Submitted:
24 January 2024
Posted:
25 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.2. Polyphenols, alkaloids and saponins
1.2.1. Polyphenols
1.2.2. Alkaloids
1.2.3. Saponins
1.2.4. Terpenes
1.2. Relationship between lifestyle, oxidative stress, and inflammation in overweight and obesity
2. Action Mechanisms of Phytochemicals against Overweight and Obesity
2.1. Lipase Inhibitors
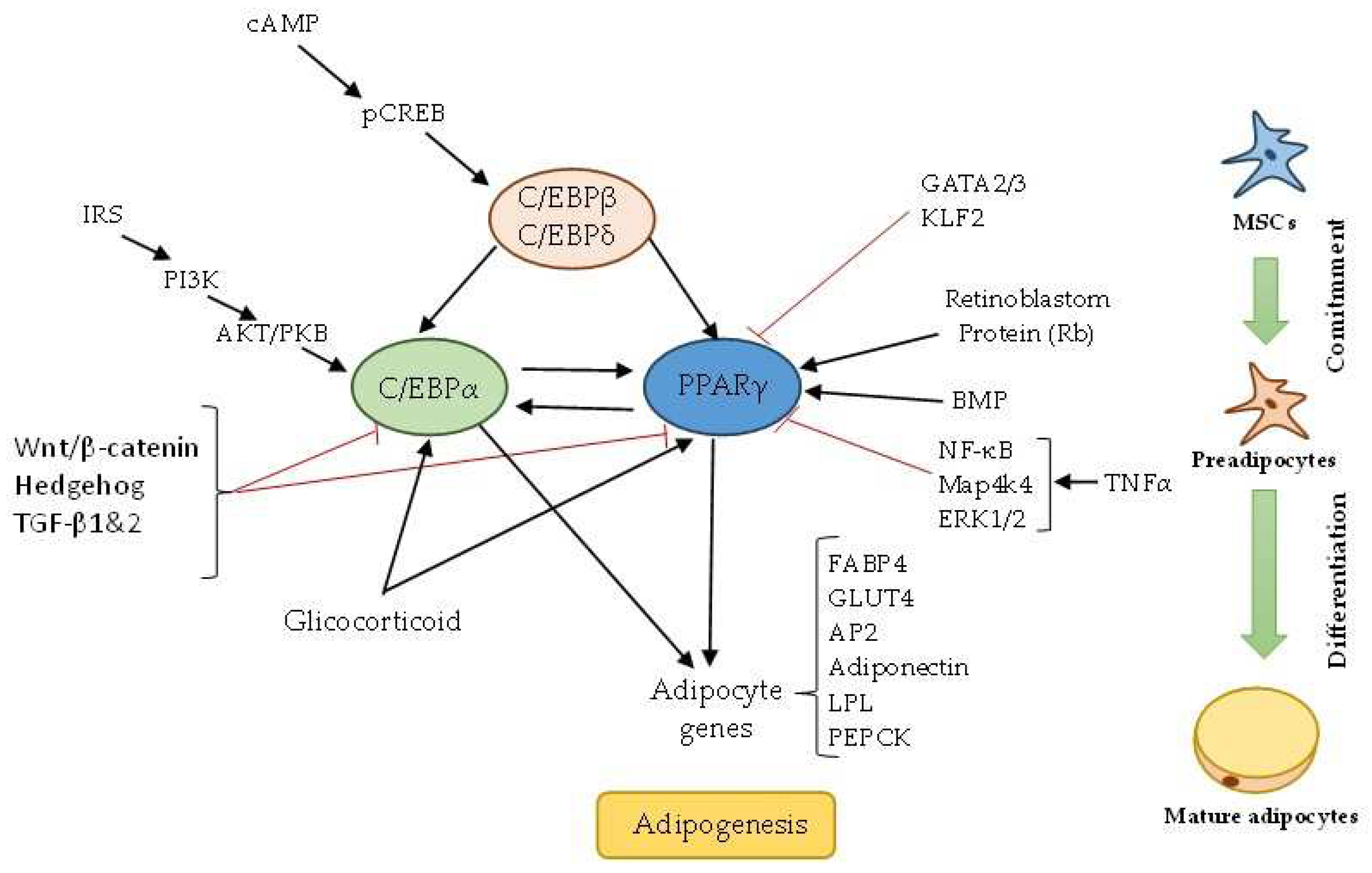
2.2. Regulation of Adipogenesis
2.3. Thermogenesis
2.5. Appetite Suppressants
3. Alkaloids modulating overweight and obesity.
4. Saponins modulating overweight and obesity.
5. Terpenes modulating overweight and obesity.
6. Conclusions and perspectives
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Adult obesity facts. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Overweight and obesity statistics. Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/overweight-obesity (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Pledger, S.L.; Ahmadizar, F. Gene-environment interactions and the effect on obesity risk in low and middle-income countries: a scoping review. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withrow, D.; Alter, D.A. The economic burden of obesity worldwide: a systematic review of the direct costs of obesity. Obesity Reviews 2011, 12, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Castejón, M.; Rodriguez-Casado, A. Dietary phytochemicals and their potential effects on obesity: A review. Pharmacological Research 2011, 64, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Grijalva, E.P.; Leyva-López, N.; Vazquez-Olivo, G.; Heredia, J.B. Oregano as a potential source of antidiabetic agents. J Food Biochem 2022, 46, e14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, S.; Molath, A.; Choksi, H.; Kumar, S.; Mehra, R. Classifications of polyphenols and their potential application in human health and diseases. Int. J. Physiol. Nutr. Phys. Educ 2021, 6, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Croft, K.D.; Kennedy, D.O.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health. Food Funct 2019, 10, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukula-Koch, W.; Widelski, J. Alkaloids. 2017; pp. 163-198.
- Abookleesh, F.L.; Al-Anzi, B.S.; Ullah, A. Potential Antiviral Action of Alkaloids. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.F. Alkaloids: Biochemistry, Ecology, and Medicinal Applications; Springer US: 2013.
- Aguilar Salguero, S.A. Relación de la estructura de las saponinas con sus aplicaciones, una revisión actualizada. 2022.
- Brahmkshatriya, P.P.; Brahmkshatriya, P.S. Terpenes: Chemistry, Biological Role, and Therapeutic Applications. In Natural Products: Phytochemistry, Botany and Metabolism of Alkaloids, Phenolics and Terpenes, Ramawat, K.G., Mérillon, J.-M., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2013; pp. 2665–2691. [Google Scholar]
- Roba, K. The role of terpene (secondary metabolite). Nat. Prod. Chem. Res. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Mabou, F.D.; Yossa, I.B.N. TERPENES: Structural classification and biological activities. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. e-ISSN 2021, 16, 2319–7676. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Sánchez, A.