Submitted:
06 January 2024
Posted:
08 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Modification of the Material
2.3. Sample Characterization
2.4. Cell Development Processes
2.5. Evisceration of the Eyeball
3. Results
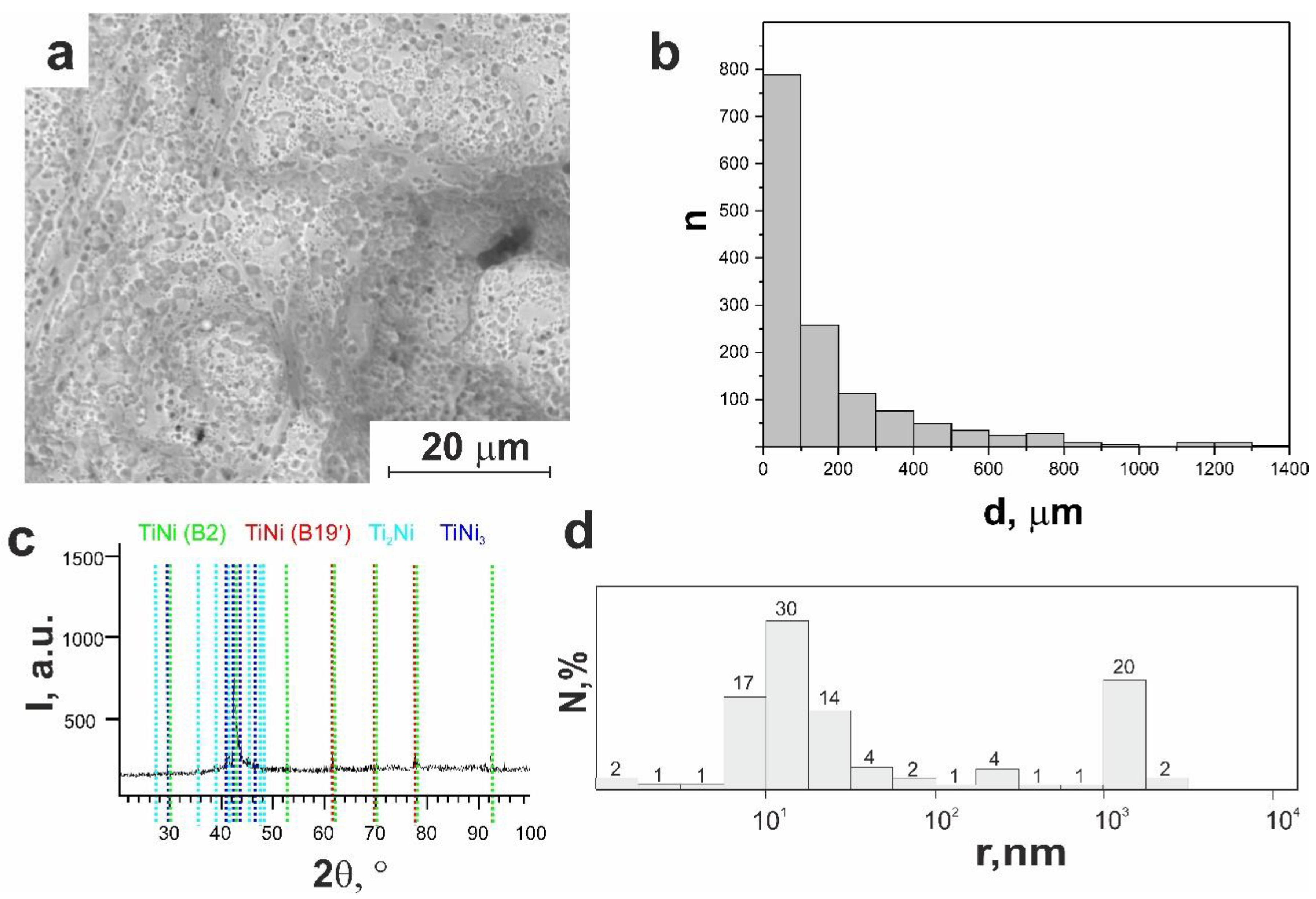
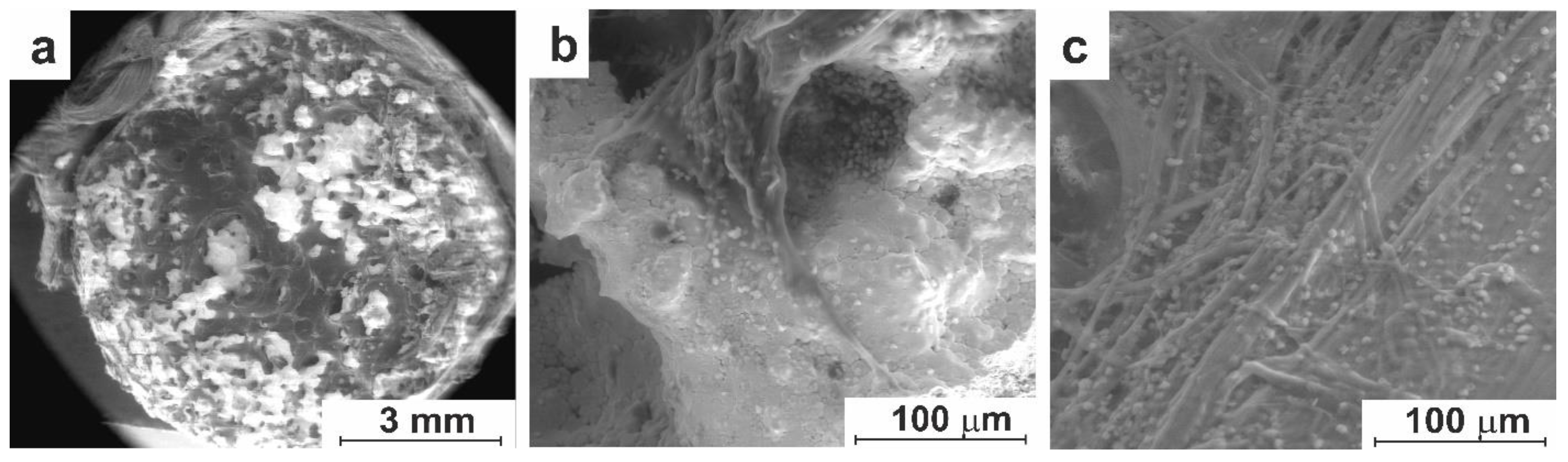
3.1. Structural Studies of TiNi Material before and after Modification
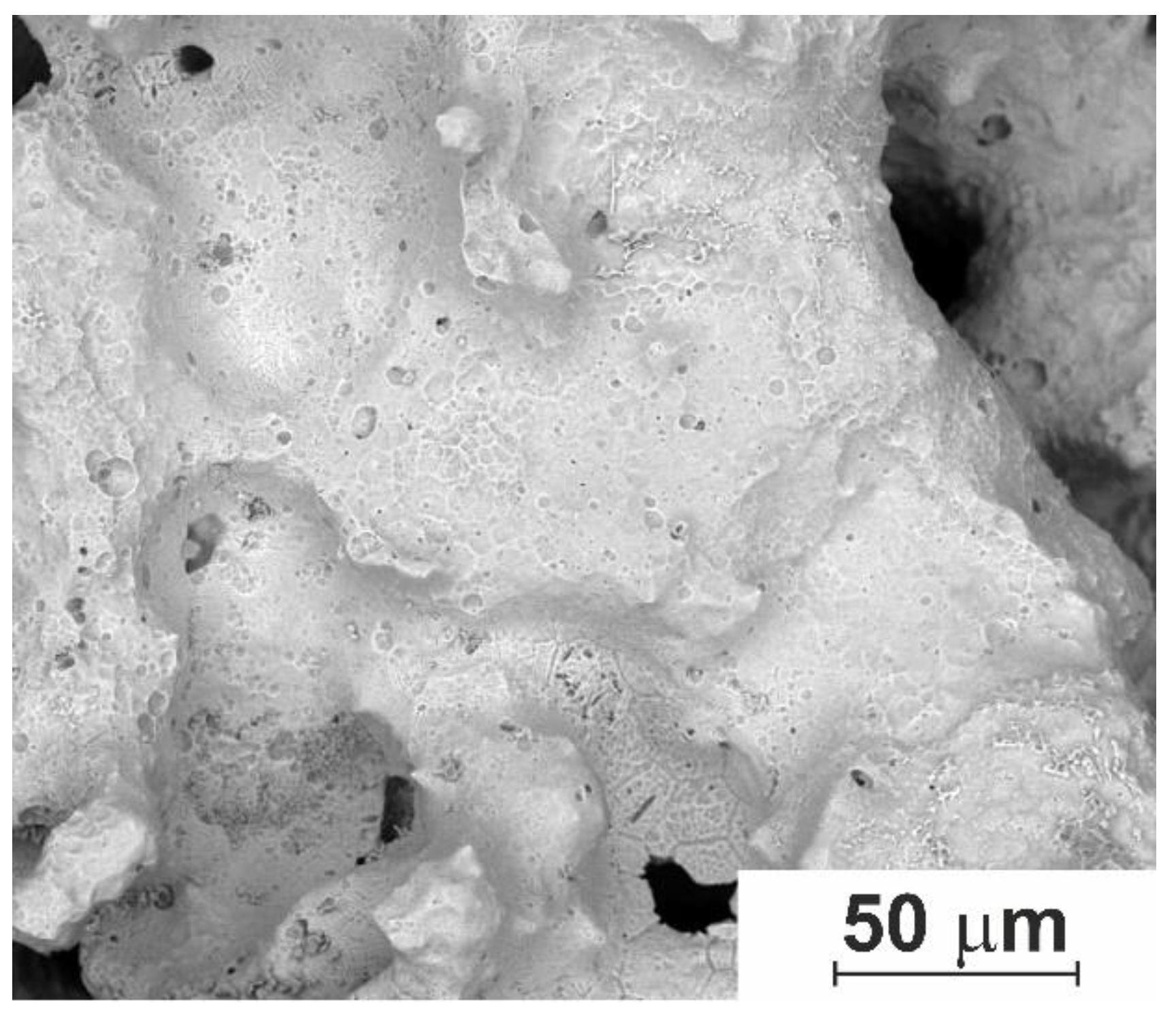
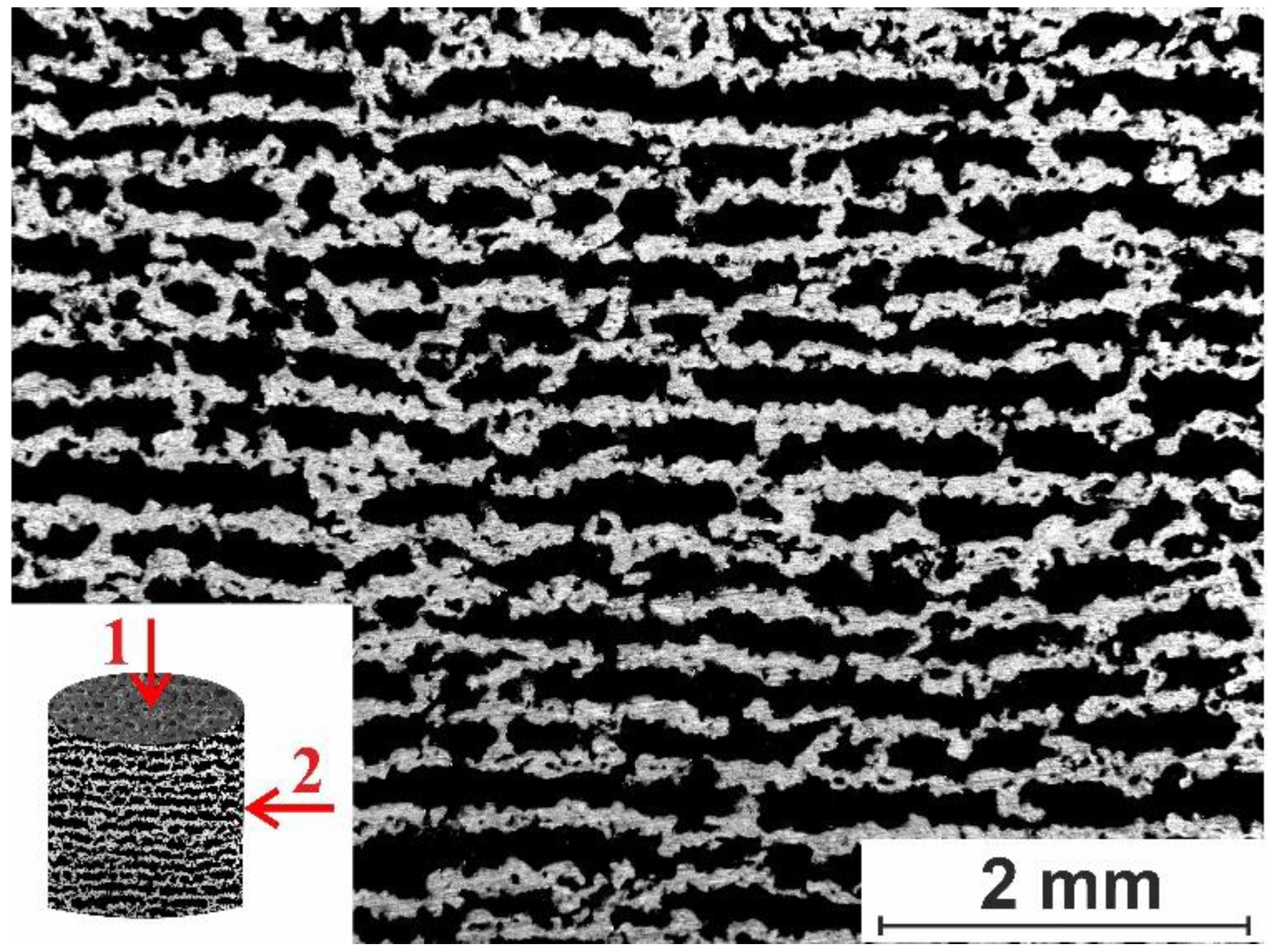
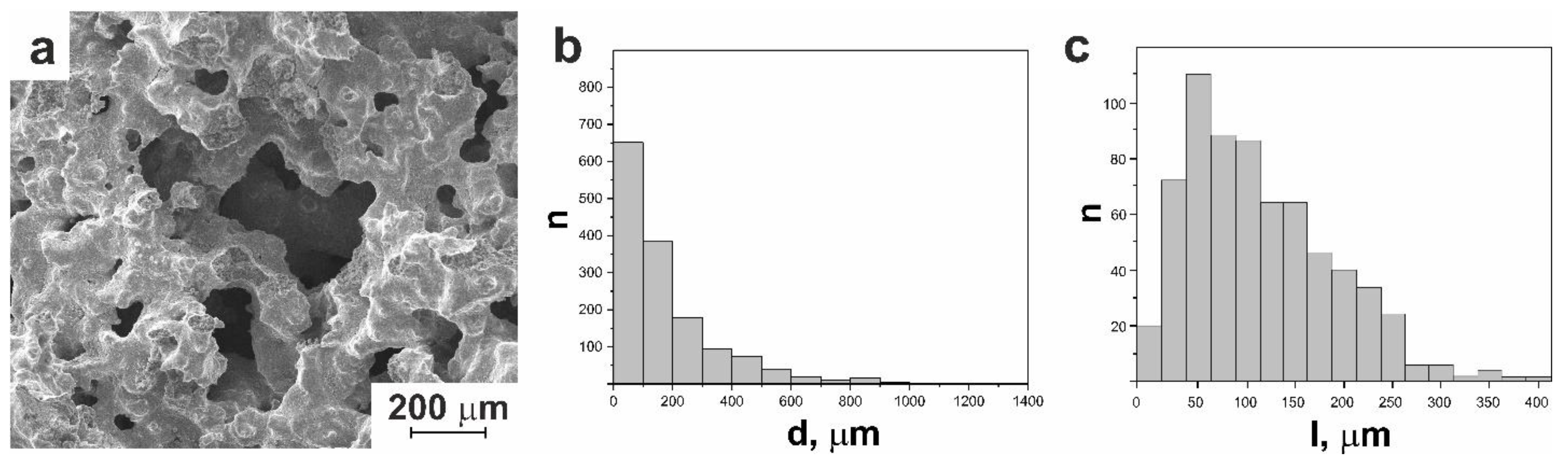
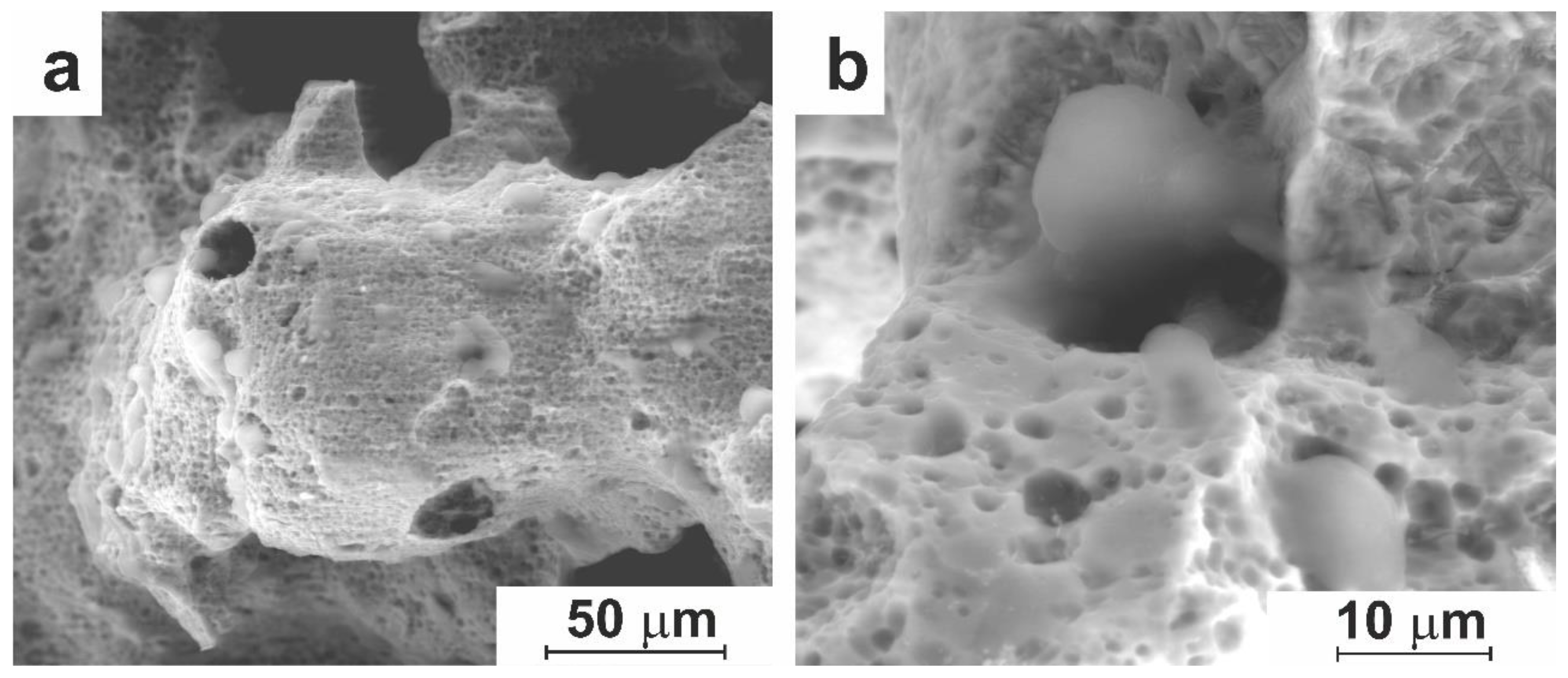
3.1.1. Macro- and Micro-Porous Structure and Permeability of Material
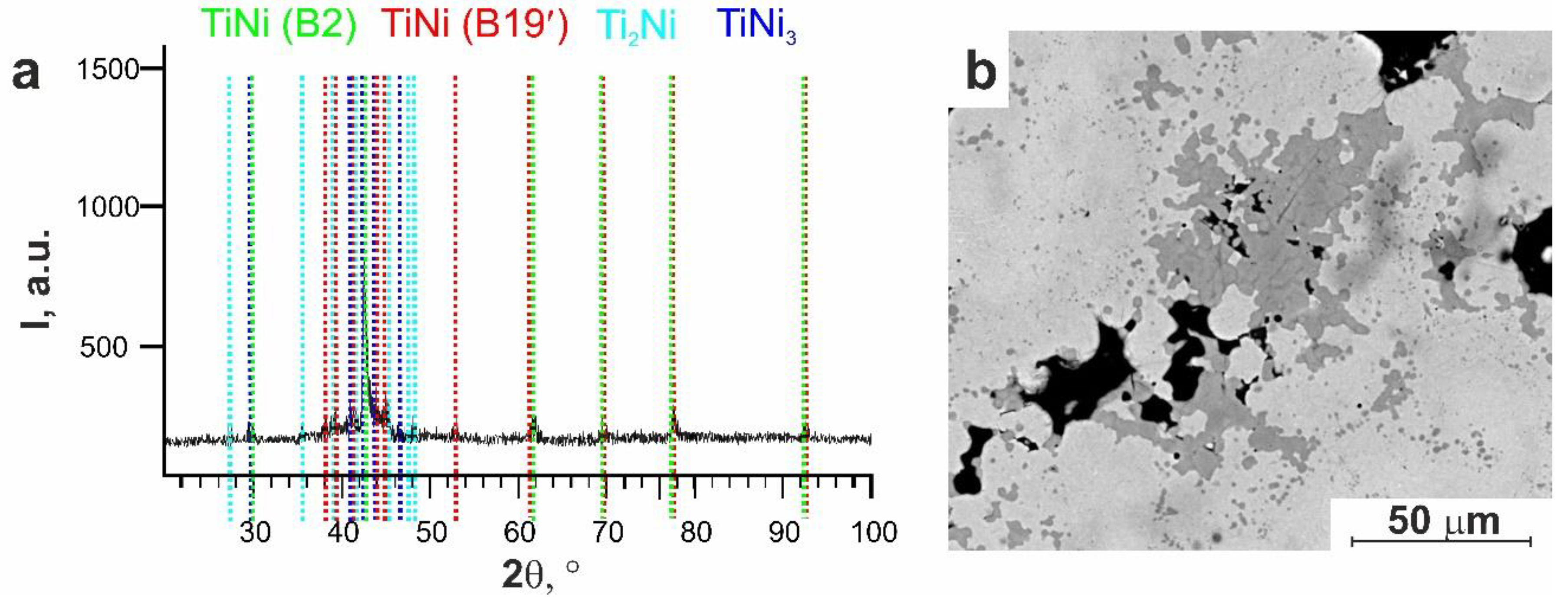
3.1.2. Surface Phase Composition
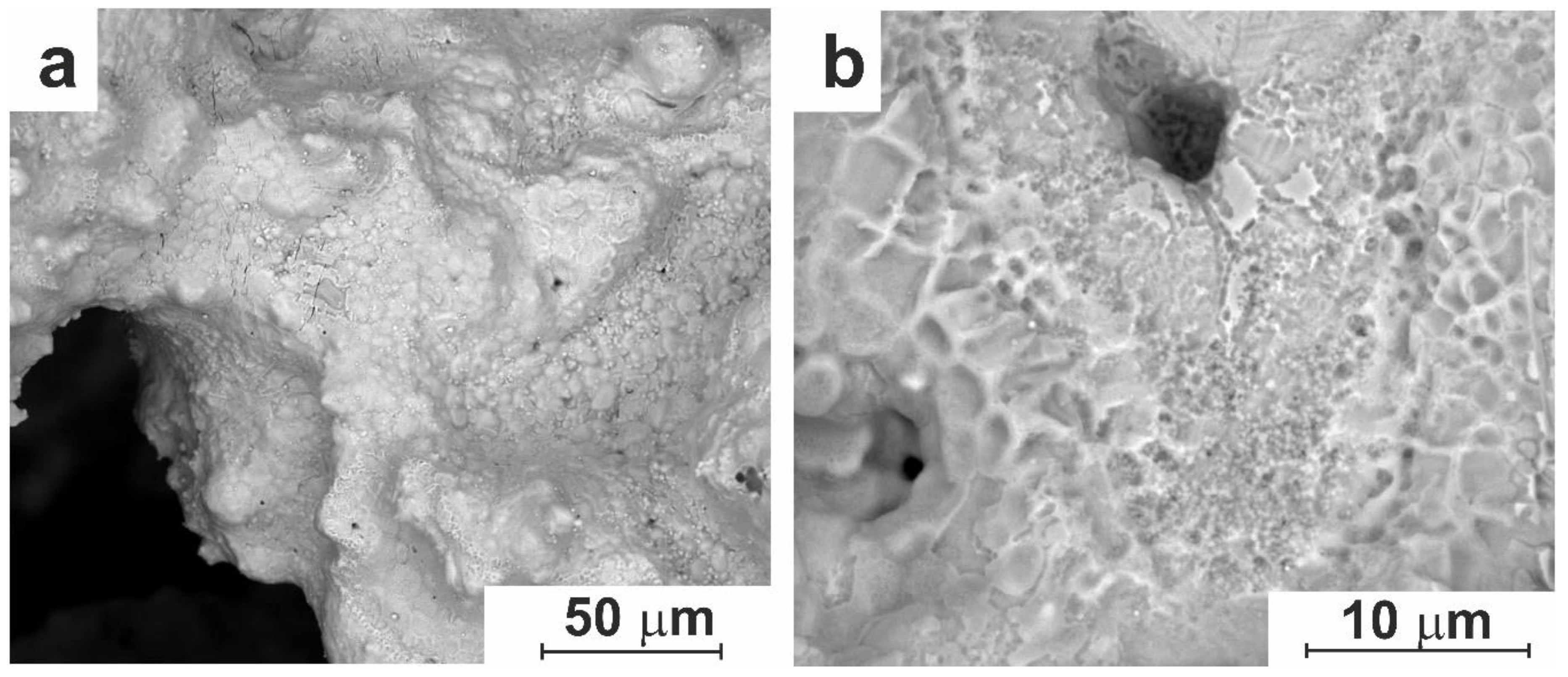
3.1.3. Surface Modifications via Etching
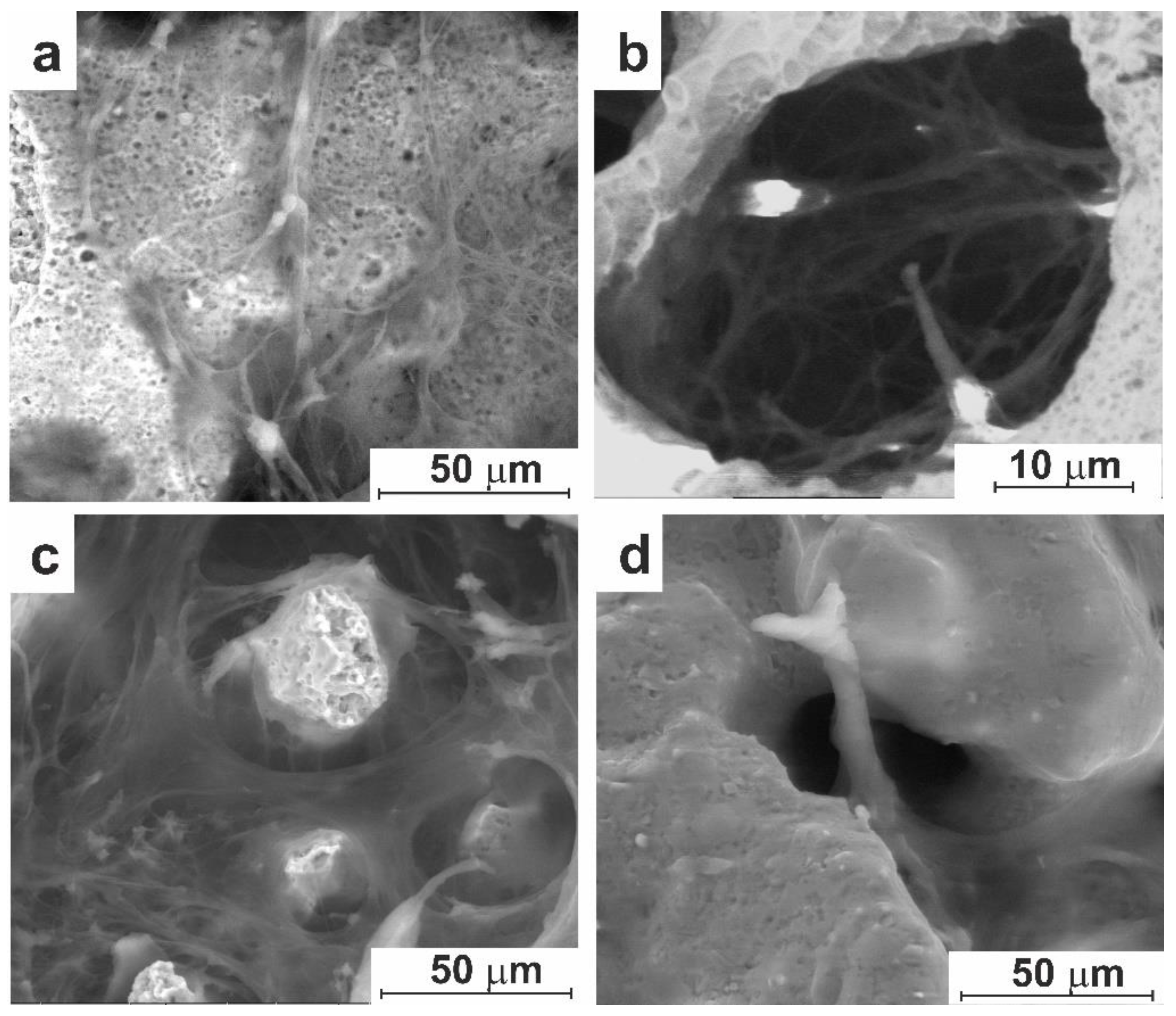
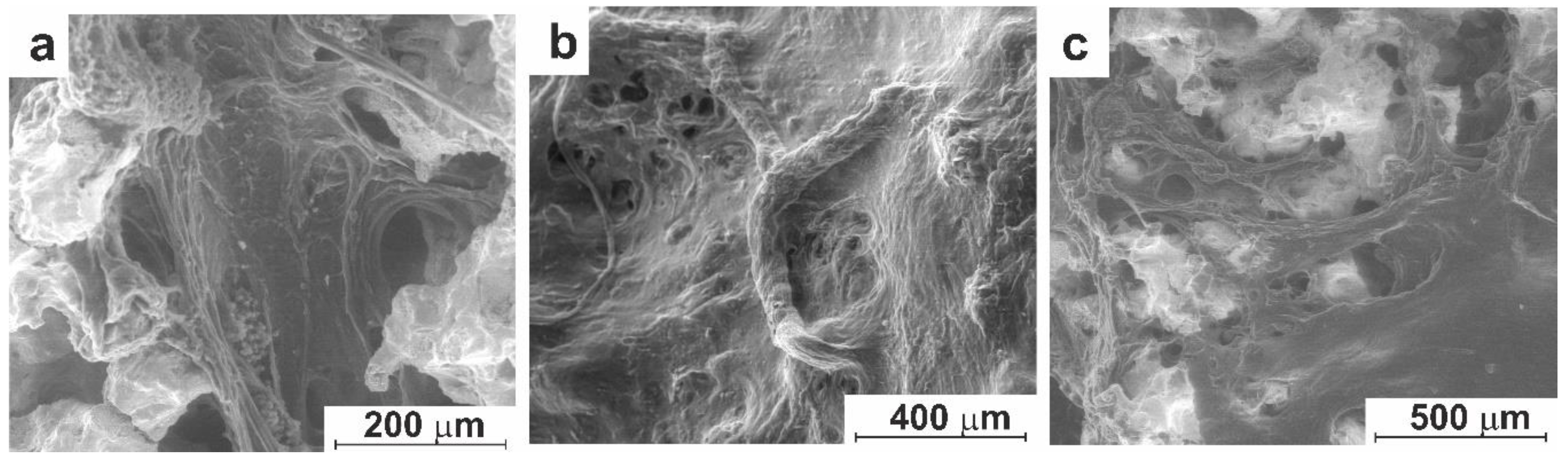
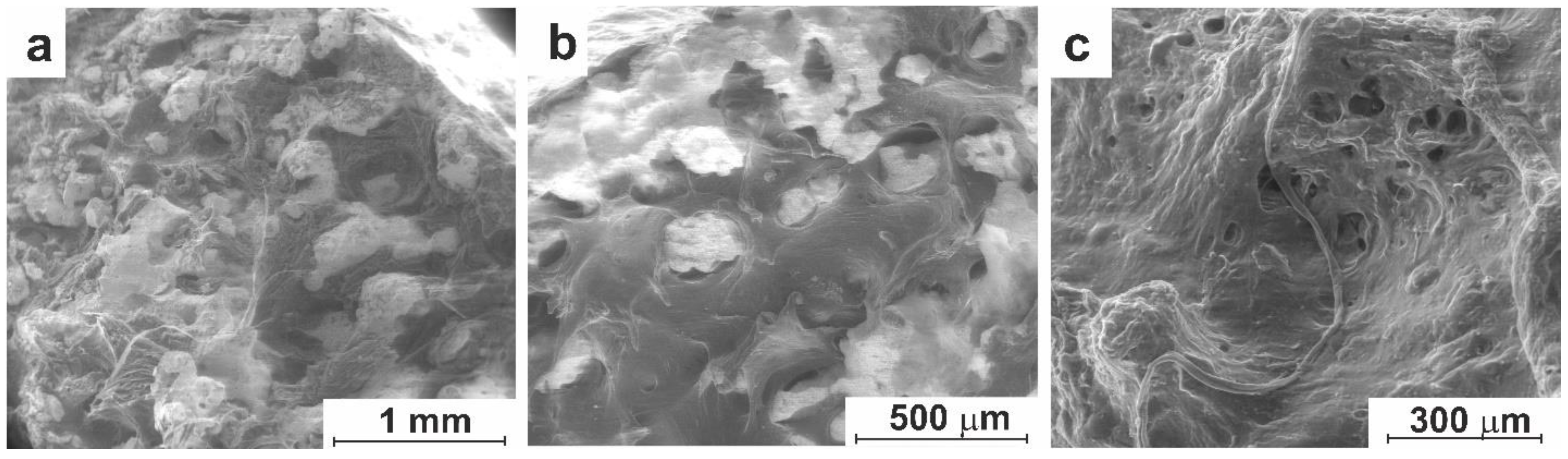
3.2. In Vitro Experiment
3.2.1. Cell Culture Cultivation
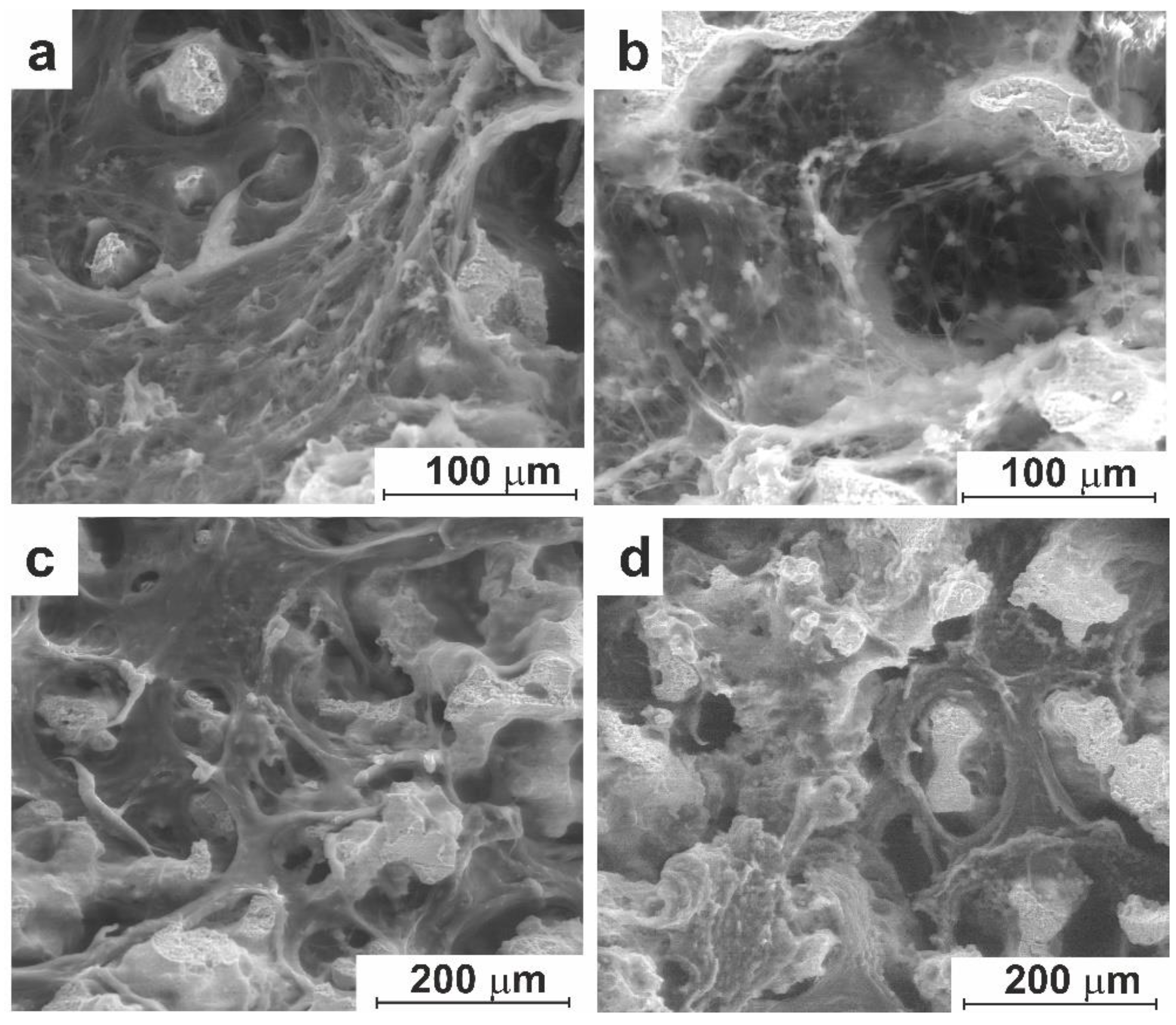
3.3. In-Vivo Studies
3.3.1. Experiment on Animals
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.Y.; Yang, X.; Fan, X.L. The Evolution of Orbital Implants and Current Breakthroughs in Material Design, Selection, Characterization, and Clinical Use. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliori, M.E. Enucleation versus Evisceration. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2002, 13, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, J. Outcomes of orbital implants after evisceration and enucleation in patients with endophthalmitis. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2010, 21, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundorova, R.A. Traumas of the Eye.; GEOTAR-Media: Moscow, Russia, 2014; p. 560. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Filatova, I.A.; Mokhammad, I.M. The modified method for evisceration in the case of buphthalmos with the use of a combination of orbital implants. Russian Pediatric Ophthalmology 2017, 12, 210–215. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castela, G. Manual of Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 1st ed.; Sociedade Portuguesa de Oftalmologia: Lisbon, Portugal, 2016; p. 308. [Google Scholar]
