Submitted:
12 January 2024
Posted:
15 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion (former Results)
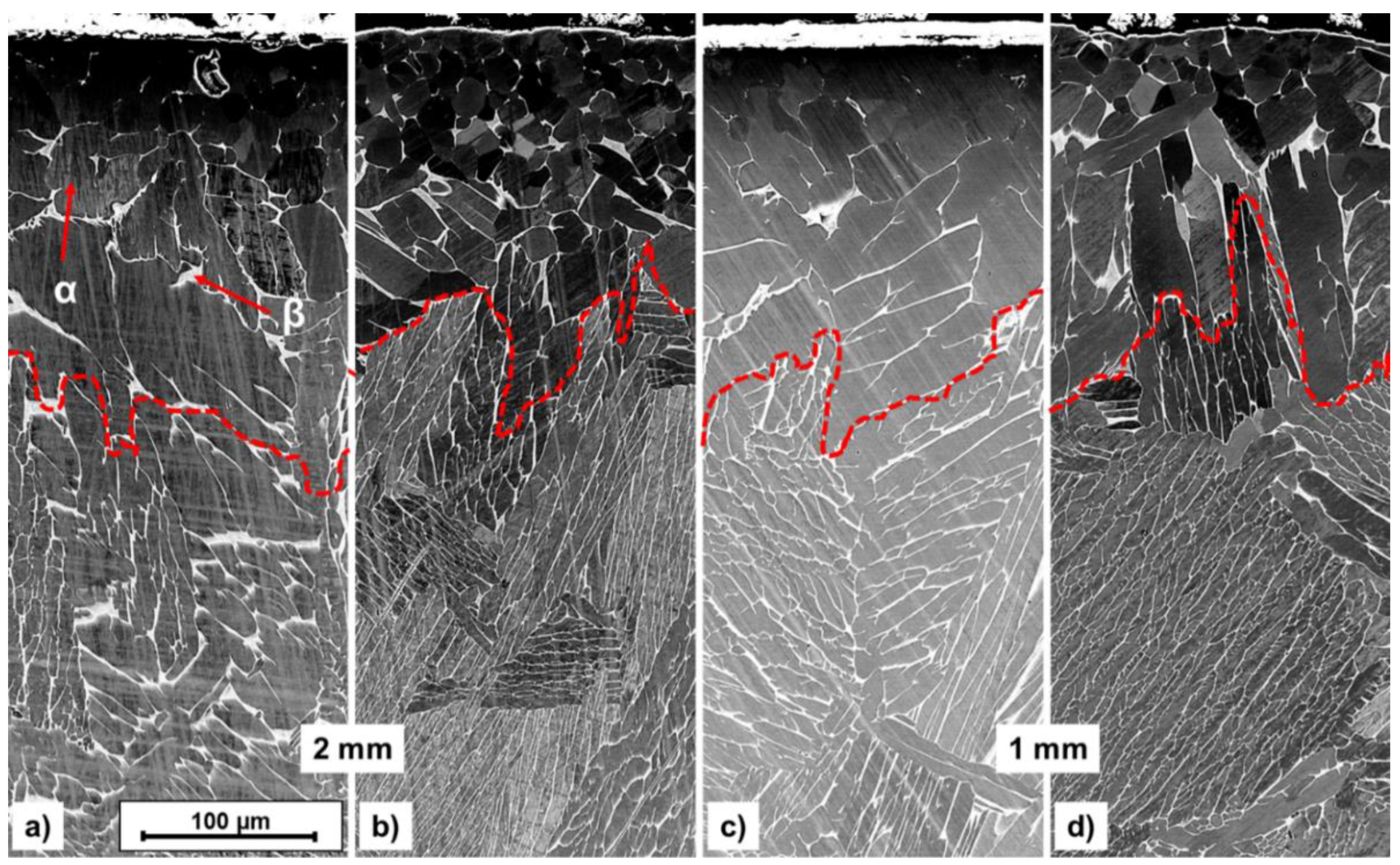
3.1. Tube-like specimen
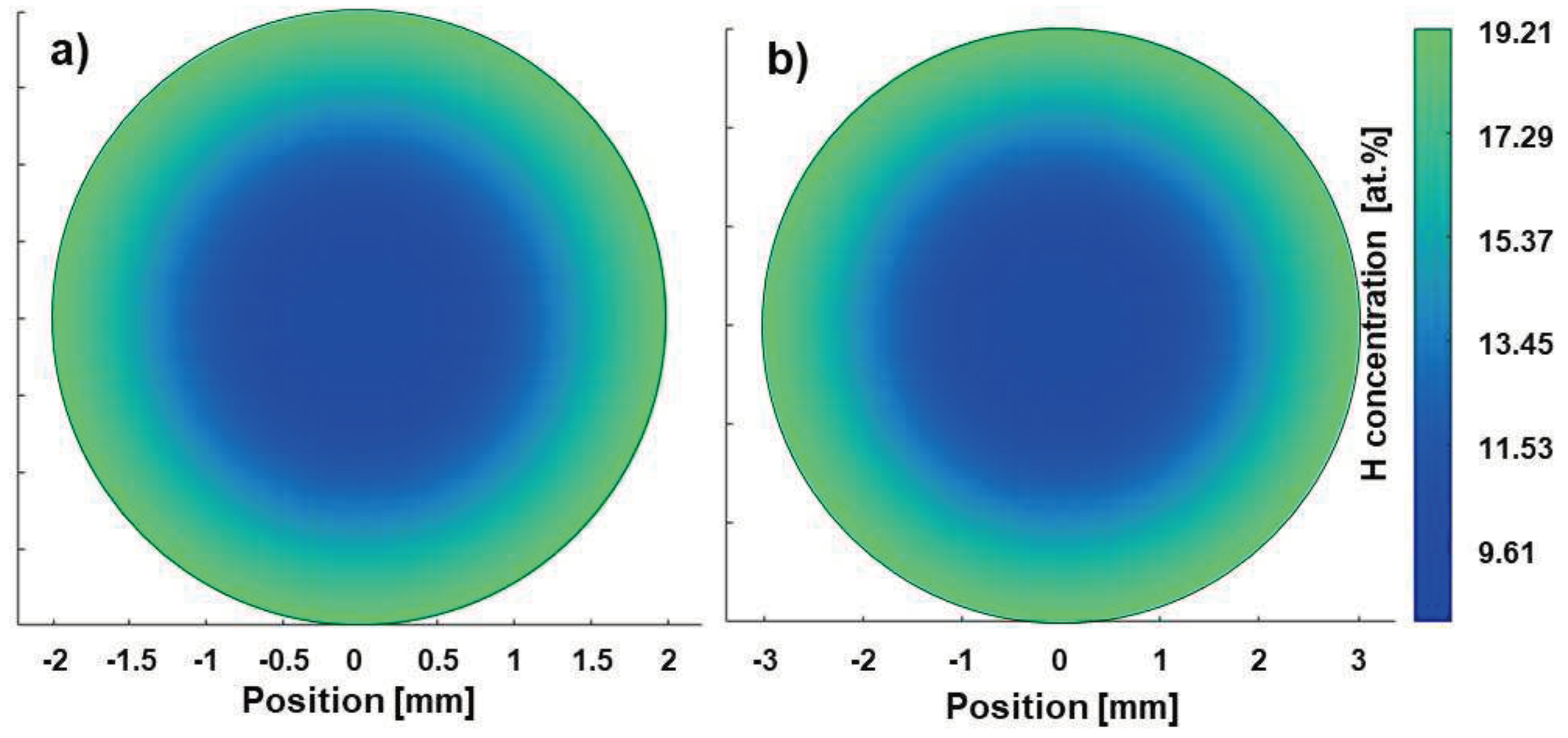
3.1.1. Calculated H concentration profiles
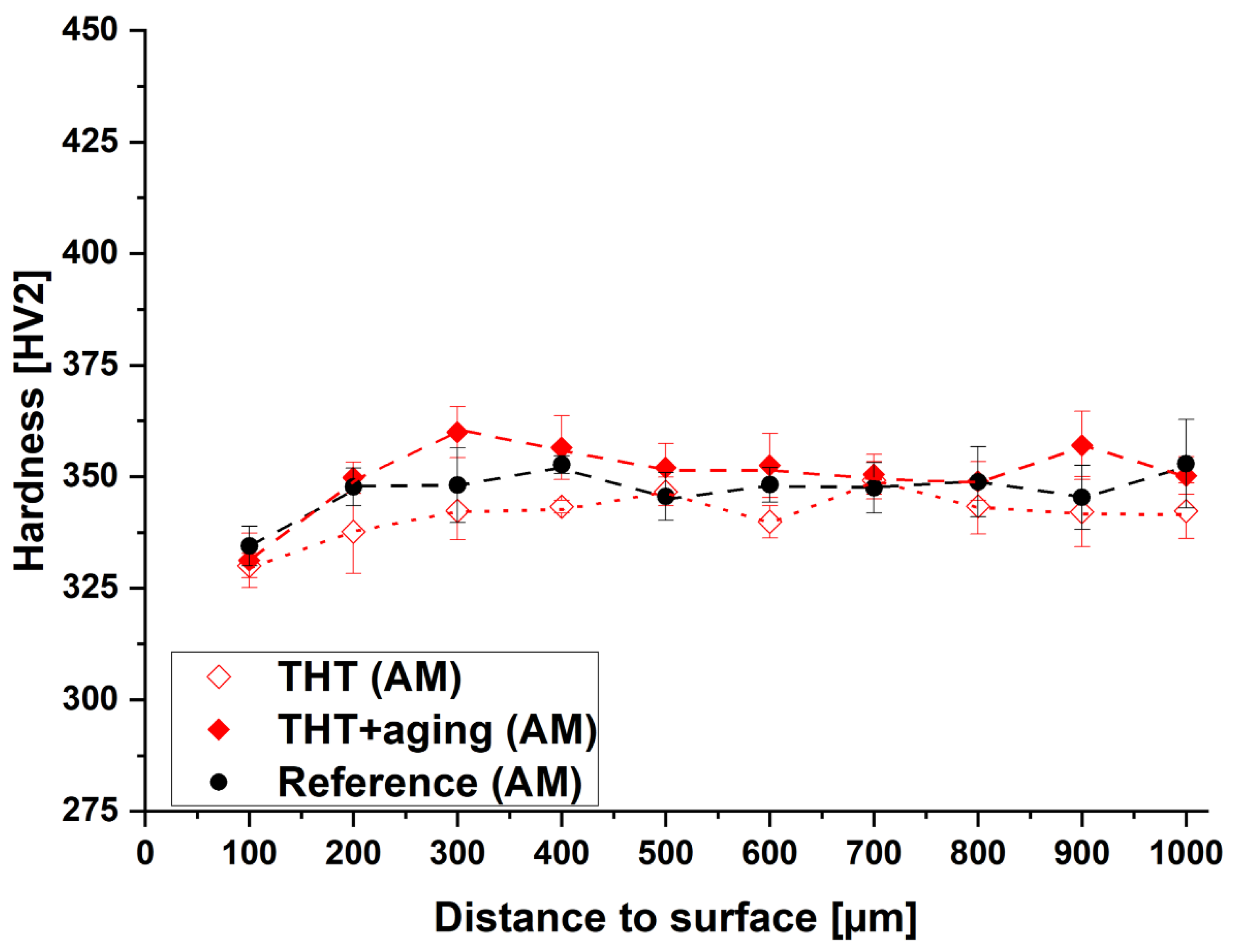
