Submitted:
22 December 2023
Posted:
26 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Theoretical Understanding
Introduction
What Is PCA?
Why Is Data Reduction Necessary Using a PCA?
When We Should Utilize PCA?
Some Basic Concepts and Terms of PCA
- ❖ Eigenvalue: it displays the variance explained or described by that specific factor from out of the overall variance [25]. Any factor which contains an eigenvalue greater than or equal to 1 captures greater variance than a single detected variable. Thus, the factor that explains or captures most of the variance in these variables in the model should be utilized in other analyses, and the factor that captures the smallest amount of variance is usually rejected [26].
- ❖ Factor loading is the correlation coefficient (r) between latent common factors and observed variables. It describes the association of each variable to the principal factor [26]. By rule of thumb, the loading factor is considered as high if the value of the loading factor is > 0.7 (i.e. the factor extracts an adequate amount of variance from that specific variable) [25].
- ❖ A complex structure happens while one variable has high correlations or loadings (0.40 or higher) on greater than one component. If variables have a complex structure, they must be rejected from the analysis. Variable is merely tested for complex structure if there is greater than one component in the output or solution. Variables loaded on merely one component are explained as having a simple structure [25,27].
- ❖ Communalities (h2) are percentages of variance of each variable which can be described by the factors. It is a sum of squared factor loadings for the variables in a row from factor analysis and existing in the diagonal in common factor analysis [27].
- ❖ Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity is the extent of inter-correlation among objects and related to Cronbach’s alpha. It tests the null hypothesis (Ho) in which the correlation matrix is an individuality matrix. The individuality matrix is a matrix that all off-diagonal components are 0 and all of the diagonal components are 1. We reject this null hypothesis if P<0.05 and it provides the smallest criteria that should be passed before a PCA should be carried out [27].
- ❖ Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) is a Measure of Sampling Adequacy (MSA) and differs between values of 0 and 1. The value closer to one is better and the value of 0.5 is recommended as a minimum [27]. Interpretation for the KMO-MSA is: below 0.50 as unacceptable, in the 0.50's as miserable, in the 0.60's as mediocre, in the 0.70's as middling, in the 0.80's as meritorious, and in the 0.90 as marvelous [28].
Testing Assumptions of PCA
- The variables involved must be dichotomously coded, either nominal or metric.
- The minimum required sample size must be more than 50 (if possible, more than 100).
- The ratio of a case to a variable in the data set must be five to one or higher.
- The correlation matrix values for the variables must comprise two or more correlations of 0.30 or higher.
- The variables with MSA < 0.50 must be rejected from analysis (observe the anti-image output of SPSS).
- The total MSA must be 0.50 or greater (KMO > 0.5).
- The Bartlett test of sphericity must be statistically significant, or P < 0.05.
- It assumes a correlation or a linear association between features and is sensitive to the values of the features.
- It assumes no missing values and is not robust against outliers.
Deriving or Developing a Factor Model
- The derived or calculated components must explain 50% or greater of the variance in all of the variables, which means they have a communality value > 0.50.
- All of the variables don't have correlations or loadings > 0.40 for more than one component, which means they don’t contain a complex structure.
- None of the components have merely one variable in them.
Detecting Variables to Be Utilized in Further Analysis
- We have components that contain more than one variable correlating to or loading on them.
- We have components that describe at least 50 percent of the variance in the involved variables.
- We have components that jointly describe greater than 60 percent of the variance in the groups of variables; we may replace the component for the variable in further analysis.
- The variables that were rejected in the analysis would be involved independently in further analysis.
- Replacement of components for independent variables is carried out by utilizing merely the highest loading or correlating variable or by merging the variables loading on all components to produce a new variable.
Note
Steps to Perform a PCA?
