Submitted:
29 December 2023
Posted:
29 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Bobos River Basin
2.2. Sampling
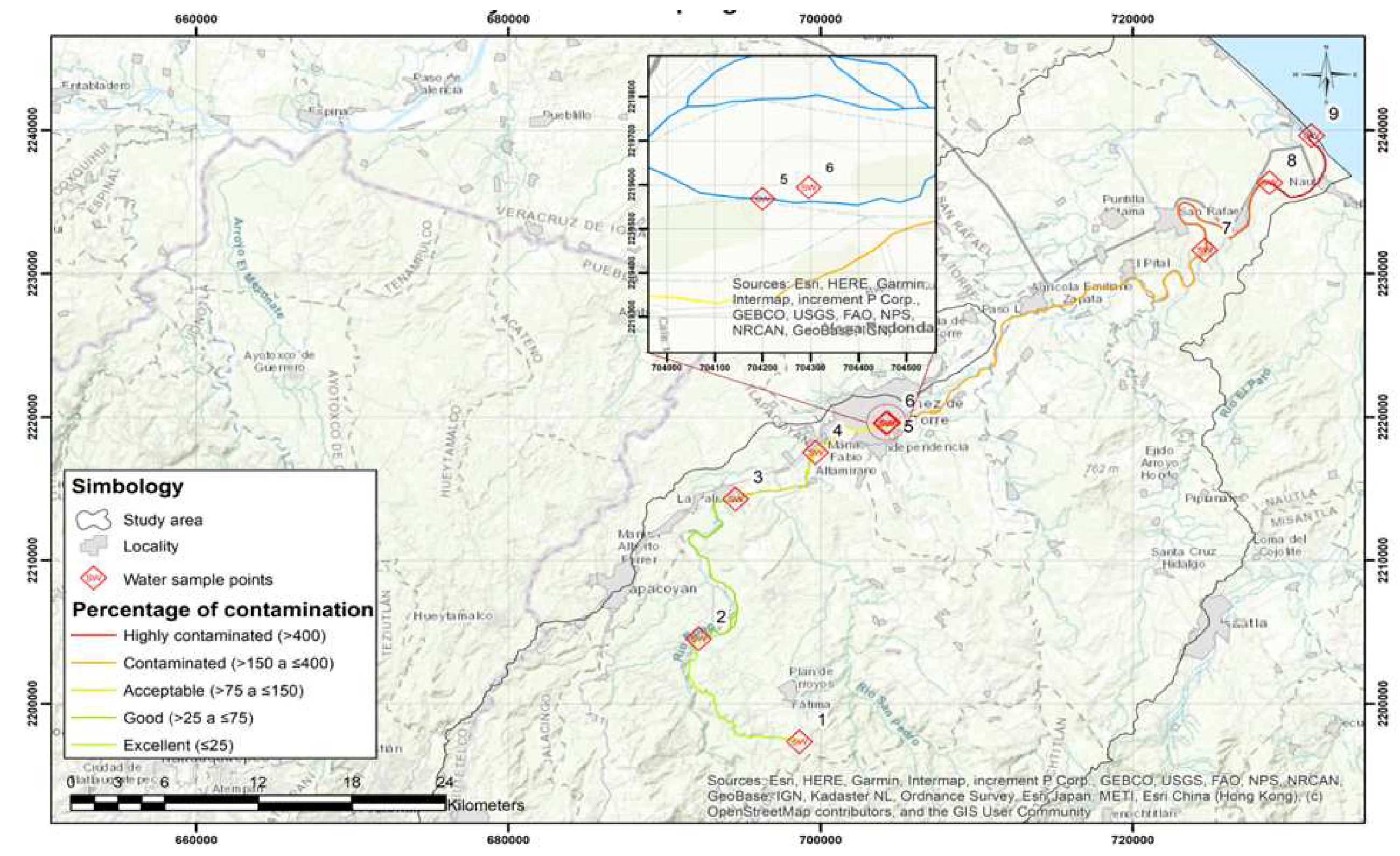
2.2.1. Area of Study
2.2.2. Water Samples
2.2.3. Quantification of NaOH (%)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen
3.2. pH and conductivity
3.3. Total Nitrogen, N-NO3-, and Total Phosphorus, P-PO4-

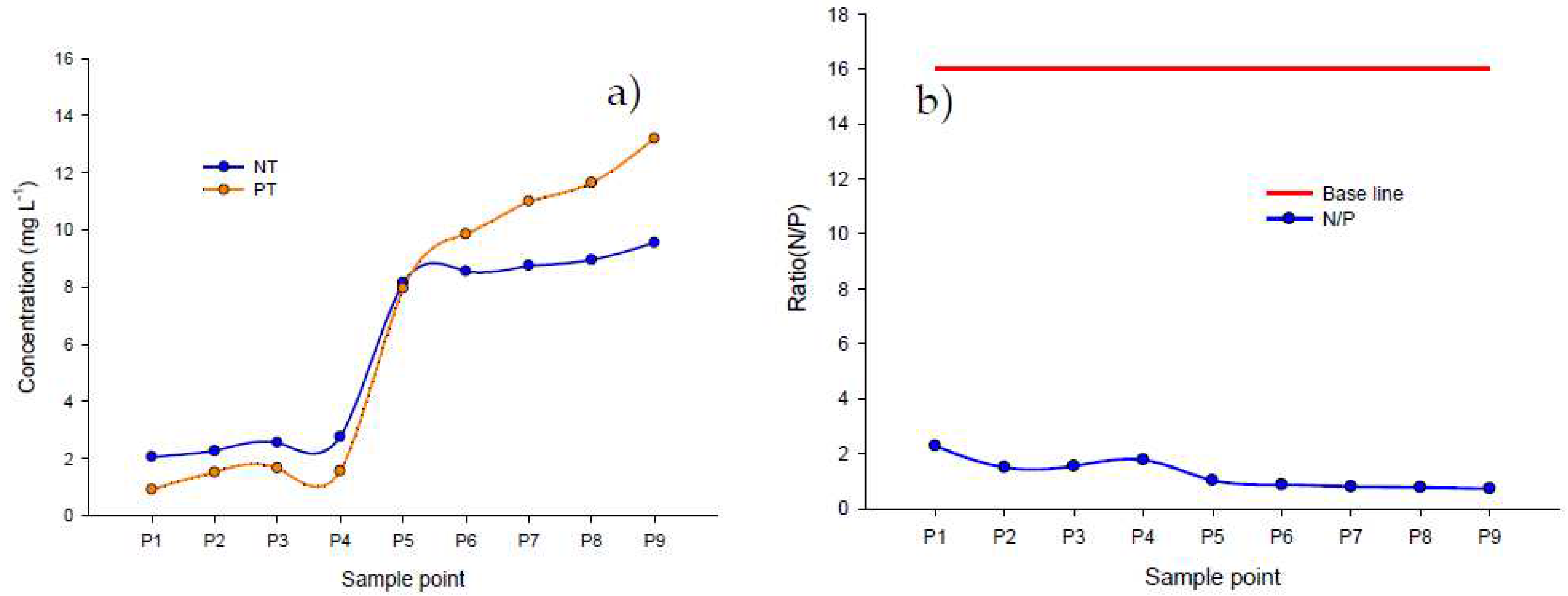
3.4. Nitrogen/Phosphorus and conductivity/DS ratio
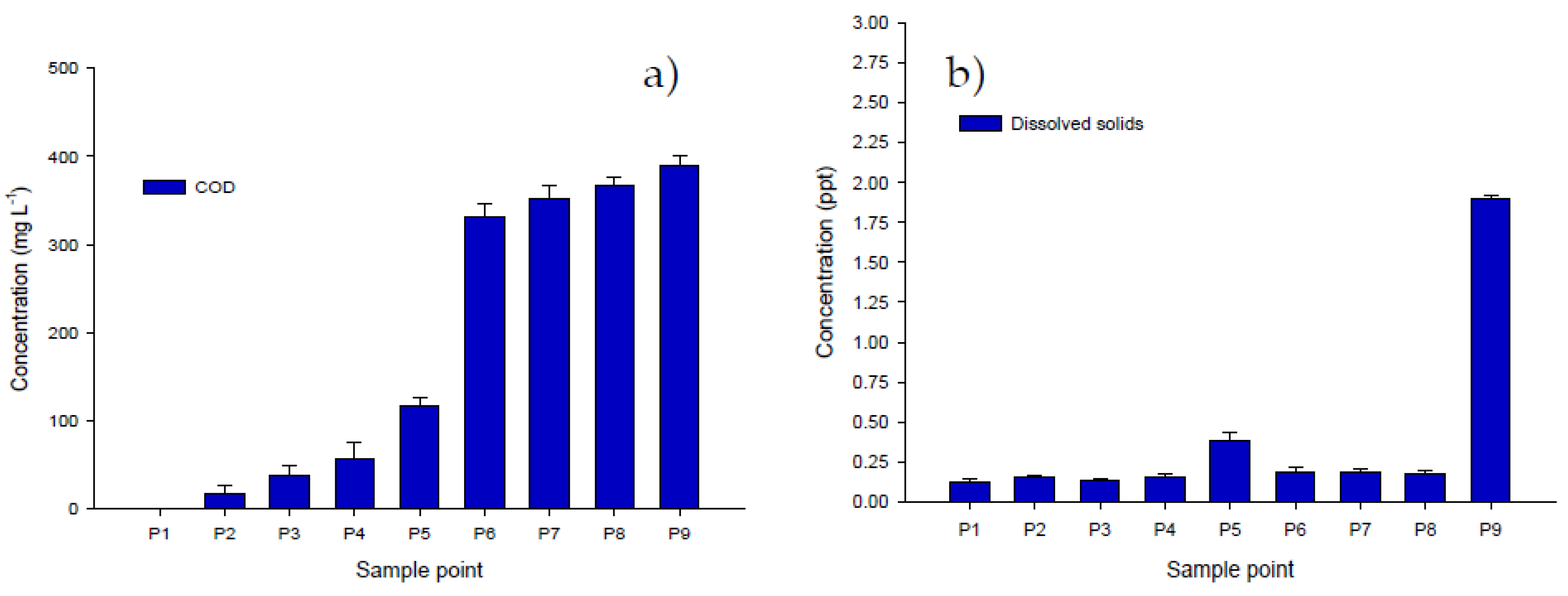
