Submitted:
02 November 2023
Posted:
02 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
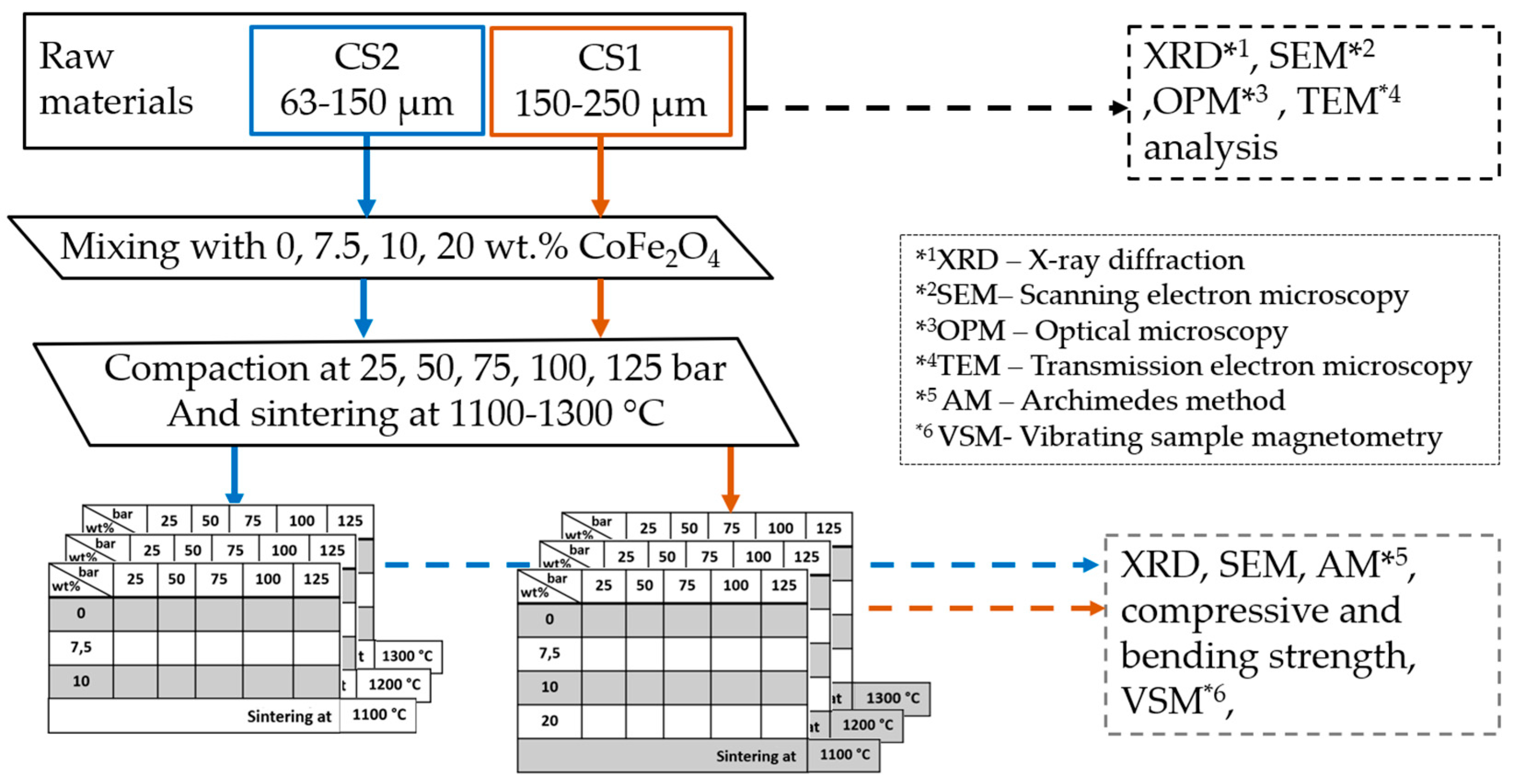
2. Materials and Methods
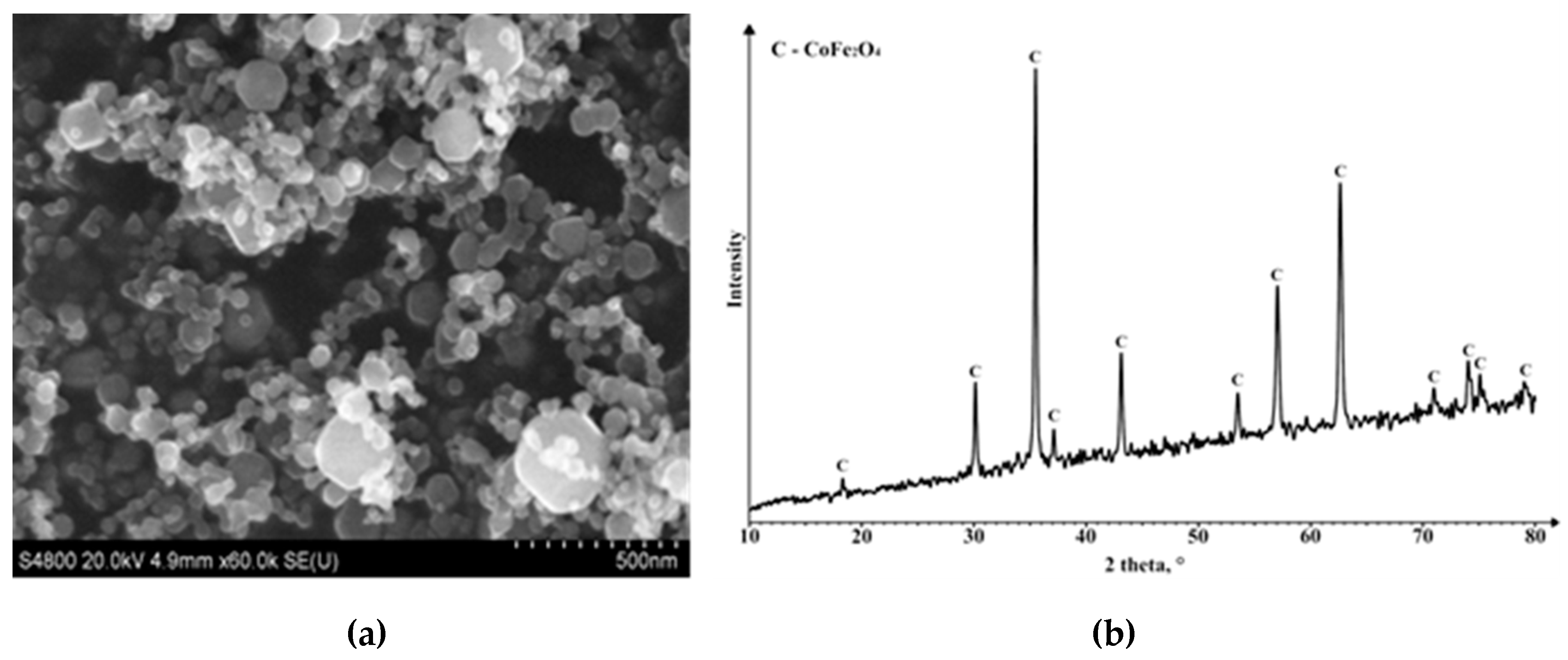
2.1. Materials
|
Ferrite |
Magnetic properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ms, emu/g | Mr, emu/g | Hc, Oe | |
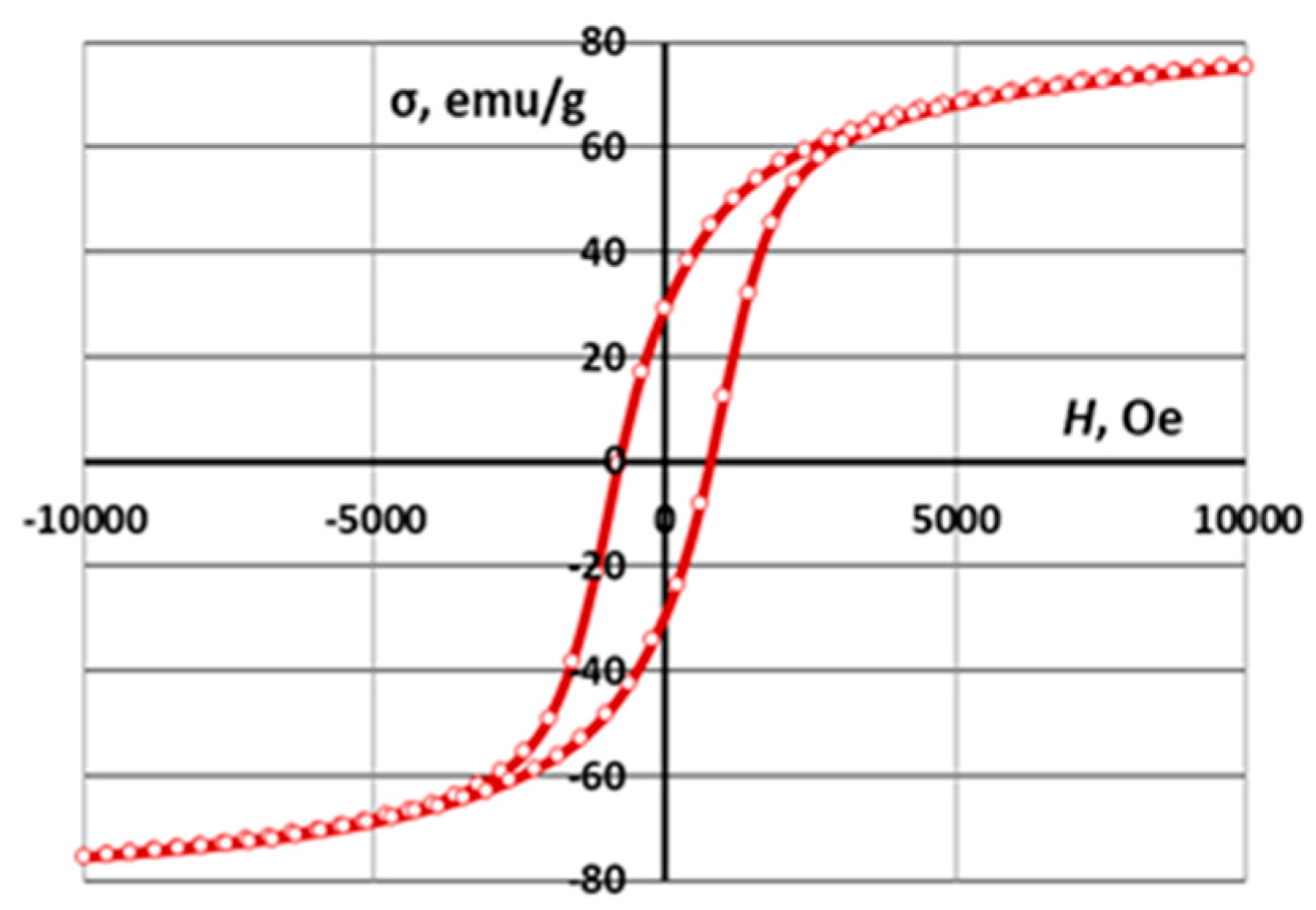
| CoFe2O4 | 75.4 | 32.0 | 780 |
2.2. Sintering process
2.3. Applied Characterization Methods
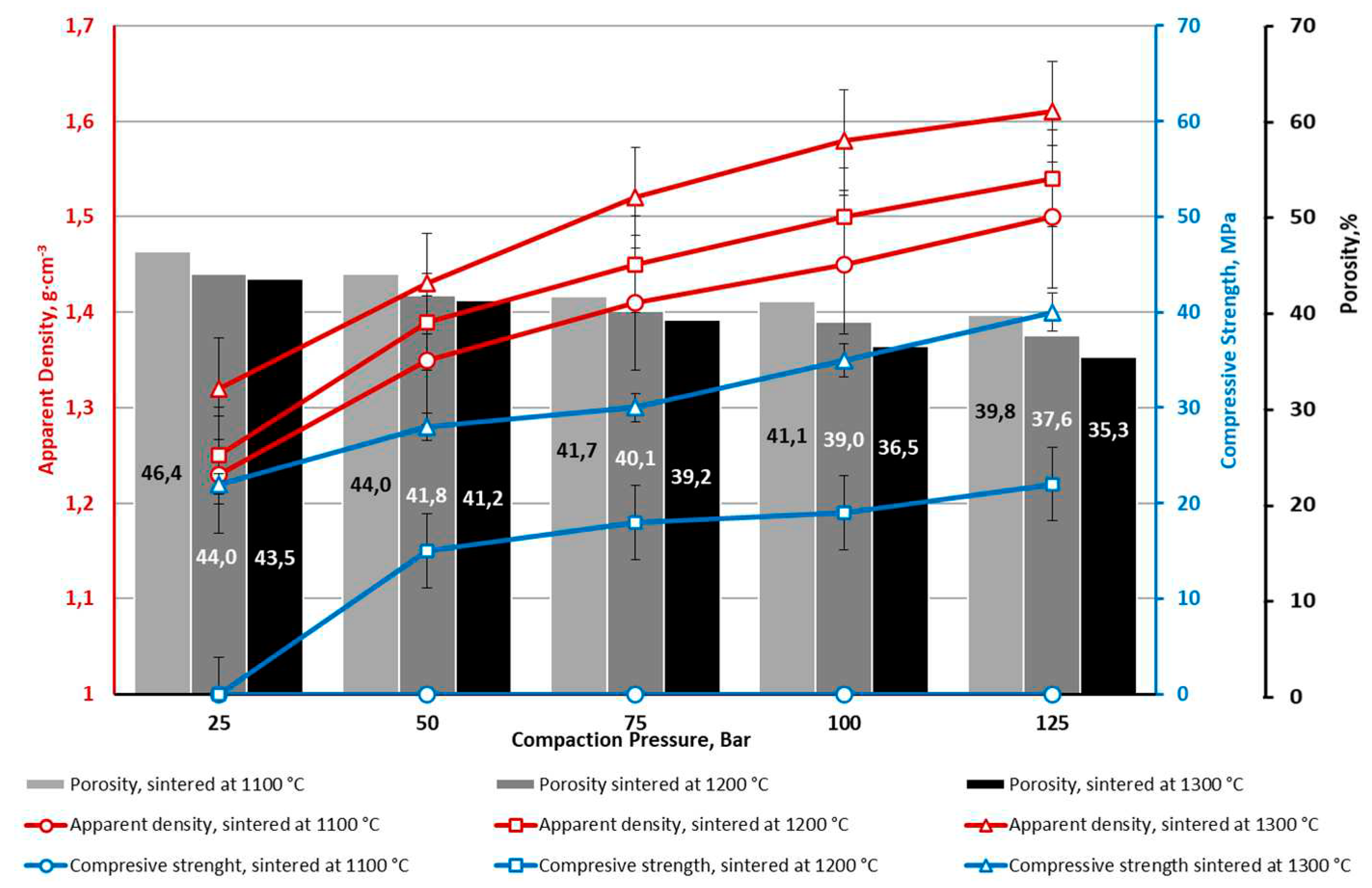
3. Results and Discussion
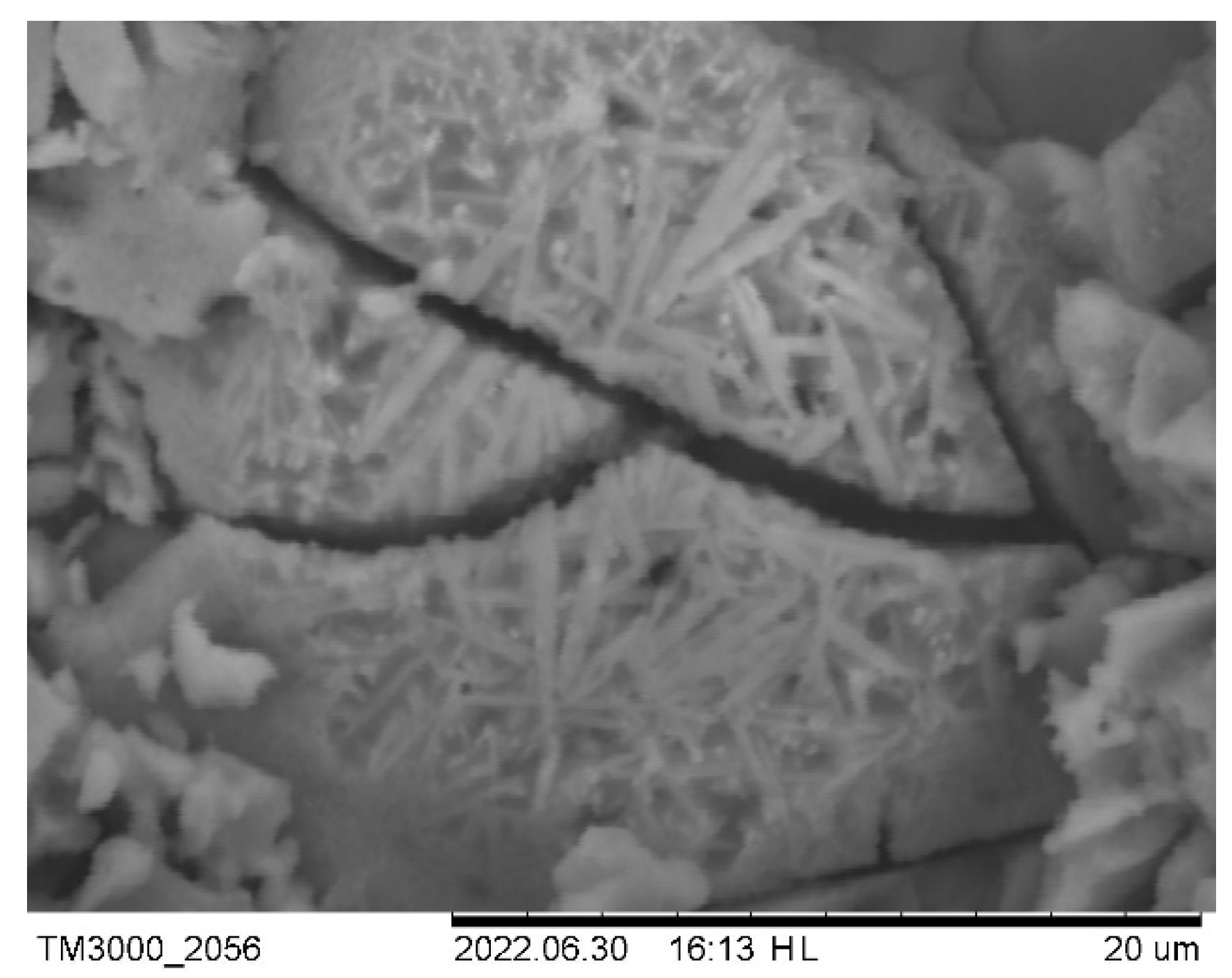
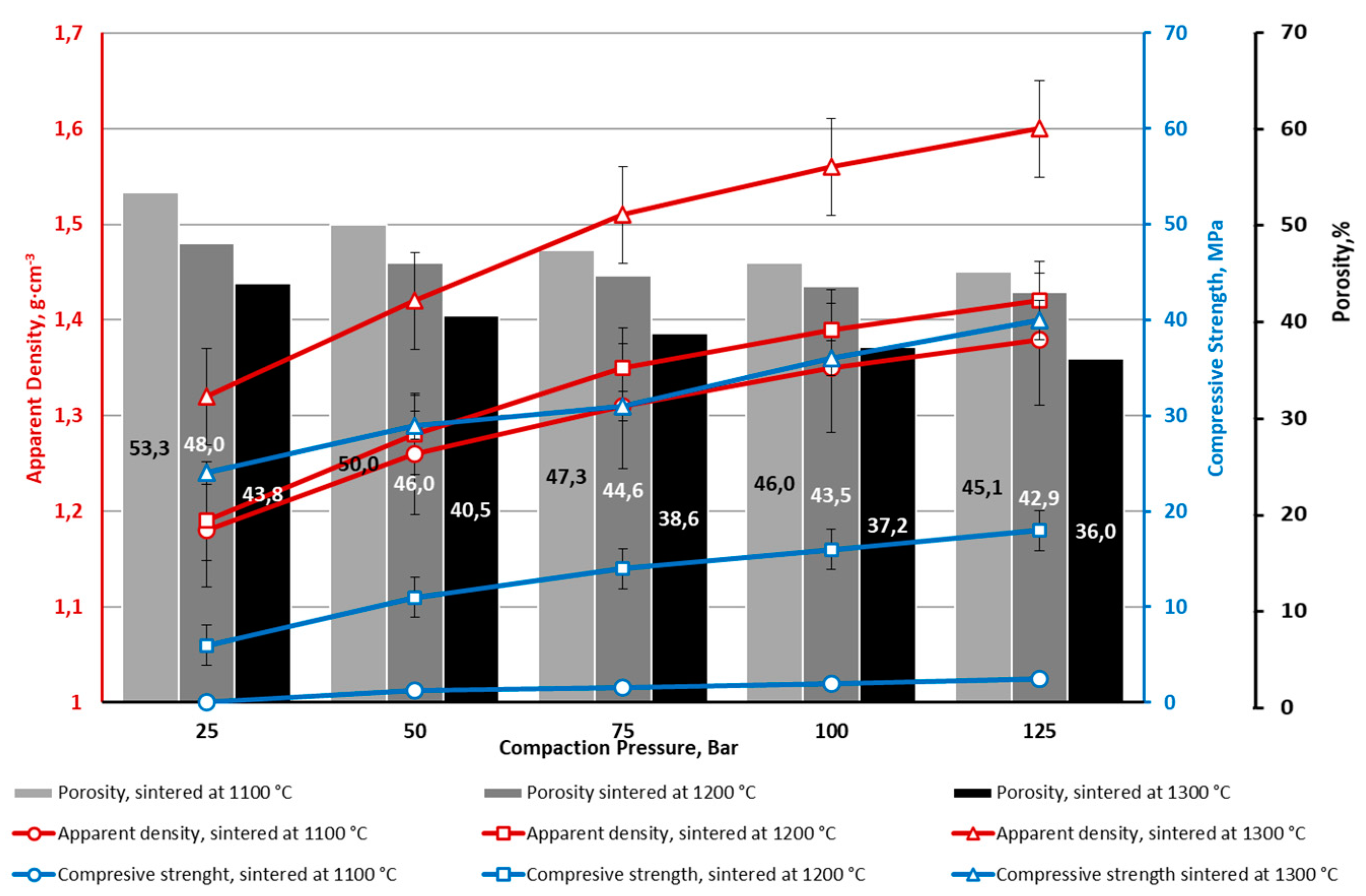
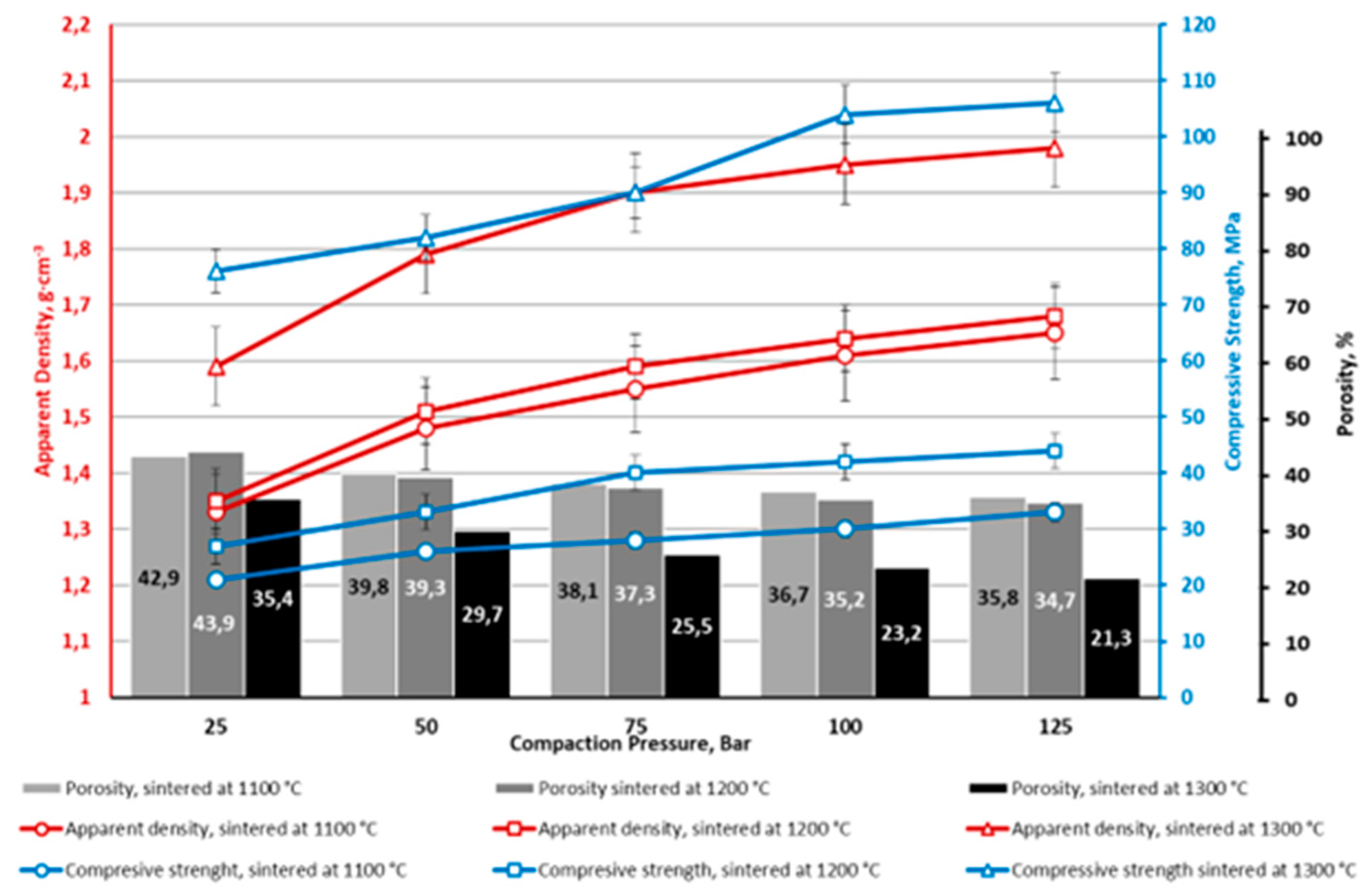
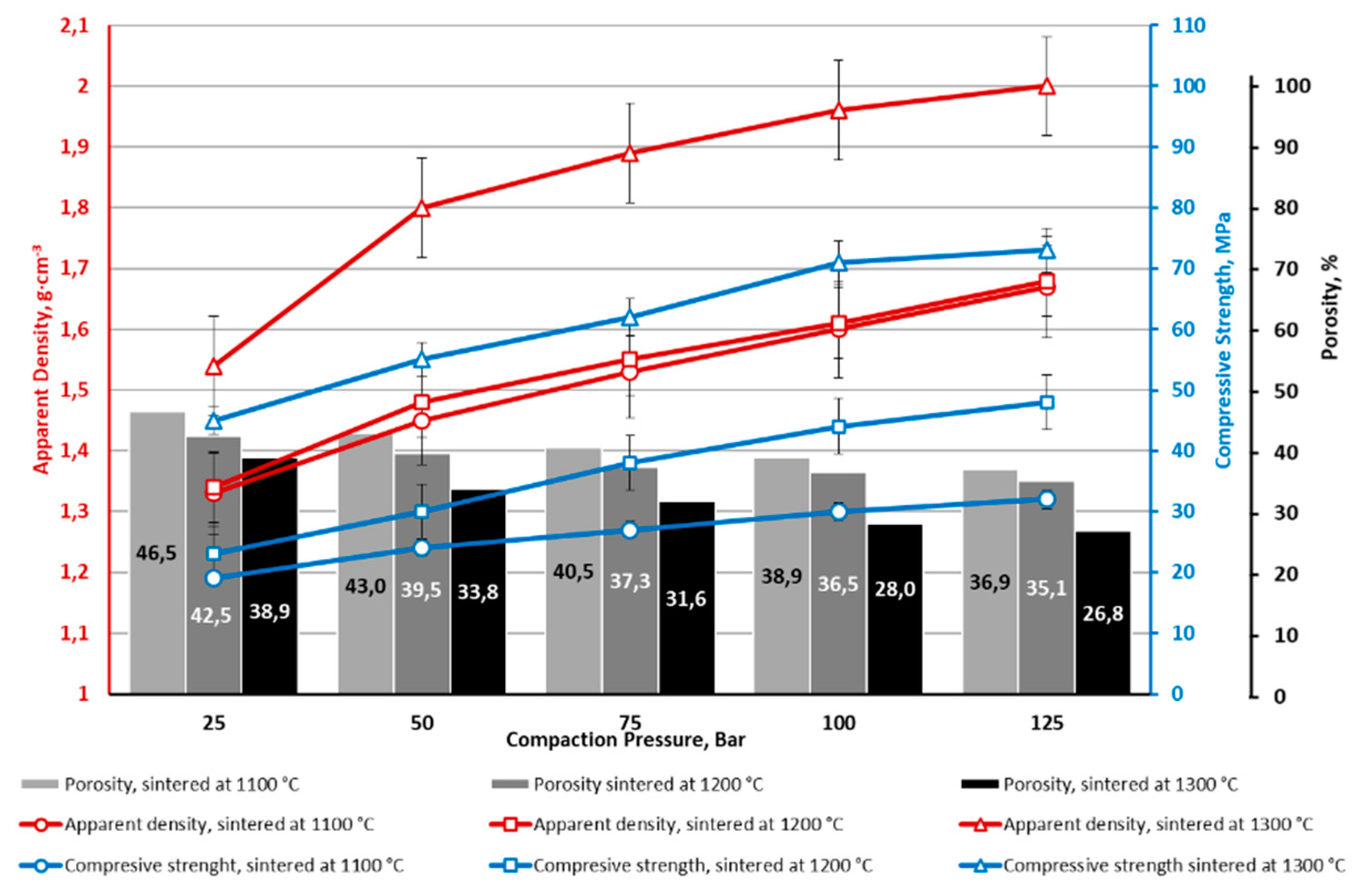
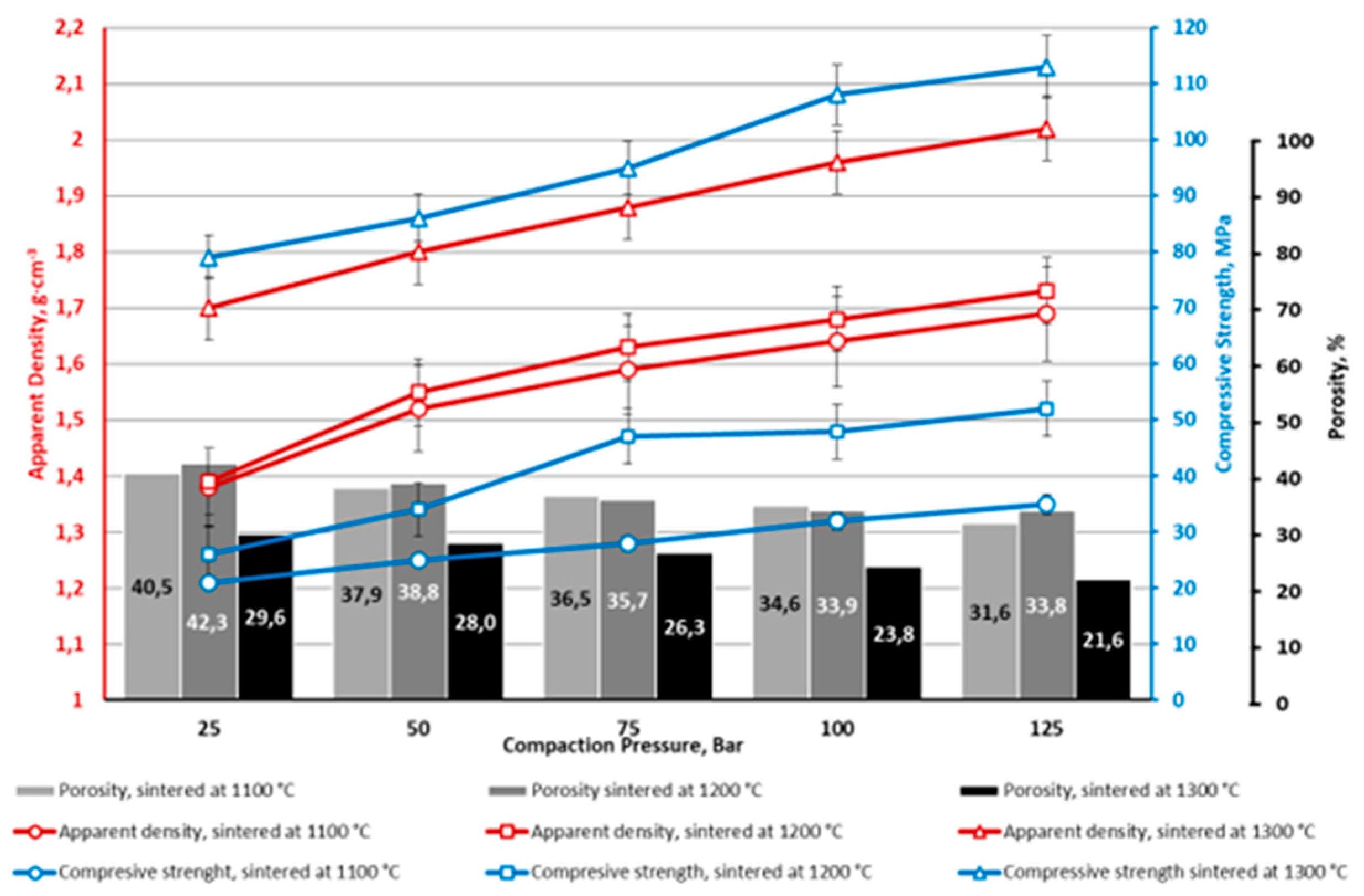
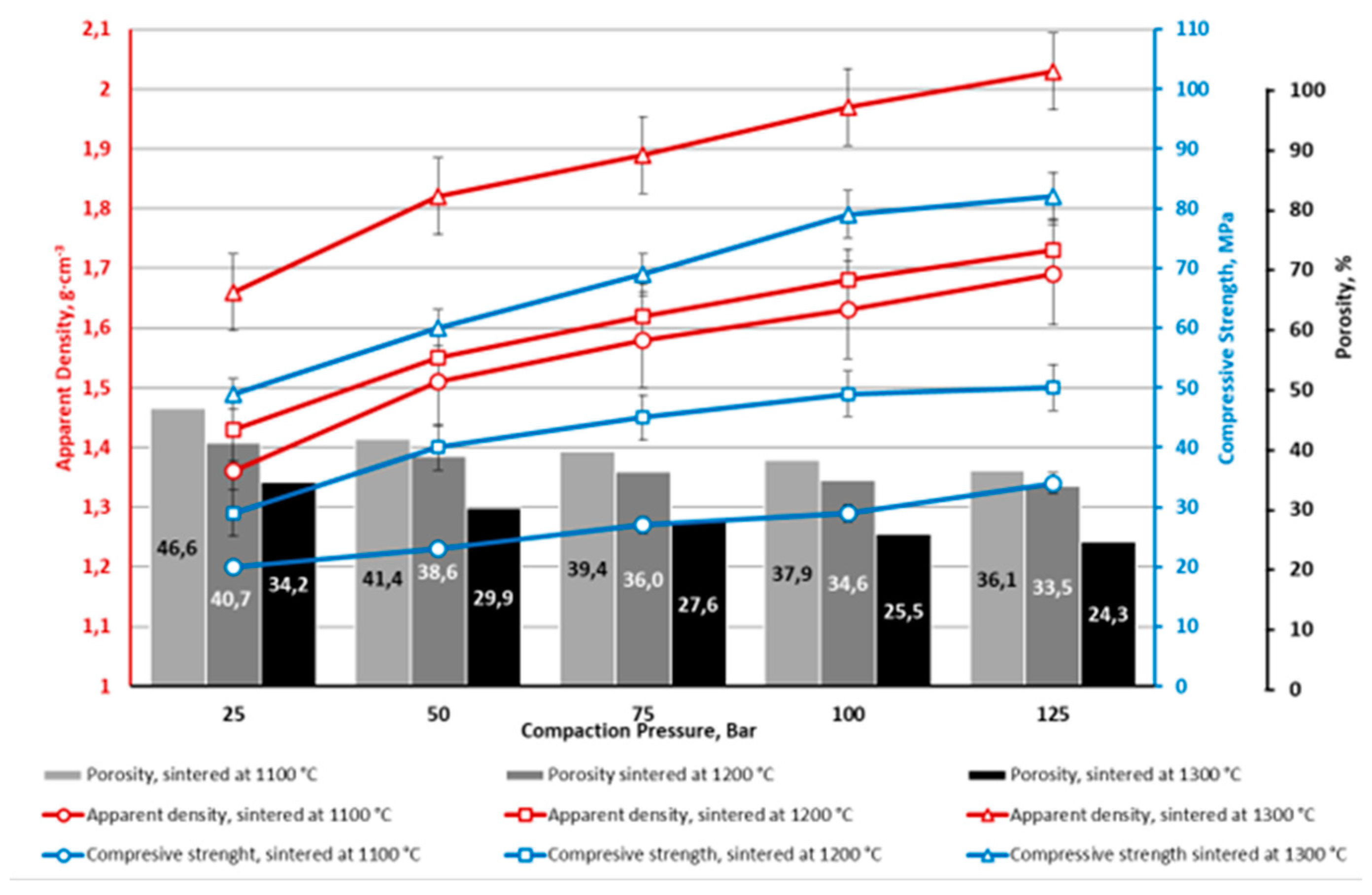
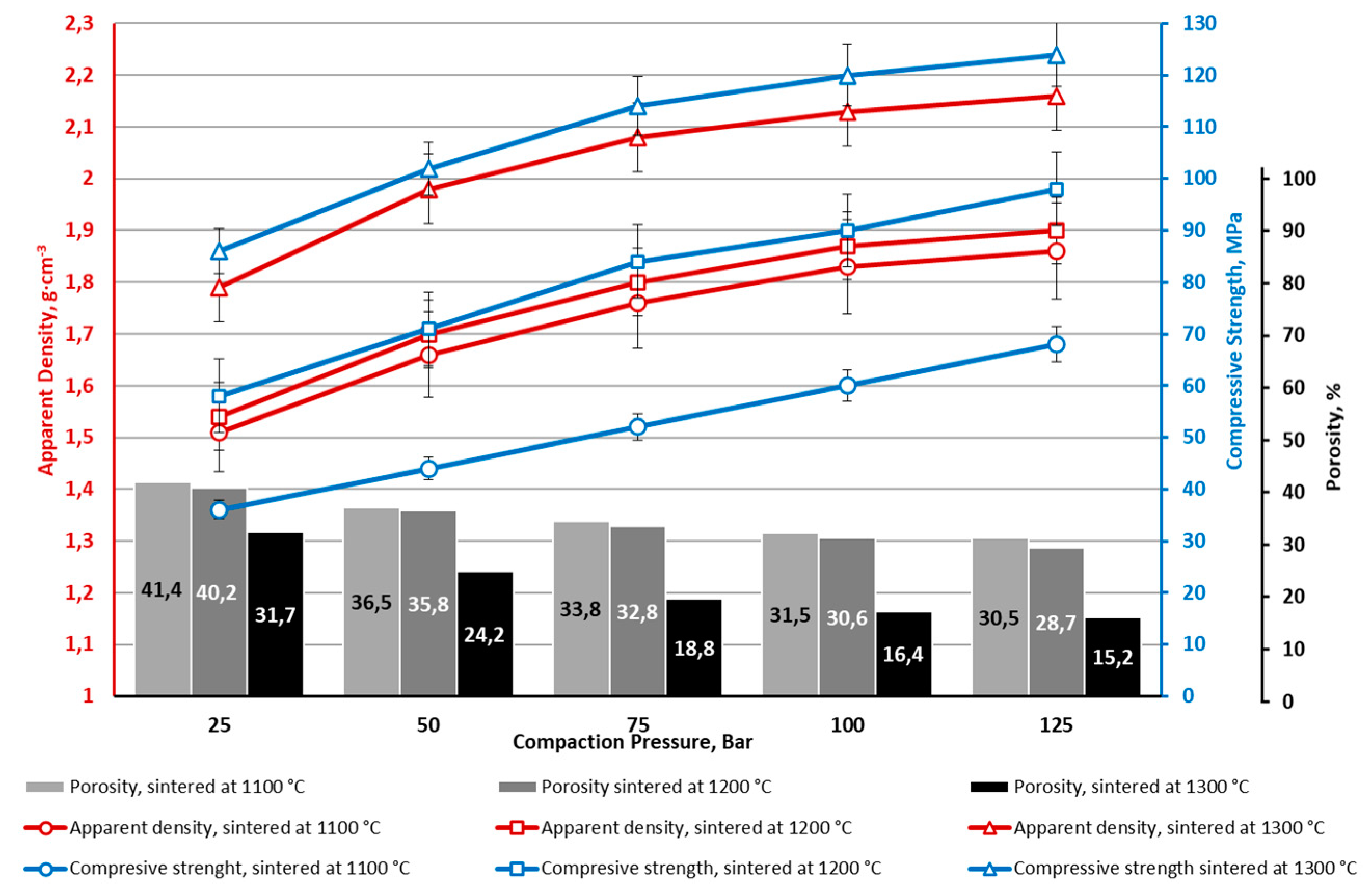
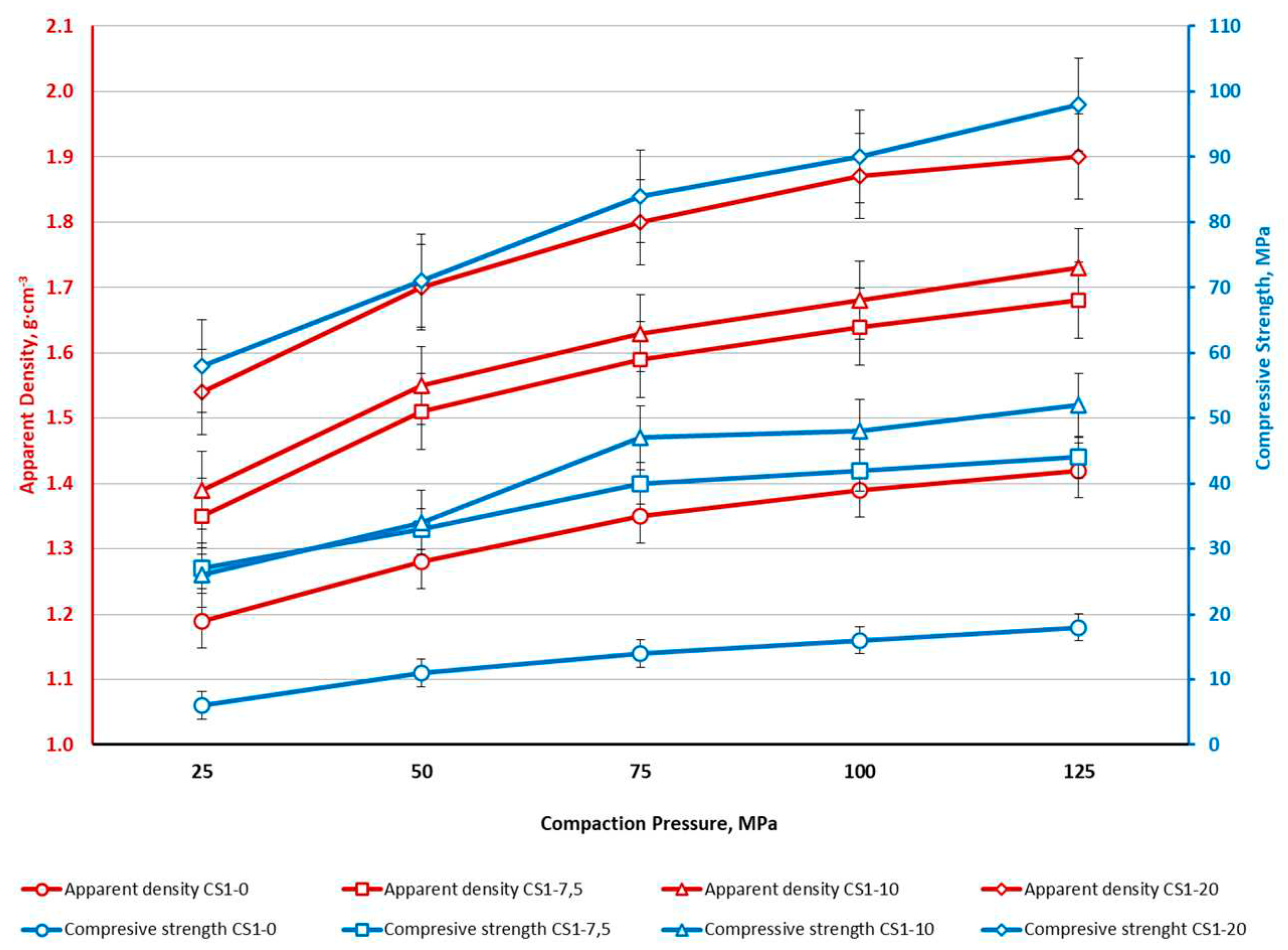
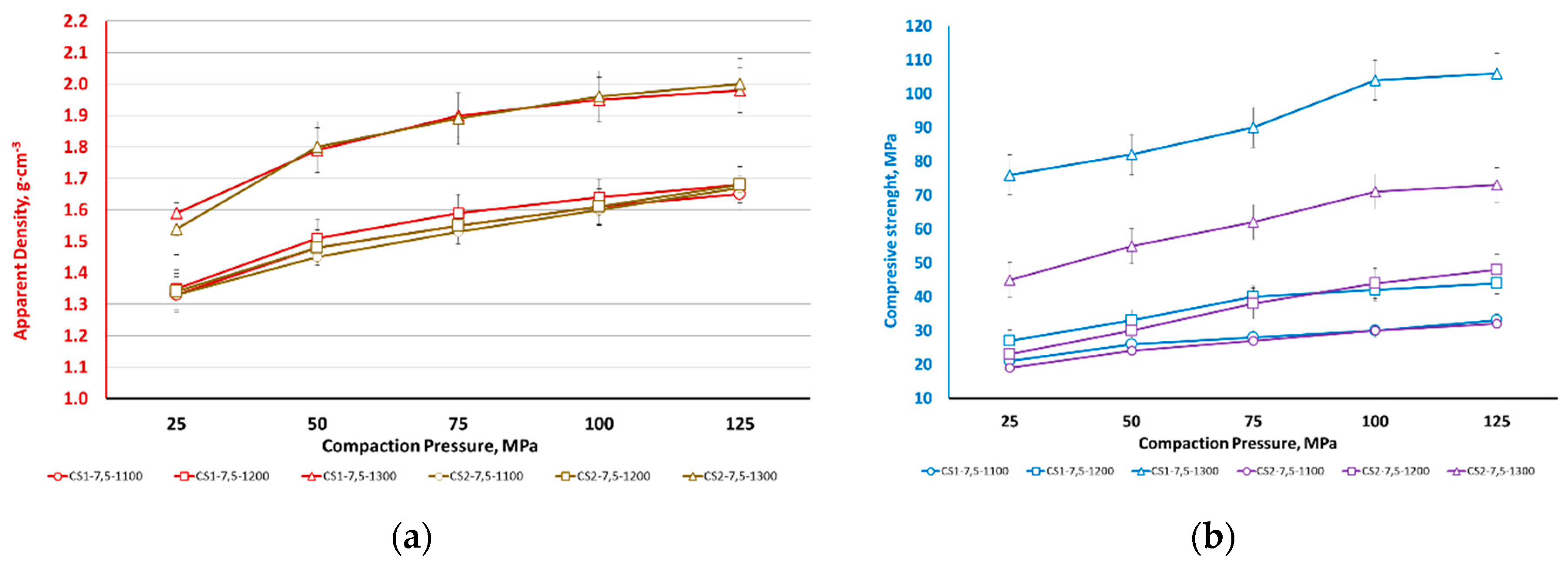
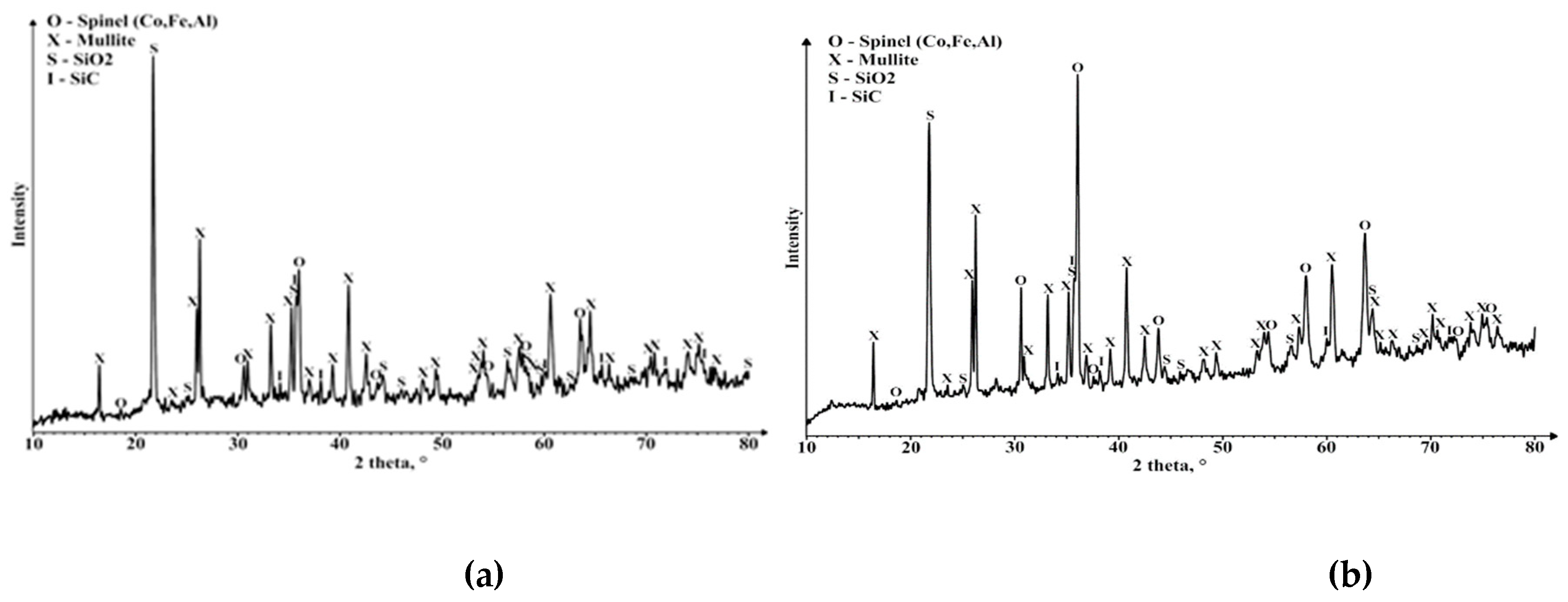

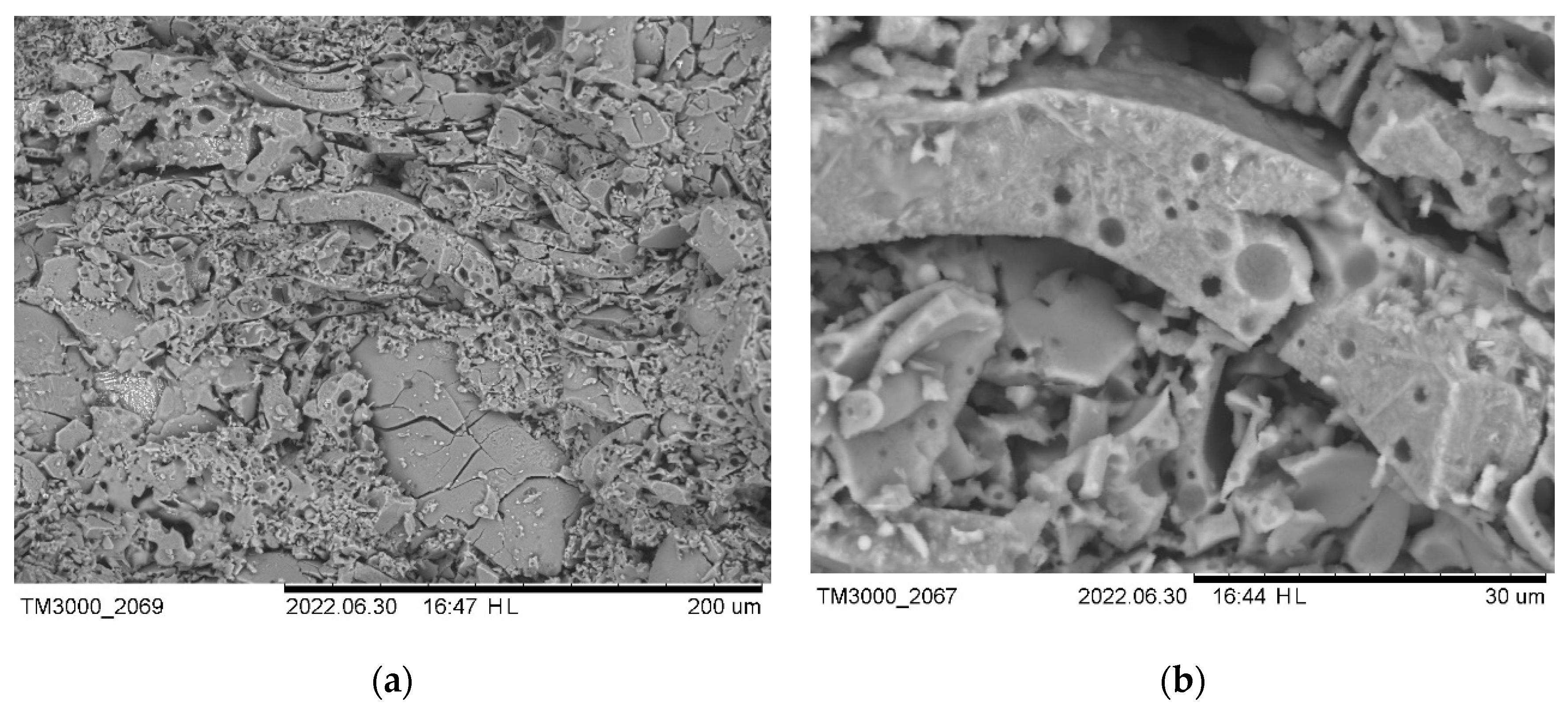
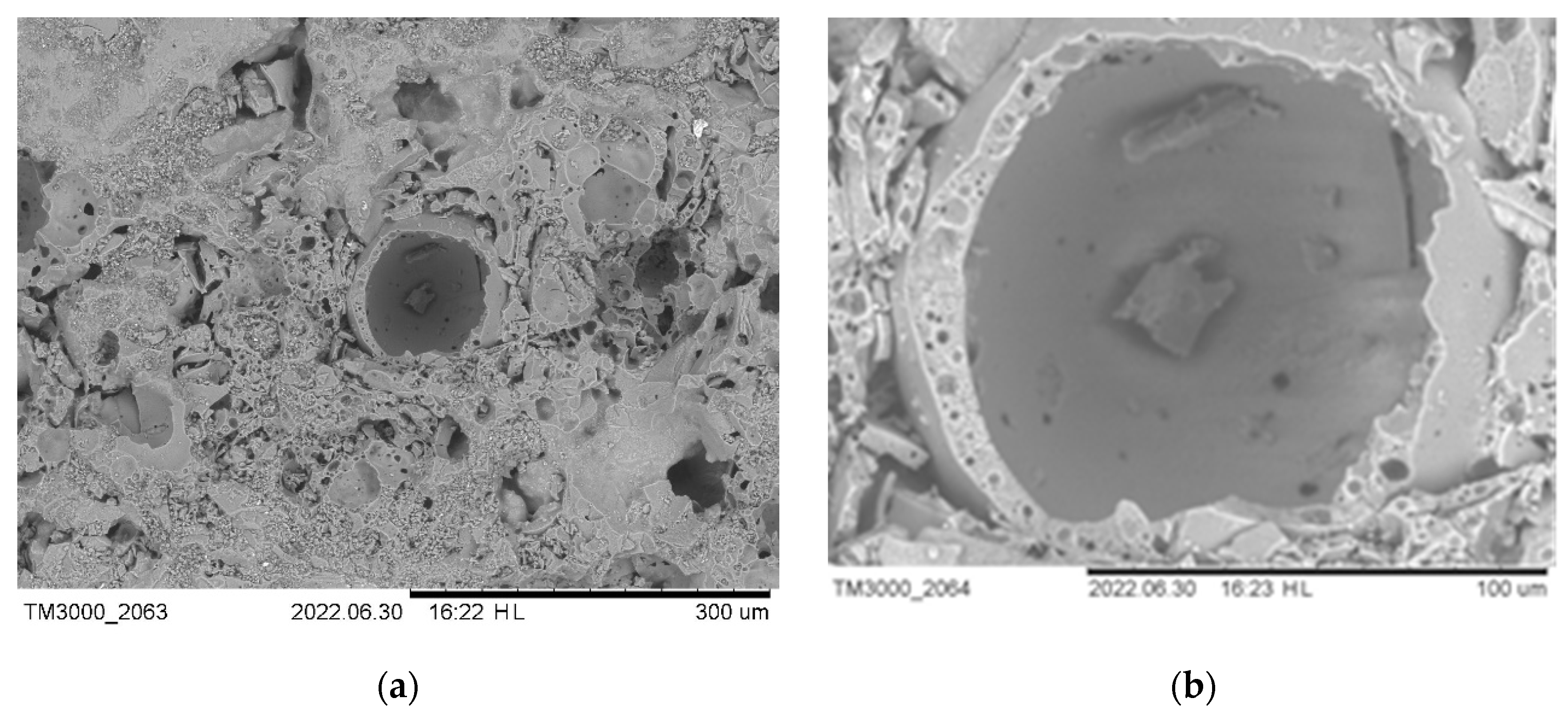
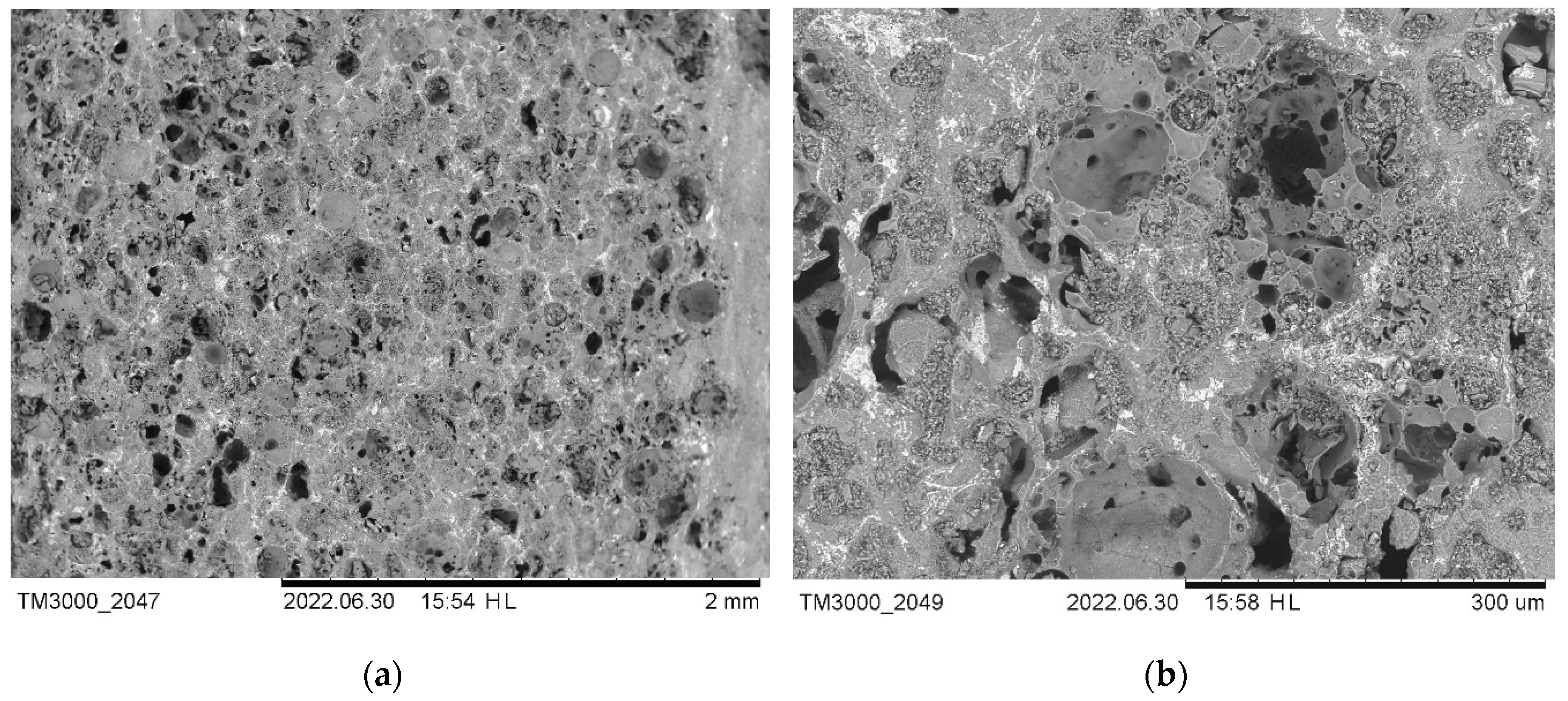
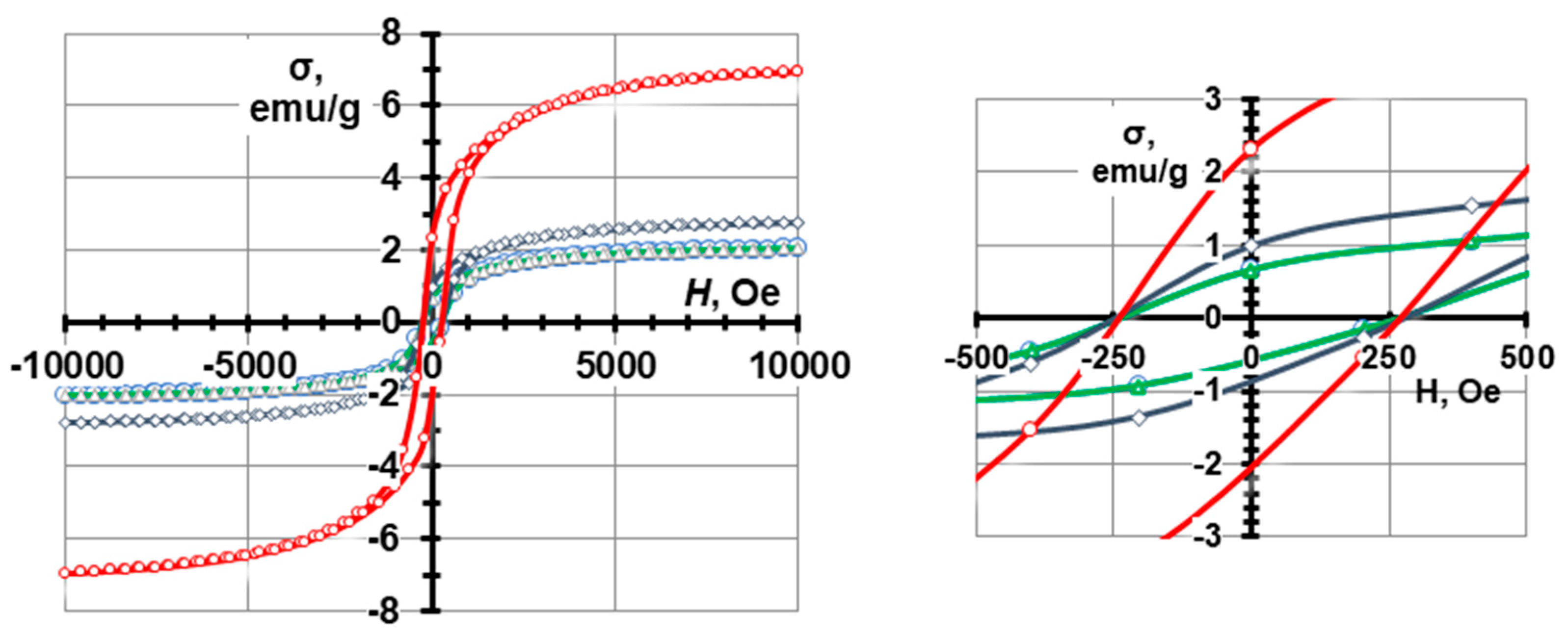
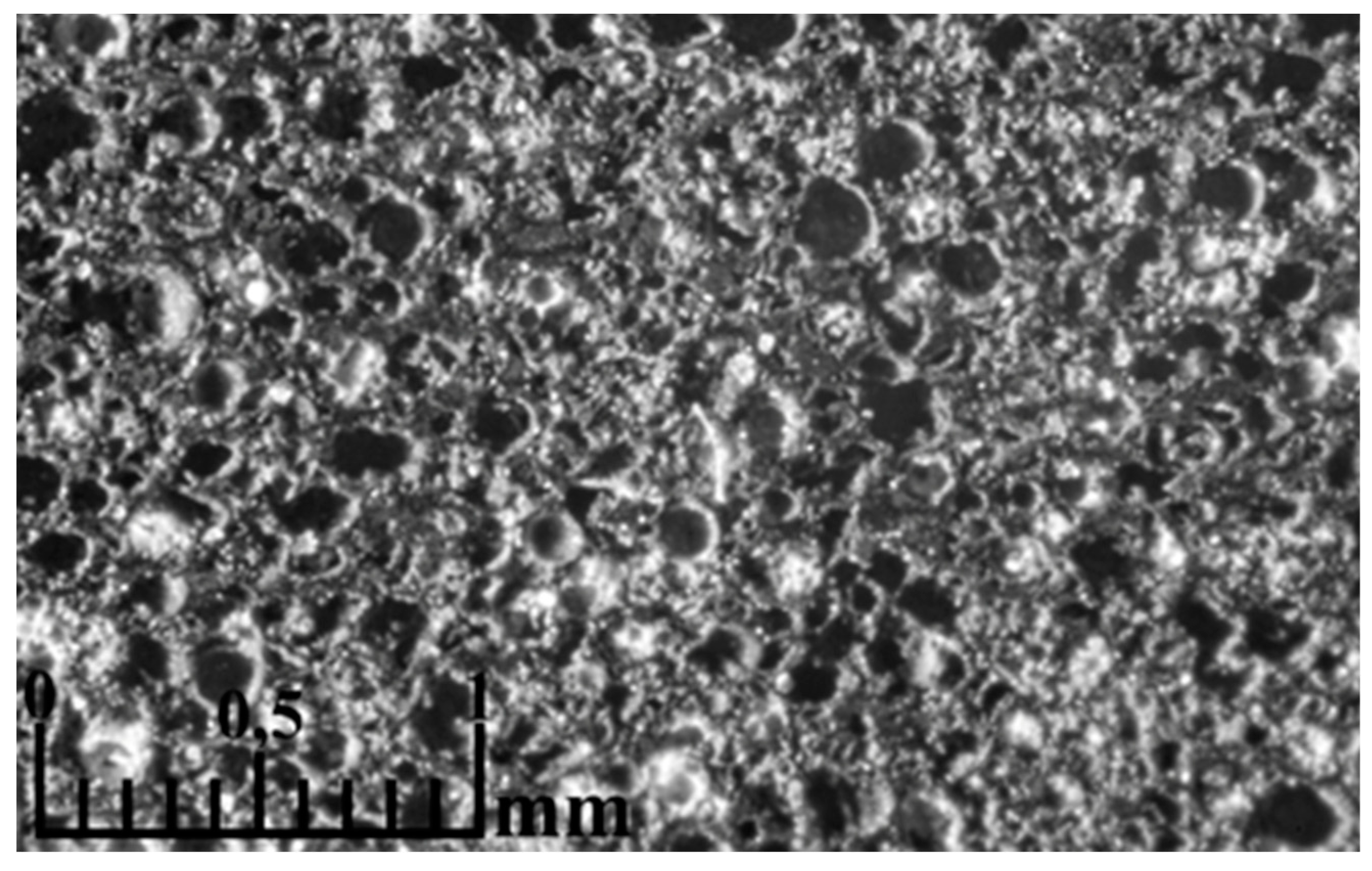
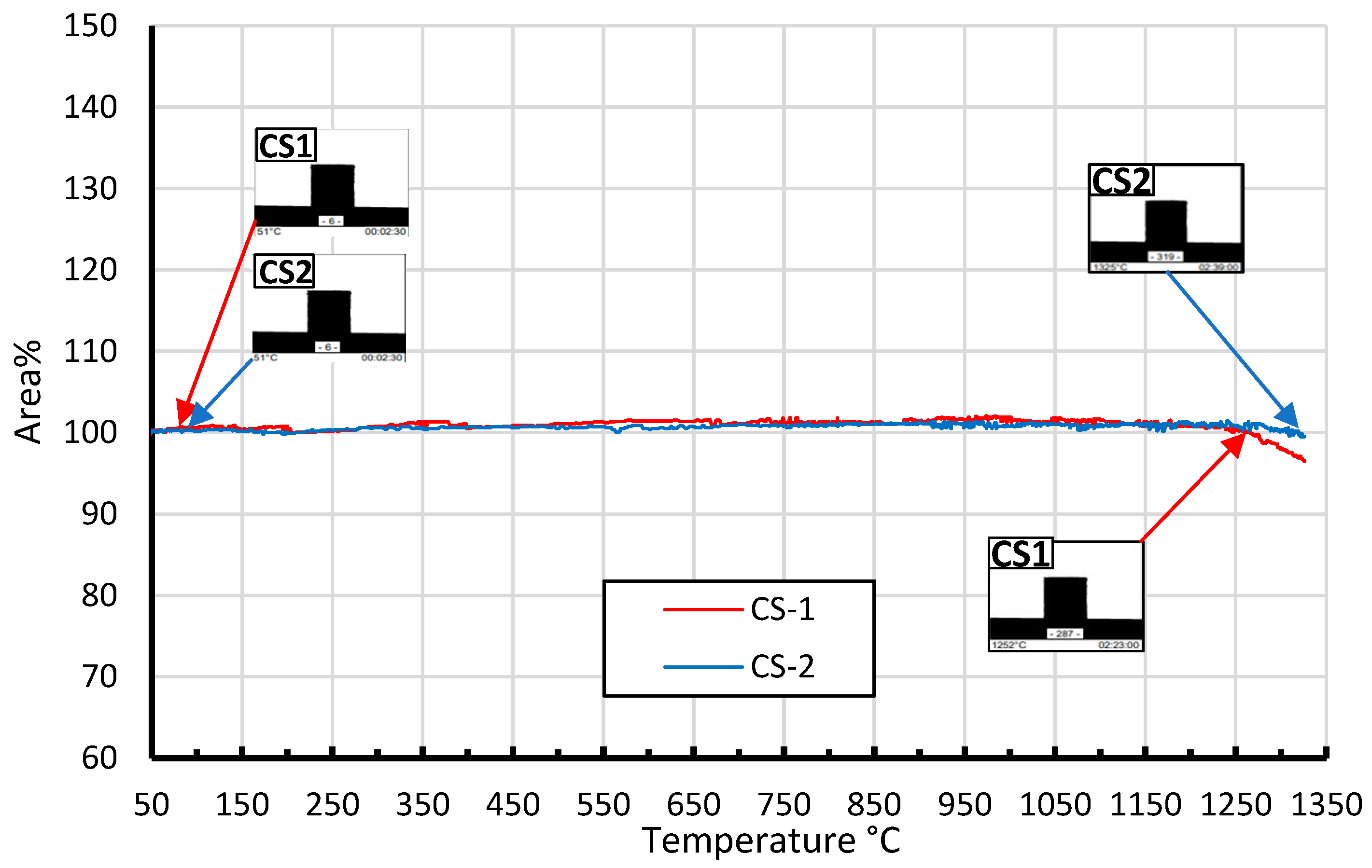
