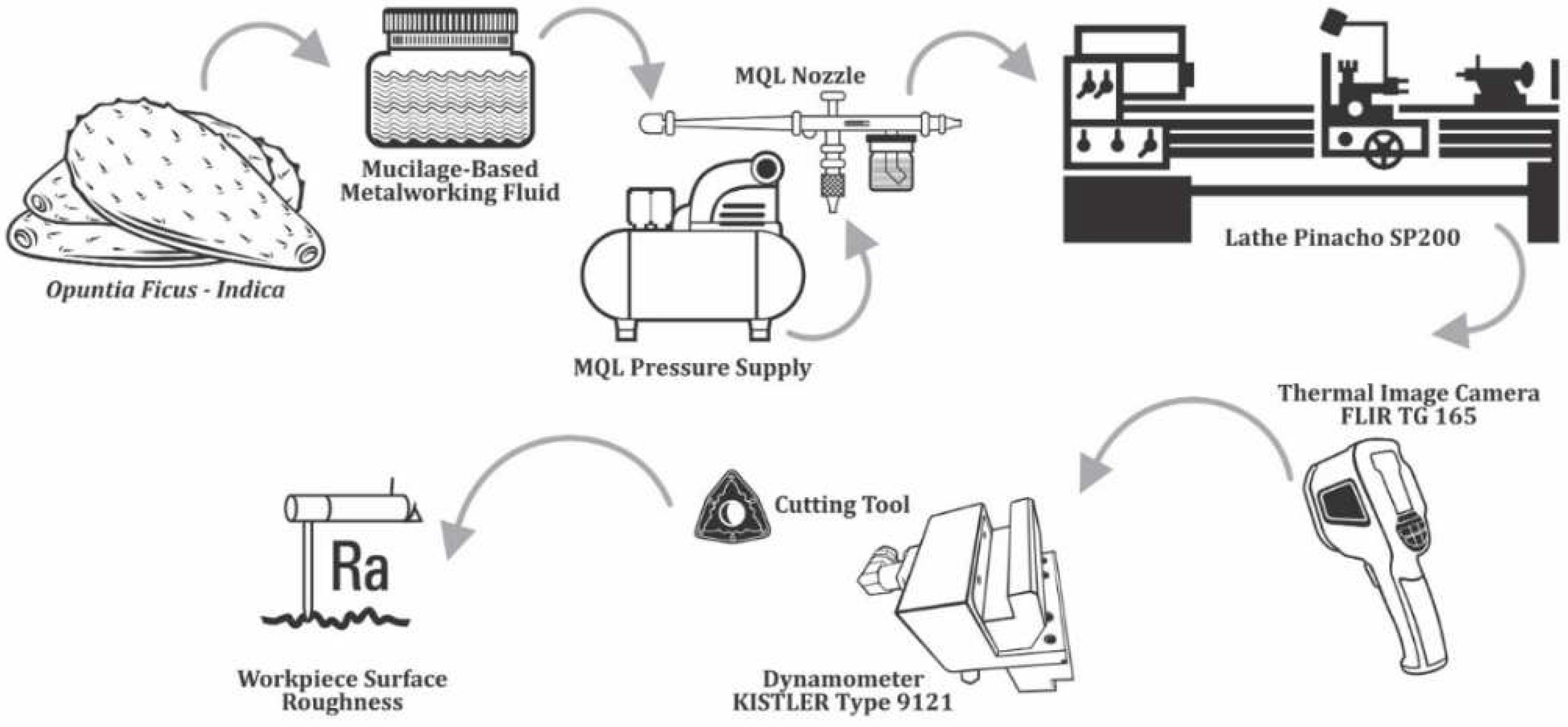
2.1. Preparation of fluid samples
2.2. Determination of the weight-average molecular weight (MW) of the mucilage
2.3. Rheological testing of the fluids
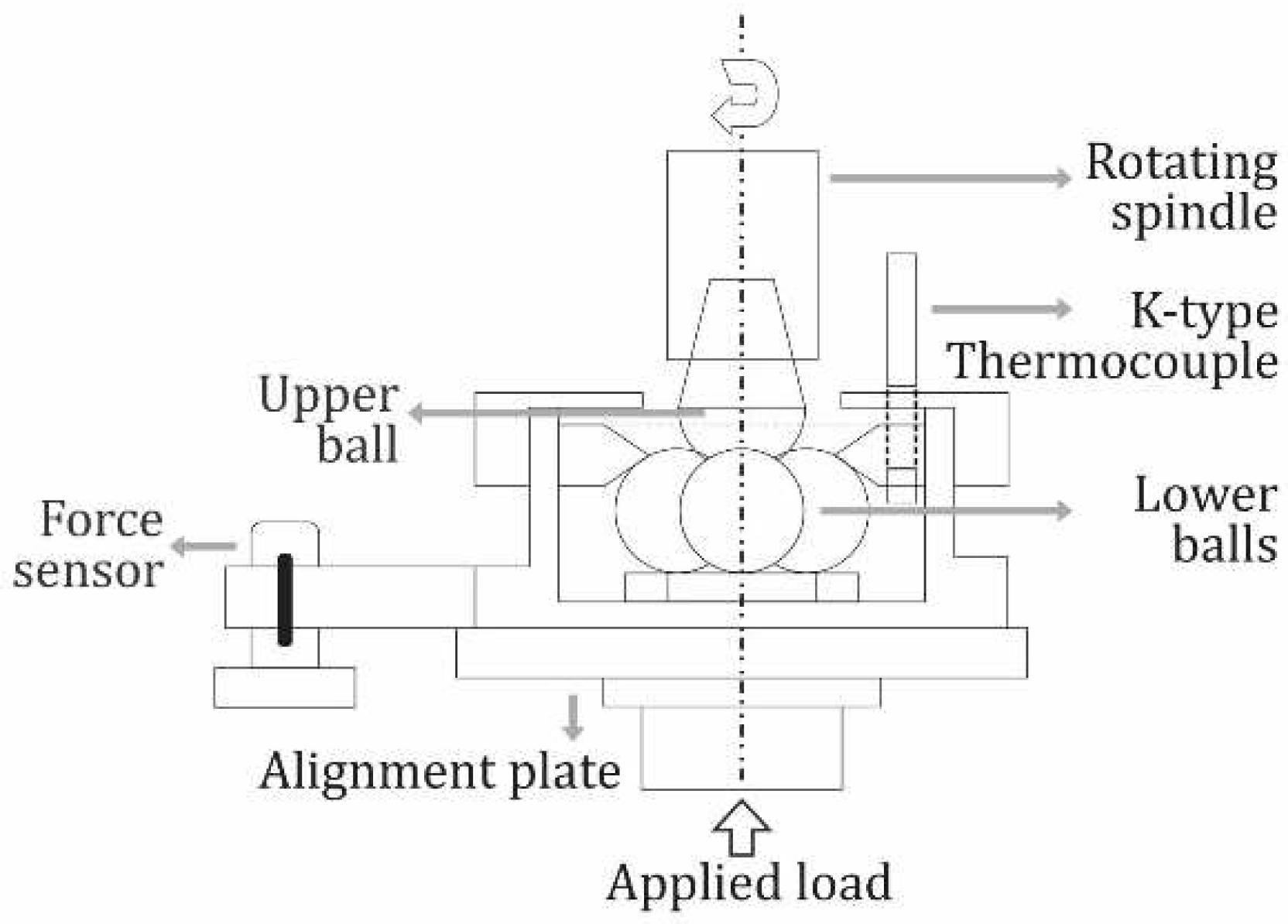
2.4. Tribological testing
2.5. Turning test
2.6. Thermal stability analysis
3. Results and Discussion
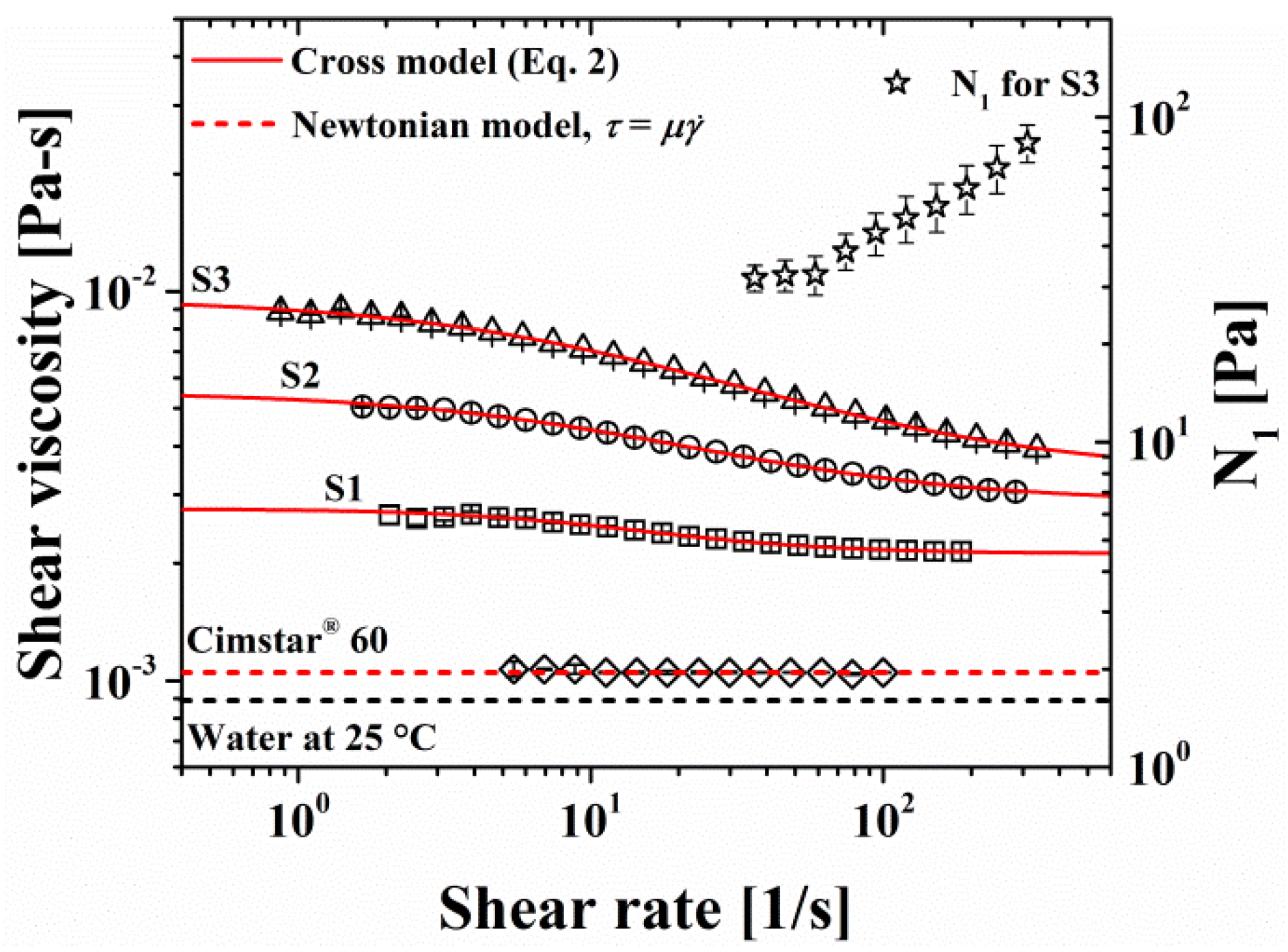
3.1. Rheological behavior of nopal mucilage solutions and cutting fluid
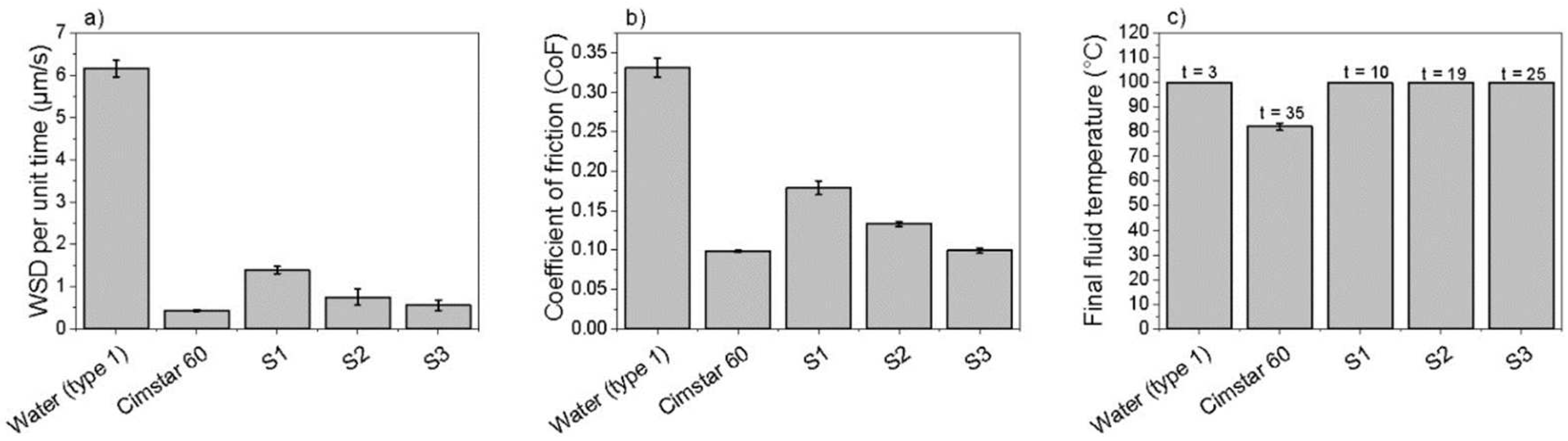
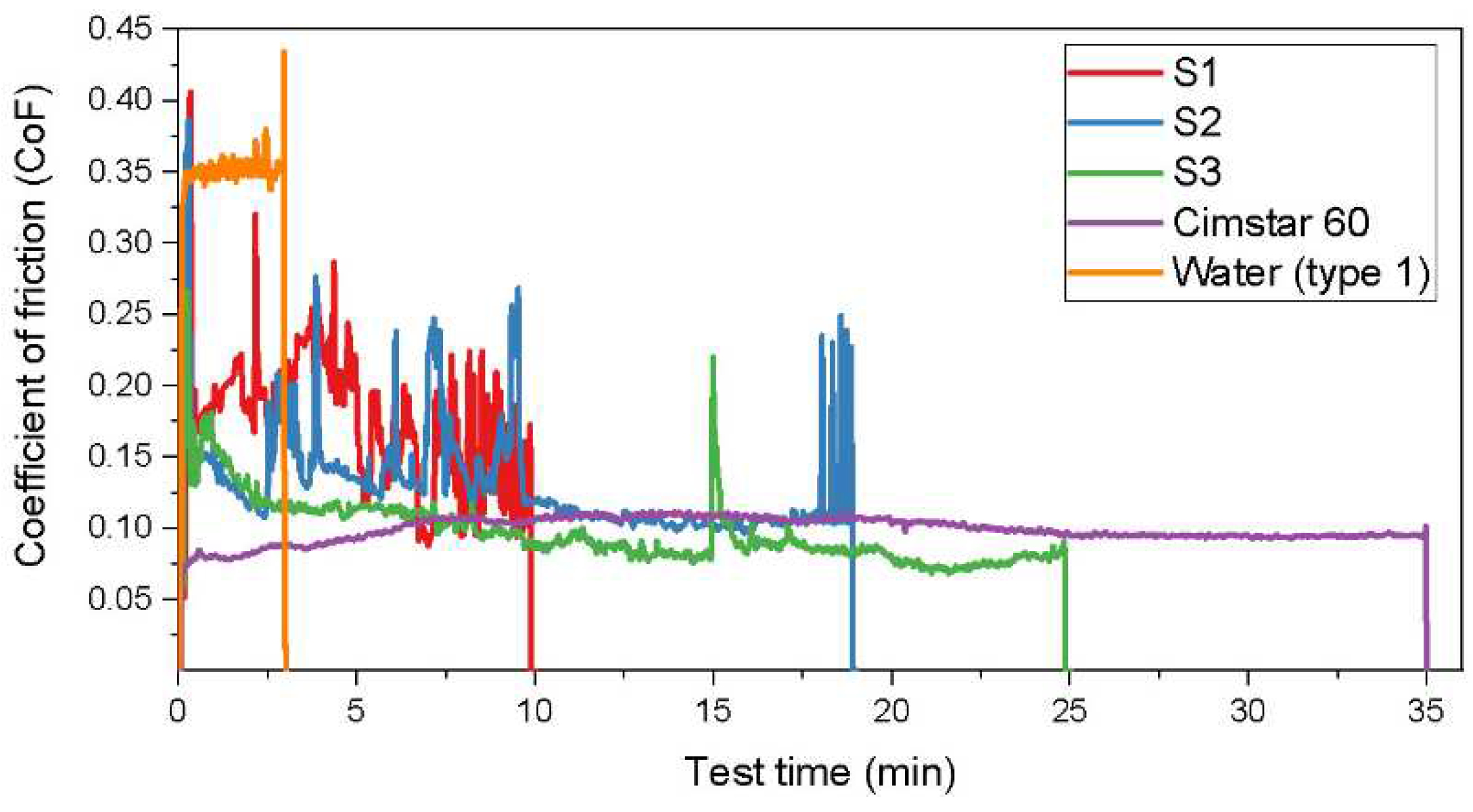
3.2. Tribological properties
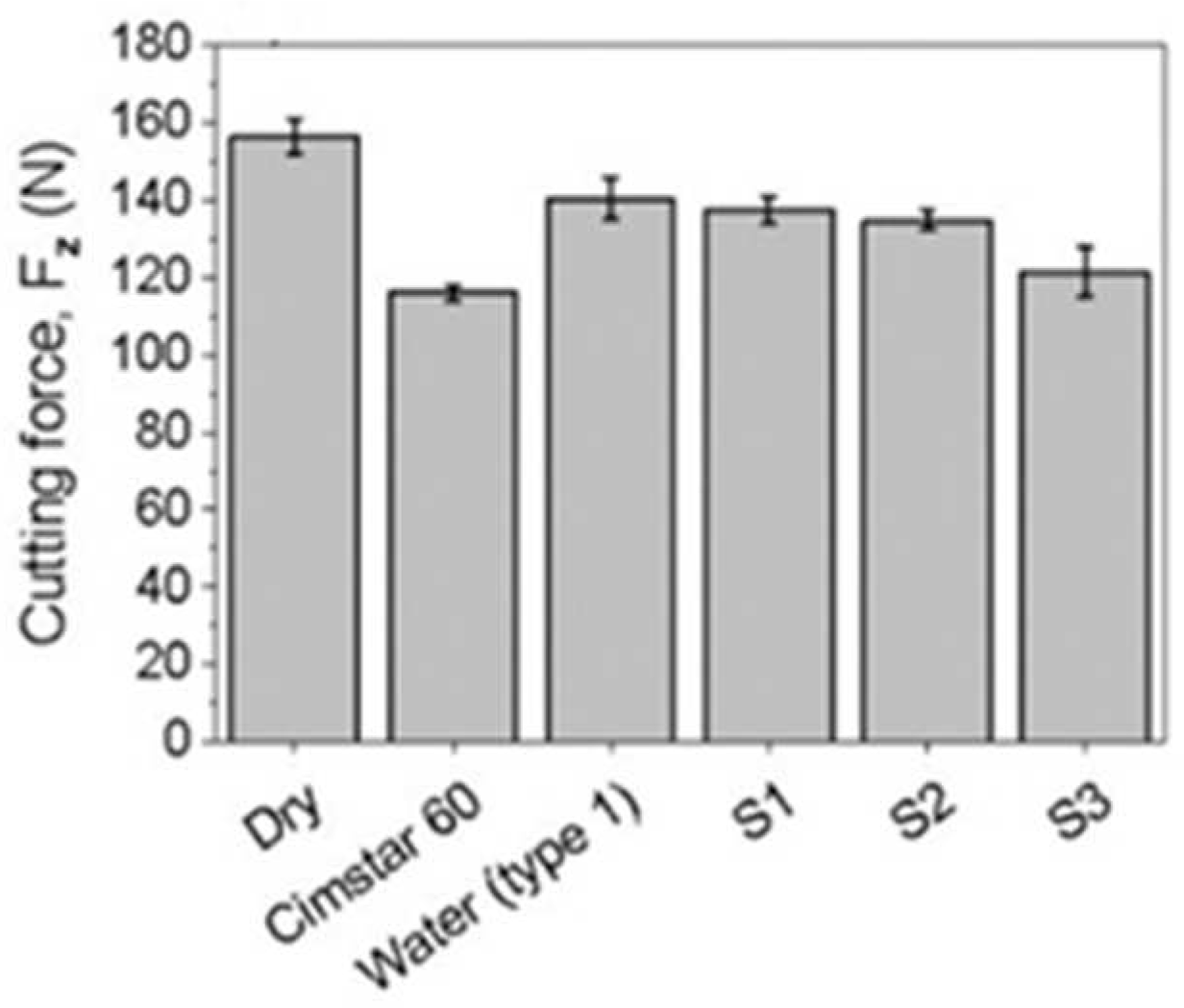
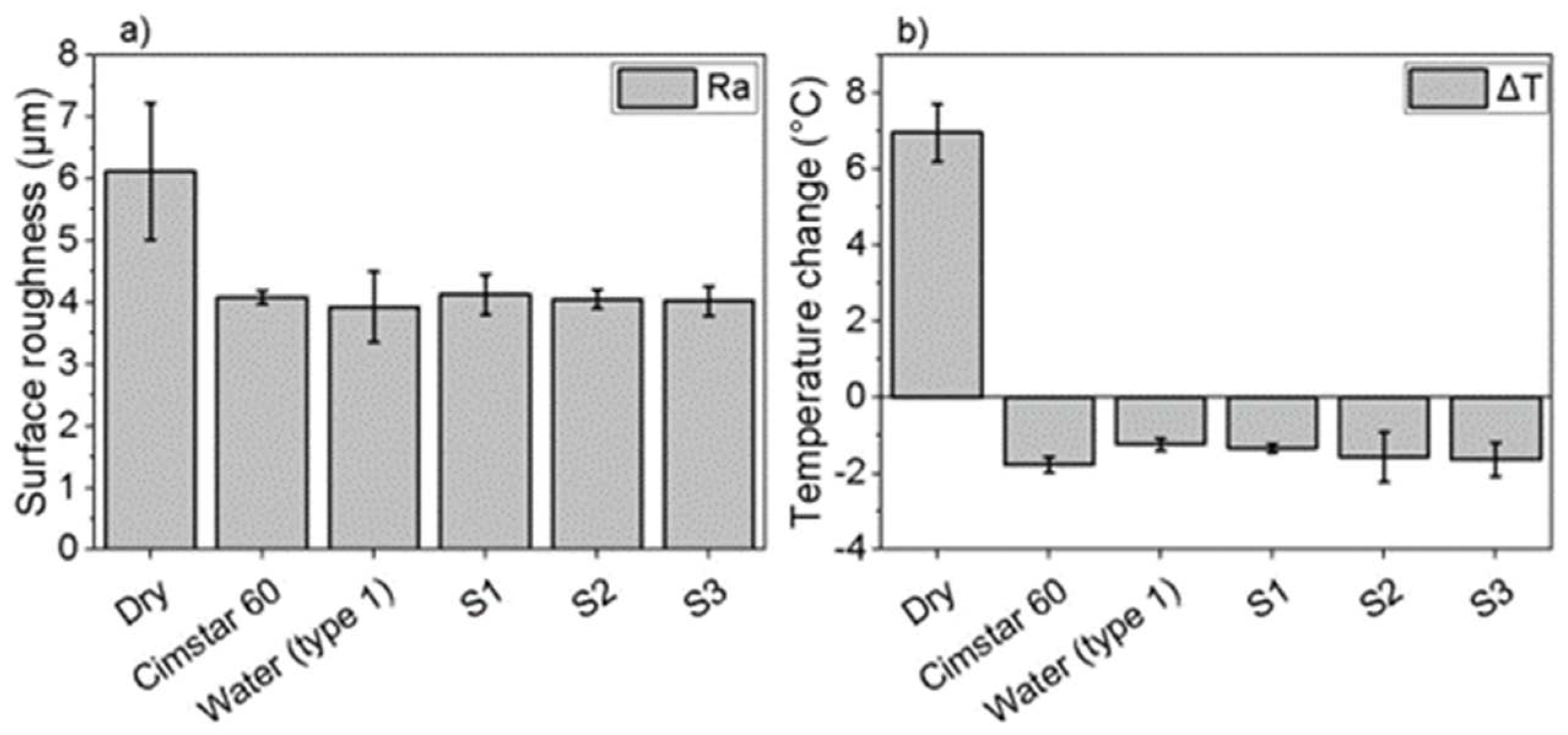
