Submitted:
12 January 2024
Posted:
24 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1 Chemicals
2.2 Experimental set-up and photolysis of PFOA and 6:2 FTAB
2.3 Radical scavenging experiments
2.4 Quantification of PFOA, 6:2 FTAB, and their metabolites by LC-MS
2.5 Fluoride and sulfate measurement by ion chromatography
2.6 Dissolved oxygen and hydrogen peroxide measurements
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Decomposition of PFOA at different pH values
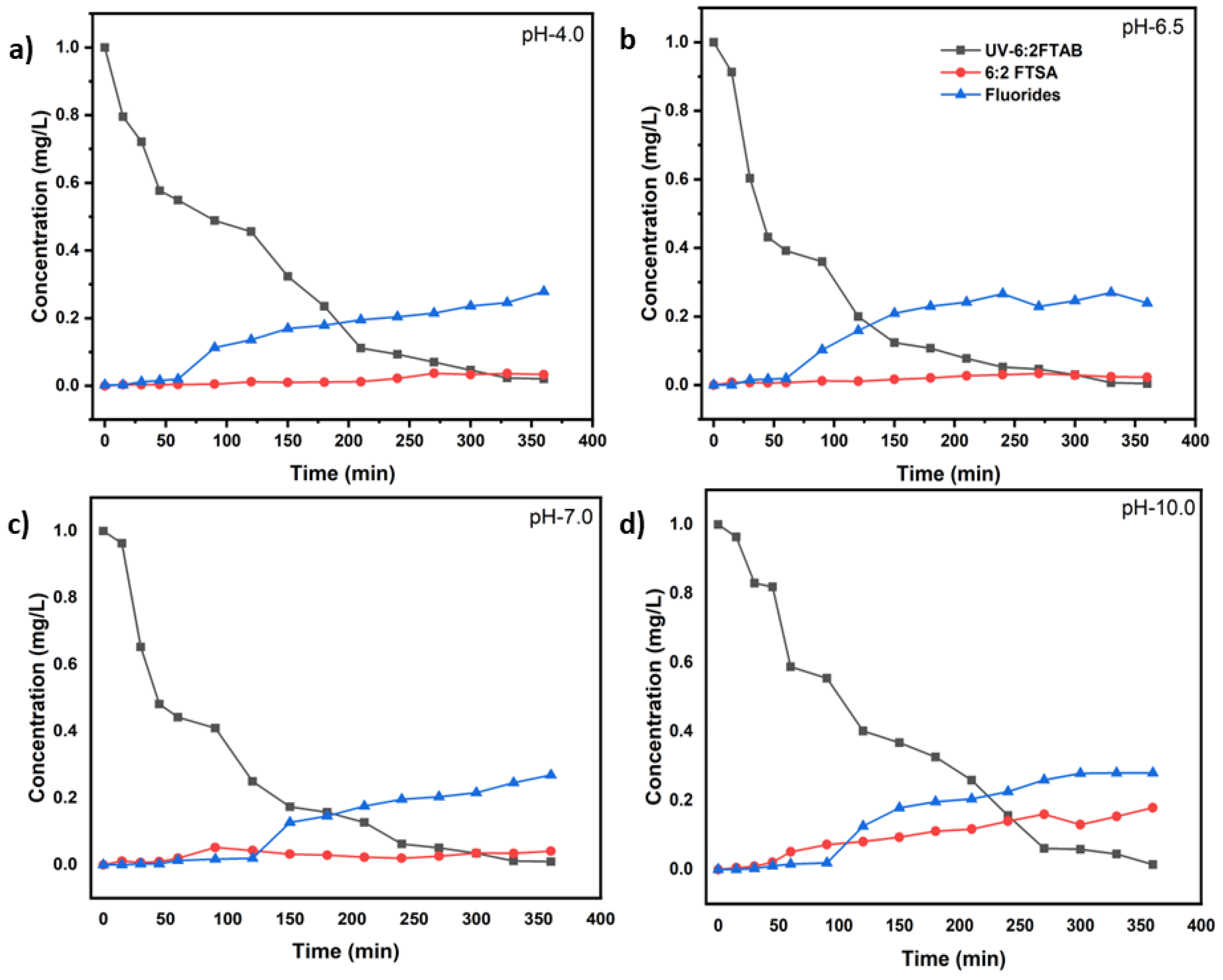
3.3. Decomposition of 6:2 FTAB at different pH values
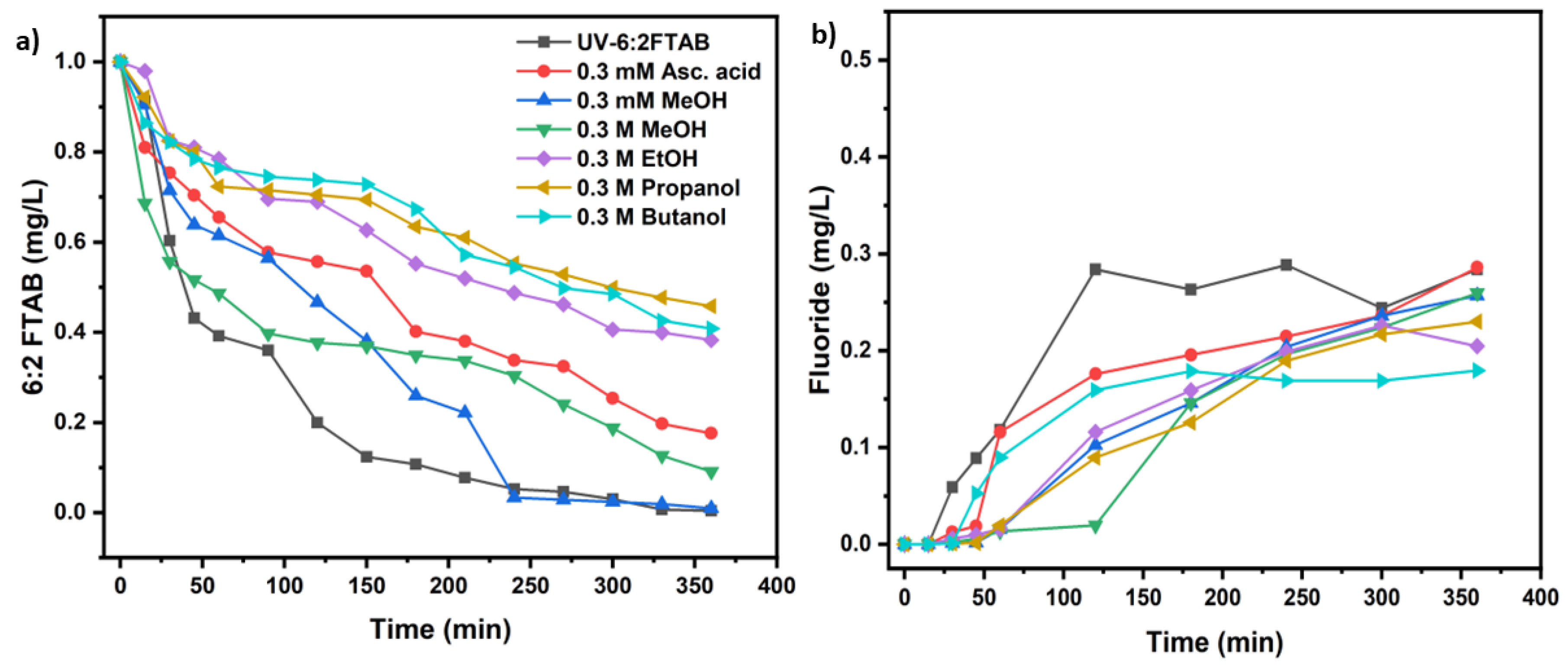
3.4 Scavengers experiments for 6:2 FTAB decomposition
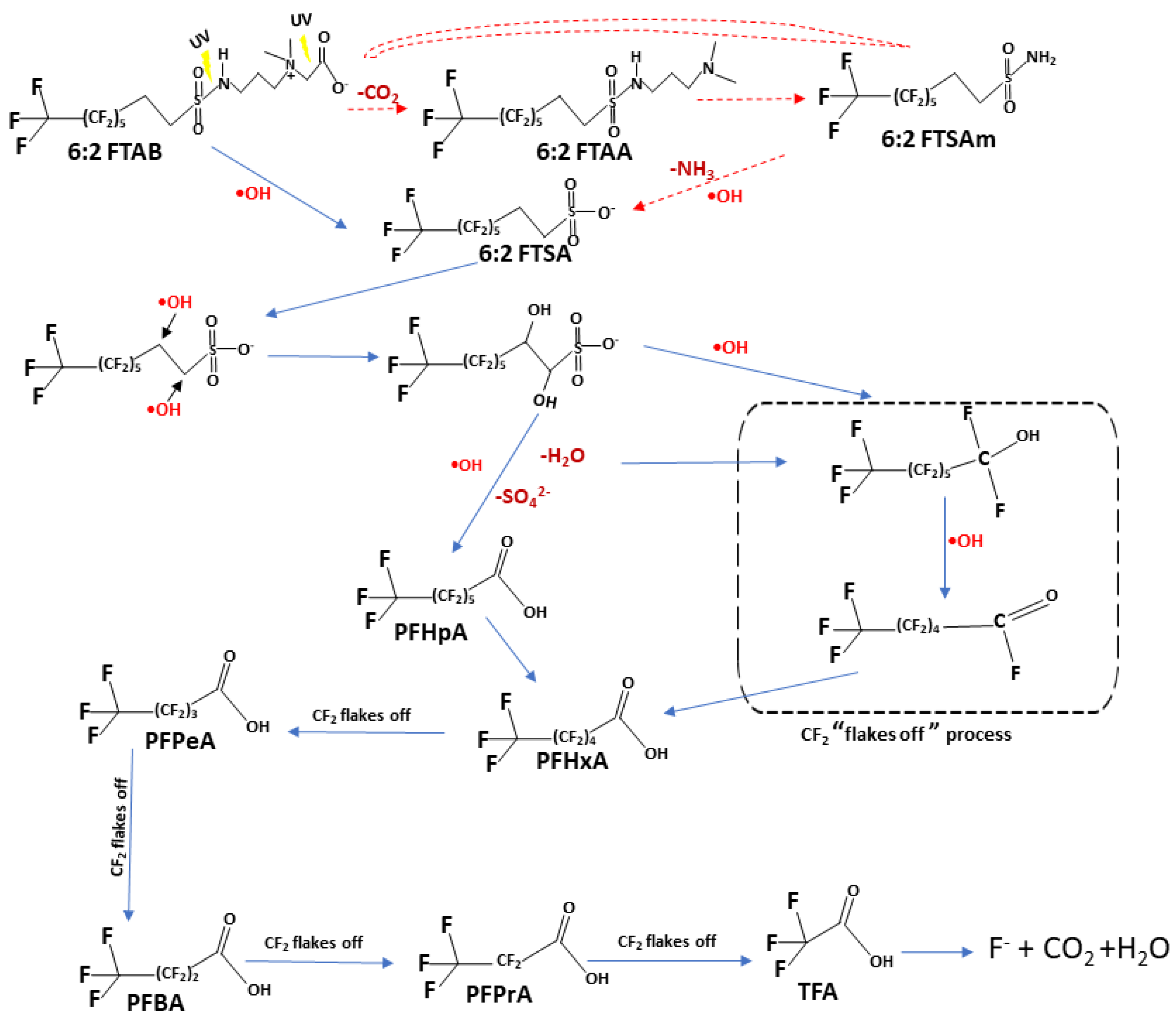
3.5. Proposed Mechanism of 6:2 FTAB decomposition
4 Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Glüge, J.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Scheringer, M.; Wang, Z. The High Persistence of PFAS Is Sufficient for Their Management as a Chemical Class. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; DeWitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Cousins, I.T. A Never-Ending Story of per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)? Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Meng, J.; Liu, S.; Lu, Y.; Khim, J.S.; Giesy, J.P. A Review of Sources, Multimedia Distribution and Health Risks of Perfluoroalkyl Acids (PFAAs) in China. Chemosphere 2015, 129, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotthoff, M.; Müller, J.; Jürling, H.; Schlummer, M.; Fiedler, D. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Consumer Products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14546–14559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; Krebs, K.A.; Roache, N.F. Perfluorocarboxylic Acid Content in 116 Articles of Commerce. Res. Triangle Park. NC US Environ. Prot. Agency 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, X.; Kim, J.; Ashley, D.C.; Huang, C.-H. Degradation and Defluorination of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances by Direct Photolysis at 222 Nm. ACS Es&t Water 2023, 3, 2776–2785. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, S.C.E.; Shukla, P.; Chen, D.; Eftekhari, E.; An, H.; Zare, F.; Ghasemi, N.; Zhang, D.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Li, Q. Emerging Technologies for PFOS/PFOA Degradation and Removal: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 153669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Dai, J. 6:2 Fluorotelomer Sulfonamide Alkylbetaine (6:2 FTAB), a Novel Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Alternative, Induced Developmental Toxicity in Zebrafish Embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 195, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, L.A.; Mabury, S.A. Identification of Novel Fluorinated Surfactants in Aqueous Film Forming Foams and Commercial Surfactant Concentrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Solla, S.R.; De Silva, A.O.; Letcher, R.J. Highly Elevated Levels of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate and Other Perfluorinated Acids Found in Biota and Surface Water Downstream of