3.1.2. Experimental determination of hardness profiles
3.3.1. Stereological parameters
3.2. AM cylindrical specimens
3.2.1. Calculated H concentration profiles
3.2.2. Experimental determination of hardness profiles
3.2.3. Stereological parameters
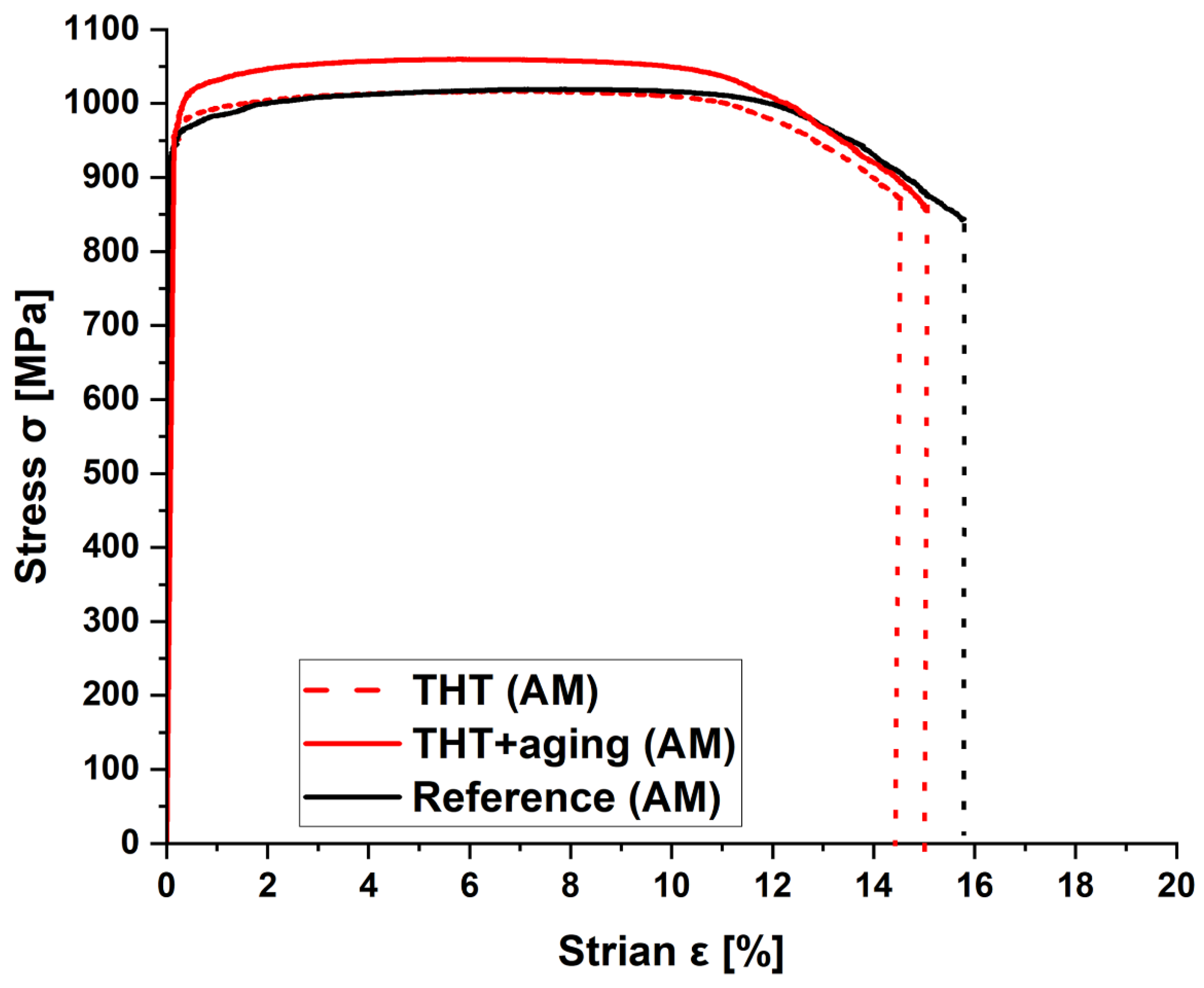
3.2.4. Tensile tests
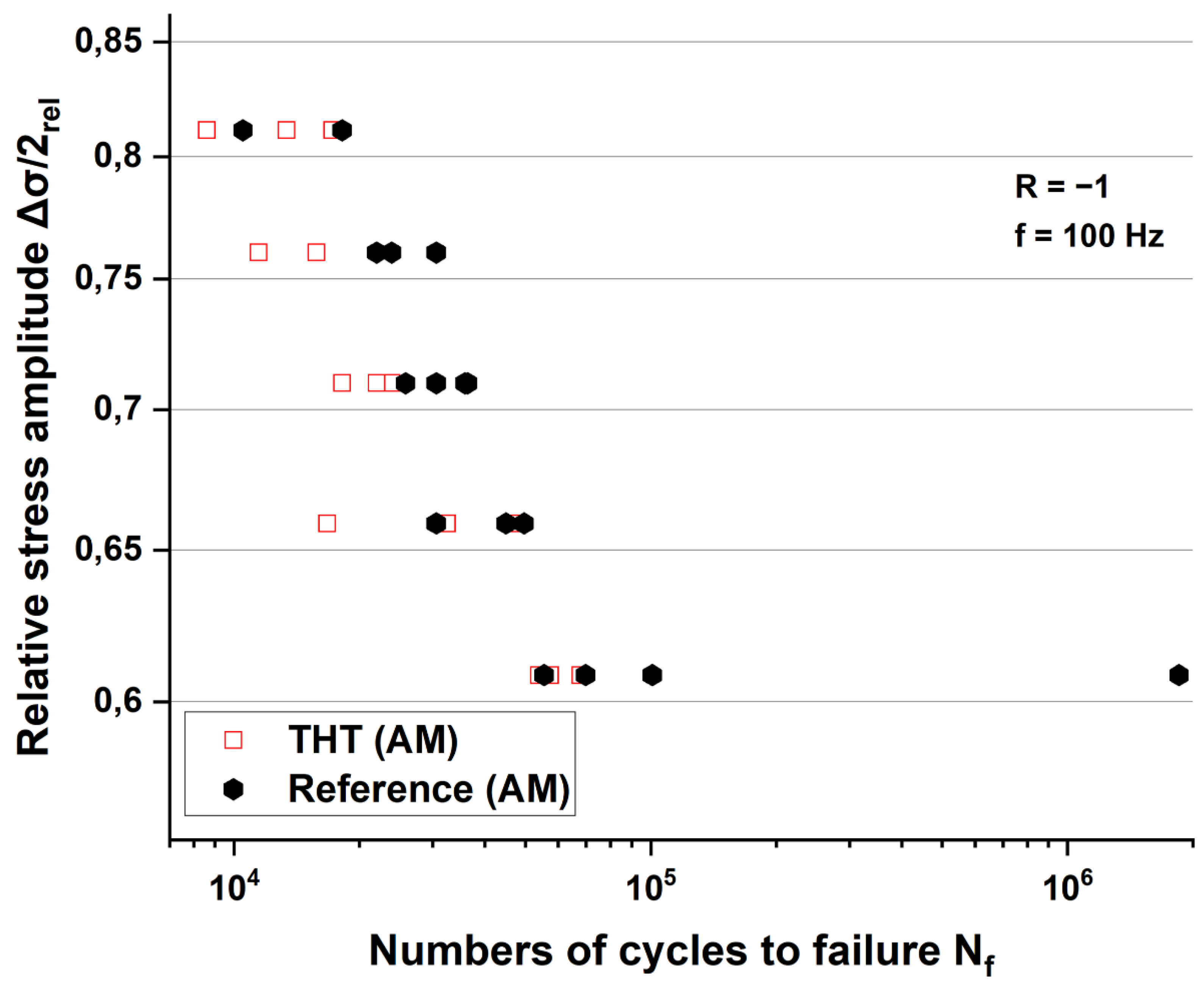
