Submitted:
19 January 2024
Posted:
22 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Fabrication and Curing of Rubber Compounds
2.2.2. Determination of Curing Characteristics
2.2.3. Investigation of Mechanical Characteristics
2.2.4. Investigation of Shielding Characteristics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Curing Process
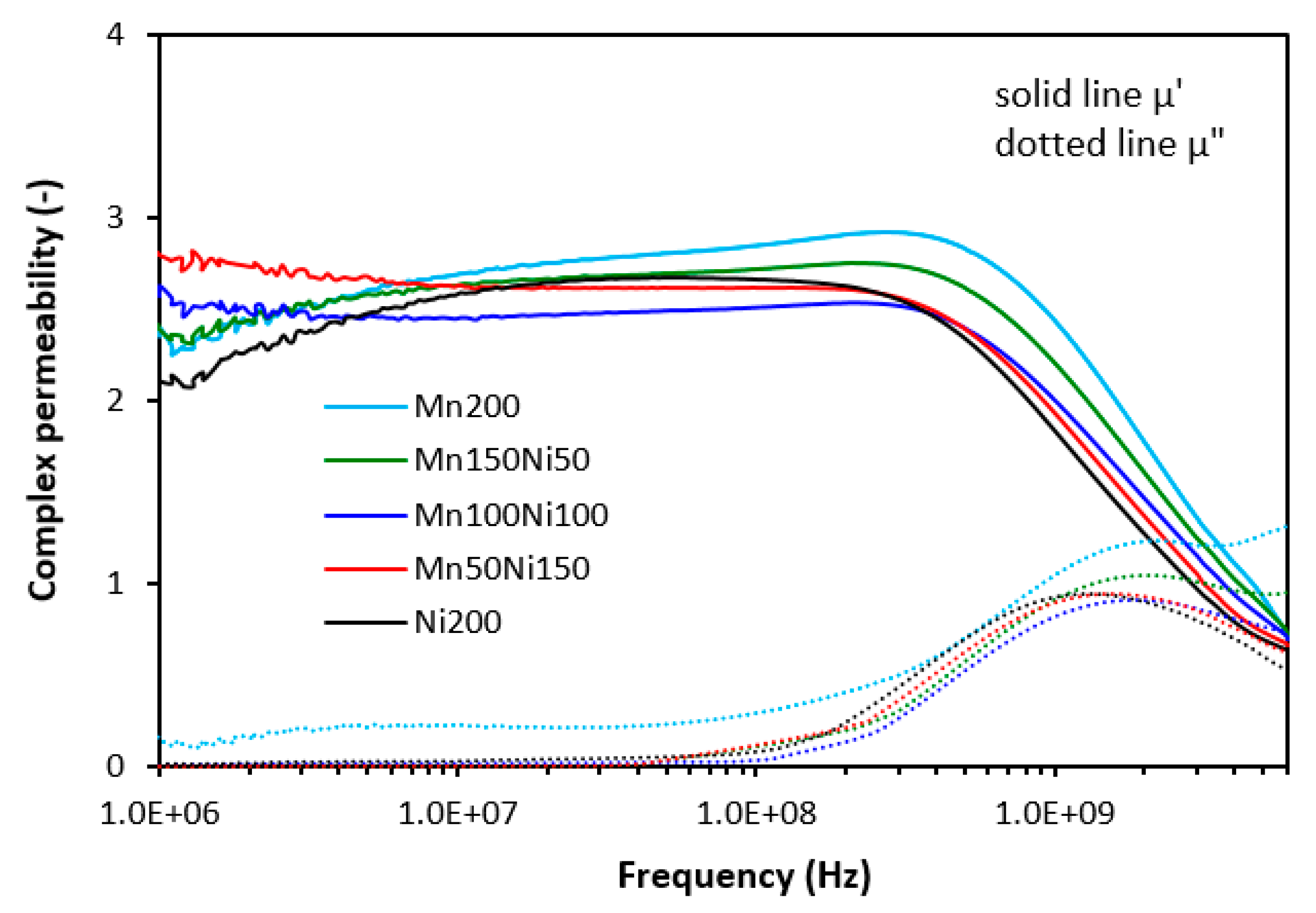
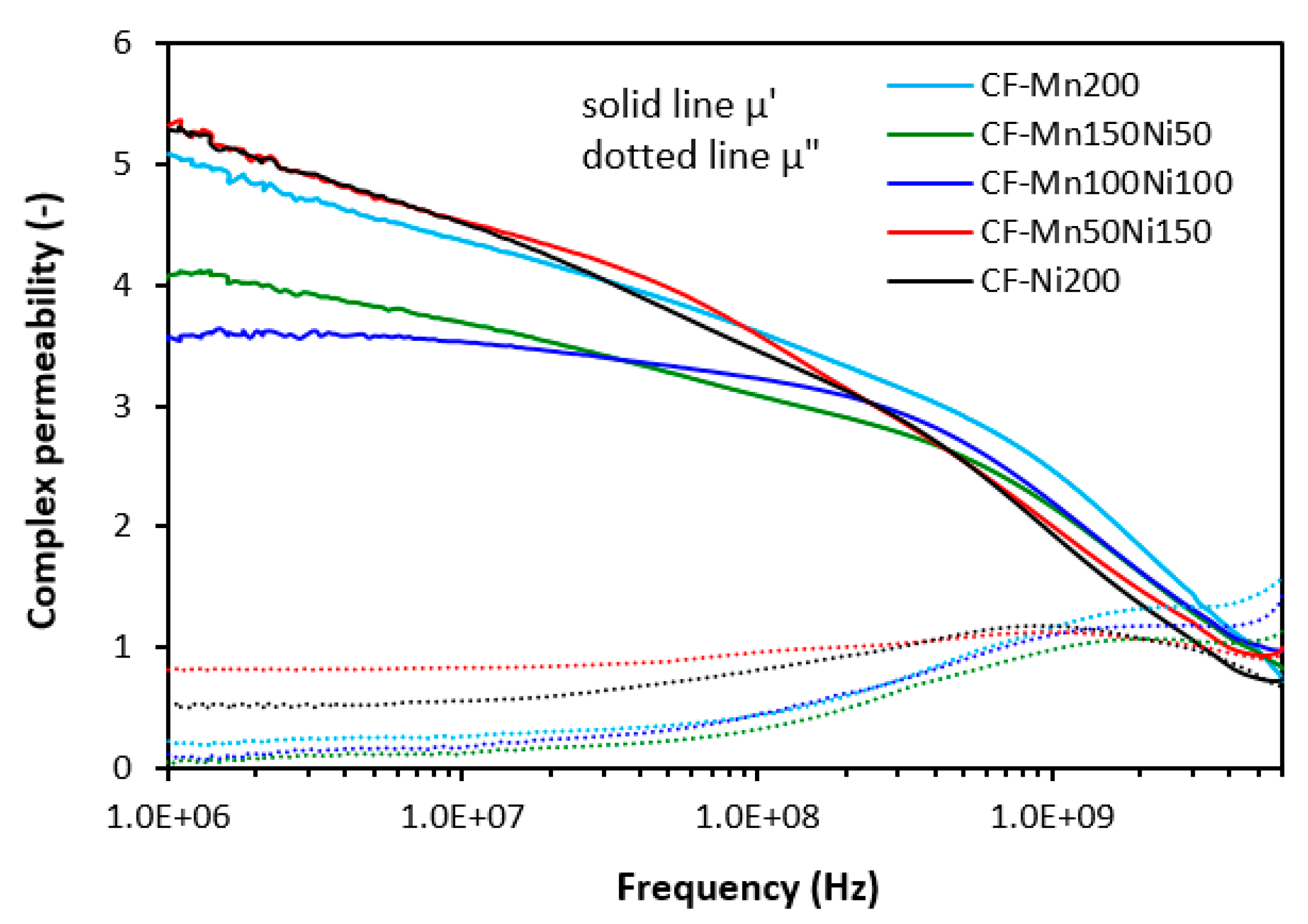
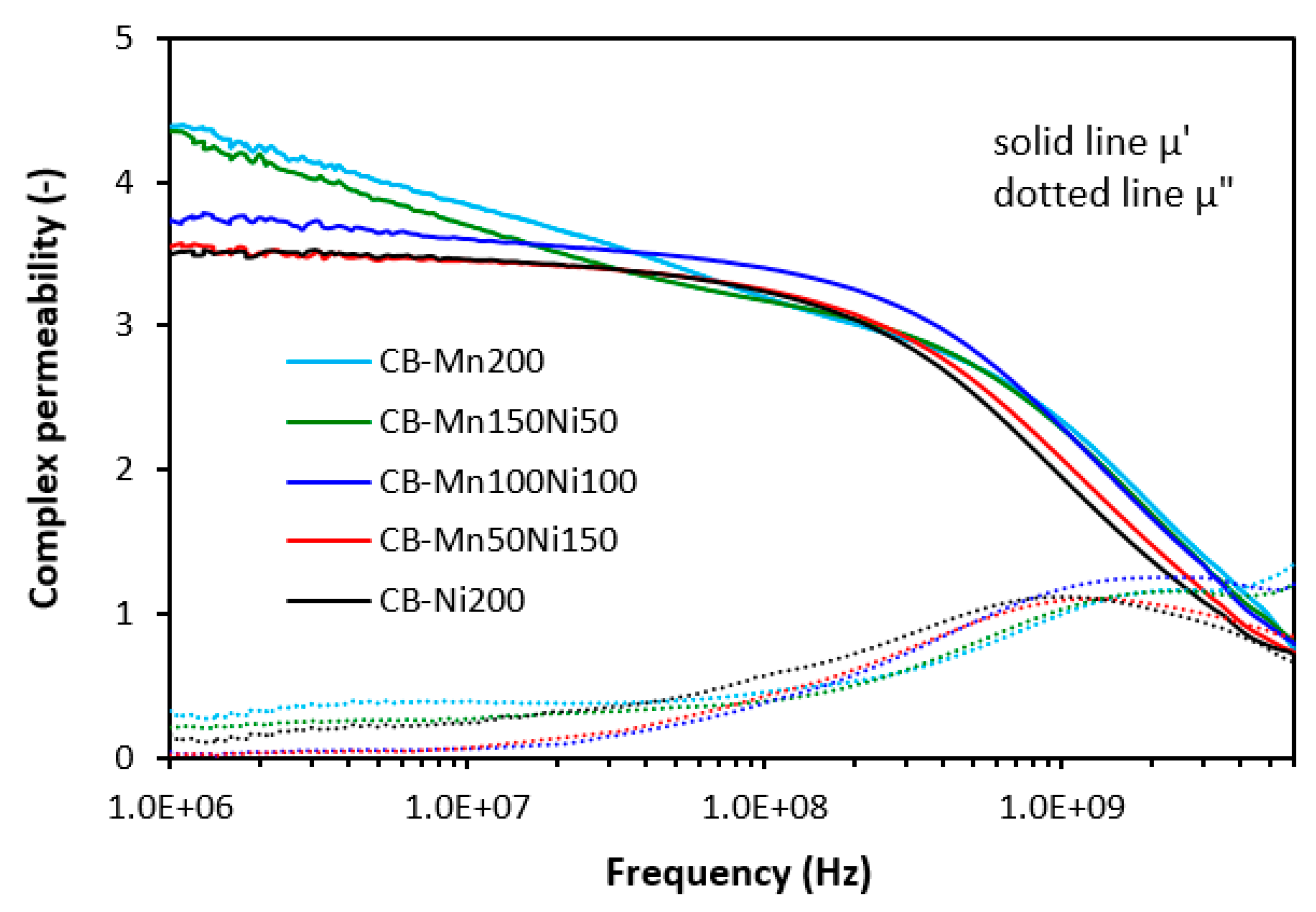
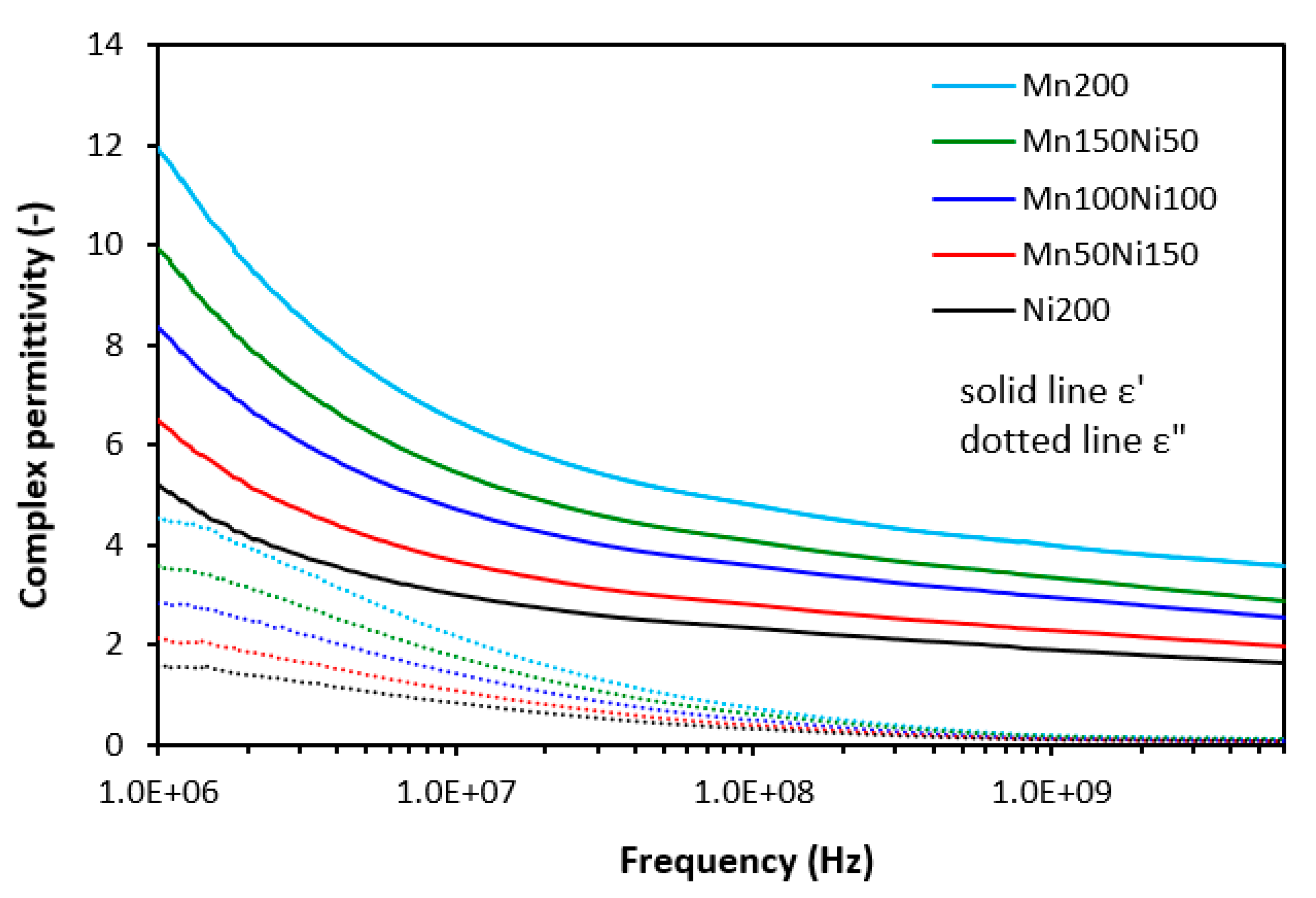
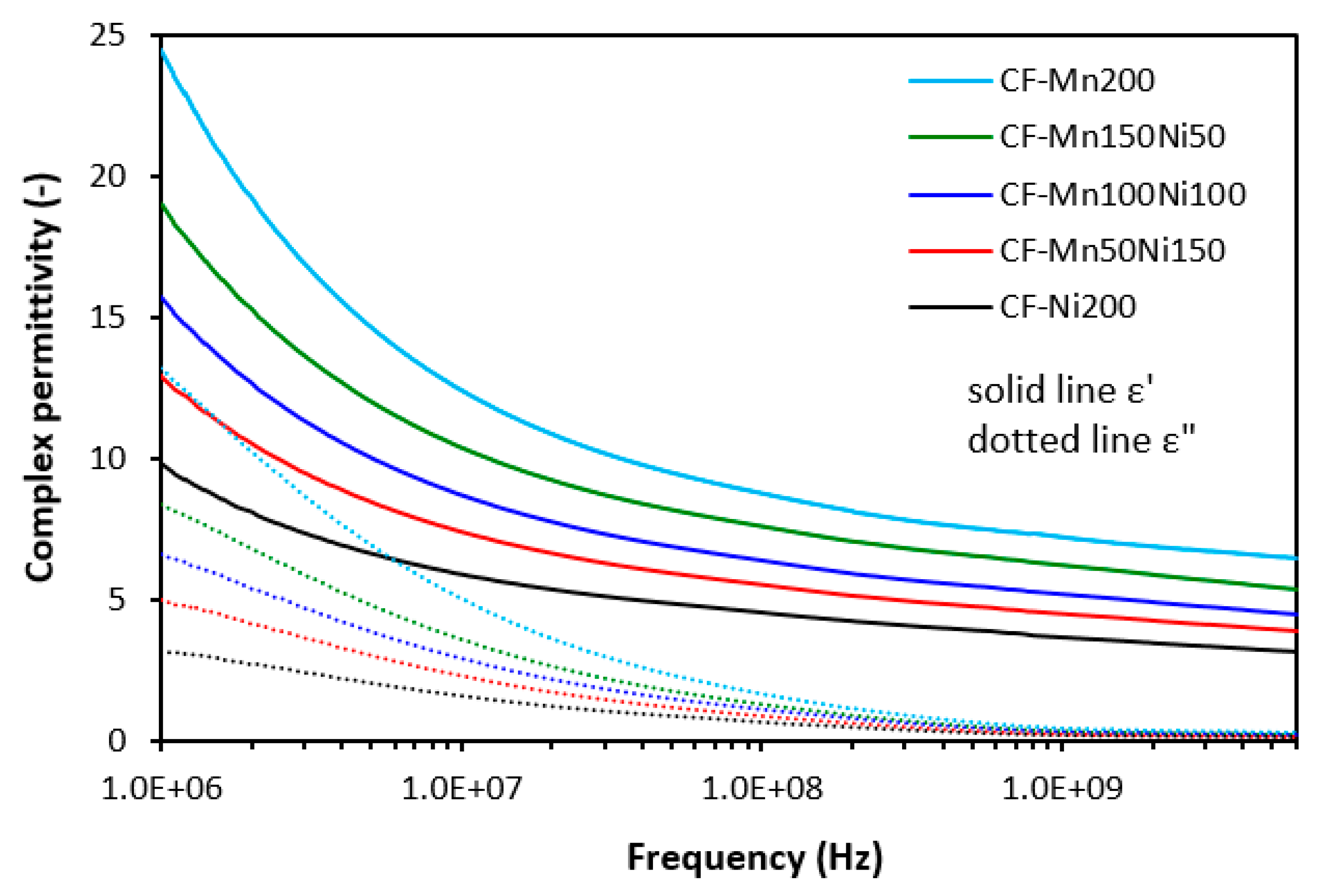
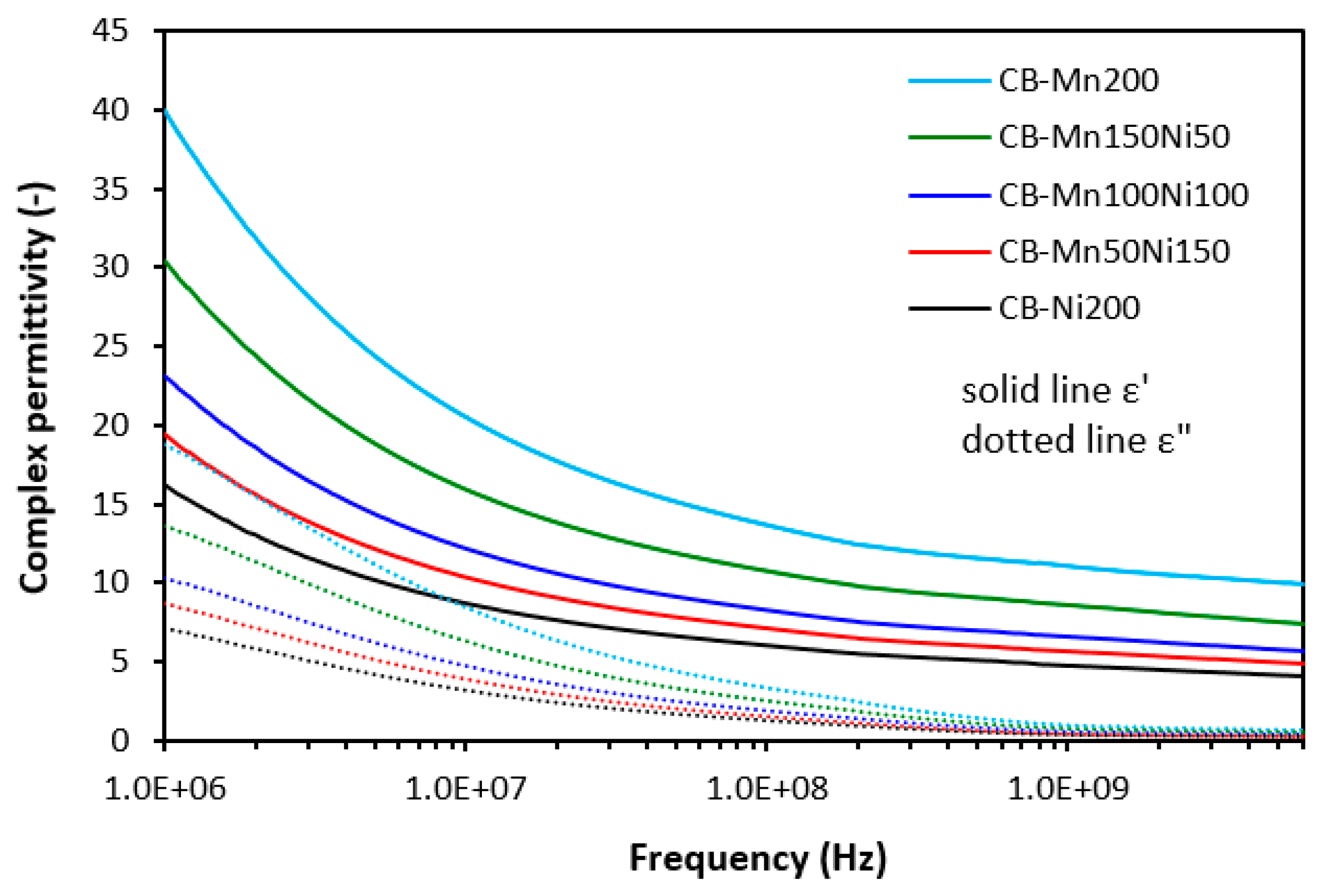
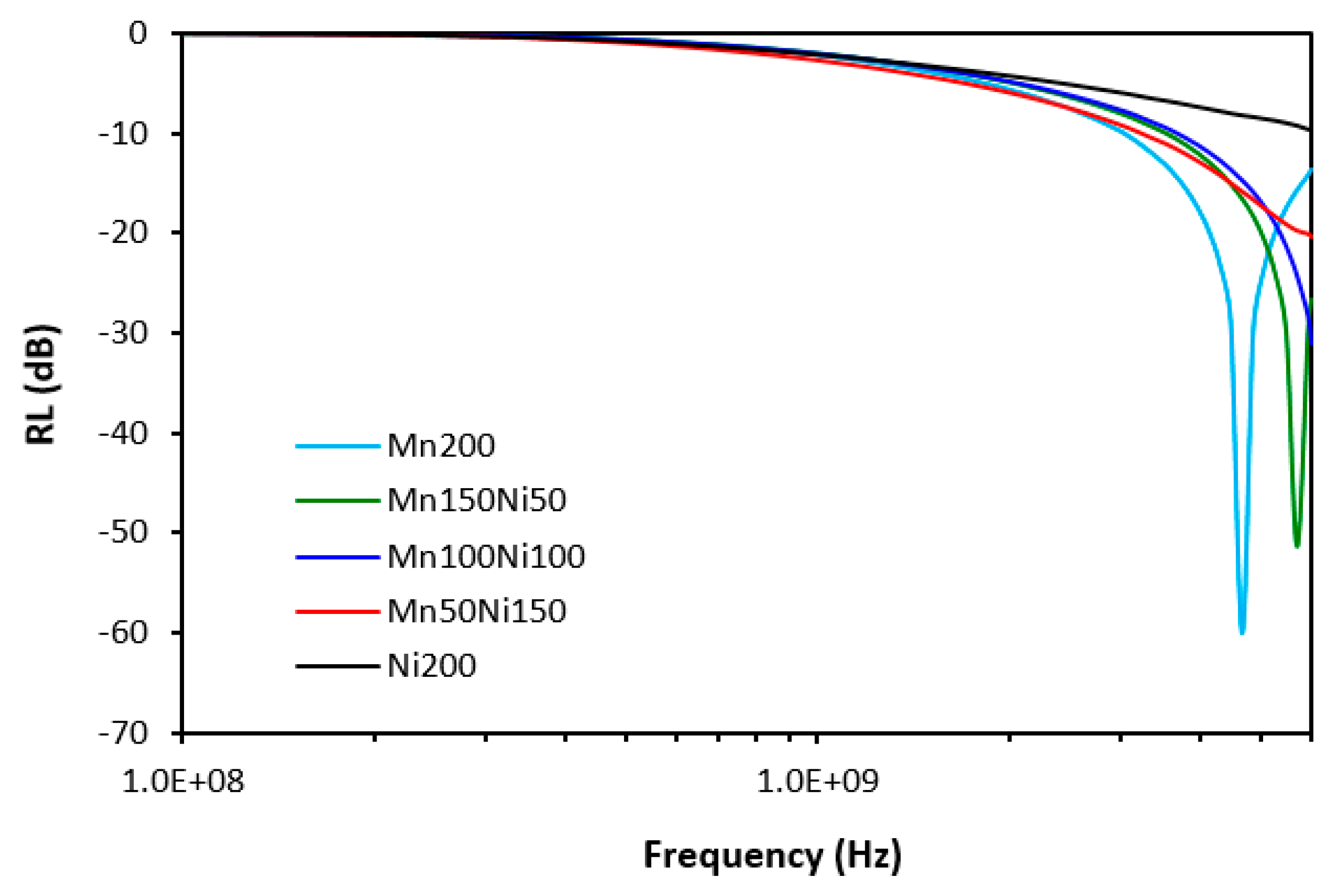
3.1. Electromagnetic Absorption Parameters and Electrical Conductivity
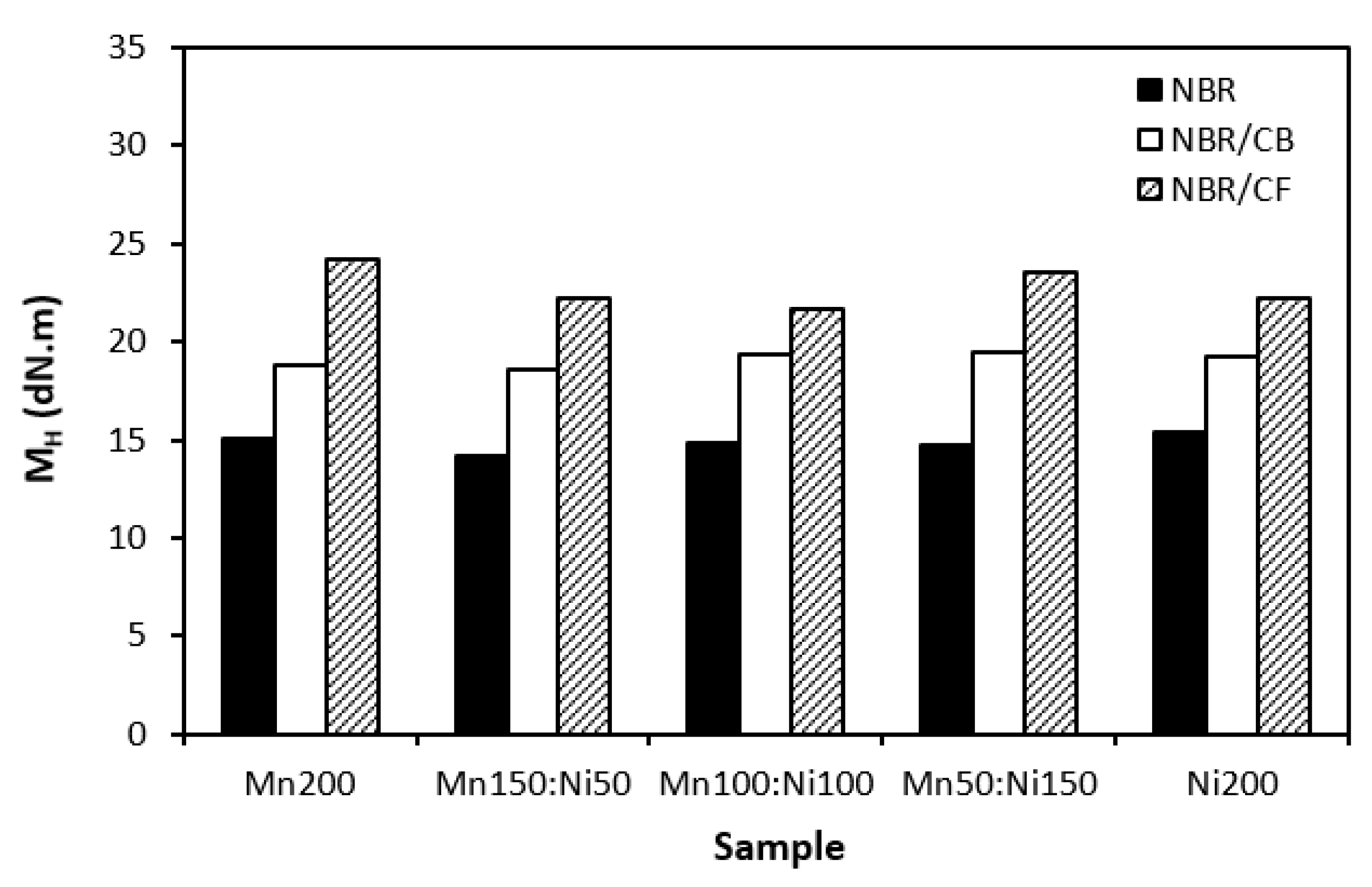
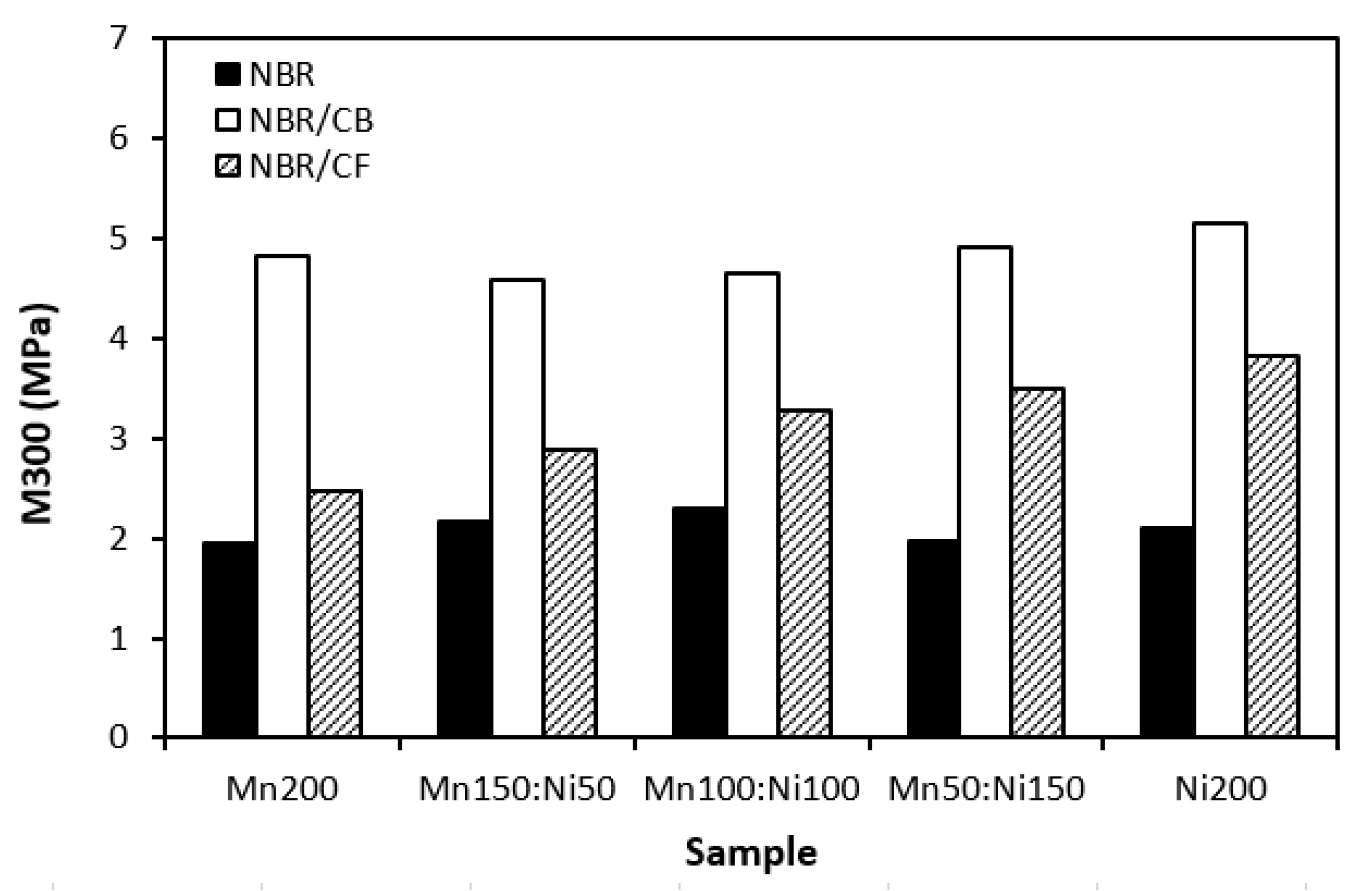
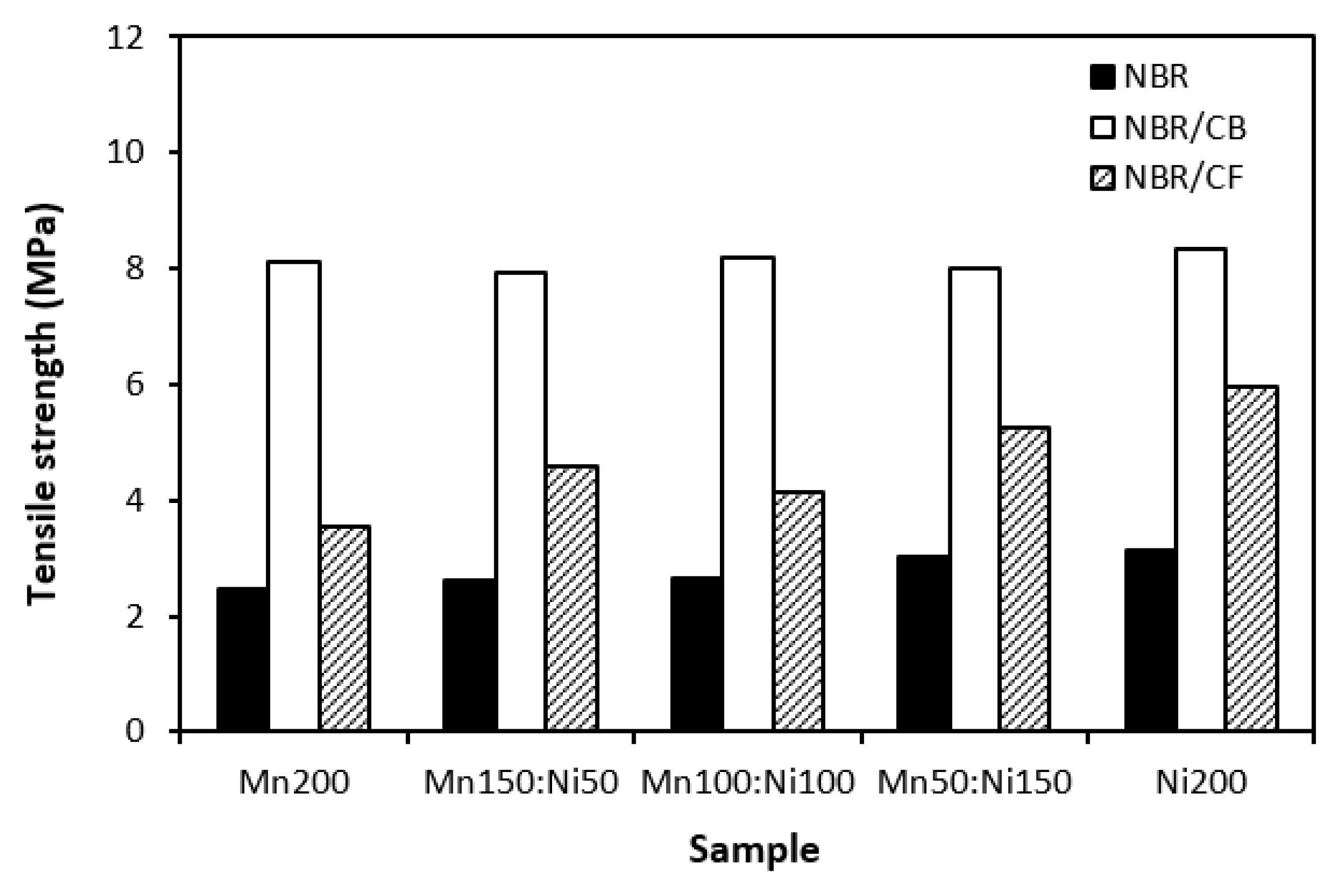
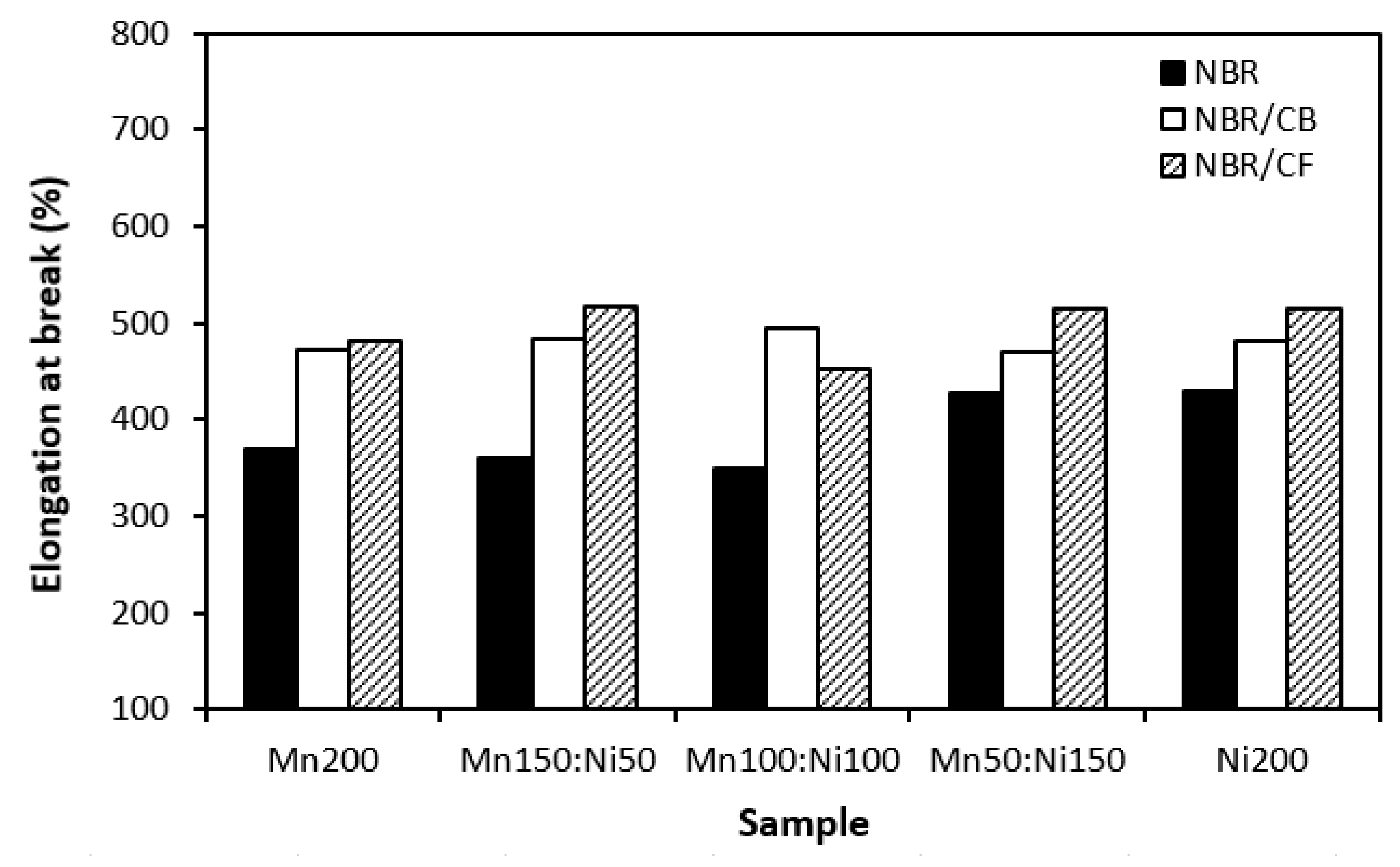
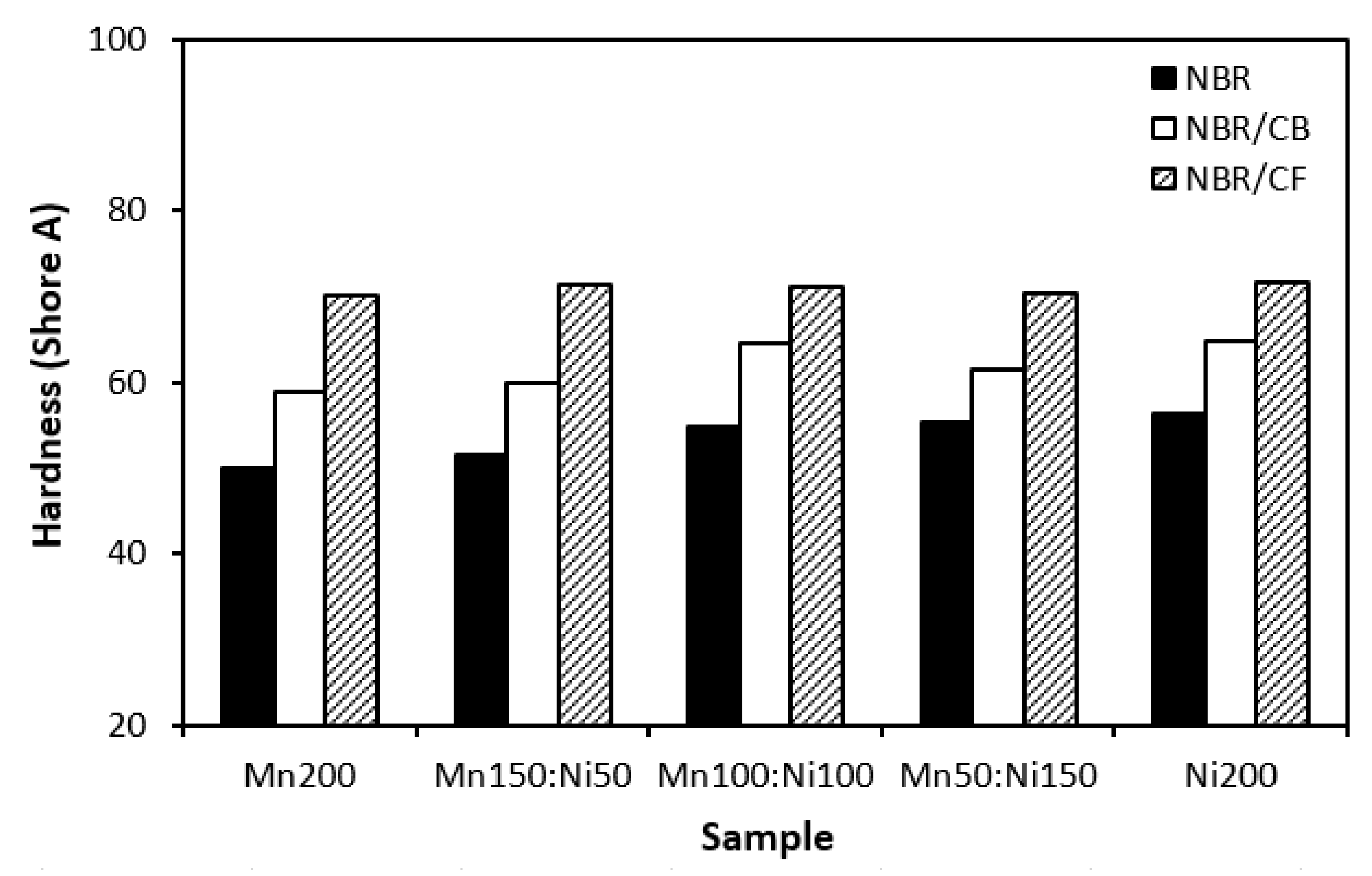
3.1. Physical-Mechanical Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Huang Y, Chen M, Xie A, Wang Y, Xu X: Recent advances in design and fabrication of nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave shielding and absorbing. Materials. 2021;14:4148. [CrossRef]
- Apakuppakul S, Methachittiphan N, Apiyasawat S: Effect of electromagnetic interference from smartphone on cardiac implantable electronic device (EMI-PHONE study). J Arrhythm. 2022;38:778-782. [CrossRef]
