Submitted:
21 December 2023
Posted:
22 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
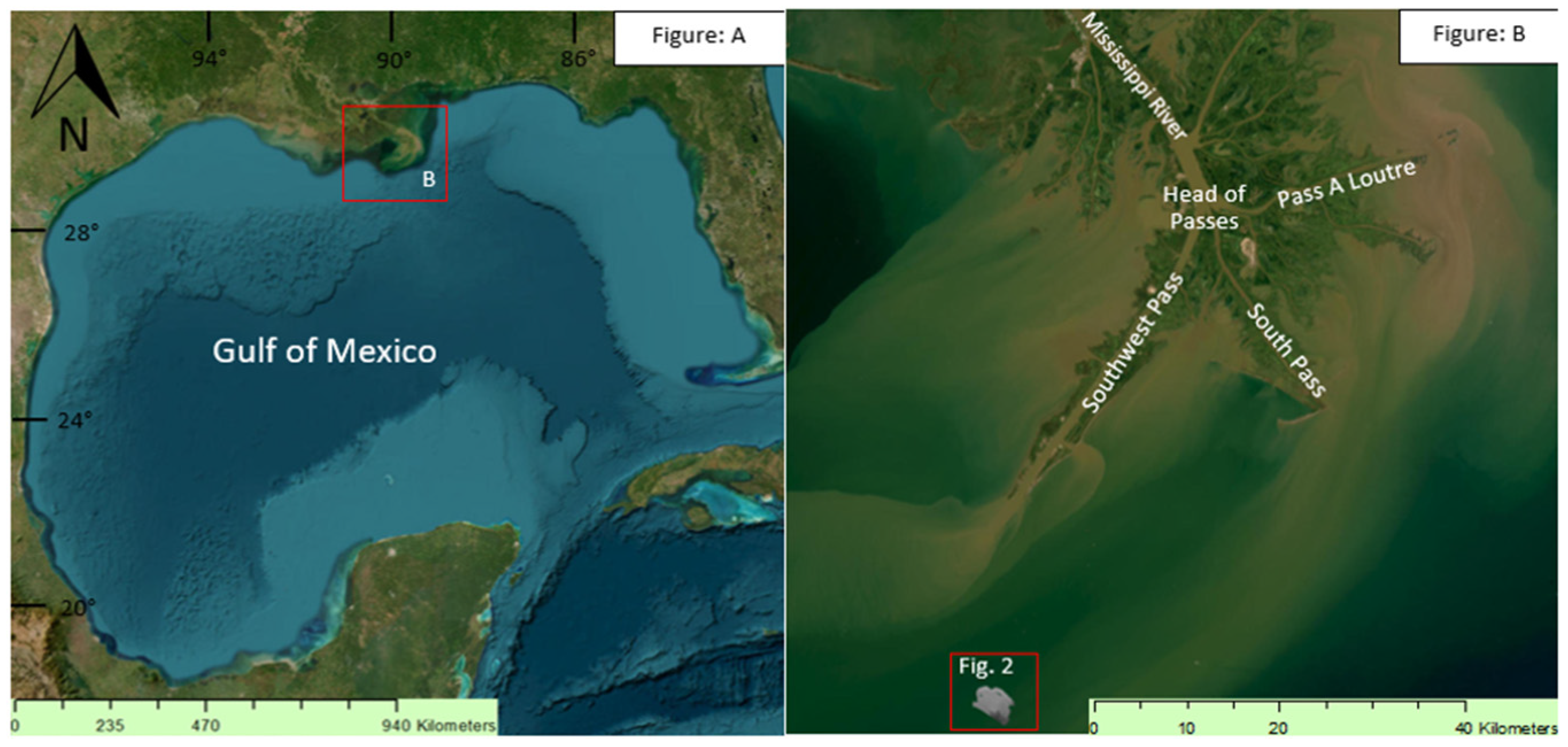
1.2. Study area
1.3. Hurricane influence
1.4. Sediment Properties and the SS Virginia
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Work and Core Processing
2.2. Sedimentological analyses
2.3. Radionuclide Analysis
3. Results
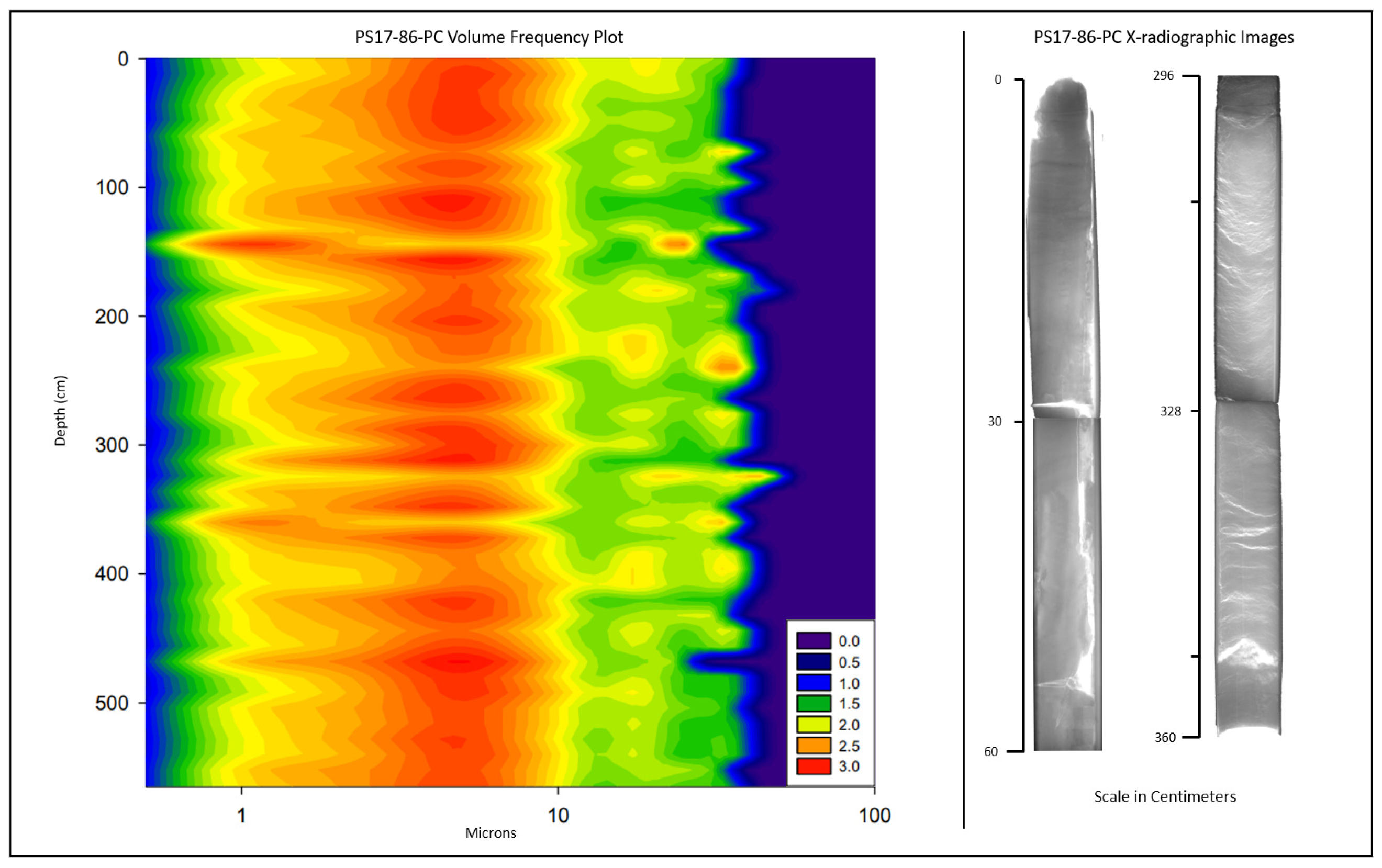
3.1. Granulometry
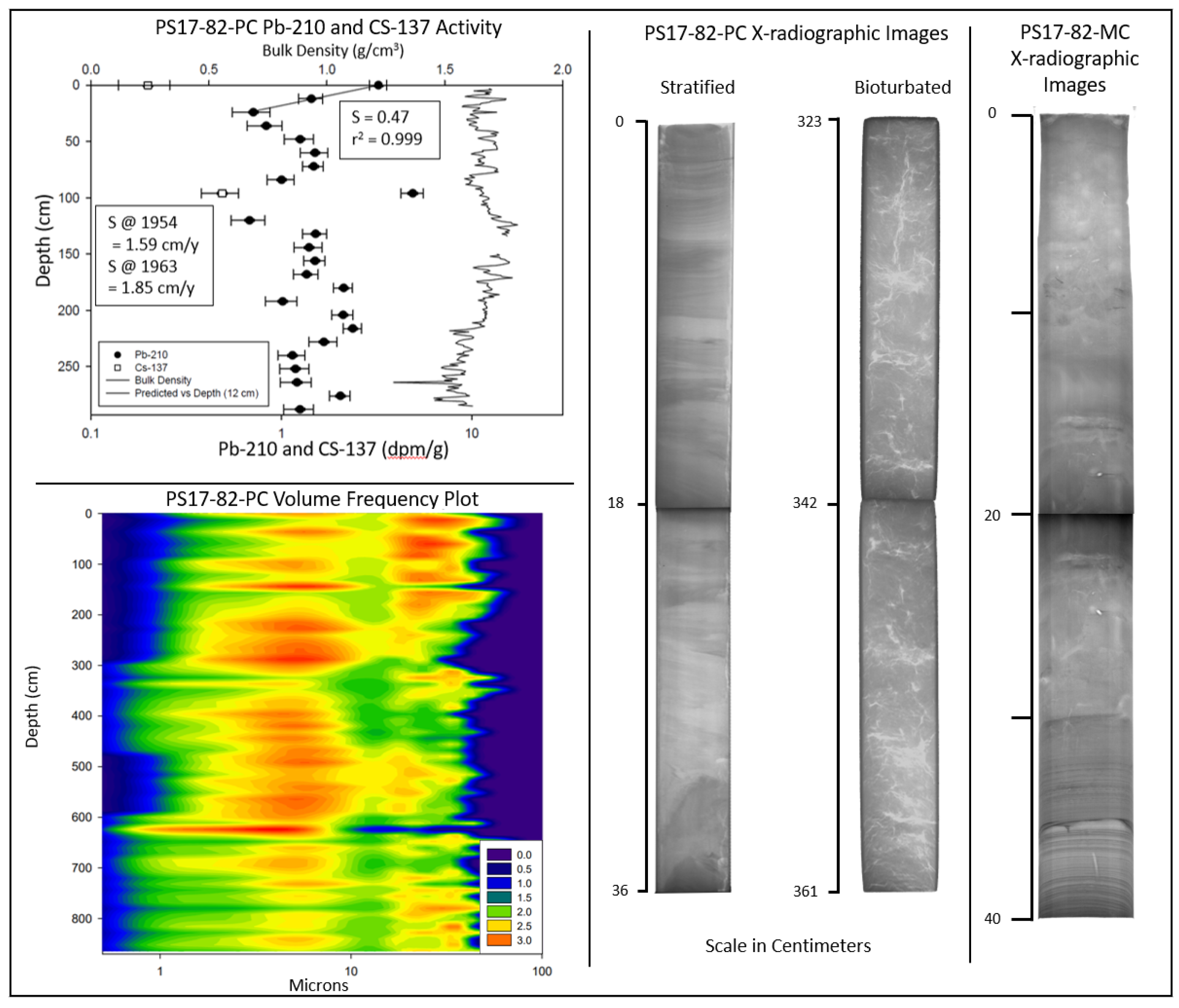
3.2. X-Radiography
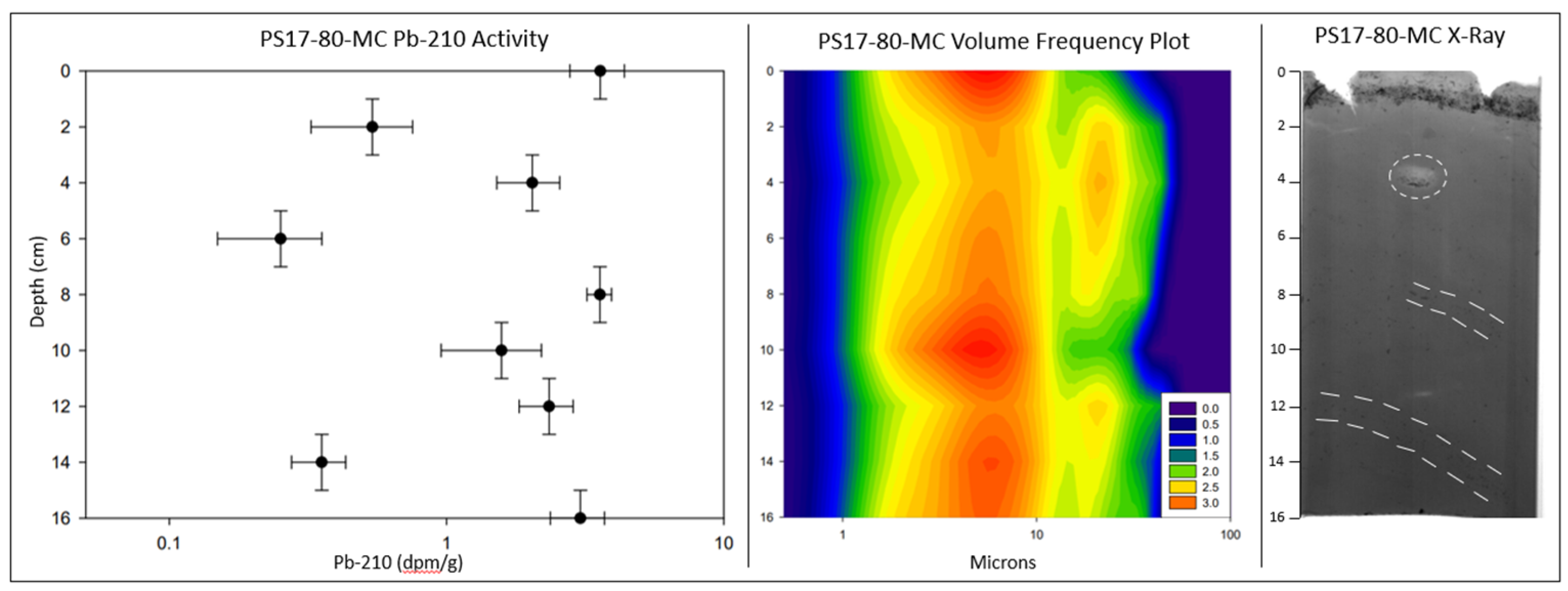
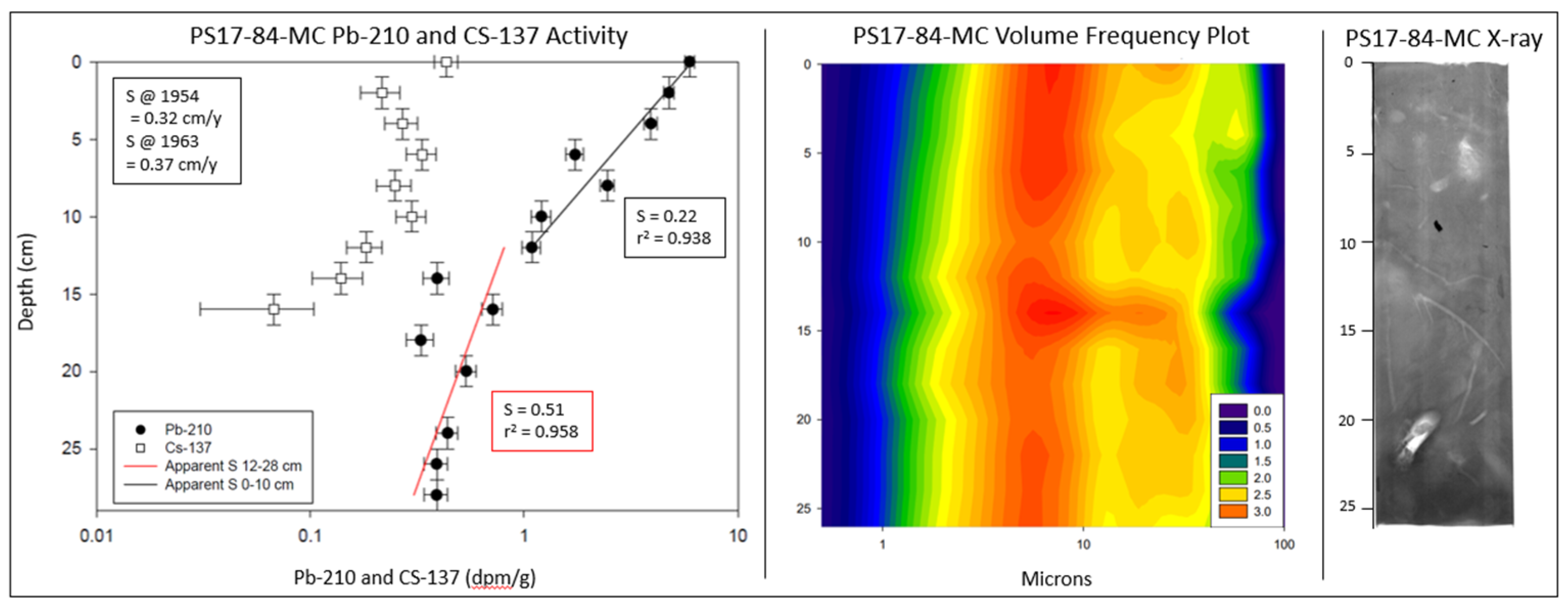
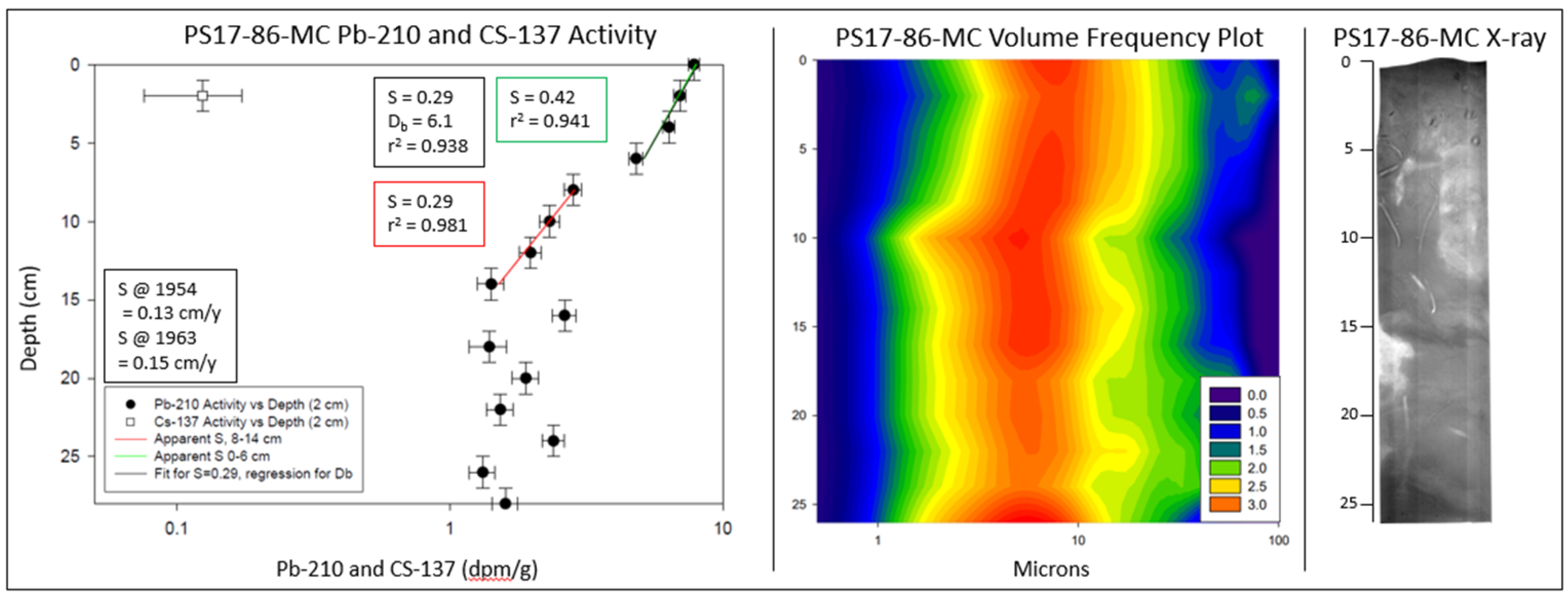
3.3. Radionuclide analysis
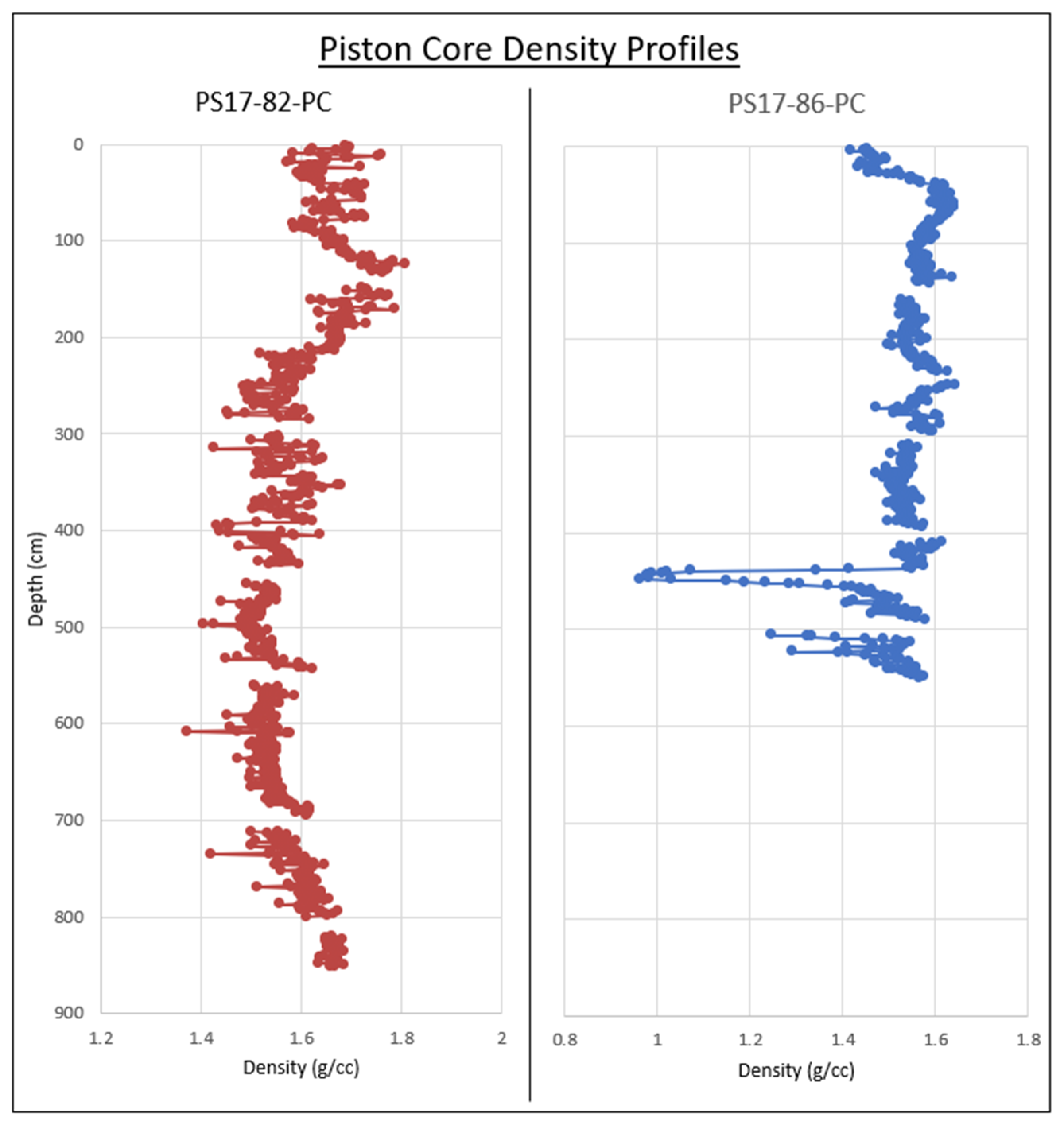
3.4. Piston Core Density
4. Discussion
4.1. Rates and Distances of Lobe Motion
4.2. Radioisotope Geochronology and Sedimentary Fabric
4.3. Sediment Resuspension Potential from Combined Waves and Currents
