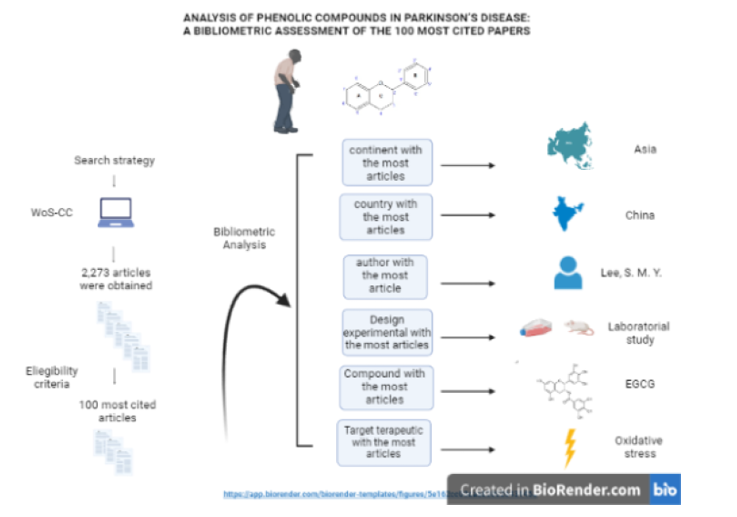
Objective: The aim of this study was to identify and characterize the 100 most cited articles on Parkinson's disease (PD) and phenolic compounds (PCs). Methods: Articles were selected in the Web of Science Core Collection up to January 2022 based on predetermined inclusion criteria, and the following bibliometric parameters were extracted: the number of citations, title, keywords, authors, year, study design, tested PC and therapeutic target. MapChart was used to create worldwide networks, and VOSviewer software was used to create bibliometric networks. Descriptive statistical analysis was used to identify the most researched PCs and therapeutic targets in PD. Results: The most cited article was also the oldest. The most recent article was published in 2020. Asia and China were the continent and the country with the most articles in the list (55% and 29%, respectively). In vitro studies were the most common experimental designs among the 100 most cited articles (46%). The most evaluated PC was epigallocatechin. Oxidative stress was the most studied therapeutic target. Conclusion: Despite the demonstrations in laboratorial studies, the results obtained point to the need for clinical studies to better elucidate this association.