- Deutschmann B, Winkler OVE G, Kastner P: Impact of electromagnetic interference on the functional safety of smart power devices for automotive applications. Elektrotech Inf tech. 2018;135(4-5):352-359. [CrossRef]
- Kaszuba-Zwoińska J, Gremba J, Gałdzińska-Calik B, Wójcik-Piotrowicz K, Thor PJ. Electromagnetic field induced biological effects in humans. Przegl Lek. 2015;72(11):636-641.
- Kim DK, Han W, Kim KW, Kim BJ: Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of direct-grown-carbon nanotubes/carbon and glass fiber-reinforced epoxy matrix composites. Materials. 2023;16:2604. [CrossRef]
- Kausar A, Ahmad I, Zhao T, Aldaghri O, Ibnaouf KH, Eisa MH, Lam TD: Graphene nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding - trends and advancements. J Compos Sci. 2023;7:384. [CrossRef]
- Gümüş E, Yaǧımlı M, Arca E: Investigation of the dielectric properties of graphite and carbon black-filled composites as electromagnetic interference shielding coatings. Appl Sci. 2023;13:8893. [CrossRef]
- Ma Y, Zhuang Y, Li Ch, Shen X, Zhang L: Improving electromagnetic interference shielding while retaining mechanical properties of carbon fiber-based composites by introducing carbon nanofiber sheet into laminate structure. Polymers. 2022;14:1658. [CrossRef]
- Chang J, Zhai H, Hu Z, Li J: Ultra-thin metal composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos B. 2022;246:110269. [CrossRef]