an International Airport, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. Environ. Int. 2012, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.M.; Barofsky, D.F.; Field, J.A. Quantitative Determination of Fluorotelomer Sulfonates in Groundwater by LC MS/MS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtz, E.F.; Higgins, C.P.; Field, J.A.; Sedlak, D.L. Persistence of Perfluoroalkyl Acid Precursors in AFFF-Impacted Groundwater and Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8187–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houtz, E.F.; Sutton, R.; Park, J.-S.; Sedlak, M. Poly-and Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Wastewater: Significance of Unknown Precursors, Manufacturing Shifts, and Likely AFFF Impacts. Water Res. 2016, 95, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, N.-U.-S.; Hossain, M.T.; Jahura, F.T.; Girase, A.; Hall, A.S.; Lu, J.; Ormond, R.B. Firefighters’ Exposure to per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) as an Occupational Hazard: A Review. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1143411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, C.M.; Muir, D.C.G.; Mabury, S.A. Biotransformation Pathways of Fluorotelomer-based Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 243–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinglasan, M.J.A.; Ye, Y.; Edwards, E.A.; Mabury, S.A. Fluorotelomer Alcohol Biodegradation Yields Poly-and Perfluorinated Acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2857–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding-Marjanovic, K.C.; Houtz, E.F.; Yi, S.; Field, J.A.; Sedlak, D.L.; Alvarez-Cohen, L. Aerobic Biotransformation of Fluorotelomer Thioether Amido Sulfonate (Lodyne) in AFFF-Amended Microcosms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7666–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, B.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Marchington, E.B.; D’Agostino, L.A.; Mabury, S.A. Organic Fluorine Content in Aqueous Film Forming Foams (AFFFs) and Biodegradation of the Foam Component 6: 2 Fluorotelomermercaptoalkylamido Sulfonate (6: 2 FTSAS). Environ. Chem. 2013, 10, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, S.A.; Mabury, S.A. Aqueous Photolysis of 8: 2 Fluorotelomer Alcohol. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. An Int. J. 2005, 24, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar]
- Mojiri, A.; Zhou, J.L.; Ozaki, N.; KarimiDermani, B.; Razmi, E.; Kasmuri, N. Occurrence of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Aquatic Environments and Their Removal by Advanced Oxidation Processes. Chemosphere 2023, 138666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Zhang, P.; Jian, L.I.U. Photodegradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid by 185 Nm Vacuum Ultraviolet Light. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 387–390. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, D.; Wei, Z.; Spinney, R.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Minakata, D.; Xiao, R.; Xie, H.-B.; Chai, L. Mechanistic Understanding of Superoxide Radical-Mediated Degradation of Perfluorocarboxylic Acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-J.; Lo, S.