- Ruchi, D. S.; Ramesh, M. S.; Vinay, A.; Setabutr, P. Evisceration and Enucleation: A National Survey of Practice Patterns in the United States. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging 2012, 43, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verigo, E.N.; Gundorova, R.A.; Sadovskaya, E.P. A comparative study of the stump and prosthesis mobility depending on the technique of eye enucleation. Russian Ophthalmological Journal 2012, 5, 14–19. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Luzjanina, V.V.; Egorov, V.V.; Smoljakova, G.P. Study of the properties of implants for oculomotor ocular stump grafting. Vestnik of the Orenburg State University 2009, 12, 84–87. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Naumenko, L.V.; Malinovskii, G.F.; Krasnyi, S.A.; Zhilyaeva, E.P. The use of allotransplant from the subcutaneous fat with plantar aponeurosis for the musculoskeletal stump formation during enucleation. Novosti Khirurgii 2021, 29, 191–197. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, K.E.; Raphael, S.S. Ocular Reactions to Plastic Materials (Polyethylene and Teflon). Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1961, 52, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitzer, S.; Simionescu, C.; Alexandrescu, C.; Burcea, M. The Anophthalmic Socket - Reconstruction Options. J. Med. Life 2014, 7, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Astakhov, Yu.S. , Nikolajenko V.P., D’yakov V. E. The use of PTFE implants in ophthalmology.; Foliant: Sankt-Peterburg, Russia, 2007; p. 256. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tsurova, L.M.; Milyudin, E.S. Comparative analysis of using different orbital implants to form postenucleational locomotor stump. Vestnik of the Orenburg State University 2014, 12, 334–337. