Submitted:
08 January 2024
Posted:
09 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
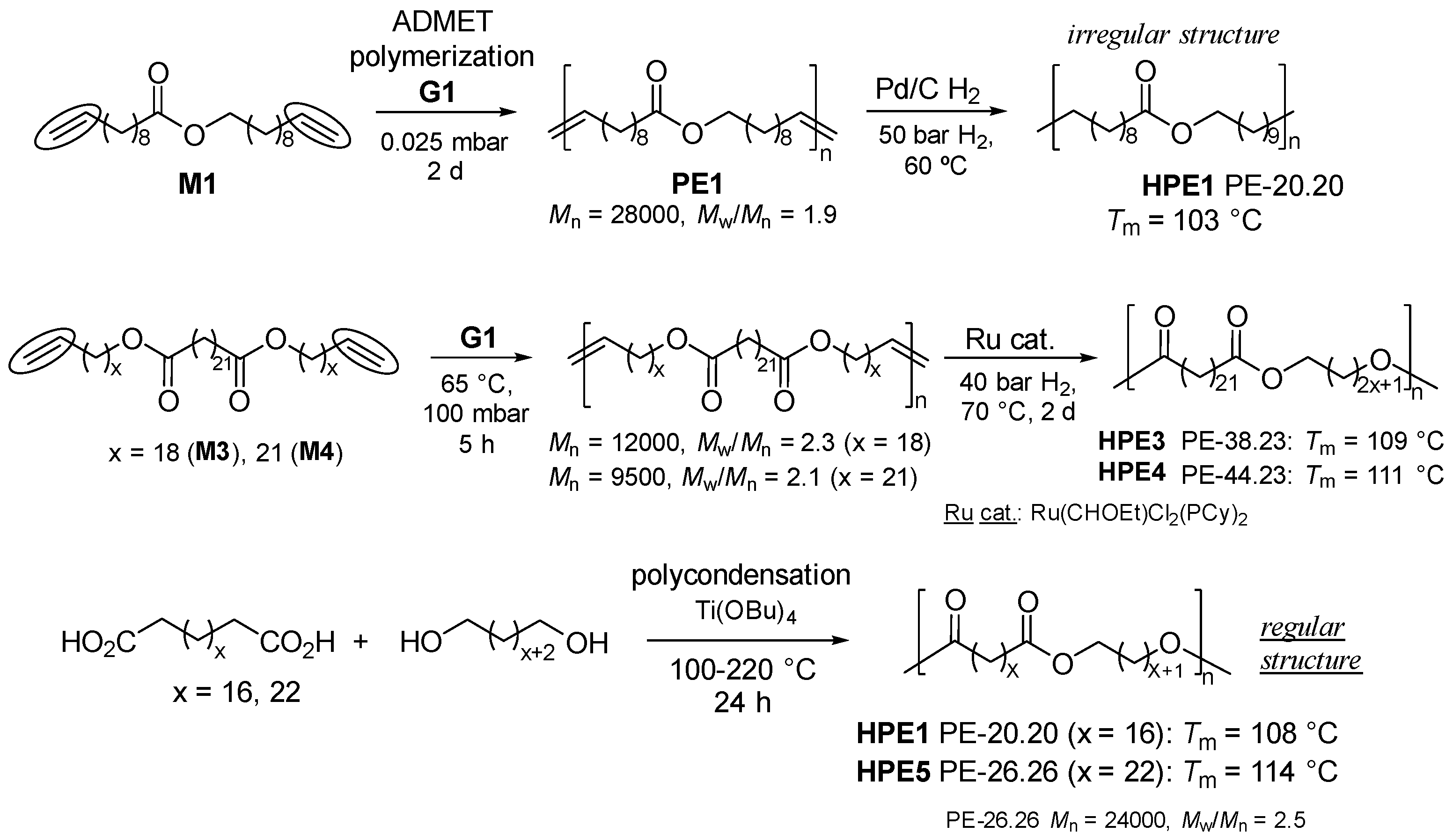
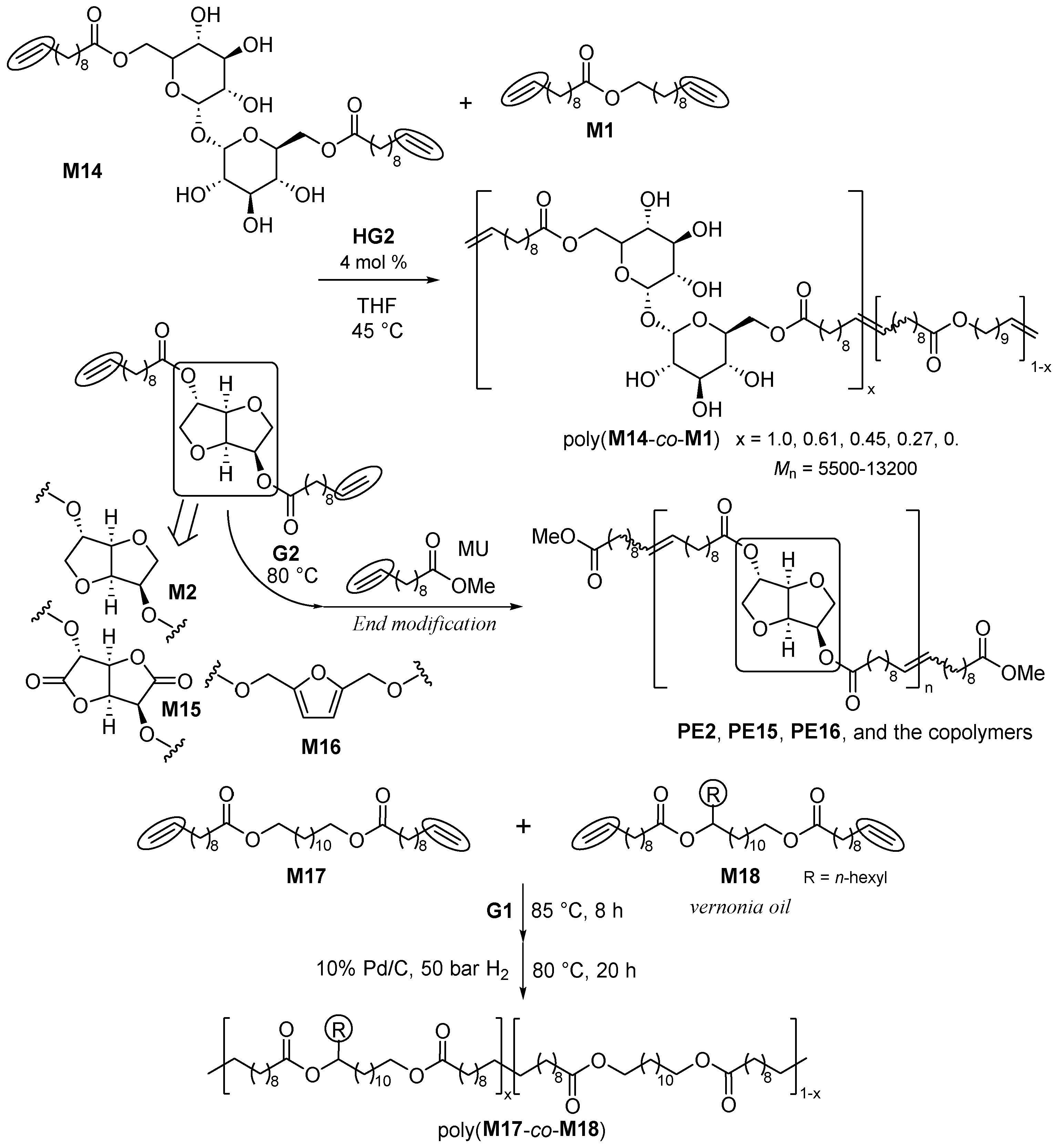
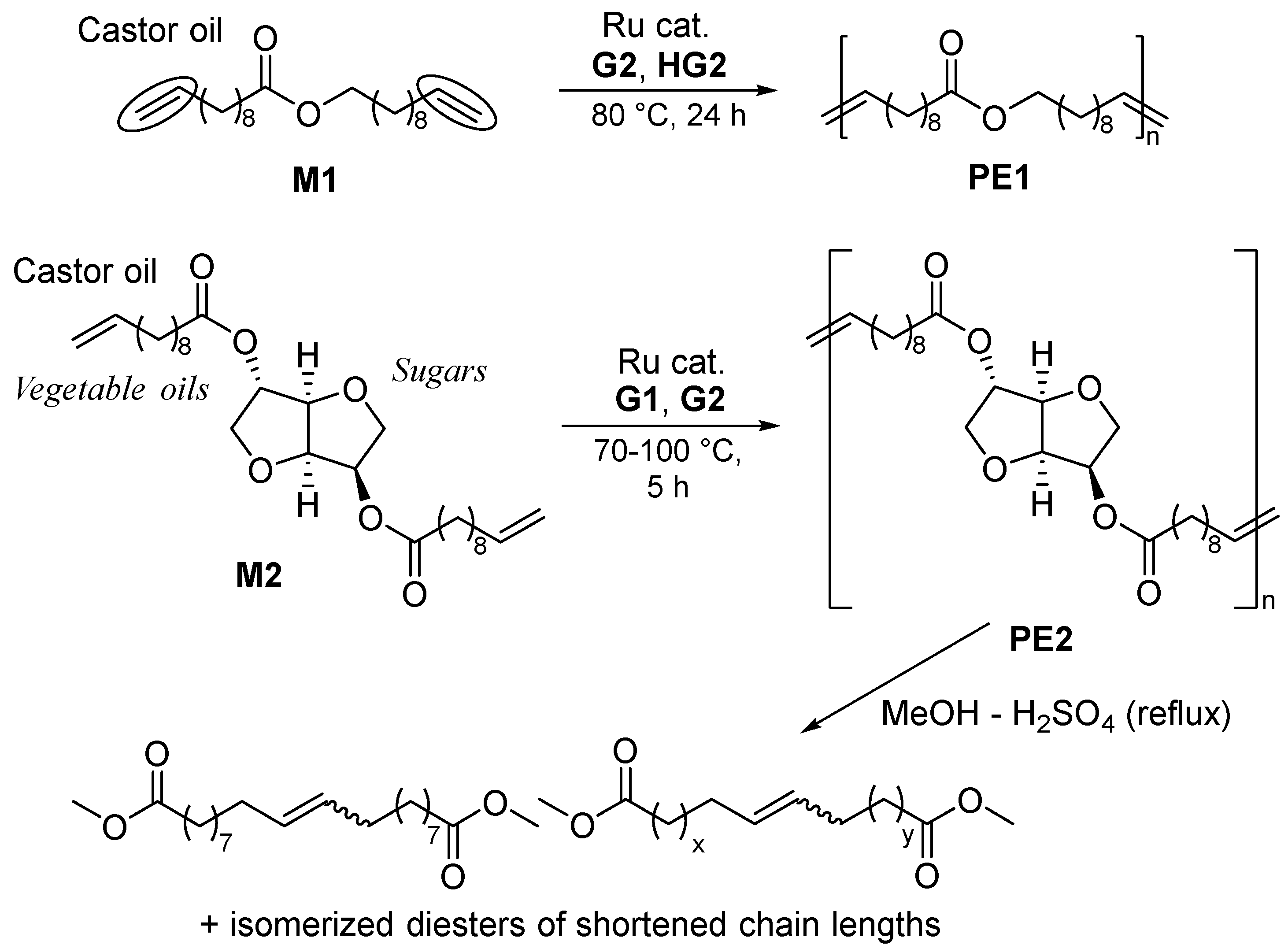
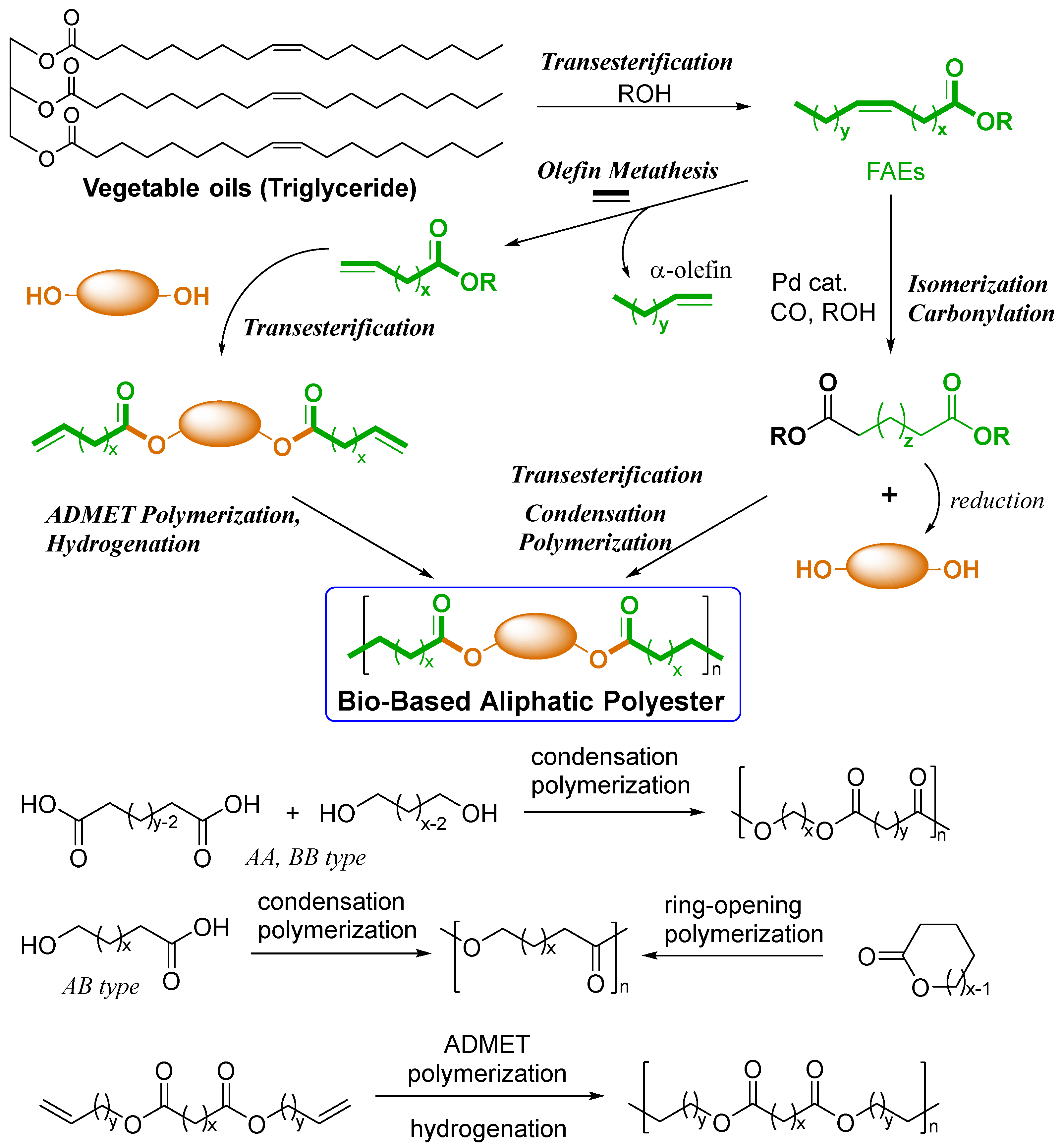
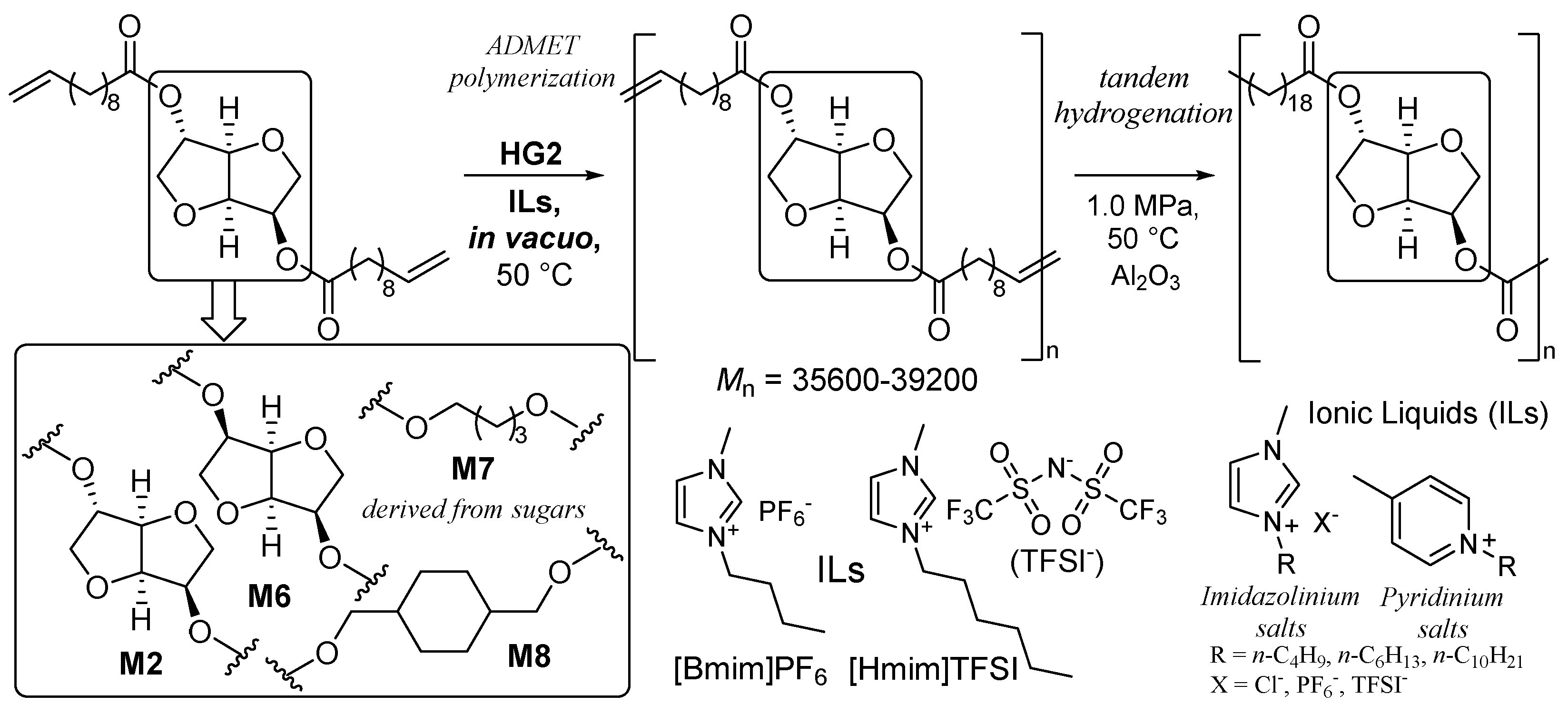
2. Synthesis of Bio-based Aliphatic Polyesters by the ADMET Polymerization.
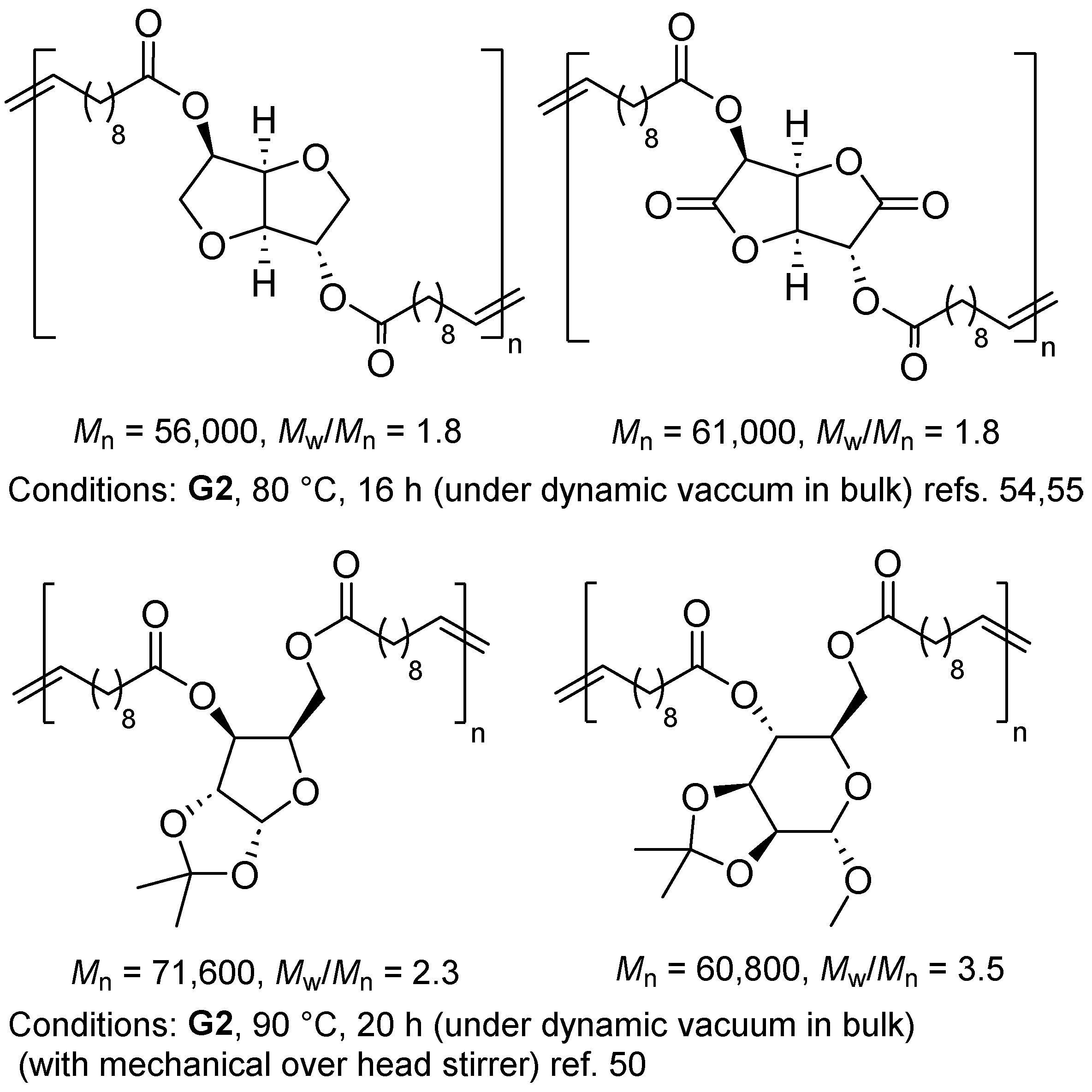
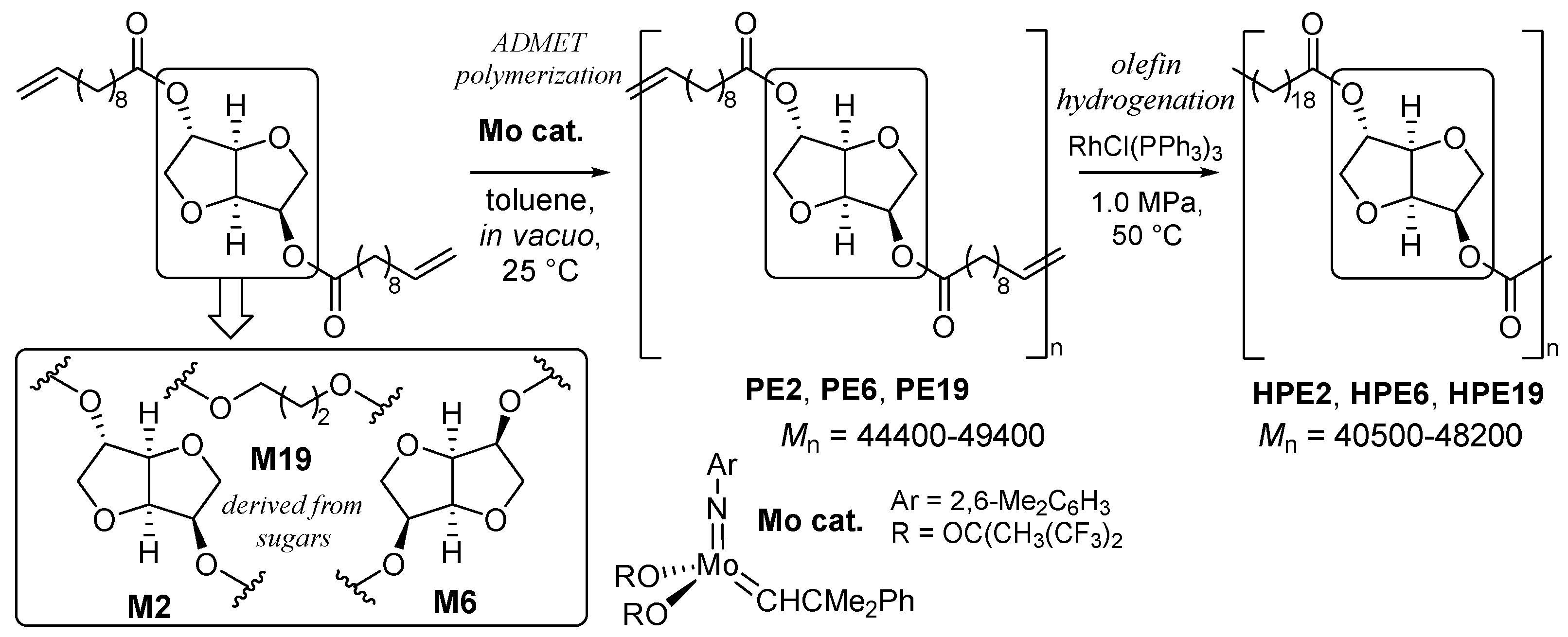
2.1. Synthesis of Aliphatic Polyesters by ADMET Polymerization and Hydrogenation.
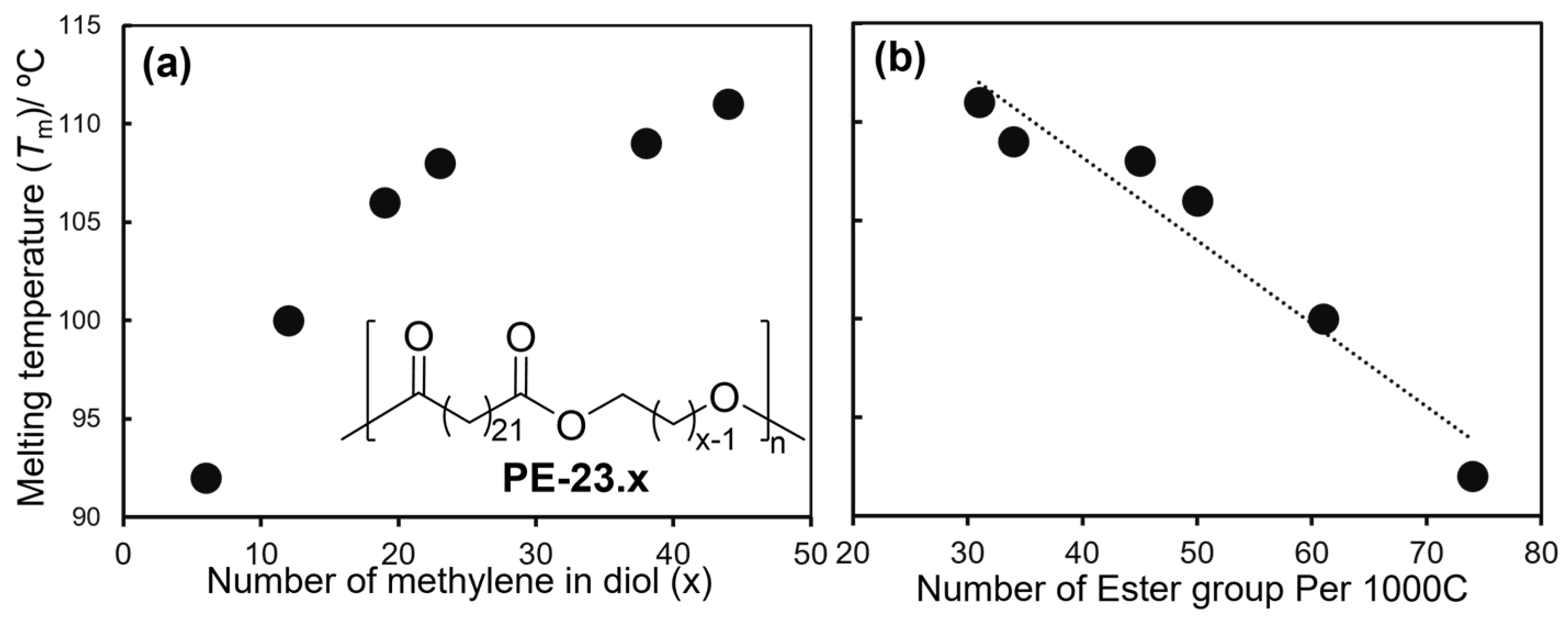
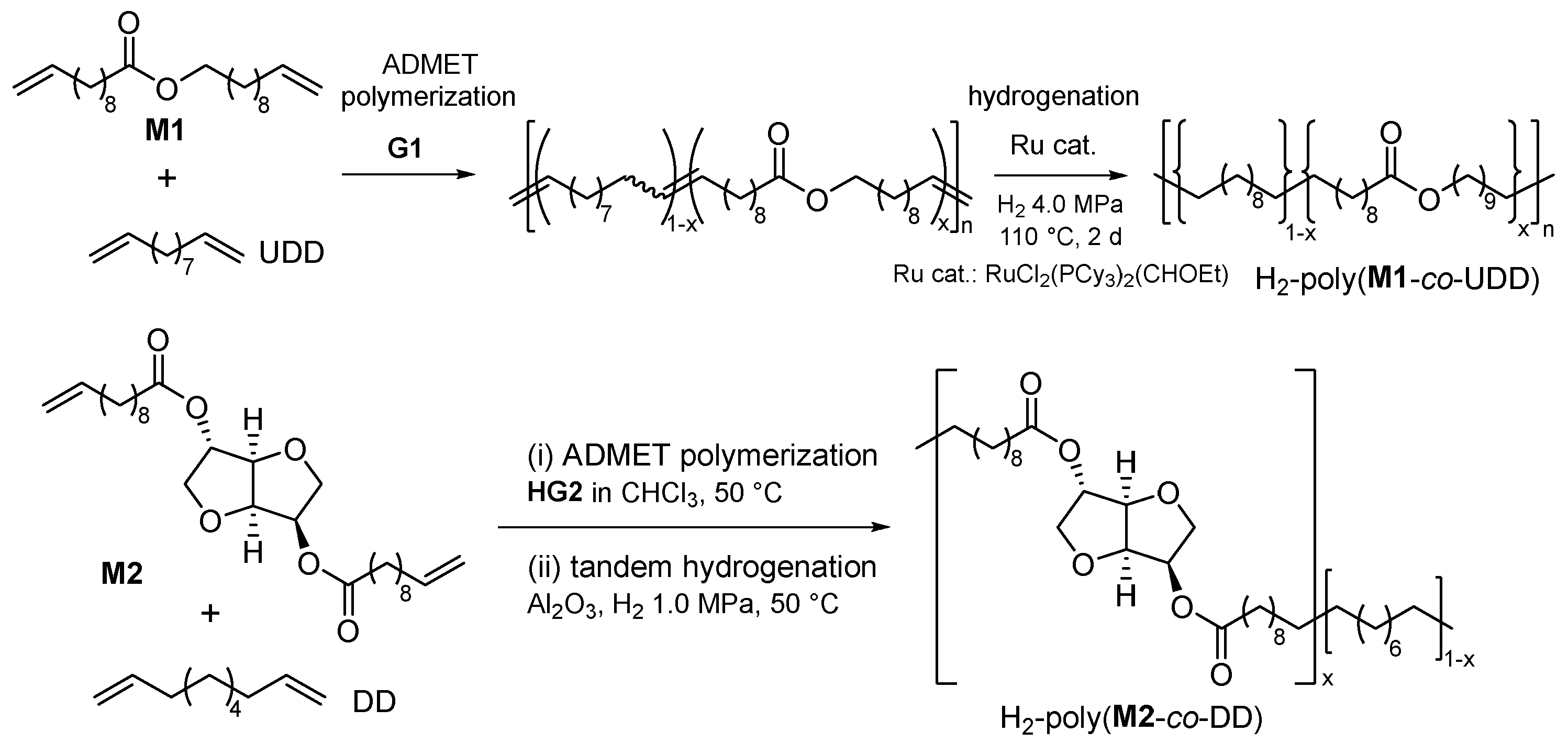
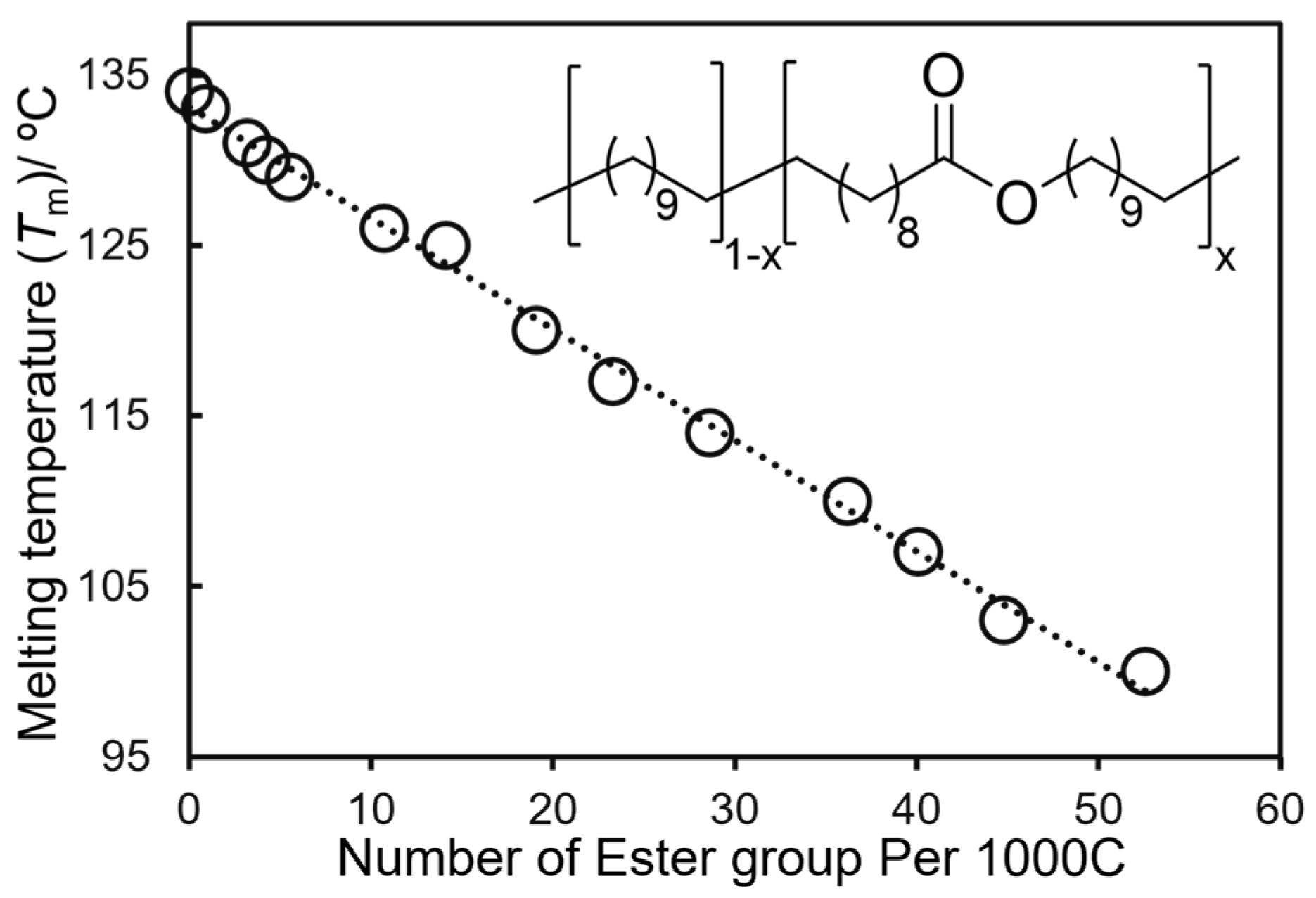
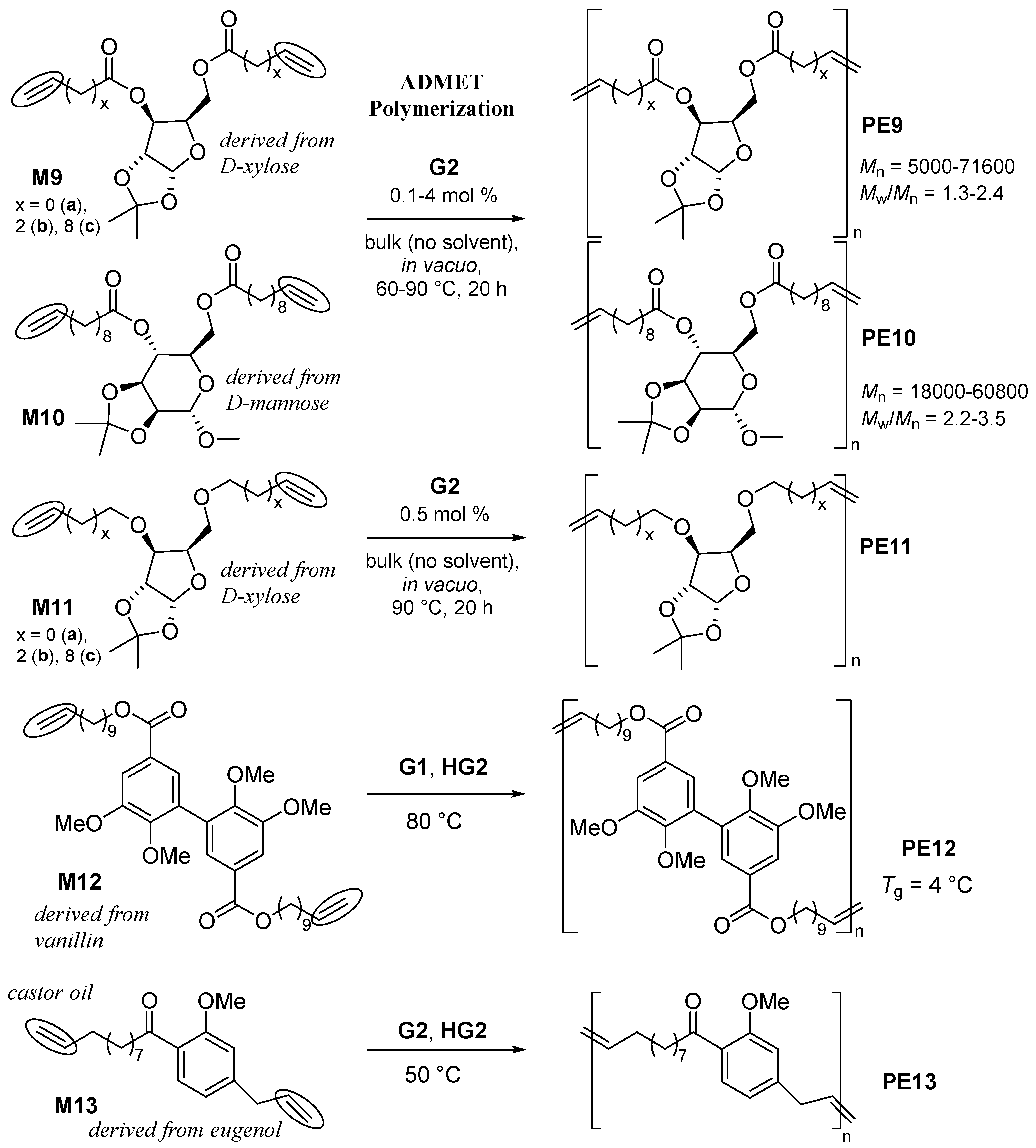
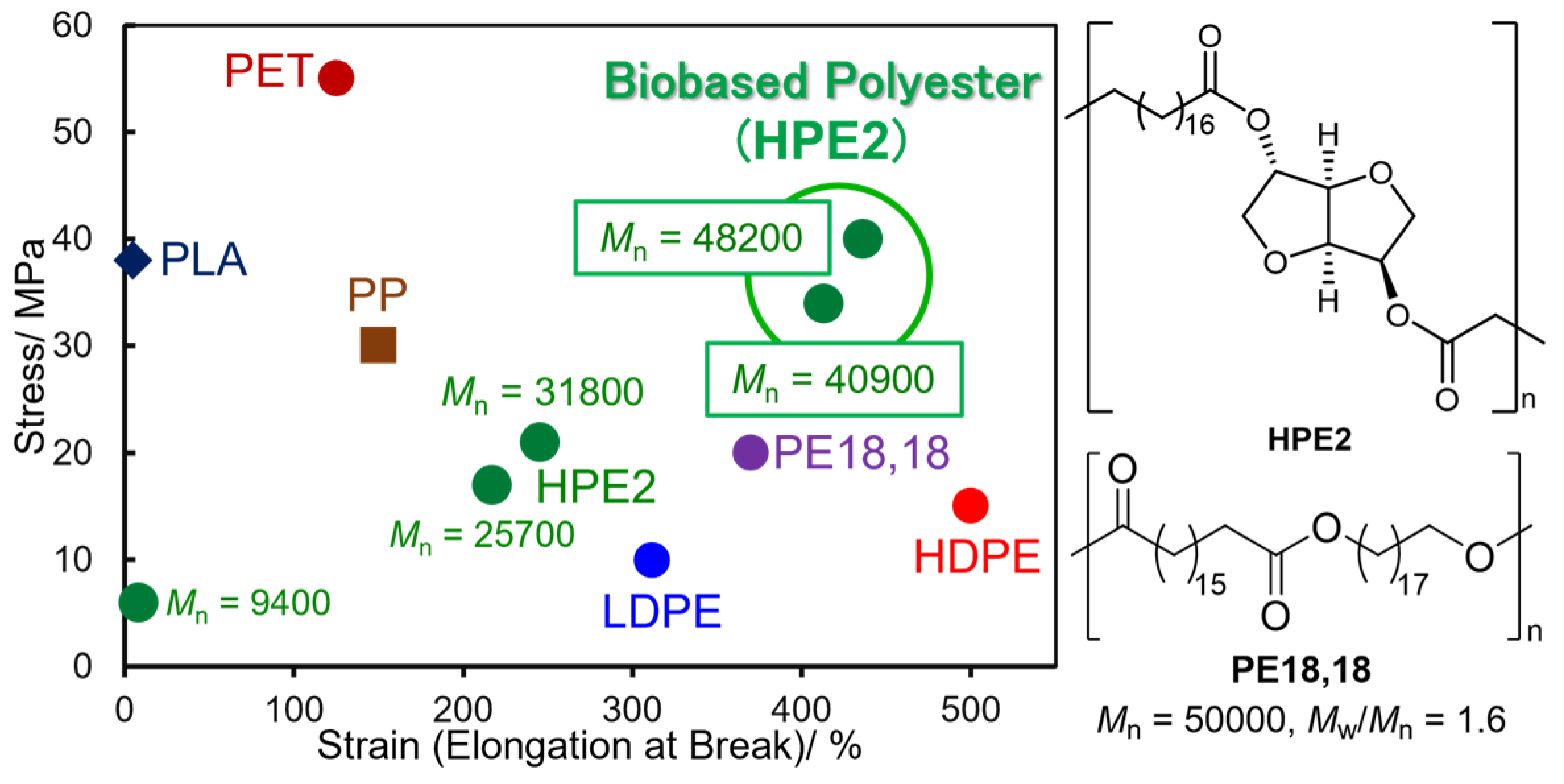
2.2. Synthesis of High Molecular Weight Polymers Exhibiting Tensile Properties Beyond Polyethylene, Polypropylene.
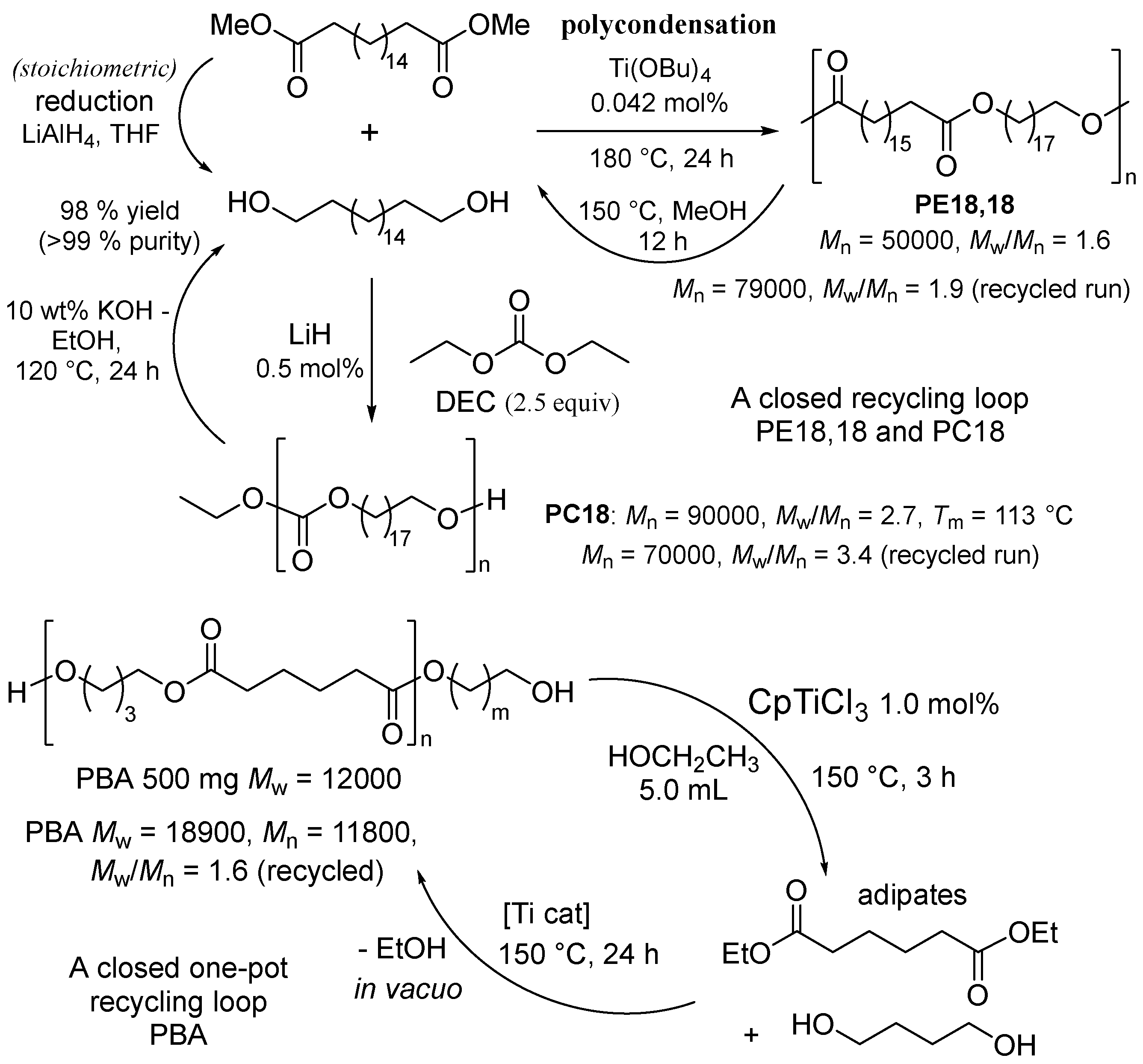
2.3. Chemical Recycling of Polyesters.
3. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selected reviews, book chapters, see references 1–11: Gandini, A., Polymers from renewable resources: A Challenge for the future of macromolecular materials. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 9491–9504. [CrossRef]
