1. Introduction
Soil salinization is an increasing threat to agricultural and forest productivity and sustainability of the environment [
1,
2,
3]. Fast-growing poplar species are economically important bioenergy resources and ecologically important for environmental conservation [
4,
5]. Enhancing salinity tolerance of
Populus for large-scale afforestation in salt-affected areas would enable sustainable bioenergy production [
1,
3]. The selection and identification of appropriate targets is essential for the genetic modification and molecular breeding of salt-resistant poplars [
1,
3]. We have previously shown that transcriptional regulation of salt-responsive genes from
Populus euphratica (a salt-tolerant poplar species), e.g.,
PeHA1,
PeTPK,
PeXTH,
PeHSF,
PeJ3,
PeJRL,
PeWRKY1,
PeREM6.5,
PePLDδ, and
PeGLABRA3, is critical for plant adaptation to the salt environment [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. Glycine-rich RNA-binding proteins (GRPs) interact with target mRNAs in the nucleus and regulate the processing and folding of the mRNAs [
17,
18,
19]. In plants, GRPs have been found to be expressed in response to various environmental stresses, such as cold, drought and salinity [
20,
21,
22,
23]. Several members of GRP family in
Arabidopsis and rice enhanced cold and freezing tolerance [
18,
20,
24,
25,
26]. Rice
OsGRP4 is involved in the plant response to high temperature stress [
27]. In
Camelina sativa, Kwak et al. (2013) have identified the differential expression of
CsGRP2a,
CsGRP2b and
CsGRP2c under salt or drought stress [
22]. Overexpression of
AtGRP2 or
AtGRP7 improves drought tolerance and grain yield of rice [
28]. Transcription of
SbGR-RNP was increased two- to fourfold in
Sorghum bicolor seedlings treated with NaCl (0.5-1.0 M, 24 h) [
29].
MhGR-RBP1 transcripts in leaves of
Malus hupehensis increased twofold after initial salt exposure (two days) but fell back to control levels after long-term treatment [
23]. However, salt induction of GRPs is less known in
P. euphratica, the salt resistant woody species [
30,
31,
32].
GRPs have been shown to affect plant salt tolerance in negative or positive ways.
Limonium bicolor LbGRP1 increased salt tolerance of tobacco plants by increasing proline content and activities of catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) [
33]. Furthermore, the
LbGRP1-transgenic tobacco can limit Na
+ content and Na
+/K
+ ratio under saline conditions [
33]. In addition, overexpression of
MhGR-RBP1 gene from
Malus prunifolia decreased the salt-promoted ROS production in
Arabidopsis [
34]. Kim et al. (2007) also showed that
AtGRP2 increases seed germination under salinity stress [
18]. Similarly, overexpression of
AtGRDP2 led to upregulation of stress-responsive genes in lettuce plants [
35]. However, expression of
Zoysia japonica ZjGRP or
Medicago sativa MsGRP inhibits seed germination and plant growth under salt stress [
36,
37].
ZjGRP overexpression resulted in downregulation of
SOD and peroxidase (
POD) genes in transgenic
Arabidopsis [
37]. Similarly, phenotype tests of
AtGRP7 and
AtGR-RBP4 transgenic lines demonstrate that GRP7 and GR-RBP4 negatively affect germination under high salt [
25,
38]. However, the
Atgrp7 mutant renders seedlings hypersensitive to NaCl [
21]. It is unknown whether
P. euphratica PeGRP2 negatively or positively mediates salt tolerance in poplar trees.
This study aims to evaluate the role of
PeGRP2 in the salt tolerance of poplar. We examined the NaCl-altered expression of
PeGRP2 in
P. euphratica seedlings. Subsequently, the
PeGRP2 gene was cloned and introduced into the hybrid poplar,
Populus tremula ×
P. alba ‘717-1B4’ (
P. ×
canescens). Phenotype tests showed that PeGRP2 negatively affected the salt tolerance of transgenic poplars. We demonstrated that
PeGRP2 overexpression renders salt tolerance by reducing photosynthesis and growth but increases Na
+ accumulation in the roots and shoots of transgenic poplars. In wild-type (WT)
P. ×
canescens and
PeGRP2-overexpressed lines, the activities of antioxidative enzymes, POD, SOD, and CAT were measured under long-term salinity. The amino acid sequence of PeGRP2 resembled the GRPs of other species, which contain a conserved RNA recognition motif domain at N-terminus and interact with target mRNA [
17,
19]. RNA affinity purification sequencing (RAP sequencing) was developed to enrich target mRNAs that physically interact with PeGRP2 in
P. ×
canescens. Glycine-rich RNA-binding proteins interact with target mRNAs and alter their stability under stress conditions [
19]. Here, we use RT-qPCR to examine the transcripts of mRNAs interacting with PeGRP2 in transgenic poplar after NaCl treatment (0 or 100 mM, 15 days). The PeGRP2-targeting mRNA transcripts were also tested in WT and served as salt and non-salt controls. Our RAP sequencing and RT-qPCR data showed that PeGRP2 negatively regulates the transcripts of several target mRNAs encoding proteins involved in photosynthesis, antioxidant defense, and Na
+ homeostasis under saline conditions, thereby reducing the ability to tolerate salinity in transgenic
P. ×
canescens. Our study provides new insights for breeding salt-resistant poplars by reducing the
GRP2 transcript.
2. Results
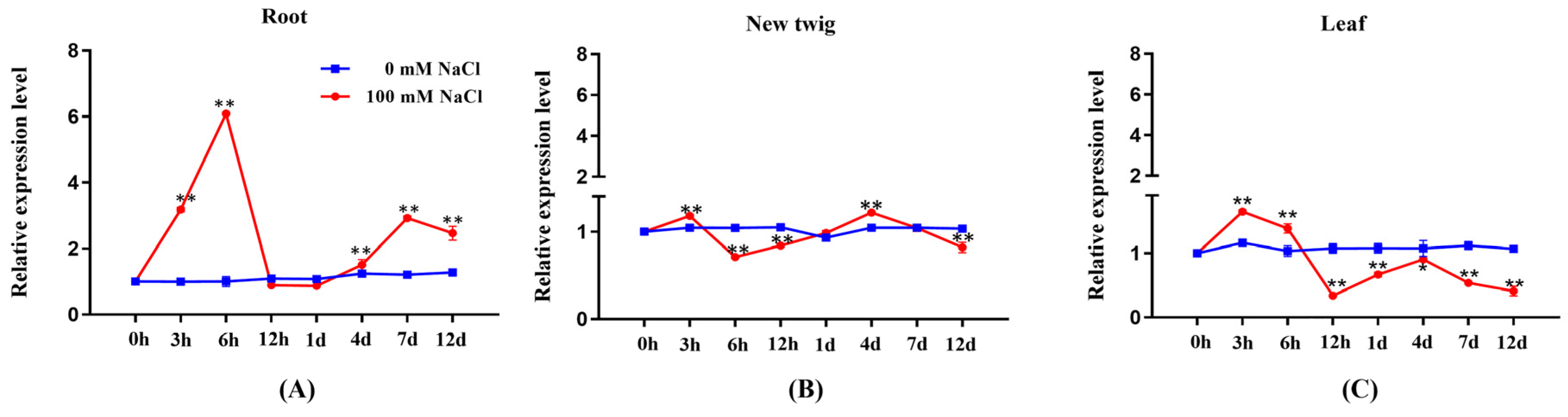
2.1. Expression Profile of PeGRP2 in Salt-Stressed P. euphratica
Table 2 fluctuated during the observation period of salt treatment (100 mM NaCl, 12 days).
PeGRP2 expression in roots tended to increase after the start of salt exposure, and peaked at 6 h, followed by a rapid drop at 12 h (
Figure 1A). Thereafter,
PeGRP2 levels remained constant in the following days, despite a 1-fold increase occurred at day 7 and day 12 (
Figure 1A). Salt-altered
PeGRP2 transcription in new twigs and leaves resembled the trend in roots, but the transient increase that occurred at 3 h was considerably lower than in roots (
Figure 1B,C). Furthermore,
PeGRP2 expression in new twigs tended to decline after day 4 and returned to a level lower than that of control plants at day 12 (
Figure 1B,C).
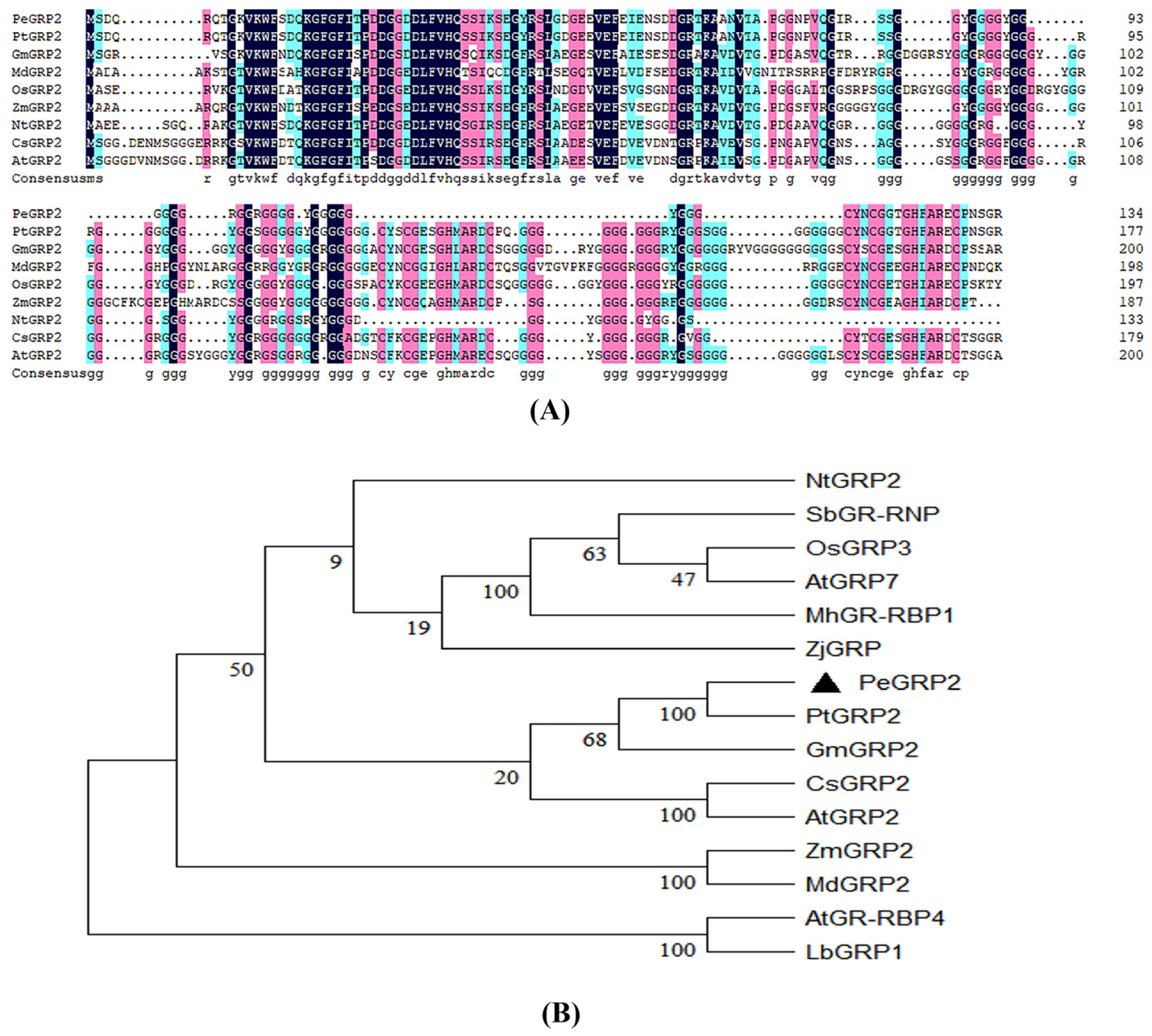
2.2. Sequence Analyses of PeGRP2
The length of
PeGRP2 sequence was 405 bp, coding for 134 amino acids; protein molecular weight was 13.44 kDa with an isoelectric point, 5.15 (
Figure 2A). PeGRP2 protein is rich in glycine at C-terminus and N-terminus contains a conserved RNA recognition motif (RRM) domain. The amino acid sequence of
P. euphratica PeGRP2 resembled the glycine-rich proteins of other species (
Figure 2A). Phylogenetic tree analysis revealed that PeGRP2 is closely related to PtGRP2 from
P. trichocarpa but distantly related to
Arabidopsis AtGRP2 (
Figure 2B).