4.4. Estimating Total Gravity-Driven Mass Transport of the SS Virginia Sediment Lobe
5. Conclusions
- Sediment accumulation rates from 210Pb and 137Cs geochronology as well as relative indicators of sedimentation and bioturbation ascertained from core X-radiographs suggest that rates of sediment accumulation on the seabed surrounding Virginia have declined since ca. the mid-20th century.
- Sediment accumulation rates are substantially lower than those of other nearby MRDF studies conducted using the same methods, such as Duxbury et al. (2020) and Keller et al. (2016), where rates are up to ~90% greater [32,41]. Using published models and data, a simple analysis of sediment resuspension potential from waves and currents suggests that annual-scale events can resuspend sediments, likely producing some combination of sediment resuspension, bypass, and possibly erosion that could help produce the low accumulation rates.
- A volumetric analysis of the lobe combined with Chaytor et al.’s (2020) flow speeds indicates that the Virginia lobe is moving at rates sufficient to evacuate the entire Virginia lobe volume over timescales of 7–1400 years [8]. If these rates are extrapolated across the entire MRDF and total mass transport is compared to fluvial sediment supply, results suggest that mudflows are moving sediment downslope at mass-transport rates far higher than the rate of annual sediment supply from the Mississippi River.
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coleman, J. M. , Prior, D. B., & Garrison, L. E. (1978). Submarine landslides in the Mississippi River Delta. All Days. [CrossRef]
- Maloney, J. M. , Bentley, S. J., Xu, K., Obelcz, J., Georgiou, I. Y., Jafari, N. H., & Miner, M. D. (2020). Mass wasting on the Mississippi River Subaqueous Delta. Earth-Science Reviews, 200, 103001. [CrossRef]