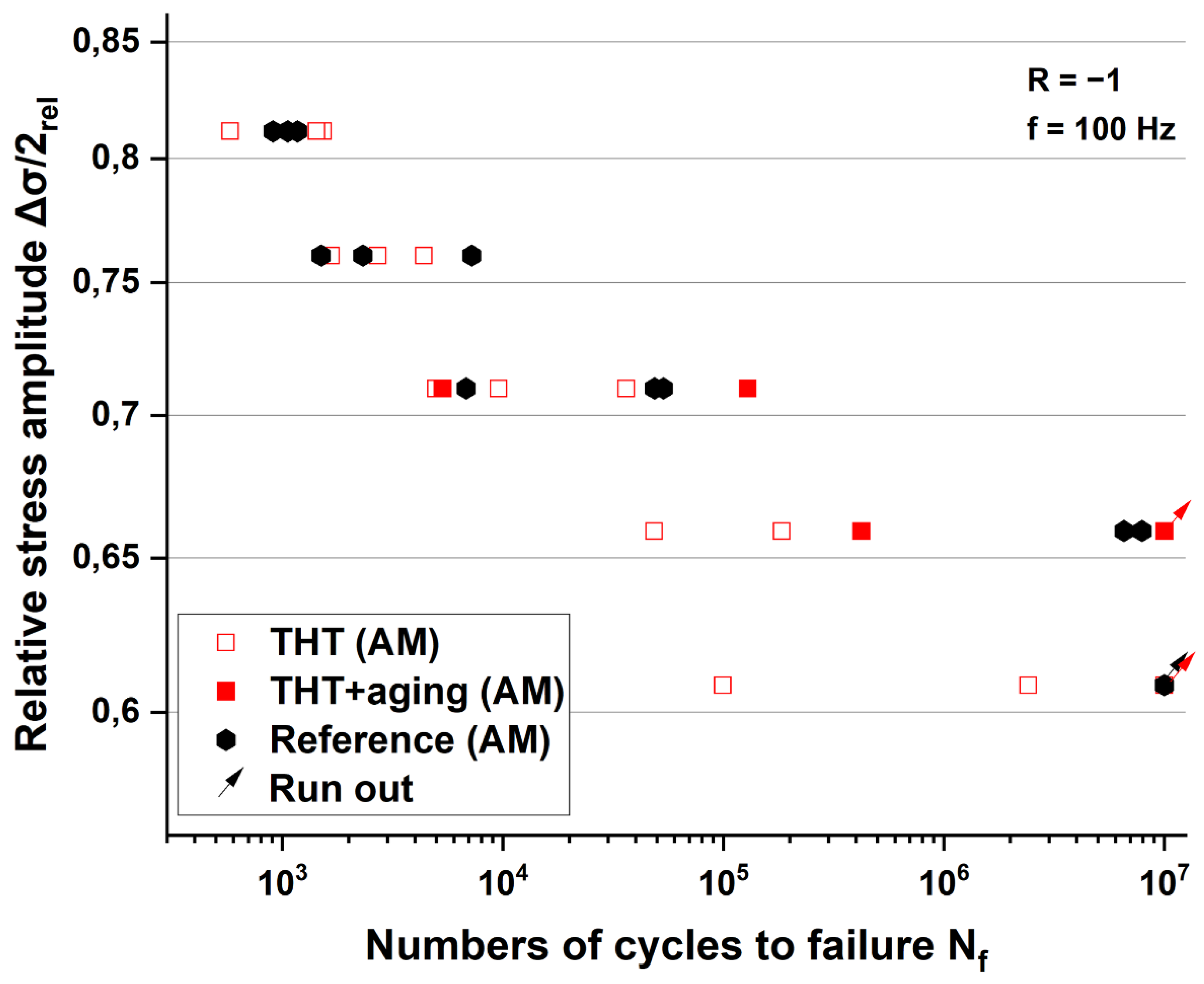
3.2.5. Wöhler curves
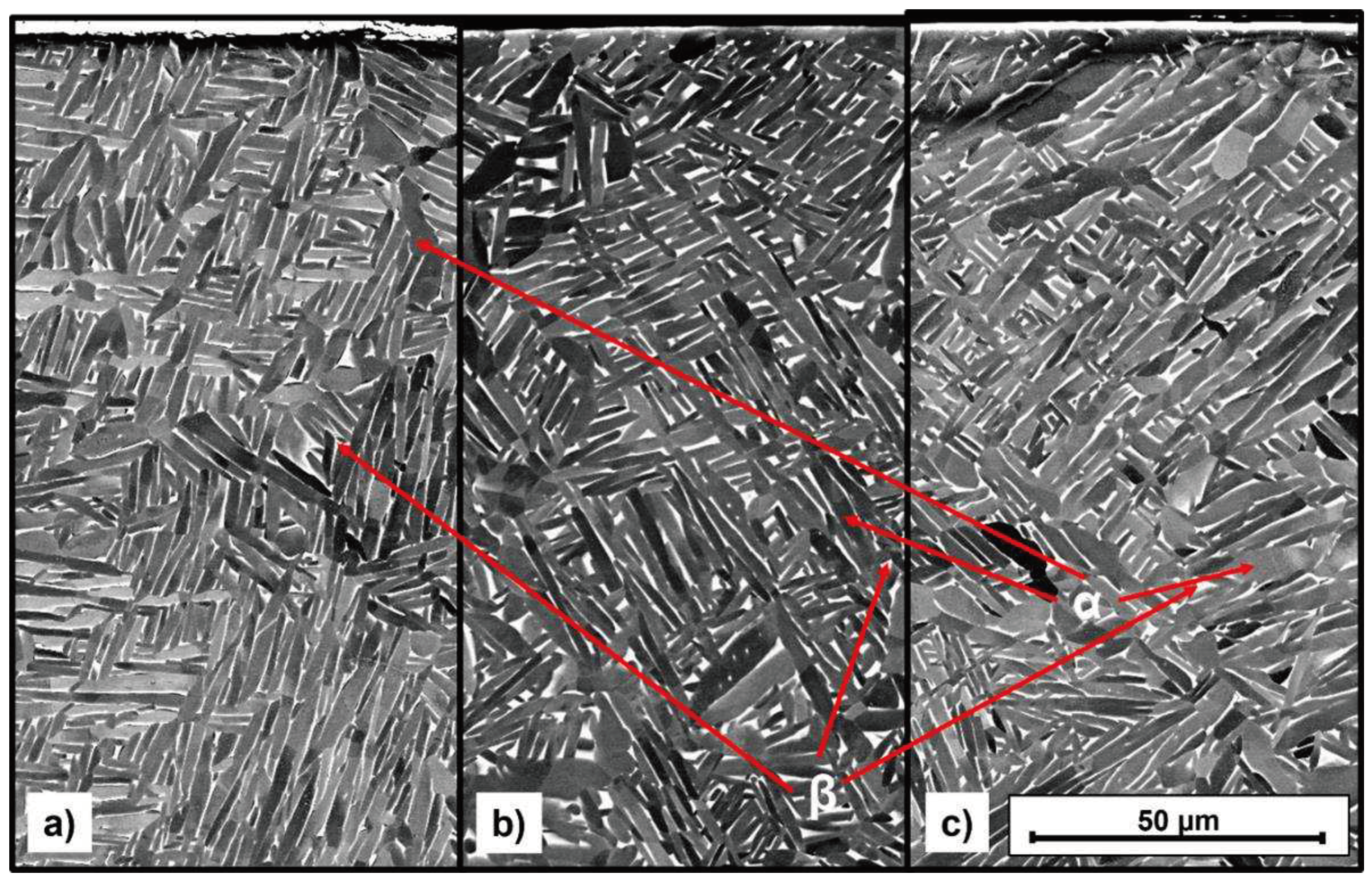
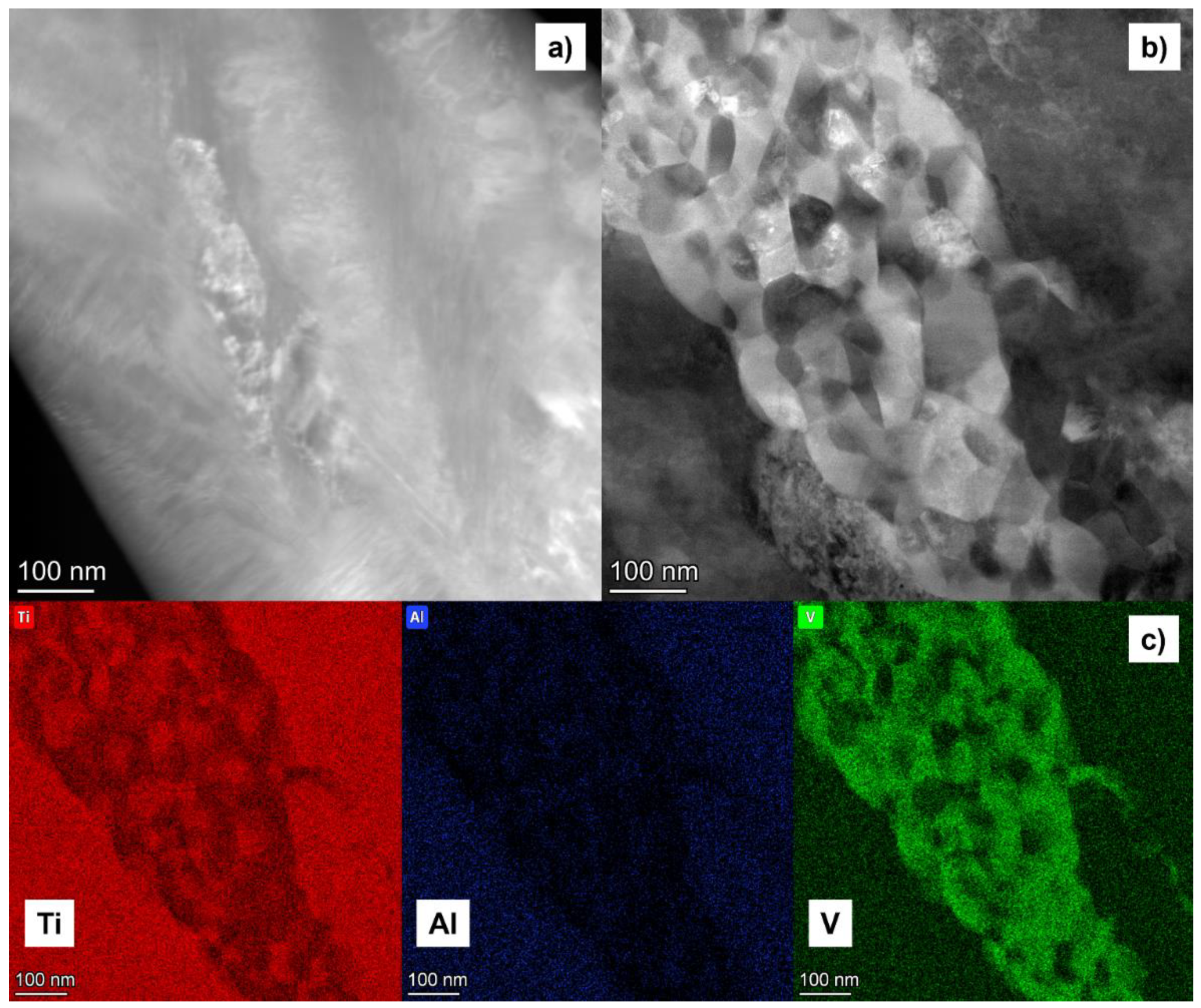
3.2.6. TEM investigations
4. Conclusion and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Conditionment
Informed Consent Conditionment
Data Availability Conditionment
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foust, M., Thomsen, D., Stickles, R., Cooper, C., Dodds, W., Development of the GE aviation low emissions TAPS combustor for next generation aircraft engines, In: , Aerospace Sciences Meetings, 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Nashville, TN, USA, 2012, AIAA 2012-0936.