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ivolgina, I.V. The peculiarities of the use of different implants in musculoskeletal stump formation after enucleation. Tambov University Reports. Series Natural and Technical Sciences 2015, 20, 577–580. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chalasani, R.; Poole-Warren, L.; Max Conway, R.; Ben-Nissan, B. Porous Orbital Implants in Enucleation: A Systematic Review. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2007, 52, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custer, P.L.; Kennedy, R.H.; Woog, J.J.; Kaltreider, S.A.; Meyer, D.R. Orbital Implants in Enucleation Surgery A Report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmol. 2003, 110, 2054–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoamanesh, A.; Pang, N.K.; Oestreicher, J.H. Complications of Orbital Implants: A Review of 542 Patients Who Have Undergone Orbital Implantation and 275 Subsequent PEG Placements. Orbit 2007, 26, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J. S.; Lew, H.; Kim, S. J.; S. Y.Lee. Exposure Rate of Hydroxyapatite Orbital Implants: A 15-Year Experience of 802 Cases. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 566–572.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filatova, I.A.; Verigo, E.N.; Pryahina, I.A. Ophthalmectomy: characteristics of ophthalmic pathology, clinical manifestation of mechanical trauma, time constraints and methods of surgery. Head and Neck Russian Journal 2014, 3, 30–35. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Grusha, la. O.; Fedorov, A.A.; Baranov, P. Yu.; Bakayeva, T.V.; Pavlyuk, A.S. Study of the three-dimensional structure and biointegrative characteristics of porous orbital implant materials. Vestnik Oftalmologii 2010, 126, 9–13. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alwitry, A.; West, S. K.; King, J.; Foss, A.J.; Abercrombie, L.C. Long-Term Follow-up of Porous Polyethylene Spherical Implants After Enucleation and Evisceration. Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 23, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziubla, T.D.; Lowman, A.M. Vascularization of PEG-Grafted Macroporous Hydrogel Sponges: A Three-Dimensional in Vitro Angiogenesis Model Using Human Microvascular Endothelial Cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2004, 68, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, Y.A.; Krivosheina, O.I.; Zapuskalov, I.V. Implant of porous titanium nickelide impregnated with autologous blood monocytes for the formation of orbital stump in the experiment. Bulletin of Siberian Medicine 2011, 10, 12–14. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, V.E.; Khodorenko, V.N.; Chekalkin, T.L. Medical Materials with Shape Memory. In Medical Materials and Shape Memory Implants, 1st ed.; NPP «MIC»: Tomsk, Russia, 2011; p. 534. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zapuskalov, I.V.; Gyunter, V.E.; Steblyuk. Shape memory implants in ophthalmology; NPP «MIC»: Tomsk, Russia, 2012; p. 189. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of TiNi based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, G.; Ozler, L.; Kaya, M.; Orhan, N. A Study on Microstructure and Porosity of NiTi Alloy Implants Produced by SHS. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 487, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, G.; Zhou, Y.; Xiangdong, D.; Otsuka, K.; Nakamura, K.; Sun, J.; Ren, X. Does Order-Disorder Transition Exist in near-Stoichiometric Ti-Ni Shape Memory Alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 2897–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldan, I.; Frenzel, J.; Shekhah, O.; Chelmowski, R.; Birkner, A.; Wöll, Ch. Surface of Ti-Ni Alloys after Their Preparation. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 470, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelatko, J.; Freitag, M.; Rak, J.; Wierzchoń, T.; Goryczka, T. Structure. of Nitride and Nitride/Oxide Layers Formed on NiTi Alloy. Solid State Phenom. 