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Bautista, M.; Esquivel-Soto, J.; Morales-González, A.; Esquivel-Chirino, C.; Durante-Montiel, I.; Sánchez-Rivera, G.; Valadez-Vega, C.; Morales-González, J.A. Inflammation, oxidative stress, and obesity. Int J Mol Sci 2011, 12, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biobaku, F.; Ghanim, H.; Batra, M.; Dandona, P. Macronutrient-Mediated Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Relevance to Insulin Resistance, Obesity, and Atherogenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2019, 104, 6118–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karam, B.S.; Chavez-Moreno, A.; Koh, W.; Akar, J.G.; Akar, F.G. Oxidative stress and inflammation as central mediators of atrial fibrillation in obesity and diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2017, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Torres, I.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Rubio-Ruiz, M.E. Reductive Stress in Inflammation-Associated Diseases and the Pro-Oxidant Effect of Antioxidant Agents. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Torres, I.; Castrejón-Téllez, V.; Soto, M.E.; Rubio-Ruiz, M.E.; Manzano-Pech, L.; Guarner-Lans, V. Oxidative Stress, Plant Natural Antioxidants, and Obesity. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, R.; Azevedo, I. Chronic inflammation in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Mediators Inflamm 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikaris, K.A. The clinical biochemistry of obesity. The Clinical Biochemist Reviews 2004, 25, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, B.; Friar, E.P.; Vohra, M.S.; Garrett, M.D.; Serpell, C.J.; Fong, I.L.; Wong, E.H. Mechanisms of action for the anti-obesogenic activities of phytochemicals. Phytochemistry 2020, 180, 112513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A.T.M.A.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamaki, K. Mode of pancreatic lipase inhibition activity in vitro by some flavonoids and non-flavonoid polyphenols. Food Research International 2015, 75, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ràfols, E.M. Tejido adiposo: heterogeneidad celular y diversidad funcional. Endocrinología y Nutrición 2014, 6, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.Q.; Lane, M.D. Adipogenesis: From Stem Cell to Adipocyte. Annual Review of Biochemistry 2012, 81, 715–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakab, J.; Miškić, B.; Mikšić, Š.; Juranić, B.; Ćosić, V.; Schwarz, D.; Včev, A. Adipogenesis as a Potential Anti-Obesity Target: A Review of Pharmacological Treatment and Natural Products. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity 2021, 14, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Shou, P.; Zheng, C.; Jiang, M.; Cao, G.; Yang, Q.; Cao, J.; Xie, N.; Velletri, T.; Zhang, X.; et al. Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells: adipocytes or osteoblasts? Cell Death & Differentiation 2016, 23, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Nic-Can, G.I.; Rodas-Junco, B.A.; Carrillo-Cocom, L.M.; Zepeda-Pedreguera, A.; Peñaloza-Cuevas, R.; Aguilar-Ayala, F.J.; Rojas-Herrera, R.A. Epigenetic Regulation of Adipogenic Differentiation by Histone Lysine Demethylation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Liu, D.; Zeng, R.; Xian, T.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Sun, Z.; Huang, B.; Huang, Q. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits adipogenesis through down-regulation of PPARγ and FAS expression mediated by PI3K-AKT signaling in 3T3-L1 cells. European Journal of Pharmacology 2017, 795, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, M.; Ganjayi, M.S.; Hanuma Kumar, G.E.N.; Parim, B.N.; Mopuri, R.; Dasari, S. A review on possible therapeutic targets to contain obesity: The role of phytochemicals. Obesity Research & Clinical Practice 2016, 10, 363–380. [Google Scholar]