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Markham, D. Shielding: Quantifying the Shielding Requirements for Portable Electronic Design and Providing New Solutions by Using a Combination of Materials and Design. Mater Des 1999, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, U.; Ekman, J.; Delsing, J. Shielding Effectiveness Data on Commercial Thermoplastic Materials. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 2006, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. -C EMI Shielding Plastics: A Review. Advances in Polymer Technology 1995, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.B.; See, K.Y.; Ma, J. Effect of Carbon Nanofiber Reinforcement on Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness of Syntactic Foam. J Mater Sci 2013, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameli, A.; Jung, P.U.; Park, C.B. Through-Plane Electrical Conductivity of Injection-Molded Polypropylene/Carbon-Fiber Composite Foams. Compos Sci Technol 2013, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Mei, H.; Xiao, S.; Xue, W.; Bai, Q.; Cheng, L. CNT/SiC Composites Produced by Direct Matrix Infiltration of Self-Assembled CNT Sponges. J Mater Sci 2017, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Bin; Yan, Q.; Zheng, W.G.; He, Z.; Yu, Z.Z. Tough Graphene-Polymer Microcellular Foams for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Zhong, Z.; Weng, G.J. An X-Band Theory of Electromagnetic Interference Shielding for Graphene-Polymer Nanocomposites. J Appl Phys 