2012, 186, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.L.; Wang, R.M.; Hu, T.; Yin, L.H.; Pu, Y.P.; Lin, P.H.; Wu, S.L.; Chung, C.Y.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Chu, P. K. Surface Structure and Biomedical Properties of Chemically Polished and Electropolished NiTi Shape Memory Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2008, 28, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Ma, Y.; Fan, Q.-C. Investigation of the Mechanism of Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis of TiNi. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 2437–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Zhang, L.N.; Wong, C.T.; Chan, K.C.; Yue, T.M. Fabrication and Characteristics of Porous NiTi Shape Memory Alloy Synthesized by Microwave Sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2011, 528, 6006–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, J.M.; Leary, M.; Subic, A.; Gibson, M.A. A Review of Shape Memory Alloy Research, Applications and Opportunities. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 1078–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.; Hastings, G. Handbook of Biomaterial Properties; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; p. 590. [Google Scholar]
- Bansiddhi, A.; Sargeant, T.D.; Stupp, S.I.; Dunand, D.C. Porous NiTi for Bone Implants: A Review. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayers, R. A.; Burkes, D.; Gottoli, G.; Yi, H.C.; Moore, J.J. The Application of Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis of Engineered Porous Composite Biomedical Materials. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2007, 22, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-B.; Yoon, K.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Nam, T.-H. Smart Materials-Fundamentals and Applications. In Vivo Result of Porous TiNi Shape Memory Alloy: Bone Response and Growth. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Panton, B.; Mao, Y.; Dawood, N.M.; Kadhum, A.