Submitted:
25 December 2023
Posted:
26 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and suppliers
2.2. Animals and samples
2.3. Isolation of Seminal Plasma (SP)
2.4. Evaluation of antioxidant activity levels of seminal pasma (SP)
2.4.1. Enzymatic antioxidants
2.4.2. Non-enzymatic antioxidants
2.5. Determination of the oxidative stress index (OSI)
2.6. Sperm cryopreservation
2.7. Assessment of sperm motility
2.8. Sperm functionality analysis
2.8.1. Plasma Membrane Integrity (SYBR14/PI)
2.8.2. Acrosome Integrity (PNA-FITC/PI)
2.8.3. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (JC-1)
2.8.4. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species: Total ROS (H2DCFDA/PI) and O2− (HE/YO-PRO-1)
2.8.5. Plasma Membrane Lipid Disorder (M540/YO-PRO-1)
2.8.6. Membrane Lipid Peroxidation (LPO)
2.9. Evaluation of DNA fragmentation
2.9.1. Preparation of semen-agarose plates and lysis of samples
2.9.2. Electrophoresis and dehydration
2.9.3. Staining and imaging
2.9.4. Comet analysis
2.10. Statistical analyses
2.10.1. Classification of ejaculates based on their cryotolerance.
2.10.2. Comparison of LPO and DNA fragmentation between good (GFE) and poor freezability ejaculates (PFE)
2.10.3. Correlations of membrane LPO and DNA fragmentation with post-thaw sperm quality parameters and activity levels of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants and the OSI of SP
3. Results
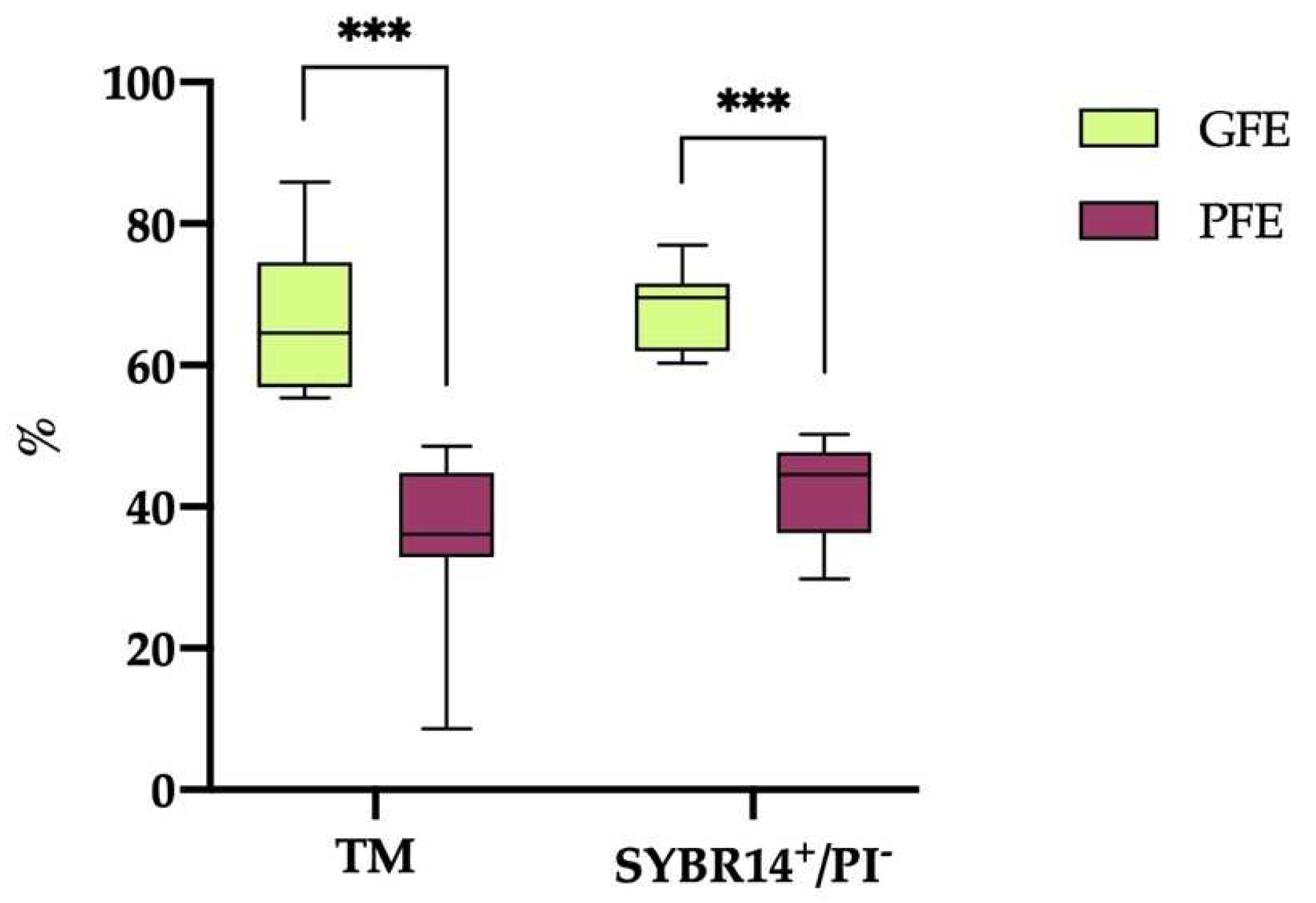
3.1. Classification of horse ejaculates into GFE and PFE groups according to their cryotolerance
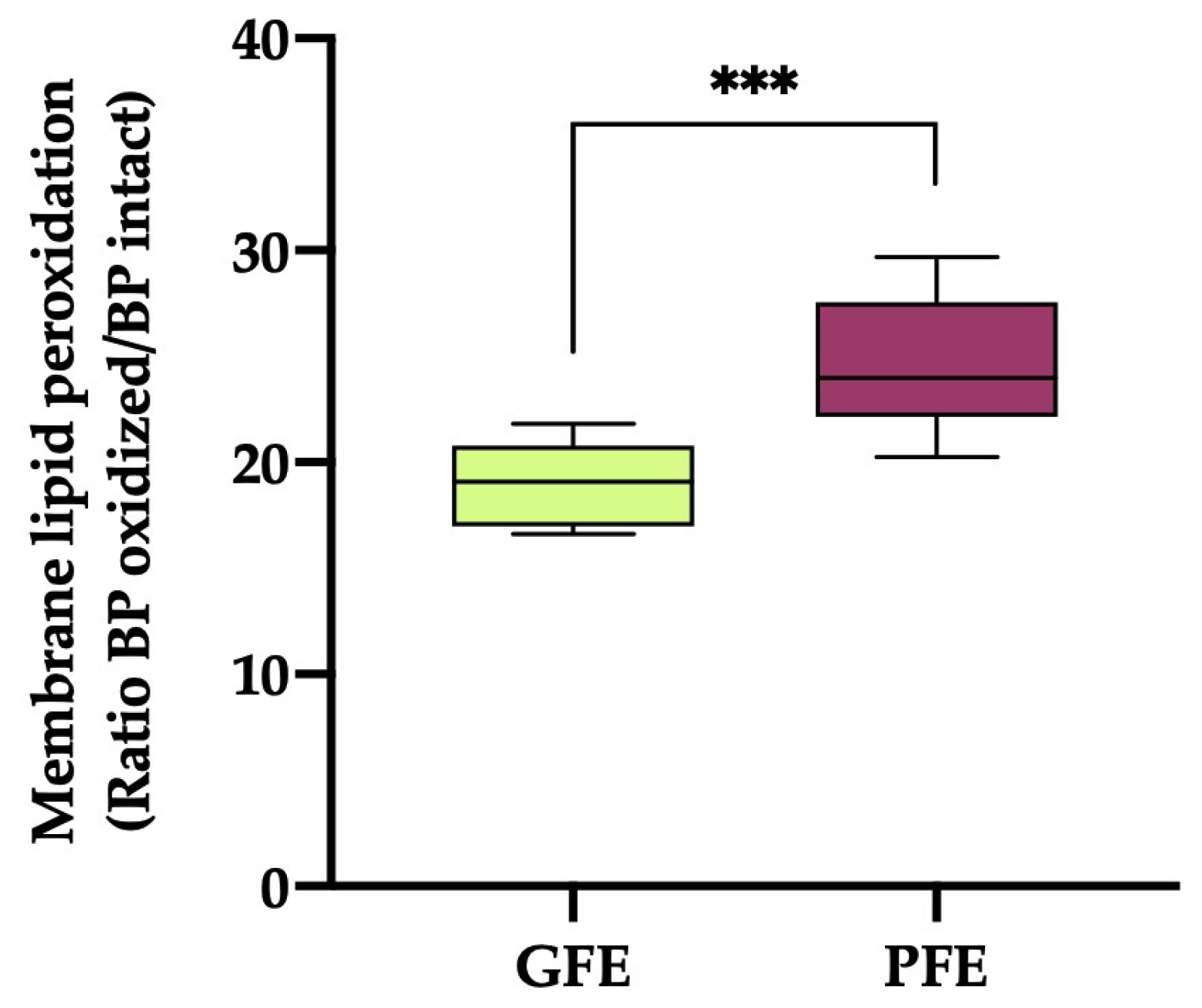
3.2. Lipid membrane peroxidation
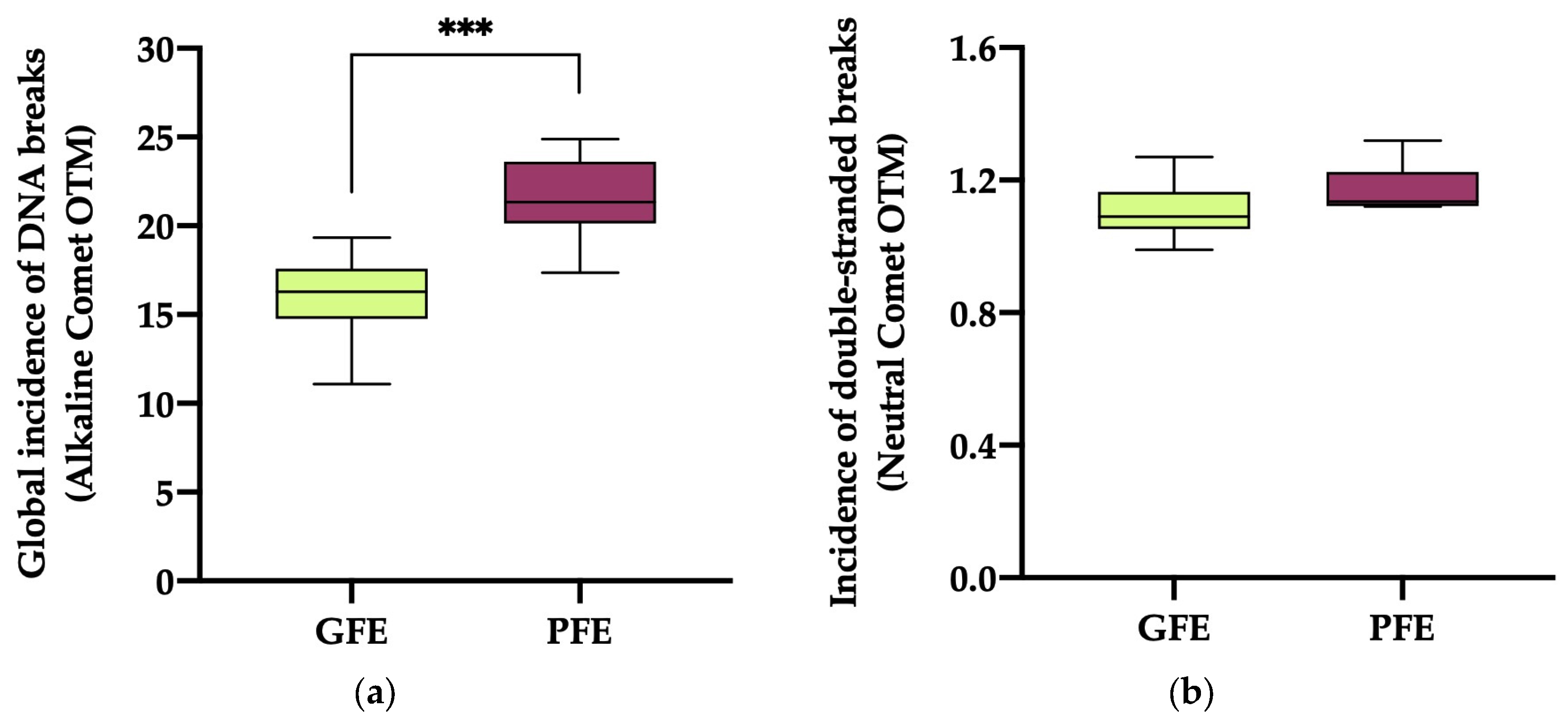
3.3. DNA fragmentation
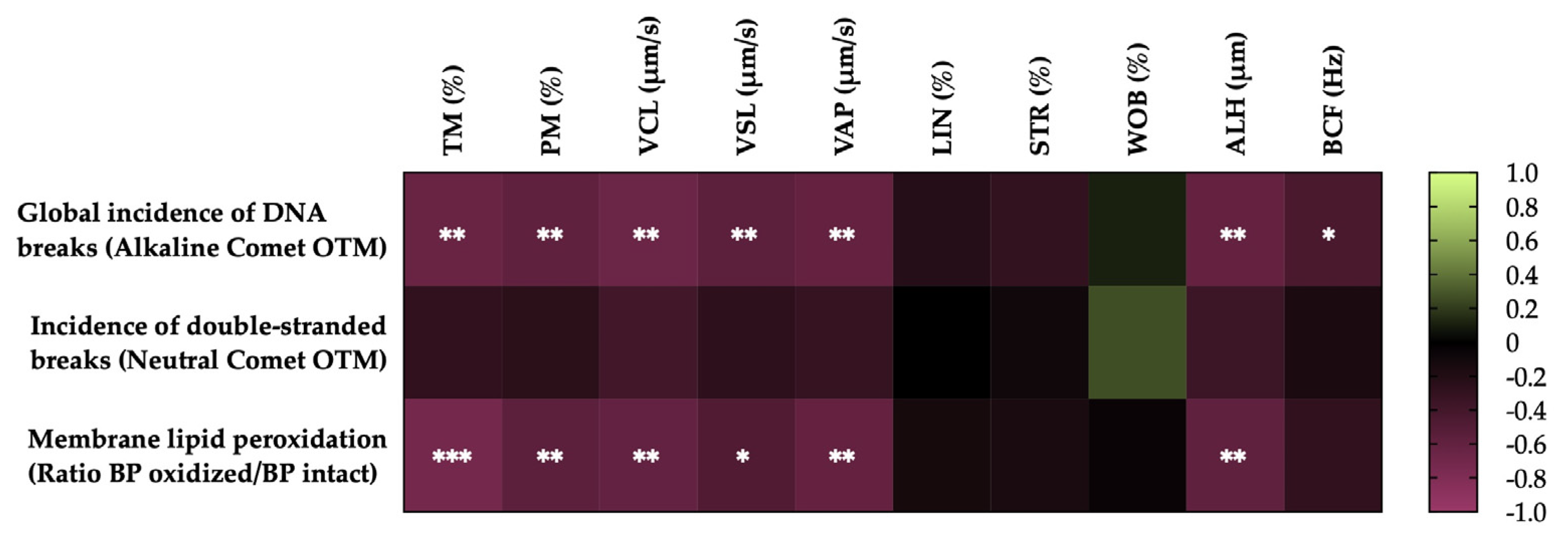
3.4. Correlations of the degree of LPO and sperm DNA fragmentation with sperm motility parameters after thawing
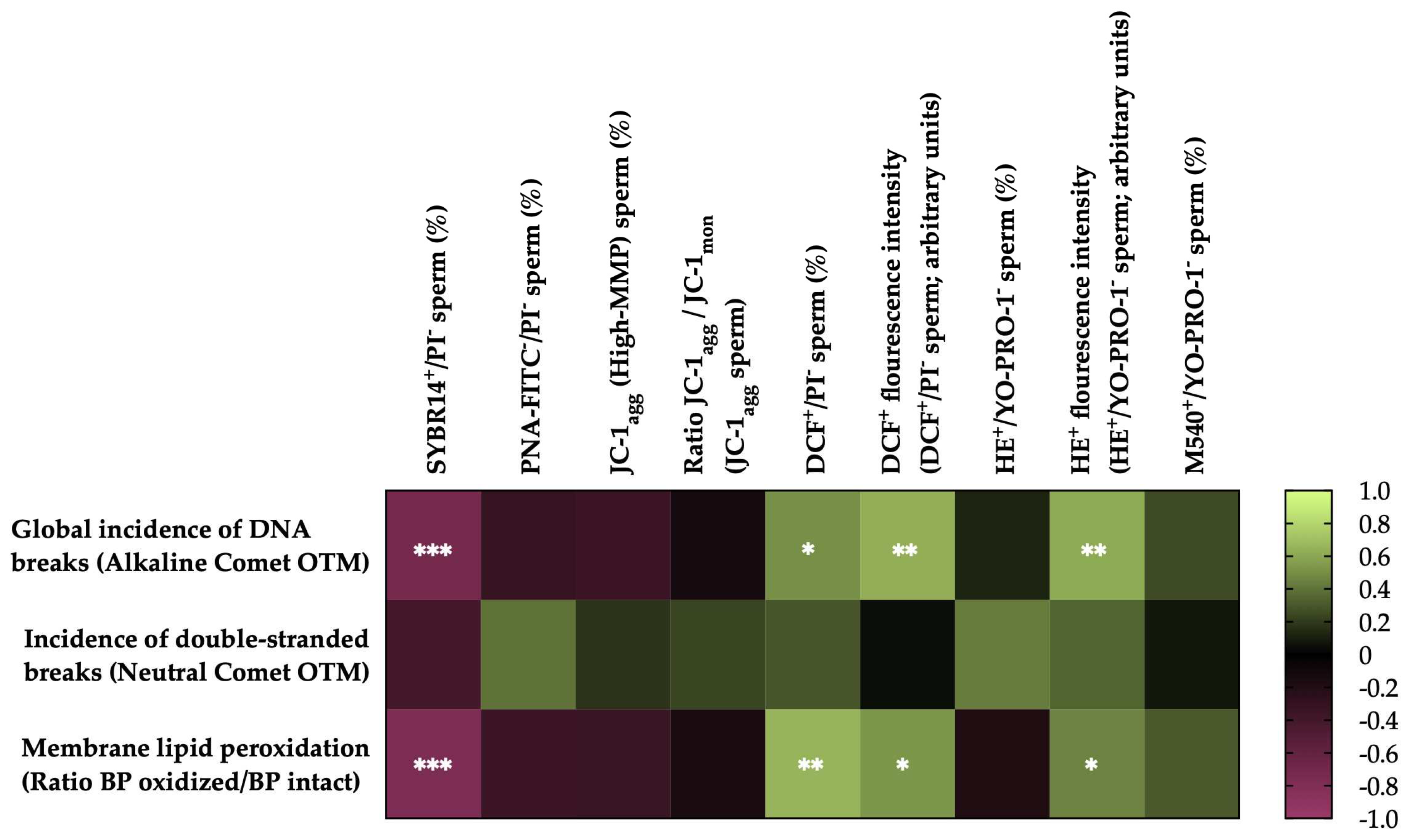
3.5. Correlations of membrane LPO and sperm DNA fragmentation with sperm functionality parameters after thawing
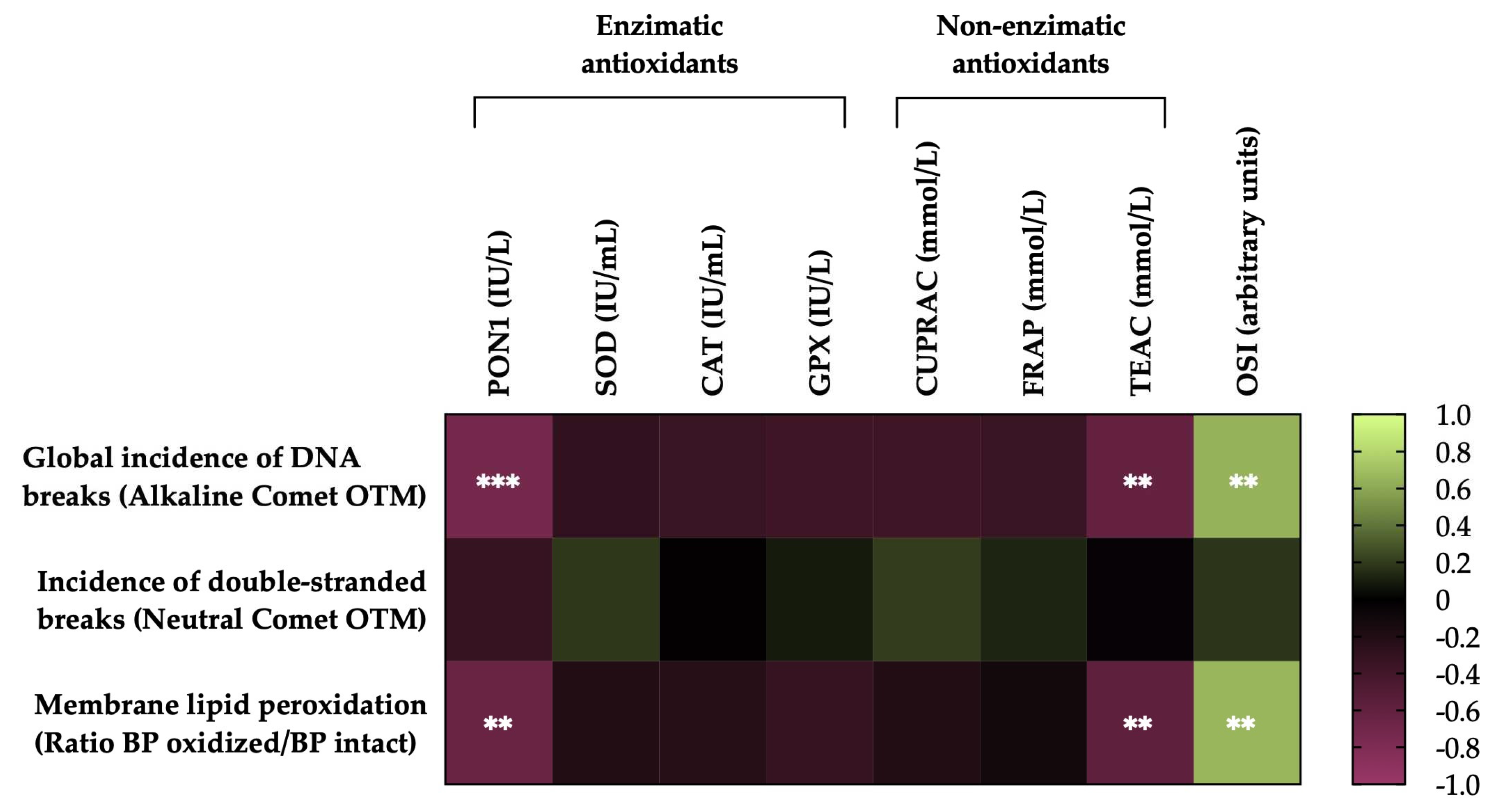
3.6. Correlations of the degree of lipid peroxidation and sperm DNA fragmentation of horse sperm after thawing with the levels of antioxidant activity (enzymatic and non-enzymatic) and the OSI of SP.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yánez-Ortiz, I.; Catalán, J.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.E.; Miró, J.; Yeste, M. Advances in Sperm Cryopreservation in Farm Animals: Cattle, Horse, Pig and Sheep. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeste, M.; Estrada, E.; Rocha, L.G.; Marín, H.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.E.; Miró, J. Cryotolerance of Stallion Spermatozoa Is Related to ROS Production and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Rather than to the Integrity of Sperm Nucleus. Andrology 2015, 3, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidament, M.; Vincent, P.; Martin, F.X.; Magistrini, M.; Blesbois, E. Differences in Ability of Jennies and Mares to Conceive with Cooled and Frozen Semen Containing Glycerol or Not. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2009, 112, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canisso, I.F.; Carvalho, G.R.; Morel, M.D.; Ker, P.G.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Silva, E.C.; Da Silva, M.A.C. Seminal Parameters and Field Fertility of Cryopreserved Donkey Jack Semen after Insemination of Horse Mares. Equine Vet. J. 2011, 43, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo Betancur, G.; Pizarro López, E.; Rojano, B.A. Estrés Oxidativo En El Semen Equino Criopreservado. Rev. Lasallista Investig. 2012, 9, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, W. Basic Aspects of Frozen Storage of Semen. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2000, 62, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.F. The Causes of Reduced Fertility with Cryopreserved Semen. Anim Reprod Sci, 2000; 60–61, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Virk, G.; Ong, C.; du Plessis, S.S. Effect of Oxidative Stress on Male Reproduction. World J. Mens. Health 2014, 32, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opuwari, C.S.; Henkel, R.R. An Update on Oxidative Damage to Spermatozoa and Oocytes. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9540142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Saleh, R.A.; Bedaiwy, M.A. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Pathophysiology of Human Reproduction. Fertil. Steril. 2003, 79, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeste, M. Sperm Cryopreservation Update: Cryodamage, Markers, and Factors Affecting the Sperm Freezability in Pigs. Theriogenology 2016, 85, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieme, H.; Oldenhof, H.; Wolkers, W. Sperm Membrane Behaviour during Cooling and Cryopreservation. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2015, 50, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponchia, R.; Bruno, A.; Renzi, A.; Landi, C.; Shaba, E.; Luongo, F.P.; Haxhiu, A.; Artini, P.G.; Luddi, A.; Governini, L.; et al. Oxidative Stress Measurement in Frozen/Thawed Human Sperm: The Protective Role of an in Vitro Treatment with Myo-Inositol. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, R.J.; Baker, M.A. Oxidative Stress, Sperm Survival and Fertility Control. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 250, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, D.S.; Ali, E.F. Perspective on Plasma Membrane Cholesterol Efflux and Spermatozoal Function. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2010, 3, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batellier, F.; Vidament, M.; Fauquant, J.; Duchamp, G.; Arnaud, G.; Yvon, J.M.; Magistrini, M. Advances in Cooled Semen Technology. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2001, 68, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, M.B.; Imam, S.N.; Dada, R. Sperm DNA Integrity Assays: Diagnostic and Prognostic Challenges and Implications in Management of Infertility. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2011, 28, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ferreyra, J.; García-Ferreyra, J. Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Its Relation With Fertility. New Discov. Embryol. 2015, 60825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, R.T.; Ohl, D.A.; Sigman, M.; Smith, G.D. Sperm DNA Damage in Male Infertility: Etiologies, Assays, and Outcomes. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2010, 27, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Barbăroșie, C.; Ambar, R.; Finelli, R. The Impact of Single- and Double-Strand DNA Breaks in Human Spermatozoa on Assisted Reproduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muiño-Blanco, T.; Pérez-Pé, R.; Cebrián-Pérez, J. Seminal Plasma Proteins and Sperm Resistance to Stress. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2008, 43, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidi, F.; Pazhohan, A.; Shabani Nashtaei, M.; Khodarahmian, M.; Nekoonam, S. The Role of Antioxidants in Sperm Freezing: A Review. Cell Tissue Bank. 2016, 17, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papas, M.; Arroyo, L.; Bassols, A.; Catalán, J.; Bonilla-Correal, S.; Gacem, S.; Yeste, M.; Miró, J. Activities of Antioxidant Seminal Plasma Enzymes (SOD, CAT, GPX and GSR) Are Higher in Jackasses than in Stallions and Are Correlated with Sperm Motility in Jackasses. Theriogenology 2019, 140, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papas, M.; Catalan, J.; Barranco, I.; Arroyo, L.; Bassols, A.; Yeste, M.; Miró, J. Total and Specific Activities of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) in Seminal Plasma Are Related with the Cryotolerance of Jackass Spermatozoa. Cryobiology 2020, 92, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guasti, P.N.; Monteiro, G.A.; Papa, F.O. Componentes do Plasma Seminal e Sua Influência Sobre a Criopreservação e Fertilidade de Espermatozóides Equinos. Veterinária e Zootec. 2012, 19, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Giovanni Restrepo, B.; Edison Pizarro, L.; Rojano, B.A. Aporte Antioxidante Del Plasma Seminal y Su Efecto Sobre La Calidad Del Semen Equino Congelado. Rev. Investig. Vet. del Perú 2019, 30, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, J.; Yánez-Ortiz, I.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; González-Aróstegui, L.G.; Rubio, C.P.; Barranco, I.; Yeste, M.; Miró, J. Seminal Plasma Antioxidants Are Related to Sperm Cryotolerance in the Horse. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowsett, K.F.; Knott, L.M. The Influence of Age and Breed on Stallion Semen. Theriogenology 1996, 46, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieme, H.; Harrison, R.A.P.; Petrunkina, A.M. Cryobiological Determinants of Frozen Semen Quality, with Special Reference to Stallion. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2008, 107, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomis, P.R.; Graham, J.K. Commercial Semen Freezing: Individual Male Variation in Cryosurvival and the Response of Stallion Sperm to Customized Freezing Protocols. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2008, 105, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, G.; Castagnetti, C.; Rizzato, G.; Mislei, B.; Iacono, E.; Merlo, B. Density Gradient Centrifugation of Sperm from a Subfertile Stallion and Effect of Seminal Plasma Addition on Fertility. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2011, 126, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, P.; Sánchez, R.; Risopatrón, J. Selección Espermática En Semen Congelado/Descongelado de Equino: Evaluación de Las Membranas Plasmática, Acrosomal y Potencial de Membrana Mitocondrial. Int. J. Morphol. 