- Bentley, S. J. , Keller, G. P., Obelcz, J., Maloney, J. M., Xu, K., Georgiou, I. Y., & Miner, M. D. (2016, December). Cohesive sedimentary processes on river-dominated deltas: New Perspectives from the Mississippi River Delta Front, gulf of mexico. NASA/ADS. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2016AGUFMEP31C..01B/abstract.
- Maloney, J. M., Bentley, S. J., Xu, K., Obelcz, J., Georgiou, I. Y., & Miner, M. D. (2018). Mississippi River Subaqueous Delta is entering a stage of retrogradation. Marine Geology, 400, 12–23. [CrossRef]
- Bentley S., J. , Xu K., Georgiou I. Y., Maloney J. (Baton Rouge, LA: Louisiana State University Coastal Studies Institute). 2022. Mass wasting processes and products of the Mississippi delta front: data synthesis and observation. 158 p. New Orleans (LA): US Dept. of Interior, Bureau of Ocean Energy Management. Cooperative Agreement No.: M13AC00013. OCS Study BOEM 2022-007.
- Bentley, S.J. , Xu, K., Xue, Z.G., Jafari, N., Glaspie, C., et al., 2024. A 21st Century Look at Mass Transport on the Subaqueous Delta of the Mississippi River: OASIS Partnership Preliminary Observations. AGU-ASLO Ocean Sciences Meeting, New Orleans, La.
- Damour, M. , Jones, D., & Chaytor, J. (2021, December). Historic shipwrecks as sentinels for monitoring subsea mudflows on the Mississippi River Delta Front. NASA/ADS. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2021AGUFMEP41D..04D/abstract.
- Chaytor, J., Baldwin, W. E., Bentley, S. J., Damour, M., Jones, D., Maloney, J., Miner, M., Obelcz, J., & Xu, K. (2020, March 26). Short and long‐term movement of mudflows of the Mississippi River Delta Front and their known and potential impacts on oil and gas infrastructure. Geological Society of London Special Publications. Retrieved November 30, 2021.