- Niinomi, M., Williams, J. C., Properties and applications ot Ti: Current status and future needs: Precipitation and recristallisation behaviour of cold deformed beta titanium alloys during continous heat treatment, In: Lütjering, G., Albrecht, J. (Hrsg.), Ti-2003 – Science and technology, Proceedings of the 10th world conference on titanium, 13.–18. Juli 2003, Hamburg, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2004, p. 93–110.
- Lee, E. W., Frazier, W., Kim, N. J., Jata K., Light weight alloys for aerospace applications IV, TMS, Warrendale, PA, USA, , 1997.
- Lütjering, G., Williams, J. C., Titanium, Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, 2. Aufl., 2007.
- Macin, V., Christ, H.-J., Influence of hydride-induced microstructure modification on mechanical properties of metastable beta titanium alloy Ti 10V–2Fe–3Al, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 40 (47), 2015, p. 16878–16891. [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O. N., Froes, F. H., Beneficial effect of hydrogen as a temporary alloying element on processing, In: Lütjering, G., Albrecht, J. (Hrsg.), Ti-2003 – Science and technology, Proceedings of the 10th world conference on titanium, 13.–18. Juli 2003, Hamburg, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2004, p. 1345–1352.
- Piskovets, V. M., Effect of thermohydrogen treatment on mechanical and process properties of low-carbon steel, Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 49 5-6, 2007, p. 301–303. [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O. N., Jonas, J. J., Froes, F. H., Recent advances in the thermohydrogen processing of titanium alloys, Journal of the Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 48 (7), 1996, p. 42–47. [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, M. K., Paramore, J. D., Fang, Z. Z., Sun, P., Manipulation of microstructure and mechanical properties during dehydrogenation of hydrogen-sintered Ti–6Al–4V, Materials Science and Engineering A, 764, 2019, p. 138244. [CrossRef]
- Macin, V., Schmidt, P., Christ, H.-J., THT of high strength beta titanium alloy Ti–10V–2Fe–3Al, In: Somerday, B. P., Sofronis, P. (Hrsg.), Hydrogen-materials interactions, Proceedings of the international hydrogen conference 2012, 9.–12. Sept. 2012, Jackson Lake Lodge, Moran, WY, USA, ASME Press, New York, USA, 2014, p. 669–676.
- Il'in, A. A., Polkin, I. S., Mamonov, A. M., Nosov, V. K., Thermohydrogen treatment - the base of hydrogen technology of titanium alloys, In: Blenkinsop, P. A., Evans, W. J., Flower, H. M. (Hrsg.), Titanium'95 – Science and Technology, Proceedings of the 8th international conference on titanium, 22.–26. Okt. 1995, Birmingham, UK, Institute of Materials, London, UK, 3. Aufl., 1996, p. 2462–2469.
- Senkov, O. N., F.H. Froes, Thermohydrogen processing of titanium alloys, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 24 (6), 1999, p. 565–576. [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O. N., Froes, F. H., Thermohydrogen processing of titanium alloys, In: Goltsov, V. A. (Hrsg.), Progress in Hydrogen Treatment of Materials, Kassiopeya Ltd., Donetsk, Ukraine, 2001.
- Sun, Z., Zhou, W., Hou, H., Strengthening of Ti–6Al–4V alloys by thermohydrogen processing, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 34 (4), 2009, p. 1971–1976. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C. D., Christ, H.-J., Hehl, A. von, Hydrogen as a temporary alloying element for establishing specific microstructural gradients in Ti–6Al–4V, Metals, 12 (8), 2022, p. 1267. [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, M. K., Vaughn, M. O., Paramore, J. D., Butler, B. G., Kudzal, A. D., Hemker, K. J., Optimization of microstructural manipulation and ductility in laser powder bed fusion Ti-6Al-4V through hydrogen heat treatments, Materials Science and Engineering A, 873, 2023, p. 145061. [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, M. K., Microstrucutre – mechanical property relationships in HSPT TI-6AL-4V, Dissertation, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, 2018.
- Sun, P., Fang, Z. Z., Koopman, M., Paramore, J., Chandran, K. R., Ren, Y., Lu, J., An experimental study of the (Ti–6Al–4V)–xH phase diagram using in situ synchrotron XRD and TGA/DSC techniques, Acta Materialia, 84, 2015, p. 29–41. [CrossRef]
- Sun, P., Fang, Z. Z., Koopman, M., Xia, Y., Paramore, J., Ravi Chandran, K. S., Ren, Y., Lu, J., Phase transformations and formation of ultra-fine microstructure during hydrogen sintering and phase transformation (HSPT) processing of Ti–6Al–4V, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 46 (12), 2015, p. 5546–5560. [CrossRef]
- Bohner, F., Gregory, J. K., Mechanical behavior of a graded aluminum alloy, Materials Science Forum, 308-311, 1999, p. 313–318. [CrossRef]
- Bohner, F., Gregory, J. K., Fracture in notched parts with a microstructural gradient, In: Trumble, K., Bowman, K., Reimanis, I. E., Sampath, S. (Hrsg.), Functionally graded materials 2000, American Ceramic Society, Westerville, OH, USA, 1. Aufl., 2001, p. 773–781.
- Schulze, V., Modern mechanical surface treatment, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2006.
- Berg, A., Kiese, J., Wagner, L., Microstructural gradients in Ti–3Al–8V–6Cr–4Zr–4Mo for excellent HCF strength and toughness, Materials Science and Engineering A, 243 (1), 1998, p. 146–149. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, L., Mechanical surface treatments on titanium, aluminum and magnesium alloys, Materials Science and Engineering A, 263 (2), 1999, p. 210–216. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, L., Gregory, J. K., Thermomechanical surface treatment of titanium alloys, Materials Science Forum, 163-165, 1994, p. 159–172. [CrossRef]
- Berg, A., Kiese, J., Wagner, L., Crack propagation in gradient microstructures in titanium alloys, In: Lee, E. W., Frazier, W., Kim, N. J., Jata K. (Hrsg.), Light weight alloys for aerospace applications IV, TMS, Warrendale, PA, USA, 1. Aufl., 1997, p. 207–216.
- Drechsler, A., Dörr, T., Kiese, J., Wagner, L., Mechanical and thermomechanical surface treatments to enhance HCF strength in high-strength β titanium alloys, In: Lee, E. W., Frazier, W., Kim, N. J., Jata K. (Hrsg.), Light weight alloys for aerospace applications IV, TMS, Warrendale, PA, USA, 1. Aufl., 1997, p. 151–161.
