Submitted:
11 January 2024
Posted:
12 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
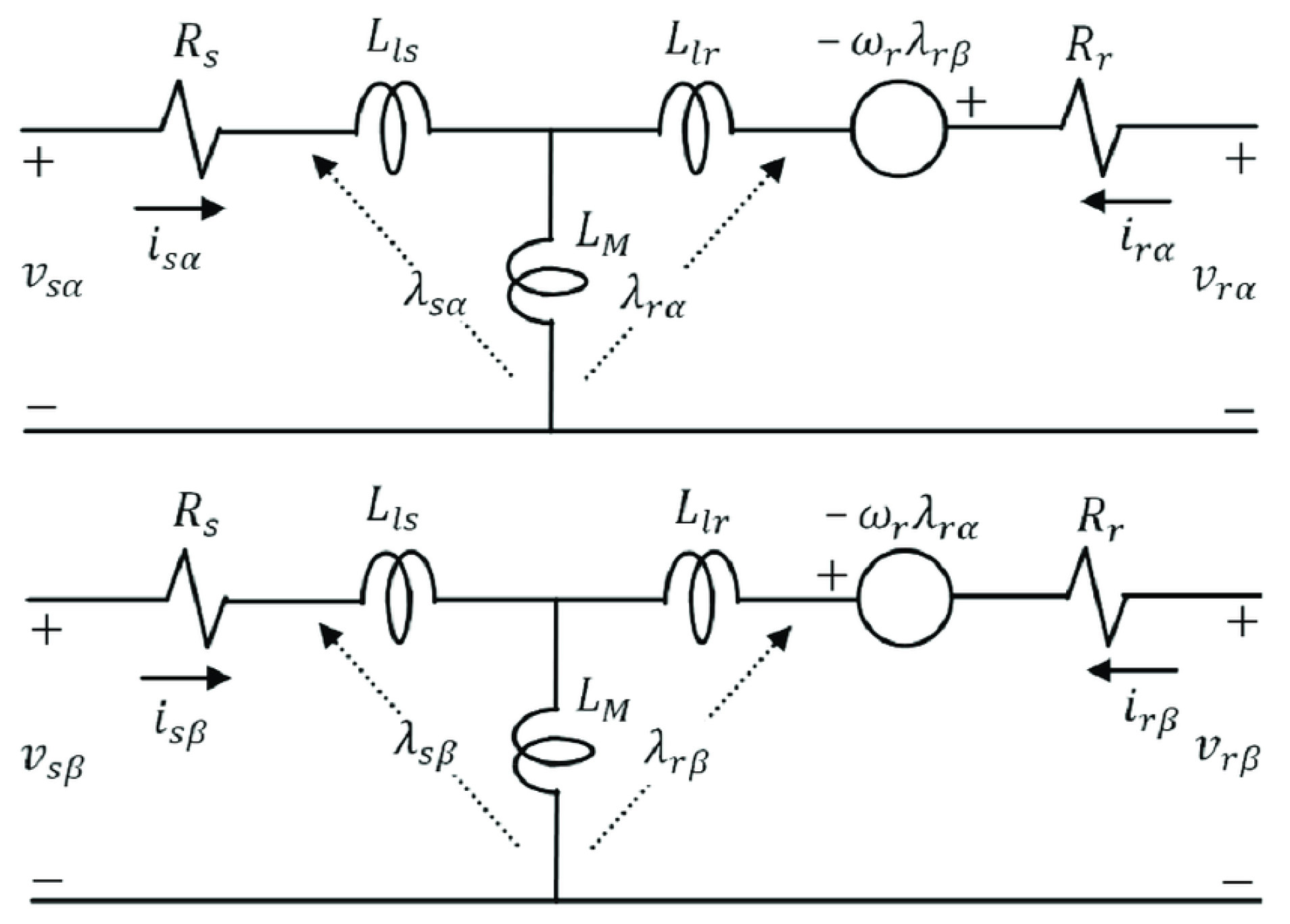
2. Dynamic model of induction motor
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- ,
- and
- ,
- .
- Because this extended IM model is non linear, the EKF algorithm is used in order to estimate the rotor speed.
3. EKF algorithm for rotor speed estimation
4. Noise covariance matrices estimation with a modified subspace model identification approach
- identifying a state-space matrices , , , and state sequence with from available input-output data using subspace model identification method. The identified state sequence can be defined aswith ;
-
comparing the identified state-space model with the deterministic part of the model used in the Kalman Filter. To this end, the both models have to be in the same basis. Therefore, we proceed to a basis change using transformation matrix T which can be computed aswhere is the observability matrix of the model used in the Kalman Filter defined asand is the observability matrix of the identified model using subspace model identification method defined asOnce is estimated with a Moore Penrose pseudo inverse, the state sequence can be moved into the "good" state basis as follows