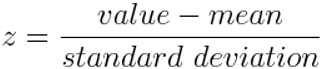
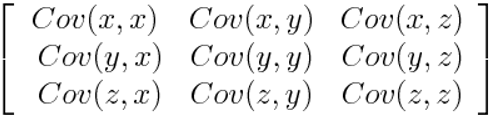
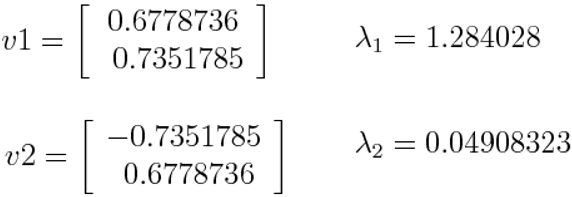
Advantages and Disadvantages of PCA
2. Practical Application of PCA
Variable Preparation for PCA
Practical Demonstration of PCA Using a Sample Data Set
Analysis of PCA Using SPSS
 dimension reduction
dimension reduction factor. Then insert all eligible variables under the variables box. Click on descriptive, then mark on univariate descriptives, coefficients, anti-image, KMO and Bartlett’s test sphericity. Click on extraction, then method fix on principal components, mark on scree plot, and covariance matrix. Click on rotation and mark on varimax. Click on continue, and finally, click on the OK button. For further clarification, see this demonstration sample data set and my Amharic language PCA demonstration video.
factor. Then insert all eligible variables under the variables box. Click on descriptive, then mark on univariate descriptives, coefficients, anti-image, KMO and Bartlett’s test sphericity. Click on extraction, then method fix on principal components, mark on scree plot, and covariance matrix. Click on rotation and mark on varimax. Click on continue, and finally, click on the OK button. For further clarification, see this demonstration sample data set and my Amharic language PCA demonstration video.First Output (Descriptive Statistics)
Second Output (Anti-Image)
Third Output (KMO and Bartlett's Test)
Fourth Output (Determining the Number of Factors or Components to Retain in the PCA)
Fifth Output (Communalities
Sixth Output (Complex Structure)
Conclusions
List of Abbreviations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Availability of Data and Materials
Acknowledgments
Competing Interests
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Consent for Publication
References
- Terms., O.G.o.S. OECD. 2008. p. 119. ISBN 978-92-64-025561. 2008.
- Makady A, d.B.A., Hillege H, Klungel O, Goettsch W; (on behalf of GetReal Work Package 1),. What Is Real-World Data? A Review of Definitions Based on Literature and Stakeholder Interviews. Value Health. 2017 Jul-Aug;20,858-865. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2017.03.008. Epub 2017 May 11. PMID: 28712614. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- “Statistical Language- What are Data. Australian Bureau of Statistics. 2013-07-13. Archived from the original on 2019-04-19. Retrieved 2022-02-29. 2019.
- Comparison/Diffen”., D.v.I.D.a. 2015. www.diffen.com. Retrieved 201-12-11.
- Iris Garner. Data in education. Available online from. https://www.learninga-z.com/site/breakroom/data-in-education.
- Joubert J, R.C., Bradshaw D, Dorrington RE, Vos T, Lopez AD. . Characteristics, availability and uses of vital registration and other mortality data sources in post-democracy South Africa. Glob Health Action. 2012 Dec 27;5:1-19. doi: 10.3402/gha.v5i0.19263. PMID: 23273252; PMCID: PMC3532367. [CrossRef]
- Wyatt D, C.J., McKevitt C,. Perceptions of the uses of routine general practice data beyond individual care in England: a qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2018 Jan 8;8,e019378. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019378. PMID: 29317420; PMCID: PMC5781155. [CrossRef]
- Peloquin D, D.M., Bierer B, Barnes M,. Disruptive and avoidable: GDPR challenges to secondary research uses of data. Eur J Hum Genet. 2020 Jun;28,697-705. doi: 10.1038/s41431-020-0596-x. Epub 2020 Mar 2. PMID: 32123329; PMCID: PMC7411058. [CrossRef]
- Tessema., G.D.a.F. Biostatistics. LECTURE NOTESFor Health Science Students. Available online from https://www.cartercenter.org/resources/pdfs/health/ephti/library/lecture_notes/env_health_science_students/ln_biostat_hss_final.pdf 2005.
- Jyotsna Vadakkanmarveettil. Data Reduction: A simple And Concise Guide (2021). Available online from https://www.jigsawacademy.com/blogs/data-science/data-reduction 2021.