- Baurick, T, N. O. L. A. | T. T.-P. (2019, February 16). 14-year Taylor Energy oil leak could prove larger than BP spill, new research says. NOLA.com. Retrieved April 25, 2023, from https://www.nola.com/news/environment/14-year-taylor-energy-oil-leak-could-prove-larger-than-bp-spill-new-research-says/article_c160c6c8-fffd-5cc2-8a13-526978df20e8.html.
- Guidroz, Walter Scott, "Subaqueous, hurricane-initiated shelf failure morpho dynamics along the Mississippi River Delta Front, north-central Gulf of Mexico" (2009). LSU Doctoral Dissertations. 1416. https://digitalcommons.lsu.edu/gradschool_dissertations/1416.
- Obelcz, J. , Xu, K., Georgiou, I. Y., Maloney, J., Bentley, S. J., & Miner, M. D. (2017). Sub-decadal submarine landslides are important drivers of deltaic sediment flux: Insights from the Mississippi River Delta Front. Geology. [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J. M. , Prior, D. B., & Garrison, L. E. (1980). Subaqueous sediment instabilities in the offshore Mississippi River delta (p. 60). Bureau of Land Management, New Orleans OCS Office.
- Moore, D.G., & Scruton, P.C. (1957). Minor Internal Structures of Some Recent Unconsolidated Sediments. AAPG Bulletin, 41, 2723-2751.
- Wright, L. D. , & Nittrouer, C. A. (1995). Dispersal of river sediments in coastal seas: Six contrasting cases. Estuaries, 18(3), 494. [CrossRef]
- Keen T, Furukawa Y, Bentley S, Slingerland R, Teague W, Dykes J, Rowley C (2006) Geological and oceanographic perspectives on event bed formation during Hurricane Katrina. Geophys Res Lett 33, L23614. [CrossRef]
- Walsh JP, Corbett DR, Mallinson D, Goni M, Dail M, Lowey K, Marcinak K, Ryan K, Smith C, Stevens A, Sumners B, Tesh T (2006) Mississippi Delta mudflow activity and 2005 Gulf Hurricanes. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 87:477–478. [CrossRef]
- Xu K, Mickey RC, Chen Q, Harris CK, Hetland RD, Hu K, Wang J (2015) Shelf sediment transport during hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Comput Geosci 90:24–39. [CrossRef]
- Denommee K, Bentley S (2013) Influence of mass-transport processes on clinoform mechanics on the southwest Louisiana Shelf. Gulf Coast Assoc Geol Soc Trans 63:205 212.
- Denommee K, Bentley SJ Sr, Harazim D, Macquaker JHS (2016) Hydrodynamic controls on sedimentary fabric development in a shelf clinothem: Southwest Louisiana Continental Shelf. Mar Geol. [CrossRef]
- Wright, L. D. , Friedrichs, C. T., Kim, S. C., & Scully, M. E. (2001). Effects of ambient currents and waves on gravity-driven sediment transport on continental shelves. Marine Geology, 175(1–4), 25–45. [CrossRef]
- Macquaker, J. H. S., Bentley, S. J., & Bohacs, K. M. (2010, October 1). Wave-enhanced sediment-gravity flows and mud dispersal across continental shelves: Reappraising sediment transport processes operating in ancient mudstone successions. Geology. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/geology/article/38/10/947/130135/Wave-enhanced-sediment-gravity-flows-and-mud.
- Allison, M. A. , Meselhe, E. A., Kleiss, B. A., & Duffy, S. M. (2023). Impact of water loss on sustainability of the Mississippi River channel in its Deltaic Reach. Hydrological Processes. [Unpublished manuscript]. [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, W.E. , Ackerman, S.D., Worley, C.R., Danforth, W.W. and Chaytor, J.D. 2018. High-resolution geo- physical data collected along the Mississippi River Delta front offshore of southeastern Louisiana. US Geo- logical Survey Field Activity 2017-003-FA. US Geo‐ logical Survey data release. [CrossRef]
- Restreppo, G. A. (2019). Deltaic wetland dynamics from seasonal to centennial scales (Order No. 29126715). Available from Dissertations & Theses @ Louisiana State University; ProQuest Dissertations & Theses A&I; ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. (2675222694). Retrieved from https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/deltaic-wetland-dynamics-seasonal-centennial/docview/2675222694/se-2.
- Baker, S. R. , & Friedman, G. M. (1969). A non-destructive core analysis technique using X-rays. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 39(4), 1371-1383. [CrossRef]
- Cochran, J. K. , Masqué, P. (2003). Short-lived U/Th series radionuclides in the ocean: Tracers for scavenging rates, export fluxes and particle dynamics. Uranium-Series Geochemistry, 461–492. [CrossRef]
- Nittrouer CA, DeMaster DJ, McKee BA, Cutshall NH, Larsen IL (1984) The effect of sediment mixing on Pb-210 accumulation rates for the Washington continental shelf. Mar Geol 54:201–221. [CrossRef]
- Berner, R. A. (1980). Early Diagenesis: A Theoretical Approach. Princeton University Press. [CrossRef]
- Aller, R. C. (1980). Quantifying solute distributions in the bioturbated zone of marine sediments by defining an average microenvironment. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 44(12), 1955–1965. [CrossRef]
- Nittrouer, C. A. , & Sternberg, R. W. (1981). The formation of sedimentary strata in an allochthonous shelf environment: The Washington Continental Shelf. Developments in Sedimentology, 201–232. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Z, Bentley SJ, Febo LA, Droxler AW, Dickens GR, Peterson LC, Opdyke BN (2008) Excess 210Pb inventories and fluxes along the continental slope and basins of the Gulf of Papua. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 113:F01S17. [CrossRef]
- Keller, G., Bentley, S. J., Georgiou, I. Y., Maloney, J., Miner, M. D., & Xu, K. (2016, October 22). River-plume sedimentation and 210PB/7be seabed delivery on the Mississippi River Delta Front. Geo-Marine Letters. Retrieved November 30, 2021, from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00367-016-0476-0.