- computing the residuals aswhere with represents the state sequence estimate in the "good" state basis performed with subspace model identification method, and , are residuals used to estimate the covariance matrices Q and R.
- transforming this discrepancy measurements into covariance matrix estimates. This part will be detailed next.
4.1. Subspace model identification
4.2. Noise covariance matrices estimation
5. Induction Motor Speed Estimation with noise covariance matrices estimation
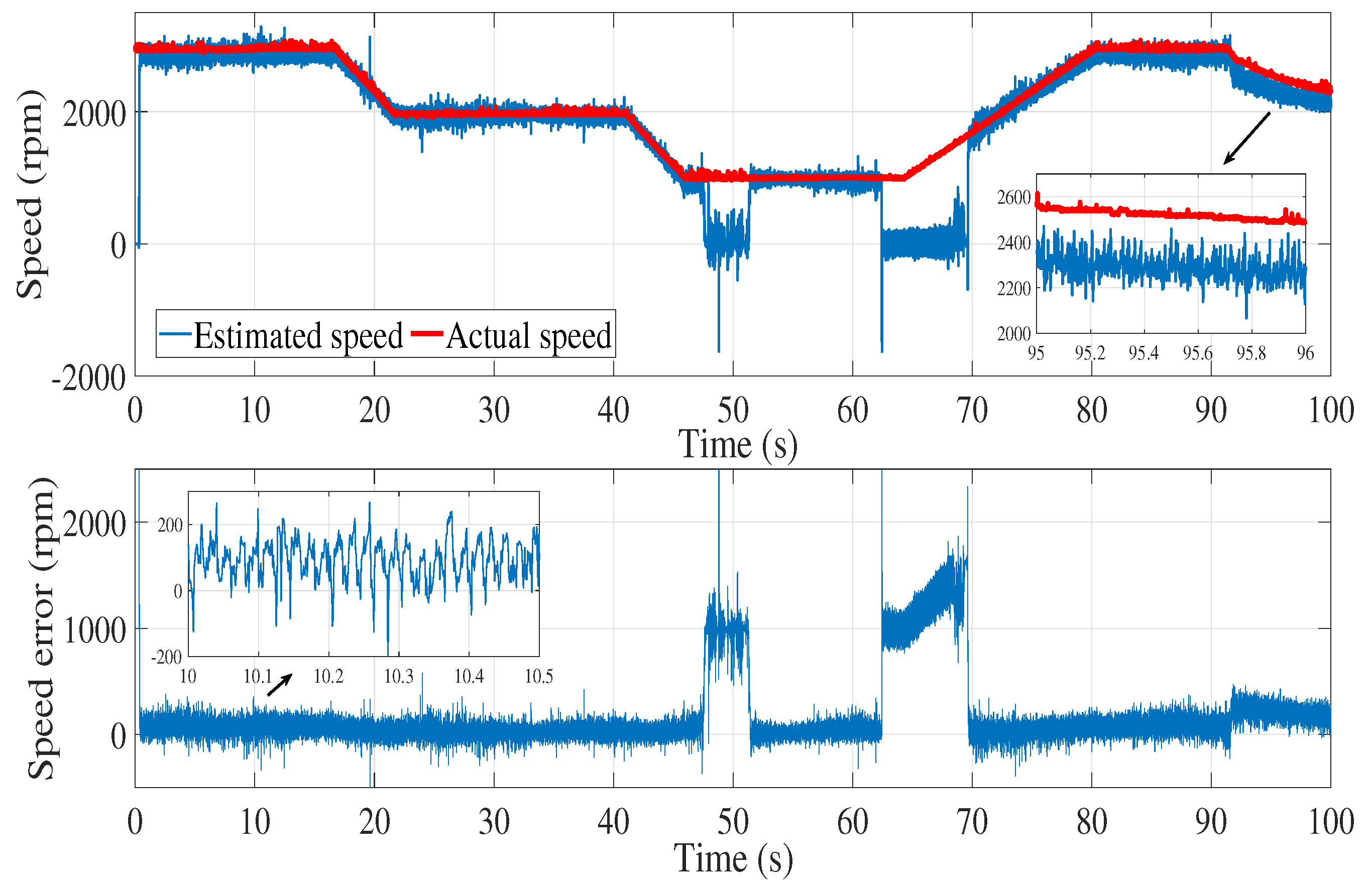
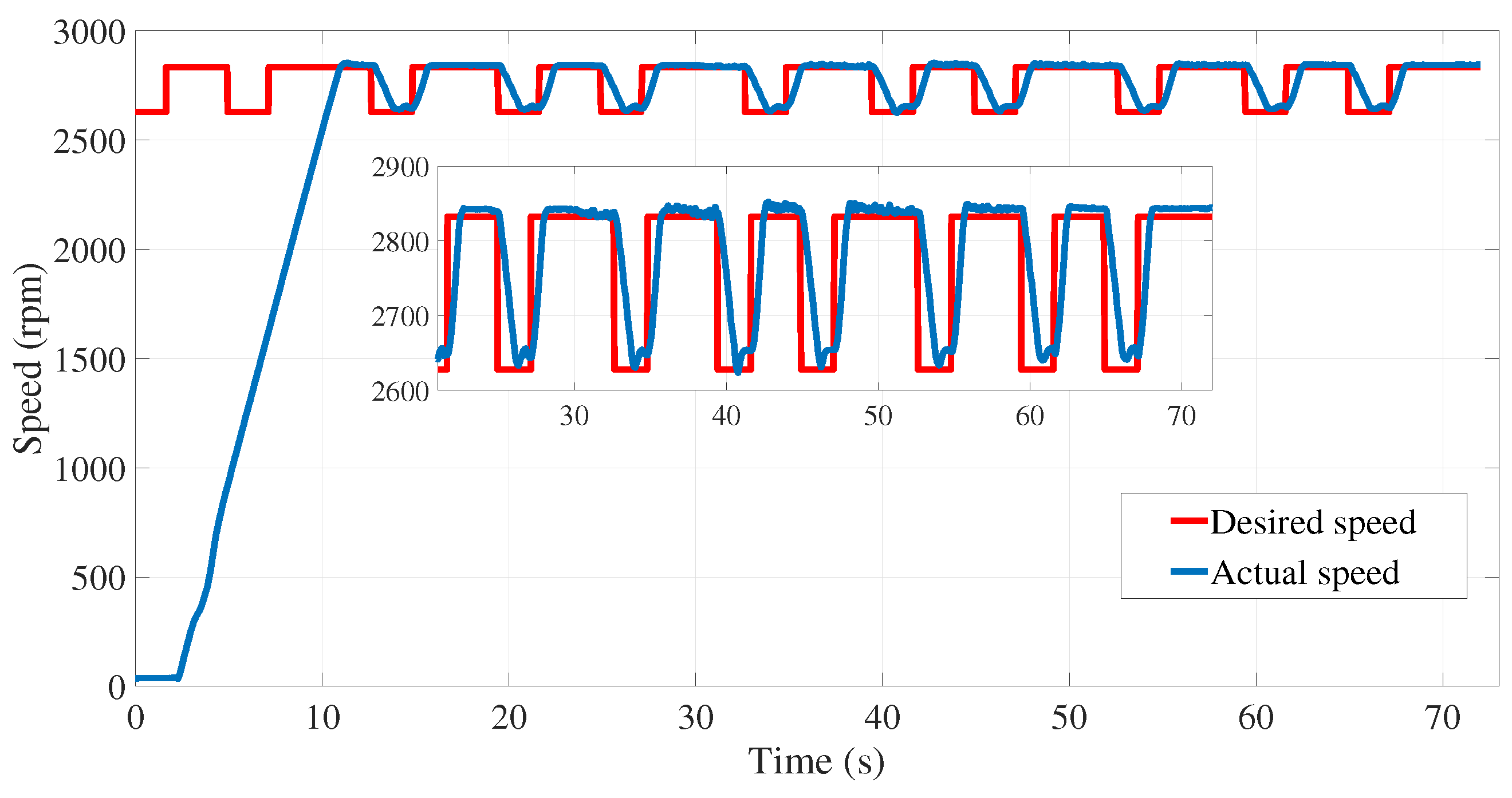
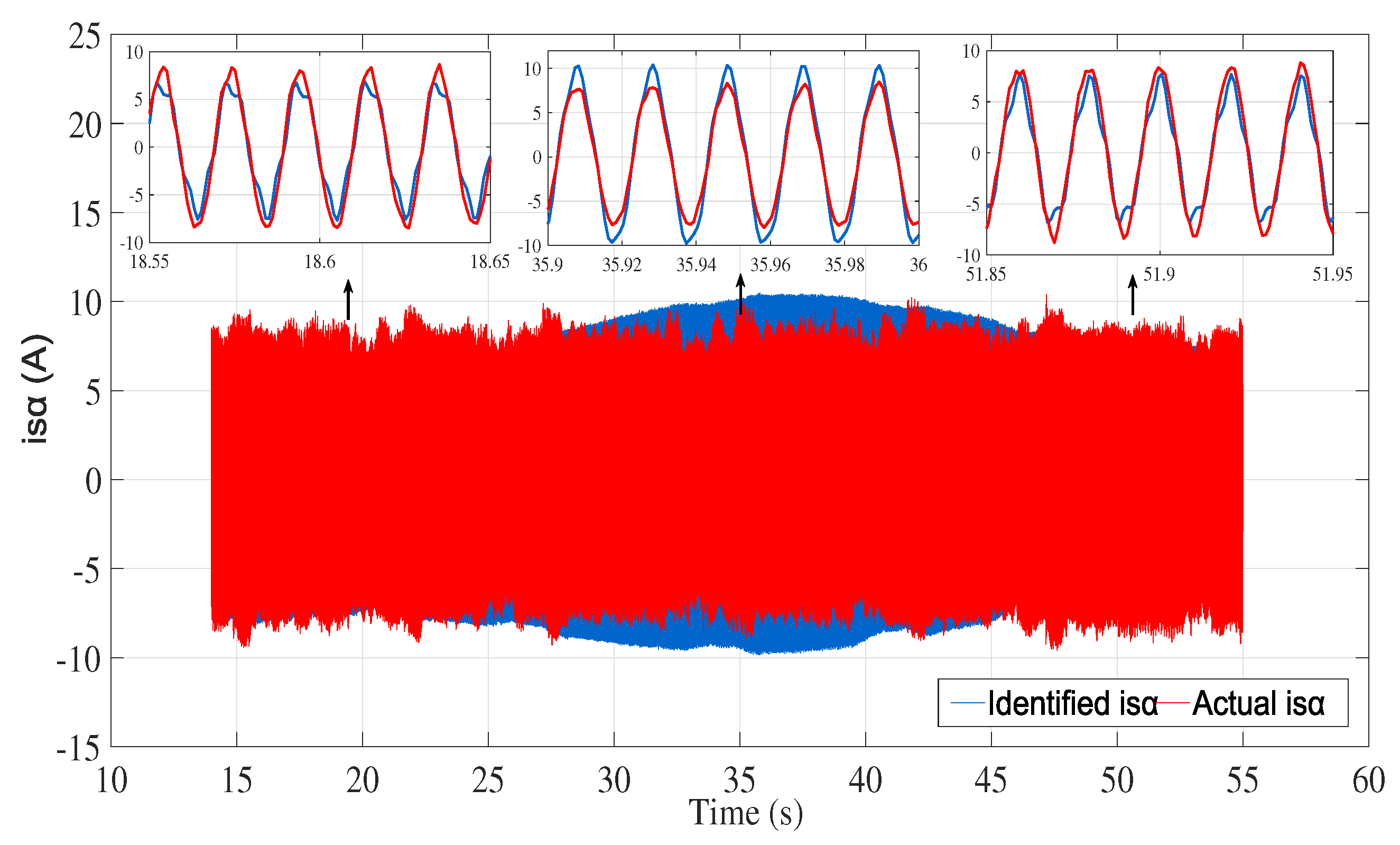
6. Results and discussion
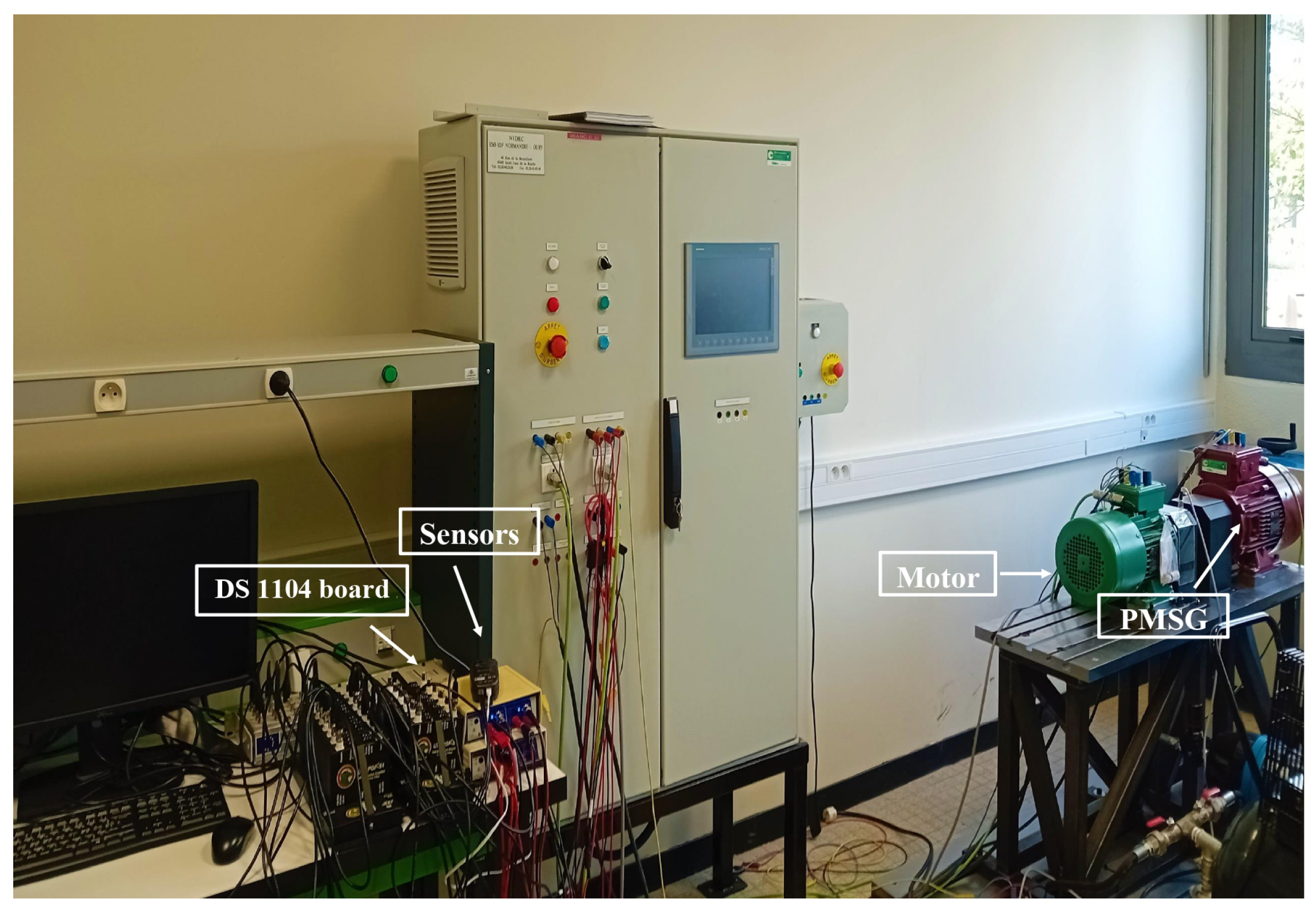
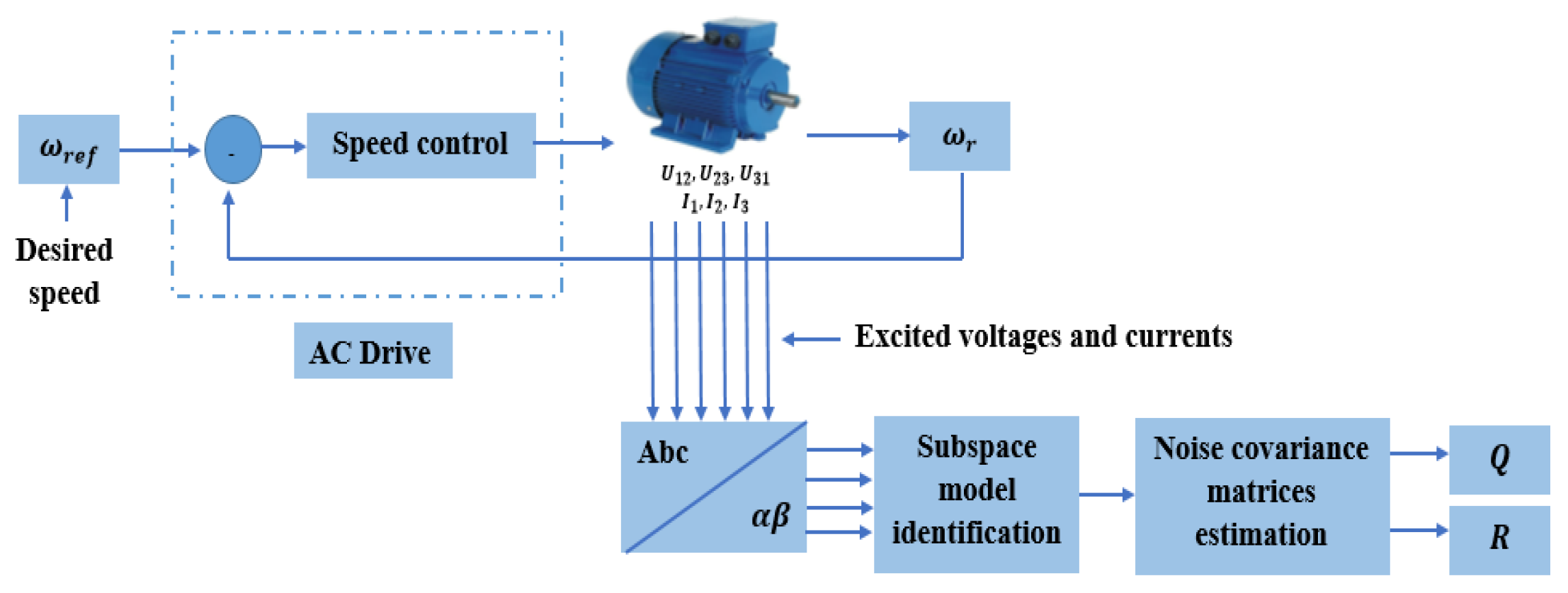
6.1. Experimental setup
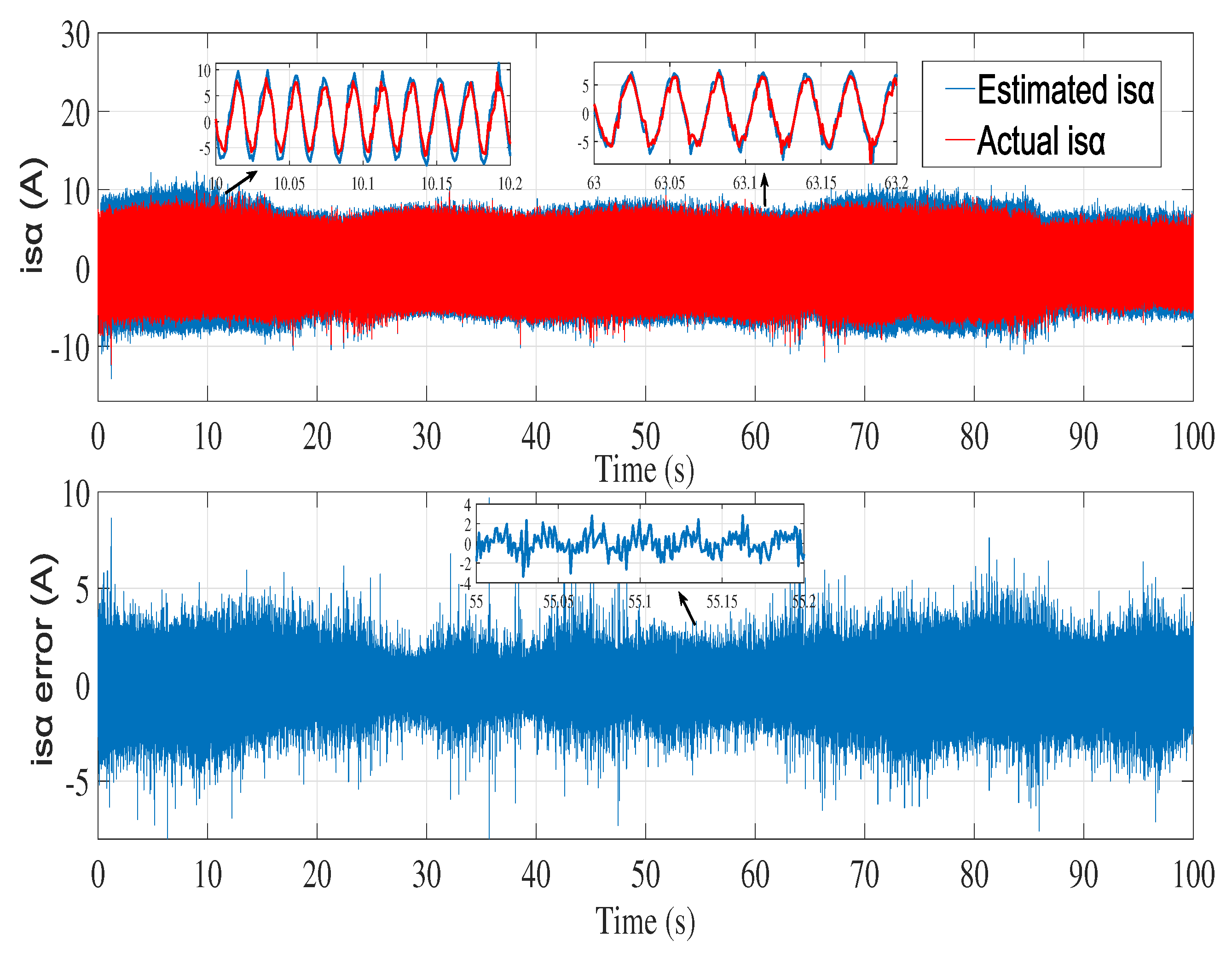
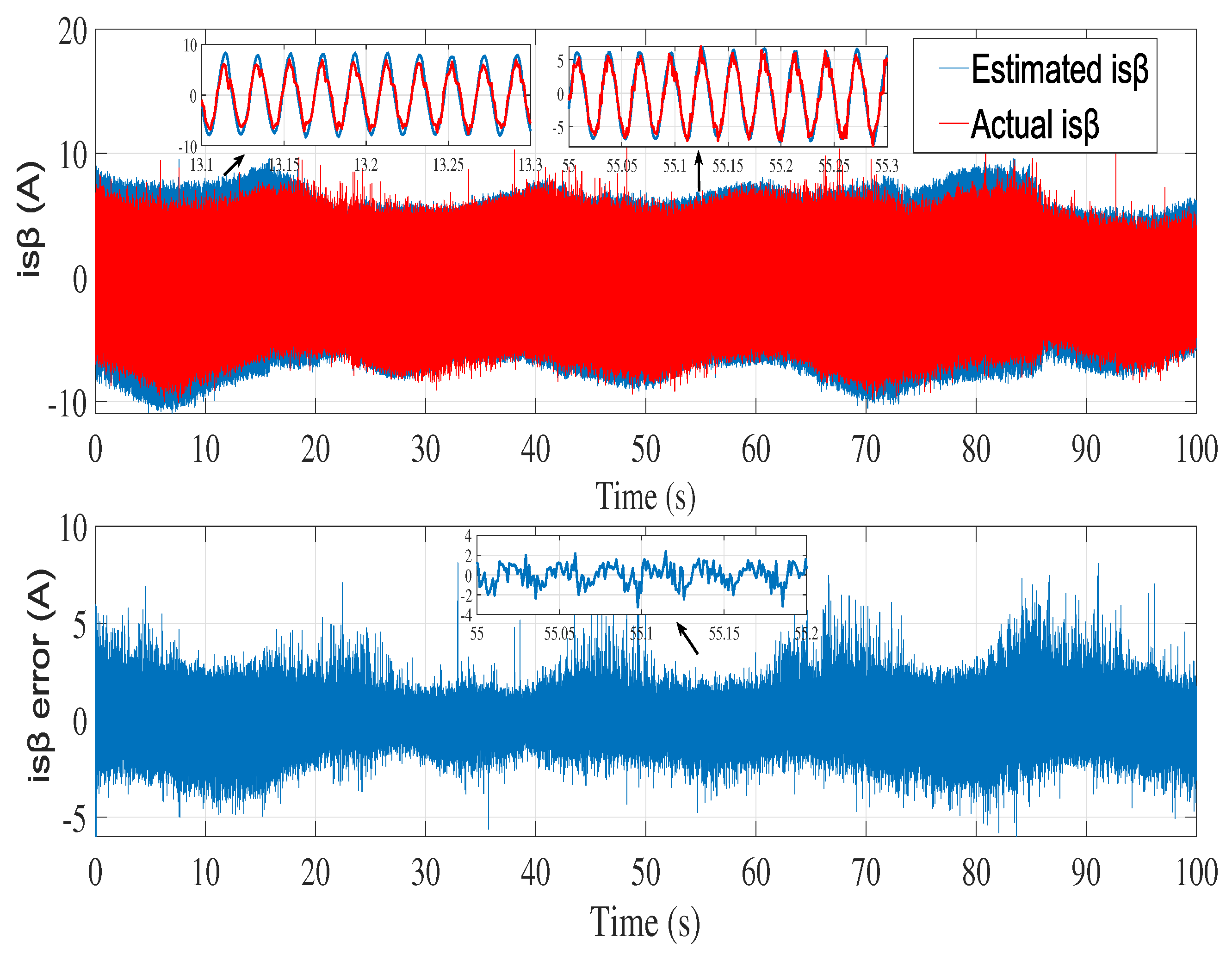
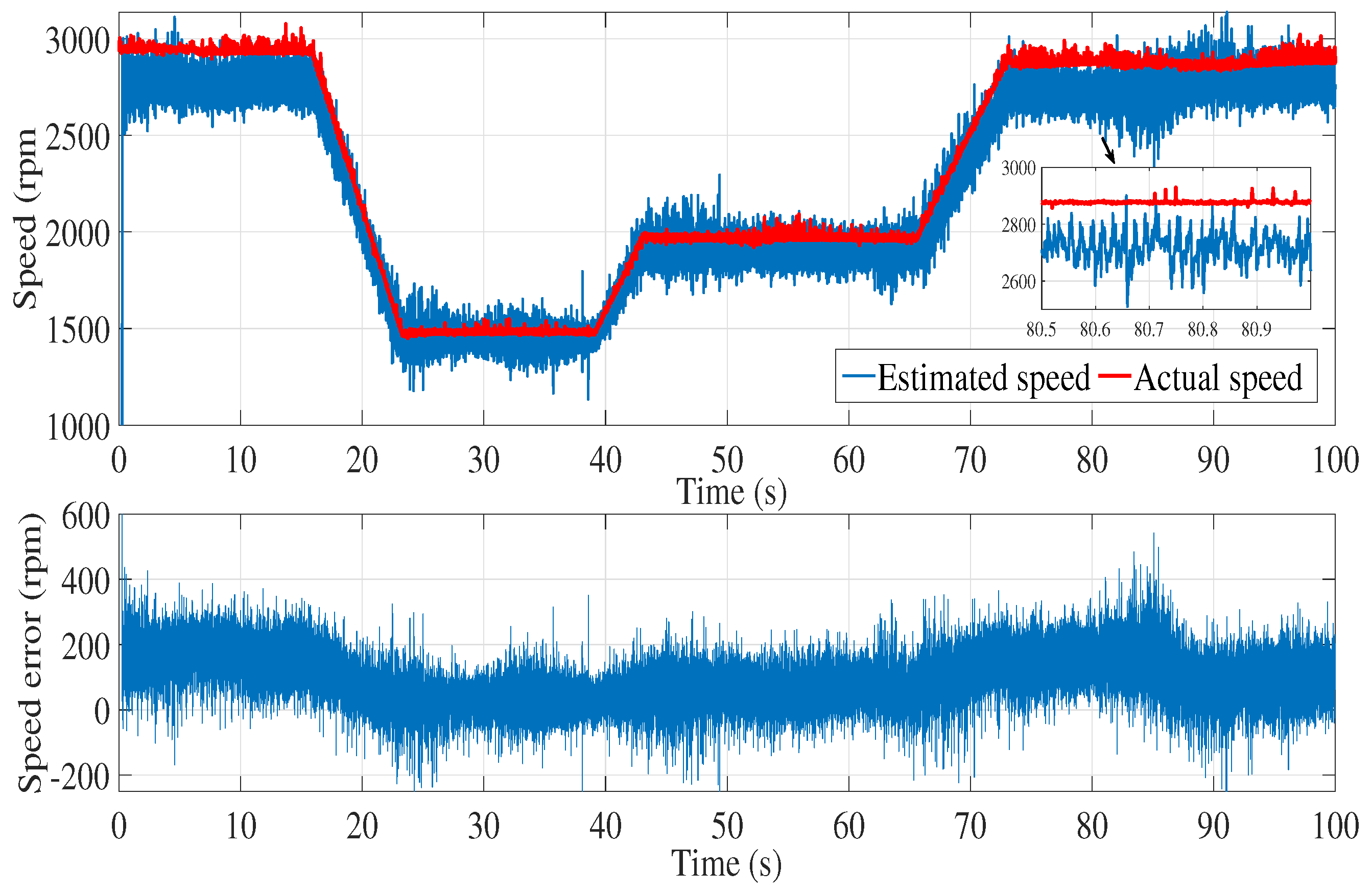
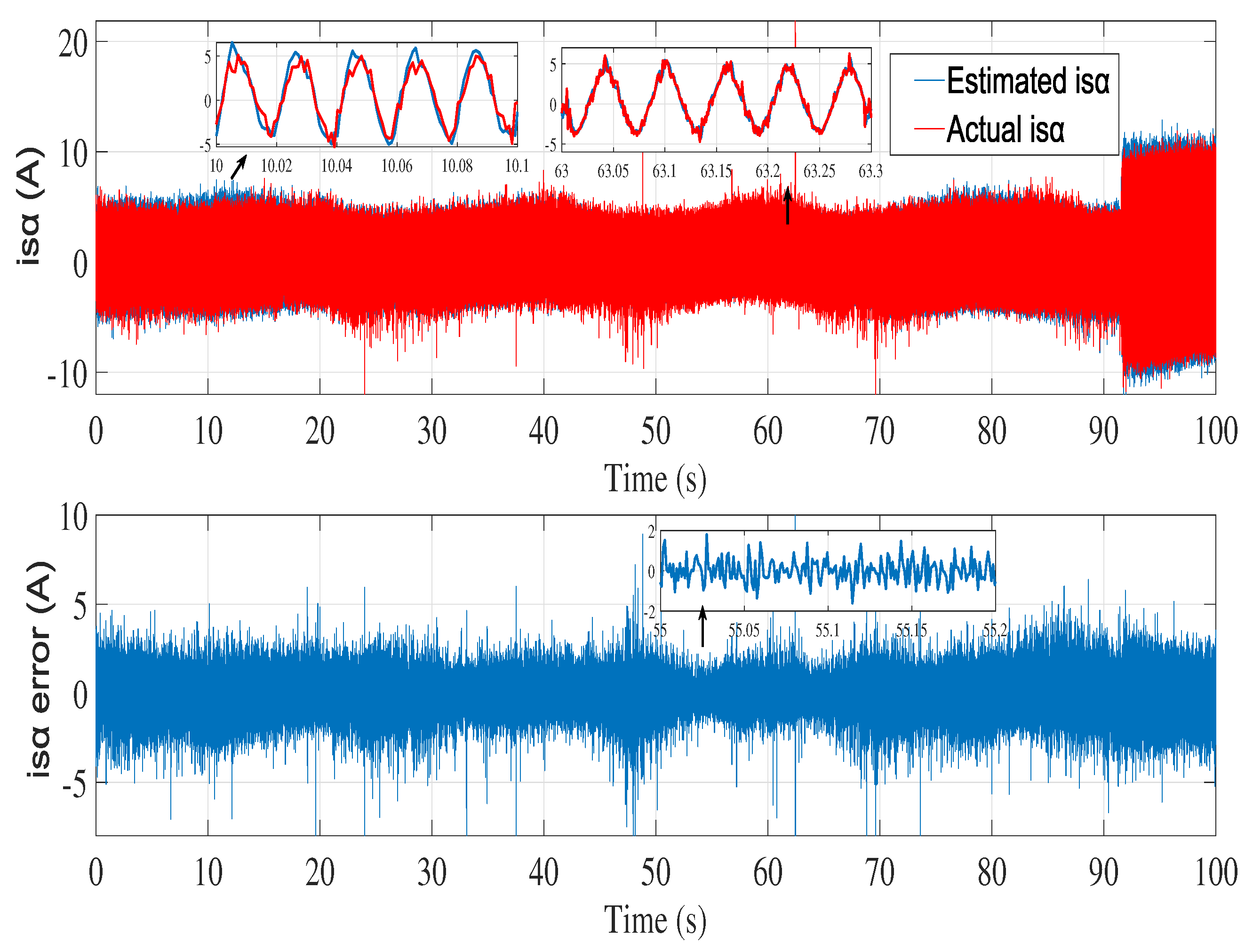
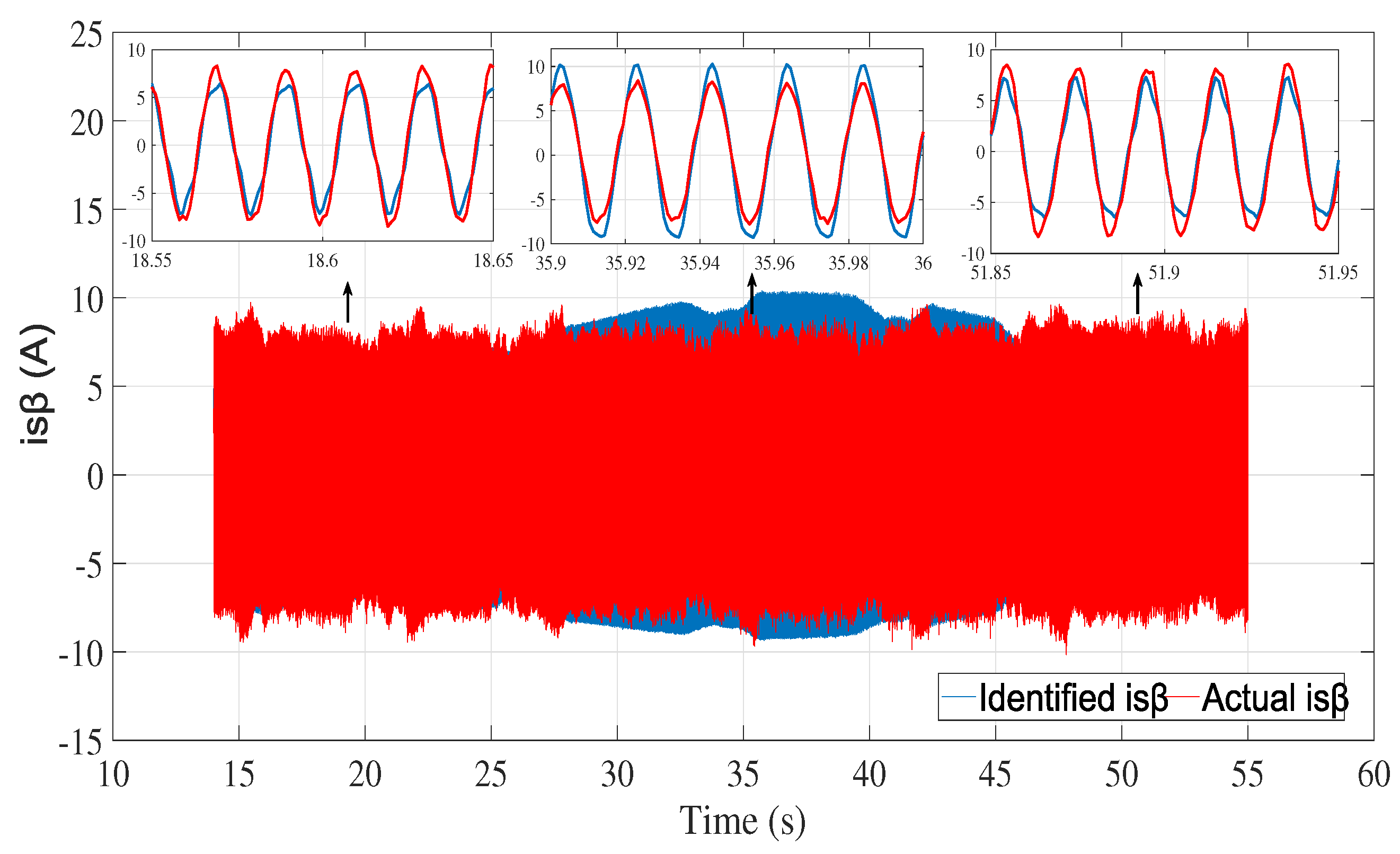
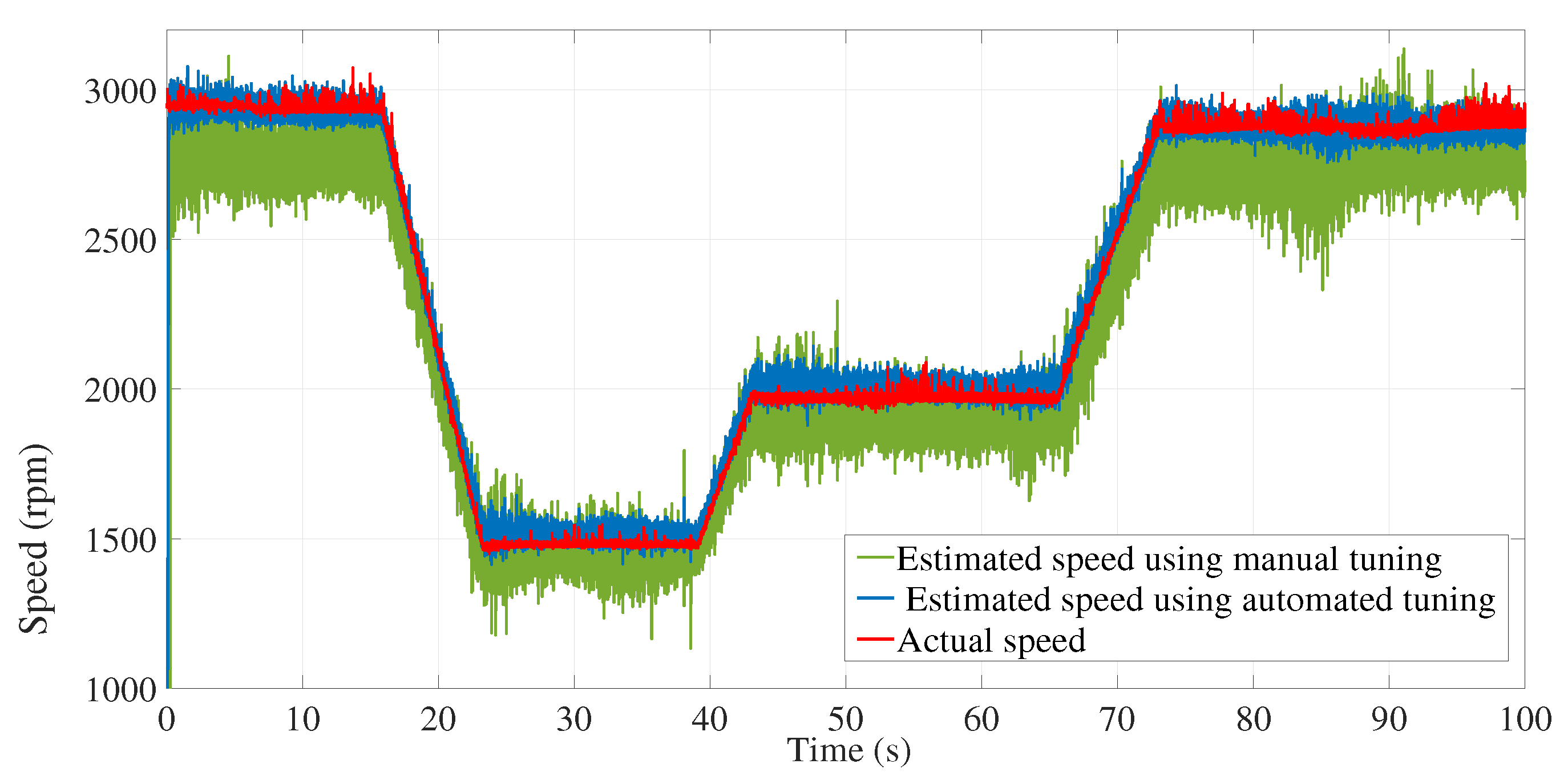