3.3. Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
3.6. Fecal coliforms (FC)
3.7. Quantification of NaOH (%)
3.8. Statistical Analysis
3.8.1. Pearson correlation
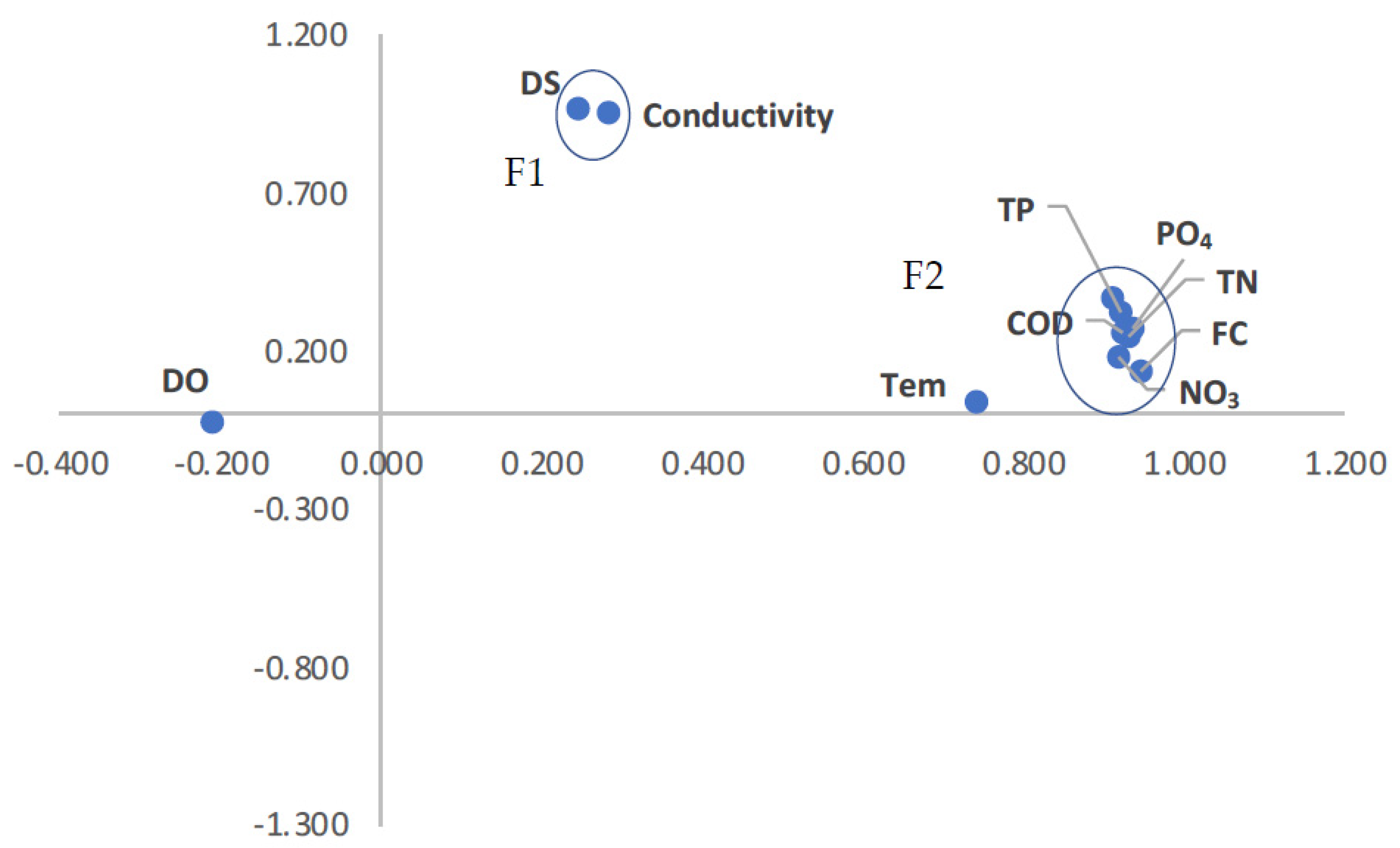
3.8.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