- Sommerfield, C. K., Nittrouer, C. A., & Alexander, C. R. (1999). 7BE as a tracer of flood sedimentation on the Northern California Continental Margin. Continental Shelf Research, 19(3), 335–361. [CrossRef]
- Rotondo KA & Bentley SJ (2003) Deposition and resuspension of fluid mud on the western Louisiana inner shelf. Gulf Coast Assoc Geol Soc Trans 53:722–731.
- Bentley, S. J. (2002, January 1). Dispersal of fine sediments from river to shelf: Process and product. AAPG Datapages/Archives. Retrieved October 4, 2022, from https://archives.datapages.com/data/gcags/data/052/052001/1055.htm.
- Galloway, N., Levy, T. and George, T. 2017. Mapping active mudflow features off Southwest Pass, Louisiana, Gulf of Mexico. Presented at Hydrographic Society of America 2017 Annual Meeting, 20–23 March, Galveston, TX, http://ushydro2019.thsoa.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Galloway_Hydro2017_MappingMudflowFeatures-1.pdf.
- Bentley, S. J. , & Nittrouer, C. A. (2003). Emplacement, modification, and preservation of event strata on a flood-dominated continental shelf: Eel shelf, Northern California. Continental Shelf Research, 23(16), 1465-1493. [CrossRef]
- Wheatcroft, R. A. , Wiberg, P. L., Alexander, C. R., Bentley, S. J., Drake, D. E., Harris, C. K., & Ogston, A. S. (2007). Post-depositional alteration and preservation of sedimentary strata. Continental Margin Sedimentation, 101–155. [CrossRef]
- Bentley, S.J., Sheremet, A., and Jaeger, J.M., 2006, Preservation potential of event layers on continental shelves: a model and observations. Continental Shelf Research 26: 2108-2124.
- Bentley, S. J. , Blum, M. D., Maloney, J., Pond, L., & Paulsell, R. (2016). The Mississippi River Source-to-sink system: Perspectives on tectonic, climatic, and anthropogenic influences, miocene to anthropocene. Earth-Science Reviews, 153, 139–174. [CrossRef]
- Duxbury, J., Bentley, S.J., Xu, K. (2023). Temporal scales of mass wasting sedimentation across the Mississippi River Delta Front delineated by 210Pb/137Cs Geochronology [Unpublished manuscript].
- Lo, E.L. , Bentley, S.J., & Xu, K. Experimental study of cohesive sediment consolidation and resuspension identifies approaches for coastal restoration: Lake Lery, Louisiana. Geo-Mar Lett 34, 499–509 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Sha, X., Xu, K., Bentley, S. J., & Robichaux, P. A. (2018). Characterization and modeling of sediment settling, consolidation, and suspension to optimize coastal Louisiana Restoration. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 203, 137–147. [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.H. , Corbett, D., Walsh, J., Young, D., Briggs, K., Cartwright, G., Friedrichs, C., Harris, C., Mickey*, R., Mitra, S., 2014. Seabed Erodibility Variations on the Louisiana Continental Shelf Before and After the 2011 Mississippi River Flood, Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 149, 283-293. [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.H. , Harris, C.K., Hetland, R.D., Kaihatu, J. M., 2011. Dispersal of Mississippi and Atchafalaya Sediment on the Texas-Louisiana Shelf: Model Estimates for the Year 1993, Continental Shelf Research, 31, 1558-1575. [CrossRef]
- Zang, Zhengchen, George Xue, Kehui Xu, Samuel J Bentley, Qin Chen, Eurico J D’Sa, Qian Ge, 2019, A Two 175 Decadal (1993–2012) Numerical Assessment of Sediment Dynamics in the Northern Gulf of Mexico, Water. [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, R., Soulsby, R., Roberts, W., Mitchener, H., (2000). Dynamics of estuarine muds: A manual for practical applications. Telford.
- Allison, M. A. , Demas, C. R., Ebersole, B. A., Kleiss, B. A., Little, C. D., Meselhe, E. A., Powell, N. J., Pratt, T. C., & Vosburg, B. M. (2012). A water and sediment budget for the lower Mississippi–Atchafalaya river in Flood Years 2008–2010: Implications for sediment discharge to the oceans and coastal restoration in Louisiana. Journal of Hydrology, 432-433, 84–97. [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Ocean Energy Management. (2023, November 11). Pipelines. Geographic mapping data in digital format. https://www.data.boem.gov/Main/Mapping.aspx.