- Froes, F. H., Eylon, D., Suryanarayana, C., Thermochemical processing of titanium alloys, Journal of the Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 42 (3), 1990, p. 26–29. [CrossRef]
- Gammeltoft-Hansen, N., Munch, S. S., Jellesen, M. S., Somers, M. A. J., Christiansen, T. L., Characterization of thermochemically surface-hardened titanium by light optical microscopy, Materials Performance and Characterization, 6 (3), 2017, p. 20160083. [CrossRef]
- Valente, E. H., Jellesen, M. S., Somers, M. A. J., Christiansen, T. L., Gaseous surface hardening of Ti–6Al–4V fabricated by selective laser melting, Surface and Coatings Technology, 383, 2020, p. 125278. [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y., Villa, M., Dahl, K. V., Wang, B., Drouet, M., Dubois, J.-B., Somers, M. A. J., Christiansen, T. L., Thermochemical surface hardening of Ti–6Al–4V: On the role of temperature and treatment media, Surface and Coatings Technology, 422, 2021, p. 127505. [CrossRef]
- Kværndrup, F. B., Kücükyildiz, Ö. C., Winther, G., Somers, M. A., Christiansen, T. L., Extreme hardening of titanium with colossal interstitial contents of nitrogen and oxygen, Materials Science and Engineering A, 813, 2021, p. 141033. [CrossRef]
- Sozańska, M., Effect of high-temperature hydrogen treatment on the microstructure and properties of titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V, Materials Science and Engineering, 22, 2011, p. 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C. D., Macin, V., Schmidt, P., Christ, H.-J., Generation of microstructural gradients for improved mechanical properties via thermohydrogen treatment of the metastable beta titanium alloys Beta C and Ti 10V–2Fe–3Al, MATEC Web of Conferences, 321, 2020, p. 12017. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C. D., Christ, H.-J., Determination of material characteristics for hydrogen uptake and release of titanium alloys as basis for the design of a THT process (Part 2), In: J. B. Langer und M. Wächter (Hrsg.), Werkstoffe und Bauteile auf dem Prüfstand, Tagungsband zur Werkstoffprüfung 2020, 3.–4. Dez. 2020, online, Berlin, 2020, p. 185–190.
- Berg, A., Wagner, L., Near-surface gradient microstructures in metastable beta-titanium alloys for improved fatigue performance, Materials Science Forum, 308-311, 1999, p. 307–312. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C. D., Christ, H.-J., Hehl, A. von, Fatigue properties of microstructural gradients in Ti–6Al–4V generated with thermohydrogen treatment, In: Zimmermann, M. (Hrsg.), Werkstoffe und Bauteile auf dem Prüfstand, Tagungsband zur Werkstoffprüfung 2022, DGM, Sankt Augustin, Germany, 2022, p. 294–299.