- Shakir MF, Tariq A, Rehan ZA, Nawab Y, Rashid IA, Afzal A, Hamid U, Raza F, Zubair K, Rizwan MS, Riaz S, Sultan A, Muttaqi M: Effect of nickel-spinal-ferrites on EMI shielding properties of polystyrene/polyaniline blend. SN Appl Sci. 2020;2:706. [CrossRef]
- Çakmakçi N, Kim G, Song H, Shin M, Jung Y, Jeong Y: Ferrite-decorated ultrathin and lightweight carbon nanotube film for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2023;6:18229-18237. [CrossRef]
- Gao Q, Wang X, Schubert DW, Liu X: Review on polymer/MXene composites for electromagnetic interference shielding applications. Adv Nanocompos. 2024;1:52-76. [CrossRef]
- Gao Y, Wang Z: Microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of Li-Zn ferrite-carbon nanotubes composite. J Magn Magn Mater. 2021;528:167808. [CrossRef]
- Huang Y, Chen M, Xie A, Xu X: Recent advances in design and fabrication of nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave shielding and absorbing. Materials. 2021;14:4148. [CrossRef]
- Xu H, Yin X, Zhu M, Li M, Zhang H, Wei H, Zhang L, Cheng L: Constructing hollow graphene nano-spheres confined in porous amorphous carbon particles for achieving full X band microwave absorption. Carbon. 2019;142:346-353. [CrossRef]
- Barathi Dassan EG, Ab Rahman AA, Zainol Abidin MS, Md Akil H: Carbon nanotube-reinforced polymer composite for electromagnetic interference application: A review. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9:768-788. [CrossRef]
