Submitted:
09 January 2024
Posted:
10 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Formulation of the P-FGM Model
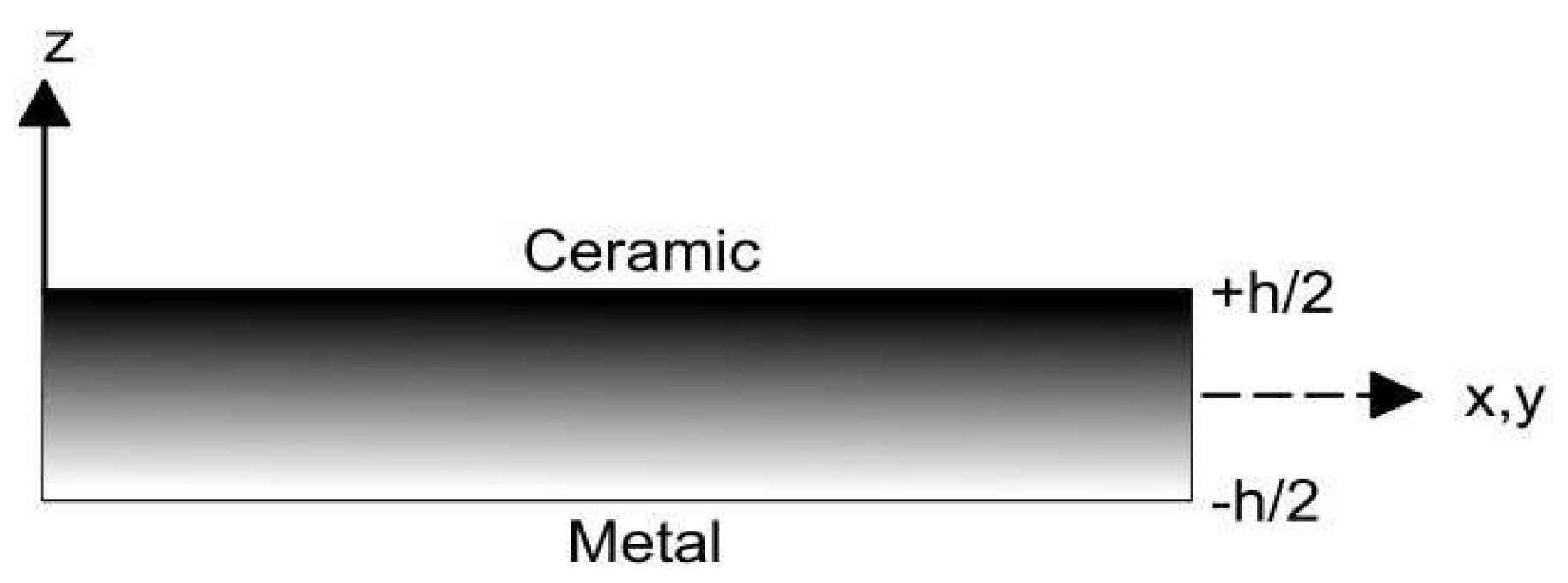
2.1. Displacement Fields and Strain-Displacement Relations
2.2. Constitutive Relations for the FGM Structures
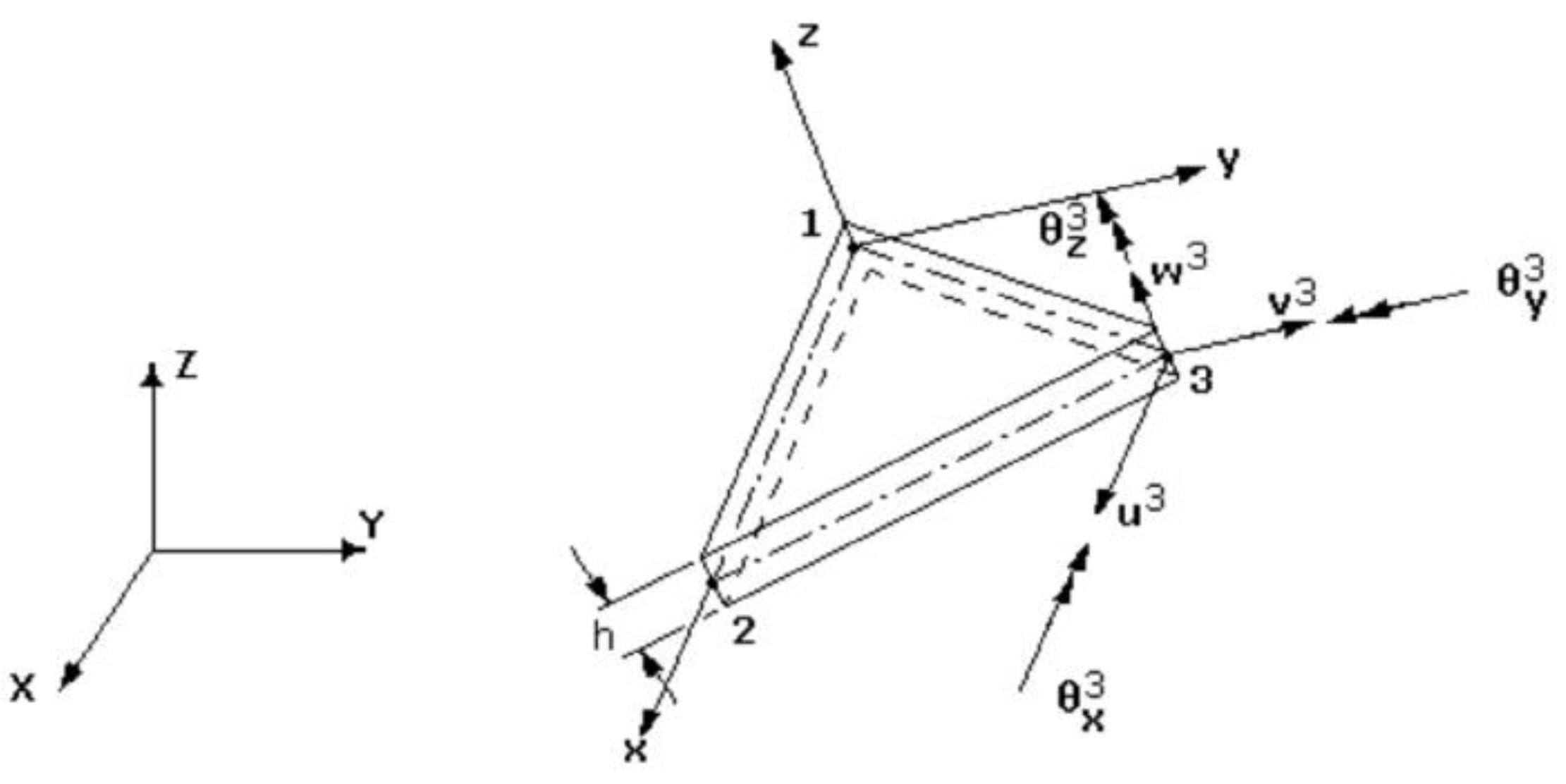
3. Finite Element Approach
4. Virtual Work Principle
4.1. Static Analysis