2017, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.B.; Fu, Z.B.; Chen, H.B.; Zhong, M.L.; Wang, C.Y. Excellent Electromagnetic Absorption Capability of Ni/Carbon Based Conductive and Magnetic Foams Synthesized via a Green One Pot Route. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Chen, M.; Pei, Y.; Seyed Shahabadi, S.I.; Che, B.; Wang, P.; Lu, X. Ultralight and Flexible Polyurethane/Silver Nanowire Nanocomposites with Unidirectional Pores for Highly Effective Electromagnetic Shielding. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Zeltmann, S.E.; Shunmugasamy, V.C.; Pinisetty, D. Applications of Polymer Matrix Syntactic Foams. JOM 2014, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzałkowska, E.; Adamczyk, Z. Influence of Chemical Composition of Fly-Ash Cenospheres on Their Grains Size. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2020, 17, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, T.F.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Kok, K.Y.; Matori, K.A.; Rashid, S.A. Effect of Temperature on Morphology, Phase Transformations and Thermal Expansions of Coal Fly Ash Cenospheres. Crystals (Basel) 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesina, A. Sustainable Application of Cenospheres in Cementitious Materials – Overview of Performance. Developments in the Built Environment 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkin, A.; Abramovskis, V.; Zalite, I.; Singh, A.K.; Mezinskis, G.; Popov, V.; Ozolins, J. Physical, Thermal, and Chemical Properties of Fly Ash Cenospheres Obtained from Different Sources. Materials 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, N.; Kuenzel, C. Cenospheres: A Review. Fuel 2017, 207, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronins, J.; Setina, J.; Sahmenko, G.; Lagzdina, S.; Shishkin, A. Pore Distribution and Water Uptake in a Cenosphere-Cement Paste Composite Material. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; 2015; Vol. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Shishkin, A.; Drozdova, M.; Kozlov, V.; Hussainova, I.; Lehmhus, D. Vibration-Assisted Sputter Coating of Cenospheres: A New Approach for Realizing Cu-Based Metal Matrix Syntactic Foams. Metals (Basel) 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, D.; Lehmhus, D.; Gupta, N.; Weise, J.; Bayoumi, M. Structure and Compressive Properties of Invar-Cenosphere Syntactic Foams. Materials 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasar, A.K.; Gupta, N.; Rohatgi, P.K.; Menezes, P.L. A Brief Review of Fly Ash as Reinforcement for Composites with Improved Mechanical and Tribological Properties. JOM 2020, 72, 2340–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doddamani, M.; Gupta, N. 3D Printing of Fly Ash-Based Syntactic Foams. In Handbook of Fly Ash; 2021.