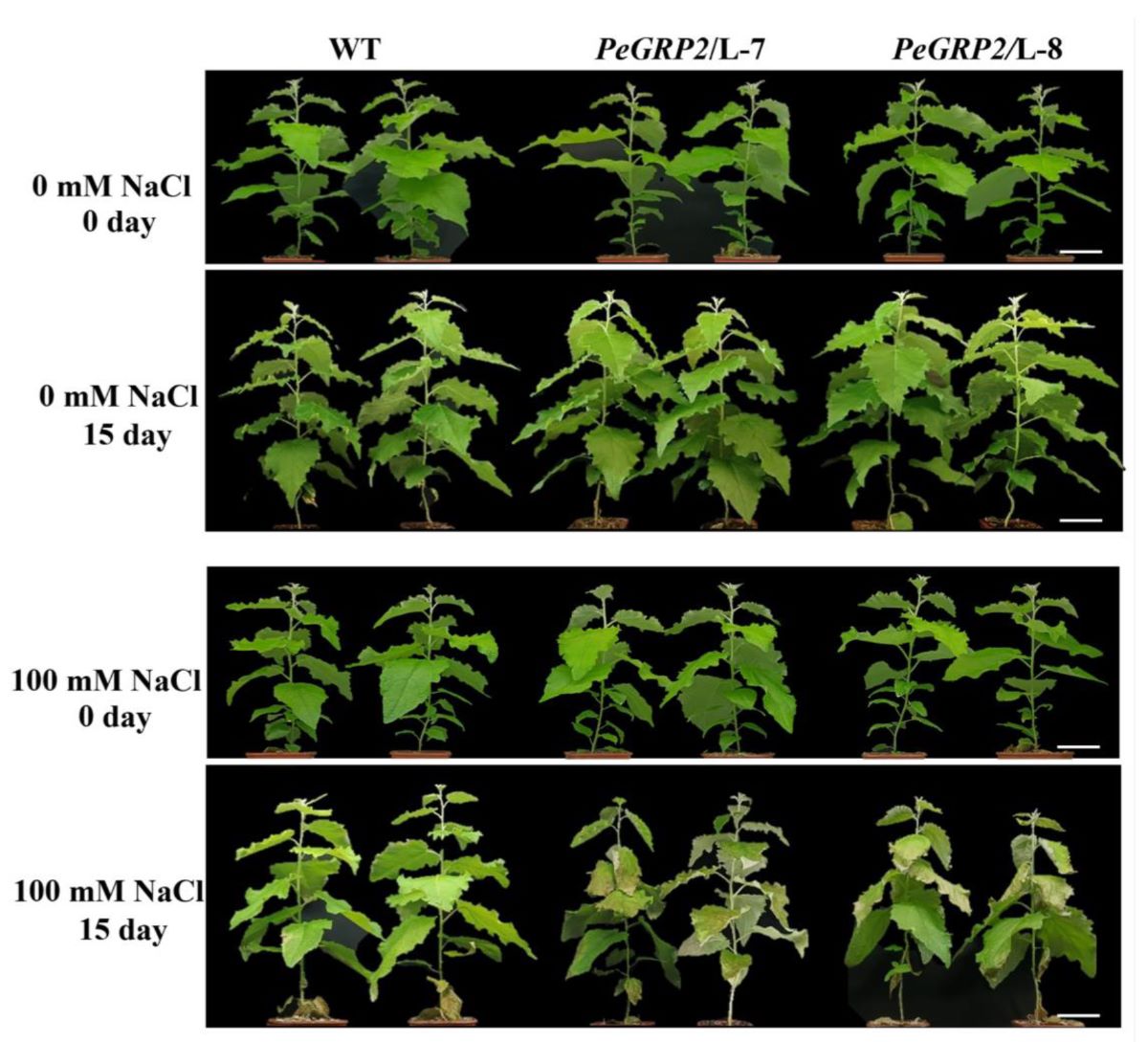
2.3. Phenotypic Tests of PeGRP2-Overexpressed Poplars Under Salt Stress
PeGRP2 was transformed into the grey poplar,
P. × canescens, to determine the importance of
PeGRP2 for salinity tolerance. Ten transgenic poplar lines (L-1, L-2, L-3, L-4, L-5, L-6, L-7, L-8, L-9, and L-10) were obtained, and the abundance of
PeGRP2 transcripts was verified by RT-qPCR and semiquantitative RT-PCR (
Figure 3A). We selected wild type (WT) and two transgenic lines with higher
PeGRP2 abundances, L-7 and L-8, for salt tests. Under salt-free conditions, shoot height, stem diameter and leaf area of
PeGRP2-overexpressing poplars were comparable to those of the WT (
Figure 3B-E). However, salt damage symptoms occurred in the mature upper leaves, but the damage was more severe in the transgenic lines (
Figure 3B). The growth of height and diameter in the transgenic plants were more restricted under long-term salinity (100 mM NaCl, 10-15 days) than at WT (
Figure 3C,D). The reduced leaf area due to NaCl was also more pronounced in the transgenic plants compared to WT (
Figure 3E). This indicates that overexpression of
PeGRP2 increases the salt sensitivity of
P. ×
canescens poplars.
2.4. Membrane Permeability and Lipid Peroxidation
We measured relative electrolyte leakage (REL) to indicate membrane permeability increased by salt [
15,
39]. NaCl treatment (100 mM, 15 days) caused a significant rise of REL in leaves, and the effect was more pronounced in
P. ×
canescens overexpressing
PeGRP2 (
Figure 3F). The content of malondialdehyde (MDA) increased in the salt-treated plants and resembled the pattern of REL (
Figure 3G). This indicates that the increased REL by salt in transgenic lines results from lipid peroxidation, as MDA content is a free radical oxidative marker [
15,
39,
40].
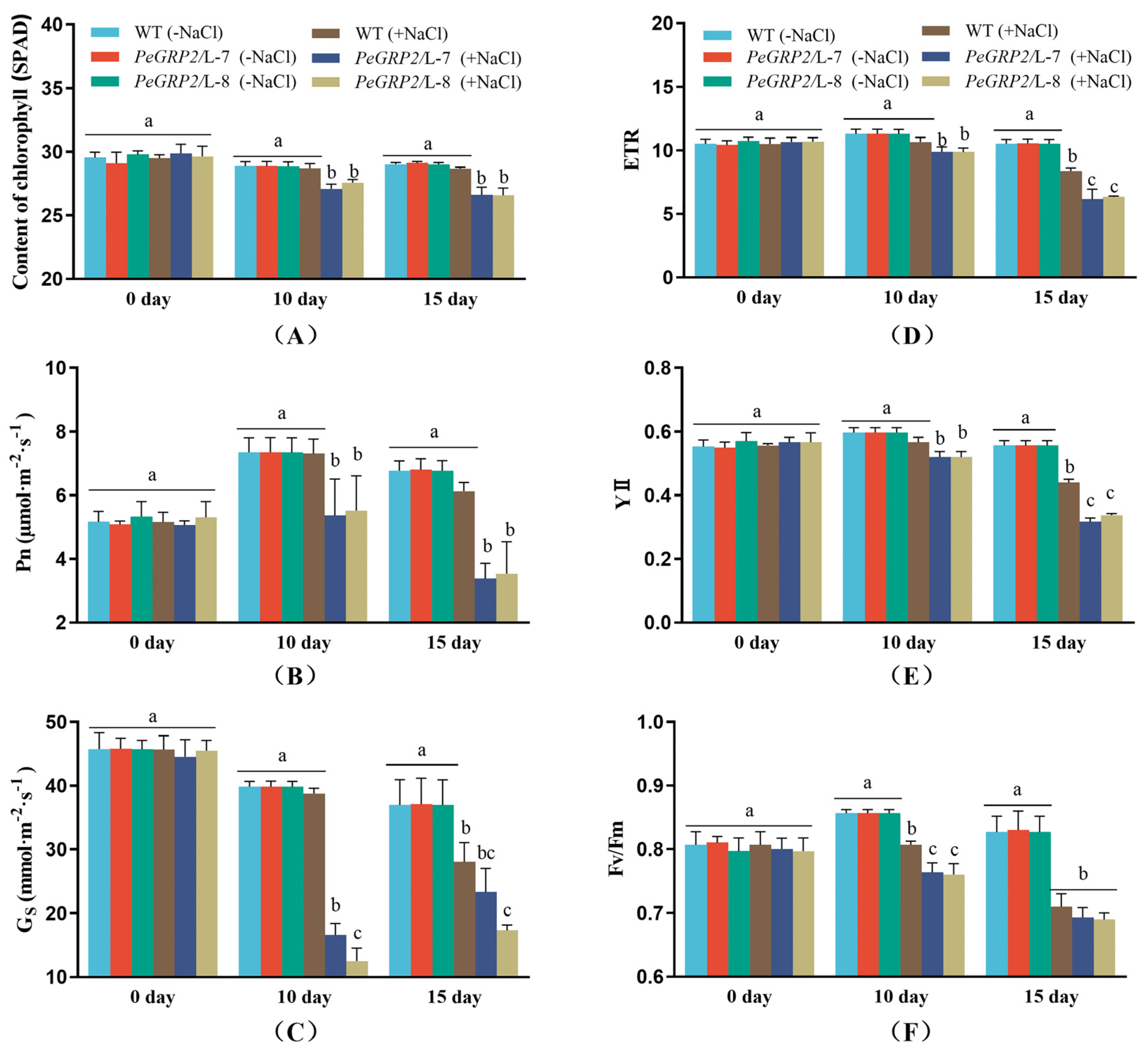
2.5. Photosynthetic Capacity of Salinised Poplars
Genotypic differences in growth performance are associated with photosynthetic capacity of WT and transgenic poplars. Chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence, and photosynthetic rate were examined in NaCl-treated poplars. Salinity did not affect chlorophyll content in the mature upper leaves of WT poplar, but significantly decreased chlorophyll content in both transgenic lines L-7 and L-8 during the salt treatment (10-15 days,
Figure 4A). Compared to the WT, Pn in L-7 and L-8 started to decrease after 10 days of salt exposure, and a sharp decrease occurred on day 15 (
Figure 4B), coinciding with a marked decrease in stomatal conductance (Gs) in the leaves (
Figure 4C). Chlorophyll fluorescence assay showed that NaCl reduced the maximum PSⅡ photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm), the actual photosynthetic quantum yield (YⅡ), and the relative electron transport rate (ETR), in WT poplars and the transgenic lines (
Figure 4D-F). Compared with WT, L-7 and L-8 showed a greater decrease in ETR, YII and Fv/Fm after 10 and 15 days of salt stress (
Figure 4D-F).