- Jolliffe IT, C.J. Principal component analysis: a review and recent developments. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2016 Apr 13;374,20150202. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2015.0202. PMID: 26953178; PMCID: PMC4792409. [CrossRef]
- PulkitS. The Ultimate Guide to 12 Dimensionality Reduction Techniques (with Python codes):https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2018/08/dimensionality-reduction-techniques-python/. 2018.
- Gleason PM, B.C., Harris JE; 115, 1072-82. , Harris JE, Zoellner J.. Publishing nutrition research: a review of multivariate techniques--part 3: data reduction methods. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015 Jul;115,1072-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2015.03.011. Epub 2015 Apr 30. PMID: 25935571. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana AC, B.A., Yehia HC, Laboissière R,. A dimension reduction technique applied to regression on high dimension, low sample size neurophysiological data sets. BMC Neurosci. 2021 Jan 4; 22,1. doi: 10.1186/s12868-020-00605-0. PMID: 33397293; PMCID: PMC7780417. [CrossRef]
- Neha T. Data Reduction. Available online from https://binaryterms.com/data-reduction.html.
- Rukshan Pramoditha. 11 Dimensionality reduction techniques you should know in 2021. Available online from: https://towardsdatascience.com/11-dimensionality-reduction-techniques-you-should-know-in-2021-dcb9500d388b 2021.
- Shreysingh, T. Difference between Dimensionality Reduction and Numerosity Reduction: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-dimensionality-reduction-and-numerosity-reduction/.
- GeeksforGeeks. Numerosity Reduction in Data Mining. Available online from https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/numerosity-reduction-in-data-mining/.
- Lever, J., Krzywinski, M. & Altman, N,. Principal component analysis. Nat Methods 14, 641–642 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Casal CA, L.J., Barreira D, Maneiro R,. Multivariate Exploratory Comparative Analysis of LaLiga Teams: Principal Component Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 19;18,3176. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18063176. PMID: 33808634; PMCID: PMC8003572. [CrossRef]
- JKLJKLLMN. FACTOR ANALYSIS. Available online from https://www.coursehero.com/file/103921107/433838251-Factor-Analysispdf/.
- Shaily Jain. Limitations, Assumptions Watch-Outs of Principal Component Analysis: https://codatalicious.medium.com/limitations-assumptions-watch-outs-of-principal-component-analysis-8483ceaa2800.
- Matt Brems. A One-Stop Shop for Principal Component Analysis. Available online from https://towardsdatascience.com/a-one-stop-shop-for-principal-component-analysis-5582fb7e0a9c.
- Rohit Dwivedi. Introduction to Principal Component Analysis in Machine Learning: https://www.analyticssteps.com/blogs/introduction-principal-component-analysis-machine-learning.
- Factor Analysis Statistics Solutions. Available online from: https://www.statisticssolutions.com/free-resources/directory-of-statistical-analyses/factor-analysis/.
- FACTOR., T.A. Factor Analysis: A Short Introduction, Part 1. Available online from https://www.theanalysisfactor.com/factor-analysis-1-introduction/.
- Factor Analysis/SPSS Annotated Output. Available online from https://stats.oarc.ucla.edu/spss/output/factor-analysis/.
- Satish, G.J.a.N., N, . ‘A case study of barriers and drivers for energy efficiency in an Indian city’, Int. J. Energy Technology and Policy, Vol. 13, No. 3, pp.266–277. 2017.
- Data analysis and computers II. Principal Component Analysis. https://media.gradebuddy.com/documents/536382/97892fb2-9f48-42c1-87ae-d706a92b762f.pdf.
- Song Y, W.J., Aben N, Michaut M, Wessels LFA, Smilde AK,. Principal component analysis of binary genomics data. Brief Bioinform. 2019 Jan 18;20,317-329. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang B, L.X., Zhao Y, Caffo B,. Semiparametric partial common principal component analysis for covariance matrices. Biometrics. 2021 Dec;77,1175-1186. doi: 10.1111/biom.13369. Epub 2020 Oct 10. PMID: 32935852. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos RO, G.B., Castro MA, Fisberg RM, Marchioni DM, Baltar VT, . Principal Component Analysis and Factor Analysis: differences and similarities in Nutritional Epidemiology application. Rev Bras Epidemiol. 2019 Jul 29;22:e190041. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laerd Statistics. Principal Components Analysis (PCA) using SPSS Statistics. https://statistics.laerd.com/spss-tutorials/principal-components-analysis-pca-using-spss-statistics.php.