-L.; Lee, Y.-C.; Kuo, J.; Wu, C.-H. Decomposition of Perfluorooctanoic Acid by Ultraviolet Light Irradiation with Pb-Modified Titanium Dioxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 303, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Lyu, C.; Sun, R.; Zhang, D.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Discerning the Inefficacy of Hydroxyl Radicals during Perfluorooctanoic Acid Degradation. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Ruiz, B.; Ribao, P.; Diban, N.; Rivero, M.J.; Ortiz, I.; Urtiaga, A. Photocatalytic Degradation and Mineralization of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) Using a Composite TiO2− RGO Catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva-Rackov, C.K.O.; Lawal, W.A.; Nfodzo, P.A.; Vianna, M.M.G.R.; do Nascimento, C.A.O.; Choi, H. Degradation of PFOA by Hydrogen Peroxide and Persulfate Activated by Iron-Modified Diatomite. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 192, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, J.; Javed, H.; Mathieu, J.; Long, M.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Comment on “Mechanistic Understanding of Superoxide Radical-Mediated Degradation of Perfluorocarboxylic Acids. ” Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5287–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Metz, J.; Eraslan, T.C.; Mathieu, J.; Wang, B.; Wu, G.; Tsai, A.-L.; Wong, M.S.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Discerning the Relevance of Superoxide in PFOA Degradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Choi, H. Photocatalytic Degradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid on Pb-doped TiO2 Coated with Reduced Graphene Oxide. Water Environ. Res. 2023, e10871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, H.; Hayakawa, E.; Einaga, H.; Kutsuna, S.; Koike, K.; Ibusuki, T.; Kiatagawa, H.; Arakawa, R. Decomposition of Environmentally Persistent Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Water by Photochemical Approaches. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6118–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Liang, Z.; Lu, X.; Chen, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, F. The Degradation Mechanisms of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) by Different Chemical Methods: A Critical Review. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-J.; Lo, S.-L.; Lee, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-C. Photocatalytic Decomposition of Perfluorooctanoic Acid by Transition-Metal Modified Titanium Dioxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 288, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Lo, S.-L.; Kuo, J. Effects of Titanate Nanotubes Synthesized by a Microwave Hydrothermal Method on Photocatalytic Decomposition of Perfluorooctanoic Acid. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4131–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.; Li, X.; Ling, Y.; Li, L. Efficient Degradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) by Photocatalytic Ozonation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 296, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Niu, J.; Ding, S.; Zhang, L. Electrochemical Degradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) by Ti/SnO2–Sb, Ti/SnO2–Sb/PbO2 and Ti/SnO2–Sb/MnO2 Anodes. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Ma, D.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, C.; Cao, C.; Zhao, P.; Huang, Q. Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Herbicide Glyphosate in Water by Magnetically Separable and Recyclable BiOBr/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites under Visible Light Irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, P. Effects of PH on Photochemical Decomposition of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Different Atmospheres by 185 Nm Vacuum Ultraviolet. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, C.-J.; Chen, P.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, W.-X. Effect of Initial Solution PH on Photo-Induced Reductive Decomposition of Perfluorooctanoic Acid. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Teng, Y.; Wang, W.; Hong, R.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, F.; Li, H.; Hao, S.; Wu, B.; et al. Enhanced UV Photoreductive Destruction of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in the Presence of Alcohols: Synergistic Mechanism of Hydroxyl Radical Quenching and Solvent Effect. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 316, 121652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.G.; Oliveros, E.; Wörner, M.; Braun, A.M. Vacuum-Ultraviolet Photolysis of Aqueous Reaction Systems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2004, 5, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, R.R.; Ozaki, H.; Okada, T.; Taniguchi, S.; Takanami, R. Factors Influencing UV Photodecomposition of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 180, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, P. Photochemical Decomposition of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) in an Anoxic Alkaline Solution by 185 Nm Vacuum Ultraviolet. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, P. Photodegradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Water under Irradiation of 254 Nm and 185 Nm Light by Use of Persulfate. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Junker, A.L.; Wen, J.; Ahrens, L.; Sillanpää, M.; Tian, J.; Cui, F.; Vergeynst, L.; Wei, Z. A Recent Overview of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Removal by Functional Framework Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbassiyazdi, E.; Kasula, M.; Modak, S.; Pala, J.; Kalantari, M.; Altaee, A.; Esfahani, M.R.; Razmjou, A. A Juxtaposed Review on Adsorptive Removal of PFAS by Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) with Carbon-Based Materials, Ion Exchange Resins, and Polymer Adsorbents. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juve, J.