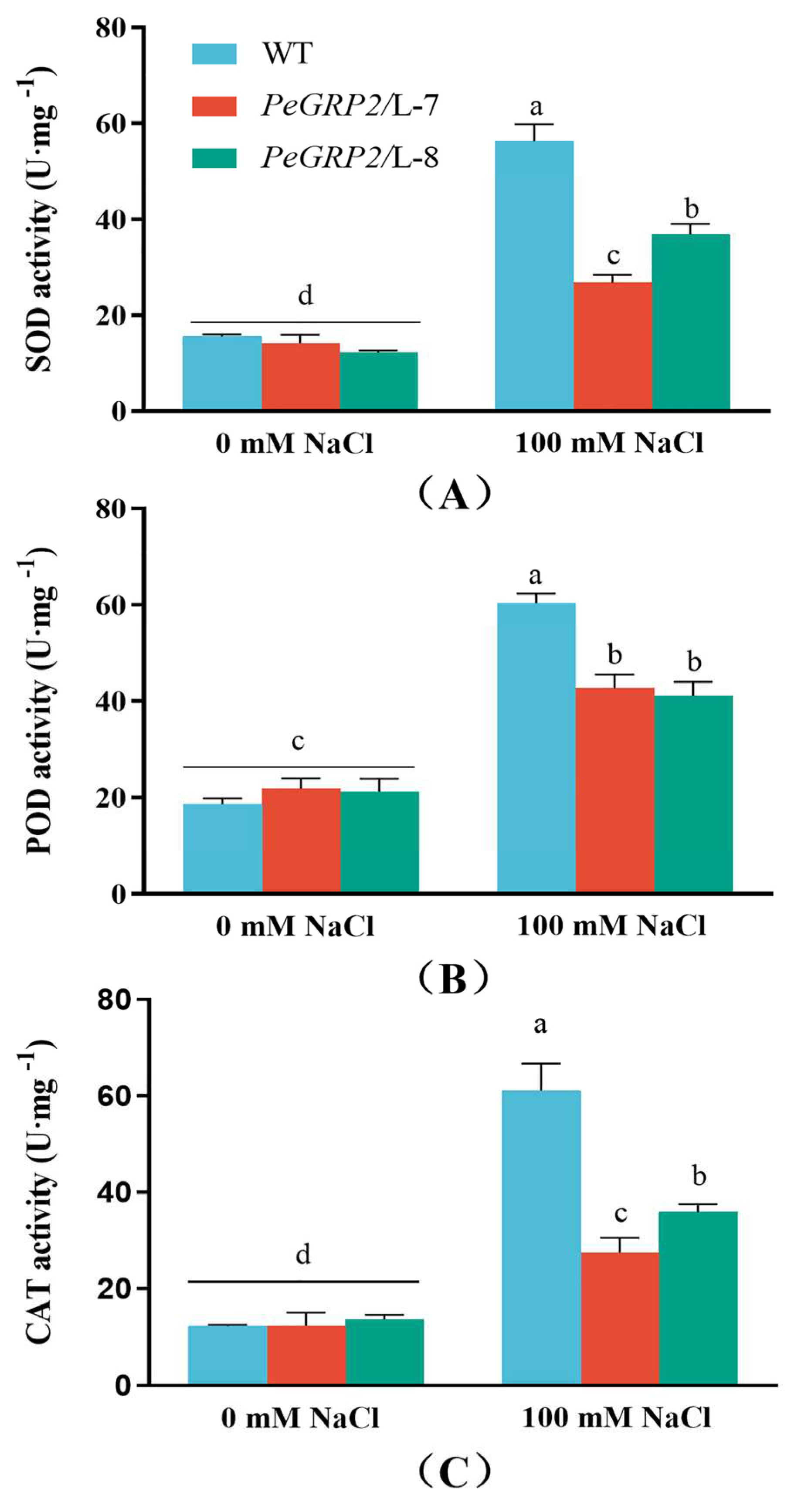
2.6. Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes
To determine whether
PeGRP2-transgenic poplars differ from the WT in ROS scavenging, POD, SOD, and CAT activity was compared under salt stress. NaCl treatment (100 mM, 15 days) increased the total activities of the tested antioxidative enzymes in WT
P. ×
canescens and
PeGRP2-overexpressed lines, but significantly lower values were observed in L-7 and L-8 (
Figure 5A-C).
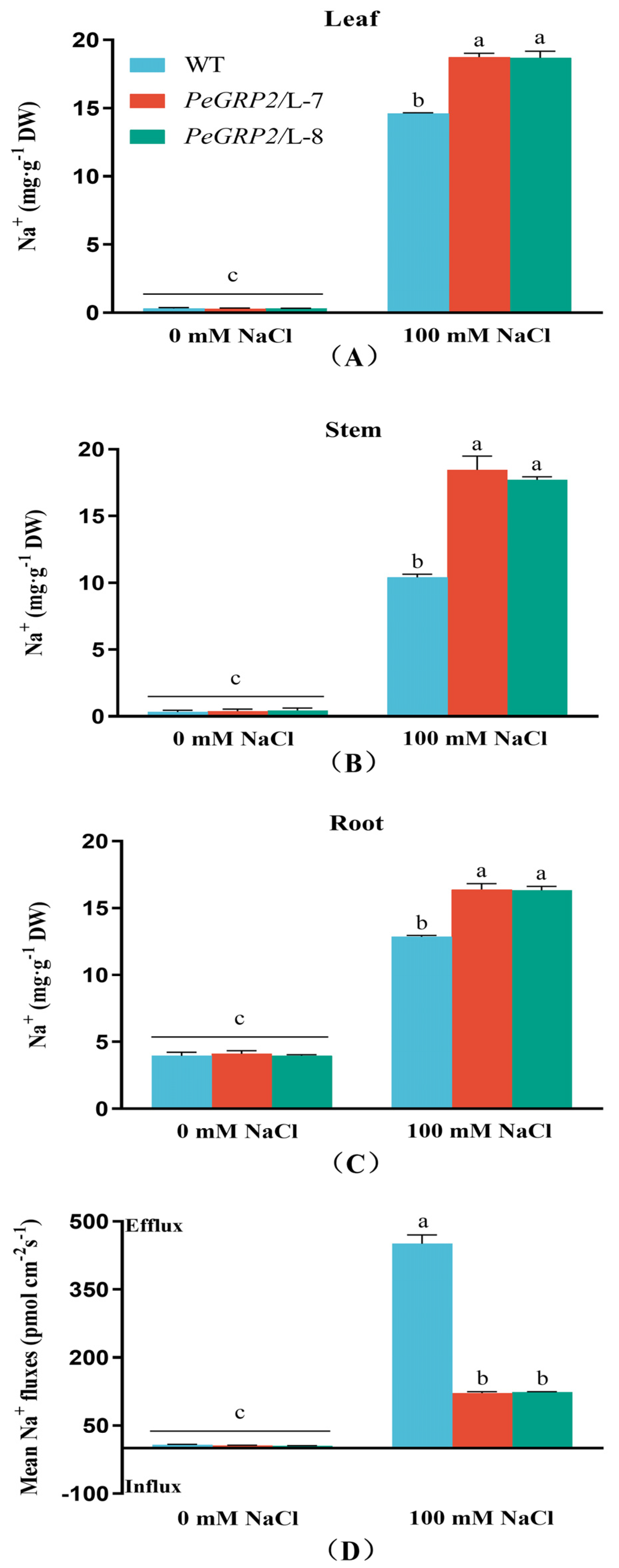
2.7. Na+ Content and Flux in Roots
Na
+ was found to accumulate in roots, stems, and leaves of NaCl-stressed poplars, with higher concentrations observed in the transgenic lines (
Figure 6A-C). Flux recordings with Na
+-selective microelectrodes showed that NaCl significantly increased Na
+ efflux despite a high flux rate in the WT poplar (
Figure 6D). The reduced ability to excrete Na
+ in transgenic lines would result in greater salt accumulation in roots and subsequent transport to the shoot (
Figure 6A-C).
2.8. PeGRP2-Interacting Target mRNAs in P. × Canescens
Our data showed that
PeGRP2-overexpressed lines differ from the WT in mediating photosynthesis, antioxidant protection and Na
+ homeostasis under salt stress. GRP proteins interact with target mRNAs and affect their stability under stress conditions [
19]. To determine whether PeGRP2 regulates target mRNAs related to photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes, and Na
+ homeostasis, RNA affinity purification sequencing (RAP sequencing) was developed to enrich target mRNAs that interact with PeGRP2 in
P. × canescens. Briefly, the PeGRP2-HaloTag protein was produced as a bait protein using the High-Yield Wheat Germ Protein Expression System, TNT SP6 [
12]. The PeGRP2-HaloTag protein was incubated with Magne HaloTag magnetic beads to form a complex of bait protein and magnetic beads. Then, the total RNA from WT
P. × canescens and
PeGRP2-transgenic poplars was added to the bait protein-magnetic bead complex solution, forming a bait protein-mRNAs-magnetic bead complex. The enriched mRNAs were eluted to construct cDNA library for sequencing on the Illumina NovaSeq platform. The PeGRP2-interacting mRNAs encoding proteins related to photosynthesis, antioxidant defense, and Na
+ homeostasis was listed in
Table 1 and categorized into three groups:
Chloroplastic photosynthetic proteins: cytochrome b6-f complex iron-sulfur subunit (PETC), photosystem II 10 kDa polypeptide (PSBR), photosystem II core complex proteins psbY (PSBY), photosystem II reaction center PSB28 protein (PSB28), chlorophyll a-b binding protein 5 (CAB5), CAB6, ribulose-1, 5 bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit N-methyltransferase (RBCMT), light-harvesting complex-like protein 3 isotype 1 (LIL3-1), oxygen-evolving enhancer protein 1 (PSBO1), PSBO2, and ferredoxin-NADP reductase (LFNR);
Antioxidant enzymes: peroxidase 42 (POD42), POD47, superoxide dismutase (SOD [Cu-Zn]2), mitochondrial SOD[Mn], transmembrane ascorbate ferrireductase 1 isoform X2 (CYB1-2), chloroplastic thioredoxin X (TRX), chloroplastic thioredoxin-like protein CDSP32 (CDSP32), chloroplastic thioredoxin M-type (TRXM), and chloroplastic peroxiredoxin Q (PRXQ);
Cation/H+ exchangers and ATPases: sodium/proton antiporter 1 (NHA1), sodium/hydrogen exchanger 2 isoform X1 (NHE2-1), vacuolar cation/proton exchanger 3 (CAX3), pyrophosphate-energized vacuolar membrane proton pump 1 (AVP1), plasma membrane (PM) -type ATPase 11, (AHA11), PM-type calcium-transporting ATPase 8 (ACA8), ACA9, AAA-ATPase At1g43910 (AATP), and mitochondrial AAA-ATPase ASD (ASD).