- Dalal J, Lather S, Gupta A, Dahiya S, Maan AS, Singh K, Dhawan SK, Ohlan A: EMI shielding properties of laminated graphene and PbTiO3 reinforced poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol. 2018;165:222-230. [CrossRef]
- Kruželák J, Kvasničáková, Hložeková K, Hudec I: Progress in polymers and polymer composites used as efficient materials for EMI shielding. Nanoscale Adv. 2021;3:123. [CrossRef]
- Pongmuksuwan P, Salayong K, Lertwiriyaprapa T, Kitisatorn W: Electromagnetic absorption and mechanical properties of natural rubber composites based on conductive carbon black and Fe3O4. Materials. 2022;15:6532. [CrossRef]
- Singh Yadav R, Kuřitka I, Vilčáková J, Machovský M, Škoda D, Urbánek P, Masař M, Gořalik M, Urbánek M, Kalina L, Havlica J: Polypropylene nanocomposite filled with spinel ferrite NiFe2O4 nanoparticles and in-situ thermally-reduced graphene oxide for electromagnetic interference shielding application. Nanomaterials. 2019;9:621. [CrossRef]
- Phan CH, Mariatti M, Koh YH: Electromagnetic interference shielding performance of epoxy composites filled with multiwalled carbon nanotubes/manganese zinc ferrite hybrid fillers. J Magn Magn Mater. 2016;401:472-478. [CrossRef]
- Sadek R, Sharawi MS, Dubois Ch, Tantawy H, Chaouki J: Reduced graphene oxide/barium ferrite ceramic nanocomposite synergism for high EMI wave absorption. ACS Omega. 2023;8:15099-15113. [CrossRef]