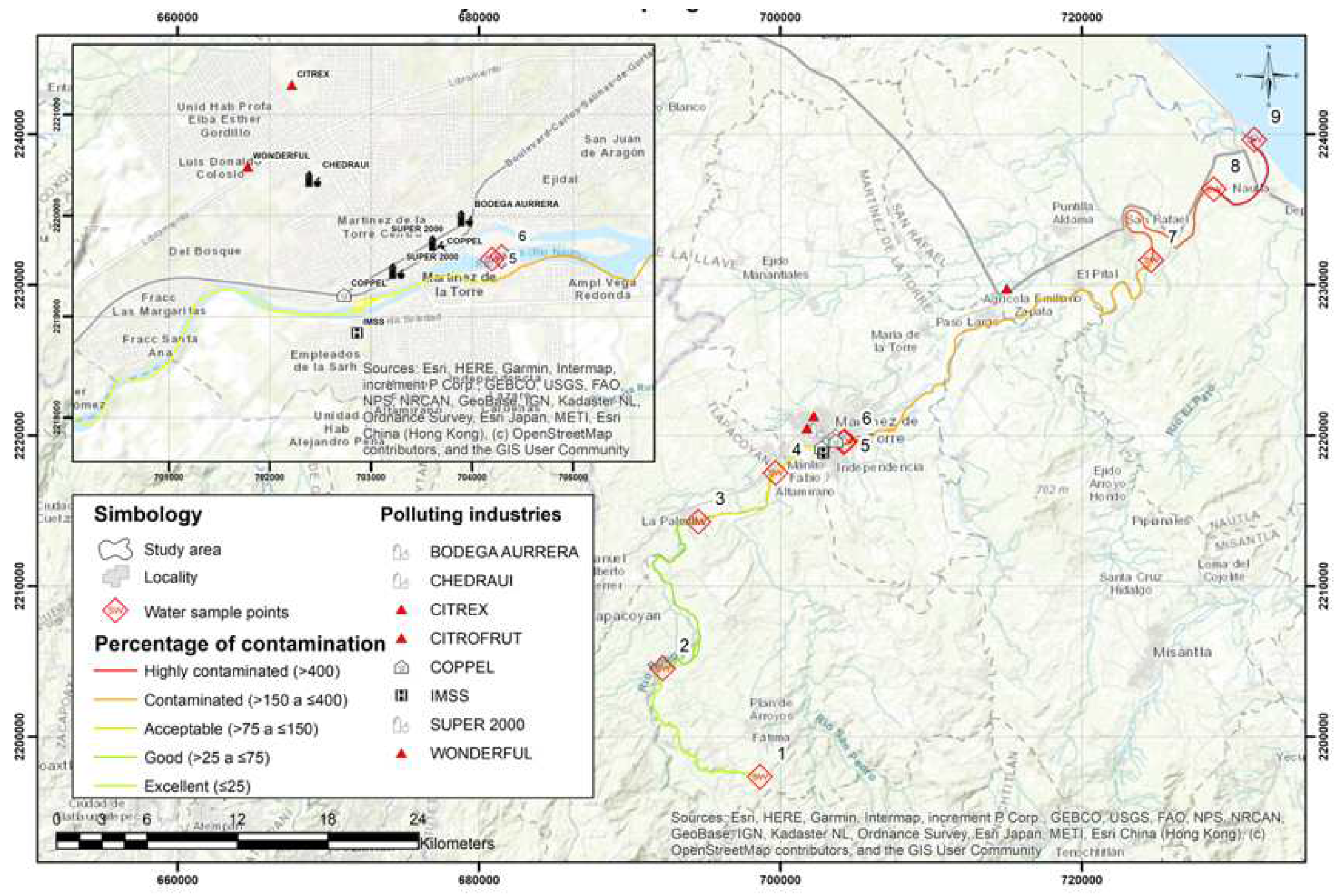
3.9. The environmental impact of Martinez de la Torre, Veracruz on the Bobos River
3.9. Preventive measures to avoid contamination of the Bobos River and to maintain sustainable development in the region.