3.3. Turning performance
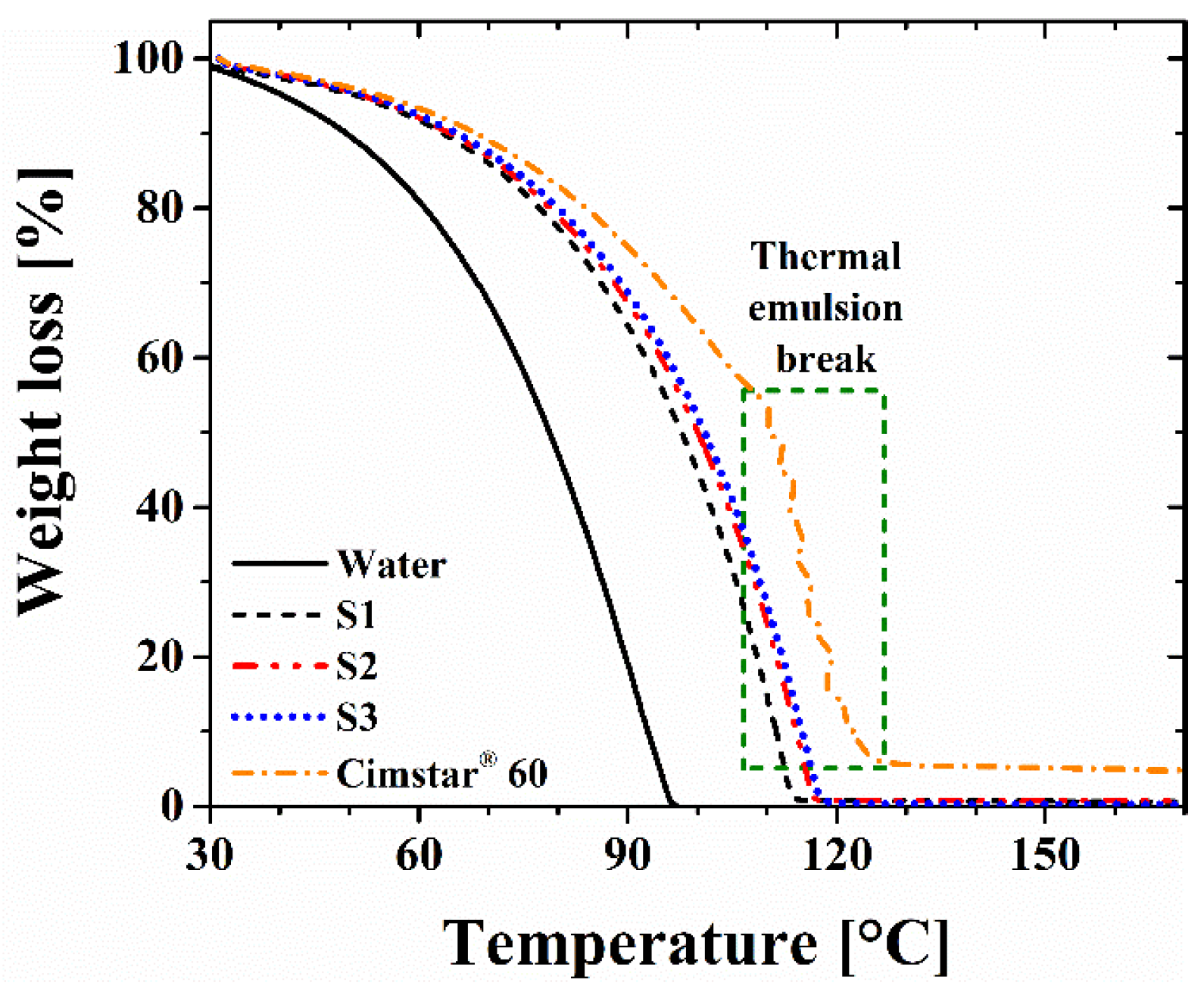
3.4. Thermal stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, S.-S., Song, J.-J., Xu, P., He, M., Xu, M.-B., & You, F.-C. (2023). A Review on Tribology Characterization and Lubricants for Water-Based Drilling Fluids. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. H., Warneke, H., Webbert, H., Rodriguez, J., Austin, E., Tokunaga, K., Rajak, D. K., & Menezes, P. L. (2021). Water-based lubricants: Development, properties, and performances. Lubricants, 9(8), 73. [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.L., Ingole, S.P., Nosonovsky, M., Kailas, S.V., Lovell, M.R. (2013). Tribology