- Kruželák J, Kvasničáková A, Hložeková K, Dosoudil R, Gořalík M, Hudec I: Electromagnetic interference shielding and physical-mechanical characteristics of rubber composites filled with manganese-zinc ferrite and carbon black. Polymers. 2021;13:616. [CrossRef]
- Li ZW, Yang ZH.: The studies of high-frequency magnetic properties and absorption characteristics for amorphous-filler composites. J Magn Magn Mater. 2015;391:172-178. [CrossRef]
- Alegaonkar AP, Baskey HB, Alegaonkar PS: Microwave scattering parameters of ferro-nanocarbon composites for tracking range countermeasures. Mater Adv. 2022;3:1660. [CrossRef]
- Pawar SP, Arjmand M, Pötschke P, Krause B, Fisher D, Bose S, Sundararaj U: Tuneable dielectric properties derived from nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes in PVDF-based nanocomposites. ACS Omega. 2018;3:9966-9980. [CrossRef]
- Koriem AA, Abd El-Aziz ME, Salem SR, Hussain AI, Turky G: Management of agricultural waste to manufacture biochar: An alternative reinforcing filler for carbon black in nitrile butadiene rubber composites. J Clean Prod. 2023;428:139360. [CrossRef]
- Sarvi A, Sundararaj U: Electrical permitivitty and electrical conductivity of multiwalled carbon nanotube-polyaniline (MWCNT-PANi) core-shell nanofibres and MWCNT-PANi/polystyrene composites. Macromol Mater Eng. 2014;299:1013-1020. [CrossRef]
- Yadav RS, Kuřitka I, Vilcakova J, Machovsky M, Skoda D, Urbánek P, Masař M, Jurča M, Urbánek M,Kalina L, Havlica J.: NiFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by dextrin from corn-mediated sol−gel combustion method and its polypropylene nanocomposites engineered with reduced graphene oxide for the reduction of electromagnetic pollution. ACS Omega. 2019;4:22069−22081. [CrossRef]