4. Conclusions
References
- M. Strokal et al., “Urbanization: an increasing source of multiple pollutants to rivers in the 21st century,” npj Urban Sustainability, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 24, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Jiang and B. C. O’Neill, “Global urbanization projections for the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways,” Global Environmental Change, vol. 42, pp. 193–199, Jan. 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Diamond et al., “Use of prospective and retrospective risk assessment methods that simplify chemical mixtures associated with treated domestic wastewater discharges,” Environ Toxicol Chem, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 690–702, Mar. 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Singh, P. Yadav, A. K. Pal, and V. Mishra, “Water Pollutants: Origin and Status,” 2020, pp. 5–20. [CrossRef]
- S. T. Coelho, “Existing Barriers for WtE in Developing Countries and Policy Recommendations,” in Municipal Solid Waste Energy Conversion in Developing Countries, Elsevier, 2020, pp. 219–234. [CrossRef]
- M. C. M. Blettler, N. Garello, L. Ginon, E. Abrial, L. A. Espinola, and K. M. Wantzen, “Massive plastic pollution in a mega-river of a developing country: Sediment deposition and ingestion by fish (Prochilodus lineatus),” Environmental Pollution, vol. 255, p. 113348, Dec. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Islam, M. K. Ahmed, M. Raknuzzaman, M. Habibullah -Al- Mamun, and M. K. Islam, “Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country,” Ecol Indic, vol. 48, pp. 282–291, Jan. 2015. [CrossRef]
- E. Calizza et al., “Isotopic biomonitoring of N pollution in rivers embedded in complex human landscapes,” Science of The Total Environment, vol. 706, p. 136081, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Ju, S. Li, Y. Xu, G. Zhang, and J. Zhang, “Intensive Livestock Production Causing Antibiotic Pollution in the Yinma River of Northeast China,” Water (Basel), vol. 11, no. 10, p. 2006, Sep. 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Wu and J. Lu, “Landscape patterns regulate non-point source nutrient pollution in an agricultural watershed,” Science of The Total Environment, vol. 669, pp. 377–388, Jun. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. del Refugio Castañeda-Chávez, F. Lango-Reynoso, and G. Navarrete-Rodríguez, “Study on Contamination by Heavy Metals in the Cotaxtla-Jamapa Basin with Influence in the Central Zone of the Gulf of Mexico,” Water Air Soil Pollut, vol. 231, no. 3, p. 99, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- D. Chalchisa, M. Megersa, and A. Beyene, “Assessment of the quality of drinking water in storage tanks and its implication on the safety of urban water supply in developing countries,” Environmental Systems Research, vol. 6, no. 1, p. 12, Jan. 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Xiao, L. Wang, L. Deng, and Z. Jin, “Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau,” Science of The Total Environment, vol. 650, pp. 2004–2012, Feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Gobierno del Estado de Veracruz, “Diagnóstico Cuenca del Río Nautla,” http://www.veracruz.gob.mx/proteccioncivil/wp-content/uploads/sites/5/2021/12/Diagn%C3%B3stico-Cuenca-del-rio-Nautla.pdf.
- Procuraduría Estatal de Protección al Medio Ambiente de Veracruz, “Programa de Ordenamiento Ecológico de la Cuenca del Río Bobos,” http://www.veracruz.gob.mx/medioambiente/poecrb/.
- APHA, “Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Pollution Control Federation.” Washington, EUA., p. 1035, 1995.
- USEPA, “Methods for chemical analysis of water and wastes,” Report No. EPA-600/4-79-020. Washington, EUA, p. 544, 1983.