2014, 32, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhauser, S.; Gösele, P.; Handler, J. Postthaw Addition of Autologous Seminal Plasma Improves Sperm Motion Characteristics in Fair and Poor Freezer Stallions. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2019, 72, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papas, M.; Catalán, J.; Fernandez-Fuertes, B.; Arroyo, L.; Bassols, A.; Miró, J.; Yeste, M. Specific Activity of Superoxide Dismutase in Stallion Seminal Plasma Is Related to Sperm Cryotolerance. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurich, J.E.; Kühne, A.; Hoppe, H.; Aurich, C. Seminal Plasma Affects Membrane Integrity and Motility of Equine Spermatozoa after Cryopreservation. Theriogenology 1996, 46, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinsko, S.P.; Crockett, E.C.; Squires, E.L. Effect of Centrifugation and Partial Removal of Seminal Plasma on Equine Spermatozoal Motility after Cooling and Storage. Theriogenology 2000, 54, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromfield, J.J. A Role for Seminal Plasma in Modulating Pregnancy Outcomes in Domestic Species. Reproduction 2016, 152, R223–R232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogielnicka-Brzozowska, M.; Kordan, W. Characteristics of Selected Seminal Plasma Proteins and Their Application in the Improvement of the Reproductive Processes in Mammals. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 14, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, N.; Oldenhof, H.; Morandini, C.; Rohn, K.; Sieme, H. Optimal Concentrations of Cryoprotective Agents for Semen from Stallions That Are Classified ‘Good’ or ‘Poor’ for Freezing. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2011, 125, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenney, R.M.; Bergman, R.V.; Cooper, W.L.; Morse, G.W. Minimal Contamination Techniques for Breeding Mares: Technique and Preliminary Findings. Proc. Am. Assoc. Equine Pr. 1975, 21, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Bamba, K. Evaluation of Acrosomal Integrity of Boar Spermatozoa by Bright Field Microscopy Using an Eosin-Nigrosin Stain. Theriogenology 1988, 29, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barranco, I.; Roca, J.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Rubér, M.; Vicente-Carrillo, A.; Atikuzzaman, M.; Ceron, J.J.; Martinez, E.A.; Rodriguez-Martinez, H. Measurement of Activity and Concentration of Paraoxonase 1 (PON-1) in Seminal Plasma and Identification of PON-2 in the Sperm of Boar Ejaculates. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 82, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Barranco, I.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Molina, M.F.; Martinez, E.A.; Rodriguez-Martinez, H.; Parrilla, I.; Roca, J. Seminal Plasma Antioxidants Are Directly Involved in Boar Sperm Cryotolerance. Theriogenology 2018, 107, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apak, R.; Güçlü, K.; Özyürek, M.; Esi̊n Karademi̊r, S.; Altun, M. Total Antioxidant Capacity Assay of Human Serum Using Copper(II)-Neocuproine as Chromogenic Oxidant: The CUPRAC Method. Free Radic. Res. 2005, 39, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, C.; Guzmán, R.; López-Fernández, E.; Casado, Á. Evaluation of the Copper(II) Reduction Assay Using Bathocuproinedisulfonic Acid Disodium Salt for the Total Antioxidant Capacity Assessment: The CUPRAC–BCS Assay. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 392, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. The Ferric Reducing Ability of Plasma (FRAP) as a Measure of “Antioxidant Power”: The FRAP Assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, C.P.; Hernández-Ruiz, J.; Martinez-Subiela, S.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Ceron, J.J. Spectrophotometric Assays for Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) in Dog Serum: An Update. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, N.J.; Rice-Evans, C.; Davies, M.J.; Gopinathan, V.; Milner, A. A Novel Method for Measuring Antioxidant Capacity and Its Application to Monitoring the Antioxidant Status in Premature Neonates. Clin. Sci. 1993, 84, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Feng, J.; Yang, Y.; Dai, C.; Lu, A.; Li, J.; Liao, Y.; Xiang, M.; Huang, Q.; Wang, D.; et al. Significance of Serum Total Oxidant/Antioxidant Status in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0170003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erel, O. A New Automated Colorimetric Method for Measuring Total Oxidant Status. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Spidlen, J.; Boyce, K.; Cai, J.; Crosbie, N.; Dalphin, M.; Furlong, J.; Gasparetto, M.; Goldberg, M.; Goralczyk, E.M.; et al. MIFlowCyt: The Minimum Information about a Flow Cytometry Experiment. Cytometry 2008, 73, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, D.L.; Johnson, L.A. Viability Assessment of Mammalian Sperm Using SYBR-14 and Propidium Iodide. Biol. Reprod. 