-M.A.; Donoso Reece, J.A.; Wong, M.S.; Wei, Z.; Ateia, M. Photocatalysts for Chemical-Free PFOA Degradation – What We Know and Where We Go from Here? J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 462, 132651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Koike, K.; Kutsuna, S.; Osaka, I.; Arakawa, R. Photochemical Decomposition of Environmentally Persistent Short-Chain Perfluorocarboxylic Acids in Water Mediated by Iron (II)/(III) Redox Reactions. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, R.; Bryant, I.M.; Jensch, R.; Liebsch, S.; Martienssen, M. Photolysis of Hexamethylenediaminetetra (Methylenephosphonic Acid)(HDTMP) Using Manganese and Hydrogen Peroxide. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Vione, D.; Rivoira, L.; Carena, L.; Castiglioni, M.; Bruzzoniti, M.C. A Review on the Degradation of Pollutants by Fenton-Like Systems Based on Zero-Valent Iron and Persulfate: Effects of Reduction Potentials, PH, and Anions Occurring in Waste Waters. MOLECULES 2021, 26, 4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Lai, C.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y. Hydroxyl Radicals Based Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) for Remediation of Soils Contaminated with Organic Compounds: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, R.; Jensch, R.; Bryant, I.M.; Fischer, T.; Liebsch, S.; Martienssen, M. Photodegradation of Ethylenediaminetetra (Methylenephosphonic Acid)–The Effect of the System Configuration. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 388, 112192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, B.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Li, J. Overlooked Formation of H2O2 during the Hydroxyl Radical-Scavenging Process When Using Alcohols as Scavengers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3386–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhirst, R.A.; Fry, S.C. The Oxidation of Dehydroascorbic Acid and 2, 3-Diketogulonate by Distinct Reactive Oxygen Species. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 3451–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poljsak, B.; Ionescu, J.G. Pro-Oxidant vs. Antioxidant Effects of Vitamin C. Handb. Vitam. C Res. Dly. Requir. Diet. sources Advers. Eff. 2009, 153. [Google Scholar]
- Plumlee, M.H.; McNeill, K.; Reinhard, M. Indirect Photolysis of Perfluorochemicals: Hydroxyl Radical-Initiated Oxidation of N-Ethyl Perfluorooctane Sulfonamido Acetate (N-EtFOSAA) and Other Perfluoroalkanesulfonamides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3662–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, E.B.; Zeidabadi, F.A.; Zhang, S.; Mohseni, M. Photo-Chemical/Catalytic Oxidative/Reductive Decomposition of per-and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), Decomposition Mechanisms and Effects of Key Factors: A Review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2022, 8, 698–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.W.; Mabury, S.A.; O’Brien, P.J. Metabolic Products and Pathways of Fluorotelomer Alcohols in Isolated Rat Hepatocytes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2005, 155, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, L.A. Environmental Chemistry of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Aqueous Film Forming Foams; University of Toronto (Canada), 2017; ISBN 0355776944.
- Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, K.; Yu, G.; Deng, S.; Wang, B. Stability of 6:2 Fluorotelomer Sulfonate in Advanced Oxidation Processes: Degradation Kinetics and Pathway. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 4634–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouborst, L. Aqueous Photolysis of 6:2 Fluorotelomer Sulfonamide Alkylbetaine.; 2016.
- Marchington, E.B. Identification of Known and Novel Fluorinated Compounds in AFFF Via£ ʹ9-NMR, LC-MS/MS, and LC-Quad-TOFMS, and the Aerobic Biodegradation of 6: 2 FtS.; Library and Archives Canada= Bibliothq̈ue et Archives Canada, 2009; ISBN 0494449268.
- Gomez-Ruiz, B.; Gómez-Lavín, S.; Diban, N.; Boiteux, V.; Colin, A.; Dauchy, X.; Urtiaga, A. Boron Doped Diamond Electrooxidation of 6: 2 Fluorotelomers and Perfluorocarboxylic Acids. Application to Industrial Wastewaters Treatment. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 798, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
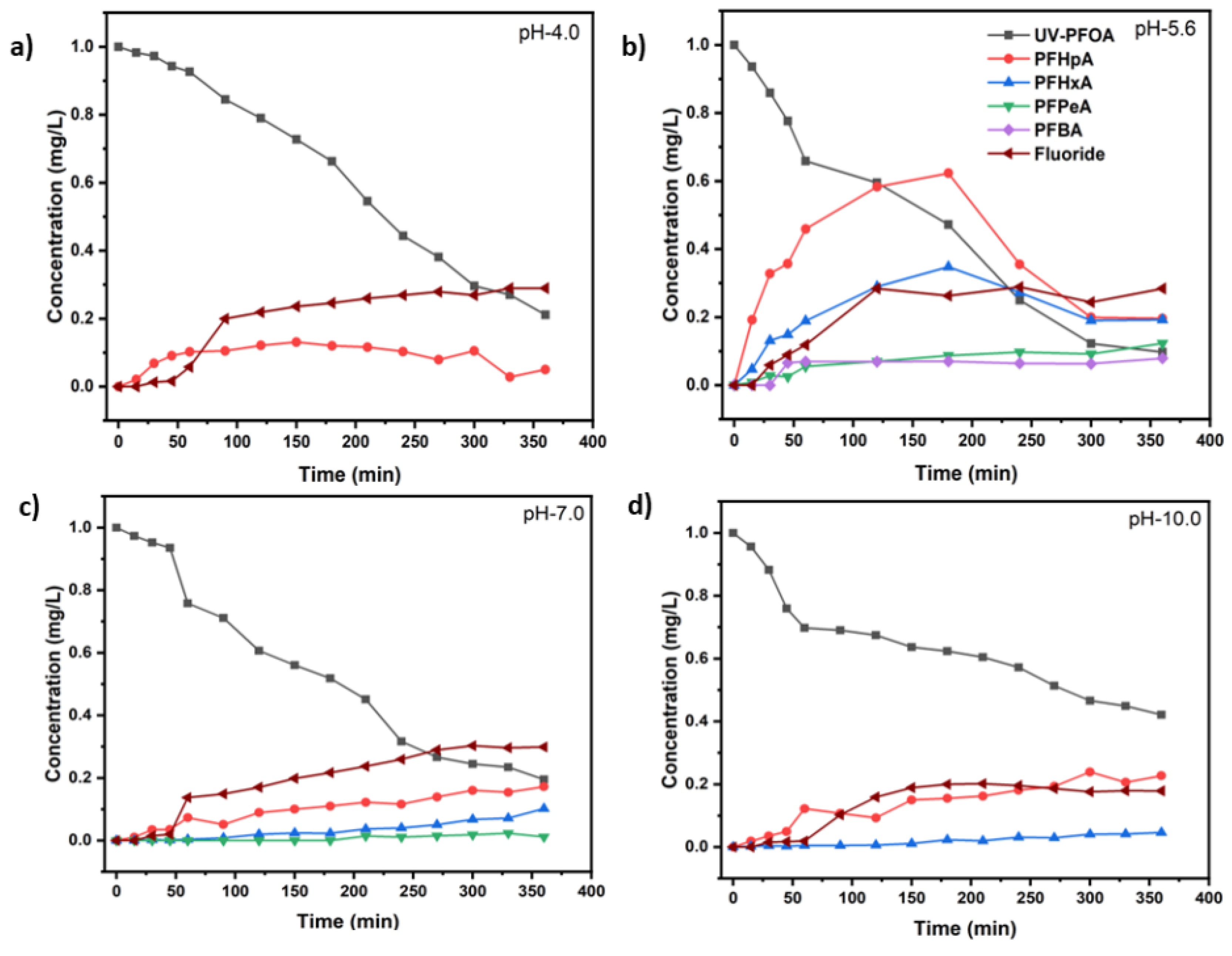