-R.; Ali, A.; Atiyah, A.A. Fabrication of Porous NiTi Shape Memory Alloy Objects by Powder Metallurgy for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 4483–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagoudas, D.C.; Vandygriff, E.L. Processing and Characterization of NiTi Porous SMA by Elevated Pressure Sintering. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2002, 13, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anikeev, S.; Hodorenko, V.; Chekalkin, T.; Gunther, V. E.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, J.-S. Fabrication and Study of Double Sintered TiNi-Based Porous Alloys. Smart Materials and Structures 2017, 26, 057001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Zhu, M.; Chung, C.Y. Biomedical Porous Shape Memory Alloys for Hard-Tissue Replacement Materials. Materials (Basel). 2018, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, D.; Shao, C.; Yi, M.; Zhang, B. Effects of Pore Size and Porosity of Surface-Modified Porous Titanium Implants on Bone Tissue Ingrowth. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 2534–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansiddhi, A.; Sargeant, T.D.; Stupp, S.I.; Dunand, D.C. Porous NiTi for Bone Implants: A Review. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, G.; Pandit, A.; Apatsidis, D.P. Fabrication Methods of Porous Metals for Use in Orthopaedic Applications. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2651–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkovsky, I. V; Volova, L.T.; Kuznetsov, M. V; Morozov, Y.G.; Parkin, I.P. Porous Biocompatible Implants and Tissue Scaffolds Synthesized by Selective Laser Sintering from Ti and NiTi. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisner, L.L.; Markov, A.B.; Proskurovsky, D.I.; Rotshtein, V.P.; Ozur, G.E.; Meisner, S.N.; Yakovlev, E.V.; Poletika, T.M.; Girsova, S.L.; Semin, V.O. Effect of inclusions on cratering behavior in TiNi shape memory alloys irradiated with a low-energy, high-current electron beam. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2016, 302, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisner, L.L.; Markov, A.B.; Rotshtein, V.P.; Ozur, G.E.; Meisner, S.N.; Yakovlev, E.V.; Gudimova, E.Y. Formation of microcraters and hierarchically-organized surface structures in TiNi shape memory alloy irradiated with a low-energy, high-current electron beam. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1683, 020145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.F. Materials Selection in Mechanical Design, 1st ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2011; p. 513. [Google Scholar]
- Saldan, I.; Frenzel, J.; Shekhah, O.; Chelmowski, R.; Birkner, A. Surface of Ti-Ni Alloys after Their Preparation. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 470, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, M.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Khalil-Allafi, J.; Khoshghadam-Pireyousefan, M.; Mostafaei, A. In-situ formation of TiN-TiO2 composite layer on NiTi shape memory alloy via fluidized bed reactor. Ceramics International 2020, 46, 21097–21106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrvarz, A.; Khalil-Allafi, J.; Etminanfar, M.; Mahdavi, S. The study of morphological evolution, biocorrosion resistance, and bioactivity of pulse electrochemically deposited Hydroxyapatite/ZnO composite on NiTi superelastic alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 423, 127628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, H.; Lan, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Pore structures of high-porosity NiTi alloys made from elemental powders with NaCl temporary space-holders. Materials Letters 2009, 63, 2402–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansiddhi, A.; Dunand, D.C. Shape-memory NiTi foams produced by replication of NaCl space-holders. Acta Biomaterialia 2008, 4, 1996–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnina, N.; Rubanik jr., V.; Rubanik, V.; Belyaev, S.; Bysha, V.; Kalganov, V.; Chepela, D. Influence of pre-heating temperature and ultrasonic vibration treatment on the structure and martensitic transformations in NiTi foams produced by SHS. Lett. Mater. 