for Scientists and Engineers; Springer: New York, NY, USA.
- Lu, Q., Zhang, T., He, B., Xu, F., Liu, S., Ye, Q., & Zhou, F. (2022). Enhanced Lubricity and anti-wear performance of zwitterionic polymer-modified N-enriched porous carbon nanosheets as water-based lubricant additive. Tribology International, 167, 107421. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X., Jiang, G., Liu, F., He, Y., Liu, R., & Dong, T. (2023). Lubricity and mechanism of Catechol-based biomimetic lubricant in water-based drilling fluid. Tribology International, 188, 108862. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H., Zhao, J., Xia, W., Cheng, X., He, A., Yun, J. H., Wang, L., Huang, H., Jiao, S., Huang, L., Zhang, S., & Jiang, Z. (2017). A study of the tribological behaviour of tio2 nano-additive water-based lubricants. Tribology International, 109, 398–408. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C., Guo, Y., & Wang, D. (2019). Pei-RGO nanosheets as a nanoadditive for enhancing the tribological properties of water-based lubricants. Tribology International, 140, 105851. [CrossRef]
- Sagraloff, N., Dobler, A., Tobie, T., Stahl, K., & Ostrowski, J. (2019). Development of an oil free water-based lubricant for Gear Applications. Lubricants, 7(4), 33. [CrossRef]
- Wijanarko, W., Khanmohammadi, H., & Espallargas, N. (2022). Ionic liquid additives in water-based lubricants for bearing steel – effect of electrical conductivity and ph on surface chemistry, friction and Wear. Frontiers in Mechanical Engineering, 7. [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Rosas, O., Blanco, S., Flores, M., Shirai, K., & Farfan-Cabrera, L. I. (2022). Partially deacetylated and fibrillated shrimp waste-derived chitin as biopolymer emulsifier for green cutting fluids—towards a cleaner production. Polymers, 14(3), 525. [CrossRef]
- Katna, R., Suhaib, M., & Agrawal, N. (2019). Nonedible vegetable oil-based cutting fluids for machining processes–A Review. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 35(1), 1–32. [CrossRef]
- Farfan-Cabrera, L. I., Rojo-Valerio, A., Calderon-Najera, J. de, Coronado-Apodaca, K. G., Iqbal, H. M. N., Parra-Saldivar, R., Franco-Morgado, M., & Elias-Zuñiga, A. (2023). Microalgae oil-based metal working fluids for sustainable minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) operations—A perspective. Lubricants, 11(5), 215. [CrossRef]
- Nee, A.C., (2015). Handbook of Manufacturing Engineering and Technology. Springer Reference.