- Zalite, I.; Heidemane, G.; Grabis, J.; Maiorov, M. The Synthesis and Characterization of Nickel and Cobalt Ferrite Nanopowders Obtained by Different Methods. In Powder Technology; 2018.
- Jauhar, S.; Kaur, J.; Goyal, A.; Singhal, S. Tuning the Properties of Cobalt Ferrite: A Road towards Diverse Applications. RSC Adv 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakradhary, V.K.; Ansari, A.; Akhtar, M.J. Design, Synthesis, and Testing of High Coercivity Cobalt Doped Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles for Magnetic Applications. J Magn Magn Mater 2019, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, I.H.; Ahmed, W.; Maqsood, A. Electrical and Magnetic Characterization of Nanocrystalline Ni-Zn Ferrite Synthesis by Co-Precipitation Route. J Magn Magn Mater 2008, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pubby, K.; Meena, S.S.; Yusuf, S.M.; Bindra Narang, S. Cobalt Substituted Nickel Ferrites via Pechini’s Sol–Gel Citrate Route: X-Band Electromagnetic Characterization. J Magn Magn Mater 2018, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagayaraj, R.; Aravazhi, S.; Chandrasekaran, G. Review on Structural and Magnetic Properties of (Co–Zn) Ferrite Nanoparticles. Int Nano Lett 