1. Introduction
Parkinson's disease is a specific subtype of Parkinsonism, and Parkinsonism is a more general term that includes various conditions with similar motor and non-motor symptoms. It's crucial for healthcare professionals to carefully evaluate and diagnose the specific cause of Parkinsonism in an individual to determine appropriate treatment and management strategies [
1,
2,
3].
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic neurodegenerative disorder that predominantly affects the motor system. It is characterized by the progressive loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain. Dopamine serves as a vital neurotransmitter, playing a pivotal role in the regulation of movement and coordination [
4,
5,
6,
7]. While the precise cause of Parkinson's disease remains unclear, it is thought that a combination of genetic and environmental factors contributes to its development. Presently, there is no cure for Parkinson's disease; however, diverse treatment options exist with the goal of symptom management and enhancing quality of life. Depending on the severity of symptoms, healthcare professionals may recommend medications, physical therapy, or, in certain cases, surgical interventions like deep brain stimulation [
4,
5,
6,
7].
The present work focused on the protein Parkin and its potential role in finding compounds to combat Parkinson's disease. Parkin is a protein associated with the regulation of cellular processes, and mutations in the Parkin gene have been linked to a familial form of Parkinson's disease [
8,
9]. Parkin, acting as a RING-between-RING E3 ligase, operates in the covalent binding of ubiquitin to particular substrates.
Mutations in Parkin have associations with Parkinson's disease, cancer, and mycobacterial infection [
8,
9]. This investigation was performed by Molecular Docking studies [
10,
11,
12].
2. Material and Methods
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin (Chain A) was taken by Protein Data Bank, ( PDB Code 4I1H).
Grid box for Blind Docking analysis was performed by Pyrx program [
13]: center_x = 60.2823; center_y = 22.4819; center_z = -12.0064; size_x = 52.1553899384; size_y = 65.1767790318; size_z = 86.6129901886
3. Results and Discussion