- Li, K., Aghazadeh, F., Hatipkarasulu, S., & Ray, T. G. (2003). Health risks from exposure to metal-working fluids in machining and grinding operations. International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics, 9(1), 75–95. [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, K. C., Sasahara, H., Rahim, E. A., & Perera, G. I. P. (2020). Green metalworking fluids for sustainable machining applications: A Review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 257, 120552. [CrossRef]
- Bambam, A. K., Dhanola, A., & Gajrani, K. K. (2023). A critical review on halogen-free ionic liquids as potential metalworking fluid additives. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 380, 121727. [CrossRef]
- Amiril, S. A. S., Rahim, E. A., Embong, Z., & Syahrullail, S. (2018). Tribological investigations on the application of oil-miscible ionic liquids additives in modified jatropha-based metalworking fluid. Tribology International, 120, 520–534. [CrossRef]
- Nessakh, F. Z., Mutelet, F., & Negadi, A. (2022). Efficiency of two working fluids constituted of a deep eutectic solvent and water in absorption heat transformer. International Journal of Energy Research, 46(15), 23578–23594. [CrossRef]
- HAYASHI, H. (1991). Recent studies on fluid film lubrication with non-newtonian lubricants. JSME International Journal. Ser. 3, Vibration, Control Engineering, Engineering for Industry, 34(1), 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Marx, N., Fernández, L., Barceló, F., & Spikes, H. (2018). Shear thinning and hydrodynamic friction of viscosity modifier-containing oils. part I: Shear thinning behaviour. Tribology Letters, 66(3). [CrossRef]
- Bair, S. (1998). Elastohydrodynamic film forming with shear thinning liquids. Journal of Tribology, 120(2), 173–178. [CrossRef]
- Bair, S., Vergne, P., & Marchetti, M. (2002). The effect of shear-thinning on film thickness for space lubricants. Tribology Transactions, 45(3), 330–333. [CrossRef]
- Bair, S., Habchi, W., Sperka, P., & Hartl, M. (2015). Quantitative elastohydrodynamic film forming for a gear oil with complex shear-thinning. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 230(3), 289–299. [CrossRef]
- Bair, S., Khonsari, M., & Winer, W. O. (1998). High-pressure rheology of lubricants and limitations of the Reynolds equation. Tribology International, 31(10), 573–586. [CrossRef]
- Hutton, J. F., Jackson, K. P., & Williamson, B. P. (1986). The effects of lubricant rheology on the performance of journal Bearings. A S L E Transactions, 29(1), 52–60. [CrossRef]
- Veltkamp, B., Jagielka, J., Velikov, K. P., & Bonn, D. (2023). Lubrication with non-newtonian fluids. Physical Review Applied, 19(1). [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, T.G., Pereira, P., Silva, M.A., Vicente, F., Ramalho, R., Costa, H.S. (2020). Chapter 44 - Prickly pear. A.K. Jaiswal (Ed.), Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Fruits and Vegetables, Academic Press, pp. 709-728. [CrossRef]
- El-Mostafa, K., El Kharrassi, Y., Badreddine, A., Andreoletti, P., Vamecq, J., El Kebbaj, M., Latruffe, N., Lizard, G., Nasser, B., & Cherkaoui-Malki, M. (2014). Nopal cactus (opuntia ficus-indica) as a source of bioactive compounds for nutrition, health and disease. Molecules, 19(9), 14879–14901. [CrossRef]
- Stintzing, F. C., Schieber, A., & Carle, R. (2001). Phytochemical and nutritional significance of Cactus Pear. European Food Research and Technology, 212(4), 396–407. [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Solano, S.V., Rodríguez-González, F., Martínez-Velarde, R., Campos-Mendiola, R., Hurtado-Salgado, M.A., Muthuswamy Ponniah, J. (2022a). Chemical composition of pear cactus mucilage at different maturity stages. Agrociencia. [CrossRef]
- Trachtenberg, S., & Mayer, A. M. (1981). Composition and properties of Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage. Phytochemistry, 20, 2665–2668. [CrossRef]
- Goycoolea, M., Cárdenas, A. (2003). Pectins from Opuntia spp.: a short review. Journal of the professional association for cactus development, 5, 17-29. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-González, F., Pérez-González, J., Muñoz-López, C. N., Vargas-Solano, S.V. & Marín-Santibáñez, B.M. (2021). Influence of age on molecular characteristics and rheological behavior of nopal mucilage. Food Science & Nutrition, 9(12), 6776-6785. [CrossRef]
- Tosif, M. M., Najda, A., Bains, A., Kaushik, R., Dhull, S. B., Chawla, P., & Walasek-Janusz, M. (2021). A comprehensive review on plant-derived mucilage: Characterization, functional properties, applications, and its utilization for Nanocarrier Fabrication. Polymers, 13(7), 1066. [CrossRef]
- Maki-Díaz, G., Peña-Valdivia, C. B., García-Nava, R., Arévalo-Galarza, M. L., Calderón-Zavala, G., & Anaya-Rosales, S. (2015). Características físicas y químicas de nopal verdura (Opuntia ficus-indica) para exportación y consumo nacional. Agrociencia, 49(1), 31-51.