- Petrossian G, Aliheidari N, Ameli A.: Thermoplastic polyurethane/lead zirconate titanate/carbon nanotube composites with very high dielectric permittivity and low dielectric loss. J Compos Sci. 2020;4:137. [CrossRef]
- Zachariah SM, Antony T, Grohens Y, Thomas S: From waste to wealth: A critical review on advanced materials for EMI shielding. J Appl Polym Sci. 2022;139:e:52974. [CrossRef]
- Naghdi S, Jaleh B, Eslamipanah M, Moradi A, Abdollahi M, Einali N, Rhee KY: Graphene family, and their hybrid structures for electromagnetic interference shielding applications: Recent trends and prospects. J Alloys Compd. 2022;900:163176. [CrossRef]
- Kruželák J, Kvasničáková A, Hložeková K, Plavec R, Dosoudil R, Gořalík M, Vilčáková J, Hudec I: Mechanical, thermal, electrical characteristics and EMI absorption shielding effectiveness of rubber composites based on ferrite and carbon fillers. Polymers, 2021;13:2937. [CrossRef]
- Li M, Zhao Y, Zhang M, Jiang S, Farooq A, Liu L, Ge A, Liu L: Recent progress in the application of cellulose in electromagnetic interference shielding materials. Macromol Mater Eng. 2022;307:2100899. [CrossRef]
- Chen W, Wang J, Zhang B, Wu Q, Su X: Enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding properties of carbon fiber veil/Fe3O4 nanoparticles/epoxy multiscale composites. Mater Res Express. 2017;4:126303. [CrossRef]