- Niinomi, M., Gong, B., Kobayashi, T., Ohyabu, Y., Toriyama, O., Fracture characteristics of Ti–6Al–4V and Ti–5Al–2.5Fe with refined microstructure using hydrogen, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 26 (5), 1995, p. 1141–1151. [CrossRef]
- Oshida, Y., Bioscience and bioengineering of titanium materials, Elsevier, London, 2. Aufl., 2013.
- Costa, J. E., Banerjee, D., Williams, J. C., Hydrogen effects in beta-titanium alloys, In: Boyer, R. R., Rosenberg, H. W. (Hrsg.), Beta titanium alloys in the 1980's, TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, USA, 1984, p. 69–84.
- Paramore, J. D., Fang, Z. Z., Dunstan, M., Sun, P., Butler, B. G., Hydrogen-enabled microstructure and fatigue strength engineering of titanium alloys, Scientific Reports, 7 (1), 2017, p. 41444. [CrossRef]
- Numakura, H., Koiwa, M., Hydride precipitation in titanium, In: Ashby, M. F., Hirth, J. P. (Hrsg.), Perspectives in hydrogen in metals, Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, 1986, p. 501–509.
- Kerr, W. R., The effect of hydrogen as a temporary alloying element on the microstructure and tensile properties of Ti–6Al–4V, Metallurgical Transactions A, 16 (6), 1985, p. 1077–1087. [CrossRef]
- Guitar, A., Vigna, G., Luppo, M. I., Microstructure and tensile properties after thermohydrogen processing of Ti–6Al–4V, Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2 (2), 2009, p. 156–163. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z., He, Z., Wu, S., Gao, X., Lei, L., Liu, C., Chen, B., Dong, C., Rotating bending fatigue mechanisms of L-PBF manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloys using in situ X-ray tomography, International Journal of Fatigue, 176, 2023, p. 107876. [CrossRef]
- Hines, J. A., Propagation of microcracks at stress amplitudes below the conventional fatigue limit in Ti–6Al–4V, Fatigue Fracture of Engineering Materials and Structures, 22 (8), 1999, p. 657. [CrossRef]
- Qazi, J. I., Rahim, J., Senkov, O. N., Froes, F. H., Phase transformations in the Ti–6Al–4V–H system, Journal of the Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 54 (2), 2002, p. 68–71. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K., Li, M. Q., Morphology and crystallographic orientation of the secondary α phase in a compressed α/β titanium alloy, Scripta Materialia, 68 (12), 2013, p. 964–967. [CrossRef]