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Levei, E.A.; Cadar, O. Recent Advances in Synthesis and Applications of MFe2O4 (M = Co, Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn) Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, C.; Chen, G.; Guan, H. Preparation and Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles/Carbon Nanotubes Composites. Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, H.; Yusuf, J.Y.; Chuan, L.K.; Soleimani, H.; bin Sabar, M.L.; Öchsner, A.; Abbas, Z.; Balogun, A.I.; Kozlowski, G. In-Situ Preparation of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles on Eggshell Membrane-Activated Carbon for Microwave Absorption. Heliyon 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molaei, S.; Ghadermazi, M. Copper-Decorated Core–Shell Structured Ordered Mesoporous Containing Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles as High-Performance Heterogeneous Catalyst toward Synthesis of Tetrazole. Sci Rep 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Santiago, A.; Grant, H.R.; Gangopadhyay, P.; Voorakaranam, R.; Norwood, R.A.; Peyghambarian, N. Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles Polymer Composites Based All-Optical Magnetometer. Opt Mater Express 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Masry, M.M.; Ramadan, R.; Ahmed, M.K. The Effect of Adding Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles on the Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Resin. Results in Materials 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endrodi, B.; Hursán, D.; Petrilla, L.; Bencsik, G.; Visy, C.; Chams, A.; Maslah, N.; Perruchot, C.; Jouini, M. Incorporation of Cobalt-Ferrite Nanoparticles into a Conducting Polymer in Aqueous Micellar Medium: Strategy to Get Photocatalytic Composites. Acta Chim Slov 2014, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, Y.; Sharma, A.; Shirage, P.M. Shape-Controlled CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles as an Excellent Material for Humidity Sensing. RSC Adv 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, P.H.; Lu, L.T.; Linh, P.H.; Manh, D.H.; Thanh Tam, L.T.; Phuc, N.X.; Phong, P.T.; Lee, I.J. Polymer-Coated Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Toxicity for Hyperthermia Applications. New Journal of Chemistry 2018, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, A.A.; Arkhipov, V.A.; Chmelyuk, N.S.; Ivanova, A. V; Vodopyanov, S.S.; Garanina, A.S.; Soldatov, M.A.; Gritsai, M.A.; Cherepanov, V.M.; Barbotina, N.N.; et al. Supporting Information Multifunctional Anisotropic Rod‐Shaped СoFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Magneto‐Mechanical Therapy FeOOH 2q (Degree) (130) FeOOH 2q (Degree) (130) (240).