- Khalilpourfarshbafi, M.; Gholami, K.; Murugan, D.D.; Abdul Sattar, M.Z.; Abdullah, N.A. Differential effects of dietary flavonoids on adipogenesis. European Journal of Nutrition 2019, 58, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambele, M.A.; Dhanraj, P.; Giles, R.; Pepper, M.S. Adipogenesis: A Complex Interplay of Multiple Molecular Determinants and Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Li, Y.; Shu, T.; Wang, J. Cytokines and inflammation in adipogenesis: an updated review. Frontiers of Medicine 2019, 13, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.H.; Ka, S.; Kim, A.Y.; Kim, J.B. Regulation of Adipocyte Differentiation via MicroRNAs. enm 2014, 29, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, C.E.; O'Rahilly, S.; Rochford, J.J. Adipogenesis at a glance. Journal of Cell Science 2011, 124, 2681–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Virtue, S.; Goie, J.Y.G.; Png, C.W.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Jiao, H.; Chua, Y.L.; Campbell, M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; et al. Regulation of adipogenic differentiation and adipose tissue inflammation by interferon regulatory factor 3. Cell Death & Differentiation 2021, 28, 3022–3035. [Google Scholar]
- Linda, C.; Urarat, N.; Rawiwun, K.; Sudarat, H.; Wanwisa, S. Inhibitory Effect of Carallia Brachiata Extract Through Regulation of Adipogenesis Pathways in 3T3-L1 Cells. Pharmacognosy Journal 2022, 14, 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Audano, M.; Pedretti, S.; Caruso, D.; Crestani, M.; De Fabiani, E.; Mitro, N. Regulatory mechanisms of the early phase of white adipocyte differentiation: an overview. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2022, 79, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, R.; Firmal, P.; Shah, V.K.; Alam, A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Epigenetic Regulation of Adipogenesis in Development of Metabolic Syndrome. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8, 619888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Matsushita, M.; Yoneshiro, T.; Okamatsu-Ogura, Y. Brown Adipose Tissue, Diet-Induced Thermogenesis, and Thermogenic Food Ingredients: From Mice to Men. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouchani, E.T.; Kazak, L.; Spiegelman, B.M. New advances in adaptive thermogenesis: UCP1 and beyond. Cell metabolism 2019, 29, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Zhu, X.; Maretich, P.; Chen, Y. Combating Obesity With Thermogenic Fat: Current Challenges and Advancements. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Chen, Y. Recruitment of Thermogenic Fat: Trigger of Fat Burning. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Kim, M.-S. Molecular Mechanisms of Appetite Regulation. dmj 2012, 36, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Elkhayat, E.S.; El Dine, R.S. Natural anti-obesity agents. Bulletin of Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University 2014, 52, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.S.; Bloom, S.R. The regulation of food intake by the gut-brain axis: implications for obesity. International Journal of Obesity 2013, 37, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. Natural Products with Anti-obesity Effects and Different Mechanisms of Action. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2016, 64, 9571–9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thawabteh, A.; Juma, S.; Bader, M.; Karaman, D.; Scrano, L.; Bufo, S.A.; Karaman, R. The Biological Activity of Natural Alkaloids against Herbivores, Cancerous Cells and Pathogens. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Grijalva, E.P.; López-Martínez, L.X.; Contreras-Angulo, L.A.; Elizalde-Romero, C.A.; Heredia, J.B. Plant Alkaloids: Structures and Bioactive Properties. In Plant-derived Bioactives: Chemistry and Mode of Action, Swamy, M.K., Ed.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2020; pp. 85–117. [Google Scholar]