4.2. Linear Buckling Analysis
4.3. Free Vibration Analysis
5. Applications
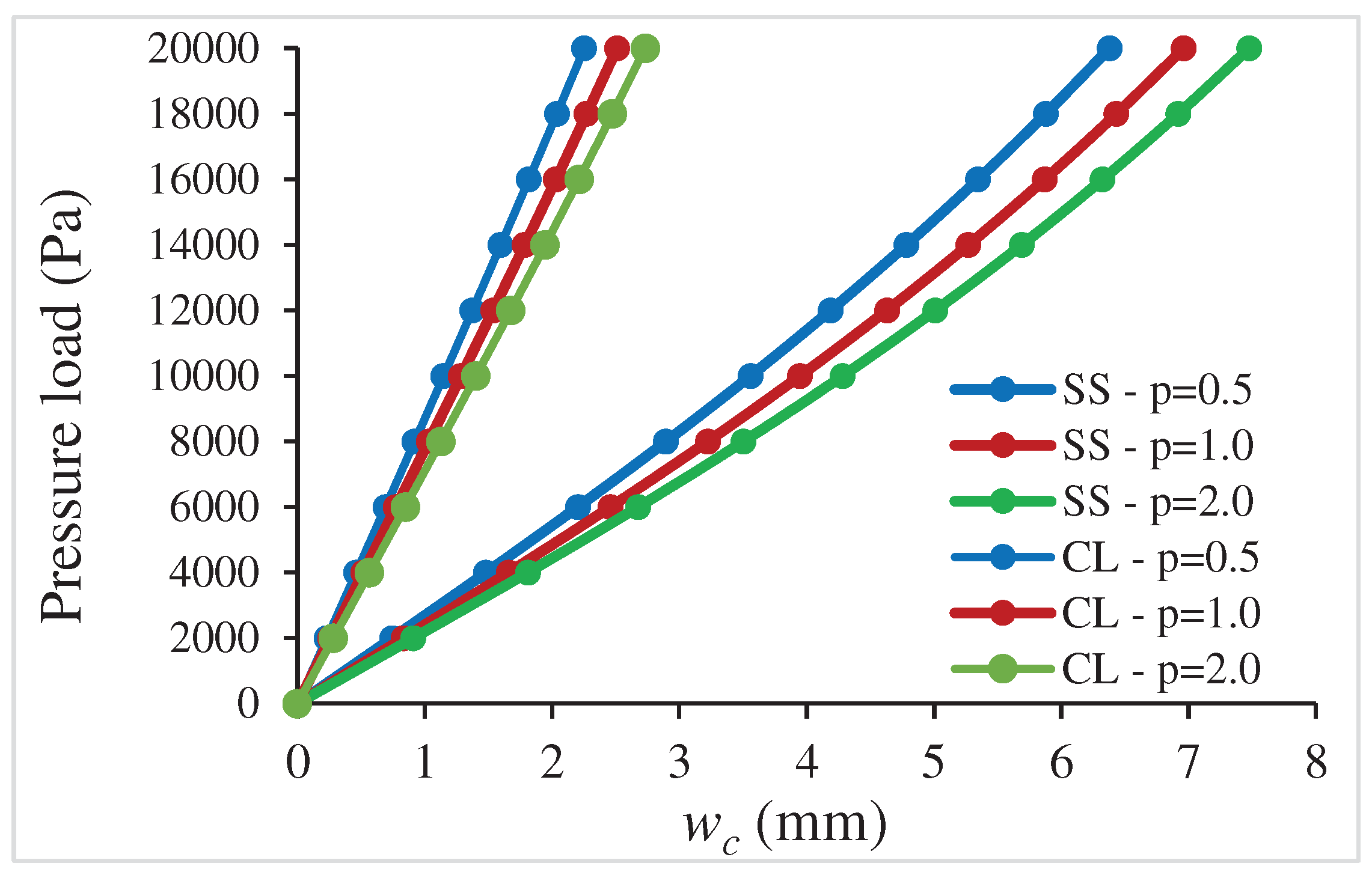
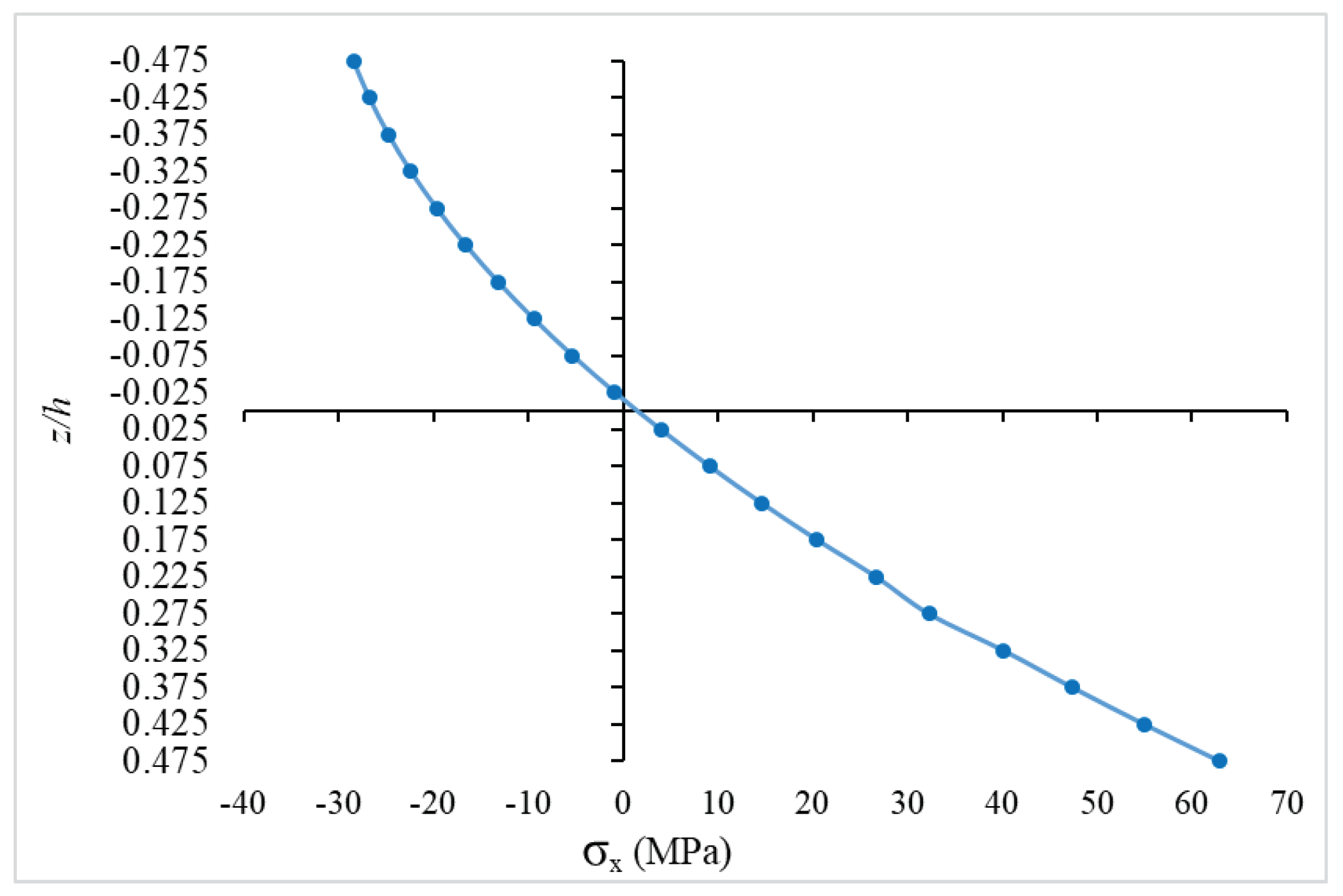
5.1. Nonlinear Analysis of a Simply Supported and Clamped FGM Square Plate under Uniform Pressure
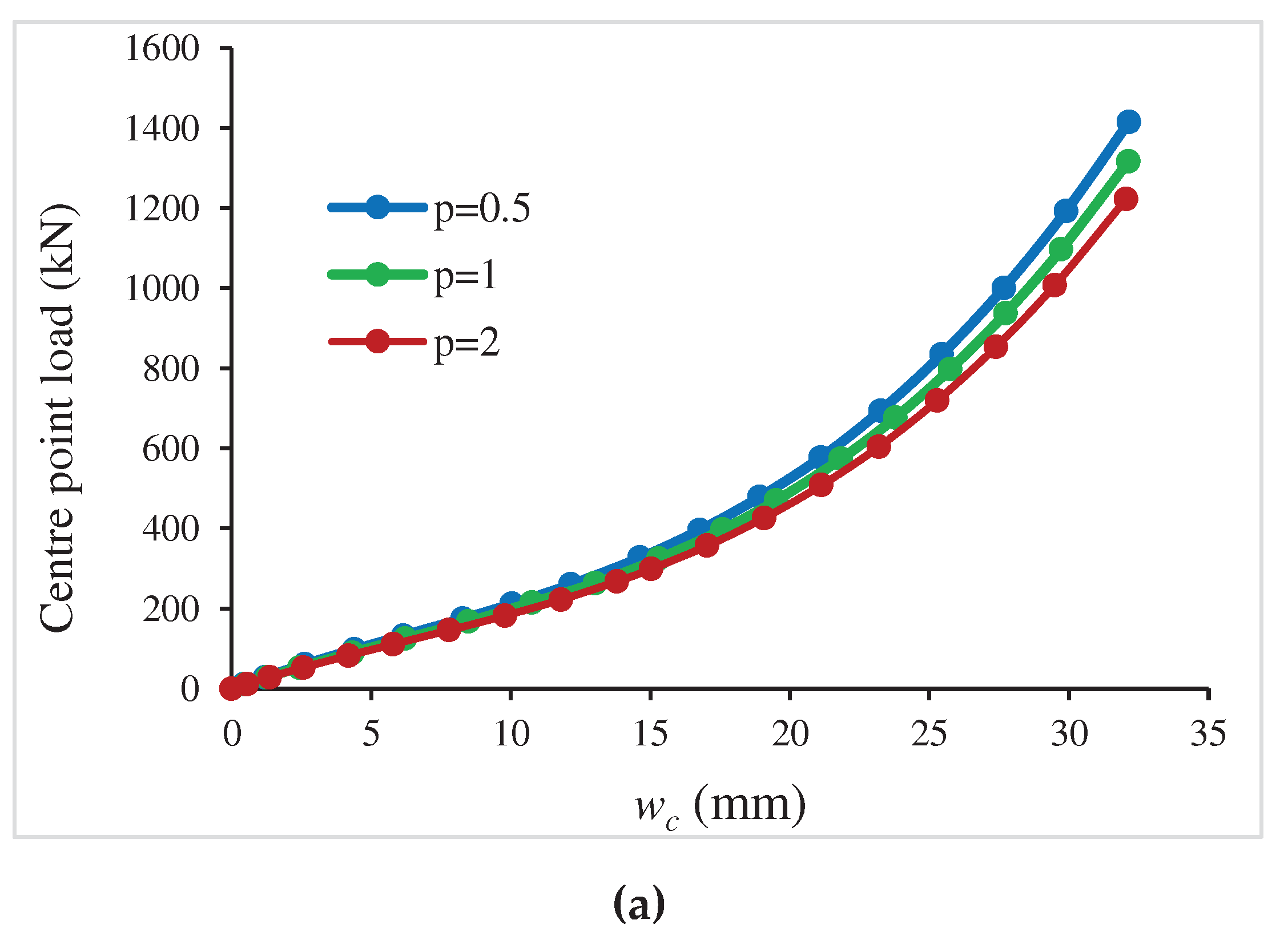
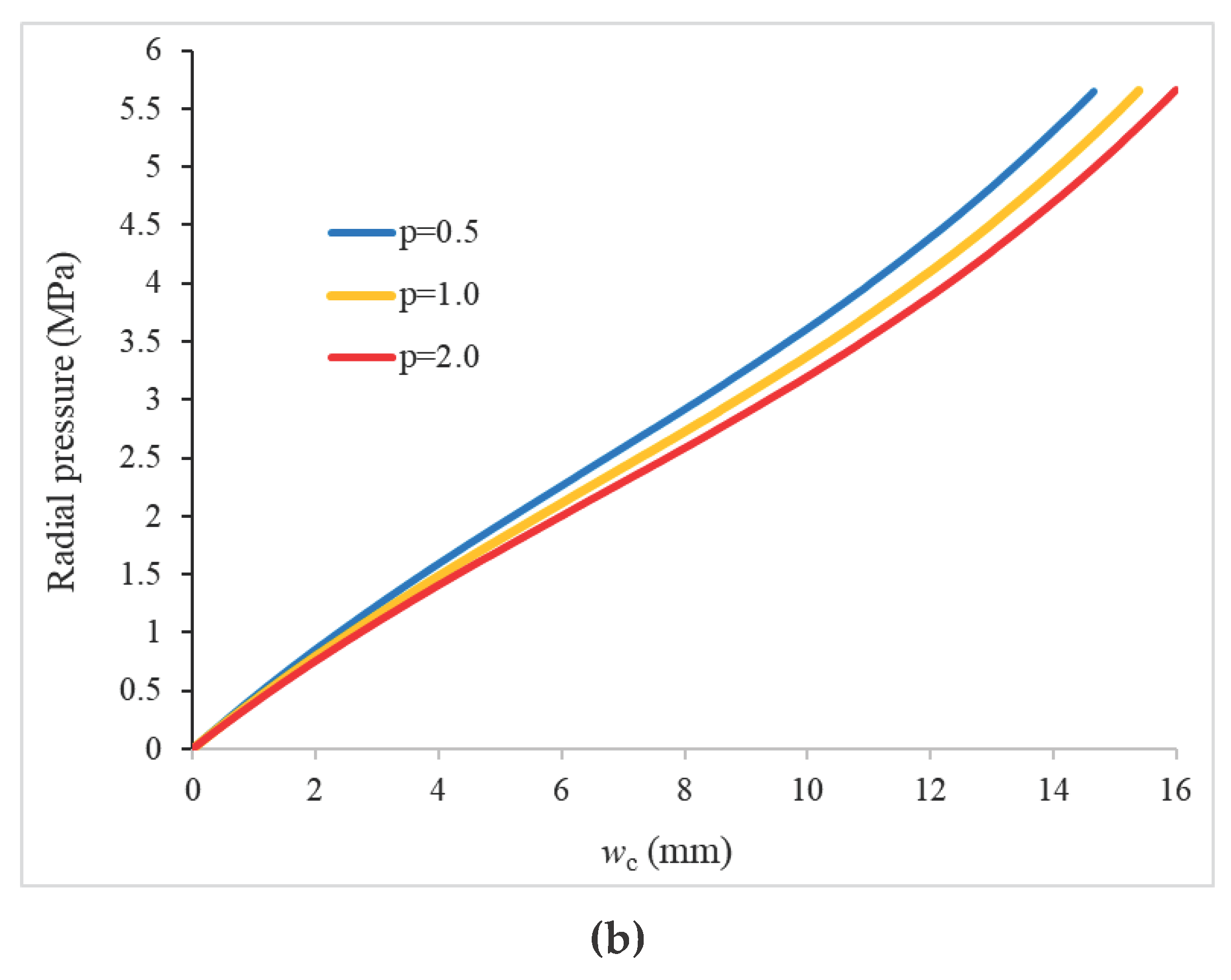
5.2. Nonlinear Analysis of a Hinged and Clamped FGM Cylindrical Panels under a Centre point Load
5.3. Critical Loads of a Clamped FGM Square Plate
5.4. Free Vibrations of a Simply Supported FGM Square Plate
5.5. Critical Loads of Hinged and Clamped FGM Cylindrical Panels
5.6 Free Vibrations of Hinged and Clamped FGM Cylindrical Panels
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddy, JN. Mechanics of Laminated Composite Plates and Shells, 2 nd Edition, CRC Press, 2004.