- R. Abdi and T. Endreny, “A River Temperature Model to Assist Managers in Identifying Thermal Pollution Causes and Solutions,” Water (Basel), vol. 11, no. 5, p. 1060, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. T. Demetillo, M. V. Japitana, and E. B. Taboada, “A system for monitoring water quality in a large aquatic area using wireless sensor network technology,” Sustainable Environment Research, vol. 29, no. 1, p. 12, Dec. 2019. [CrossRef]
- O. Bozorg-Haddad, M. Delpasand, and H. A. Loáiciga, “Water quality, hygiene, and health,” in Economical, Political, and Social Issues in Water Resources, Elsevier, 2021, pp. 217–257. [CrossRef]
- K. Dębska, B. Rutkowska, W. Szulc, and D. Gozdowski, “Changes in Selected Water Quality Parameters in the Utrata River as a Function of Catchment Area Land Use,” Water (Basel), vol. 13, no. 21, p. 2989, Oct. 2021. [CrossRef]
- I. Giri, R. K.C., and U. R. Khadka, “Water quality status in Bagmati river of Kathmandu valley, Nepal,” in Ecological Significance of River Ecosystems, Elsevier, 2022, pp. 481–502. [CrossRef]
- N. Zhao, Z. Fan, and M. Zhao, “A New Approach for Estimating Dissolved Oxygen Based on a High-Accuracy Surface Modeling Method,” Sensors, vol. 21, no. 12, p. 3954, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Hazen, J. Craig, C. Good, and L. Crowder, “Vertical distribution of fish biomass in hypoxic waters on the Gulf of Mexico shelf,” Mar Ecol Prog Ser, vol. 375, pp. 195–207, Jan. 2009. [CrossRef]
- M. Dai et al., “Oxygen depletion in the upper reach of the Pearl River estuary during a winter drought,” Mar Chem, vol. 102, no. 1–2, pp. 159–169, Nov. 2006. [CrossRef]
- T. Rajendiran, C. Sabarathinam, B. Panda, and V. Elumalai, “Influence of Dissolved Oxygen, Water Level and Temperature on Dissolved Organic Carbon in Coastal Groundwater,” Hydrology, vol. 10, no. 4, p. 85, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- F. Akhter, H. R. Siddiquei, M. E. E. Alahi, and S. C. Mukhopadhyay, “Recent Advancement of the Sensors for Monitoring the Water Quality Parameters in Smart Fisheries Farming,” Computers, vol. 10, no. 3, p. 26, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- O. Mitryasova and V. Pohrebennyk, “Hydrochemical Indicators of Water System Analysis as Factors of the Environmental Quality State,” 2020, pp. 91–104. [CrossRef]
- M. P. Patel, B. Gami, A. Patel, P. Patel, and B. Patel, “Climatic and anthropogenic impact on groundwater quality of agriculture dominated areas of southern and central Gujarat, India,” Groundw Sustain Dev, vol. 10, p. 100306, Apr. 2020. [CrossRef]
- I. B. Koki and A. S. Bayero, “Assessment of Water Quality in Rivers and Lakes With Respect to Heavy Metals and General Water Quality Parameters: A Review.,” Int J Sci Res, vol. 4, 2016.
- A. Mathur, “Conductivity: Water Quality Assesment,” International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 1–3, 2015.
- E. A. Ríos-Villamizar, M. T. F. Piedade, J. G. Da Costa, J. M. Adeney, and W. J. Junk, “Chemistry of different Amazonian water types for river classification: a preliminary review,” Sep. 2013, pp. 17–28. [CrossRef]
- S. R., Carpenter, N. F., Caraco, D. L., Correll, R. W., Howarth, A. N., Sharpley, and V. H. Smith, “Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen,” Ecological applications, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 559–568, 1998. [CrossRef]
- Z. Rivas et al., “Nitrógeno y fósforo totales de los ríos tributarios al sistema lago de Maracaibo, Venezuela,” Interciencia, vol. 34, no. 5, pp. 308–314, 2009.
- Secretaría de Salud y Asistencia, “Salud ambiental, agua para uso y consumo humano-Lí-mites permisibles de calidad y tratamientos a que debe someterse el agua para su potabilización.,” NOM-127-SSA1-1994. https://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=4866379&fecha=18/01/1996#gsc.tab=0.
- R. Bhateria and D. Jain, “Water quality assessment of lake water: a review,” Sustain Water Resour Manag, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 161–173, Jun. 2016. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, “Guidelines for drinking-water quality,” World Health Organization, 2011.
- V. M. Arteaga-Cortez, A. Quevedo-Nolasco, D. H. del Valle-Paniagua, M. Castro-Popoca, Á. Bravo-Vinaja, and J. A. Ramírez-Zierold, “Estado del arte: una revisión actual a los mecanismos que realizan los humedales artificiales para la remoción de nitrógeno y fósforo,” Tecnología y ciencias del agua, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 319–342, Sep. 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. O. Fadiran, S. C. Dlamini, and A. Mavuso, “A comparative study of the phosphate levels in some surface and ground water bodiesof Swaziland</b>,” Bull Chem Soc Ethiop, vol. 22, no. 2, Jul. 2008. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu, Y. Zhu, X. Qiao, B. Zheng, S. Chang, and Q. Fu, “Investigation of nitrogen and phosphorus contents in water in the tributaries of Danjiangkou Reservoir,” R Soc Open Sci, vol. 5, no. 1, p. 170624, Jan. 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. M. Penn, J. J. Pauer, and R. J. Mihelcic, “Biochemical Oxygen Demand,” vol. II, 2017.