- Peters, J. O., Lütjering, G., Comparison of the fatigue and fracture of α+β and β titanium alloys, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 32 (11), 2001, p. 2805–2818. [CrossRef]
- Atzori, B., Meneghetti, G., Susmel, L., Material fatigue properties for assessing mechanical components weakened by notches and defects, Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 28 1-2, 2005, p. 83–97. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R., Nag, S., Stechschulte, J., Fraser, H. L., Strengthening mechanisms in Ti–Nb–Zr–Ta and Ti–Mo–Zr–Fe orthopaedic alloys, Biomaterials, 25 (17), 2004, p. 3413–3419. [CrossRef]
- Koblischka-Veneva, A., Koblischka, M. R., Schmauch, J., Noudem, J., Murakami, M., Analysis of the microstructure of bulk MgB2 using TEM, EBSD and t-EBSD, Journal of microscopy, 274 (3), 2019, p. 123–131. [CrossRef]
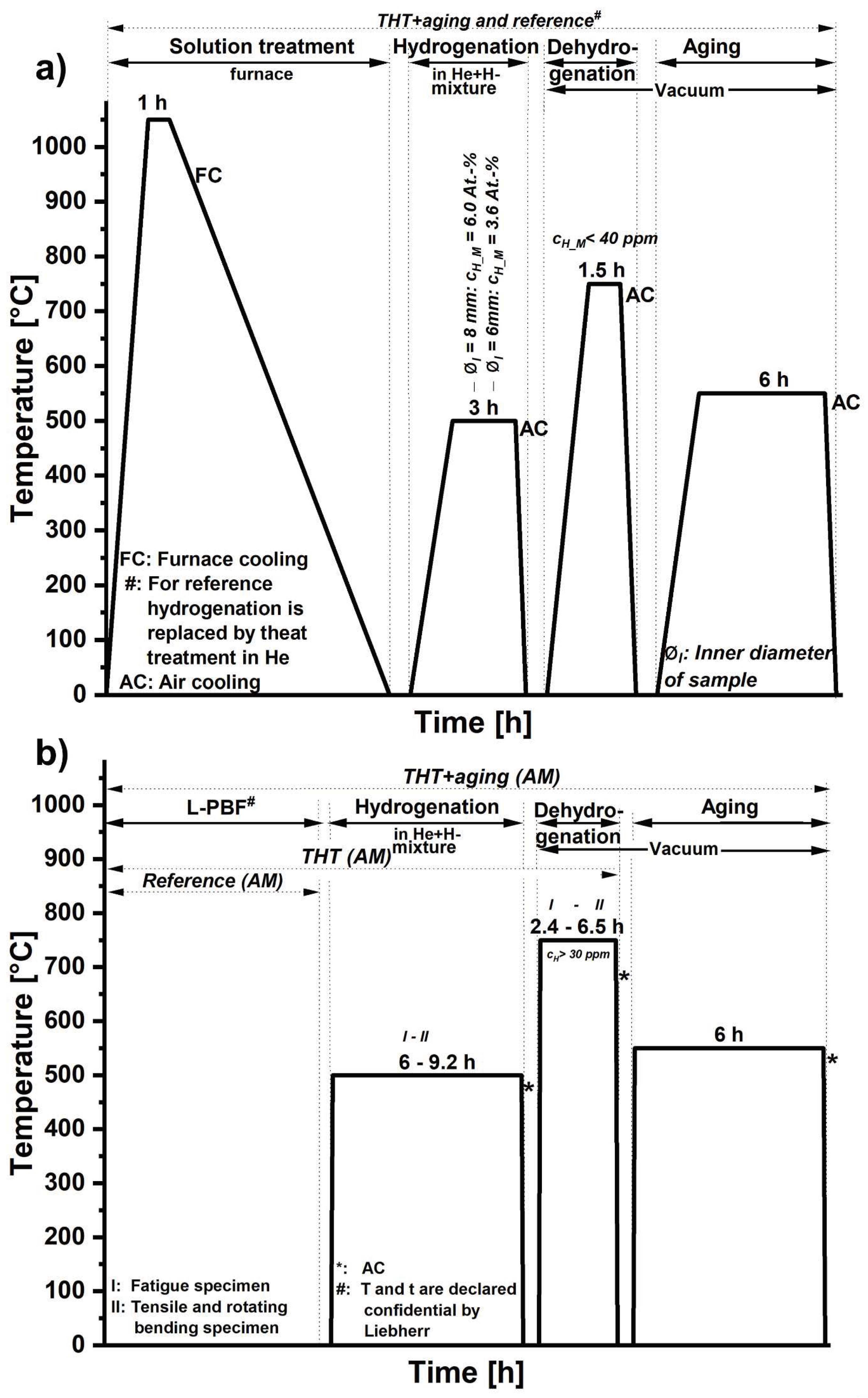
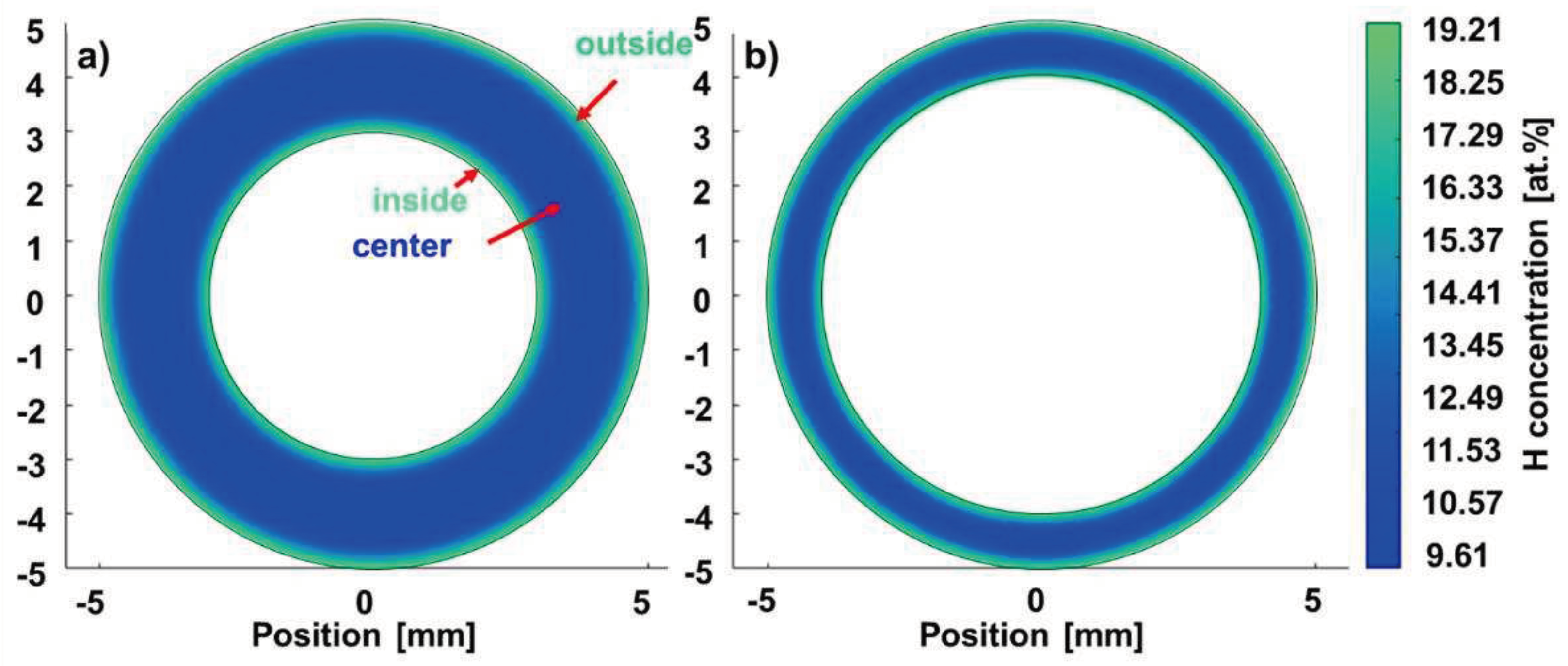
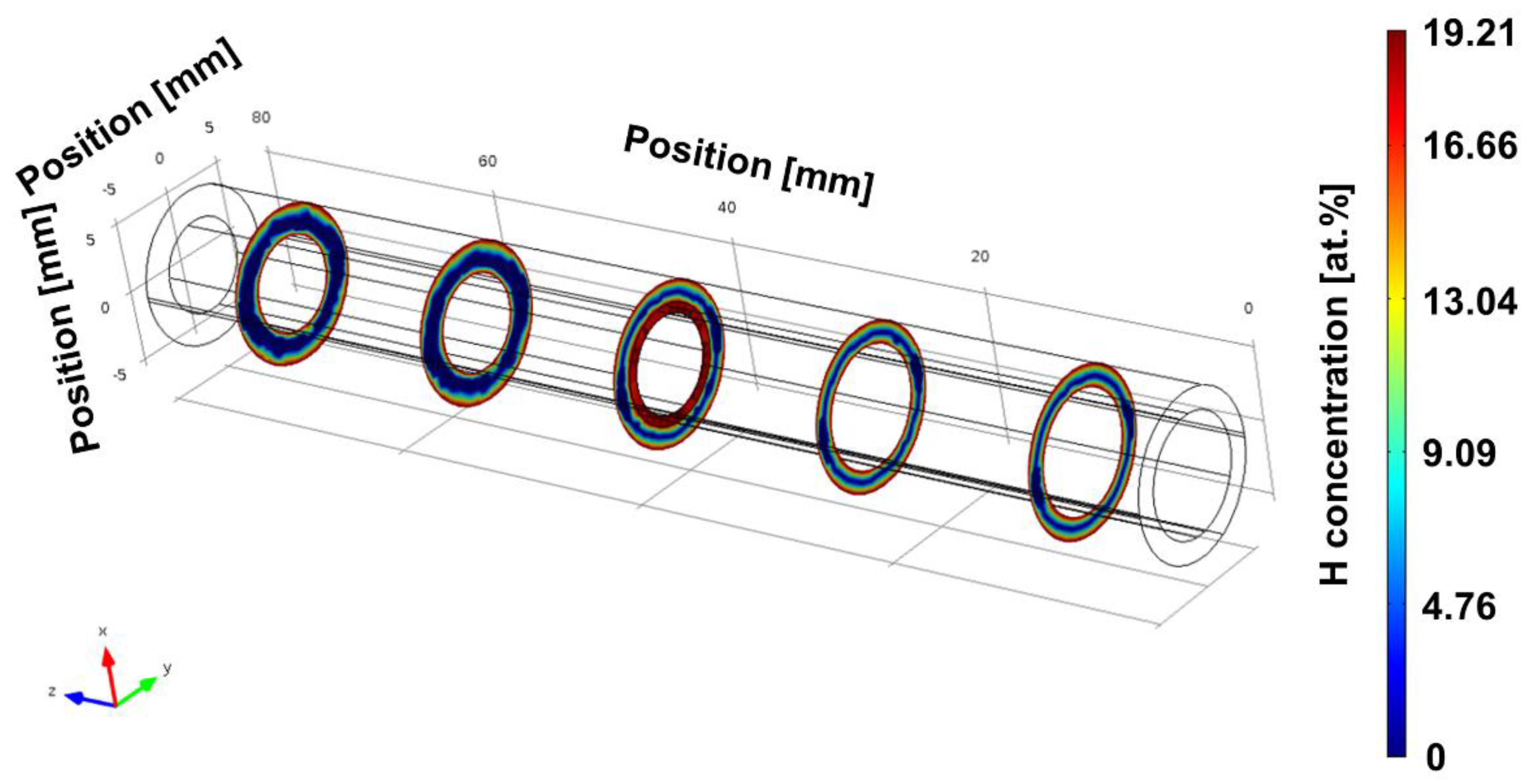
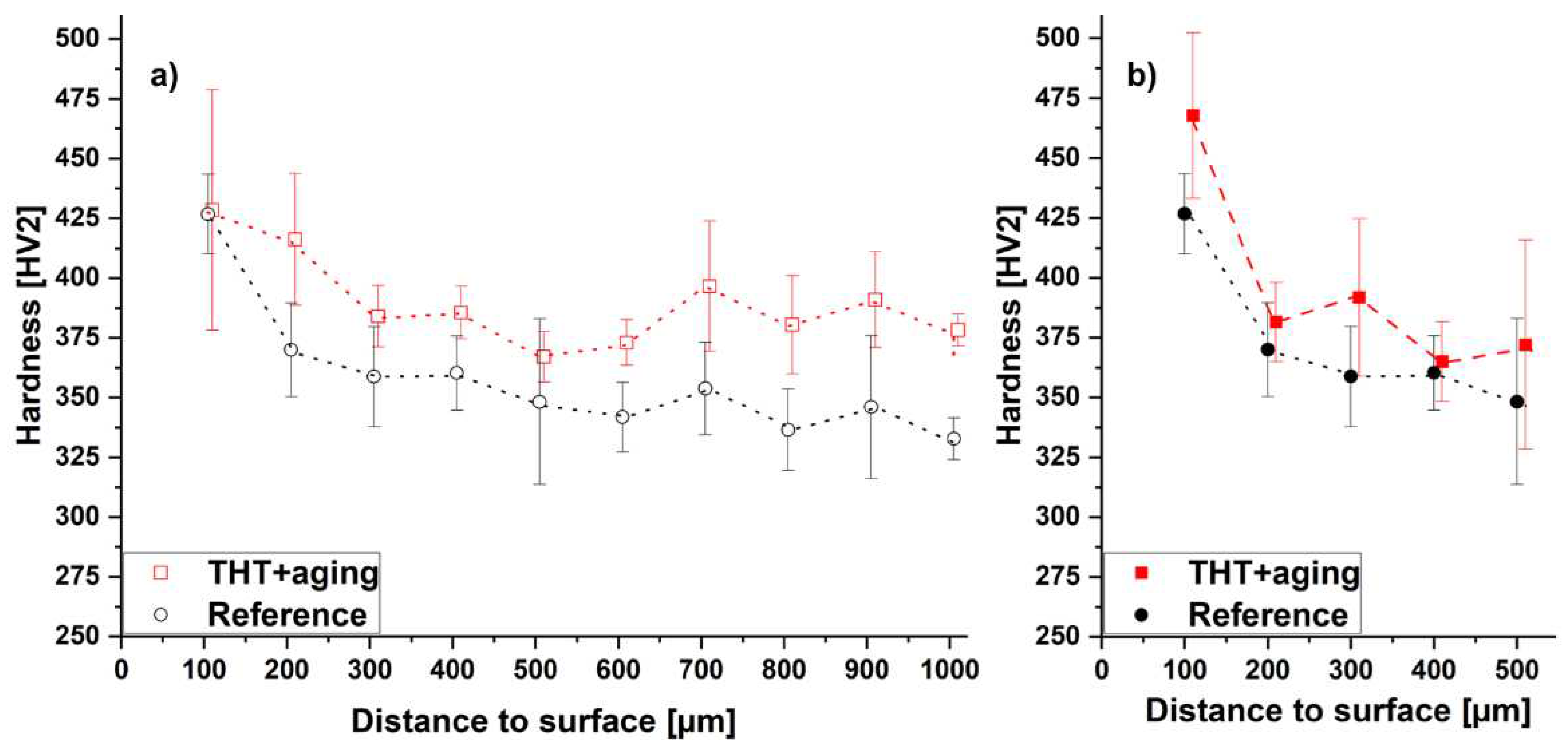
| Specimen type | Hydrogenation | Dehydrogenation | ||||||
| tH [h] |
cH_M [at.%] inner/outer |
ti [s] | SCFH | tD [h] | cH_M [at.%] | ti [s] | SCFD | |
| Tube-like | 3 | 3.6/6.0 | 160 | 23.5 | 3 | 0.2 | 220 | 14.3 |
| Wall thickness | Condition | α colony width [µm] | α lamellar width [µm] | ||
| Surface | Center | Surface | Center | ||
| 2 mm | THT+aging | 21–156 | 172–562 | 2–10 | 3–12 |
| Reference | 64–199 | 349–376 | 3–13 | 3–11 | |
| 1 mm | THT+aging | 80–232 | 128–191 | 2–17 | 2–27 |
| Reference | 80–244 | 166–281 | 6–19 | 6–25 | |
| Specimen type | Hydrogenation | Dehydrogenation | ||||||
| tH [h] |
cH_M [At.-%] Inner/outer |
ti [s] | SCFH | tD [h] | cH_M [At.-%] | ti [s] | SCFD | |
| AM specimens for fatigue | 6 | 13.7 | 230 | 16.5 | 2.4 | 0.2 | 220 | 17.4 |
| and for rotating bending/tensile tests | 9.2 | 14.0 | 16.8 | 6.5 | 0.1 | |||
| Condition | β phase fraction [vol.%] | α lamellae width [µm] | ||
| Near surface | Center | Near surface | Center | |
| THT | 9.6±2.2 | 11.0±0.1 | 1.8±0.6 | 2.3±0.8 |
| THT+aging | 7.7±0.1 | 8.9±1.4 | 1.5±0.7 | 2.1±0.6 |
| Reference | 6.0±2.3 | 2.3±0,8 | ||
| Condition | Young‘s modulus [GPa] | Tensile strength σUTS [MPa] | Yield strength σYS [MPa] | Percent tensile elongation EL [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| THT | 116 ± 2 | 1021 ± 3 | 969 ± 3 | 16.1 ± 0.1 |
| THT+aging | 122 ±1 | 1056 ± 6 | 1014 ± 1 | 16.1 ± 0.7 |
| Reference | 115 ± 3 | 1021 ± 15 | 986 ± 19 | 15.6 ± 1.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