- Xu L, Wan S, Heng Y, Wang S, Yang J, Dong Y, Fu Y, Ni Q: Double layered design for electromagnetic interference shielding with ultra-low reflection features: PDMS including carbon fibre on top and graphene on bottom. Compos Sci Technol. 2023;231:109797. [CrossRef]
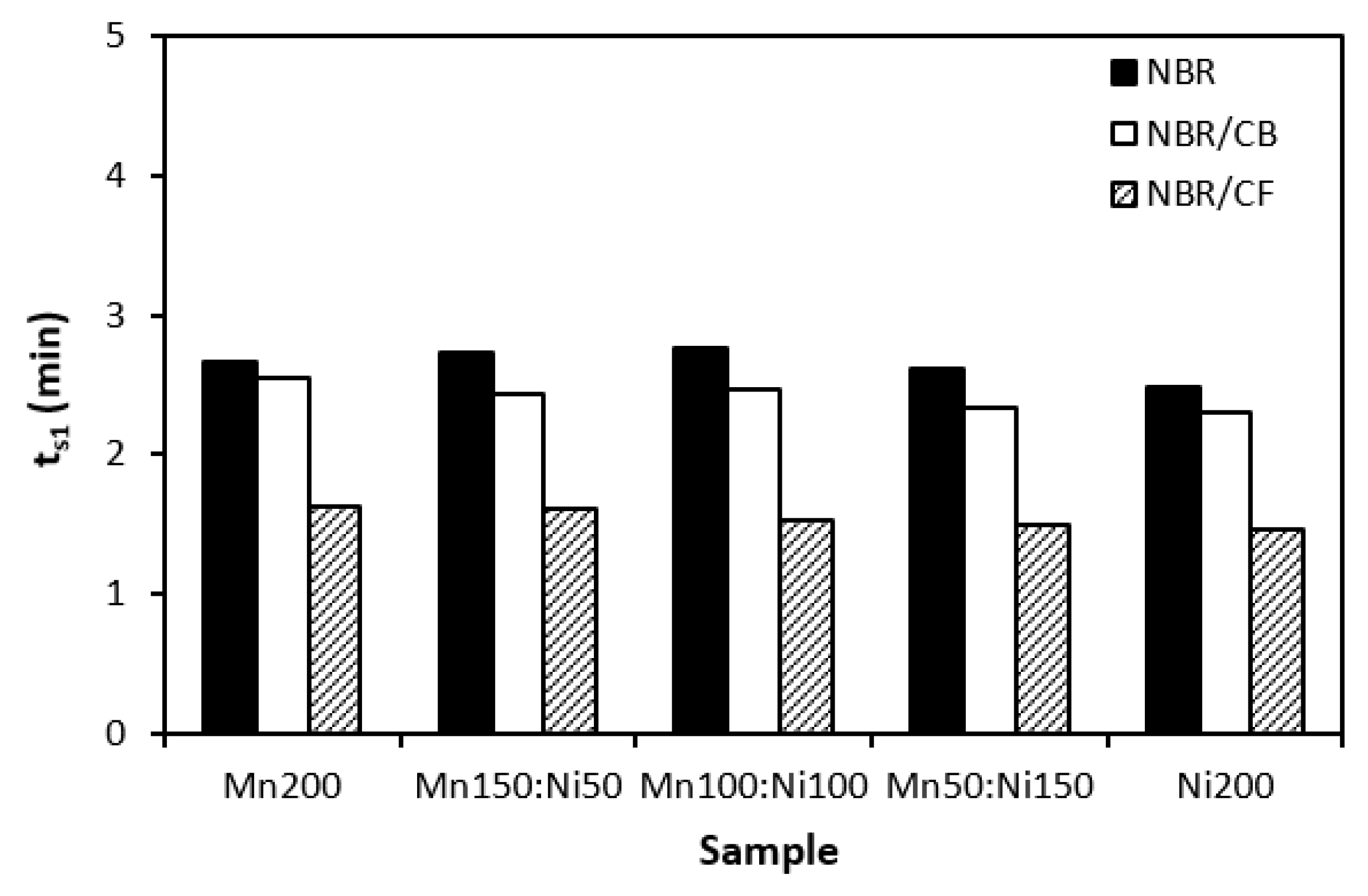
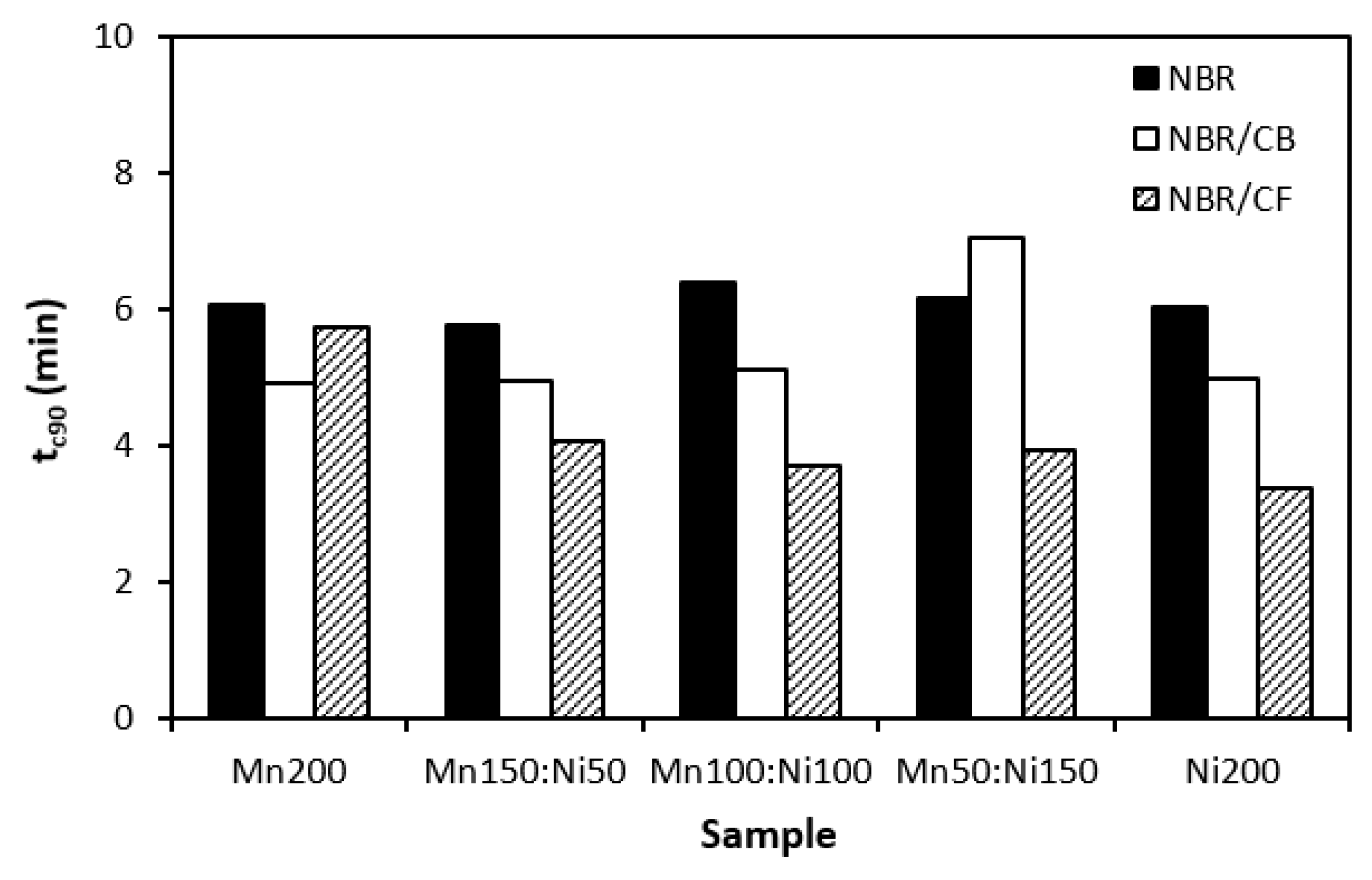
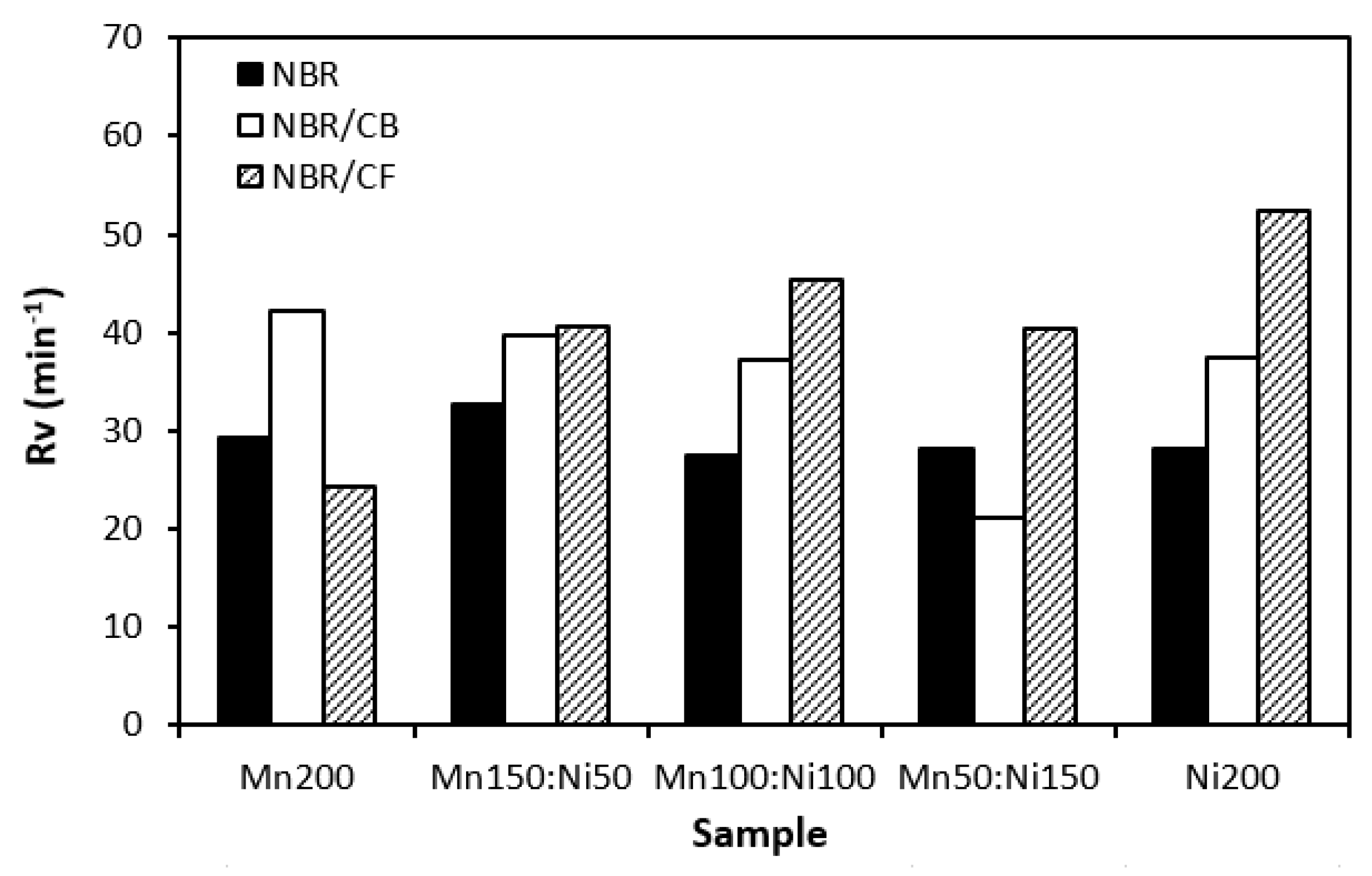
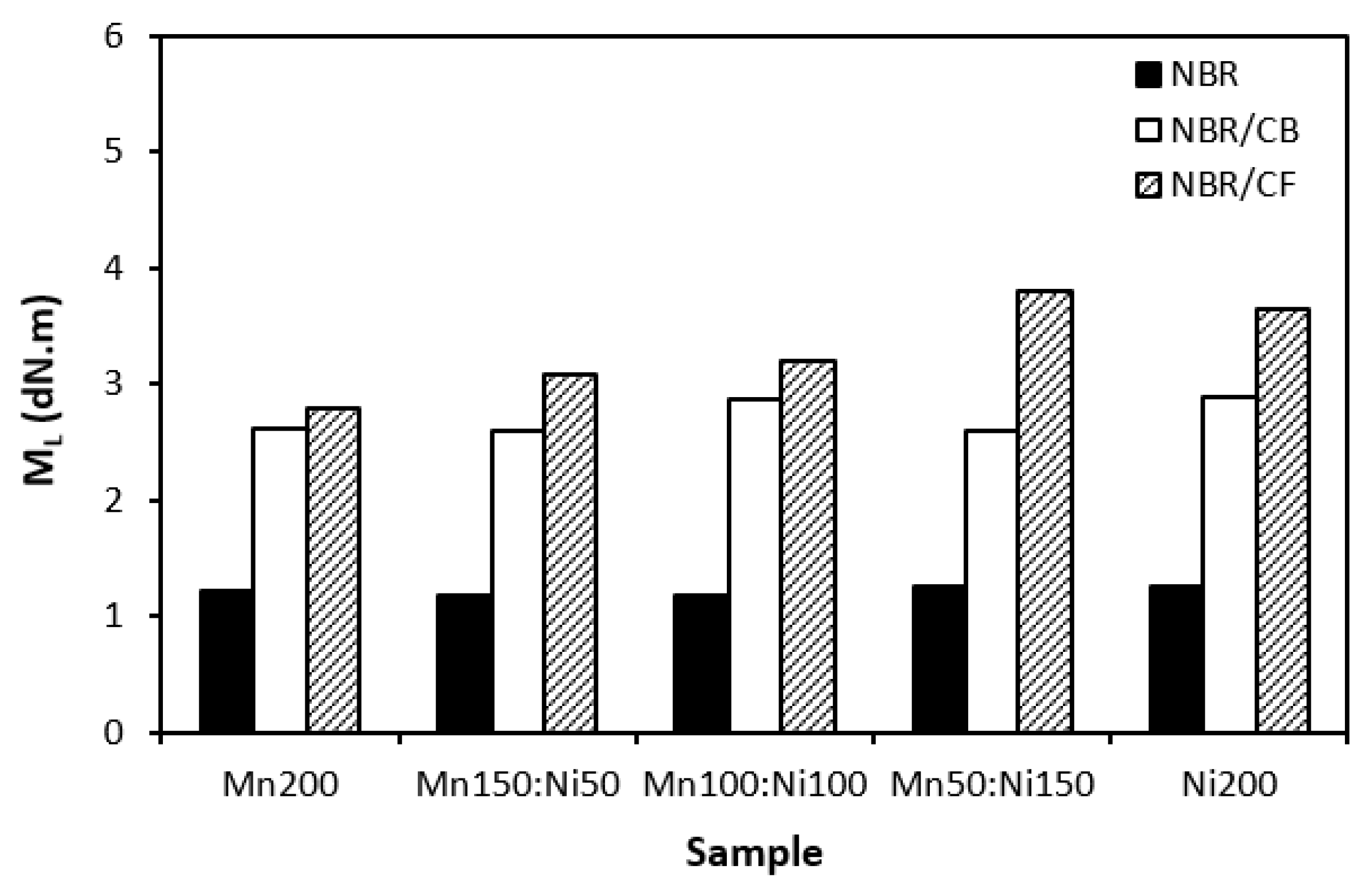

| filler | Particle size distribution | D10 | D50 | ||
| MnZn ferrite | 0.7-50 µm | 4.7 µm | 16.3 µm | ||
| NiZn ferrite | 0.2-70 µm | 3.0 µm | 21.4 µm | ||
| NBR | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| ZnO | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||
| stearic acid | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||
| CBS | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | ||
| sulfur | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | ||
| MnZn ferrite | 200 | 150 | 100 | 50 | 0 | ||
| NiZn ferrite | 0 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 200 | ||
| designation | Mn200 |
Mn150 Ni50 |
Mn100 Ni100 |
Mn50 Ni150 |
Ni200 |
| NBR | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| ZnO | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||
| stearic acid | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||