- ASTM. (2021). Standard D4172-21, Standard Test Method for Wear Preventive Characteristics of Lubricating Fluid (Four-Ball Method), ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2021. www.astm.org.
- Singh, G., Aggarwal, V., & Singh, S. (2020). Critical review on ecological, economical and technological aspects of minimum quantity lubrication towards sustainable machining. Journal of Cleaner Production, 271, 122185. [CrossRef]
- Bair, S., & Qureshi, F. (2003). Ordinary shear thinning behavior and its effect upon EHL film thickness. Tribology Series, 693–699. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Azam, A., Zhang, G., Dorgham, A., Liu, Y., Wilson, M. C., & Neville, A. (2022). Understanding the mechanism of load-carrying capacity between parallel rough surfaces through a deterministic mixed lubrication model. Lubricants, 10(1), 12. [CrossRef]
- Hu, S., Meng, F., & Doi, M. (2023). Effect of fluid viscoelasticity, shear stress, and interface tension on the lift force in lubricated contacts. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 159(16). [CrossRef]
- Farfan-Cabrera, L. I., Franco-Morgado, M., González-Sánchez, A., Pérez-González, J., & Marín-Santibáñez, B. M. (2022). Microalgae biomass as a new potential source of sustainable green lubricants. Molecules, 27(4), 1205. [CrossRef]
- Zainal, N. A., Zulkifli, N. W. M., Gulzar, M., & Masjuki, H. H. (2018). A review on the chemistry, production, and technological potential of bio-based lubricants. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 82, 80–102. [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M. F., & Mörsel, J. T. (2003). Recovered lipids from prickly pear [opuntia ficus-indica (L.) mill] peel: A good source of polyunsaturated fatty acids, natural antioxidant vitamins and sterols. Food Chemistry, 83(3), 447–456. [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Rosas, O.A., Alvis-Sánchez, J.A., Tormos, B., Marín-Santibáñez, B.M., Pérez-González, J., & Farfan-Cabrera, L.I. (2023). Enhancement of low-viscosity synthetic oil using graphene nanoparticles as additives for enduring electrified tribological environments. Tribology International, 188, 108848. [CrossRef]
- Nagabhooshanam, N., Baskar, S., Prabhu, T. R., & Arumugam, S. (2020). Evaluation of tribological characteristics of nano zirconia dispersed biodegradable canola oil methyl ester metalworking fluid. Tribology International, 151, 106510. [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value | |
| Fluid sample quantity (mL) | 25 | |
| Starting temperature (°C) | 25±1 | |
| Relative humidity (%) | 36 | |
| Machine speed (RPM) | 1200 | |
| Load (kg) | 40 | |
| Length of lever arm (cm) | 5.275 | |
| Test duration (min) | Water (type 1) | 3 |
| Cimstar 60 in tap water | 35 | |
| S1 | 10 | |
| S2 | 19 | |
| S3 | 25 | |
| Test repeats | 3 | |
| Parameter | Type/value | |
| Lubrication | Lubrication type | MQL |
| Fluid feed (m3/h) | 4x10-5 | |
| Air pressure (MPa) | 0.4 | |
| Fluid nozzle diameter (mm) | 20 | |
| Nozzle-workpiece distance (mm) | 0.4 | |
| Cutting process | Workpiece material | AISI 1018 steel bars (25.4mm diameter) |
| Cutting tool | WNmG 080404e-Fm Grade T9325 (Pramet) coated carbide insert | |
| Surface Speed (m/min) | 70 | |
| Rotational Speed (RPM) | 860 | |
| Feed (mm/rev) | 0.15 | |
| Cutting time (s) | 39±2 | |
| Depth of Cut (mm) | 0.5 | |
| Room temperature (°C) | 25±1 | |
| Test repeats | 4 | |
| Nopal mucilage solutions | Cross model parameters | |||
| η0 [mPa-s] | η∞ [mPa-s] | c [s] | p [1] | |
| S1 | 2.76±0.019 | 2.12±0.004 | 0.073±0.003 | 1.26±0.04 |
| S2 | 5.52±0.059 | 2.87±0.048 | 0.067±0.002 | 0.832±0.039 |
| S3 | 9.61±0.119 | 3.38±0.043 | 0.062±0.002 | 0.751±0.022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





