Submitted:
09 January 2024
Posted:
10 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
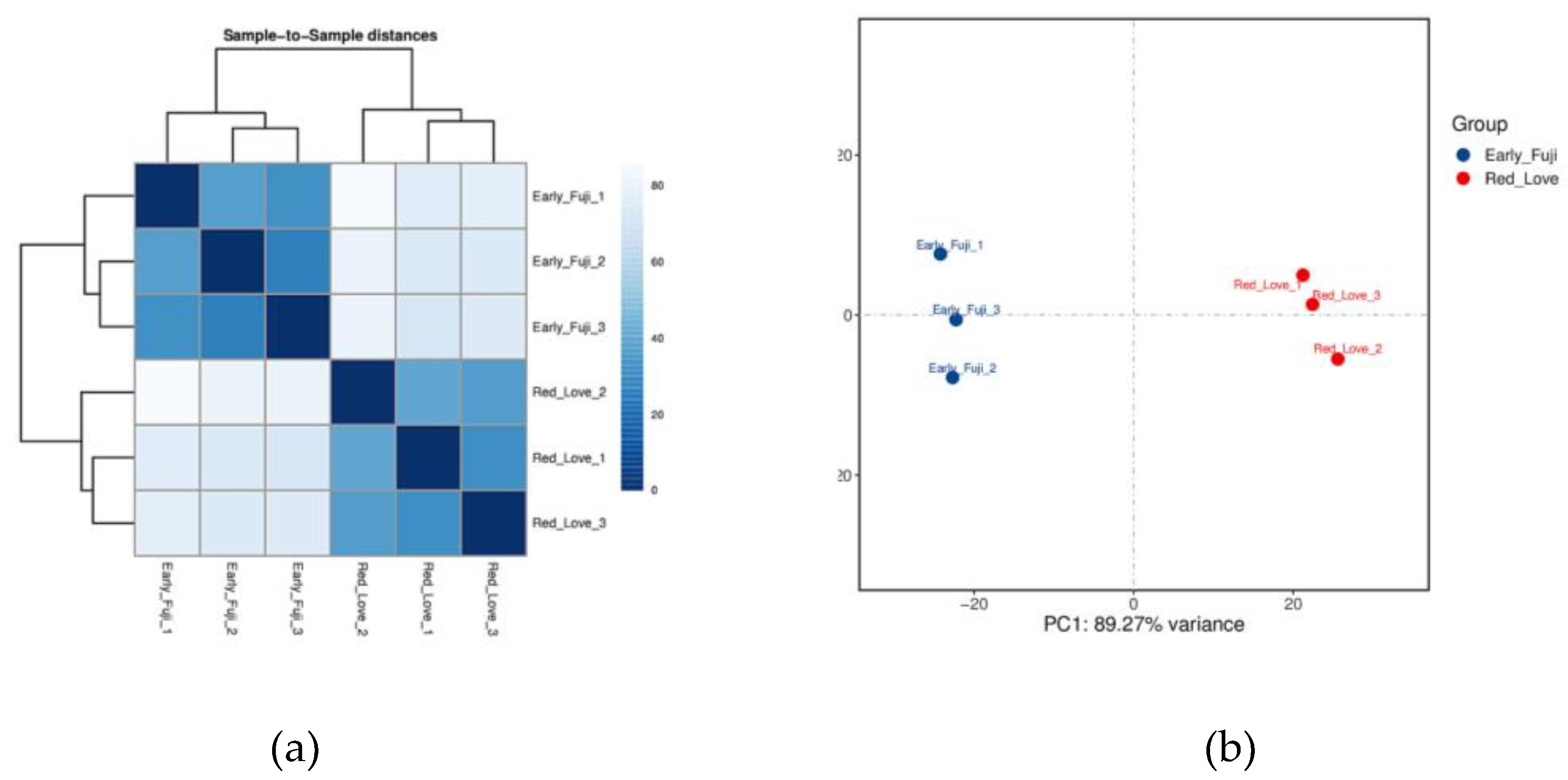
2.1. Transcriptome Profiling
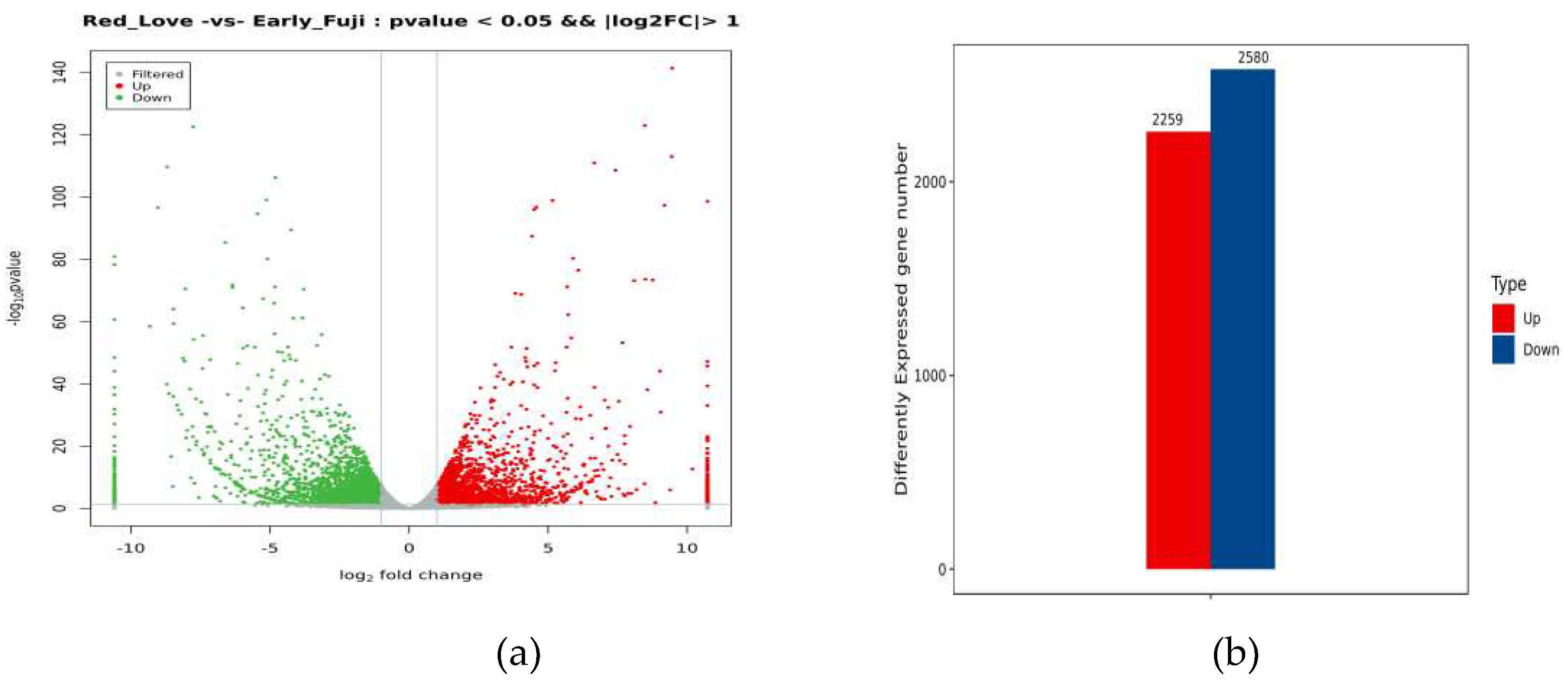
2.2. Differentially Expressed Genes
2.3. Functional Categories of DEGs
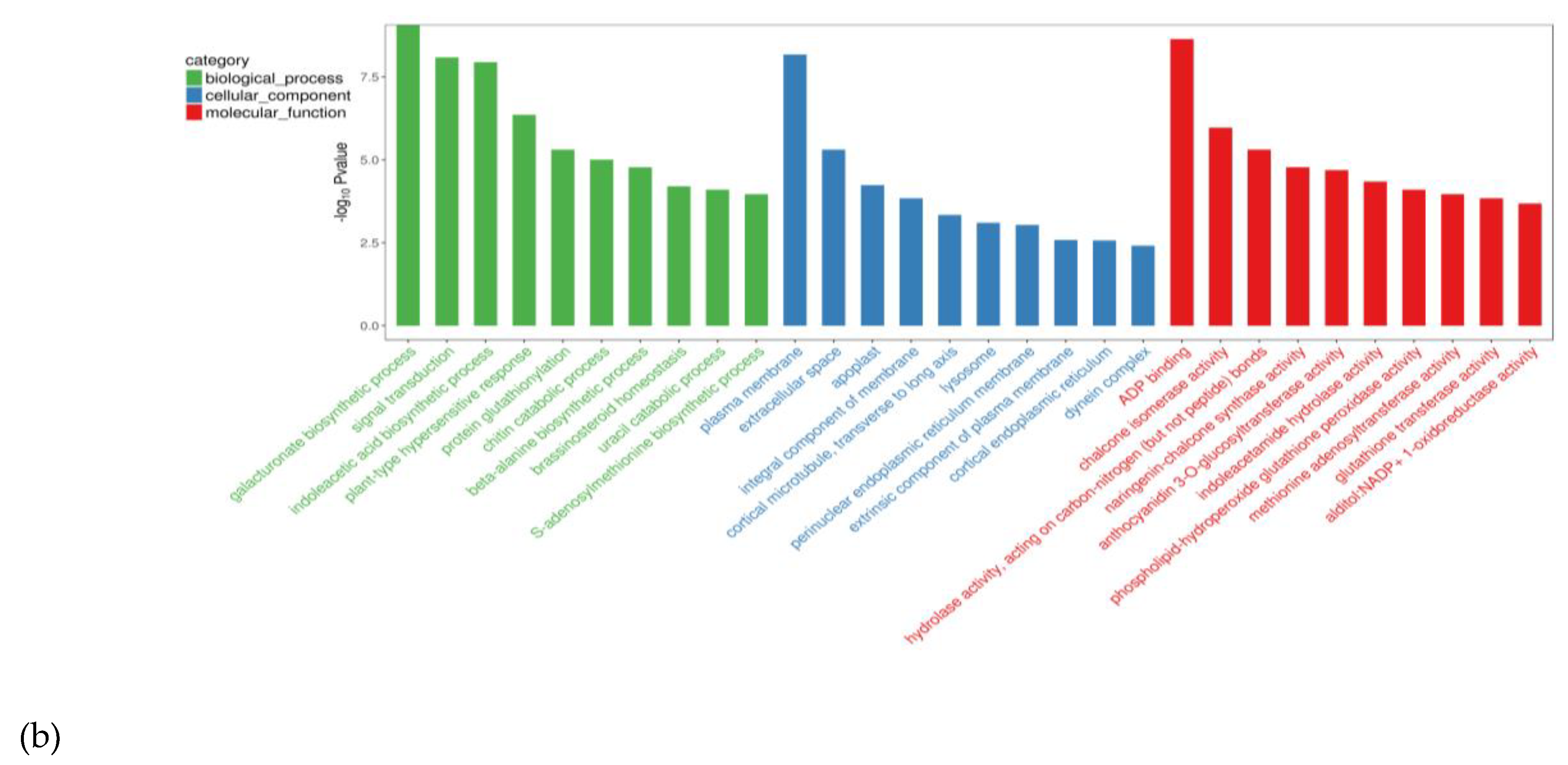
2.3.1. GO Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
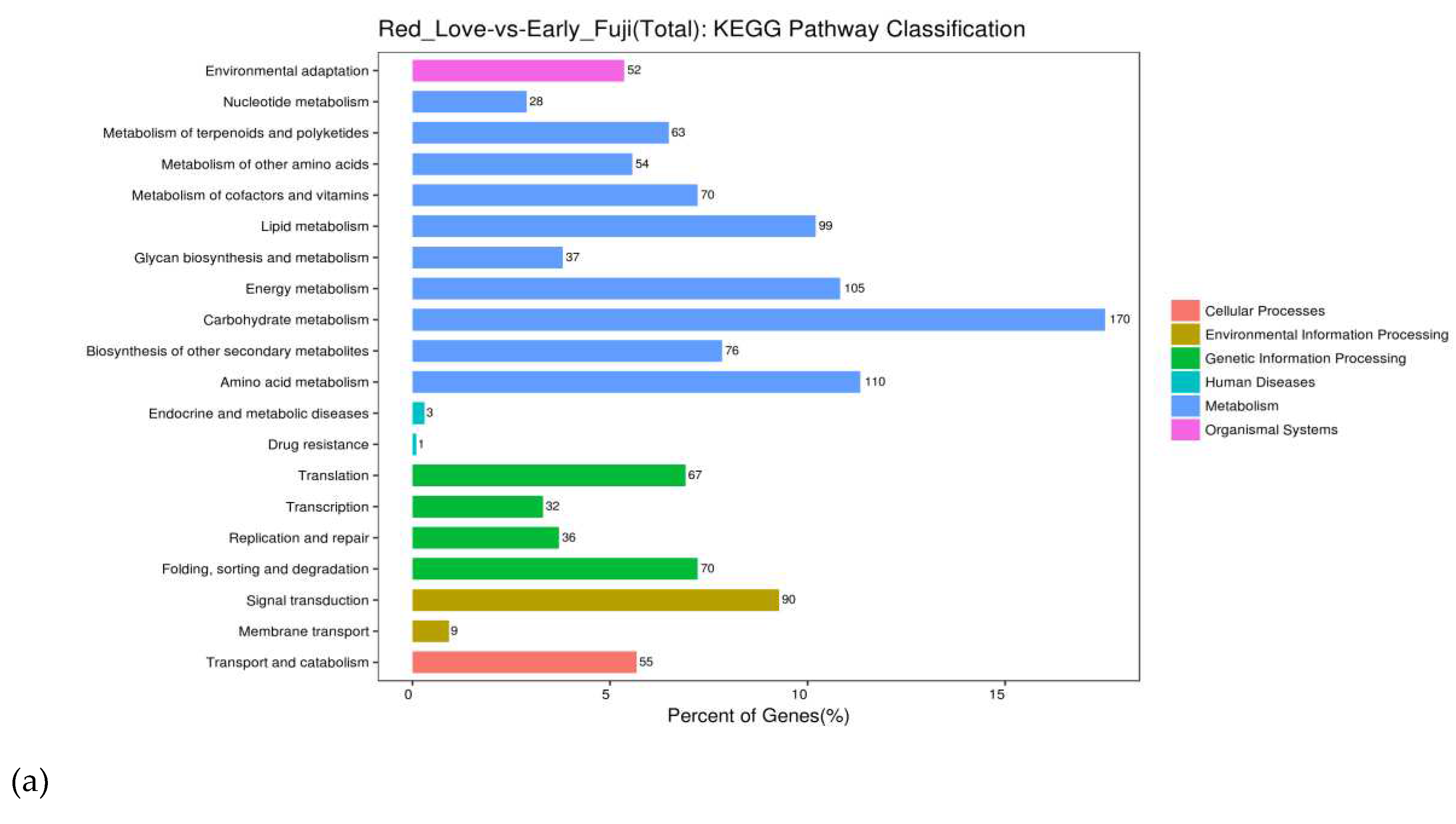
2.3.2. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
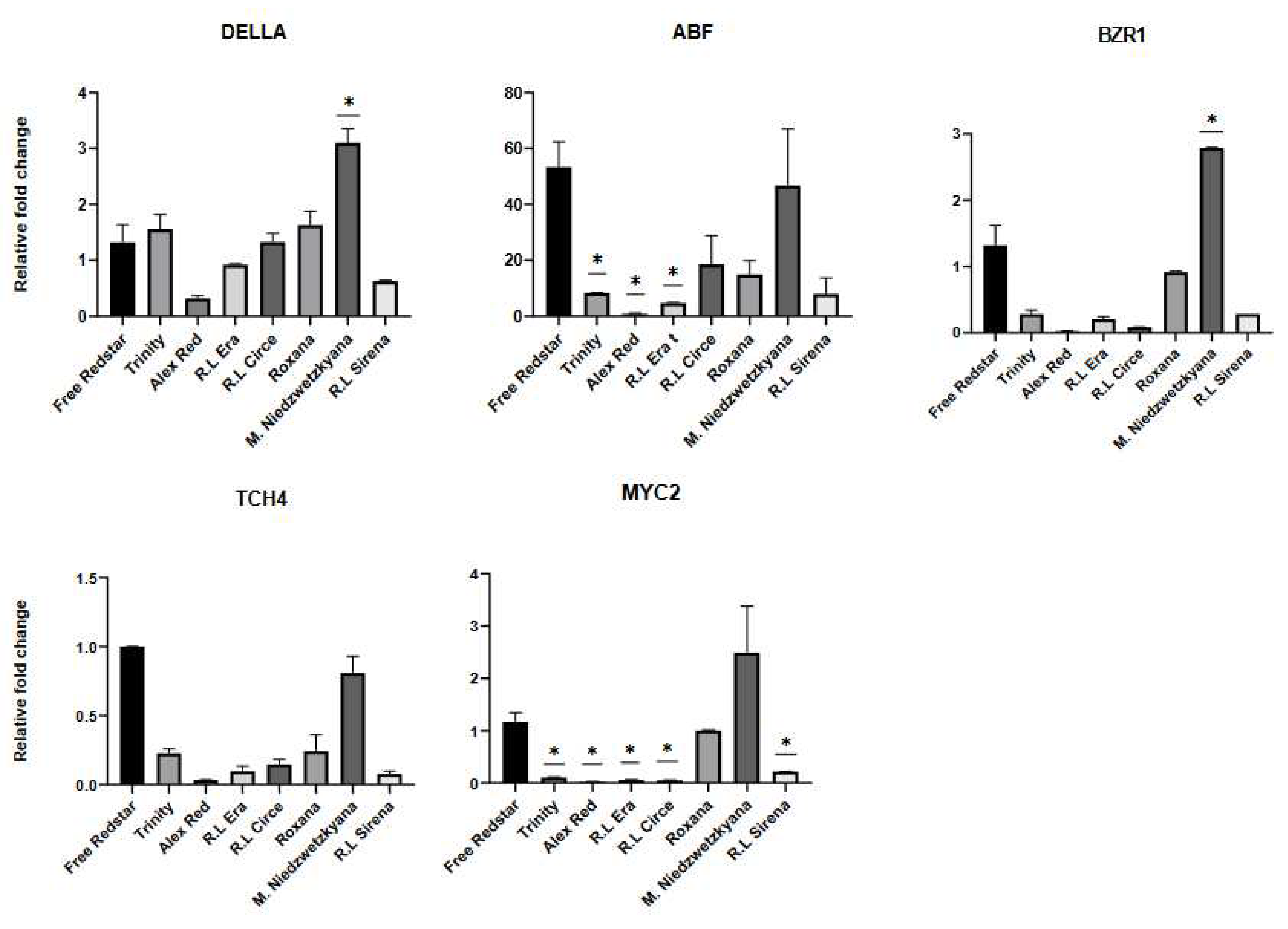
2.4. Validation of Activity of Genes from Plant Hormone and Signal Transduction Pathway by RT-qPCR
2.5. The activity of the Structural Genes in Red-Fleshed Apple Cultivars
2.6. Genes from Signal Transduction Pathway Shows Inconsistencies in Regard Expression Profiles in Comparison to RNA-seq Experiment but Significant Intergenic Correlation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. RNA Extraction
4.3. RNA-seq Analysis
4.4. GO Enrichment Analysis
4.5. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Differential Genes
4.6. cDNA Synthesis and RT-qPCR
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Velasco, R.; Zharkikh, A.; Affourtit, J.; Dhingra, A.; Cestaro, A.; Kalyanaraman, A.; Fontana, P.; Bhatnagar, S.K.; Troggio, M.; Pruss, D.; et al. The genome of the domesticated apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.). Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, X. Genetics and genomics of fruit color development in apple. In The Apple Genome; Korban, S.S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 271–295. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en.