- Barbosa AT, Ferreira AJM. Geometrically nonlinear analysis of functionally graded plates and shells. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures. 2000, 17, 40–48. [CrossRef]
- Woo J, Meguid, SA. Nonlinear analysis of functionally graded plates and shallow shells. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2001, 38, 7409–7421. [CrossRef]
- Yang J, Shen HS. Nonlinear analysis of functionally graded plates under transverse and in-plane loads. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 2003, 38, 467–482. [CrossRef]
- Reddy JN, Arciniega RA, Free vibration analysis of functionally graded plates. In: Analysis and Design of Plated Structures: Dynamics. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, UK, 2006.
- Arciniega RA, Reddy JN. Large deformation analysis of functionally graded shells. International Journal of Solids and Structures. 2007, 44, 2036–2052. [CrossRef]
- Kim KD, Lomboy GR, Han SC. Geometrically nonlinear analysis of functionally graded material (FGM) plates and shells using a four-node quasi-conforming shell element. Journal of Composite Materials. 2008, 42, 485–511. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Z, Liew KM. Geometrically nonlinear analysis of functionally graded shells. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences. 2009, 51, 131–144. [CrossRef]
- Tran, LV, Ferreira, AJM, Nguyen-Xuan, H. Isogeometric analysis of functionally graded plates using higher-order shear deformation theory. Composites Part B: Engineering. 2013, 51, 368–383. [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh N, Natarajan S, Gonzalez-Estrada OA, Rabczuk T, Bui TQ, Bordas SPA. NURBS-based finite element analysis of functionally graded plates: Static bending, vibration, buckling and flutter. Composite Structures. 2013, 99, 309–326. [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S, Ferreira, AJM, Bordas, S, Carrera, E, Cinefra, M, Zenkour, AM. Analysis of Functionally Graded Material Plates Using Triangular Elements with Cell-Based Smoothed Discrete Shear Gap Method. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2014; Article ID 247932, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Moita JS, Araújo AL, Mota Soares CM, Mota Soares CA, Herskovits J. Material and Geometric Nonlinear Analysis of Functionally Graded Plate-Shell Type Structures. Appl Compos Mater. 2016, 23, 4, 537–554. [CrossRef]