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by the progressive damage of certain parts of the brain [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. The main symptoms include:
- -
Involuntary movements of one or more parts of the body (tremor)
- -
Slowness of movements (bradykinesia)
- -
Muscle rigidity
The exact cause of Parkinson's disease remains uncertain, it is believed that a combination of genetic and environmental factors plays a role in its development [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. The present work focused on E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin with natural compounds. From docking investigations Amentoflavone showed excellent binding energy score of about -10 kcal/mol. Indeed, The E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin demonstrates a strong binding affinity with docked amentoflavone, evidenced by a high binding energy of -10 kcal/mol.
Nevertheless, additional biological studies are imperative not only to validate its potential efficacy against Parkinson's and assess its safety concerning toxicity but also to conduct further computational analyses capable of confirming these initial assessments.
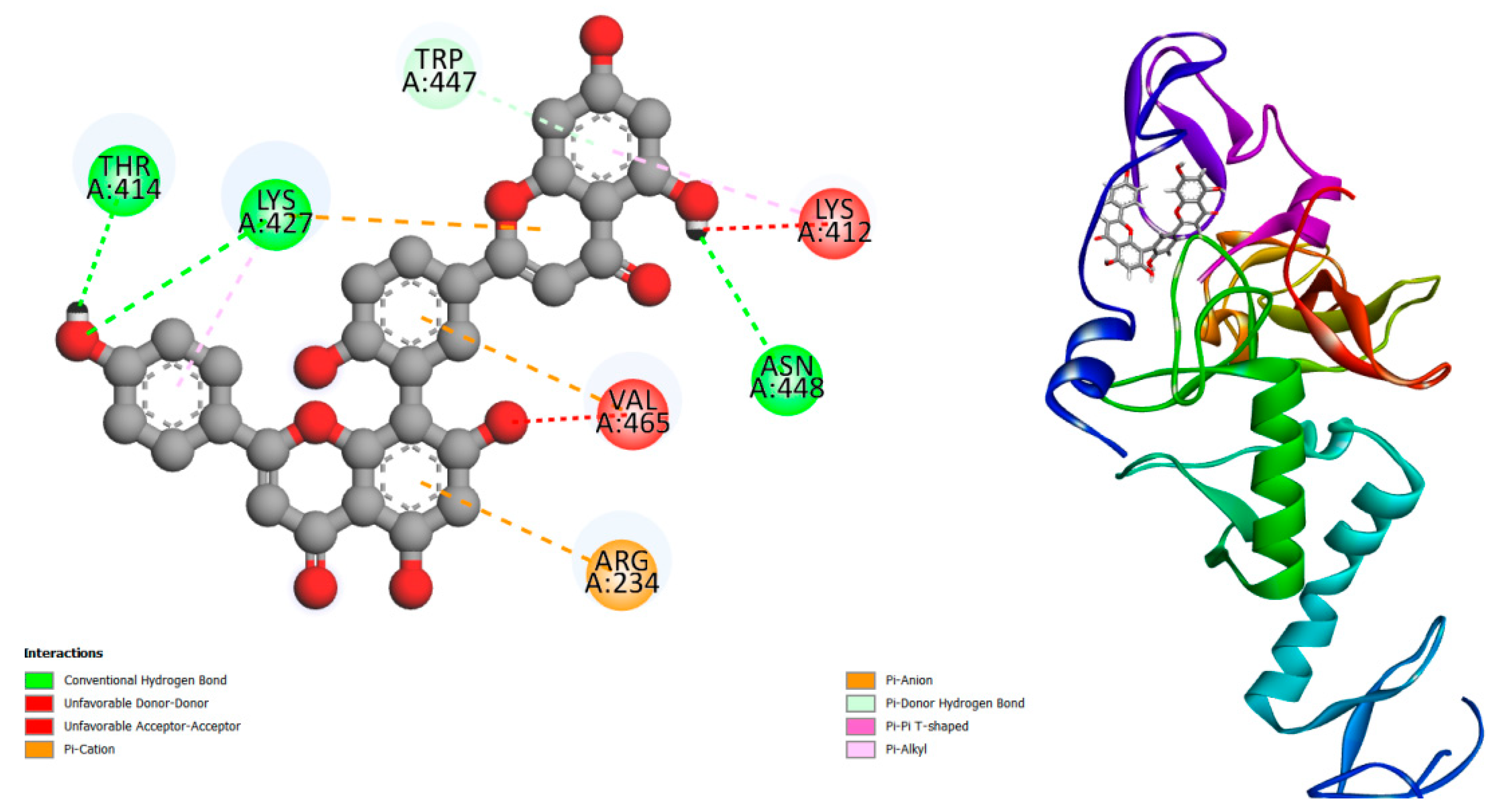
Figure 1.
displays the docking outcomes of E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin ( in conjunction with Amentoflavone -10 kcal/mol within the potential Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina through the pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Amentoflavone Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Amentoflavone.
Figure 1.
displays the docking outcomes of E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin ( in conjunction with Amentoflavone -10 kcal/mol within the potential Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina through the pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Amentoflavone Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Amentoflavone.
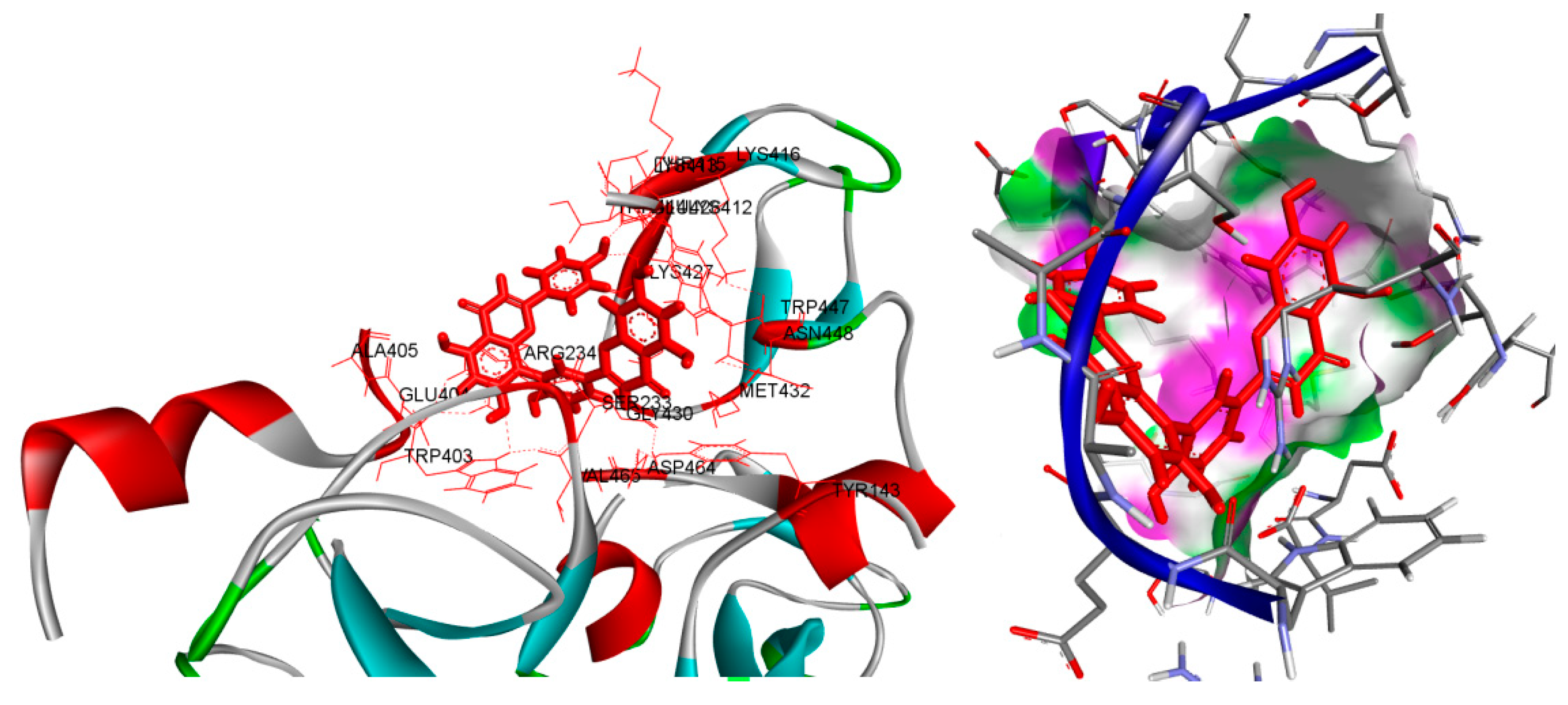
Figure 2.
displays the characterization of E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin (in conjunction with Amentoflavone -10 kcal/mol within the potential Ligand Binding Site.
Figure 2.
displays the characterization of E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin (in conjunction with Amentoflavone -10 kcal/mol within the potential Ligand Binding Site.
4. Conclusion