1995, 53, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathi, R.; Colenbrander, B.; Bevers, M.M.; Gadella, B.M. Evaluation of in Vitro Capacitation of Stallion Spermatozoa. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 65, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Ferrusola, C.; Sotillo-Galán, Y.; Varela-Fernández, E.; Gallardo-Bolaños, J.M.; Muriel, A.; González-Fernández, L.; Tapia, J.A.; Peña, F.J. Detection of “Apoptosis-like” Changes during the Cryopreservation Process in Equine Sperm. J. Androl. 2008, 29, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalán, J.; Papas, M.; Trujillo-Rojas, L.; Blanco-Prieto, O.; Bonilla-Correal, S.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.E.; Miró, J.; Yeste, M. Red LED Light Acts on the Mitochondrial Electron Chain of Donkey Sperm and Its Effects Depend on the Time of Exposure to Light. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 588621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthrie, H.D.; Welch, G.R. Determination of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species and High Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in Percoll-Treated Viable Boar Sperm Using Fluorescence-Activated Flow Cytometry1. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeste, M.; Estrada, E.; Rivera Del Álamo, M.M.; Bonet, S.; Rigau, T.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.E. The Increase in Phosphorylation Levels of Serine Residues of Protein HSP70 during Holding Time at 17°C Is Concomitant with a Higher Cryotolerance of Boar Spermatozoa. PLoS One 2014, 9, 90887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega Ferrusola, C.; González Fernández, L.; Morrell, J.M.; Salazar Sandoval, C.; Macías García, B.; Rodríguez-Martinez, H.; Tapia, J.A.; Peña, F.J. Lipid Peroxidation, Assessed with BODIPY-C11, Increases after Cryopreservation of Stallion Spermatozoa, Is Stallion-Dependent and Is Related to Apoptotic-like Changes. Reproduction 2009, 138, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanovas, A.; Ribas-Maynou, J.; Lara-Cerrillo, S.; Jimenez-Macedo, A.R.; Hortal, O.; Benet, J.; Carrera, J.; García-Peiró, A. Double-Stranded Sperm DNA Damage Is a Cause of Delay in Embryo Development and Can Impair Implantation Rates. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 111, 699–707.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langie, S.A.S.; Azqueta, A.; Collins, A.R. The Comet Assay: Past, Present, and Future. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 162652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.; Aston, K.I.; Emery, B.R.; Hotaling, J.; Carrell, D.T. Sperm DNA Damage Output Parameters Measured by the Alkaline Comet Assay and Their Importance. Andrologia 2017, 49, e12608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morató, R.; Prieto-Martínez, N.; Muiño, R.; Hidalgo, C.O.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.E.; Bonet, S.; Yeste, M. Aquaporin 11 Is Related to Cryotolerance and Fertilising Ability of Frozen–Thawed Bull Spermatozoa. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2018, 30, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, H.D.; Welch, G.R. Effects of Reactive Oxygen Species on Sperm Function. Theriogenology 2012, 78, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.; Pinto-Pinho, P.; Gaivão, I.; Martins-Bessa, A.; Gomes, Z.; Moutinho, O.; Oliveira, M.M.; Peixoto, F.; Pinto-Leite, R. Sperm DNA Damage and Seminal Antioxidant Activity in Subfertile Men. Andrologia 2021, 53, e14027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Meo, S.; Reed, T.T.; Venditti, P.; Victor, V.M. Harmful and Beneficial Role of ROS. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7909186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.K.; Bilaspuri, G.S. Impacts of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants on Semen Functions. Vet. Med. Int. 2010, 2010, 686137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Oxidative Stress: A Concept in Redox Biology and Medicine. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, R.J. Reactive Oxygen Species as Mediators of Sperm Capacitation and Pathological Damage. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2017, 84, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, V.; Ravichandran, A.; Thiagarajan, N.; Govindarajan, M.; Dhandayuthapani, S.; Suresh, S. Seminal Reactive Oxygen Species and Total Antioxidant Capacity: Correlations with Sperm Parameters and Impact on Male Infertility. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2018, 45, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas-Maynou, J.; Delgado-Bermúdez, A.; Mateo-Otero, Y.; Viñolas, E.; Hidalgo, C.O.; Ward, W.S.; Yeste, M. Determination of Double- and Single-Stranded DNA Breaks in Bovine Sperm Is Predictive of Their Fertilizing Capacity. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neild, D.M.; Brouwers, J.F.H.M.; Colenbrander, B.; Agüero, A.; Gadella, B.M. Lipid Peroxide Formation in Relation to Membrane Stability of Fresh and Frozen Thawed Stallion Spermatozoa. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2005, 72, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías García, B.; González Fernández, L.; Ortega Ferrusola, C.; Morillo Rodríguez, A.; Gallardo Bolaños, J.M.; Rodríguez Martinez, H.; Tapia, J.A.; Morcuende, D.; Peña, F.J. Fatty Acids and Plasmalogens of the Phospholipids of the Sperm Membranes and Their Relation with the Post-Thaw Quality of Stallion Spermatozoa. Theriogenology 2011, 75, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurich, C.; Ortega Ferrusola, C.; Peña Vega, F.J.; Schrammel, N.; Morcuende, D.; Aurich, J. Seasonal Changes in the Sperm Fatty Acid Composition of Shetland Pony Stallions. Theriogenology 2018, 107, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, R.J.; Clarkson, J.S.; Fishel, S. Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species, Lipid Peroxidation, and Human Sperm Function. Biol. Reprod. 1989, 41, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalán, J.; Yánez-Ortiz, I.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; González-Arostegui, L.G.; Rubio, C.P.; Yeste, M.; Miró, J.; Barranco, I. Impact of Seminal Plasma Antioxidants on Donkey Sperm Cryotolerance. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 11, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.K.; Agarwal, A. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Male Infertility. Urology 1996, 48, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, F.J.; O’Flaherty, C.; Ortiz Rodríguez, J.M.; Martín Cano, F.E.; Gaitskell-Phillips, G.L.; Gil, M.C.; Ferrusola, C.O. Redox Regulation and Oxidative Stress: The Particular Case of the Stallion Spermatozoa. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucak, M.N.; Sariözkan, S.; Tuncer, P.B.; Sakin, F.; Ateşşahin, A.; Kulaksiz, R.; Çevik, M. The Effect of Antioxidants on Post-Thawed Angora Goat (Capra Hircus Ancryrensis) Sperm Parameters, Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant Activities. Small Rumin. Res. 2010, 89, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Virk, G.; Ong, C.; Plessis, S.S. du Effect of Oxidative Stress on Male Reproduction. World J. Mens. Health 2014, 32, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alyethodi, R.R.; Sirohi, A.S.; Karthik, S.; Tyagi, S.; Perumal, P.; Singh, U.; Sharma, A.; Kundu, A. Role of Seminal MDA, ROS, and Antioxidants in Cryopreservation and Their Kinetics under the Influence of Ejaculatory Abstinence in Bovine Semen. Cryobiology 2021, 98, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segundo Salinas, M.B.; Lertwichaikul, T.; Khunkaew, C.; Boonyayatra, S.; Sringarm, K.; Chuammitri, P.; Sathanawongs, A. Freezability Biomarkers in the Epididymal Spermatozoa of Swamp Buffalo. Cryobiology 2022, 106, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Fernández, J.; Gómez-Izquierdo, E.; Tomás, C.; Mocé, E.; De Mercado, E. Is Sperm Freezability Related to the Post-Thaw Lipid Peroxidation and the Formation of Reactive Oxygen Species in Boars? Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2013, 48, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintus, E.; Luis, J.; Santaella, R.-; Drevet, J.R.; Sorrentino, R. Impact of Oxidative Stress on Male Reproduction in Domestic and Wild Animals. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, B.A.; Vo, A.T.; Baumber, J. Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species by Equine Spermatozoa. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega Ferrusola, C.; González Fernandez, L.; Macías García, B.; Salazar-Sandoval, C.; Morillo Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez Martinez, H.; Tapia, J.A.; Peña, F.J. Effect of Cryopreservation on Nitric Oxide Production by Stallion Spermatozoa. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mislei, B.; Bucci, D.; Malama, E.; Bollwein, H.; Mari, G. Seasonal Changes in ROS Concentrations and Sperm Quality in Unfrozen and Frozen-Thawed Stallion Semen. Theriogenology 2020, 144, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darr, C.R.; Cortopassi, G.A.; Datta, S.; Varner, D.D.; Meyers, S.A. Mitochondrial Oxygen Consumption Is a Unique Indicator of Stallion Spermatozoal Health and Varies with Cryopreservation Media. Theriogenology 2016, 86, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Gagnon, C. Production of Reactive Oxygen Species by Spermatozoa Undergoing Cooling, Freezing, and Thawing. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2001, 59, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, N.; Riaz, A.; Anzar, M.; Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, N.; Riaz, A.; Anzar, M. Sperm Survival Kinetics in Different Types of Bull Semen: Progressive Motility, Plasma Membrane Integrity, Acrosomal Status and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2015, 27, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürler, H.; Malama, E.; Heppelmann, M.; Calisici, O.; Leiding, C.; Kastelic, J.P.; Bollwein, H. Effects of Cryopreservation on Sperm Viability, Synthesis of Reactive Oxygen Species, and DNA Damage of Bovine Sperm. Theriogenology 2016, 86, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostek, A.; Dietrich, M.A.; Słowińska, M.; Ciereszko, A. Cryopreservation of Bull Semen Is Associated with Carbonylation of Sperm Proteins. Theriogenology 2017, 92, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheuquemán, C.; Faúndez, R.; Sánchez, R.; Risopatrón, J. Changes in Sperm Function and Structure after Freezing in Domestic Cat Spermatozoa. Andrologia 2018, 50, e13080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awda, B.J.; Mackenzie-Bell, M.; Buhr, M.M. Reactive Oxygen Species and Boar Sperm Function. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, Y.J. Changes in Sperm Membrane and ROS Following Cryopreservation of Liquid Boar Semen Stored at 15 °C. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2011, 124, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeste, M.; Flores, E.; Estrada, E.; Bonet, S.; Rigau, T.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.E.; Yeste, M.; Flores, E.; Estrada, E.; Bonet, S.; et al. Reduced Glutathione and Procaine Hydrochloride Protect the Nucleoprotein Structure of Boar Spermatozoa during Freeze–Thawing by Stabilising Disulfide Bonds. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2013, 25, 1036–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeste, M.; Estrada, E.; Casas, I.; Bonet, S.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.E. Good and Bad Freezability Boar Ejaculates Differ in the Integrity of Nucleoprotein Structure after Freeze-Thawing but Not in ROS Levels. Theriogenology 2013, 79, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Qiu, S.; Chen, X.; Cai, B.; Xie, H. Freeze-Thawing Impairs the Motility, Plasma Membrane Integrity and Mitochondria Function of Boar Spermatozoa through Generating Excessive ROS. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente-Lara, A.; Hesser, A.; Christensen, B.; Gonzales, K.; Meyers, S. Effects from Aging on Semen Quality of Fresh and Cryopreserved Semen in Labrador Retrievers. Theriogenology 2019, 132, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neagu, V.R.; García, B.M.; Rodríguez, A.M.; Ferrusola, C.O.; Bolaños, J.M.G.; Fernández, L.G.; Tapia, J.A.; Peña, F.J. Determination of Glutation Peroxidase and Superoxide Dismutase Activities in Canine Seminal Plasma and Its Relation with Sperm Quality and Lipid Peroxidation Post Thaw. Theriogenology 2011, 75, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucio, C.F.; Regazzi, F.M.; Silva, L.C.G.; Angrimani, D.S.R.; Nichi, M.; Vannucchi, C.I. Oxidative Stress at Different Stages of Two-Step Semen Cryopreservation Procedures in Dogs. Theriogenology 2016, 85, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro L, E.; Restrepo B, G.; Echeverry Z, J.; Rojano, B. Efecto Del Plasma Seminal Sobre El Estado Redox Del Semen Equino Criopreservado. Rev. MVZ Córdoba 2013, 18, 3672–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.A.; Prasad, J.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Das, G.K.; Kumar, N.; Balamurugan, B.; Katiyar, R.; Verma, M.R. Effect of Cholesterol Loaded Cyclodextrin (CLC) on Lipid Peroxidation and Reactive Oxygen Species Levels during Cryopreservation of Buffalo (Bubalus Bubalis) Spermatozoa. Asian Pacific J. Reprod. 2016, 5, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.A.; Prasad, J.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Das, G.K.; Balamurugan, B.; Verma, M.R. Study on Correlation of Sperm Quality Parameters with Antioxidant and Oxidant Status of Buffalo Bull Semen during Various Stages of Cryopreservation. Andrologia 2018, 50, e12970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Khan, M.I. ur R.; Ahmad, M.; Iqbal, S. Effect of Age on Lipid Peroxidation of Fresh and Frozen-Thawed Semen of Nili-Ravi Buffalo Bulls. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 17, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Chakraborty, D.; Mandal, M.K.; Chakraborti, K.; Agarwal, A.; Bhattacharyya, A.K. Effect of Pentoxifylline Containing Human Sperm Cryopreservation Medium on Post-Thaw Motility of Human Spermatozoa and Lipid Peroxidation Status of Human Semen. Fertil. Steril. 