- Moita, JS, Araújo, AL, Correia VF, Mota Soares, CM, Herskovits, J. Higher-order finite element models for the static linear and nonlinear behaviour of functionally graded material plate-shell structures Composite Structures. 2019, 212, 465–475. [CrossRef]
- Bao, G, Wang L. Multiple cracking in functionally graded ceramic/metal coatings. International Journal of Solids and Structures. 1995, 32, 2853–2871. [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C. The Finite Element Method. New York, USA: McGraw-Hill, 1977.
- Bathe KJ, Ho, LW. A simple and effective element for analysis of general shell structures. Computers and Structures. 1981, 13, 673–681. [CrossRef]
- K.J. Bathe, Finite Element Procedures in Engineering Analysis. Prentice-Hall Inc, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, 1982. [CrossRef]
- Moita JS, Araújo AL, Martins, PG, Mota Soares, CM, Mota Soares, CA. Analysis of active-passive plate structures using a simple and efficient finite element model. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures. 2011, 18, 159–169. [CrossRef]
- Crisfield, MA. A fast incremental/iterative solution procedure that handles snap-through. Computers and Structures. 1980, 62, 13–55. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Xuan, H, Tran, LV, Thai, CH, Nguyen-Thoi, T. Analysis of functionally graded plates by an efficient finite element method with node-based strain smoothing. Thin-Walled Structures. 2012, 54, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Wu,T-L, Shukla, KK, Huang, JH. Free vibration analysis of functionally graded curved8 panels using a higher-order finite element formulation. Composite Structures. 2007, 81, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X, Liew KM. A mesh-free method for analysis of the thermal and mechanical buckling of functionally graded cylindrical shell panels. Comput Mech. 2010, 45, 297–310.
- Pradyumna, S, Bandyopadhyay, JN. Free vibration analysis of functionally graded curved panels using a higher-order finite element formulation. Journal of Sound and Vibration. 2008, 318, 176–192. [CrossRef]
- Neves, AMA, Ferreira JM, Carrera E , Cinefra, M, Roque, CMC , Jorge, RMN, Soares, CMM. Free vibration analysis of functionally graded shells by a higher-order shear deformation theory and radial basis functions collocation, accounting for through-the-thickness deformations. European Journal of Mechanics A/Solids. 2013, 37, 24–34. [CrossRef]