- Meier, M. A. R.; Metzger, J. O.; Schubert, U. S. Plant oil renewable resources as green alternatives in polymer science. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1788–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Larock, R. C. Vegetable oil-based polymeric materials: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1893–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, U.; Bornscheuer, U.; Meier, M. A. R.; Metzger, J. O.; Schäfer, H. J. Oils and fats as renewable raw materials in chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3854–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmyer, M. A.; Tolman, W. B. Aliphatic polyester block polymers: Renewable, degradable, and sustainable. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2390–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempfle, F.; Ortmann, P.; Mecking, S. Long-chain aliphatic polymers to bridge the gap between semicrystalline polyolefins and traditional polycondensates. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 4597–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monomers and polymers from chemically modified plant oils and their fatty acids. In Polymers from Plant Oils, 2nd Ed.; Gandini, A.; Lacerda, T. M. Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA and Scrivener Publishing LLC, Beverly, MA, USA, 2019, pp.33-82.
- Nomura, K.; Awang, N. W. B. Synthesis of bio-based aliphatic polyesters from plant oils by efficient molecular catalysis: A selected survey from recent reports. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 5486–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häußler, M.; Eck, M.; Rothauer, D.; Mecking, S. Closed-loop recycling of polyethylene-like materials. Nature 2021, 590, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermann, U.; Bornscheuer, U. T.; Feussner, I.; Meier, M. A. R.; Metzger, J. O. Fatty acids and their derivatives as renewable platform molecules for the chemical industry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20144–20165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worch, J. C.; Dove, A. P. 100th Anniversary of macromolecular science viewpoint: Toward catalytic chemical recycling of waste (and future) plastics. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishioka, R.; Kitakuni, E.; Ichikawa, Y. Aliphatic polyesters: “Bionolle”. In Biopolymers; Steinbüchel, A., Doi, Y., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; Vol. 4, pp. 275–297. [Google Scholar]
- Korshak, W. V.; Vinogradova, S. V. Polyesters of 1,20-eicosanediol. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR, Div. Chem. Sci. 1953, 2, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, C. W. The melting points of chain polymers. J. Polym. Sci. 1955, 16, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J. J.; Hillmyer, M. A.; Reineke, T. M. Isosorbide-based polymethacrylates. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mahmud, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Shen, Z.; Liu, X. Bio-based amorphous polyesters with high Tg: Trade-off between rigid and flexible cyclic diols. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6401–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M. E.; Long, T. E. Synthetic methods in step-growth polymers; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Le Fevere de Ten Hove, C.; Penelle, J.; Ivanov, D. A.; Jonas, A. M. Encoding crystal microstructure and chain folding in the chemical structure of synthetic polymers. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menges, M. G.; Penelle, J.; Le Fevere de Ten Hove, C.; Jonas, A. M.; Schmidt-Rohr, K. Characterization of long-chain aliphatic polyesters: Crystalline and supramolecular structure of PE22,4 elucidated by X-ray scattering and nuclear magnetic resonance. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 8714–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesle, P.; Stempfle, F.; Hess, S. K.; Zimmerer, J.; Río Bartulos, C.; Lepetit, B.; Eckert, A.; Kroth, P. G.; Mecking, S. Synthetic polyester from Algae oil. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6800–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atallah, P.; Wagener, K. B.; Schulz, M. D. ADMET: The future revealed. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 4735–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribyl, J.; Wagener, K. B.; Rojas, G. ADMET polymers: synthesis, structure elucidation, and function. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 14–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Abdellatif, M. M.; Nomura, K. Olefin metathesis polymerization: Some recent developments in the precise polymerizations for synthesis of advanced materials (by ROMP, ADMET). Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 619–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trnka, T. M.; Grubbs, R. H. The development of L2X2Ru=CHR olefin metathesis catalysts: An organometallic success story. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samojzowicz, C.; Bieniek, M.; Grela, K. Ruthenium-based olefin metathesis catalysts bearing N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3708–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubbs, R. H.; Wenzel, A. G.; O’Leary, D. J.; Khosravi, E. Eds. Handbook of Metathesis 2nd Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015.