2005, 84, S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, J.; Nashtaei, M.S.; Khosravizadeh, Z.; Mahdavinezhad, F.; Nekoonam, S.; Esfandyari, S.; Amidi, F. Effect of Sulforaphane on Apoptosis, Reactive Oxygen Species and Lipids Peroxidation of Human Sperm during Cryopreservation. Cryobiology 2021, 99, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arando, A.; Delgado, J.V.; Fernández-Prior, A.; León, J.M.; Bermúdez-Oria, A.; Nogales, S.; Pérez-Marín, C.C. Effect of Different Olive Oil-Derived Antioxidants (Hydroxytyrosol and 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylglycol) on the Quality of Frozen-Thawed Ram Sperm. Cryobiology 2019, 86, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güngör, İ.H.; Tektemur, A.; Arkali, G.; Dayan Cinkara, S.; Acisu, T.C.; Koca, R.H.; Etem Önalan, E.; Özer Kaya, Ş.; Kizil, M.; Sönmez, M.; et al. Effect of Freeze–Thawing Process on Lipid Peroxidation, MiRNAs, Ion Channels, Apoptosis and Global DNA Methylation in Ram Spermatozoa. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2021, 33, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partyka, A.; Łukaszewicz, E.; Nizański, W. Effect of Cryopreservation on Sperm Parameters, Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant Enzymes Activity in Fowl Semen. Theriogenology 2012, 77, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Páramo, S.; Diogo, P.; Dinis, M.T.; Herráez, M.P.; Sarasquete, C.; Cabrita, E. Sea Bass Sperm Freezability Is Influenced by Motility Variables and Membrane Lipid Composition but Not by Membrane Integrity and Lipid Peroxidation. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2012, 131, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.M.; Lewis, S.E.M.; McKelvey-Martin, V.J.; Thompson, W. A Comparison of Baseline and Induced DNA Damage in Human Spermatozoa from Fertile and Infertile Men, Using a Modified Comet Assay. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1996, 2, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, H.; Kasai, H.; Yamaguchi, R.; Tanaka, T.; Fukuda, J. Increased Oxidative Deoxyribonucleic Acid Damage in the Spermatozoa of Infertile Male Patients. Fertil. Steril. 1997, 68, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twigg, J.P.; Irvine, D.S.; Aitken, R.J. Oxidative Damage to DNA in Human Spermatozoa Does Not Preclude Pronucleus Formation at Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 13, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Chao, H.T.; Pan, R.L.; Wei, Y.H. Hydroxyl Radical-Induced Decline in Motility and Increase in Lipid Peroxidation and DNA Modification in Human Sperm. IUBMB Life 1997, 43, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twigg, J.; Fulton, N.; Gomez, E.; Stewart Irvine, D.; John Aitken, R. Analysis of the Impact of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Generation on the Structural and Functional Integrity of Human Spermatozoa: Lipid Peroxidation, DNA Fragmentation and Effectiveness of Antioxidants. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 13, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, R.J.; Notarianni, L.J.; Jefferies, T.M. Seminal Plasma Reduces Exogenous Oxidative Damage to Human Sperm, Determined by the Measurement of DNA Strand Breaks and Lipid Peroxidation. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2000, 447, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKelvey-Martin, V.J.; Melia, N.; Walsh, I.K.; Johnston, S.R.; Hughes, C.M.; Lewis, S.E.M.; Thompson, W. Two Potential Clinical Applications of the Alkaline Single-Cell Gel Electrophoresis Assay: (1) Human Bladder Washings and Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder; and (2) Human Sperm and Male Infertility. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1997, 375, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, R.J.; Gordon, E.; Harkiss, D.; Twigg, J.P.; Milne, P.; Jennings, Z.; Irvine, D.S. Relative Impact of Oxidative Stress on the Functional Competence and Genomic Integrity of Human Spermatozoa. Biol. Reprod. 1998, 59, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, S.; Jurisicova, A.; Sun, J.G.; Casper, R.F. Reactive Oxygen Species: Potential Cause for DNA Fragmentation in Human Spermatozoa. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 13, 896–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, E.T.; McClure, N.; Lewis, S.E.M. The Effect of Ascorbate and α-Tocopherol Supplementation in Vitro on DNA Integrity and Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced DNA Damage in Human Spermatozoa. Mutagenesis 1999, 14, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.; Roca, J.; Ballester, J.; Vázquez, J.M.; Martínez, E.A.; Johannisson, A.; Saravia, F.; Rodríguez-Martínez, H. Differences in SCSA Outcome among Boars with Different Sperm Freezability. Int. J. Androl. 2006, 29, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaresan, A.; Johannisson, A.; Al-Essawe, E.M.; Morrell, J.M. Sperm Viability, Reactive Oxygen Species, and DNA Fragmentation Index Combined Can Discriminate between above- and below-Average Fertility Bulls. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 5824–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumber, J.; Ball, B.A.; Linfor, J.J.; Meyers, S.A. Reactive Oxygen Species and Cryopreservation Promote DNA Fragmentation in Equine Spermatozoa. J. Androl. 2003, 24, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, R.; Feitosa, W.B.; Siqueira, A.F.P.; Nichi, M.; Paula-Lopes, F.F.; Marques, M.G.; Peres, M.A.; Barnabe, V.H.; Visintin, J.A.; Assumpçaõ, M.E.O. Influence of Bovine Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Oxidative Stress on Early Embryo in Vitro Development Outcome. Reproduction 2013, 146, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, L.; Strzezek, J. Effects of Freezing–Thawing on DNA Integrity of Boar Spermatozoa Assessed by the Neutral Comet Assay. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2005, 40, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peris, S.I.; Bilodeau, J.F.; Dufour, M.; Bailey, J.L. Impact of Cryopreservation and Reactive Oxygen Species on DNA Integrity, Lipid Peroxidation, and Functional Parameters in Ram Sperm. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2007, 74, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas-Maynou, J.; Fernández-Encinas, A.; García-Peiró, A.; Prada, E.; Abad, C.; Amengual, M.J.; Navarro, J.; Benet, J. Human Semen Cryopreservation: A Sperm DNA Fragmentation Study with Alkaline and Neutral Comet Assay. Andrology 2014, 2, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, B.A.; Gravance, C.G.; Medina, V.; Baumber, J.; Liu, I.K.M. Catalase Activity in Equine Semen. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 61, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucca, M.S.; Goularte, K.L.; Rovani, M.T.; Schneider, A.; Gasperin, B.G.; Lucia, T.; Rossi, C.A.R. Paraoxonase 1 Activity in the Sperm-Rich Portion of Boar Ejaculates Is Positively Associated with Sperm Quality. Anim. Reprod. 2022, 19, e20220039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barranco, I.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Perez-Patiño, C.; Alkmin, D.V.; Ceron, J.J.; Martinez, E.A.; Rodriguez-Martinez, H.; Roca, J. The Activity of Paraoxonase Type 1 (PON-1) in Boar Seminal Plasma and Its Relationship with Sperm Quality, Functionality, and in Vivo Fertility. Andrology 2015, 3, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, J.; Marsillach, J.; Joven, J. The Paraoxonases: Role in Human Diseases and Methodological Difficulties in Measurement. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2009, 46, 83–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackness, M.I.; Arrol, S.; Abbott, C.; Durrington, P.N. Protection of Low-Density Lipoprotein against Oxidative Modification by High-Density Lipoprotein Associated Paraoxonase. Atherosclerosis 1993, 104, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviram, M.; Rosenblat, M.; Billecke, S.; Erogul, J.; Sorenson, R.; Bisgaier, C.L.; Newton, R.S.; La Du, B. Human Serum Paraoxonase (PON 1) Is Inactivated by Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein and Preserved by Antioxidants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 892–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavilani, H.; Fattahi, A.; Esfahani, M.; Khodadadi, I.; Karimi, J.; Bahrayni, E.; Vatannejad, A.; Vaisi-Raygani, A.; Ghorbani, M.; Latifi, Z. Genotype and Phenotype Frequencies of Paraoxonase 1 in Fertile and Infertile Men. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2014, 60, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, R.J.; De Iuliis, G.N. On the Possible Origins of DNA Damage in Human Spermatozoa. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 16, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Marín, C.; Gosálvez, J.; Roy, R. Types, Causes, Detection and Repair of DNA Fragmentation in Animal and Human Sperm Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 14026–14052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürler, H.; Calisici, O.; Bollwein, H. Inter- and Intra-Individual Variability of Total Antioxidant Capacity of Bovine Seminal Plasma and Relationships with Sperm Quality before and after Cryopreservation. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 155, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barranco, I.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Perez-Patinõ, C.; Parrilla, I.; Ceron, J.J.; Martinez, E.A.; Rodriguez-Martinez, H.; Roca, J. High Total Antioxidant Capacity of the Porcine Seminal Plasma (SP-TAC) Relates to Sperm Survival and Fertility. Sci. Reports. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuk, M.; Lewinska, A.; Oklejewicz, B.; Bartosz, G.; Tischner, M.; Bugno-Poniewierska, M. Redox Status of Equine Seminal Plasma Reflects the Pattern and Magnitude of DNA Damage in Sperm Cells. Theriogenology 2010, 74, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