| CBS | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | ||
| sulfur | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | ||
| CB or CF | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | ||
| MnZn ferrite | 200 | 150 | 100 | 50 | 0 | ||
| NiZn ferrite | 0 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 200 | ||
| designation | CB, CF-Mn200 |
CB, CF-Mn150 Ni50 |
CB, CF-Mn100 Ni100 |
CB, CF-Mn50 Ni150 |
CB, CF-Ni200 |
| sample | RLmin (dB) | fm (MHz) | Δf (MHz) -10 dB | Δf (MHz) -20 dB | ||
| Mn200 | -60.1 | 4670 | 2950 | 1100 | ||
| Mn150Ni50 | -51.4 | 5700 | 2450 | 980 | ||
| Mn100Ni100 | -31.1 | 6000 | 2300 | 630 | ||
| Mn50Ni150 | 20.3 | 6000 | 2800 | 200 | ||
| Ni200 | -9.7 | 6000 | - | - | ||
| sample | RLmin (dB) | fm (MHz) | Δf (MHz) -10 dB | Δf (MHz) -20 dB | ||
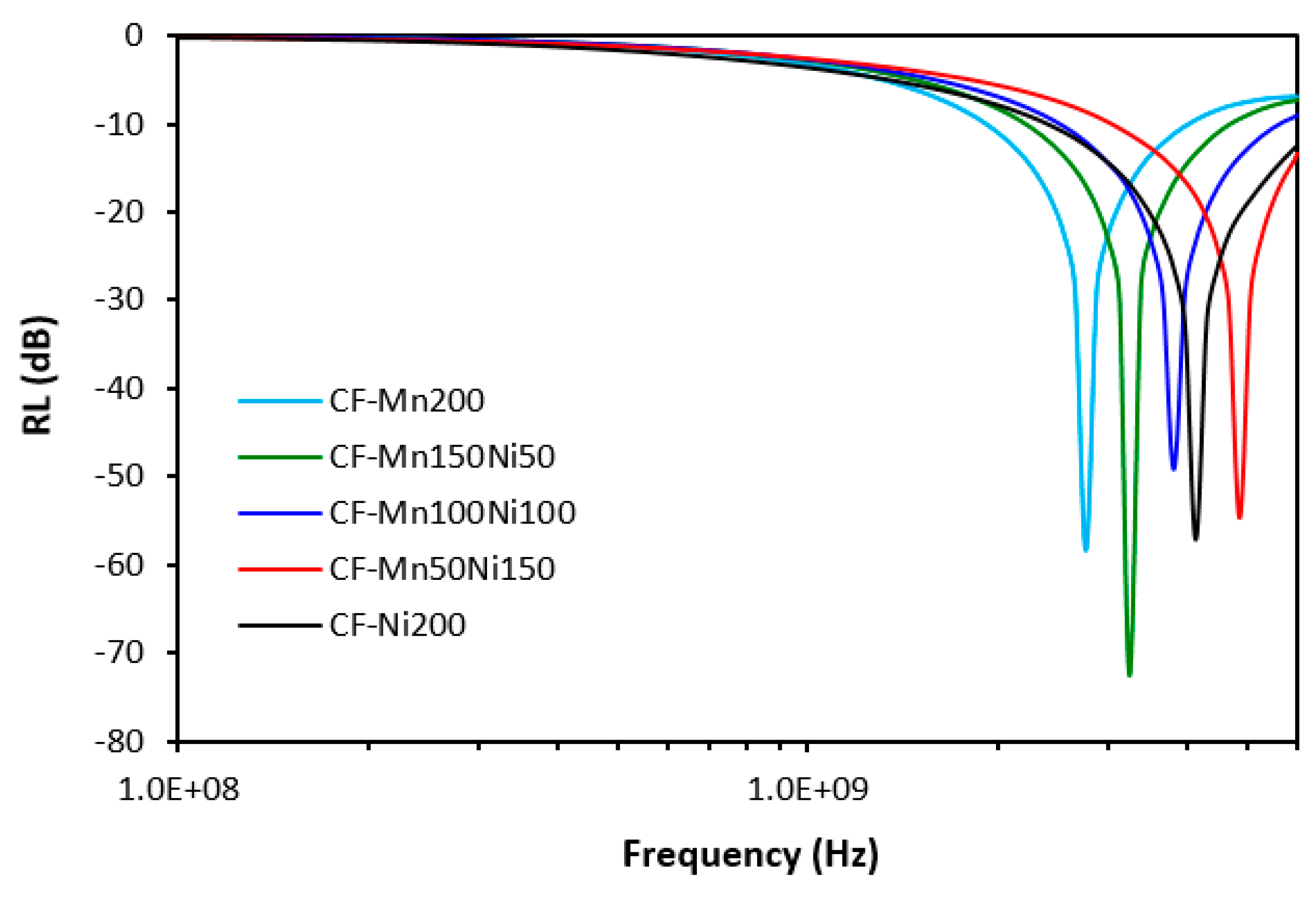
| CF-Mn200 | -58.3 | 2769 | 2130 | 600 | ||
| CF-Mn150Ni50 | -72.6 | 3250 | 2500 | 720 | ||
| CF-Mn100Ni100 | -49.2 | 3820 | 3140 | 900 | ||
| CF-Mn50Ni150 | -54.8 | 4860 | 2980 | 1130 | ||
| CF-Ni200 | -57.0 | 4140 | 3600 | 1380 | ||
| sample | RLmin (dB) | fm (MHz) | Δf (MHz) -10 dB | Δf (MHz) -20 dB | ||
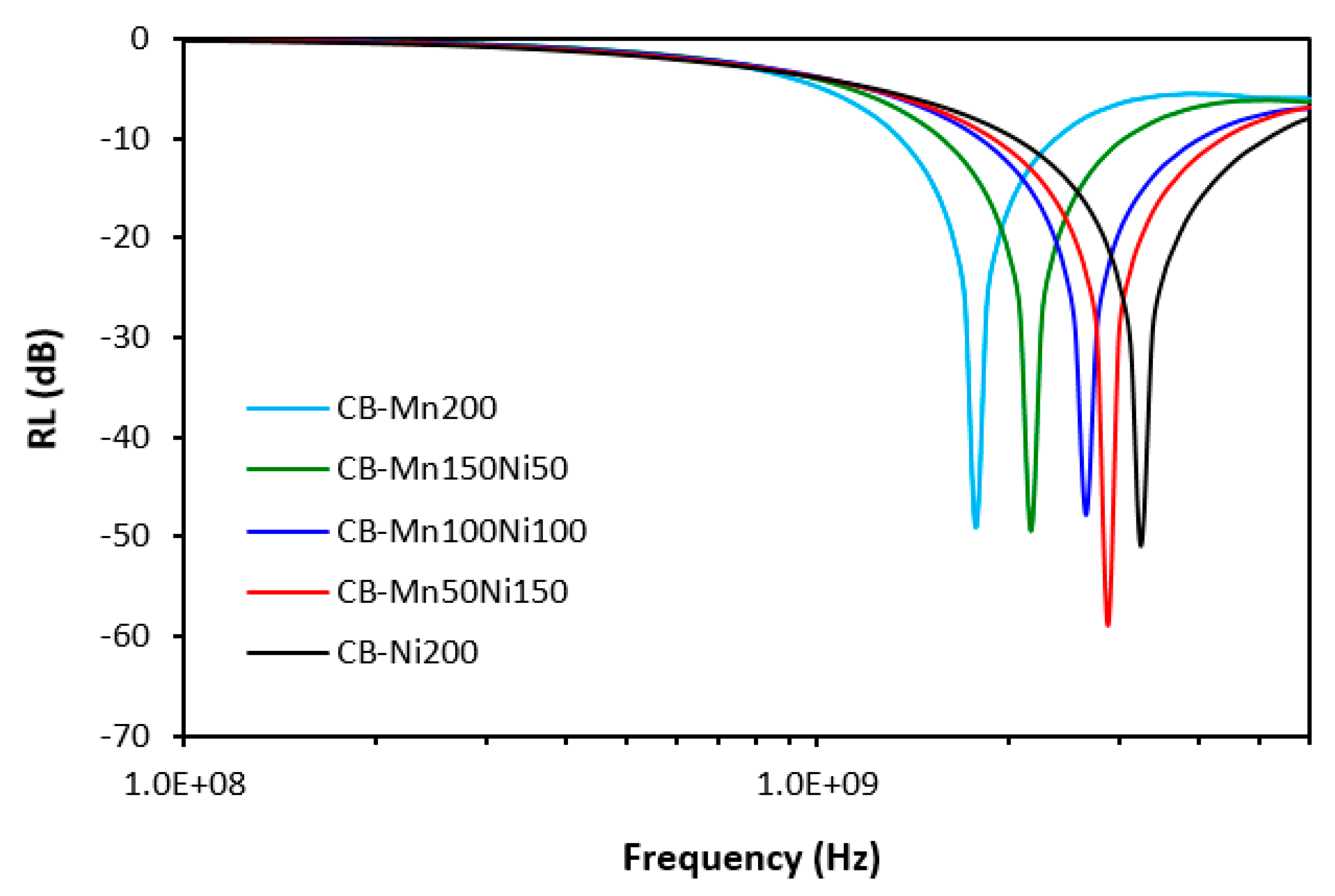
| CB-Mn200 | -49.0 | 1780 | 1060 | 300 | ||
| CB-Mn150Ni50 | -49.5 | 2180 | 1500 | 430 | ||
| CB-Mn100Ni100 | -47.8 | 2660 | 2240 | 600 | ||
| CB-Mn50Ni150 | -59.0 | 2880 | 2500 | 700 | ||
| CB-Ni200 | -51.0 | 3250 | 3100 | 880 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