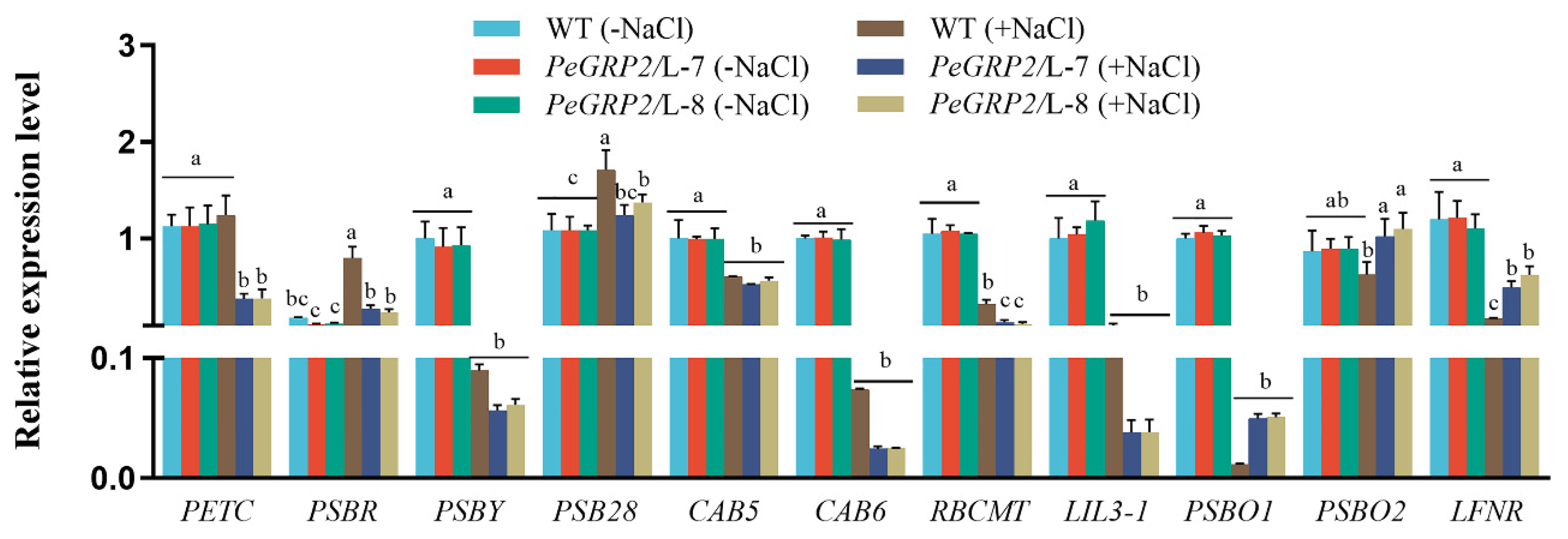
2.9. Transcriptional Profiling of PeGRP2-Interacting mRNAs Under Salt Stress
GRPs have been shown to modify the stability of target mRNAs under stress conditions [
19]. Here, we use RT-qPCR to examine the transcripts of PeGRP2-interacting mRNAs in transgenic poplars after NaCl treatment (0 or 100 mM, 15 days). PeGRP2 target mRNA transcripts were also tested in WT and served as no-salt and salt controls. NaCl-altered transcripts of PeGRP2 target mRNAs in all tested lines are briefly listed below and shown in
Figure 7,
Figure 8 and
Figure 9.
2.9.1. Transcripts of PeGRP2 Target mRNAs Encoding Photosynthetic Proteins
Under salt-free conditions, the transcripts of PeGRP2-interacting mRNAs,
PETC,
PSBR,
PSBY,
PSB28,
CAB5,
CAB6,
RBCMT, LIL3-1,
PSBO1,
PSBO2 and
LFNR in transgenic lines (L7 and L8) are similar to those in WT poplar (
Figure 7). However, NaCl decreased the transcripts of these PeGRP2 target mRNAs,
PETC,
PSBY,
CAB5,
CAB6,
RBCMT,
LIL3-1,
PSBO1,
LFNR, in transgenic lines with a few exceptions (
PSBR,
PSB28 and
PSBO2,
Figure 7). Overall, most PeGRP2-interacting mRNAs involved in photosynthesis processes, for example photosynthetic light harvest and reaction (
PSBY,
CAB5,
CAB6,
LIL3-1), oxygen-evolving (
PSBO1), electron transport (
PETC and
LFNR), and carbon fixation (
RBCMT), were down-regulated relative to the few unchanged target mRNAs under NaCl stress (
Figure 7). This is consistent with the salt-reduced maximum photochemical efficiency of PSII, actual photosynthetic quantum yield, relative electron transport rate, and net photosynthetic rate in the transgenic poplars (
Figure 4B,D-F). Compared to plants with
PeGRP2-transgenes, transcripts of photosynthesis-related mRNAs were less reduced (
RBCMT), not changed (
PETC), or even increased (
PSBR and
PSB28) in WT after salt exposure (
Figure 7). This agrees with the less restricted YII, Fv/Fm, ETR, and Pn values in the salt-stressed poplars of WT (
Figure 4B,D-F).
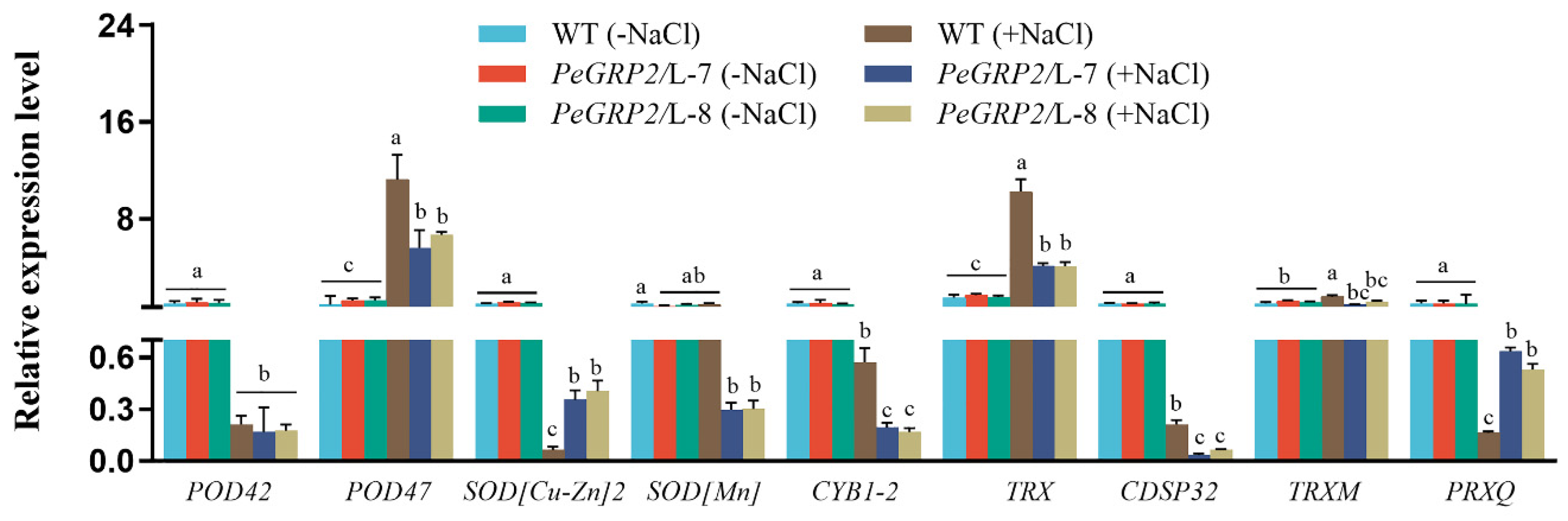
2.9.2. Transcripts of PeGRP2 Target mRNAs Encoding Antioxidant Enzymes
NaCl was shown to increase transcripts of PeGRP2 target mRNAs such as
POD47 and
TRX in plants overexpressed with
PeGRP2 (
Figure 8). However, the salt-elevated transcripts of
POD47 and
TRX were typically lower in
PeGRP2-overexpressed poplars than in the WT (
Figure 8). In contrast, NaCl decreased the transcripts of
POD42,
SOD[Cu-Zn]2,
SOD[Mn],
CYB1-2,
CDSP32, and
PRXQ in transgenic lines (
Figure 8). In particular, the target mRNAs of PeGRP2,
SOD[Mn],
CYB1-2,
CDSP32, were more strongly suppressed by NaCl in
PeGRP2-transgnic lines L-7 and L-8 compared to WT (
Figure 8). While NaCl suppression of
SOD[Cu-Zn]2 and
PRXQ transcripts was more pronounced in the WT (
Figure 8). Our data suggest that PeGRP2 differentially regulates the stability of target mRNAs that encode antioxidant enzymes under salinity, which differs from no-salt controls in which the transcript of PeGRP2-interacting mRNAs remained at a similar level in all genotypes tested.