- Balaji, M.; Ganjayi, M.S.; Kumar, G.E.H.; Parim, B.N.; Mopuri, R.; Dasari, S. A review on possible therapeutic targets to contain obesity: The role of phytochemicals. Obesity research & clinical practice 2016, 10, 363–380. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.; Yu, H.; Gao, L.; Lu, Y.-T.; Xu, Z.; Liu, H.; Gu, L.-Q.; Ye, J.-M.; Huang, Z.-S. Natural alkaloid bouchardatine ameliorates metabolic disorders in high-fat diet-fed mice by stimulating the sirtuin 1/liver kinase B-1/AMPK axis. British Journal of Pharmacology 2017, 174, 2457–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Lian, C.-F.; Sun, Q.-W.; Wang, T.-T.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Ye, J.; Gao, L.-L.; Yang, Y.-F.; Liu, S.-N.; Shen, Z.-F.; et al. Ramulus Mori (Sangzhi) Alkaloids Alleviate High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirillo, A.; Catapano, A.L. Berberine, a plant alkaloid with lipid- and glucose-lowering properties: From in vitro evidence to clinical studies. Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Woo, S.L.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, J.; Botchlett, R.; Liu, M.; Pei, Y.; Xu, H.; Cai, Y.; et al. Berberine Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis and Suppresses Liver and Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Mice with Diet-induced Obesity. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 22612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Feng, X.; Liu, X.; Deng, C.; Hu, C.H. Berberine Alleviates Olanzapine-Induced Adipogenesis via the AMPKα-SREBP Pathway in 3T3-L1 Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Wang, Y. Berberine alleviates hepatic lipid accumulation by increasing ABCA1 through the protein kinase C δ pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2018, 498, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.R.; Zuo, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.B.; Kong, W.J.; Wang, A.P.; Jiang, J.D. Berberine inhibits adipocyte differentiation, proliferation and adiposity through down-regulating galectin-3. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 13415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, T.; Ma, G.; Zheng, L.; Jiang, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, N.; He, Z.; Song, X.; et al. Berberine modulates deacetylation of PPARγ to promote adipose tissue remodeling and thermogenesis via AMPK/SIRT1 pathway. Int J Biol Sci 2021, 17, 3173–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, R.; Ni, Y.; Ma, X.; Hou, M.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Ji, M. Oral berberine ameliorates high-fat diet-induced obesity by activating TAS2Rs in tuft and endocrine cells in the gut. Life Sci. 2022, 311, 121141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Hou, T.; Gao, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X. Discovery of eight alkaloids with D1 and D2 antagonist activity in leaves of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. Using FLIPR assays. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 278, 114335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xia, J.; Xu, J.-f.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J.-J.; Tang, F.; Ao, H.; Peng, C. Nuciferine, an active ingredient derived from lotus leaf, lights up the way for the potential treatment of obesity and obesity-related diseases. Pharmacol. Res 2022, 175, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, W.; Du, X.