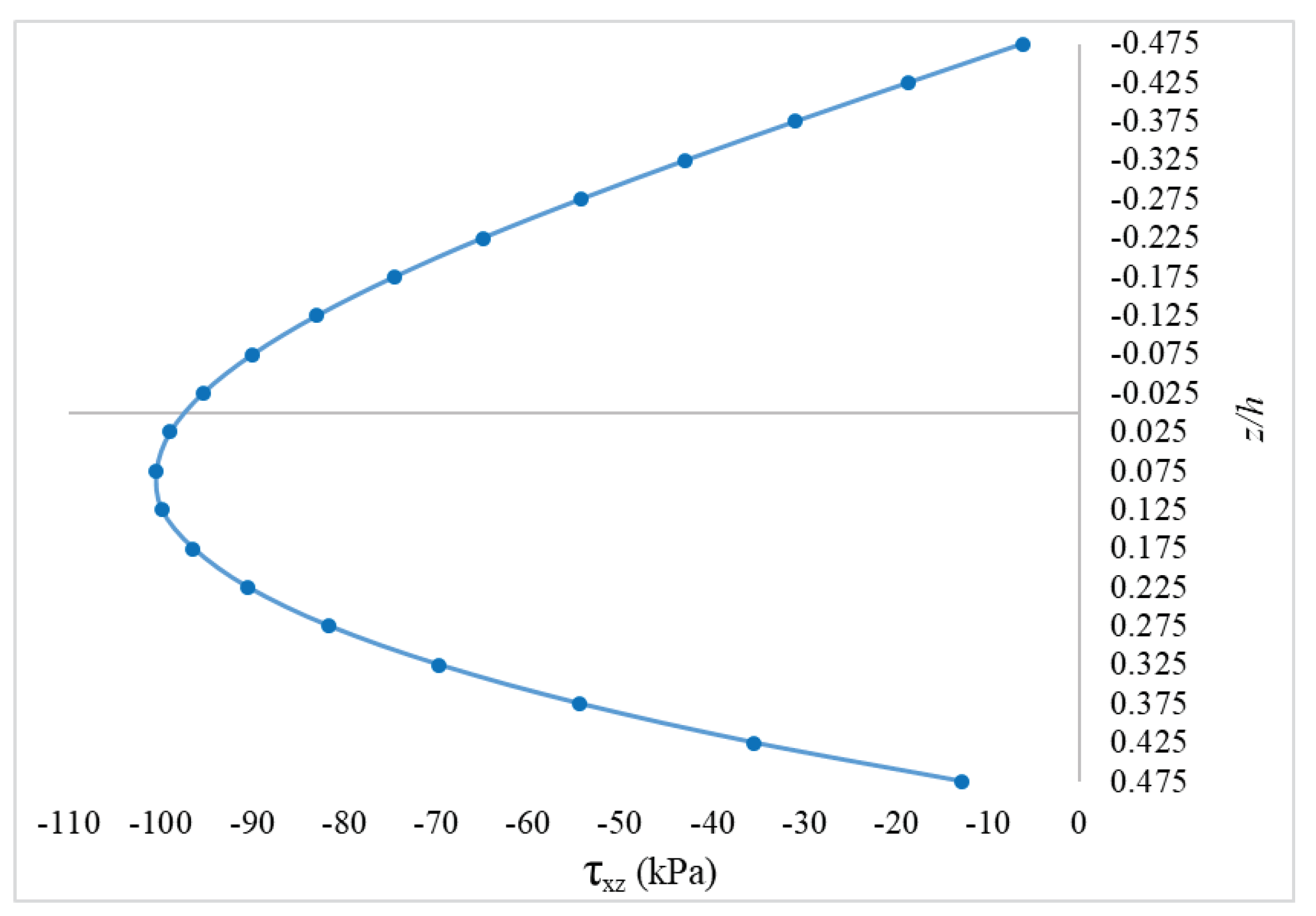
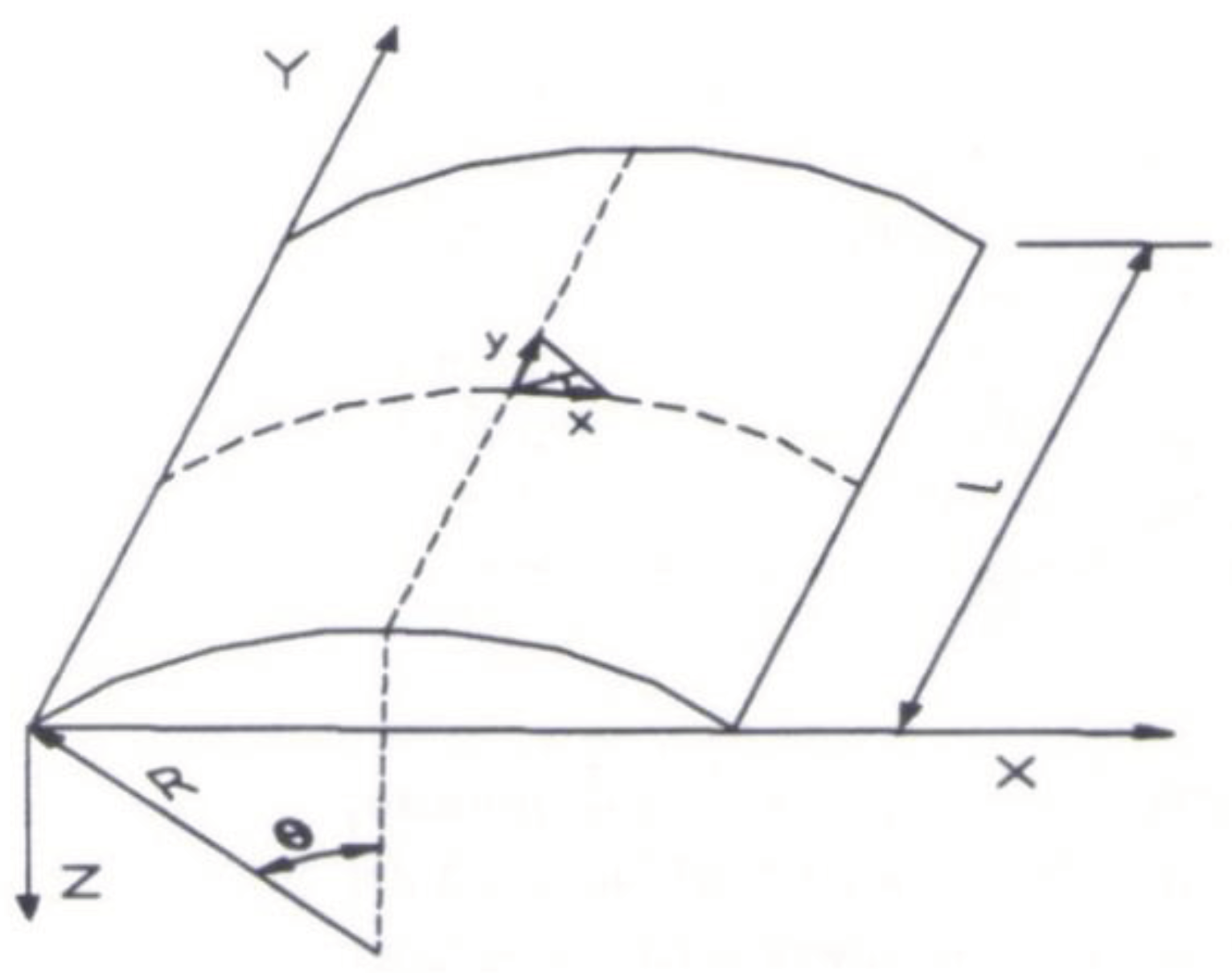

| Power-law index | |||||||
| mode source | ceramic | p=0.2 | p=0.5 | p=1.0 | p=2.0 | p=5.0 | metal |
| 1 PM 1 Ref. [20] |
203.833 203.497 |
181.190 180.331 |
160.204 159.529 |
142.854 142.533 |
130.327 130.342 |
120.066 120.471 |
94.492 - |
| 2 PM | 230.012 | 204.622 | 180.998 | 161.336 | 146.936 | 135.029 | 106.628 |
| 3 PM | 372.296 | 331.653 | 293.574 | 261.502 | 237.458 | 217.276 | 172.587 |
| 4 PM | 473.132 | 421.549 | 373.224 | 332.490 | 301.889 | 276.107 | 219.332 |
| Power-law index | |||||
| mode source | ceramic | p=1.0 | p=2.0 | p=5.0 | metal |
| 1 PM 1 Ref. [21] |
9.187 9.158 |
4.606 4.618 |
3.571 3.579 |
3.020 3.034 |
1.690 - |
| 2 PM | 10.688 | 5.342 | 4.155 | 3.493 | 1.969 |
| 3 PM | 18.099 | 9.047 | 7.036 | 5.908 | 3.334 |
| Mode | source | ceramic | p=1.0 | p=2.0 | metal |
| 1 | PM Ref. [9] |
0.2462 0.2461 |
0.2275 0.2185 |
0.2254 0.2190 |
0.2112 0.2113 |
| 2 | PM Ref. [9] |
0.4539 0.4539 |
0.4342 0.4118 |
0.4237 0.4039 |
0.3899 0.3897 |
| 3 | PM Ref. [9] |
0.4539 0.4539 |
0.4342 0.4118 |
0.4237 0.4039 |
0.3899 0.3897 |
| 4 | PM Ref. [9] |
0.5379 0.5385 |
0.5013 0.4794 |
0.4930 0.4768 |
0.4620 0.4623 |
| 5 | PM Ref. [9] |
0.5379 0.5385 |
0.5010 0.4794 |
0.4930 0.4768 |
0.4620 0.4623 |
| (a) | ||||||
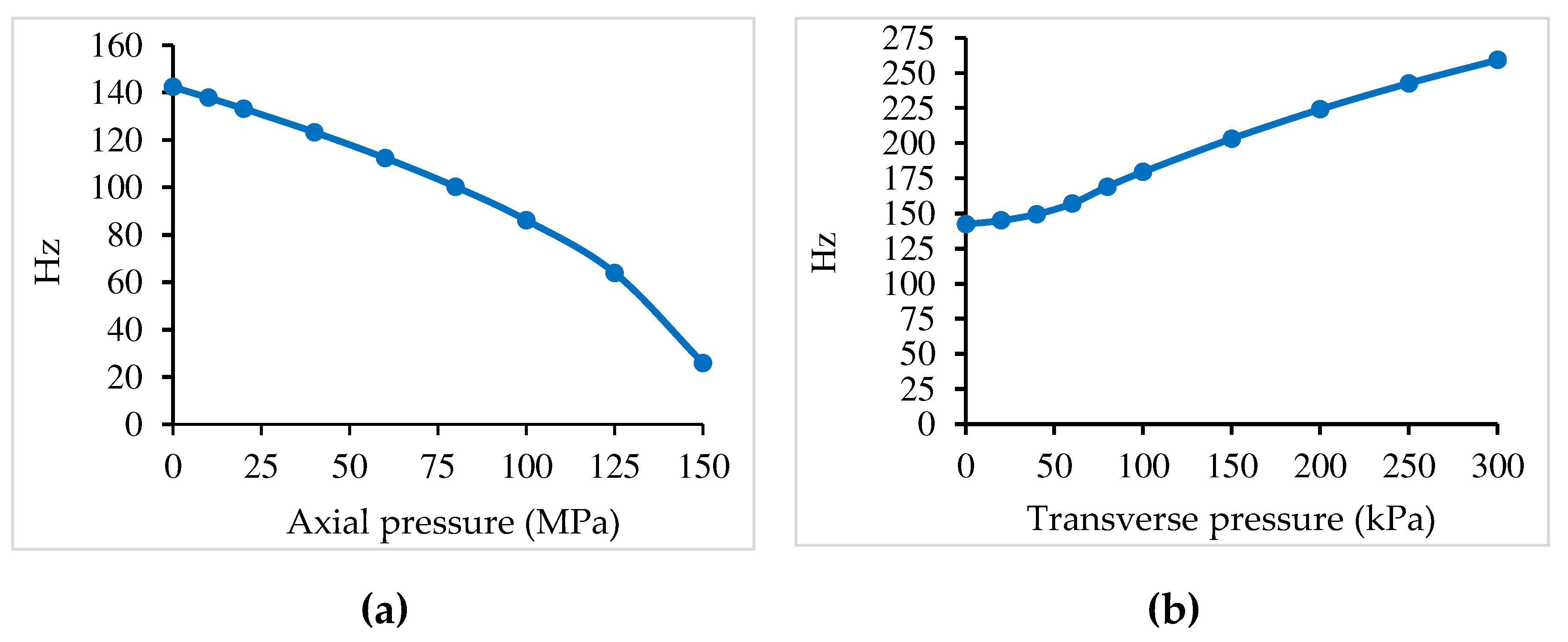
| mode | plate unloaded | px=2 MPa | pz=20 kPa | px=2 MPa+pz=20 kPa | ||
| 1 | 142.325 | 141.442 | 144.252 | 143.185 | ||
| 2 | 291.271 | 290.132 | 292.259 | 290.786 | ||
| 3 | 292.066 | 291.098 | 293.134 | 292.019 | ||
| 4 | 432.917 | 431.828 | 433.395 | 432.224 | ||
| (b) | ||||||
| mode | plate unloaded | px=4 MPa | pz=40 kPa | px=4 MPa+pz=40 kPa | ||
| 1 | 142.325 | 140.552 | 149.526 | 147.391 | ||
| 2 | 291.271 | 288.854 | 295.034 | 291.357 | ||
| 3 | 292.066 | 290.042 | 295.806 | 293.672 | ||
| 4 | 432.917 | 430.741 | 435.552 | 432.328 | ||
| (c) | ||||||
| mode | plate unloaded | px=10 MPa | pz=60 kPa | px=10 MPa+pz=60 kPa | ||
| 1 | 142.325 | 137.843 | 157.010 | 154.310 | ||
| 2 | 291.271 | 284.797 | 299.130 | 292.997 | ||
| 3 | 292.066 | 287.177 | 299.768 | 296.824 | ||
| 4 | 432.917 | 427.461 | 438.402 | 433.154 | ||