| UV test with PFOA (Co=1 mg/L) | k(s-1) | t1/2 (min) | PFOA Decomposition (%) | Maximum Fluoride release (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV-pH 4.0 | (8.85 ± 1.13)×10−5 | 130 ± 2 | 85.2 ± 1.6 | 29.0 ± 3.5 |
| UV-pH 5.6 | (1.08 ± 0.30)×10−4 | 107 ± 2 | 90.3 ± 2.5 | 28.8 ± 4.8 |
| UV-pH 7.0 | (7.57 ± 1.70)×10−5 | 152 ± 3 | 80.5 ± 4.0 | 30.3 ± 5.4 |
| UV-pH 10.0 | (4.00 ± 1.15)×10−5 | 288 ± 3 | 57.9 ± 1.8 | 20.2 ± 3.5 |
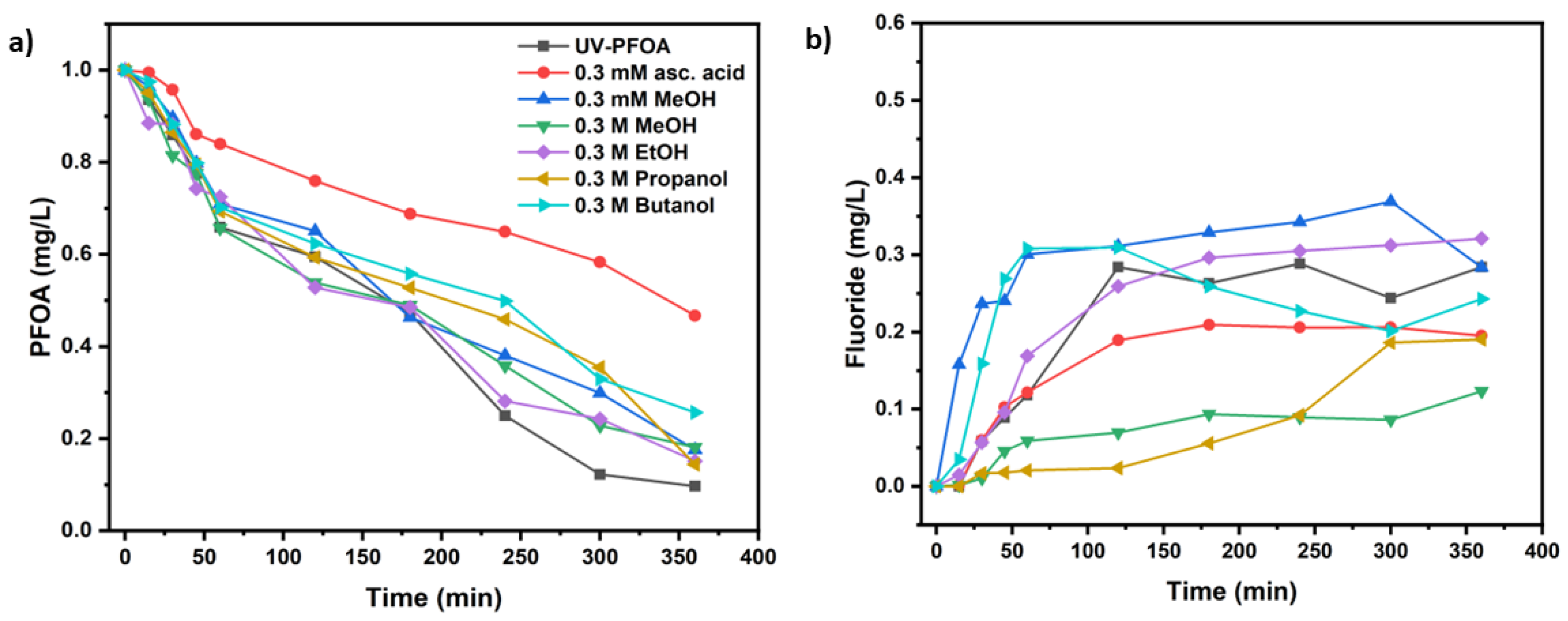
| UV test with PFOA (Co=1 mg/L), Initial pH | k (s-1) | t1/2 (min) | PFOA Decomposition (%) | Fluoride release (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methanol 0.3 mM at t=0 (pH-5.05) | (8.06 ± 1.5)×10−5 | 143 ± 3 | 82.6 ±2.9 | 36.9 ± 1.3 |
| Methanol 0.3 M at t=0 (pH-5.05) | (7.91 ± 0.2)×10−5 | 146 ± 4 | 81.9 ± 2.7 | 12.3 ± 4.3 |
| Ethanol 0.3 M at t=0 (pH-5.71) | (8.74 ± 1.2)×10−5 | 132 ± 5 | 84.9 ± 1.9 | 32.1 ± 3.2 |
| Propanol 0.3 M at t=0(pH-5.75) | (9.00 ± 1.9)×10−5 | 128 ± 5 | 85.7 ± 1.5 | 19.0 ± 2.8 |
| Butanol 0.3 M at t=0(pH-5.57) | (6.30 ± 1.5)×10−5 | 183 ± 3 | 74.3 ± 4.2 | 30.8 ± 4.6 |
| Ascorbic acid 0.3 mM at t=0 and t=1 h (pH-4.27) | (3.52 ± 1.3)×10−5 | 327 ± 6 | 53.3 ± 5.2 | 20.9 ± 4.2 |