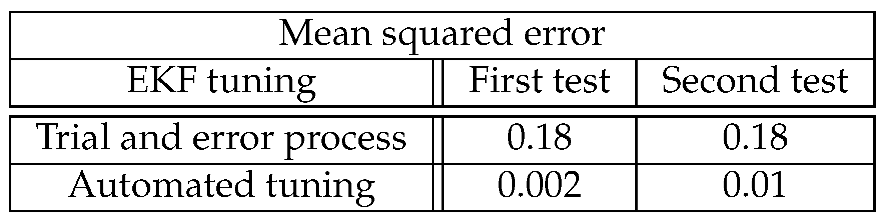
6.2. Experimental results
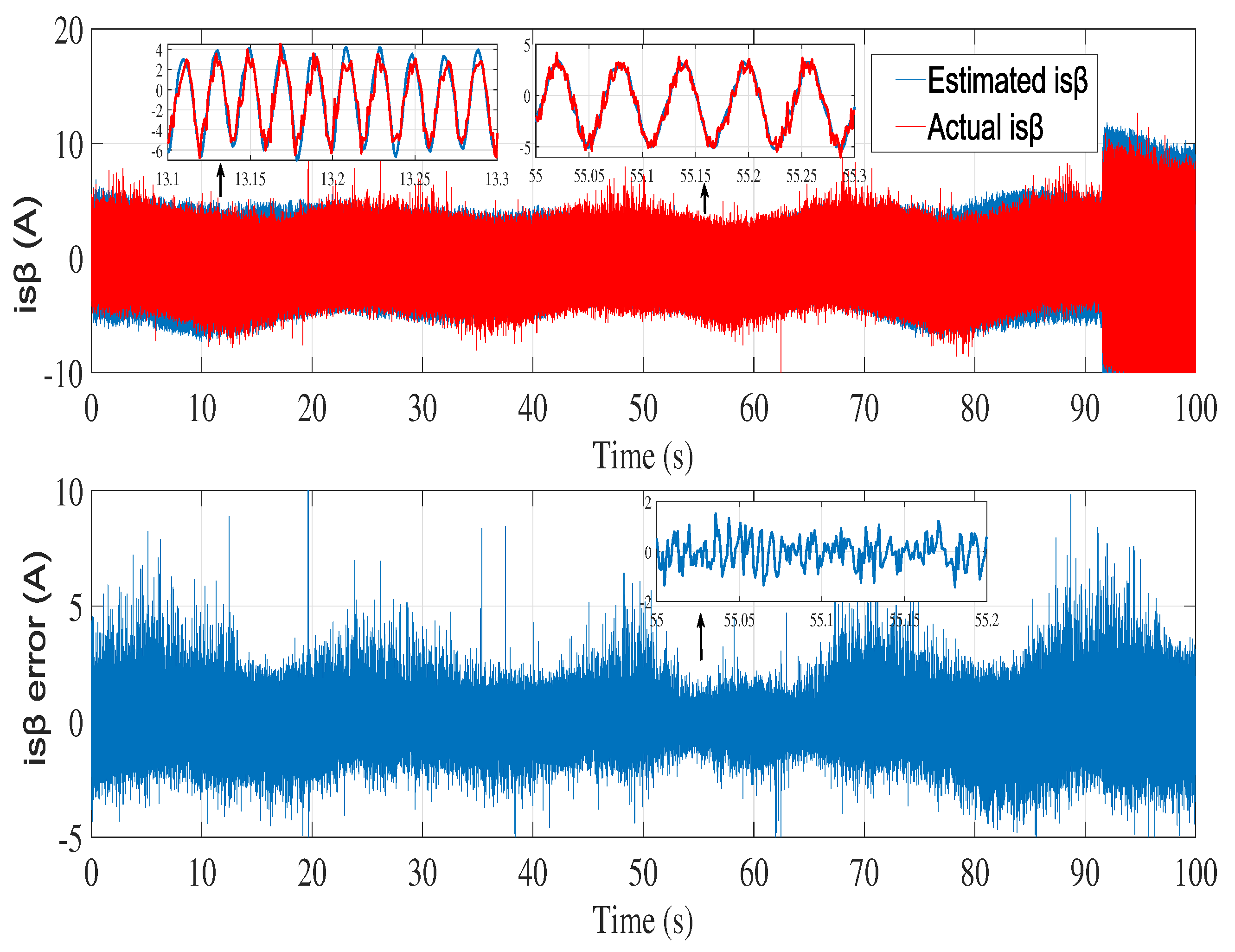
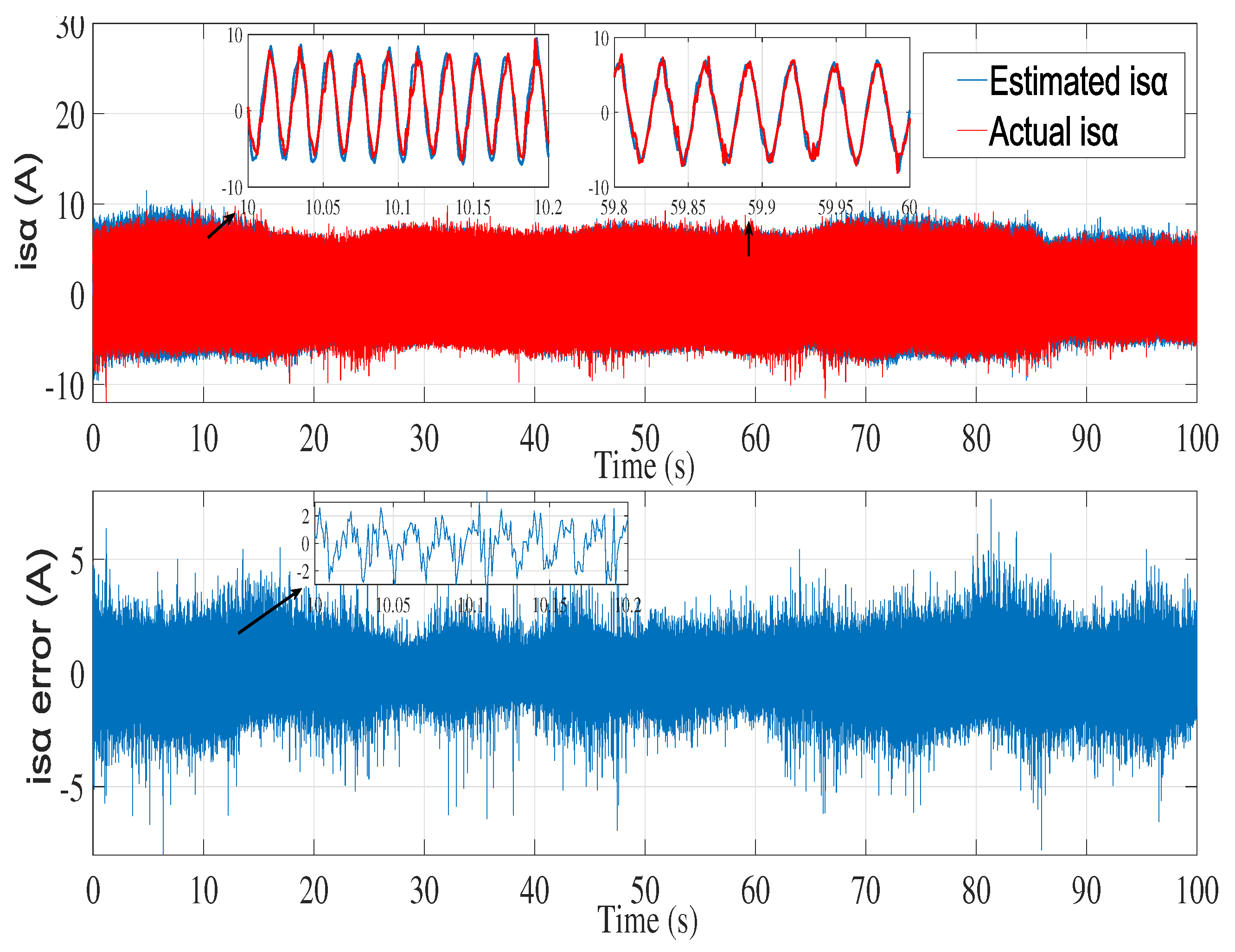
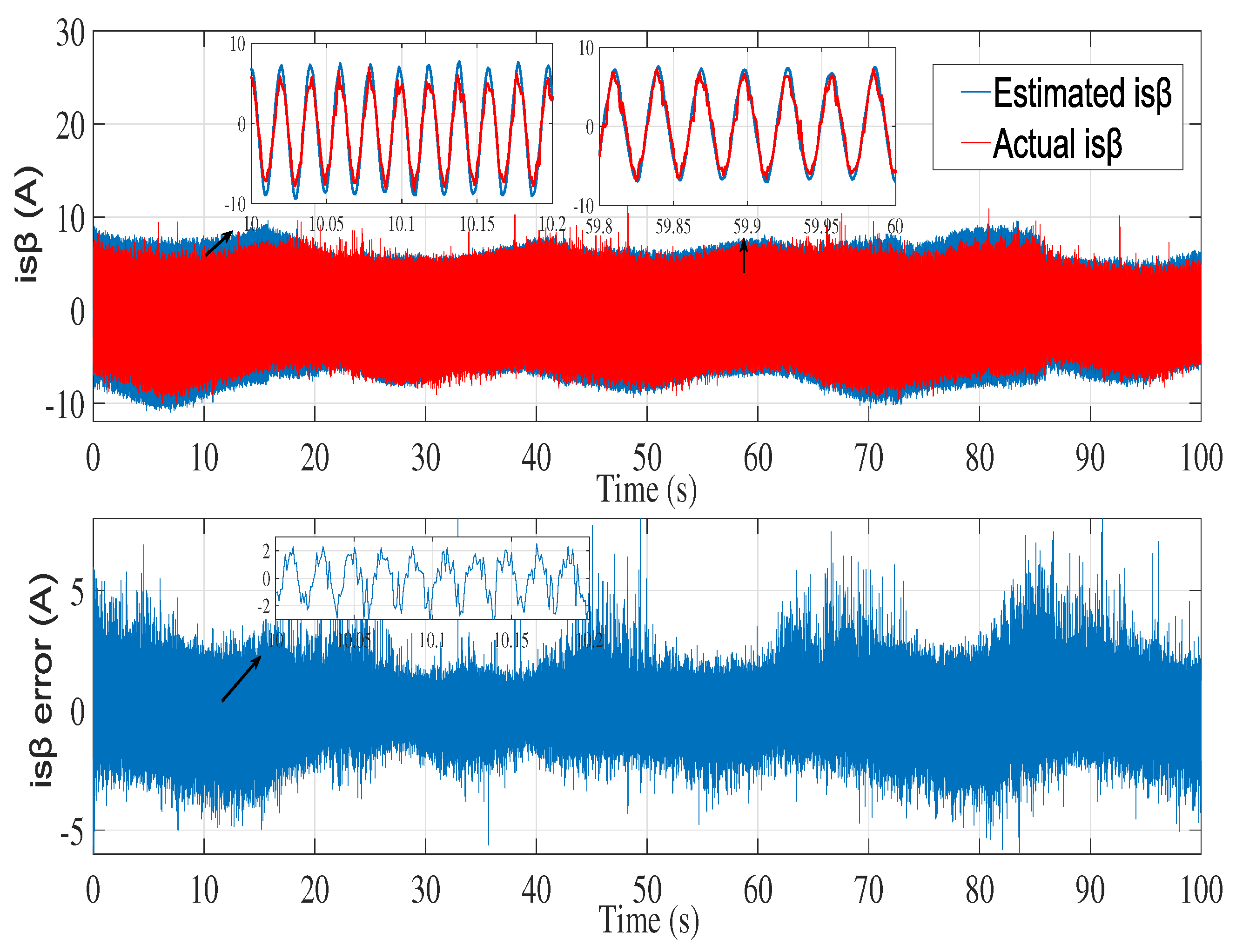
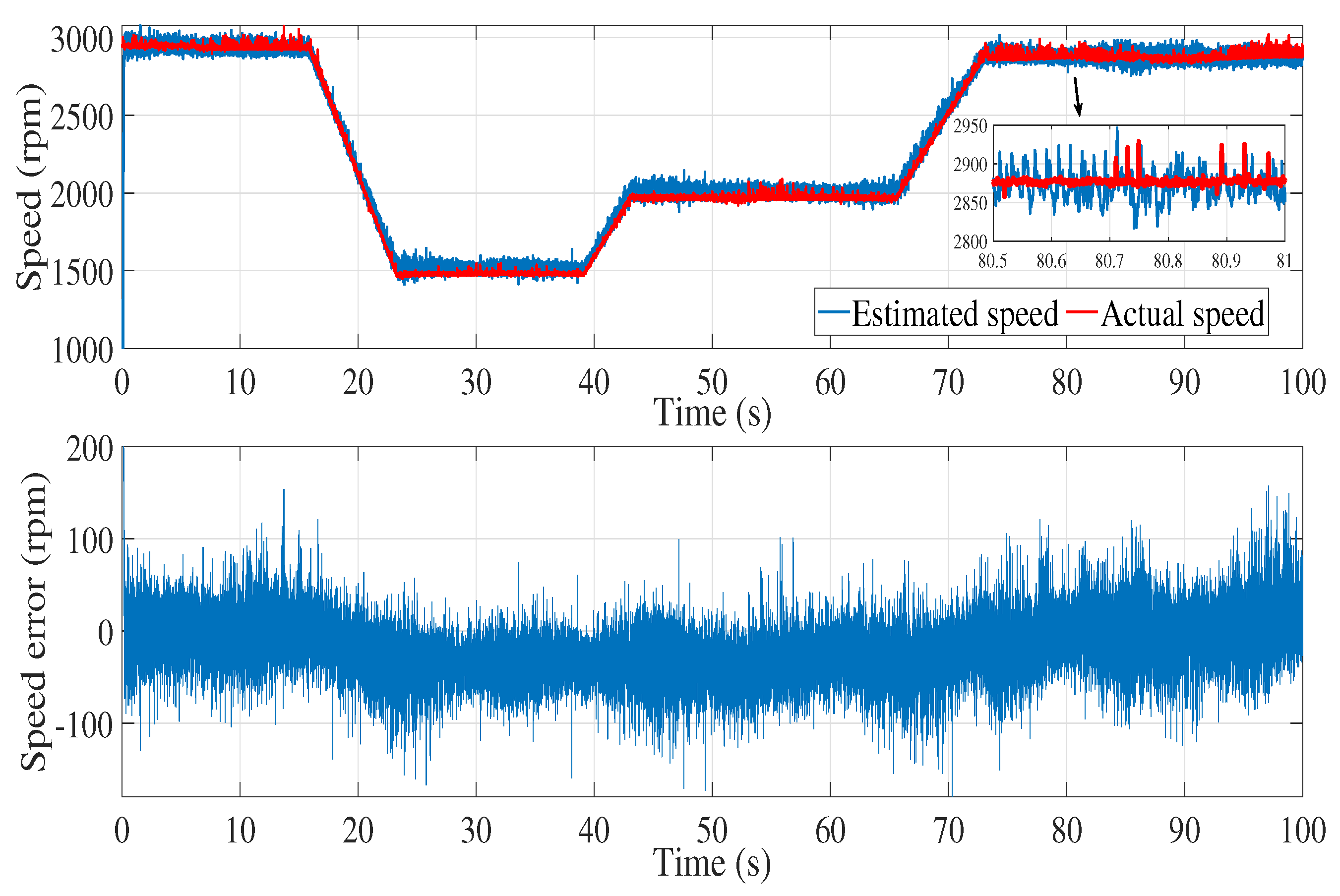
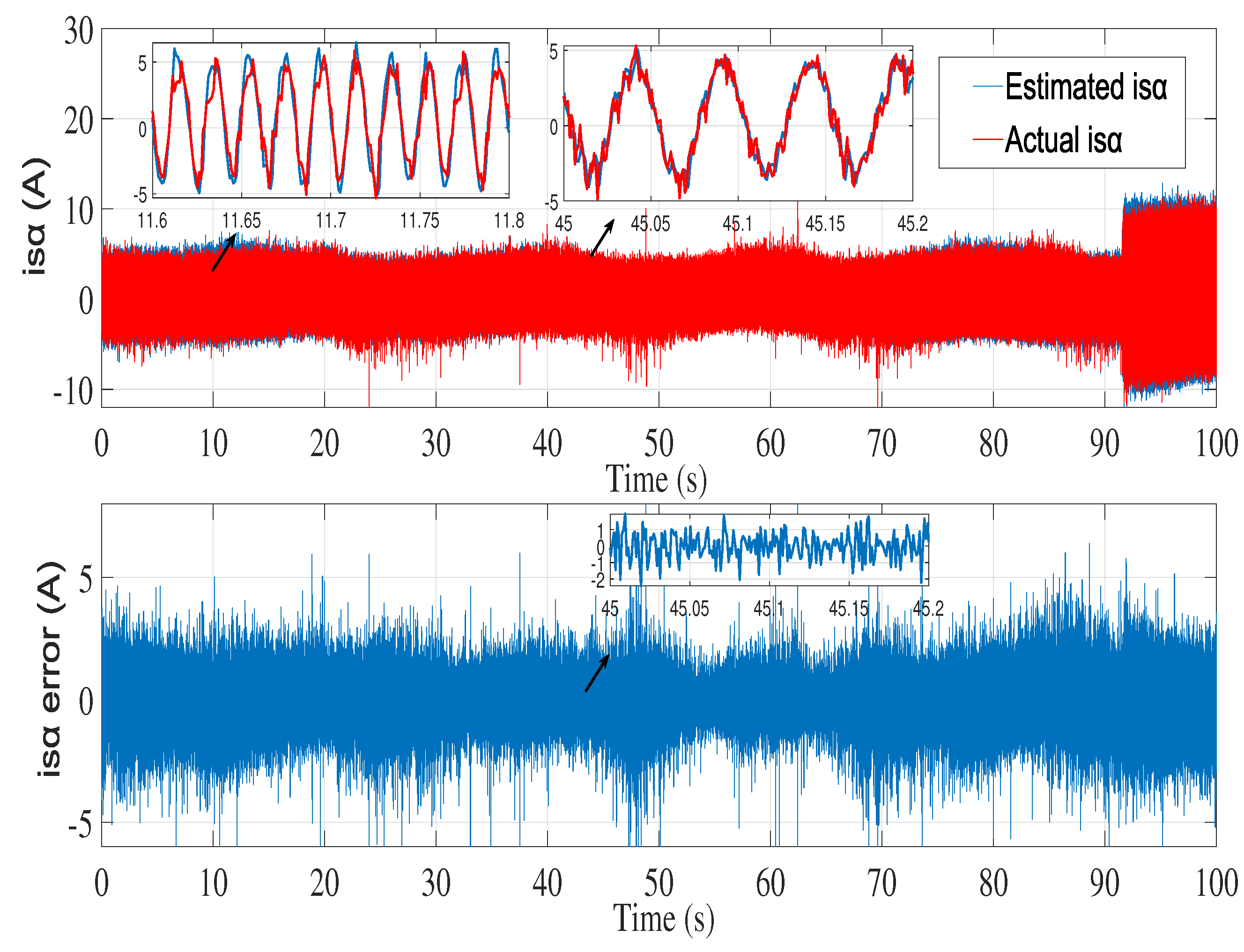
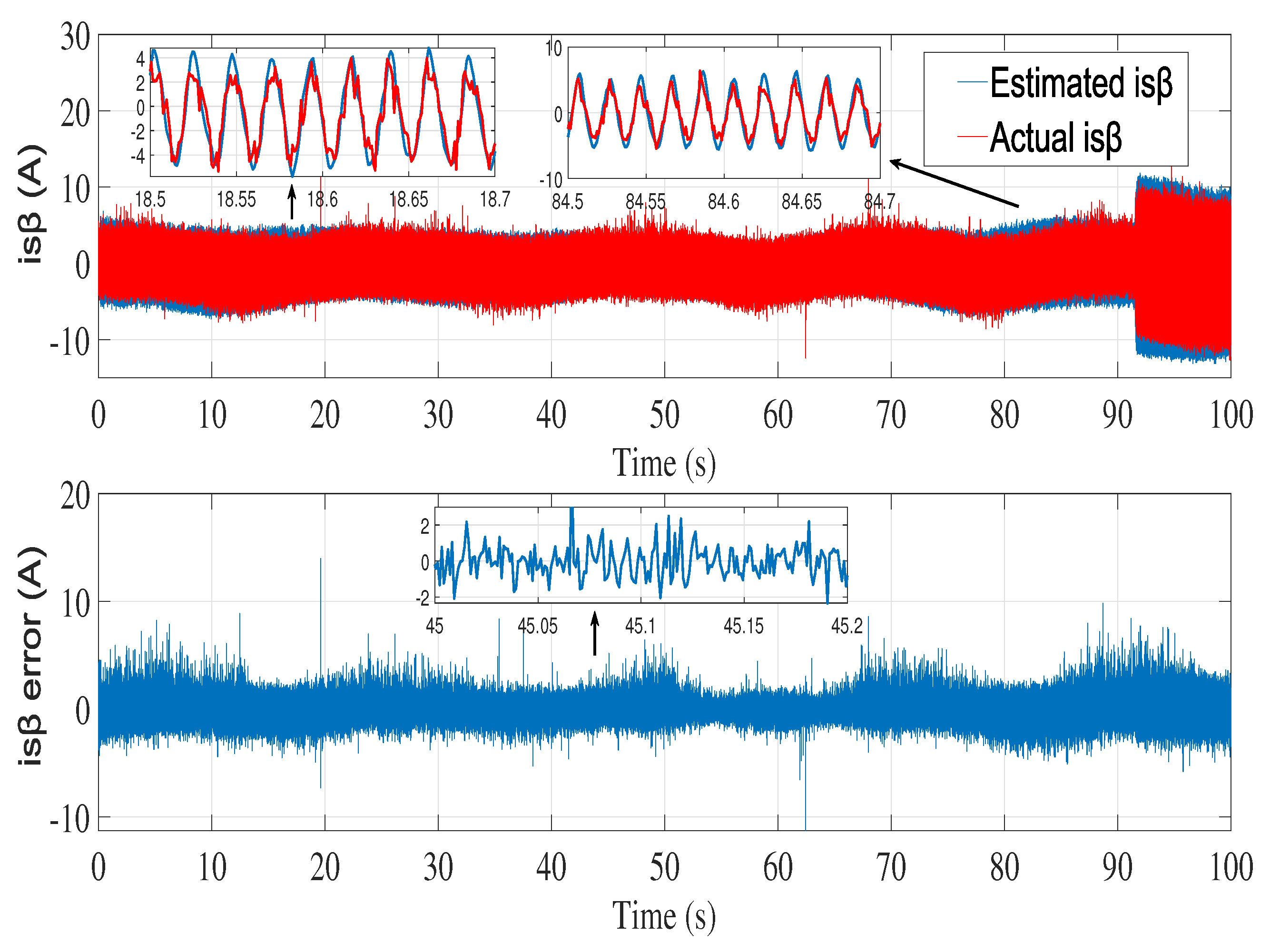
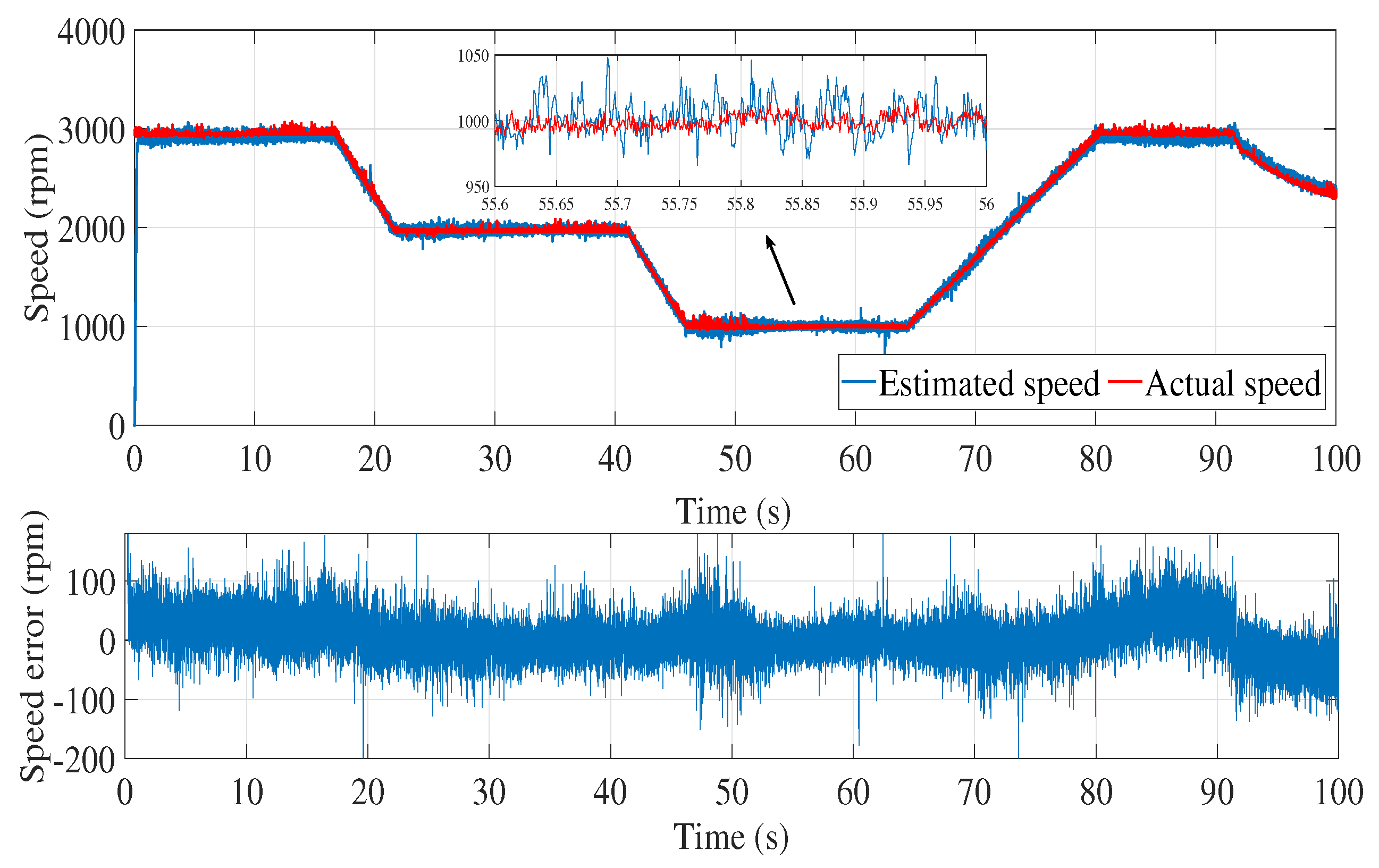
7. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Rashid, M.H. Power electronics handbook; Butterworth-heinemann, 2017.
- Vieira, R.P.; Gastaldini, C.C.; Azzolin, R.Z.; Gründling, H.A. Sensorless sliding-mode rotor speed observer of induction machines based on magnetizing current estimation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2013, 61, 4573–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accetta, A.; Cirrincione, M.; Pucci, M.; Vitale, G. Closed-loop MRAS speed observer for linear induction motor drives. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2014, 51, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R.; Sul, S.K.; Park, M.H. Speed sensorless vector control of induction motor using extended Kalman filter. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 1994, 30, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.; Chan, T.; Wong, Y.; Ho, S.L. Speed estimation of an induction motor drive using extended Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE Power Engineering Society Winter Meeting. Conference Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37077). IEEE; 2000; 1, pp. 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.; Chan, T.; Wong, Y.; Ho, S.L. Speed estimation of an induction motor drive using an optimized extended Kalman filter. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2002, 49, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, M.; Sbita, L.; Abdelkrim, M.N. EKF-Algorithm for Induction Motor State Estimation and Parameter Identification.
- Barut, M.; Bogosyan, S.; Gokasan, M. Speed-sensorless estimation for induction motors using extended Kalman filters. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2007, 54, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osamah Basheer Noori, M.O.M. Flux and Speed Estimation of Induction Motors using Extended Kalman Filter. International Journal of Computer Applications 2018, 181, 0975–8887. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, M.; Gokasan, M.; Bogosyan, S. Fuzzy based parameter tuning of EKF observers for sensorless control of Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion. IEEE; 2014; pp. 1174–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Xiao, L.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Zhong, Y. A speed and flux estimation method of induction motor using fuzzy extended kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Power Electronics and Application Conference and Exposition. IEEE; 2014; pp. 693–698. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.X.; Hu, J.T. Speed and load torque estimation of induction motors based on an adaptive extended Kalman filter. Advanced Materials Research 2012, 433, 7004–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Zhong, Y. A speed and flux observer of induction motor based on extended Kalman filter and Markov chain. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2016, 32, 7096–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, G.; Du, C.