| (a) | |||||||||
| Source | mode | p=0 | p=0.5 | p=1.0 | p=2.0 | p=5.0 | |||
| Ref. [22] PM |
1 | 1.7195 1.7380 |
1.3700 1.3884 |
1.2229 1.2316 |
1.1025 1.1065 |
0.9949 0.9973 |
|||
| Ref. [22] PM |
2 | 1.8416 1.9480 |
1.4575 1.5385 |
1.3001 1.3669 |
1.1796 1.2365 |
1.0750 1.1247 |
|||
| Ref. [22] PM |
3 | 2.3913 2.2300 |
1.8863 1.7310 |
1.6837 1.5331 |
1.4017 1.3836 |
1.4018 1.2675 |
|||
| (b) | |||||||||
| Power-law index | |||||||||
| mode | ceramic | p=0.5 | p=1.0 | p=5.0 | Metal | ||||
| 1 | 0.1330 | 0.1137 | 0.1060 | 0.0943 | 0.0836 | ||||
| 2 | 0.1595 | 0.1369 | 0.1277 | 0.1132 | 0.1004 | ||||
| 3 | 0.3294 | 2.9664 | 0.2680 | 0.2405 | 0.2073 | ||||
| (c) | |||||||||
| Power-law index | |||||||||
| mode | ceramic | p=0.5 | p=1.0 | p=5.0 | Metal | ||||
| 1 | 2.0668 | 1.7809 | 1.6638 | 1.4779 | 1.3004 | ||||
| 2 | 2.1679 | 1.8604 | 1.7404 | 1.5626 | 1.3640 | ||||
| 3 | 3.4575 | 2.9664 | 2.7747 | 2.4919 | 2.1754 | ||||
| . | Power-law index | |||
| Mode | source | Ceramic | p=0.5 | p=1.0 |
|
1 |
PM Ref. [23] Ref. [24] |
102.807 102.923 102.787 |
86.285 87.545 85.478 |
77.186 77.077 77.638 |
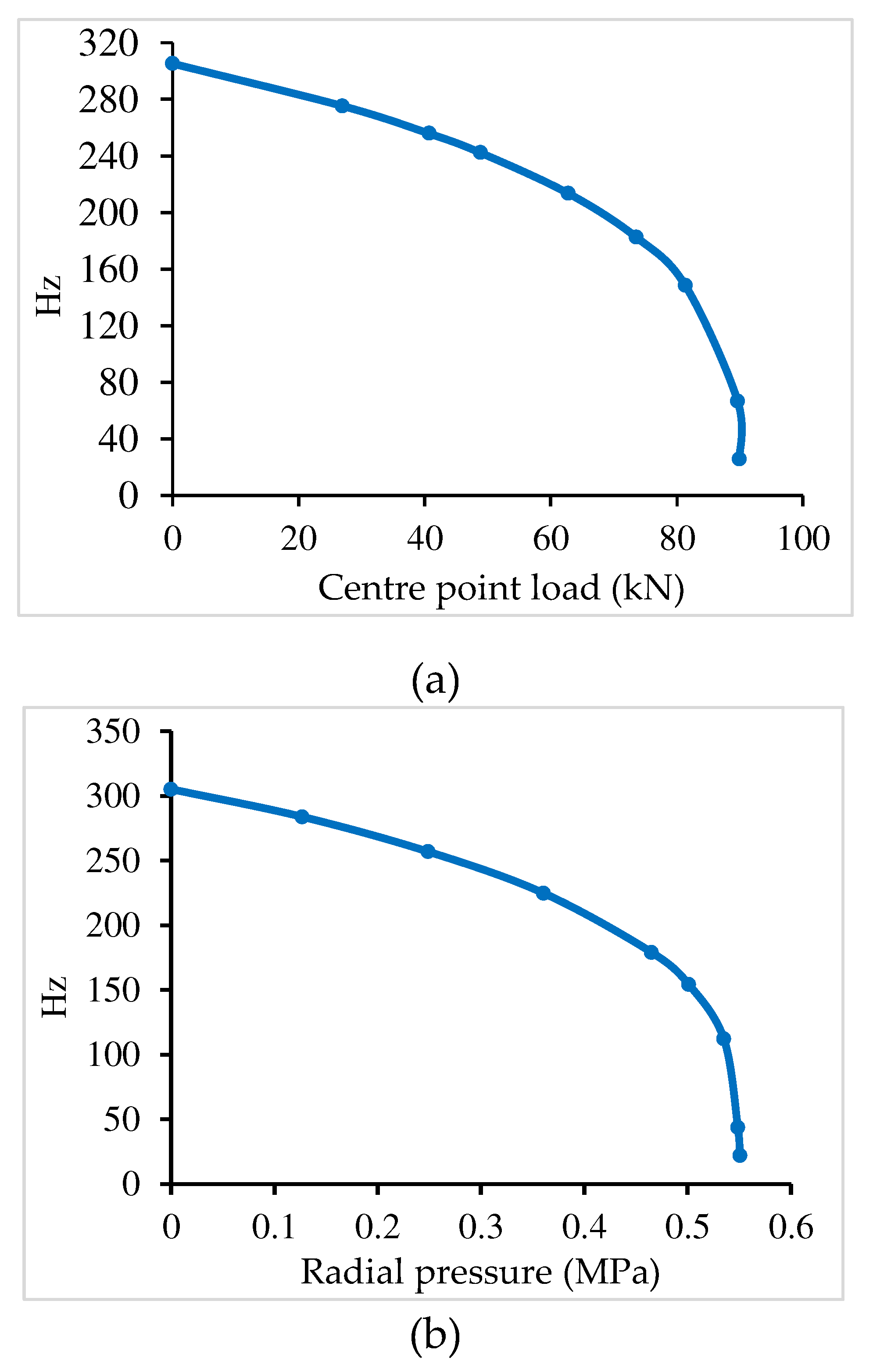
| (a) | |||||
| Index p | Frequency | Hinged Unloaded |
Hinged py=20.0 MPa |
Hinged Pc=20 kN |
Hinged py=20 MPa +Pc=20 kN |
| 1 | 313.274 | 316.566 | 295.679 | 300.890 | |
| 0.5 | 2 | 351.139 | 355.694 | 340.132 | 345.626 |
| 3 | 479.608 | 479.055 | 465.256 | 465.001 | |
| 1 | 305.210 | 310.625 | 286.167 | 291.501 | |
| 1.0 | 2 | 343.077 | 348.121 | 331.984 | 337.146 |
| 3 | 473.809 | 473.269 | 458.445 | 458.245 | |
| 1 | 297.077 | 302.268 | 275.787 | 281.273 | |
| 5.0 | 2 | 335.446 | 339.251 | 321.954 | 326.915 |
| 3 | 471.027 | 470.347 | 454.304 | 454.022 | |
| (b) | |||||
| Index p | Frequency |
Hinged Unloaded |
Hinged py=40.0 MPa |
Hinged Pc=40 kN |
Hinged py=40 MPa +Pc=40 kN |
| 1 | 313.274 | 320.973 | 276.674 | 282.668 | |
| 0.5 | 2 | 351.139 | 353.198 | 335.139 | 332.018 |
| 3 | 479.608 | 478.479 | 449.294 | 448.897 | |
| 1 | 305.210 | 313.219 | 261.988 | 271.357 | |
| 1.0 | 2 | 343.077 | 345.654 | 316.605 | 322.333 |
| 3 | 473.809 | 472.696 | 440.668 | 440.884 | |
| 1 | 297.077 | 305.536 | 249.127 | 258.280 | |
| 5.0 | 2 | 335.446 | 336.296 | 305.175 | 309.792 |
| 3 | 471.027 | 469.658 | 434.684 | 434.823 | |
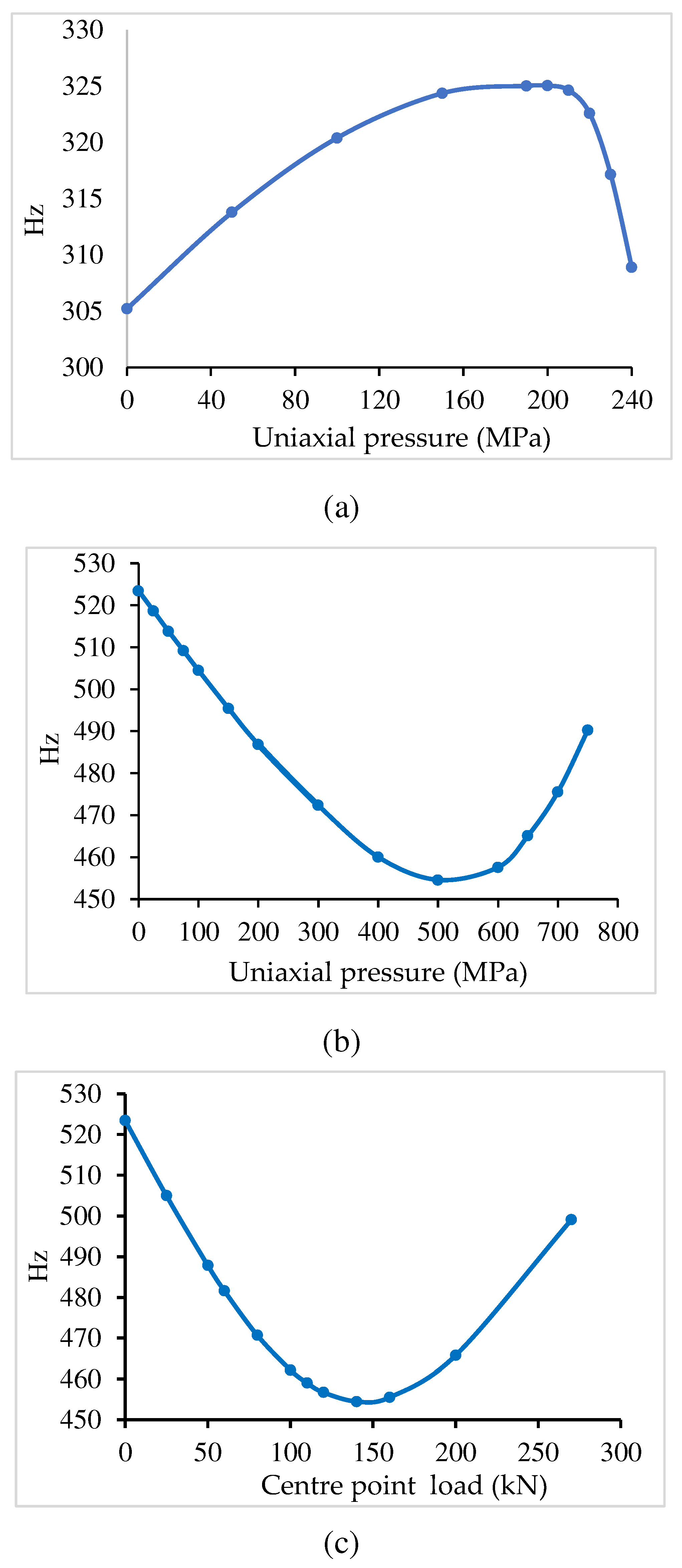
| (a) | |||||