- A. Grzyb, A. Wolna-Maruwka, and A. Niewiadomska, “The Significance of Microbial Transformation of Nitrogen Compounds in the Light of Integrated Crop Management,” Agronomy, vol. 11, no. 7, p. 1415, Jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Lee, S. Lee, S. Yu, and D. Rhew, “Relationships between water quality parameters in rivers and lakes: BOD5, COD, NBOPs, and TOC,” Environ Monit Assess, vol. 188, no. 4, p. 252, Apr. 2016. [CrossRef]
- G. Pérez Castresana et al., “Atoyac River Pollution in the Metropolitan Area of Puebla, México,” Water (Basel), vol. 10, no. 3, p. 267, Mar. 2018. [CrossRef]
- G. E. Adjovu, H. Stephen, D. James, and S. Ahmad, “Measurement of Total Dissolved Solids and Total Suspended Solids in Water Systems: A Review of the Issues, Conventional, and Remote Sensing Techniques,” Remote Sens (Basel), vol. 15, no. 14, p. 3534, Jul. 2023. [CrossRef]
- F. E. Akpan, M. V. Akpan, and U. U. Inyang, “Geoelectrical Investigation Of Groundwater Quality Through Estimates Of Total Dissolved Solids And Electrical Conductivity In Parts Of Akwa Ibom State, Southern Nigeria,” Malaysian Journal of Geosciences, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 32–37, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- OMS (Organización Mundial de la Salusd, “Guías para la calidad del agua potable. Cuarta edición,” Ginebra: OMS, 2011.
- M. Seo, H. Lee, and Y. Kim, “Relationship between Coliform Bacteria and Water Quality Factors at Weir Stations in the Nakdong River, South Korea,” Water (Basel), vol. 11, no. 6, p. 1171, Jun. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. N. Guentzel, “Escherichia, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia, Citrobacter, and Proteus.,” in In: Baron S, editor. Medical Microbiology. 4th edition. Galveston (TX): University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston., 1996.
- M. Mishra, A. P. Arukha, A. K. Patel, N. Behera, T. K. Mohanta, and D. Yadav, “Multi-Drug Resistant Coliform: Water Sanitary Standards and Health Hazards,” Front Pharmacol, vol. 9, Jun. 2018. [CrossRef]
- C. P. Dillon, “Process Industries: Corrosion,” in Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, Elsevier, 2001, pp. 7856–7860. [CrossRef]
- S. E. Gad, “Lye,” in Encyclopedia of Toxicology, Elsevier, 2024, pp. 997–1001. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Naylor, H. Kaiser, and C. L. W. Jones, “The effect of dosing with sodium hydroxide (NaOH−) on water pH and growth of Haliotis midae in an abalone serial-use raceway,” Aquaculture International, Aug. 2012. [CrossRef]
- F. Janekovi and T. Novak, “PCA – A Powerful Method for Analyze Ecological Niches,” in Principal Component Analysis - Multidisciplinary Applications, InTech, 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Choo-in, “The relationship between the total dissolved solids and the conductivity value of drinking water, surface water and wastewater,” in The 2019 International Academic Research Conference in Amsterdam, 2019, pp. 11–16.
- L. Riđanović, S. Riđanović, D. Jurica, and P. Spasojević, “Evaluation of Water Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen Regimes in River Neretva,” 2010.
- C. Kim, Y. Nishimura, and T. Nagata, “Role of dissolved organic matter in hypolimnetic mineralization of carbon and nitrogen in a large, monomictic lake,” Limnol Oceanogr, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 70–78, Jan. 2006. [CrossRef]
- G. L. I. Silva, “The housing problem in Veracruz: The case of Martinez de la Torre,” Centro de Estudios Económicos y Sociales del Instituto de Investigaciones y Estudios Superiores Económicos y Sociales de la Universidad Veracruzana., pp. 281–306, 1995.
- INEGI, “Martínez de la Torre,” https://www.inegi.org.mx/app/ageeml/#datos_generales/30/30081.
- A. V. Garza, “Agricultural reuse of wastewater from Cd. Juarez, (Chih., Mexico).,” in In the Juarez Valley and its impact on public health., 2020, p. 10.
- E. M. García-Salazar, “Wastewater as a generator of agricultural activity space in the Mezquital Valley, Hidalgo, Mexico.,” Journal of contemporary food and regional development., vol. 29, no. 54, pp. 2–34, 2019.
- E. M. García-Salazar and M. E. Fuentes-Carrasco, “The wastewater dispute in Mexico as a paradoxical ecological-distributive conflicts.,” Regions & Cohesion, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 54–79, 2021.