- Van Nocker, S.; Berry, G.; Najdowski, J.; Michelutti, R.; Luffman, M.; Forsline, P.; Alsmairat, N.; Beaudry, R.; Nair, M.G.; Ordidge, M. Genetic diversity of red-fleshed apples (Malus). Euphytica 2012, 185, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieszczakowska-Frąc, M.; Buczek, M.; Kruczyńska, D.; Markowski, J. Cloudy red-fleshed apple juice production and quality. Pol. J. Natur. Sc. 2015, 30, 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.Q.; Li, Y.N. The RAPD evidence for the phylogenetic relationship of the closely related species of cultivated apple. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2000, 47, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Malus sieversii: the origin, flavonoid synthesis mechanism, and breeding of red-skinned and red-fleshed apples. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Chen, X. Research progress of fruit color development in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Xu, H.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, N.; Qiu, H.; Qu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, X. MYB12 and MYB22 play essential roles in proanthocyanidin and flavonol synthesis in red-fleshed apple (Malus sieversii f. niedzwetzkyana). Plant J. 2017, 90, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliepaard, C.; Alston, F.H.; Van Arkel, G.; Brown, L.M.; Chevreau, E.; Dunemann, F.; Evans, K.M.; Gardiner, S.; Guilford, P.; Van Heusden, A.W.; Janse, J.; Laurens, F.; Lynn, J.R.; Manganaris, A.G.; den Nijs, A.P.M.; Periam, N.; Rikkerink, E.; Roche, P.; Ryder, C.; Sansavini, S.; Schmidt, H.; Tartarini, S.; Verhaegh, J.J.; Vrielink-van Ginkel, M.; King, G.J. Aligning male and female linkage maps of apple (Malus pumila Mill.) using multi-allelic markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1998, 97, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagné, D.; Carlisle, C.M.; Blond, C.; Volz, R.K.; Whitworth, C.J.; Oraguzie, N.C.; Crowhurst, R.N.; Allan, A.C.; Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; Gardiner, S.E. Mapping a candidate gene (MdMYB10) for red flesh and foliage colour in apple. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagné, D.; Krieger, C.; Rassam, M.; Sullivan, M.; Fraser, J.; André, C.; Pindo, M.; Troggio, M.; Gardiner, S.E.; Henry, R.A.; Allan, A.C.; McGhie, T.K.; Laing, W.A. QTL and candidate gene mapping for polyphenolic composition in apple fruit. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Feng, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Doonan, J.H.; Batchelor, W.D.; Xiong, L.; Yan, J. Crop Phenomics and High-Throughput Phenotyping: Past Decades, Current Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 187–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertog, M.G.; Feskens, E.J.; Hollman, P.C.; Katan, M.B.; Kromhout, D. Dietary antioxidant flavonoids and risk of coronary heart disease: the Zutphen Elderly Study. Lancet 1993, 342, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knekt, P.; Kumpulainen, J.; Järvinen, R.; Rissanen, H.; Heliövaara, M.; Reunanen, A.; Hakulinen, T.; Aromaa, A. Flavonoid intake and risk of chronic diseases. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takos, A.M.; Jaffé, F.W.; Jacob, S.R.; Bogs, J.; Robinson, S.P.; Walker, A.R. Light-induced expression of a MYB gene regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in red apples. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1216–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treutter, D. Biosynthesis of phenolic compounds and its regulation in apple. Plant Growth Regul. 2001, 34, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, M.K.; Shirley, B.W. Analysis of flavanone 3-hydroxylase in Arabidopsis seedlings. Coordinate regulation with chalcone synthase and chalcone isomerase. Plant Physiol. 