| Index p | Frequency | Clamped Unloaded |
Clamped py=25 MPa |
Clamped Pc=20 kN |
Clamped py=25 MPa +Pc=20 kN |
| 1 | 530.354 | 525.088 | 517.085 | 512.525 | |
| 0.5 | 2 | 910.949 | 906.395 | 902.049 | 897.850 |
| 3 | 950.677 | 940.616 | 944.500 | 935.275 | |
| 1 | 523.455 | 518.643 | 509.337 | 504.472 | |
| 1.0 | 2 | 899.626 | 894.811 | 890.297 | 885.837 |
| 3 | 938.582 | 927.958 | 932.117 | 922.348 | |
| 1 | 515.247 | 509.832 | 500.414 | 494.868 | |
| 5.0 | 2 | 892.631 | 887.328 | 882.877 | 877.858 |
| 3 | 929.081 | 917.333 | 922.329 | 911.439 | |
| (b) | |||||
| Index p | Frequency |
Clamped Unloaded |
Clamped py=50 MPa |
Clamped Pc=40 kN |
Clamped py=50 MPa +Pc=40 kN |
| 1 | 530.354 | 521.489 | 504.152 | 493.762 | |
| 0.5 | 2 | 910.949 | 901.861 | 893.429 | 884.175 |
| 3 | 950.677 | 930.478 | 938.769 | 919.380 | |
| 1 | 523.455 | 513.874 | 495.884 | 484.824 | |
| 1.0 | 2 | 899.626 | 890.029 | 881.296 | 871.642 |
| 3 | 938.582 | 927.243 | 926.165 | 905.783 | |
| 1 | 515.247 | 509.832 | 486.434 | 473.780 | |
| 5.0 | 2 | 892.631 | 881.968 | 873.564 | 862.640 |
| 3 | 929.081 | 905.471 | 916.220 | 893.425 | |
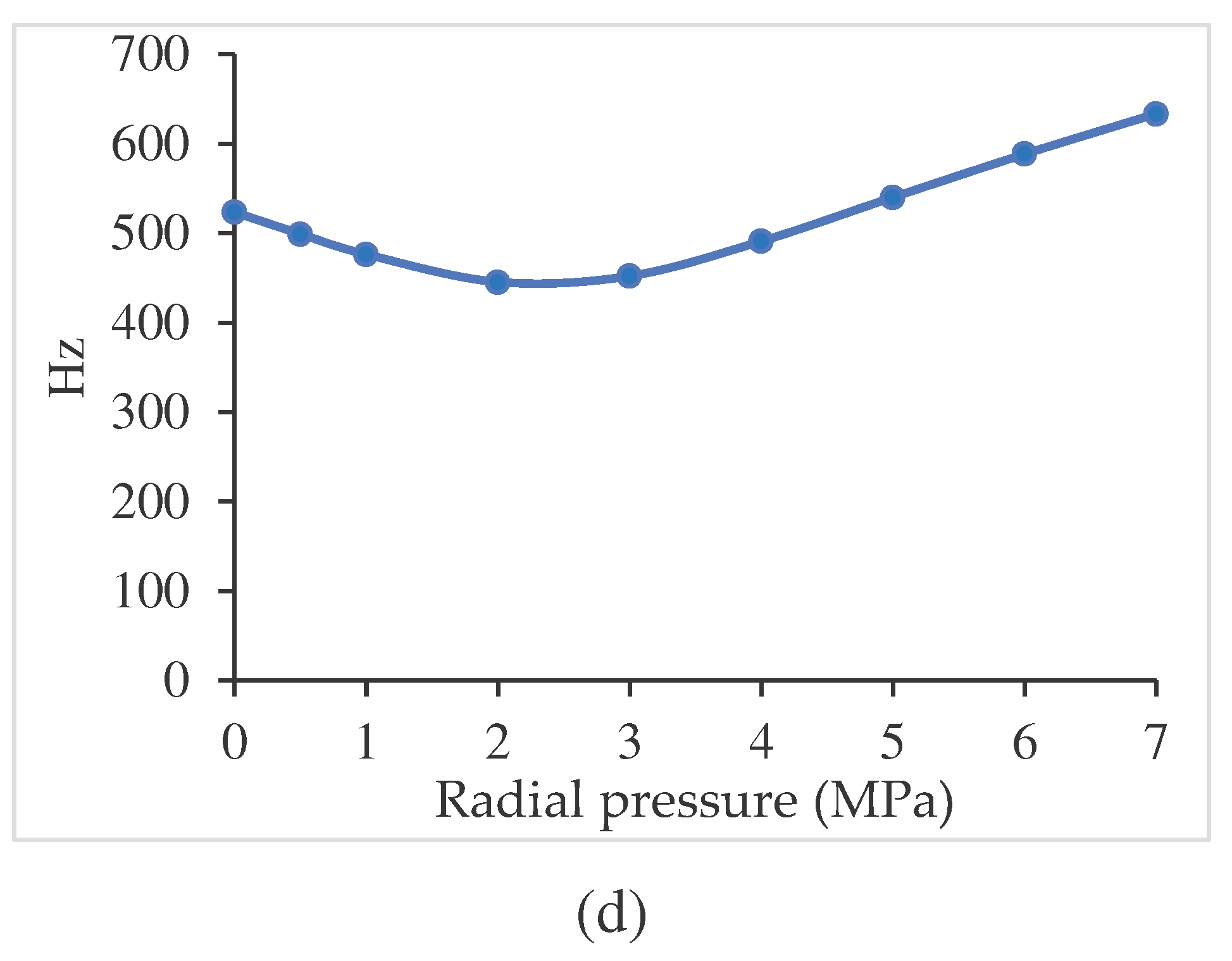
| (a) | |||||
| Index p | Frequency | Clamped Unloaded |
Clamped py=25 MPa |
Clamped pr=1 MPa |
Clamped py=25 MPa + pr=1 MPa |
| 1 | 530.354 | 525.746 | 487.428 | 483.450 | |
| 0.5 | 2 | 910.949 | 906.135 | 878.406 | 875.414 |
| 3 | 950.677 | 940.051 | 928.638 | 921.602 | |
| 1 | 523.455 | 518.375 | 478.441 | 474.085 | |
| 1.0 | 2 | 899.626 | 894.541 | 865.624 | 862.355 |
| 3 | 938.582 | 927.362 | 915.678 | 908.076 | |
| 1 | 515.247 | 509.531 | 468.468 | 463.246 | |
| 5.0 | 2 | 892.631 | 886.980 | 857.417 | 853.489 |
| 3 | 929.081 | 916.673 | 905.549 | 896.673 | |
| (b) | |||||
| Index p | Frequency |
Clamped Unloaded |
Clamped py=50 MPa |
Clamped pr=2 MPa |
Clamped py=50 MPa + pr=2 MPa |
| 1 | 530.354 | 521.489 | 453.350 | 442.269 | |
| 0.5 | 2 | 910.949 | 901.862 | 849.881 | 842.178 |
| 3 | 950.677 | 930.474 | 914.233 | 895.260 | |
| 1 | 523.455 | 513.874 | 445.354 | 432.959 | |
| 1.0 | 2 | 899.626 | 890.029 | 837.117 | 828.118 |
| 3 | 938.582 | 917.243 | 902.145 | 880.988 | |
| 1 | 515.247 | 504.466 | 439.559 | 423.800 | |
| 5.0 | 2 | 892.631 | 881.968 | 830.819 | 819.155 |
| 3 | 929.081 | 905.471 | 894.629 | 869.139 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