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Zhong, Y. An adaptive speed estimation method based on a strong tracking extended Kalman filter with a least-square algorithm for induction motors. Journal of Power Electronics 2017, 17, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Symmetric-strong-tracking-extended-Kalman-filter-based sensorless control of induction motor drives for modeling error reduction. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2018, 15, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerdali, E.; Barut, M. Extended Kalman filter based speed-sensorless load torque and inertia estimations with observability analysis for induction motors. Power Electronics and Drives 2018, 3, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerdali, E. Adaptive extended Kalman filter for speed-sensorless control of induction motors. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2018, 34, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerdali, E. strong tracking extended Kalman filter based speed and load torque estimations of induction motor. In Proceedings of the 2019 1st Global Power, Energy and Communication Conference (GPECOM). IEEE; 2019; pp. 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zerdali, E.; Yildiz, R.; Inan, R.; Demir, R.; Barut, M. Improved speed and load torque estimations with adaptive fading extended Kalman filter. International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems 2021, 31, e12684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussot, V.; Mercère, G.; Dairay, T.; Arvis, V.; Vayssettes, J. Noise covariance matrix estimation with subspace model identification for Kalman filtering. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing 2021, 35, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaegen, M.; Verdult, V. Filtering and system identification: a least squares approach; Cambridge university press, 2007.
- Van Overschee, P.; De Moor, B. Subspace identification for linear systems: Theory—Implementation—Applications; Springer Science & Business Media, 2012.
- Katayama, T.; et al. Subspace methods for system identification; Vol. 1, Springer, 2005.
- Mercere, G. Regression techniques for subspace-based black-box state-space system identification: an overview. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1305.7121 2013.
- Kailath, T.; Sayed, A.H.; Hassibi, B. Linear Estimation (Information and System Sciences Series). Technical report, Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 2000.
- O’Rourke, C.J.; Qasim, M.M.; Overlin, M.R.; Kirtley, J.L. A geometric interpretation of reference frames and transformations: dq0, clarke, and park. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2019, 34, 2070–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, F. Performance improvement of induction motor drives with model-based predictive torque control. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences 2020, 28, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böcker, J. Discrete-time model of an induction motor. European Transactions on Electrical Power 1991, 1, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D. Optimal state estimation: Kalman, H∞ and nonlinear approaches; Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Peternell, K.; Scherrer, W.; Deistler, M. Statistical analysis of novel subspace identification methods. Signal Processing 1996, 52, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