- Nikolai Janakiev. Understanding the Covariance Matrix. Available online from https://datascienceplus.com/understanding-the-covariance-matrix/. 2018.
- Stat Trek. Variance-Covariance Matrix. https://stattrek.com/matrix-algebra/covariance-matrix.aspx.
- Hoffman, K.a.K., R,. "Characteristic Values." §6.2 in Linear Algebra, 2nd ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, p. 182, 1971. 1971.
- Marcus, M.a.M., H. . Introduction to Linear Algebra. New York: Dover, p. 145, 1988.
- Fry K., F.R., Chakraborty N.M,. Measuring Equity with Nationally Representative Wealth Quintiles. Washington, DC: PSI. . 2014.
- Ahmed R, S.M., Abose S, Assefa B, Nuramo A, Alemu A, et al,. Levels and associated factors of the maternal healthcare continuum in Hadiya zone, Southern Ethiopia: A multilevel analysis. PLoS ONE 17, e0275752. [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.; Kumaranayake, L. Constructing socio-economic status indices: how to use principal components analysis. Health policy and planning 2006, 21, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Principal component analysis. Available online from https://slideplayer.com/slide/4238108/.
- Central Statistical Agency (CSA) [Ethiopia] and ICF. Mini Ethiopia Demographic and Health Survey 2019: Key Indicators Report. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, and Rockville, Maryland, USA. CSA and ICF. 2019. 2019.
| S.no | Variables | Given values |
| 1 | Main source of drinking water | Improved: Piped water, tube well or borehole, protected well, protected spring = 1 Unimproved: Unprotected well, Surface water (river and dam), Unprotected spring, Lake/pond/stream/canal = 0 |
| 2 | Main source of water used for other purposes such as cooking and hand washing | Improved: Piped water, tube well or borehole, protected well, protected spring = 1 Unimproved: Unprotected well, Unprotected spring, Lake/pond/stream/canal, Surface water (River/dam) = 0 |
| 3 | Where is that water source located? | In own dwelling or yard/plot = 1 Elsewhere = 0 |
| 4 | Type of toilet facilities | Improved: comprise any non-shared toilet of the subsequent kinds: pour/flush toilets to septic tanks, piped sewer systems, and pit latrines; pit latrines with slabs; ventilated improved pit (VIP) latrines; and composting toilets = 1 Unimproved: Pit latrine without slab/open pit, bucket toilet and hanging toilet = 0 |
| 5 | Where is this toilet facility located? | In own dwelling or yard/plot = 1 Elsewhere = 0 |
| 6 | Type of fuel the household mainly use for cooking | Clean fuels include electricity, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), natural gas, kerosene, and biogas = 1 Solid fuels include coal, charcoal, wood, straw/shrub/grass, agricultural crops, and animal dung = 0 |
| 7 | Where is the cooking usually done? | In the house and outdoors = 0 In a separate building = 1 |
| 8 | Who is the owner of the house? | Me = 1 Rental, family, and relative = 0 |
| 9 | Main material of the roof of the house | Natural roofing (no roof, mud, and sod) = 0 Rudimentary and finished roofing = 1 |
| 10 | Main material of the floor of the house | Natural floor (Earth/sand, dung) = 0 Rudimentary and finished floor = 1 |
| 11 | Main material of the wall of the house | Natural walls (no walls, cane/palm/trunks/bamboo, dirt) = 0 Rudimentary and finished wall = 1 |
| 12 | All other categorical variables were considered as yes and no form | Yes = 1 and no =0 |