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, G. Nuciferine ameliorates nonesterified fatty acid-induced bovine mammary epithelial cell lipid accumulation, apoptosis, and impaired migration via activating LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem 2022, 71, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.-T.; Liao, J.-B.; Yang, Z.-X.; Cui, H.-T.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Wen, W.-B.; Wang, H.-W. Effect of nuciferine on gut microbiota and inflammatory response in obese model mice. Zhongyaocai 2021, 46, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Guo, T.; Zou, L.; Gong, Y.; Wu, B.; Yi, Z.; Jia, T.; Zhao, S.; Shi, L.; Li, L.; et al. Evodiamine Attenuates P2X(7)-Mediated Inflammatory Injury of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Exposed to High Free Fatty Acids. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018, 2018, 5082817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Huang, K.; Zhou, J. Hepatic AMP Kinase as a Potential Target for Treating Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Evidence from Studies of Natural Products. Curr Med Chem 2018, 25, 889–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.N.; Xiang, J.Z.; Qi, Z.; Du, M. Plant extracts in prevention of obesity. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2022, 62, 2221–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Song, Z.; Xue, W.; Sheng, J.; Shu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Liang, J.; Yao, X. Synthesis and structure–activity relationship of nuciferine derivatives as potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Med Chem Res 2014, 23, 3178–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Zahoor, I.; Albarrati, A.; Albratty, M.; Meraya, A.M.; Najmi, A.; Bungau, S. Expatiating the Pharmacological and Nanotechnological Aspects of the Alkaloidal Drug Berberine: Current and Future Trends. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liao, C.; Quan, J.; Bode, A.M.; Cao, Y.; Luo, X. Natural alkaloid and polyphenol compounds targeting lipid metabolism: Treatment implications in metabolic diseases. Eur J Pharmacol 2020, 870, 172922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Han, H.-K.; Choi, C.-I. Saikosaponin A and D Inhibit Adipogenesis via the AMPK and MAPK Signaling Pathways in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Khan, M.Z.; Shin, J.H.; Shin, T.S.; Lee, Y.B.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, J.D. Pharmacological Approaches to Attenuate Inflammation and Obesity with Natural Products Formulations by Regulating the Associated Promoting Molecular Signaling Pathways. BioMed Research International 2021, 2021, 2521273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, M.; Jin, Z.; Yaqoob, S.; Zheng, M.; Cai, D.; Liu, J.; Guo, S. Ginsenoside Rg2 inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and suppresses obesity in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice through the AMPK pathway. Food & Function 2019, 10, 3603–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-T.; Nakamura, Y.; Akasaka, T.; Katakura, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Shirouchi, B.; Jiang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Sato, M. Soyasaponin ameliorates obesity and reduces hepatic triacylglycerol accumulation by suppressing lipogenesis in high-fat diet-fed mice. J Food Sci. 2021, 86, 2103–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Lim, S.M.; Jung, J.I.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Cha, K.M.; Oh, T.K.; Moon, J.M.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Extract Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in C57BL/6N Mice by Upregulating SIRT1. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.L.; Geng, C.A.; Huang, X.Y.; Ma, Y.B.; Zheng, X.H.; Yang, T.H.; Chen, X.L.; Yin, X.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, J.J. Bioassay-guided isolation of saikosaponins with agonistic activity on 5-hydroxytryptamine 2C receptor from Bupleurum chinense and their potential use for the treatment of obesity. Chin J Nat Med 2017, 15, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Di, L.; Shan, J. A review of saponin intervention in metabolic syndrome suggests further study on intestinal microbiota. Pharmacol. Res 2020, 160, 105088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Ali, E.S.; Mubarak, M.S. Anti-obesity Effect of Plant Diterpenes and their Derivatives: A Review. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Takahashi, N.; Hirai, S.; Kawada, T. Various Terpenoids Derived from Herbal and Dietary Plants Function as PPAR Modulators and Regulate Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism. PPAR Res. 2010, 2010, 483958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, M.; Yadav, P.; Vashishth, D.; Sharma, K.; Kumar, A.; Chahal, J.; Dalal, S.; Kataria, S.K. A Review on Obesity Management through Natural Compounds and a Green Nanomedicine-Based Approach. Molecules. 2021, 26, 3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachura, N.; Kupczyński, R.; Lewandowska, K.; Włodarczyk, M.; Klemens, M.; Kuropka, P.; Nowaczyk, R.; Krzystek-Korpacka, M.; Bednarz-Misa, I.; Sozański, T.; et al. Biochemical and Molecular Investigation of the Effect of Saponins and Terpenoids Derived from Leaves of Ilex aquifolium on Lipid Metabolism of Obese Zucker Rats. Molecules. 2022, 27, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peet, D.J.; Turley, S.D.; Ma, W.; Janowski, B.A.; Lobaccaro, J.-M.A.; Hammer, R.E.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.J.C. Cholesterol and Bile Acid Metabolism are Impaired in Mice Lacking the Nuclear Oxysterol Receptor Lxrα. Cell. 1998, 93, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahrita, L.; Moriai, K.; Iwata, R.; Itoh, K.; Kato, E. Quassinoids in Brucea javanica are Potent Stimulators of Lipolysis in Adipocytes. Fitoterapia. 2019, 137, 104250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tammam, M.A.; Aly, O.; Pereira, F.; Mahdy, A.; El-Demerdash, A. Unveiling the Potential of Marine-Derived Diterpenes from the order Alcyonacea as Promising Anti-obesity Agents. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2024, 100175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix-Castejón, M.; Herranz-López, M.; Pérez Gago, A.; Olivares-Vicente, M.; Caturla, N.; Roche, E.; Micol, V. Hibiscus and lemon verbena polyphenols modulate appetite-related biomarkers in overweight subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Food. Funct. 2018, 9, 3173–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz-López, M.; Olivares-Vicente, M.; Boix-Castejón, M.; Caturla, N.; Roche, E.; Micol, V. Differential effects of a combination of Hibiscus sabdariffa and Lippia citriodora polyphenols in overweight/obese subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Tenorio, I.I.; Domínguez-López, A.; Miliar-García, Á.; Escalona-Cardoso, G.N.; Real-Sandoval, S.A.; Gómez-Alcalá, A.; Jaramillo-Flores, M.E. Modulation of the mRNA of the Nlrp3 inflammasome by Morin and PUFAs in an obesity model induced by a high-fat diet. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yu, S.; Lambert, J.D. Dietary cocoa ameliorates obesity-related inflammation in high fat-fed mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