1996, 111, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; Putterill, J.; Stevenson, D.E.; Kutty-Amma, S.; Allan, A.C. Red coloration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J. 2007, 49, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick-Pérez, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hayes, J.; Salazar, A.; Zabotina, O.A.; Hong, M. Structure and interactions of plant cell-wall polysaccharides by two- and three-dimensional magic-angle-spinning solid-state NMR. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone Ferreyra, M.L.; Rius, S.P.; Casati, P. Flavonoids: biosynthesis, biological functions, and biotechnological applications. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Yonekura-Sakakibara, K.; Nakabayashi, R.; Higashi, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Tohge, T.; Fernie, A.R. The flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis: structural and genetic diversity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 72, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, C.; Kotoda, N.; Wada, M.; Kondo, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Soejima, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tsuba, T.; Moriguchi, T. Anthocyanin biosynthetic genes are coordinately expressed during red coloration in apple skin. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 40, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.; Hiraoka, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Honda, C.; Terahara, N. Changes in the expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes during apple development. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2002, 127, 971–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koes, R.; Verweij, W.; Quattrocchio, F. Flavonoids: a colorful model for the regulation and evolution of biochemical pathways. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, E.; Soltani, B.M.; Yadollahi, A.; Hosseini, E. Independence of color intensity variation in red flesh apples from the number of repeat units in promoter region of the MdMYB10 gene as an allele to MdMYB1 and MdMYBA. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 10, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Hichri, I.; Barrieu, F.; Bogs, J.; Kappel, C.; Delrot, S.; Lauvergeat, V. Recent advances in the transcriptional regulation of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 2465–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Feng, S.; Chen, X. Synergistic effects of light and temperature on anthocyanin biosynthesis in callus cultures of red-fleshed apple (Malus sieversii f. niedzwetzkyana). Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult. 2016, 127, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, X. Transcriptomic Analysis of Red-Fleshed Apples Reveals the Novel Role of MdWRKY11 in Flavonoid and Anthocyanin Biosynthesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7076–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Jiang, H.; Mao, Z.; Wang, N.; Jiang, S.; Xu, H.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. The R2R3-MYB transcription factor MdMYB24-like is involved in methyl jasmonate-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 139, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espley, R.V.; Brendolise, C.; Chagné, D.; Kutty-Amma, S.; Green, S.; Volz, R.; Putterill, J.; Schouten, H.J.; Gardiner, S.E.; Hellens, R.P.; Allan, A.C. Multiple repeats of a promoter segment causes transcription factor autoregulation in red apples. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espley, R.V.; Bovy, A.; Bava, C.; Jaeger, S.R.; Tomes, S.; Norling, C.; Crawford, J.; Rowan, D.; McGhie, T.K.; Brendolise, C.; Putterill, J.; Schouten, H.J.; Hellens, R.P.; Allan, A.C. Analysis of genetically modified red-fleshed apples reveals effects on growth and consumer attributes. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2013, 11, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagné, D.; Crowhurst, R.N.; Troggio, M.; Davey, M.W.; Gilmore, B.; Lawley, C.; Vanderzande, S.; Hellens, R.P.; Kumar, S.; Cestaro, A.; Velasco, R.; Main, D.; Rees, J.D.; Iezzoni, A.; Mockler, T.; Wilhelm, L.; Van de Weg, E.; Gardiner, S.E.; Bassil, N.; Peace, C. Genome-Wide SNP Detection, Validation, and Development of an 8K SNP Array for Apple. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, C.; Moriya, S. Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Apple Fruit. Hort. J. 2018, 87, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, H.S.; Guillen, F.; Bowen, J.H.; Tacken, E.; Putterill, J.; Schaffer, R.J.; Johnston, J.W. Mining the apple genome reveals a family of nine ethylene receptor genes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2012, 72, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Yu, J.; Li, T.; Yang, W.; Zhang, S.; Su, H.; Wang, L. A novel NAC transcription factor, MdNAC42, regulates anthocyanin accumulation in red-fleshed apple by interacting with MdMYB10. Tree Physiol. 2020, 40, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, N.; Chen, X. MdJa2 Participates in the Brassinosteroid Signaling Pathway to Regulate the Synthesis of Anthocyanin and Proanthocyanidin in Red-Fleshed Apple. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 830349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Qu, C.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Z.; Xu, H.; Fang, H.; Su, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, N.; Chen, X. The proanthocyanidin-specific transcription factor MdMYBPA1 initiates anthocyanin synthesis under low-temperature conditions in red-fleshed apples. Plant J. 2018, 96, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wang, N.; Liu, J.; Qu, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Lu, N.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. The molecular mechanism underlying anthocyanin metabolism in apple using the MdMYB16 and MdbHLH33 genes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 94, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everaert, C.; Luypaert, M.; Maag, J.L.V.; Cheng, Q.X.; Dinger, M.E.; Hellemans, J.; Mestdagh, P. Benchmarking of RNA-sequencing analysis workflows using whole-transcriptome RT-qPCR expression data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharkawy, I.; Liang, D.; Xu, K. Transcriptome analysis of an apple (Malus × domestica) yellow fruit somatic mutation identifies a gene network module highly associated with anthocyanin and epigenetic regulation. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 7359–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, I.; Tariq, R.; Nazir, T.; Khan, I.; Basit, A.; Gul, H.; Anwar, T.; Awan, S.A.; Bacha, S.A.S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Cong, P. RNA-Seq profiling reveals the plant hormones and molecular mechanisms stimulating the early ripening in apple. Genomics 2021, 113, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; An, Y.Y.; Wang, L.J. 24-Epibrassinolide enhances 5-ALA-induced anthocyanin and flavonol accumulation in calli of ‘Fuji’ apple flesh. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult. 2018, 134, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Li, L.; Yin, Y. Recent advances in the regulation of brassinosteroid signaling and biosynthesis pathways. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisso, J.; Altmann, T.; Müssig, C. Metabolic changes in fruits of the tomato dx mutant. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 2232–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symons, G.M.; Davies, C.; Shavrukov, Y.; Dry, I.B.; Reid, J.B.; Thomas, M.R. Grapes on steroids. Brassinosteroids are involved in grape berry ripening. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.Q.; Mao, W.H.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.H.; Asami, T.; Yu, J.Q. A role of brassinosteroids in early fruit development in cucumber. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, L.; Li, C.L.; Xing, Y.; Qin, L.; Shen, Y.Y. Brassinosteroid is involved in strawberry fruit ripening. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 69, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Asamizu, E.; Shibata, D.; Nakamura, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Awai, K.; Amagai, M.; Kuwata, C.; Tsugane, T.; Masuda, T.; Shimada, H.; Takamiya, K.; Ohta, H.; Tabata, S. Monitoring of methyl jasmonate-responsive genes in Arabidopsis by cDNA macroarray: Self-activation of jasmonic acid biosynthesis and crosstalk with other phytohormone signaling pathways. DNA Res. 2001, 8, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Song, S.; Ren, Q.; Wu, D.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Fan, M.; Peng, W.; Ren, C.; Xie, D. The Jasmonate-ZIM-domain proteins interact with the WD-Repeat/bHLH/MYB complexes to regulate Jasmonate-mediated anthocyanin accumulation and trichome initiation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1795–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.H.; Tian, Y.; Chen, K.Q.; Liu, X.J.; Liu, D.D.; Xie, X.B.; Cheng, C.G.; Cong, P.H.; Hao, Y.J. MdMYB9 and MdMYB11 are involved in the regulation of the JA-induced biosynthesis of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin in apples. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Yu, D. Arabidopsis WRKY45 Interacts with the DELLA Protein RGL1 to Positively Regulate Age-Triggered Leaf Senescence. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1174–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.H.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, R.; Wu, S.J.; An, M.M.; Li, M.; Wang, C.Z.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, X.S. Effect of auxin, cytokinin and nitrogen on anthocyanin biosynthesis in callus cultures of red-fleshed apple (Malus sieversii f. niedzwetzkyana). Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult. 2015, 120, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deikman, J.; Hammer, P.E. Induction of Anthocyanin Accumulation by Cytokinins in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Jeong, C.Y.; Kang, G.; Yoo, S.; Hong, S.; Lee, H. MYBD employed by HY5 increases anthocyanin accumulation via repression of MYBL2 in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2015, 84, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, N.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.S. Transcriptome profiling reveals auxin suppressed anthocyanin biosynthesis in red-fleshed apple callus (Malus sieversii f. niedzwetzkyana). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2015, 123, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Joyce, D.C. ABA effects n ethylene production, PAL activity, anthocyanin and polyphenol contents of strawberry fruit. Plant Grow Regul. 2023, 39, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, T.; Shiozaki, S.; Ogata, T.; Horiuchi, S. Effects of abscisic acid and shading treatments on the level of anthocyanin and resveratrol in skin of kyoho grape berry. Acta Hortic. 2000, 514, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Saini, M.K.; Sinhg, J.; Pongener, A.; Singh, G.S. Postharvest application of abscisic acid promotes anthocyanin accumulation in pericarp of litchi fruit without adversely affecting postharvest quality. Postharv. Biol. Technol. 2014, 96, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, T. RNA Isolation From Highly Viscous Samples Rich in Polyphenols and Polysaccharides. Plant. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2002, 20, 417–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential Expression of RNA-Seq Data at the Gene Level–the DESeq Package. Eur. Mol. Biol. Lab. 2012, 10, f1000research. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, A.; Pimentel, H.; Trapnell, C.; Pachter, L. Identification of novel transcripts in annotated genomes using RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2325–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexa, A.; Rahnenfuhrer, J. topGO: Enrichment analysis for gene ontology. R Package Version 2010, 2, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta DeltaC(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