| 13 | All continuous variables were treated as continuous | |
| 14 | “I don’t know” response often coded as 999 for categorical variables | 999 = 0 |
| 15 | “I don’t know” response and any missing value often coded as 999 to zero for continuous variables | 999 and missing value = 0 |
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Analysis N | |
|---|---|---|---|
| have_television_in_house | .02 | .132 | 622 |
| have_radio_in_house | .37 | .484 | 622 |
| roofing_material_for_house | .67 | .472 | 622 |
| floor_material_for_house | .82 | .380 | 622 |
| wall_material_for_house | .84 | .368 | 622 |
| have_cow | .68 | .466 | 622 |
| have_ox | .46 | .499 | 622 |
| have_donkey | .05 | .221 | 622 |
| have_goat | .18 | .382 | 622 |
| have_sheep | .24 | .426 | 622 |
| have_hen | .24 | .429 | 622 |
| have_you_farm_land | .99 | .080 | 622 |
| have_bank_books_any_of_family_member | .08 | .270 | 622 |
| have_you_mobile | .37 | .483 | 622 |
| have_you_moter | .13 | .339 | 622 |
| main_sourse_of_drinking_water | .78 | .415 | 622 |
| total_duration_to_get_water | .83 | .378 | 622 |
| have_you_toilet_facility | .72 | .448 | 622 |
| how_often_family_use_toilet | .57 | .496 | 622 |
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy. | .765 | |
| Bartlett's Test of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 3745.338 |
| Df | 171 | |
| Sig. | .000 | |
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 4.432 | 23.328 | 23.328 | 4.432 | 23.328 | 23.328 |
| 2 | 2.084 | 10.970 | 34.298 | 2.084 | 10.970 | 34.298 |
| 3 | 1.558 | 8.202 | 42.500 | 1.558 | 8.202 | 42.500 |
| 4 | 1.242 | 6.539 | 49.039 | 1.242 | 6.539 | 49.039 |
| 5 | 1.069 | 5.626 | 54.665 | 1.069 | 5.626 | 54.665 |
| 6 | 1.041 | 5.477 | 60.142 | 1.041 | 5.477 | 60.142 |
| 7 | .989 | 5.204 | 65.346 | |||
| 8 | .910 | 4.792 | 70.138 | |||
| 9 | .894 | 4.704 | 74.842 | |||
| 10 | .805 | 4.239 | 79.081 | |||
| 11 | .763 | 4.018 | 83.099 | |||
| 12 | .590 | 3.106 | 86.204 | |||
| 13 | .564 | 2.966 | 89.171 | |||
| 14 | .522 | 2.745 | 91.916 | |||
| 15 | .468 | 2.462 | 94.379 | |||
| 16 | .380 | 2.000 | 96.379 | |||
| 17 | .350 | 1.843 | 98.221 | |||
| 18 | .255 | 1.344 | 99.566 | |||
| 19 | .082 | .434 | 100.000 | |||
| Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis. | ||||||
| Initial | Extraction | |
| have_television_in_house | 1.000 | .663 |
| have_radio_in_house | 1.000 | .598 |
| roofing_material_for_house | 1.000 | .468 |
| floor_material_for_house | 1.000 | .818 |
| wall_material_for_house | 1.000 | .831 |
| have_cow | 1.000 | .668 |
| have_ox | 1.000 | .685 |
| have_donkey | 1.000 | .376 |
| have_goat | 1.000 | .676 |
| have_sheep | 1.000 | .669 |
| have_hen | 1.000 | .545 |
| have_bank_books_any_of_family_member | 1.000 | .646 |
| have_you_mobile | 1.000 | .482 |
| have_you_moter | 1.000 | .531 |
| main_sourse_of_drinking_water | 1.000 | .566 |
| total_duration_to_get_water | 1.000 | .598 |
| have_you_toilet_facility | 1.000 | .790 |
| how_often_family_use_toilet | 1.000 | .777 |
| Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis. | ||
| Initial | Extraction | |
| have_television_in_house | 1.000 | .714 |
| have_radio_in_house | 1.000 | .603 |
| roofing_material_for_house | 1.000 | .483 |
| floor_material_for_house | 1.000 | .821 |
| wall_material_for_house | 1.000 | .832 |
| have_cow | 1.000 | .728 |
| have_ox | 1.000 | .737 |
| have_goat | 1.000 | .694 |
| have_sheep | 1.000 | .678 |
| have_hen | 1.000 | .534 |
| have_bank_books_any_of_family_member | 1.000 | .652 |