- SEMARNAT, “D3_R_AGUA05_01. Compendio de Información Ambiental.,” https://apps1.semarnat.gob.mx:8443/dgeia/compendio_2020/dgeiawf.semarnat.gob.mx_8080/approot/dgeia_mce/html/RECUADROS_INT_GLOS/D3_AGUA/D3_AGUA04/D3_R_AGUA05_01.htm.
- I. Caamal Cauich, V. G. Pat Fernández, F. Jerónimo Ascencio, L. E. Santoyo Rodríguez, and J. G. Ramos García, “Análisis de los costos de producción del limón persa en el municipio de Tlapacoyan, Veracruz,” Revista Biológico Agropecuaria Tuxpan, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 10–18, Jul. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Heraldo de México, “Citrusper genera contaminación.,” https://elheraldodemartinez.com.mx/estado/martinez-de-la-torre/63638-citrusper-genera-contaminacion.html.
- PROFEPA, “Inspecciona PROFEMA a empresas ubicadas en Río Filobobos en Veracruz,” https://www.profepa.gob.mx/innovaportal/v/7181/1/mx.wap/inspecciona_profepa_a_empresas_ubicadas_en_rio_filobobos_en_veracruz.html.
| Parameter | SW1 | SW2 | SW3 | SW4 | SW5 | SW6 | SW7 | SW8 | SW9 |
| Temperature (°C) | 20.21±0.28 | 26.7±.014 | 29.60.71 | 30.25±0.64 | 29.80±0.4 | 29.40±0.42 | 30.50±0.57 | 30.30±0.14 | 30.35±0.21 |
| DO (mg L-1 ) | 0.15±0.7 | 0.25±0.07 | 6.45±1.06 | 0.30±0.14 | 2.64±0.05 | 0.25±0.021 | 0.15±0.07 | 0.35±0.21 | 0.60±0.14 |
| Sites |
pH | Conductivity (mS ) |
|---|---|---|
| SW1 | 7.85±0.02 | 0.30±0.14 |
| SW2 | 8.60±0.14 | 0.27±0.01 |
| SW3 | 8.65±0.07 | 0.27±0.01 |
| SW4 | 7.50±0.14 | 0.26±0.03 |
| SW5 | 6.40±0.71 | 0.72±0.03 |
| SW6 | 8.25±0.21 | 0.34±0.04 |
| SW7 | 7.75±0.04 | 0.75±0.02 |
| SW8 | 7.78±0.05 | 0.37±0.02 |
| SW9 | 7.87±0.09 | 3.81±0.04 |
| Sampling points |
FC (UFC 100 ml-1 ) |
| SW1 | 0 × 100±0 × 100 |
| SW2 | 7.255 × 102±1.0677 × 102 |
| SW3 | 1.215 × 103±1.3435 × 102 |
| SW4 | 8.16625 × 104±7.425 × 101 |
| SW5 | 8 × 104±8.48528 × 103 |
| SW6 | 1.91 × 105±5.65685 × 103 |
| SW7 | 2.2 × 105±2.12132 × 104 |
| SW8 | 2.385 × 105±3.53553 × 103 |
| SW9 | 3.2 × 105±3.707107 × 104 |
| Parameter | Temp | pH | DO | Conductiv | DS | TN | NO3 | TP | PO4 | COD | FC | |
| Parameter | 1 | |||||||||||
| Temp | 0.714* | 1 | ||||||||||
| pH | -0.233 | -0.161 | 1 | |||||||||
| DO | -0.229 | 0.193 | 0.131 | 1 | ||||||||
| Conductiv | 0.611 | 0.252 | -0.098 | -0.120 | 1 | |||||||
| DS | 0.580 | 0.244 | -0.102 | -0.096 | .993** | 1 | ||||||
| TN | .919** | 0.579 | -0.381 | -0.250 | 0.496 | 0.462 | 1 | |||||
| NO3 | .887** | 0.512 | -0.041 | -0.348 | 0.435 | 0.404 | .917** | 1 | ||||
| TP | .952** | 0.563 | -0.267 | -0.286 | 0.569 | 0.530 | .985** | .940** | 1 | |||
| PO4 | .937** | 0.561 | -0.266 | -0.286 | 0.521 | 0.483 | .990** | .953** | .997** | 1 | ||
| COD | .946** | 0.559 | -0.074 | -0.348 | 0.511 | 0.466 | .921** | .973** | .964** | .963** | 1 | |
| FC | .896** | .876** | -0.234 | -0.071 | 0.396 | 0.375 | .881** | .821** | .866** | .872** | .831** | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