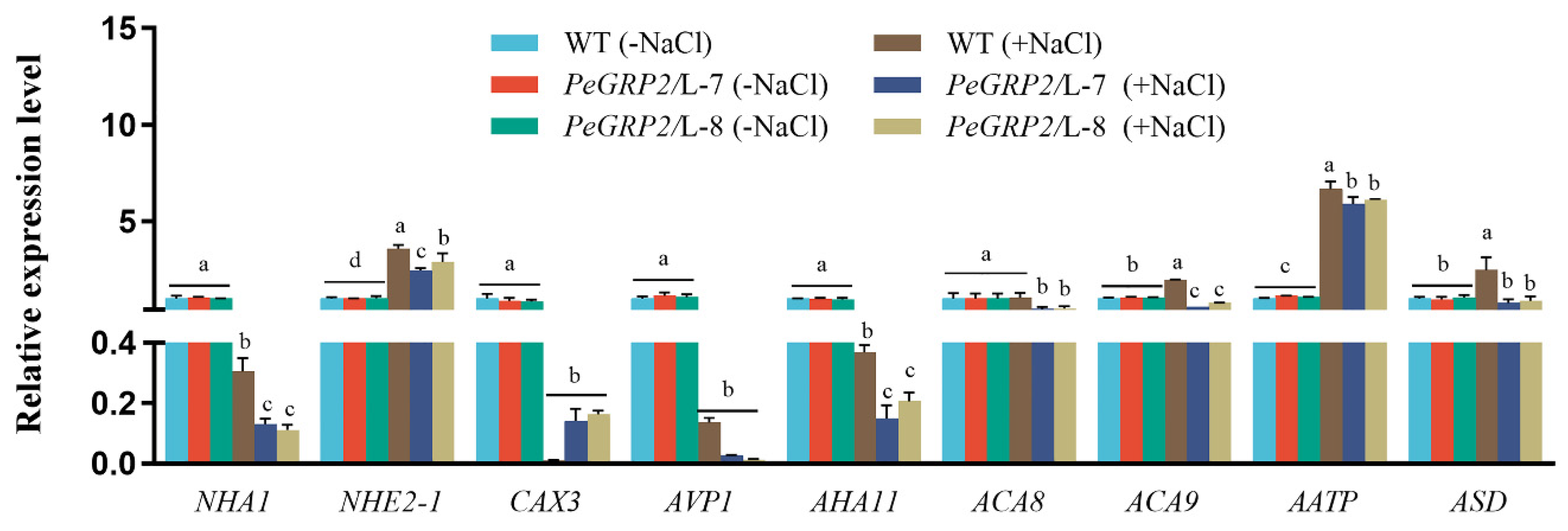
2.9.3. Transcripts of PeGRP2 Target mRNAs Encoding Cation/H+ Exchangers and ATPases
NaCl decreased the transcripts of PeGRP2-interacting mRNAs encoding cation/H
+ exchangers,
NHA1, and
CAX3, but increased the
NHE2-1 transcript in transgenic lines (
Figure 9). Compared to WT poplar,
PeGRP2-transgenic plants exhibited lower levels of
NHA1 and
NHE2-1 under saline conditions (
Figure 9). Therefore, PeGRP2 negatively regulates the stability of target mRNAs encoding Na
+/H
+ antiporters under salt conditions.
RT-qPCR analysis of target mRNAs interacting with PeGRP2 showed that NaCl significantly decreased the transcript of
AVP1,
AHA11,
ACA8 and
ACA9, but increased the transcript of
AATP in transgenic plants (
Figure 9). Compared with transgenic lines, NaCl produced a less decrease in the transcripts of
AHA11,
ACA8, and
ACA9 in WT poplars, and
AATP and
ASD remained at a higher level under salt stress (
Figure 9). Overall, transcripts of all tested ATPase-encoding mRNAs were typically lower in
PeGRP2-overexpressed lines than in the WT, indicating that PeGRP2 negatively regulates the stability of target mRNAs encoding ATPases under salt stress.
3. Discussion
3.1. PeGRP2 Increases Salt Sensitivity of Transgenic P. × canescens
In this study, overexpression of
P. euphratica PeGRP2 increased the sensitivity of
P. ×
canescens to NaCl stress. Salt treatment resulted in greater impairment of shoot height, stem diameter and leaf area in
PeGRP2-overexpressed poplar compared to the WT (
Figure 3). Our data suggest that
PeGRP2 negatively regulates salt tolerance in poplar. This is consistent with the finding that ectopic expression of
ZjGRP or
MsGRP inhibits seed germination and plant growth under salt treatment [
36,
37]. Similarly, AtGRP7 and AtGR-RBP4 negatively affect germination in salt medium [
25,
38]. However, these results are inconsistent to Kim et al. (2007), who found that AtGRP2 increased seed germination under salinity [
18]. In addition, plant growth and flowering were promoted in lettuce plants overexpressing
AtGRDP2 [
35]. These contrasting results indicate that GRP proteins play different roles in regulating the response of plants to salinity. In agreement with this, Park et al. (2009) also found that CSDP1 and CSDP2 function in opposite ways in salt-exposed plants [
41]. GRP2 sequence analysis showed that PeGRP2 is homologous to
P. trichocarpa PtGRP2 but distinct from
Arabidopsis AtGRP2 (
Figure 2), implying that the function of PeGRP2 is different from that of AtGRP2.
PeGRP2 in
P. euphratica leaves tended to decrease after a transient increase after 3-6 h of NaCl exposure (
Figure 1). Similarly, the
MhGR-RBP1 gene of
Malus hupehensis increased after initial salinity, but markedly decreased with longer duration of stress [
23]. The pattern of
PeGRP2 transcription contrasts with salt-invoked
GRP orthologs,
SbGR-RNP, in
Sorghum bicolor [
29]. Thus, down-regulation of
PeGRP2 favors adaptation of the salt-resistant poplar
P. euphratica to saline conditions, as
PeGRP2 overexpression resulted in excessive Na
+ accumulation and growth suppression in poplars (
Figure 3 and
Figure 6). The PeGRP2 suppression of salt tolerance is mainly due to the reduced ability to maintain photosynthesis, Na
+, and ROS homeostasis in the transgenic poplars (
Figure 4,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). We developed RNA affinity purification sequencing (RAP sequencing) to identify target mRNAs that directly interact with PeGRP2 in poplar (
Table 1). Our RAP sequencing in conjunction with RT-qPCR revealed that PeGRP2 negatively regulates the stability of several target mRNAs encoding photosynthetic proteins, antioxidant enzymes, ATPases and Na
+/H
+ transporters in transgenic poplar under salt stress (
Figure 7,
Figure 8 and
Figure 9).
3.2. PeGRP2 Interacts with Targeting mRNAs Encoding Photosynthetic Proteins and Affects Photosynthesis Under Salt Stress
The reduction of chlorophyll content and photosynthesis by NaCl impaired the shoot and leaf growth of poplar (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). The salt-decreased photosynthetic capacity was accompanied by reduced transcripts of PeGRP2-targeting mRNAs encoding photosynthetic proteins involved in light harvesting and reaction, electron transport, oxygen evolution, and CO
2 fixation (
Figure 7). NaCl significantly decreased transcripts of
PETC,
PSBY,
CAB5,
CAB6,
RBCMT,
LIL3-1,
PSBO1, and
LFNR, which showed physical interactions with PeGRP2 in transgenic poplar (
Figure 7). The salt-reduced transcripts of photosynthetic proteins resulted in reduced maximum photochemical efficiency of PSII, actual photosynthetic quantum yield, relative electron transport rate, and net photosynthetic rate in transgenic poplar (
Figure 4). Compared with plants transformed with
PeGRP2, NaCl increased the transcript of
PSBR and
PSB28 in WT poplar, and
PETC and
RBCMT showed less or not reduced transcripts after salt exposure (
Figure 7). In accordance, YII, Fv/Fm, ETR, and Pn were less restricted in WT poplars under salt conditions, compared with
PeGRP2-overexpressed lines (
Figure 4). We found that PeGRP2 decreased the transcript of target mRNAs irrespective of salt-simulated
PSB28 and
PSBR and salt-inhibited
PETC and
RBCMT under salt stress (
Figure 7). It is possible that NaCl changed the association of PeGRP2 with its target mRNAs [
19], thereby negatively regulating the stability of mRNAs and reducing photosynthesis in transgenic poplar.
3.3. PeGRP2 Interacts with Targeting mRNAs Encoding Antioxidant Enzymes and Affects ROS Scavenging Capacity Under Salt Stress
NaCl caused significant activation of POD, SOD, and CAT in WT and transgenic poplars (
Figure 5). Accordingly, NaCl increased the transcripts of several PeGRP2-interacting mRNAs, such as
POD47,
TRX and/or
TRXM, in the salt-stressed poplars, although the transcripts were typically lower in the
PeGRP2-overespressed lines (
Figure 8). However, salt repressed transcripts of other PeGRP2-interacting mRNAs,
POD42,
SOD[Cu-Zn]2,
SOD[Mn],
CYB1-2,
CDSP32, and
PRXQ, in the transgenic poplars (
Figure 8). Compared with
PeGRP2 transgenic lines,
SOD[Mn],
CYB1-2 and
CDSP32 transcripts were less reduced by salt in WT (
Figure 8). The lower stimulation of
POD47,
TRX and
TRXM together with the greater reduction of
SOD[Mn],
CYB1-2 and
CDSP32 probably resulted in a less pronounced increase in antioxidant enzyme activity in the transgenic poplar under salinity (
Figure 5 and
Figure 8). The impaired activity and transcripts of antioxidant enzymes led to the failure to remove salt-induced ROS during long-term salt stress, which exacerbated the process of lipid peroxidation of membranes. As a result, the REL and MDA content of transgenic
P. ×
canescens were remarkable higher than those of WT poplar (
Figure 3). In the leaves of
P. popularis, we found that salt exposure increased the activity of APX, CAT and GR [
42,
43] and the transcription of
POD,
CAT,
GST,
GRX and
TRX [
44]. However, the salt-induced production of ROS exceeded the antioxidant capacity of the enzymatic system, resulting in oxidative damage in the salt-sensitive poplar [
42,
43]. Our results agree with Teng et al. (2017), who found that
ZjGRP overexpression resulted in downregulated
SOD and
POD in
Arabidopsis, and transgenic plants exhibited salt-sensitive traits [
37]. In contrast,
MhGR-RBP1 overexpression decreased the salt-produced ROS in
Arabidopsis [
34], and
LbGRP1-overexpressed tobacco plants showed increased proline content and activities of CAT and SOD under salt stress [
33]. Apparently, GRP regulates antioxidant defense in a species-specific manner. In our study, RAP sequencing and RT-qPCR showed that PeGRP2 interacts with target mRNAs to negatively regulate their stability, independent of salt-simulated
POD47 and
TRX and salt-inhibited
SOD[Mn],
CYB1-2 and
CDSP32 (
Figure 8). The data from RAP sequencing combined with RT-qPCR are consistent with the results from RNA immunoprecipitation analysis and proteomic analysis. RNA immunoprecipitation analysis revealed that
OsGRP3 negatively regulates the expression of ROS-regulatory genes in rice, such as metallothionein 1d (
MT1d) and peroxidase 1 (
POX1), under water-deficit conditions [
19]. Proteomic analyses showed that mitochondrial Mn-SOD, mitochondrial peroxiredoxin, whose function is related to the control of ROS homeostasis, is suppressed by AtGRP2 under cold stress [
18]. Therefore, it is possible that PeGRP2 interacts with target mRNAs of several antioxidant enzymes to negatively regulate their stability under salinity, resulting in a reduced ability to eliminate salt-generated ROS in transgenic poplars.