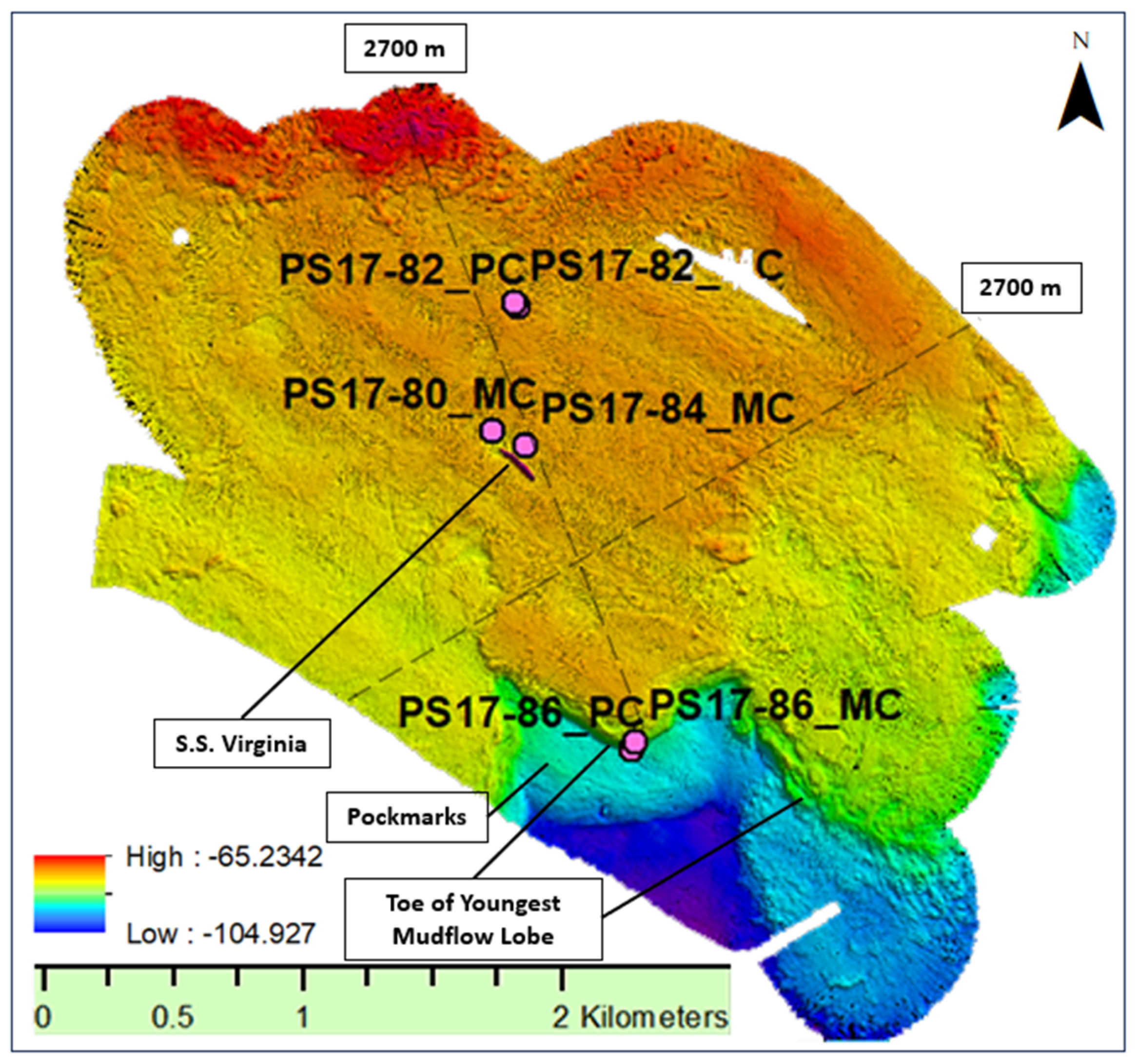
| Station | Distance from SW Pass (km) | Distance from SS Virginia (m) | Depth from Sea Level (m) | Penetration Depth (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS17-80-MC | 18.99 | 150 | 84.7 | 18 |
| PS17-82-MC | 18.49 | 612 | 83.7 | 40 |
| PS17-84-MC | 19.03 | 69 | 84.3 | 28 |
| PS17-86-MC | 20.17 | 1174 | 88.8 | 34 |
| PS17-82-PC | 18.5 | 595 | 83.8 | 862 |
| PS17-86-PC | 20.14 | 1192 | 89 | 564 |
| Station | 210Pb SAR (cm/y) | r2 | 210Pb Depth Range (cm) | 210Pb SAR (cm/y) | r2 | 210Pb Depth Range (cm) | Db | r2 | Db Depth Range (cm) | 137Cs SAR 1954 (cm/y) | 137Cs Depth Range (cm/y) | 137Cs SAR 1963 (cm/y) | 137Cs Depth Range (cm/y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS17-84-MC | 0.22 | 0.938 | 0-12 | 0.51 | 0.433 | 12-25 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0.32 | 0-16 | 0.37 | 0-8 |
| PS17-86-MC | 0.42 | 0.981 | 0-6 | 0.29 | 0.981 | 8-14 | 6.1 | 0.938 | 0-6 | 0.13 | 0-4 | 0.15 | 0-4 |
| PS17-82-PC | 0.47 | 0.999 | 0-24 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1.59 | 0-96 | 1.85 | 0-96 |
| Depth Interval (m) | Lobe volume undergoing transport (x 106 m3) | Dry Mass (x 106 metric tons per m3) | Percentage of Annual Sediment Load at Baton Rouge | Mass Transport Rate 2004-2006, Mt/y, using speed of 183 m/y (Figure 7), across full width of lobe | Transport Rate 2006-2009, t/y, using speed of 54 m/y (Figure 7), across full width of lobe | Mass Transport Rate 2009-2016, Mt/y using speed of 0.9 m/y (Figure 7), across full width of lobe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 120 | 120 | 130 | 22,000 | 2,200 | 108 |
| 8 | 59 | 62 | 66 | 11,000 | 1,100 | 56 |
| 2.6 | 19 | 20 | 22 | 4,000 | 360 | 18 |
| Speed of Flow (m/y) | Transit Time (y) to Evacuate Full Lobe Volume Past the Present Front of the Lobe | Transit Time (y) for a Volume Equivalent to one Year Sediment Load at Baton Rouge | Transit Time (y) for a year-equivalent Discharge Volume Across Entire Delta Front (if front is 100 km across, and lobe width is 2 km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 183 | 15 | 12 | 0.06 |
| 54 | 50 | 40 | 0.2 |
| 0.9 | 2985 | 2407 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