- Vougioukalakis, G.; Grubbs, R. H. Ruthenium-based heterocyclic carbene-coordinated olefin metathesis catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1746–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskam, H. J.; Fox, H. H.; Yap, B. K.; McConville, H. D.; O`Dell, R.; Lichtenstein, J. B.; Schrock, R. R. Ligand variation in alkylidene complexes of the type Mo(CHR)(NR’)(OR”)2. J. Organomet. Chem. 1993, 459, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrock, R. R.; Hoveyda, A. H. Molybdenum and tungsten imido alkylidene complexes as efficient olefin-metathesis catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 4592–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- For example, Miyashita, T.; Kunisawa, M.; Sueki, S.; Nomura, K. Synthesis of poly(arylene vinylene)s containing different end groups by combined acyclic diene metathesis polymerization with Wittig-type coupling. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5288-5293. [CrossRef]
- Kojima, K.; Wang, X.; Go, L.; Makino, R.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shimoyama, D.; Abdellatif, M. M.; Kadota, J.; Hirano, H.; Nomura, K. , Synthesis of high molecular weight bio-based aliphatic polyesters exhibiting tensile properties beyond polyethylene. ACS Macro Lett. 2023, 12, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, A.; Meier, M. A. R. Acyclic diene metathesis with a monomer from renewable resources: Control of molecular weight and one-step preparation of block copolymers. ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokou, P. A.; Meier, M. A. R. Use of a renewable and degradable monomer to study the temperature-dependent olefin isomerization during ADMET polymerizations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1664–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulman, M.; Grubbs, R. H. Ruthenium carbene-based olefin metathesis initiators: Catalyst decomposition and longevity. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 7202–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, S. E.; Wagener, K. B. Comparison of the kinetics of acyclic diene metathesis promoted by Grubbs ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts. Macromolecules 2001, 35, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B. Catalysis at the interface of ruthenium carbene and ruthenium hydride chemistry: Organometallic aspects and applications to organic synthesis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 1865–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S. H.; Wenzel, A. G.; Salguero, T. T.; Day, M. W.; Grubbs, R. H. Decomposition of ruthenium olefin metathesis catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7961–7968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higman, C. S.; Lanterna, A. E.; Marin, M. L.; Scaiano, J. C.; Fogg, D. E. Catalyst decomposition during olefin metathesis yields isomerization-active ruthenium nanoparticles. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 2446–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawiczuk, M.; Marczyk, A.; Trzaskowski, B. Decomposition of ruthenium olefin metathesis catalyst. Catalysts 2020, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokou, P. A. : Meier, M. A. R. Studying and suppressing olefin isomerization side reactions during ADMET polymerizations. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzaskowski, J.; Quinzler, D.; Bährle, C.; Mecking, S. Aliphatic long-chain C20 polyesters from olefin metathesis. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 1352–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stempfle, F.; Ortmann, P.; Mecking, S. Which polyesters can mimic polyethylene? Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela, C.; Silvestre, A. J. D.; Meier, M. A. R. Plant oil-based long-chain C26 monomers and their polymers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2012, 213, 2220–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempfle, F.; Quinzler, D.; Heckler, I.; Mecking, S. Long-chain linear C19 and C23 monomers and polycondensates from unsaturated fatty acid esters. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4159–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumanet, P.-J.; Jarroux, N.; Goujard, L.; Le Petit, J.; Raoul, Y.; Bennevault, V.; Guégan, P. Synthesis of linear polyesters from monomers based on 1,18-(Z)-octadec-9-enedioic acid and their biodegradability. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 16853–16860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Chaijaroen, P.; Abdellatif, M. M. Synthesis of bio-based long-chain polyesters by acyclic diene metathesis polymerization and tandem hydrogenation and depolymerization with ethylene. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 18301–18312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortmann, P.; Mecking, S. Long-spaced aliphatic polyesters. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 7213–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Abdellatif, M. M.; Nomura, K. Synthesis of semi-crystalline long chain aliphatic polyesters by ADMET copolymerization of dianhydro-D-glucityl bis(undec-10-enoate) with 1,9-decadiene and tandem hydrogenation. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccini, M.; Leak, D. J.; Chuck, C. J.; Buchard, A. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 2681-2691. [CrossRef]