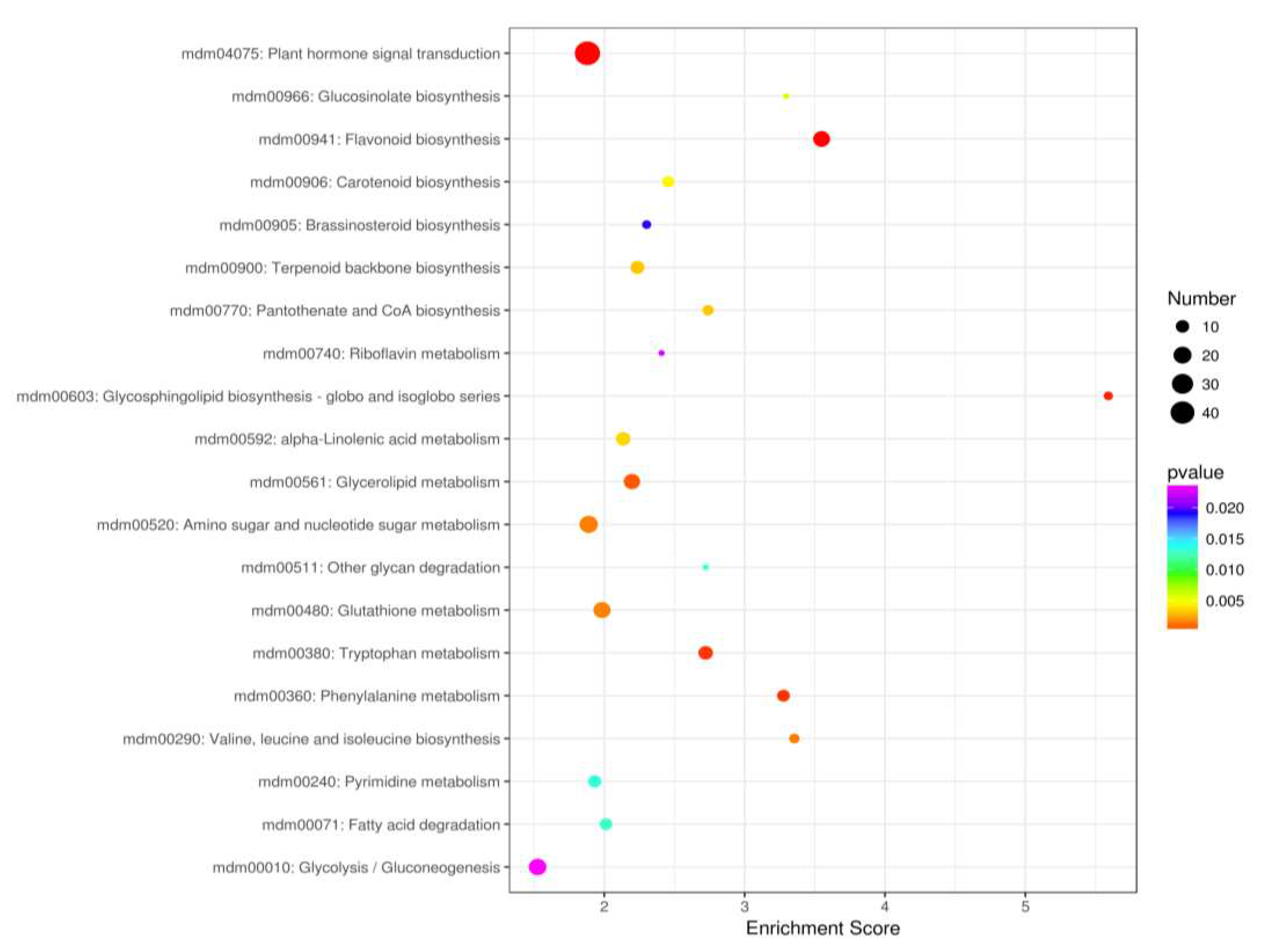
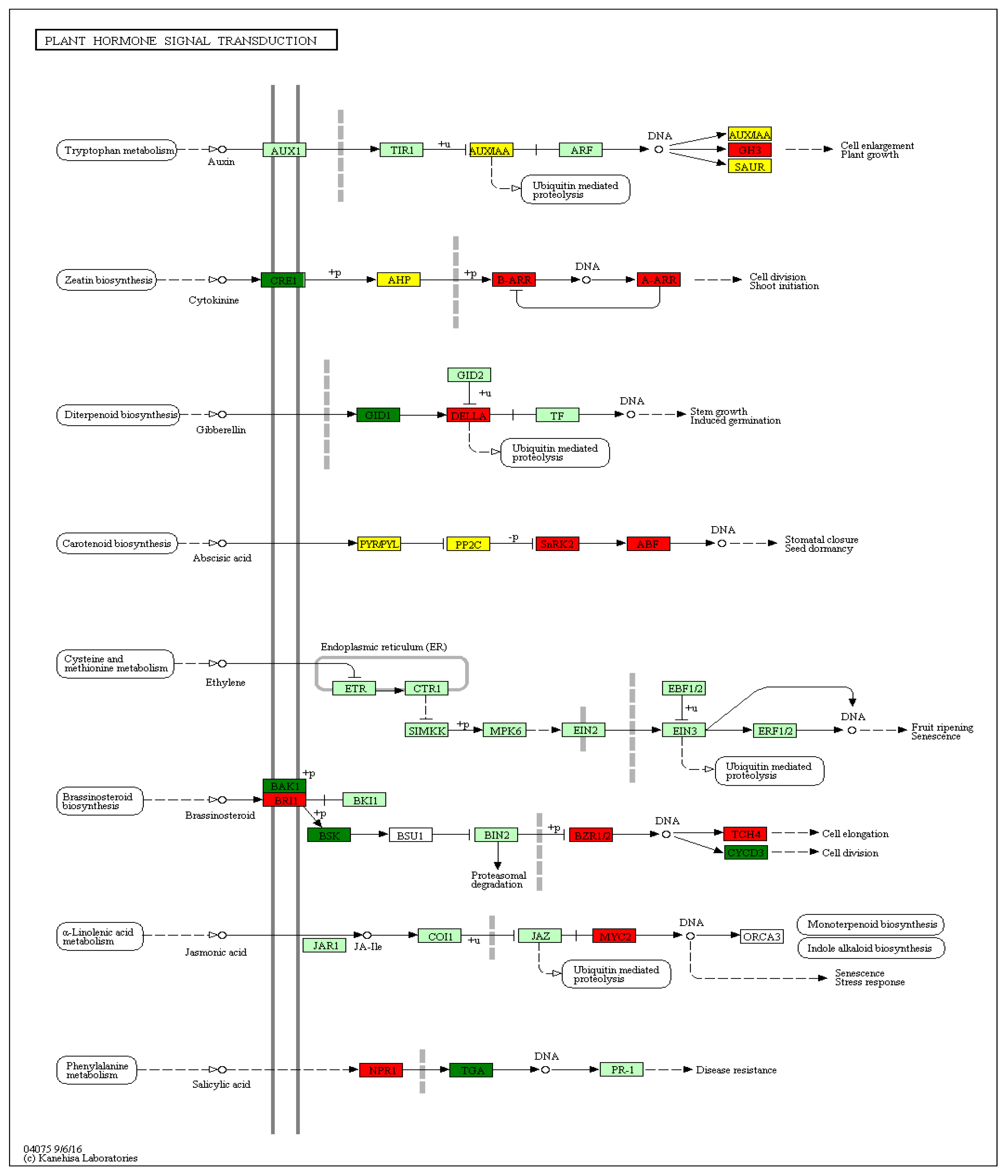

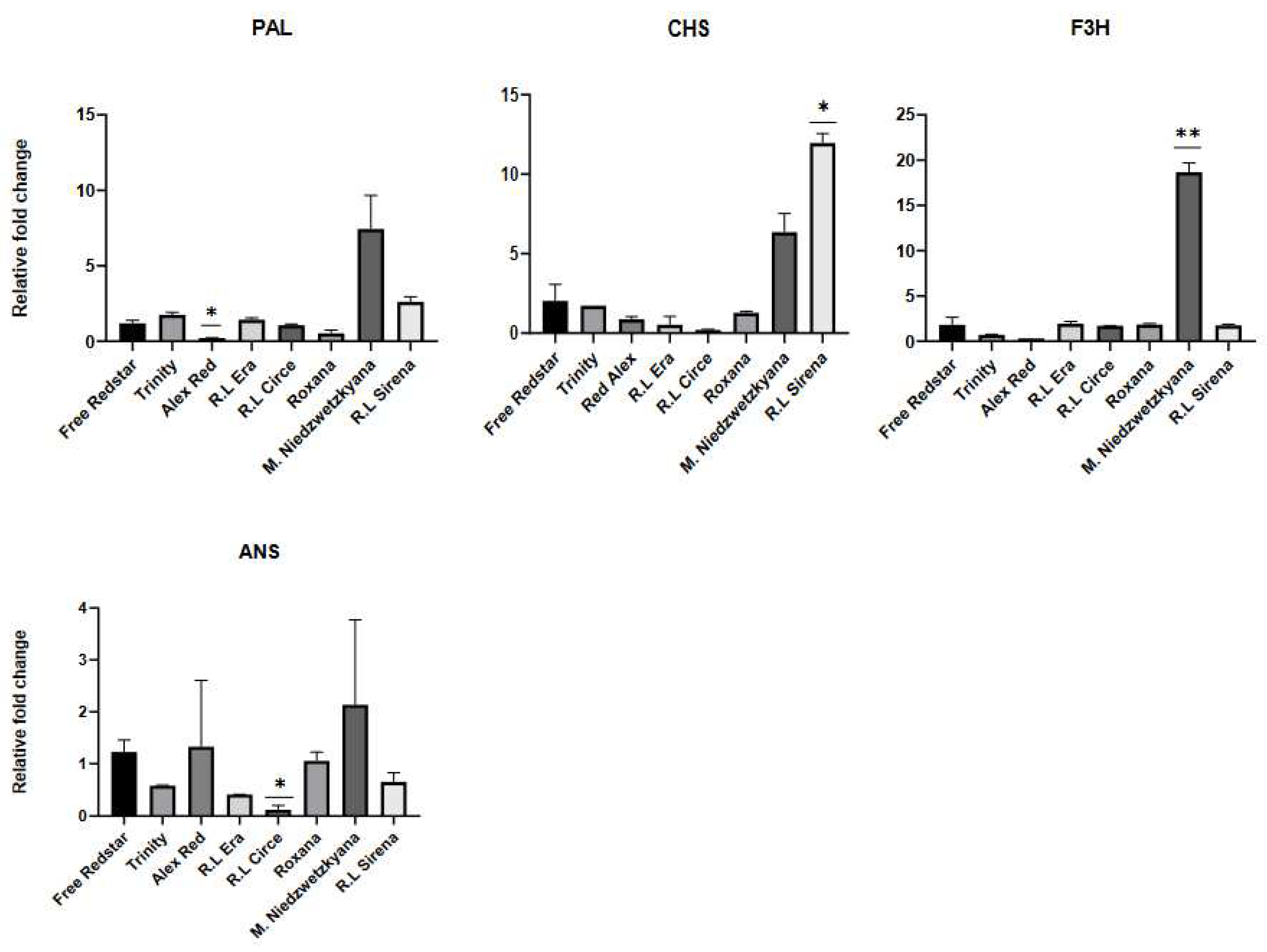
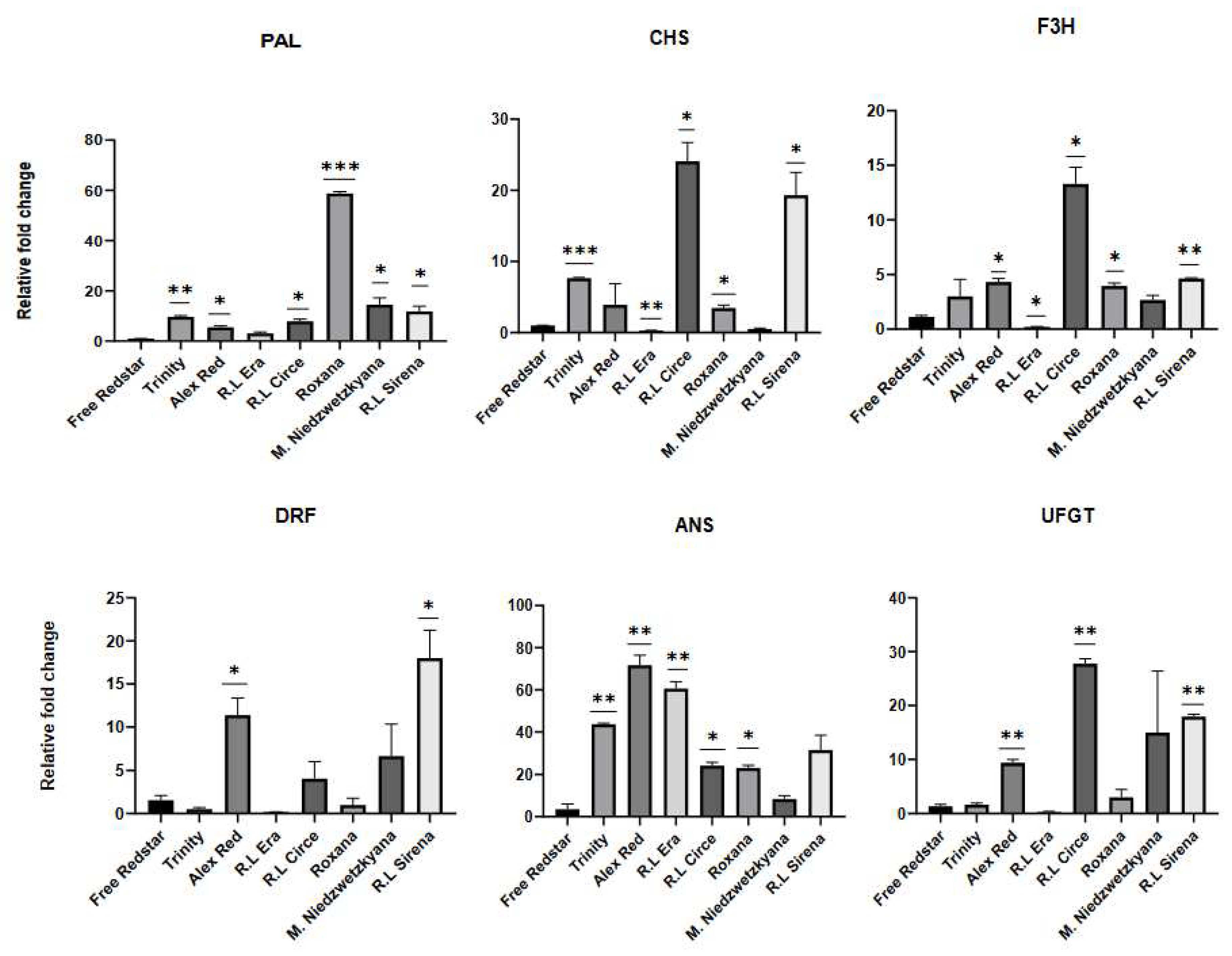
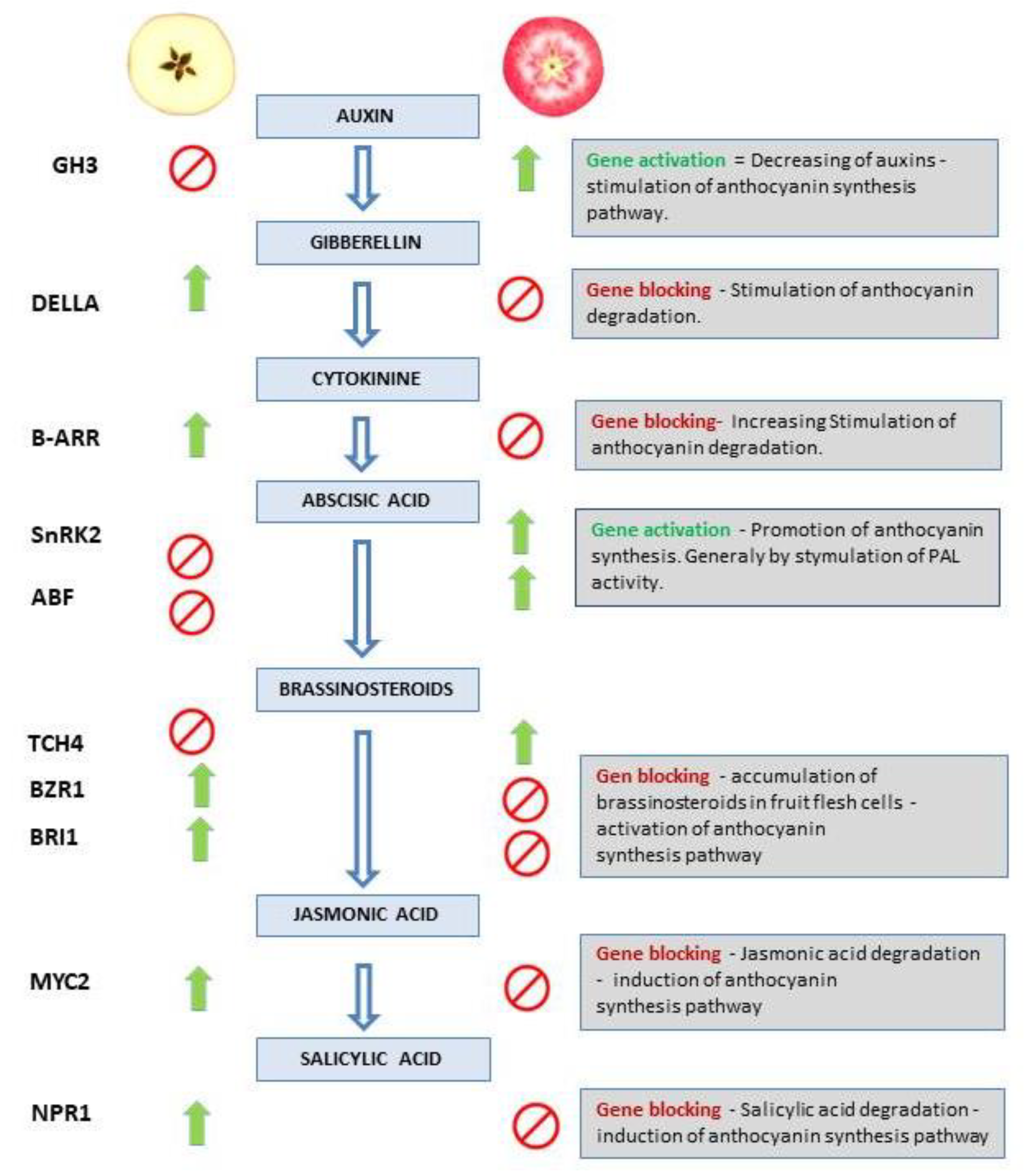
| Gene name | Locus | Hormone signaling pathway | Cellular localization and gene function | FoldChange (FC) |
| GH3 | LOC103436425 | Auxin | probable indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase GH3.1; auxin responsive GH3 gene family | 24,2 |
| B-ARR | LOC103400015 | Cytokinin | two-component response regulator ARR1-like isoform X1; regulator ARR-B family; Response_reg Myb_DNA-binding | 4,1 |
| DELLA | LOC103406747 | Gibberellin | DELLA protein GAI-like; DELLA protein | 2,6 |
| SnRK2 | LOC103429475 | ABA | serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2; kinase PK_Tyr_Ser-Thr Choline_kinase PPP1R21_C; Cytoplasm, signaling pathway kinase family. | 2,7 |
| ABF | LOC103446587 | ABA | ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE 5-like protein 2; ABA responsive element binding factor. | 20,6 |
| BRI1 | LOC103410973 | Brassinosteroids | Plasma membrane, receptor S160/ brassinosteroid insensitive protein 1 | 2,2 |
| BZR1/2 | LOC103440434 | Brassinosteroids | BES1/BZR1 homolog protein 2-like; brassinosteroid resistant 1/2 | 5,2 |
| TCH4 | LOC103409272 | Brassinosteroids | probable xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase protein 23 precursor; cell wall xyloglucan:xyloglucosyl transferase TCH4; | 5,7 |
| MYC2 | LOC103404780 | Jasmonic acid | Transcription factor; bHLH-MYC | 2,1 |
| NPR1 | LOC103454562 | Salicylic acid | Protein ubiqitination, BTB/POZ domain and ankyrin repeat-containing regulatory protein NPR1 | 2,9 |
| (a) | ||||||||||||||||||
| ABF | B-ARR | BZR1 | NPR1 | DELLA | GH3 | MYC2 | SnRK2 | BRI1 | TCH4 | |||||||||
| ANS | ** | |||||||||||||||||
| CHS | ||||||||||||||||||
| DRF | **** | *** | ** | ** | **** | |||||||||||||
| F3H | **** | * | **** | * | ** | **** | ||||||||||||
| PAL | * | * | ||||||||||||||||
| UFGT | ** | * | **** | *** | *** | * | ||||||||||||
| (b) | ||||||||||||||||||
| ABF | B-ARR | BZR1 | NPR1 | DELLA | GH3 | MYC2 | SnRK2 | BRI1 | TCH4 | |||||||||
| ANS | ||||||||||||||||||
| CHS | * | * | * | * | ||||||||||||||
| DFR | ||||||||||||||||||
| F3H | ||||||||||||||||||
| PAL | ** | ** | ** | |||||||||||||||
| UFGT1 | *** | **** | ** | * | ** | **** | * | *** | **** | *** | ||||||||
| Gene abbreviation | Oligo 5’ | Oligo 3’ | Reference | |
| Differentially expressed genes | TCH4 | ctcaactggggaaccctaca | ggcattccaaaaagttgcat | This study - revealed in RNA-seq |
| BZR1 | tagtccgtcgtcttcgtcct | gagacggcgtaaaatgggta | ||
| BRI1 | gctttggaccaccttgacat | cacaagctctgcacacgaat | ||
| MYC2 | tgtttgggctgcagactatg | tccttcatttccatggtgg | ||
| NPR1 | gccttgagctcgtacagtcc | agaccccatttgatgagctg | ||
| GH3 | acagatccttcccgcctagt | aattggtgcgccataggtag | ||
| B-ARR | acttgcttcgccaaaagaaa | tgccatatattgcgcagttc | ||
| DELLA | tagtgacggttgtggagcag | ctccacttgcttagcggttc | ||
| SnRK2 | ggcgaatccttactgtacgc | gtctatgctctgggctggag | ||
| ABF | acaacggtcaccatcaacaa | ctgacgtcctcttccctcac | ||
| Structural genes | ANS | caatttggcctcaaacacct | tgagcttcaacaccaagtgc | Kondo et al. [24] |
| PAL | cggaaacttggactcggtaa | gatggagcctcttgcttgtc | ||
| DFR | gagtccgaatccgtttgtgtca | atgtttgtgggggctgtcgatg | ||
| UFGT | tccctttcactagccatgcaag | gtggaggatggagtttttacc | ||
| F3H | ggtgaactcaaacagcagca | ccactttggctttctccaag | ||
| CHS | acccacttggtcttttgcac | actaggccctcggaaggtaa | ||
| Reference | ACTIN | gactgtgaaactgcgaatggctca | catgaatcatcagagcaacgggca | Xu et al. [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