| have_you_mobile | 1.000 | .484 |
| have_you_moter | 1.000 | .525 |
| main_sourse_of_drinking_water | 1.000 | .563 |
| total_duration_to_get_water | 1.000 | .603 |
| have_you_toilet_facility | 1.000 | .817 |
| how_often_family_use_toilet | 1.000 | .793 |
| Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis. | ||
| Initial | Extraction | |
| have_television_in_house | 1.000 | .716 |
| have_radio_in_house | 1.000 | .579 |
| floor_material_for_house | 1.000 | .816 |
| wall_material_for_house | 1.000 | .832 |
| have_cow | 1.000 | .748 |
| have_ox | 1.000 | .749 |
| have_goat | 1.000 | .694 |
| have_sheep | 1.000 | .695 |
| have_hen | 1.000 | .517 |
| have_bank_books_any_of_family_member | 1.000 | .621 |
| have_you_mobile | 1.000 | .513 |
| have_you_moter | 1.000 | .569 |
| main_sourse_of_drinking_water | 1.000 | .588 |
| total_duration_to_get_water | 1.000 | .721 |
| have_you_toilet_facility | 1.000 | .835 |
| how_often_family_use_toilet | 1.000 | .812 |
| Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis. | ||
| Component | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| have_television_in_house | .073 | .023 | .089 | .018 | -.022 | -.837 |
| have_radio_in_house | .575 | .253 | .346 | -.145 | .134 | -.161 |
| floor_material_for_house | -.786 | -.137 | -.032 | -.026 | -.025 | .420 |
| wall_material_for_house | -.798 | -.114 | -.064 | -.019 | .007 | .421 |
| have_cow | .126 | .092 | .805 | .198 | .167 | -.091 |
| have_ox | .219 | .058 | .821 | -.068 | .099 | -.093 |
| have_goat | -.009 | -.039 | -.042 | .805 | .193 | -.073 |
| have_sheep | .122 | .063 | .144 | .809 | -.014 | .027 |
| have_hen | -.067 | .232 | .415 | .395 | -.319 | .170 |
| have_bank_books_any_of_family_member | .769 | .028 | .029 | .012 | .062 | .153 |
| have_you_mobile | .528 | .156 | .384 | .106 | .078 | .211 |
| have_you_moter | .736 | .002 | .124 | .106 | .021 | .035 |
| main_sourse_of_drinking_water | .111 | .369 | .174 | .178 | .605 | -.109 |
| total_duration_to_get_water | .040 | .068 | .105 | .043 | .832 | .098 |
| have_you_toilet_facility | .107 | .894 | .113 | .059 | .087 | -.023 |
| how_often_family_use_toilet | .144 | .875 | .075 | -.011 | .138 | -.018 |
| Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis. Rotation Method: Varimax with Kaiser Normalization. | ||||||
| a. Rotation converged in 6 iterations. | ||||||
| Component | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| have_television_in_house | .072 | .039 | .065 | .030 | .900 |
| have_radio_in_house | .573 | .303 | .332 | -.154 | .173 |
| floor_material_for_house | -.703 | -.176 | -.059 | -.007 | -.347 |
| have_cow | .140 | .157 | .812 | .189 | .084 |
| have_ox | .233 | .101 | .820 | -.083 | .087 |
| have_goat | -.008 | .048 | -.023 | .827 | .088 |
| have_sheep | .127 | .062 | .162 | .793 | -.060 |
| have_hen | -.068 | .095 | .430 | .333 | -.281 |
| have_bank_books_any_of_family_member | .795 | .044 | -.001 | .009 | -.091 |
| have_you_mobile | .582 | .173 | .330 | .110 | -.111 |
| have_you_moter | .780 | .011 | .075 | .110 | .071 |
| main_sourse_of_drinking_water | .114 | .551 | .192 | .211 | .141 |
| have_you_toilet_facility | .094 | .889 | .100 | .033 | -.037 |
| how_often_family_use_toilet | .138 | .874 | .058 | -.033 | -.023 |
| Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis. Rotation Method: Varimax with Kaiser Normalization. | |||||
| a. Rotation converged in 5 iterations. | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