3.4. PeGRP2 Interacts with Targeting mRNAs Encoding ATPases and Na+/H+ Transporters and Affects Na+ Homeostasis Under Salt Stress
In addition to affecting photosynthesis and antioxidant defense, PeGRP2 impairs ion homeostasis in salt-stressed poplar plants.
PeGRP2-overexpressed
P. ×
canescens exhibited greater Na
+ accumulation in roots, stems and leaves compared to WT poplar (
Figure 6). The buildup of Na
+ in shoots was due to the low ability of roots to excrete Na
+ ions. NMT data showed that transgenic poplars had significantly lower Na
+ efflux at the root tips (
Figure 6), indicating that a greater amount of salt ions absorbed by the roots was translocated to the shoot [
30,
31,
32,
45]. Our data are inconsistent with transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing
LbGRP, in which transgenic plants accumulated lower Na
+ content under saline conditions [
33]. In general, Na
+ excess leads to ion-specific toxicity and ROS production in poplar leaves [
42,
43,
44]. Compared with WT poplars, NaCl caused a greater reduction in the transcripts of
AHA11 and
NHA1, which physically interact with PeGRP2 in transgenic poplar (
Figure 9). This could reduce the antiport Na
+/H
+ across the PM in leaf cells [
44,
45,
46,
47], although the transcripts of PeGRP2-targeting mRNAs,
AATP,
NHE2-1 and
ASD were increased or unchanged by NaCl (
Figure 9). Moreover, the downregulated transcript of Ca
2+-ATPase,
ACA8 and
ACA9 in the transgenic poplar (
Figure 9), suggests that PeGRP2 negatively regulates the stability of its target RNAs and thus impairs Ca
2+-SOS signaling for Na
+ extrusion under salt conditions. In accordance, the transgenic poplars showed downregulated transcripts of
SOS2 and
SOS3 under salt stress (Supplemental
Figure S1). Vacuolar salt compartmentalization might also be impaired in the transgenic lines, as a decrease in
AVP1 and
CAX3 transcript was observed under salt stress (
Figure 9). The reduced extrusion of Na
+ from the cytosol and the accompanied restriction of vacuolar Na
+ compartmentalization would result in an excess of toxic Na
+ in the cytoplasm [
48]. Consequently, the accumulated Na
+ ions in the cytosol would lead to increased ROS production and decreased photosynthesis [
42,
43,
49,
50].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. NaCl Treatment of P. euphratica
P. euphratica seedlings were well watered and fertilized for three months in a greenhouse [
15,
51]. Uniform seedlings were treated with NaCl solution (0 or 100 mM) for 12 days. Fine roots, new twigs, and upper leaves (5
th to 20
th from the shoot tip) were collected on day 1 (0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h), day 4, day 7 and day 12. The samples were immediately frozen in liquid N
2 and stored at -80 °C. Total RNA was isolated for
PeGRP2 cloning and RT-qPCR analysis.
4.2. PeGRP2 Cloning and Sequence Analysis
The E.Z.N.A.
® Plant RNA Kit (Omega Bio-Tek, Guangzhou, China) was used to isolate total RNA from
P. euphratica leaves. After removal of genomic DNA with the DNA Remover Mix, the reverse transcriptase kit HiFiScript RT MasterMix (Cowin Bio, Jiangsu, China) was used for first-strand cDNA synthesis.
PeGRP2 was cloned by PCR amplification with the following specific primers: forward 5’-ATGGCTGCCGAGGTTGAGTATA-3’ and reverse 5’-CTAATCCCTCCAGCTACCAC-3’. Multiple sequence alignments and phylogenetic analyses of GRP proteins were performed as previously described [
15,
16]. The GenBank accession numbers of GRP2 orthologs are listed in
Supplementary Table S1.
4.3. PeGRP2 Transformation to P. × canescens
Transformation of
PeGRP2 into
P. × canescens was performed according to Leplé JC et al. (1992) with modifications [
52]. Briefly, the cDNA sequence of
PeGRP2 was ligated into the part-CAM-FLAG Flag vector, with the Xba I and Xho I sites driven by the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter. Subsequently, the
PeGRP2 overexpression construct was transferred to
Agrobacterium tumefaciens (strain GV3101) for plant transformation. Ten lines overexpressing
PeGRP2, i.e., L-1, L-2, L-3, L-4, L-5, L-6, L-7, L-8, L-9 and L-10, were obtained and verified by both semiquantitative RT-PCR and RT-qPCR.
Tissue cultures of stem segment in MS solid medium were used to propagate the plantlets [
53]. They were cultivated in a climate incubator with the following settings: temperature of 23 °C, relative humidity of 55-60%, photoperiod of 16 h (light) /8 h (dark) and photoactive radiation of 150 μmol m
-2 s
-1.
P. × canescens plantlets were grown in tissue culture flasks for 3-4 weeks and then acclimated in hydroponics for 3 weeks before planting in pots for soil culture. The nursey soil contained peat, silica sand and potting soil in a ratio of 1:1:1. Plantlets were cultured in a climate room for four weeks and used for phenotype testing.
4.4. Phenotype Test of Salt Tolerance
4.4.1. Growth Measurement
Uniform plants of wild-type (WT) P. × canescens and two transgenic lines, L-7 and L-8, were treated with NaCl saline (0 or 100 mM) for 15 days. Shoot height, stem diameter, and leaf area growth of developing leaves were measured at day 1, day 10, and day 15.
4.4.2. Relative Electrolyte Leakage (REL) and Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content
Leaf samples of WT
P. × canescens and two
PeGRP2-overexpressed lines, L-7 and L-8, were collected after 15 days of NaCl treatment (0 or 100 mM). REL was calculated by the initial relative conductivity (EC1) before boiling and the final conductivity (EC2) after boiling: REL (%) = (EC1/EC2) × 100% [
39,
54]. The content of MDA was determined with the Micro MDA Assay Kit (BC0025) (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology, Beijing, China).
4.4.3. Measurement of Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Gas Exchange
Chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence, and gas exchange were measured after WT poplars and PeGRP2-transgenic lines were treated with NaCl (0 or 100 mM) for 10 and 15 days. Chlorophyll content of upper mature leaves was measured with a portable chlorophyll meter, SPAD-502-PLUS (Konica Minolta Optics, Japan). The maximum PSⅡ photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm), the actual photosynthetic quantum yield (YⅡ) and the relative electron transport rate (ETR) were examined with a pulse-amplitude modulated (PAM) chlorophyll fluorometer, JUNIOR-PAM (Heinz Walz GmbH, Effeltrich, Germany). The net photosynthetic rate (Pn), and stomatal conductance (Gs) of upper mature leaves were measured with a portable photosynthetic transpiration meter, Yaxin-1102 (Beijing Yaxin Liyi Technology, Beijing, China).
4.5. Determination of Antioxidative Enzyme Activity
WT P. × canescens and two PeGRP2-overexpressed lines, L-7 and L-8, were salinized for 15 days with NaCl (0 or 100 mM). The leaves were sampled and used to measure total activities of antioxidative enzymes. POD, SOD, and CAT activity was examined using the assay kits of POD (BC0090), CAT (BC0205), and SOD (BC0175) (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology, Beijing, China), respectively.
4.6. Na+ Concentration in Root, Leaf and Stem
Roots, stems, and leaves were collected from WT P. × canescens and PeGRP2-overexpressed lines, L-7 and L-8, after 15 days of salt treatment (0 or 100 mM NaCl). The oven-dried samples (60 °C, 5 days) were digested with H2SO4-H2O2 and used for Na+ determination with an atomic absorption spectrometer (Varian SPA -220FS, Palo Alto, CA, USA).
4.7. Flux Records of Na+ in Roots
Net Na
+ fluxes at root tips were recorded using a Non-invasive Micro-test system (NMT) [
45,
55]. Roots were collected from WT
P. × canescens and
PeGRP2-overexpressed lines, L-7 and L-8, after 15 days of salt treatment (0 or 100 mM NaCl). Root tips were equilibrated for 30 min in measuring solution (0.1 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM CaCl
2, 0.1 mM MgCl
2, and 0.5 mM KCl, pH 5.7). The selective microelectrodes for Na
+ were calculated and used to monitor net fluxes of Na
+ in the apical meristem (300 μm from the root tip). Continuous recordings were made at each measuring point for 5-8 min, and the average fluxes at each point were calculated. Three to four individual plants of each genotype were used for flux recording.
4.8. RNA Affinity Purification Sequencing
RNA affinity purification sequencing (RAP sequencing) was performed with reference to the DNA affinity purification sequencing (DAP sequencing) protocol as described previously [
12], but with modifications. In brief, full-length
PeGRP2 was ligated into the pFN19K (HaloTag) T7 SP6 Flexi vector (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The HaloTag-PeGRP2 protein was produced using the TNT SP6 High-Yield Wheat Germ Protein Expression System (Promega, USA) as a bait protein. The expression of PeGRP2 protein was determined by Western blot and purified using Magne HaloTag Beads (Promega, USA). Total RNA was extracted from leaves of WT
P. × canescens and
PeGRP2-transgenic lines with the EASYspin Plus kit (Aidlab, China). Subsequently mRNA was enriched using the Hieff NGS mRNA Isolation Master Kit (Yeasen, China). The covalently conjunct beads and HaloTag-PeGRP2 protein were incubated with mRNA from WT or transgenic poplars in binding buffer (10 mM HEPES, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM MgCl
2, 20 mM KCl, pH7.3). The bait protein was not added to the negative control but followed the same procedures as that introduced with the HaloTag-PeGRP2 protein. The beads were washed with washing buffer (10 mM HEPES, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM MgCl
2, 0.1% Tween-20, 20 mM KCl, pH7.3). Finally, the mRNA was eluted from the beads with nuclease free water. The cDNA library was constructed using the RNA-seq Library Prep Kit (MICH Scientific, China), followed by sequencing on the Illumina NovaSeq platform. To identify PeGRP2-binding mRNAs, we used fastp software to filter reads [
56]. All clean reads were mapped using hisat2 to the reference genome [
57]. And the enriched mRNAs were analyzed using the software featureCounts version 2.0.4 [
58].