2022, 12, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnina, N.; Palani, I.A.; Belyaev, S.; Singh, S.; Liulchak, P.; Karaseva, U.; Mani Prabu, S.S.; Jayachandran, S.; Kalganov, V.; Iaparova, E.; Demidova, E. Influence of Heat Treatment on the Structure and Martensitic Transformation in NiTi Alloy Produced by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Materialia 2021, 20, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Mitra, I.; Avila, J.D.; Upadhyayula, M.; Bose, S. Porous metal implants: processing, properties, and challenges. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2023, 5, 032014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemenz, P.C. Foundations of Colloid Science, 3rd ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, USA, 1997; p. 650. [Google Scholar]
- Che, H.-Q.; Ma, Y.; Fan, Q.-C. Investigation of the mechanism of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of TiNi. J Mater Sci. 2011, 46, 2437–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, V.E.; Khodorenko, V.N.; Chekalkin, T.L. Problems of biocompatibility of metallic materials. Implants with Shape Memory 2011, 1–2, 5–16. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Itin, V.I.; Pribytkov, G.A.; Khlusov, LA.; Zagrebin, L.V.; Shestov, S.S. Implant-carrier of cells made of porous permeable titanium. Cellular Transplantation and Tissue Engineering 2006, 1, 59–63. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, A.R.A.; Chaplain, M.A.J.; Rejniak, K. A.; Fozard, J.A. Single-Cell-Based Models in Biology and Medicine. Mathematical Medicine and Biology. A Journal of the IMA 2008, 25, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, Y. M. Cell as an architectural miracle. Cytoskeleton, capable of feeling and remembering. Soros Educational Journal. Biology 1996, 4, 4–10. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