| UV test with 6:2 FTAB (Co=1mg/L) | k (s−1) | t1/2 (min) | 6:2 FTAB Decomposition (%) | Fluoride release (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV-pH 4.0 | (1.80 ± 0.06)×10−4 | 64.1 ± 7.2 | 98.0 ± 3.1 | 27.9 ± 5.0 |
| UV-pH 6.5 | (2.52 ± 0.16)×10−4 | 45.7 ± 1.7 | 99.6 ± 0.5 | 27.0 ± 4.7 |
| UV-pH 7.0 | (2.16 ± 0.29)×10−4 | 53.3 ± 3.9 | 99.1 ± 0.2 | 26.9 ± 3.2 |
| UV-pH 10.0 | (1.97 ± 0.14)×10−4 | 58.4 ± 6.2 | 98.6 ± 1.4 | 28.0 ± 4.2 |
| UV test with 6:2 FTAB (Co=1mg/L) | k(s-1) | t1/2 (min) | 6:2 FTAB Decomposition (%) | Fluoride release (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methanol 0.3 mM at t=0 | (2.15 ± 0.12)×10−4 | 54 ± 4 | 99.0 ± 0.7 | 25.7 ± 4.4 |
| Methanol 0.3 M at t=0 | (1.10 ± 0.24)×10−4 | 104 ± 8 | 90.9 ± 4.3 | 26.0 ± 2.6 |
| Ethanol 0.3 M at t=0 | (4.44 ± 0.41)×10−5 | 260 ± 7 | 61.7 ± 2.9 | 22.6 ± 3.7 |
| Propanol 0.3 M at t=0 | (3.61 ± 0.32)×10−5 | 319 ± 7 | 54.2 ± 2.6 | 23.0 ± 2.0 |
| Butanol 0.3 M at t=0 | (4.15 ± 0.97)×10−5 | 279 ± 10 | 59.2 ± 3.5 | 18.0 ± 4.3 |
| Ascorbic acid 0.3 mM, at t=0 and t= 1 h | (8.04 ± 0.55)×10−5 | 144 ± 8 | 82.4 ± 4.2 | 25.6 ± 2.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