4.9. RT-qPCR Analysis
RT-qPCR was used to determine the transcription of
PeGRP2 in roots, new twigs and leaves of
P. euphratica during the period of salt treatment (0 or 100 mM, 12 days). The transcripts of PeGRP2-targeting mRNAs in transgenic
P. × canescens were examined under control and NaCl treatment (100 mM, 15 days). The transcripts of PeGRP2-interacting mRNAs were also tested at WT
P. ×
canescens and served as non-salt and salt controls. RNA isolation from
P. euphratica and
P. ×
canescens was performed using the Plant RNA Kit R6827 (Omega, Norcross, Georgia). Then cDNA was synthesized by reverse transcription with HiFiScript gDNA Removal RT Master Mix (ComWin Biotech, Jiangsu, China) as a template for RT-qPCR. The reaction system was prepared according to UltraSYBR mixture (Low ROX) (Beijing ComWin Biotech, Beijing, China) and monitored in real time using LineGene 9600 Plus (Bioer Technology, Hangzhou, China).
PeActin7 and
PcUBQ served as internal controls for
P. euphratica [
16] and
P. ×
canescens [
59]. Three individual biological replicates were set up for each treatment.
4.10. Data Analysis
Na
+ flux was calculated using the NMT flux rate conversion table JCal V3.3 from Xuyue (
http://www.xuyue.net/). All experimental data were statistically analyzed using SPSS version 19.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). The one-way ANOVA method was used to compare means between treatments. For post hoc multiple comparisons, the least significant difference (LSD) method was used.
P < 0.05 was considered a significant difference unless otherwise stated.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, P. euphratica PeGRP2 negatively regulates salt tolerance in poplars. Overexpression of PeGRP2 in P. × canescens resulted in reduced ability to maintain photosynthesis, antioxidant protection, and Na+ homeostasis under salt stress. The target mRNAs interacting with PeGRP2 were identified by RNA affinity purification sequencing. RT-qPCR assays of PeGRP2-transgenic poplar showed that NaCl inhibited the transcripts of target mRNAs encoding photosynthetic proteins involved in photosynthetic light yield and reaction (PETC, PSBY, LIL3-1, CAB5, CAB6), oxygen evolution (PSBO1), electron transport (LFNR), and carbon fixation (RBCMT), leading to a consequent reduction of YII, Fv/Fm, ETR, and Pn under salt treatment. NaCl reduced the transcripts of antioxidative enzymes that showed interaction with PeGRP2, such as POD42, SOD[Cu-Zn]2, SOD[Mn], CYB1-2, CDSP32 and PRXQ, although POD47 and TRX showed increased transcripts in transgenic poplars. The lower stimulation of antioxidant enzymes results in the inability of transgenic poplars to scavenge salt-induced ROS in the long-term stress. PeGRP2-overexpressed P. × canescens exhibited Na+ buildup in roots, stems, and leaves due to the low ability to excrete Na+ ions in the roots. NaCl decreased the transcripts of AHA11, NHA1, ACA8, ACA9, CAX3, and AVP1, which physically interact with PeGRP2 in transgenic P. × canescens, resulting in decreased cytosol Na+ extrusion and vacuolar Na+ compartmentalization in leaf cells. We noticed that PeGRP2 exerts negative effects on the stability of target mRNAs under saline conditions, particularly those encoding photosynthetic proteins (PETC and RBCMT), antioxidant enzymes (SOD[Mn], CDSP32 and CYB1-2), ATPases (AHA11, ACA8 and ACA9), and Na+/H+ antiporter (NHA1), resulting in a decreased ability to tolerate salinity stress in transgenic P. × canescens. Accordingly, down-regulation of PeGRP2 contributes to salt adaptation for the salt-resistant poplar P. euphratica during prolonged salt exposure. Therefore, this study provides new insights for breeding salt-resistant poplars by reducing the GRP2 transcript.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Table S1: Accession numbers of GRP orthologs used in multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis; Table S2: Primers used for RT-qPCR; Figure S1: Transcription analysis of PcSOS1, PcSOS2 and PcSOS3 in wild-type (WT) grey poplar and transgenic lines overexpressing PeGRP2 under salt stress.
Author Contributions
J.L. (Jing Li): Investigation, Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing-original draft. R.Z.: Investigation, Data curation, Resources, Methodology, Validation. J.L. (Jian Liu): Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization. J.Y.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Resources. S.M.: Investigation, Methodology, Resources. K.Y.: Investigation, Methodology, Visualization. Y.Z.: Investigation, Methodology. Z.L.: Investigation, Methodology. C.Y.: Investigation, Methodology. N.Z.: Methodology, Resources. X.Z: Resources. S.C.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was supported jointly by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 32371828, 32071730 and 31770643), and the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities, China (111 Project, grant no. B13007).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
We thank Shan Liang (Bluescape Hebei Biotech Co., Ltd, Baoding, China) for the contribution to HaloTag protein expression, Western blot, and RNA sequencing. We thank Jinchi Zhou (The Plat form of Large Instruments and Equipment, Beijing Forestry University) for permission and assistance in the use of ICP-OES.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
AATP: AAA-ATPase; ACA8, 9: plasma membrane-type calcium-transporting ATPase 8, 9; AHA11: plasma membrane-type ATPase 11; ASD: mitochondrial AAA-ATPase; AVP1: pyrophosphate-energized vacuolar membrane proton pump 1; CAB5, 6: chlorophyll a-b binding protein 5, 6; CAT: catalase; CAX3: vacuolar cation/proton exchanger 3; CDSP32: chloroplastic thioredoxin-like protein CDSP32; CYB1-2: transmembrane ascorbate ferrireductase 1 isoform X2; ETR: relative electron transport rate; Fv/Fm: maximum PSⅡ photochemical efficiency; GLABRA3: bHLH transcription factor GLABRA 3; Gs: stomatal conductance; HA1: plasma membrane H+-ATPase 1; HSF: heat-shock transcription factor; J3: DnaJ homologous protein 3; JRL: jacalin-related mannose-binding lectin; LFNR: chloroplastic ferredoxin-NADP reductase; LIL3-1: chloroplastic light-harvesting complex-like protein 3 isotype 1; NHE2-1: sodium/hydrogen exchanger 2 isoform X1; NMT: non-invasive micro-test; PETC: chloroplastic cytochrome b6-f complex iron-sulfur subunit; PLDδ: phospholipase Dδ; PM: plasma membrane; Pn: net photosynthetic rate; POD42, 47: peroxidase 42, 47; PRXQ: chloroplastic peroxiredoxin Q; PSB28: photosystem II reaction center PSB28 protein; PSBO1, 2: oxygen-evolving enhancer protein 1, 2; PSBR: photosystem II 10 kDa polypeptide; PSBY: photosystem II core complex proteins psbY; RAP sequencing: RNA affinity purification sequencing; RBCMT: ribulose-1, 5 bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit N-methyltransferase; REL: relative electrolyte leakage; REM6.5: remorin 6.5; ROS: reactive oxygen species; RT-qPCR: Real-time quantitative PCR; SOD[Cu-Zn]2: superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] 2; SOD[Mn]: mitochondrial superoxide dismutase [Mn]; TPK: two-pore potassium channel; TRX: chloroplastic thioredoxin X; TRXM: chloroplastic thioredoxin M-type; WRKY1: WRKY 1 transcription factor; XTH: xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase; YⅡ: actual photosynthetic quantum yield.
References
- Chen, S.L.; Polle, A. Salinity tolerance of Populus. Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 317–333.
- Chen, S.L.; Hawighorst, P.; Sun, J.; Polle, A. Salt tolerance in Populus: Significance of stress signaling networks, mycorrhization, and soil amendments for cellular and whole-plant nutrition. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 107, 113–124. [CrossRef]
- Polle, A.; Chen, S.L. On the salty side of life: Molecular, physiological and anatomical adaptation and acclimation of trees to extreme habitats. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 1794–1816. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.B.; Polle, A. Wood composition and energy content in a poplar short rotation plantation on fertilized agricultural land in a future CO2 atmosphere. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 38-47. [CrossRef]
- Polle, A.; Douglas, C. The molecular physiology of poplars: paving the way for knowledge-based biomass production. Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 239-241. [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.S.; Wang, W.; Sun, J.; Ding, M.Q.; Zhao, R.; Deng, S.R.; Wang, F.F.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.J.; et al. Populus euphratica XTH overexpression enhances salinity tolerance by the development of leaf succulence in transgenic tobacco plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 4225-4238. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.F.; Deng, S.R.; Ding, M.Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, M.J.; Zhu, H.P.; Han, Y.S.; Shen, Z.D.; Jing, X.S.; Zhang, F.; et al. Overexpression of a poplar two-pore K+ channel enhances salinity tolerance in tobacco cells. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ. Cult. 2013, 112, 19-31. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Ding, M.Q.; Deng, S.R.; Hou, P.C.; Ma, X.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, F.F.; Sa, G.; et al. Overexpression of PeHA1 enhances hydrogen peroxide signaling in salt-stressed Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 71, 37–48. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.D.; Ding, M.Q.; Sun, J.; Deng, S.R.; Zhao, R.; Wang, M.J.; Ma, X.J.; Wang, F.F.; Zhang, H.L.; Qian, Z.Y.; et al. Overexpression of PeHSF mediates leaf ROS homeostasis in transgenic tobacco lines grown under salt stress conditions. Plant Cell. Tissue Organ. Cult. 2013, 115, 299-308. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.D.; Yao, J.; Sun, J.; Chang, L.W.; Wang, S.J.; Ding, M.Q.; Qian, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhao, N.; Sa, G.; et al. Populus euphratica HSF binds the promoter of WRKY1 to enhance salt tolerance. Plant Sci. 2015, 235, 89–100. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Wang, Y.; Sa, G.; Zhang, Y.H.; Deng, J.Y.; Deng, S.R.; Wang, M.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Yao, J.; Ma, X.Y.; et al. Populus euphratica J3 mediates root K+/Na+ homeostasis by activating plasma membrane H+-ATPase in transgenic Arabidopsis under NaCl salinity. Plant Cell. Tissue Organ. Cult. 2017, 131, 75-88.
- Yao, J.; Shen, Z.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.H.; Sang, G.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, H.L.; Deng, C.; Liu, J.; et al. Populus euphratica WRKY1 binds the promoter of H+-ATPase gene to enhance gene expression and salt tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 1527–1539. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Deng, C.; Wu, X.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.N.; Deng, S.R.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, X.Y.; et al. Populus euphratica remorin 6.5 activates plasma membrane H+-ATPases to mediate salt tolerance. Tree Physiol. 2020, 40, 731–745. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Deng, C.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.N.; Deng, S.R.; Zhao, N.; Sa, G.; Zhou, X.Y.; Lu, C.F.; et al. Populus euphratica JRL mediates ABA response, ionic and ROS homeostasis in Arabidopsis under salt stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 815. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, J.; Yin, K.X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Deng, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.N.; Hou, S.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; et al. Populus euphratica phospholipase Dδ increases salt tolerance by regulating K+/Na+ and ROS homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4911.
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, K.X.; Yao, J.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.; Yan, C.X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, N.; et al. Populus euphratica GLABRA3 binds PLDδ promoters to enhance salt tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8208.
- Lorkovic, Z.J.; Barta, A. Genome analysis: RNA recognition motif (RRM) and K homology (KH) domain RNA-binding proteins from the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 623-35.