- Caldeira, L.E.; Guaglianoni, W.C.; Venturini, J.; Arcaro, S.; Bergmann, C.P.; Bragança, S.R. Sintering-Dependent Mechanical and Magnetic Properties of Spinel Cobalt Ferrite (CoFe2O4) Ceramics Prepared via Sol-Gel Synthesis. Ceram Int 2020, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tan, R.; Yao, Z.; Lin, H.; Li, Z. Preparation of CoFe2O4 Hollow Spheres with Carbon Sphere Templates and Their Wave Absorption Performance. Mater Chem Phys 2020, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, R.; Chen, X.; Xiong, C.; Dong, L. Broadband and Lightweight Microwave Absorber Constructed by in Situ Growth of Hierarchical CoFe2O4/Reduced Graphene Oxide Porous Nanocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Shishkin, A.; Koppel, T.; Gupta, N. Porous Materials for EMI Shielding. In Materials for Potential EMI Shielding Applications Processing, Properties and Current Trends; Kuruvilla, J., Runcy, W., Gejo, G., Eds.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, 2019; pp. 287–314. ISBN 978-0-12-817590-3. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, R.S.; Anju; Jamatia, T. ; Kuřitka, I.; Vilčáková, J.; Škoda, D.; Urbánek, P.; Machovský, M.; Masař, M.; Urbánek, M.; et al. Excellent, Lightweight and Flexible Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Nanocomposites Based on Polypropylene with MnFe2O4 Spinel Ferrite Nanoparticles and Reduced Graphene Oxide. Nanomaterials 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Z. Microwave Absorption and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties of Li-Zn Ferrite-Carbon Nanotubes Composite. J Magn Magn Mater 2021, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, C.H.; Mariatti, M.; Koh, Y.H. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Performance of Epoxy Composites Filled with Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes/Manganese Zinc Ferrite Hybrid Fillers. J Magn Magn Mater 2016, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalite, I.; Heidemane, G.; Kodols, M.; Grabis, J.; Maiorov, M. The Synthesis, Characterization and Sintering of Nickel and Cobalt Ferrite Nanopowders. Medziagotyra 2012, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Li, Y.S. Synthesis and Microwave Absorbing Properties of Cobalt Ferrite. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; 2018; Vol. 292. [Google Scholar]
- Zalite, I.; Heidemane, G.; Krumiņa, A.; Rašmane, D.; Grabis, J.; Maiorov, M. Characteristics of Sintered Materials Obtained from Ferrite Nanopowders Synthesised with Different Methods. In Proceedings of the Key Engineering Materials; 2018; Vol. 762. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, Y.J.; Lee, J.J.; Tugirumubano, A.; Go, S.H.; Kim, H.G.; Kwac, L.K. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Behavior of Magnetic Carbon Fibers Prepared by Electroless Feconi-Plating. Materials 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q. Magnetic Field-Induced Strategy for Synergistic CI/Ti3C2Tx/PVDF Multilayer Structured Composite Films with Excellent Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Performance. J Mater Sci Technol 2022, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Matin, M.A.; Hakim, M.A.; Islam, M.F. Effects of CoFe2O4 Substitution on Magnetic Properties of NiFe2O4 Spinel Ferrite. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; 2018; Vol. 438. [Google Scholar]
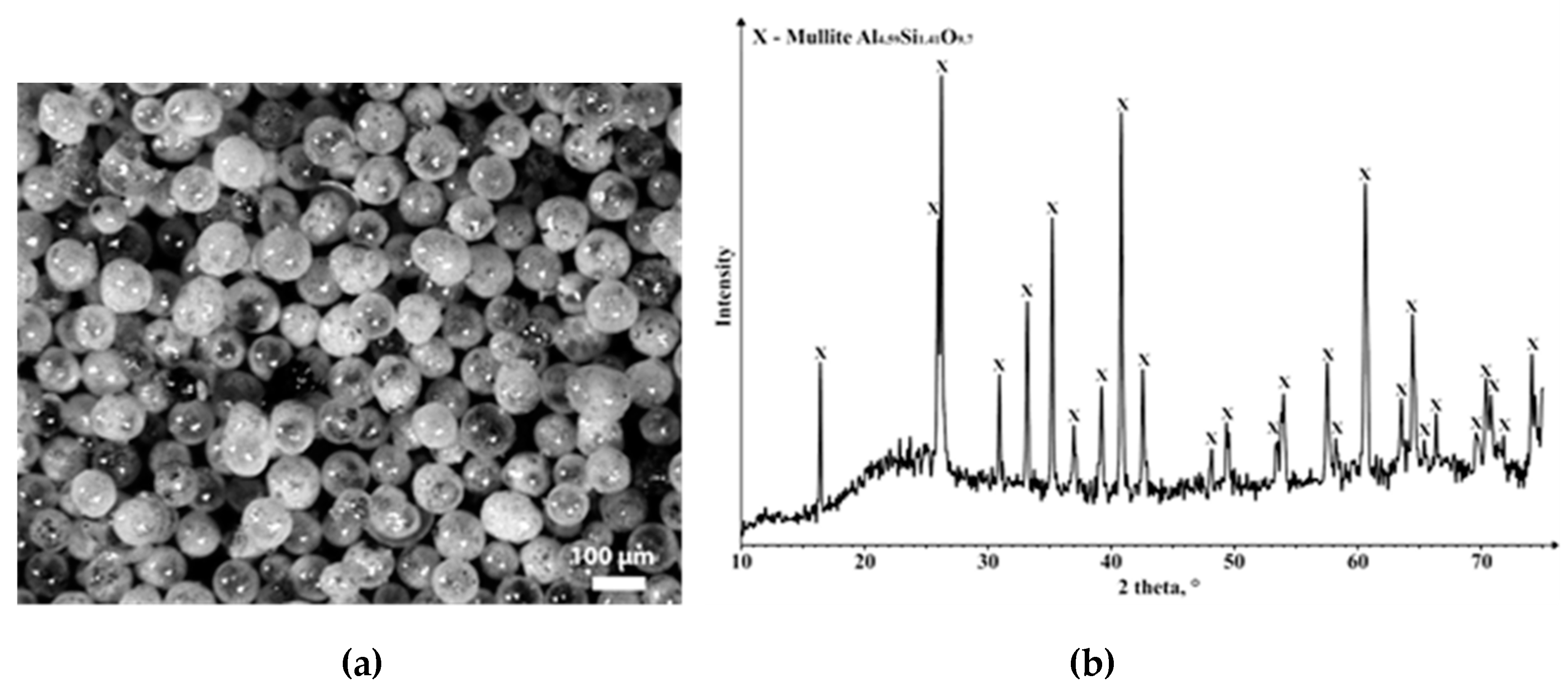
| Sample | Density,g·cm–3 (%) |
Water absorption (W), % |
Apparent porosity(π), % | Compressive strength(σcomp.), MPa | Bending strength (σbend.)., MPa | Flexural modulus, MPa | Deformation (ε), % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS1-0 | 1.03 (32.2) | 50.7 | 52.0 | 12.4±0.1 | 7.1±0.4 | 1960±180 | 0.39 |
| CS1-7.5 | 1.17 (35.0) | 45.9 | 49.9 | 29.3±2.8 | 10.2±0.3 | 5190±130 | 0.41 |
| CS1-10 | 1.31 (38.4) | 33.7 | 44.2 | 47.4±12.6 | 17,9±1.6 | 4830±450 | 0.52 |
| CS2-0 | 1.05 (32.8) | 48.8 | 51.3 | 17.4±5.8 | 6.0±0.4 | 2690±310 | 0.21 |
| CS2-10 | 1.32 (38.9) | 34.2 | 45.1 | 41.7±6.2 | 12.3±1.9 | 5220±490 | 0.23 |
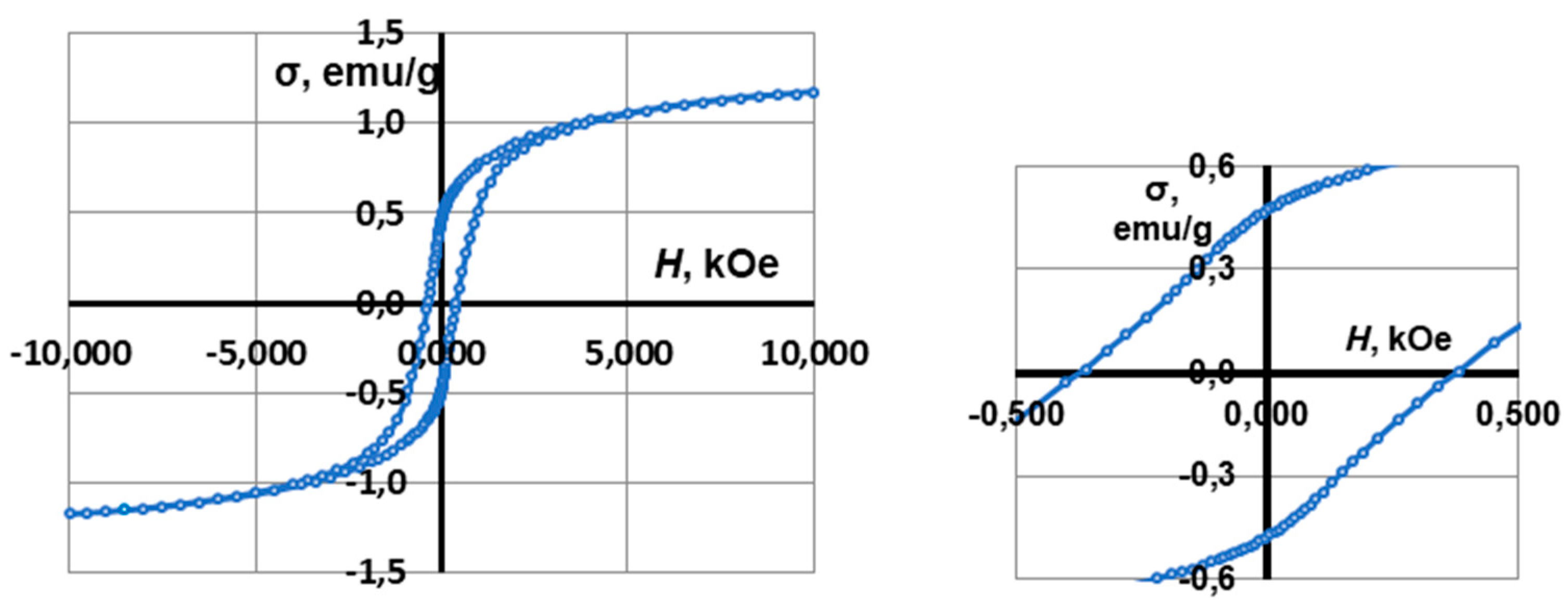
| Sample | Magnetic properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ms, emu/g | Mr, emu/g | Hc, Oe | |
| CS2 - 7.5 wt.% CoFe2O4 | 1.17 | 0.47 | 375 |
| CS3 – 7.5 wt.% CoFe2O4 | 2.04 | 0.65 | 275 |
| CS3 – 10 wt.% CoFe2O4 | 2.78 | 1.00 | 275 |
| CS3 – 20 wt.% CoFe2O4 | 6.93 | 2.30 | 275 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).