This computational study focused on exploring the interaction between the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin and natural compounds, with Amentoflavone demonstrating a notable binding energy score (-10 kcal/mol). The strong binding affinity observed during docking suggests a potential therapeutic role for Amentoflavone in Parkinson's disease. However, it is crucial to underscore that further biological studies are imperative to validate the efficacy of Amentoflavone against Parkinson's and to assess its safety in terms of toxicity.
References
- Thenganatt, M.A.; Jankovic, J. Parkinson disease subtypes. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rooden, S.M.; Colas, F.; Martínez-Martín, P.; Visser, M.; Verbaan, D.; Marinus, J.; van Hilten, J.J.; et al. Clinical subtypes of Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marras, C.; Chaudhuri, K. R. Nonmotor features of Parkinson's disease subtypes. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloem, B. R.; Okun, M. S.; Klein, C. Parkinson's disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, L. V.; Lang, A. E. Parkinson's disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsden, C. D. Parkinson's disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samii, A.; Nutt, J. G.; Ransom, B.R. Parkinson's disease. Lancet 2004, 363, 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, D.; Li, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wang, D.; Sun, Z.; Yang, L.; et al. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Research Reviews, 2023, 84, 101817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, E. M.; Frankel, K. S.; Shaw, G. S. Parkin and mitochondrial signalling. Cell. Signal. 2023, 106, 110631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X. Y.; Zhang, H. X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular docking: a powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr. Comput. -Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Mehrotra, R. J. J. C. An overview of molecular docking. JSM Chem. 2016, 4, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A. J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallakyan, S.; Olson, A. J. Small-molecule library screening by docking with PyRx. Chemical Biol. Methods Protocols 2015, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).