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.J.; Jang, B.S.; Jung, C.H.; Ahn, S.J.; Goh, C.H.; Cho, K.; Han, O.; Kang, H.S. Functional characterization of a glycine-rich RNA-binding protein 2 in Arabidopsis thaliana under abiotic stress conditions. Plant J. 2007, 50, 439-451. [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Lee, D.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, S.C.; Redillas, M.; Seo, J.S.; Kim, J.K. The rice glycine-rich protein 3 confers drought tolerance by regulating mRNA stability of ROS scavenging-related genes. Rice 2021, 14, 31. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, W.Y.; Kwak, K.J.; Oh, S.H.; Han, Y.S.; Kang, H. Glycine-rich RNA-binding proteins are functionally conserved in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa during cold adaptation process. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 2317-2325. [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.Q.; Jiang, L.; Song, S.Y.; Jing, R.; Xu, G.S. AtGRP7 is involved in the regulation of abscisic acid and stress responses in Arabidopsis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2006, 11, 526-535. [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.J.; Kang, H.; Han, K.H.; Ahn, S.J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and stress-responsive expression of genes encoding glycine-rich RNA-binding proteins in Camelina sativa L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 68, 44-51. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Wang, R.C.; Liang, D.; Ma, F.W.; Shu, H. R. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a glycine-rich RNA-binding protein gene from Malus hupehensis Rehd. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 4145-4153. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.O.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, H. Cold-inducible zinc finger-containing glycine-rich RNA-binding protein contributes to the enhancement of freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2005, 42, 890-900.
- Kim, J.S.; Jung, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.A.; Goh, C.H.; Woo, Y.; Oh, S.H.; Han, Y.S.; Kang, H. Glycine-rich RNA-binding protein 7 affects abiotic stress responses by regulating stomata opening and closing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2008, 55, 455-466. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, W.Y.; Kwak, K.J.; Oh, S.H.; Han, Y.S.; Kang, H. Zinc finger-containing glycine-rich RNA-binding protein in Oryza sativa has an RNA chaperone activity under cold stress conditions. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 759-768.
- Sahi, C.; Agarwal, M.; Singh, A.; Grover, A. Molecular characterization of a novel isoform of rice (Oryza sativa L.) glycine rich-RNA binding protein and evidence for its involvement in high temperature stress response. Plant Sci. 2007, 173, 144-155. [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.H.; Kwak, K.J.; Kim, M.K.; Park, S.J.; Yang, K.Y.; Kang, H. Expression of Arabidopsis glycine-rich RNA-binding protein AtGRP2 or AtGRP7 improves grain yield of rice (Oryza sativa) under drought stress conditions. Plant Sci. 2014, 214, 106-112. [CrossRef]
- Aneeta; Sanan-Mishra, N.; Tuteja, N.; Kumar Sopory, S. Salinity- and ABA-induced up-regulation and light-mediated modulation of mRNA encoding glycine-rich RNA-binding protein from Sorghum bicolor. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun. 2002, 296, 1063-1068. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Li, J.K.; Wang, S.S.; Hüttermann, A.; Altman, A. Salt, nutrient uptake and transport, and ABA of Populus euphratica; a hybrid in response to increasing soil NaCl. Trees-Struct. Funct. 2001, 15, 186–194. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Li, J.K.; Fritz, E.; Wang, S.S.; Hüttermann, A. Sodium and chloride distribution in roots and transport in three poplar genotypes under increasing NaCl stress. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 168, 217–230. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Li, J.K.; Wang, S.S.; Fritz, E.; Hüttermann, A.; Altman, A. Effects of NaCl on shoot growth, transpiration, ion compartmentation, and transport in regenerated plants of Populus euphratica and Populus tomentosa. Can. J. For. Res. 2003, 33, 967-975.
- Wang, C.; Zhang, D.W.; Wang, Y.C.; Zheng, L.; Yang, C.P. A glycine-rich RNA-binding protein can mediate physiological responses in transgenic plants under salt stress. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 1047-1053. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.X.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y.L.; Li, M.J.; Ma, F.W. Overexpression of MpGR-RBP1, a glycine-rich RNA-binding protein gene from Malus prunifolia (Willd.) Borkh., confers salt stress tolerance and protects against oxidative stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ. Cult. 2014, 119, 635-646. [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Amaro, M.A.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, A.A.; Rodriguez-Kessler, M.; Hernandez-Lucero, E.; Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Ibanez-Salazar, A.; Delgado-Sanchez, P.; Jimenez-Bremont, J.F. Overexpression of AtGRDP2, a novel glycine-rich domain protein, accelerates plant growth and improves stress tolerance. Front Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 782.
- Long, R.C.; Yang, Q.C.; Kang, J.M.; Zhang, T.J.; Wang, H.M.; Li, M.N.; Zhang, Z. Overexpression of a novel salt stress-induced glycine-rich protein gene from alfalfa causes salt and ABA sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 1289-1298. [CrossRef]
- Teng, K.; Tan, P.H.; Xiao, G.Z.; Han, L.B.; Chang, Z.H.; Chao, Y.H. Heterologous expression of a novel Zoysia japonica salt-induced glycine-rich RNA-binding protein gene, ZjGRP, caused salt sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 179-191. [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.J.; Kim, Y.O.; Kang, H. Characterization of transgenic Arabidopsis plants overexpressing GR-RBP4 under high salinity, dehydration, or cold stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 3007-3016. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, Y.A.; Deng, C.; Deng, S.R.; Li, N.F.; Zhao, C.J.; Zhao, R.; Liang, S.; Chen, S.L. The Arabidopsis Ca2+-dependent protein kinase CPK12 is involved in plant response to salt stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4062. [CrossRef]
- Farmer, E.E.; Mueller, M. J. ROS-mediated lipid peroxidation and RES-activated signaling. Annu Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 429-450.
- Park, S.J.; Kwak, K.J.; Oh, T.R.; Kim, Y.O.; Kang, H. Cold shock domain proteins affect seed germination and growth of Arabidopsis thaliana under abiotic stress conditions. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 869-878. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.G.; Chen, S.L.; Zhou, X.Y.; Shen, X.; Deng, L.; Zhu, H.J.; Shao, J.; Shi, Y.; Dai, S.X.; Fritz, E.; et al. Ionic homeostasis and reactive oxygen species control in leaves and xylem sap of two poplars subjected to NaCl stress. Tree Physiol. 2008, 28, 947–957. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.G.; Chen, S.L.; Deng, L.; Fritz, E.; Hüttermann, A.; Polle, A. Leaf photosynthesis, fluorescence response to salinity and the relevance to chloroplast salt compartmentation and anti-oxidative stress in two poplars. Trees 2007, 21, 581–591. [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.Q.; Hou, P.C.; Shen, X.; Wang, M.J.; Deng, S.R.; Sun, J.; Xiao, F.; Wang, R.G.; Zhou, X.Y.; Lu, C.F.; et al. Salt-induced expression of genes related to Na+/K+ and ROS homeostasis in leaves of salt-resistant and salt-sensitive poplar species. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 73, 251–269.
- Sun, J.; Dai, S.X.; Wang, R.G.; Chen, S.L.; Li, N.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Lu, C.F.; Shen, X.; Zheng, X.J.; Hu, Z.M.; et al. Calcium mediates root K+/Na+ homeostasis in poplar species differing in salt tolerance. Tree Physiol. 2009, 29, 1175–1186.
- Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.D.; Sun, J.; Yu, Y.C.; Deng, S.R.; Li, Z.Y.; Sun, C.H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, R.; Shen, X.; et al. NaCl-elicited, vacuolar Ca2+ release facilitates prolonged cytosolic Ca2+ signaling in the salt response of Populus euphratica cells. Cell Calcium. 2015, 57, 348–365. [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Deng, S.R.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, M.J.; Ding, M.Q.; Zhao, R.; Shen, X.; Zhou, X.Y.; Lu, C.F.; et al. Extracellular ATP signaling is mediated by H2O2 and cytosolic Ca2+ in the salt response of Populus euphratica cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e53136. [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Deng, L.; Li, J.K.; Zhou, X.Y.; Li, N.Y.; Zhang, D.C.; Lu, Y.J.; Wang, R.G.; Sun, J.A.; Lu, C.F.; et al. Effect of NaCl on leaf H+-ATPase and the relevance to salt tolerance in two contrasting poplar species. Trees-Struct. Funct. 2010, 24, 597-607.
- Li, N.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Zhou, X.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Shao, J.; Wang, R.G.; Fritz, E.; Hüttermann, A.; Polle, A. Effect of NaCl on photosynthesis, salt accumulation and ion compartmentation in two mangrove species, Kandelia candel and Bruguiera gymnorhiza. Aquat. Bot. 2008, 88, 303-310. [CrossRef]
- Li, N.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Wang, R.G.; Li, J.K.; Lu, C.F.; Chen, S.L. Salt compartmentation and antioxidant defense in roots and leaves of two non-salt secretor mangroves under salt stress. In: S. Sharma (Ed.) Mangrove Ecosystem Ecology and Function. InTechOpen 2018, pp. 81–104.
- Zhang, Y.L.; Sun, Y.L.; Liu, X.J.; Deng, J.Y.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Y.A.; Deng, S.R.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhao, N.; Li, J.K.; et al. Populus euphratica apyrases increase drought tolerance by modulating stomatal aperture in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9892. [CrossRef]
- Leple, J.C.; Brasileiro, A.C.; Michel, M.F.; Delmotte, F.; Jouanin, L. Transgenic poplars: expression of chimeric genes using four different constructs. Plant Cell Rep. 1992, 11, 137-141. [CrossRef]
- Gafur, A.; Schützendübel, A.; Langenfeld-Heyser, R.; Fritz, E.; Polle, A. Compatible and incompetent Paxillus involutus isolates for ectomycorrhiza formation in vitro with poplar (Populus × canescens) differ in H2O2 production. Plant Biol. 2004, 6, 91-99.
- Deng, S.R.; Sun, J.; Zhao, R.; Ding, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.N.; Sun, Y.L.; Wang, W.; Tan, Y.Q.; Liu, D.D.; Ma, X.J.; et al. Populus euphratica APYRASE2 enhances cold tolerance by modulating vesicular trafficking and extracellular ATP in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 530–548. [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhu, Z.M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.A.; Yu, D.D.; Hou, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yao, J.; Zhang, H.L.; et al. Ectomycorrhizal fungal strains facilitate Cd2+ enrichment in a woody hyperaccumulator under co-existing stress of cadmium and salt. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11651. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Gu, J. Fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 884-890.
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923-930. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.D.; Sun, J.; Yao, J.; Wang, S.J.; Ding, M.Q.; Zhang, H.L.; Qian, Z.Y.; Zhao, N.; Sa, G.; Zhao, R.; et al. High rates of virus-induced gene silencing by tobacco rattle virus in Populus. Tree Physiol. 2015, 35, 1016-1029. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).