- Piccini, M.; Lightfoot, J.; Castro, D. B.; Buchard, A. Xylose-Based Polyethers and Polyesters Via ADMET Polymerizationtoward Polyethylene-Like Materials. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5870–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llevot, A.; Grau, E.; Carlotti, S.; Greliera, S.; Cramail, H. ADMET polymerization of bio-based biphenyl compounds. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 7693–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.; Samart, C.; Kongparakul, S.; Nomura, K. Synthesis of new polyesters by acyclic diene metathesis polymerization of bio-based α,ω-dienes prepared from eugenol and castor oil (undecenoate). RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 10245–10252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibert, G.; Grau, E.; Pintori, D.; Lecommandoux, S.; Cramail, H. ADMET polymerization of α,ω-unsaturated glycolipids: synthesis and physico-chemical properties of the resulting polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3731–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearouse, W. C.; Lillie, L. M.; Reineke, T. M.; Tolman, W. B. Sustainable Polyesters Derived from Glucose and Castor Oil: BuildingBlock Structure Impacts Properties. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillie, L. M. W.; Tolman, B. T.; Reineke, M. Structure/property relationships in copolymers comprising renewable isosorbide, glucarodilactone, and 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)-furan subunits. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3746–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebarbé, T.; Neqal, M.; Grau, E.; Alfos, C.; Cramail, H. Branched polyethylene mimicry by metathesis copolymerization of fatty acid-based α,ω-dienes. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q. Structures and Interactions of Ionic Liquids, Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S. Ionic Liquids. Physicochemical Properties; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Liu, X.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Multiscale studies on ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6636–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; He, H.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Dong, K.; Huo, F.; Zhang, S. Insights into ionic liquids: From Z-bonds to quasi-liquids. JACS Au 2022, 2, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, J.; Xin, J.; Zhang, S. Efficient biomass pretreatment process based on the simple reuse of a low-viscosity ionic-liquid solvent system. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 12738–12750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, J.; Lu, X.; Xin, J.; Zhang, S. High aluminum content beta zeolite as an active Lewis acid catalyst for γ-valerolactone decarboxylation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 11841–11848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amesho, K. T. T.; Lin, Y.-C.; Mohan, S. V.; Halder, S.; Ponnusamy, V. K.; Jhang, S.-R. Deep eutectic solvents in the transformation of biomass into biofuels and fine chemicals: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022. web released. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, S.; Yao, X.; Kang, Y.; Xin, J.; Ibrahim, T.; Xu, J.; Lu, X. A Renewable co-solvent promoting the selective removal of lignin by increasing the total number of hydrogen bonds. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 6393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simocko, C.; Yang, Y.; Swager, T. M.; Wagener, K. B. Metathesis step-growth polymerizations in ionic liquid. ACS Macro Letters. 2013, 2, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, D.; Autenrieth, B.; Buchmeiser, M. R. First acyclic diene metathesis polymerization under biphasic conditions using a dicationic ruthenium alkylidene: access to high-molecular-weight polymers with very low ruthenium contamination. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponkratov, D. O.; Shaplov, A. S.; Vygodskii, Y. S. Metathesis polymerization in ionic media. Polym. Sci., Ser. C. 2019, 61, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selected reports for ADMET polymerization in high boiling point solvent, refs. 63-65: Weychardt, H.; Plenio, H. Acyclic diene metathesis polymerization of divinylarenes and divinylferrocenes with Grubbs-type olefin metathesis catalysts. Organometallics 2008, 27, 1479-1485. [CrossRef]
- Sydlik, S. A.; Delgado, P. A.; Inomata, S.; VanVeller, B.; Yang, Y.; Swager, T. M.; Wagener, K. B. Triptycene-containing polyetherolefins via acyclic diene metathesis polymerization. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, J. M.; Romero, Z.; Moreno, A.; Huber, D. L.; Simocko, C. ADMET polymerization in affordable, commercially available, high boiling solvents. SN Applied Sciences 2020, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Nomura, K. Synthesis of high molecular weight bio-based aliphatic polyesters by acyclic diene metathesis polymerization in ionic liquids. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 7222–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chin, A. L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Tong, R. Resilient poly(α-hydroxy acids) with improved strength and ductility via scalable stereosequence-controlled polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 16813–16823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, K.; Aoki, T.; Ohki, Y.; Kikkawa, S.; Yamazoe, S. Transesterification of methyl-10-undecenoate and poly(ethylene adipate) catalyzed by (cyclopentadienyl)titanium trichlorides as model chemical conversions of plant oils and acid-, base-free chemical recycling of aliphatic polyesters. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 12504–12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohki, Y.; Ogiwara, Y.; Nomura, K. Depolymerization of polyesters by transesterification with ethanol using (cyclopentadienyl)titanium trichlorides. Catalysts 2023, 13, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
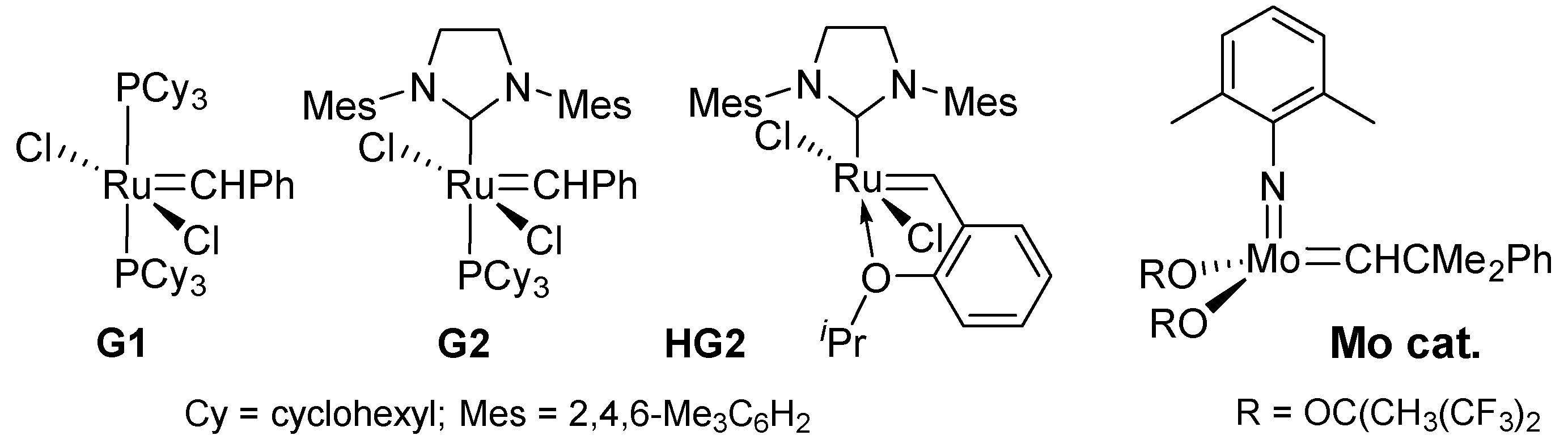
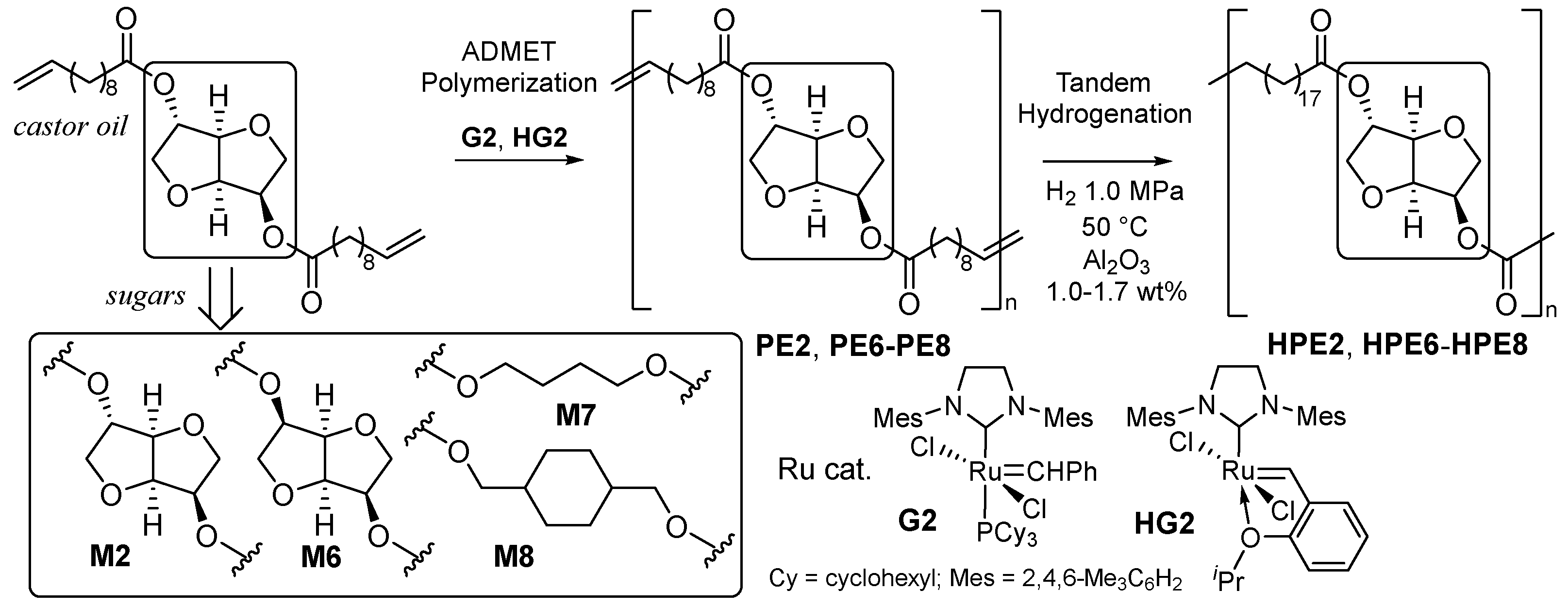
| Ru cat. | temp. / °C |
nitrogen purge 2 | Mn3 | Mw/Mn3 | isomerization 4 / % |
| G2 | 60 | no | 5600 | 1.65 | 48 |
| G1 | 70 | no | 4400 | 1.57 | 3 |
| G2 | 70 | no | 6000 | 1.71 | 49 |
| G1 | 80 | no | 4750 | 1.56 | 4 |
| G2 | 80 | no | 6100 | 1.61 | 69 |
| G1 | 80 | yes | 6600 | 1.77 | 3 |
| G2 | 80 | yes | 8400 | 1.75 | 76 |
| G1 | 90 | no | 5450 | 1.69 | 3 |
| G2 | 90 | no | 6200 | 1.65 | 66 |
| G1 | 100 | no | 5000 | 1.61 | 42 5 |
| monomer | yield 2/ % | Mn3 | Mw/Mn3 |
| M2 | 93 | 39,200 | 1.95 |
| M24 | 86 | 37,500 | 1.91 |
| M6 | 92 | 26,000 | 1.95 |
| M7 | 89 | 33,400 | 2.30 |
| M7 4 | 87 | 34,900 | 1.82 |
| M8 | 94 | 38,800 | 3.38 |
| monomer (μmol) | cat./ mol% | yield 2/ % | Mn3 / g·mol-1 | Mw/Mn3 |
| M2 (90.5) | 5.0 | 99 | 16000 | 1.79 |
| M2 (90.5) | 2.5 | 90 | 25100 | 1.43 |
| M2 (90.5) | 1.0 | 88 | 34400 | 1.49 |
| M2 (272) | 1.0 | 88 | 46100 | 2.08 |
| M2 (272) | 1.0 | 91 | 46100 | 1.84 |
| M6 (272) | 1.0 | 87 | 34800 | 1.87 |
| M19 (272) | 1.0 | 99 | 67200 | 2.27 |
| M2 (272) | 0.5 | 90 | 48700 | 2.04 |
| M2 (543) 4 | 0.5 | 91 | 49400 | 2.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).