Submitted:
21 December 2023
Posted:
21 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
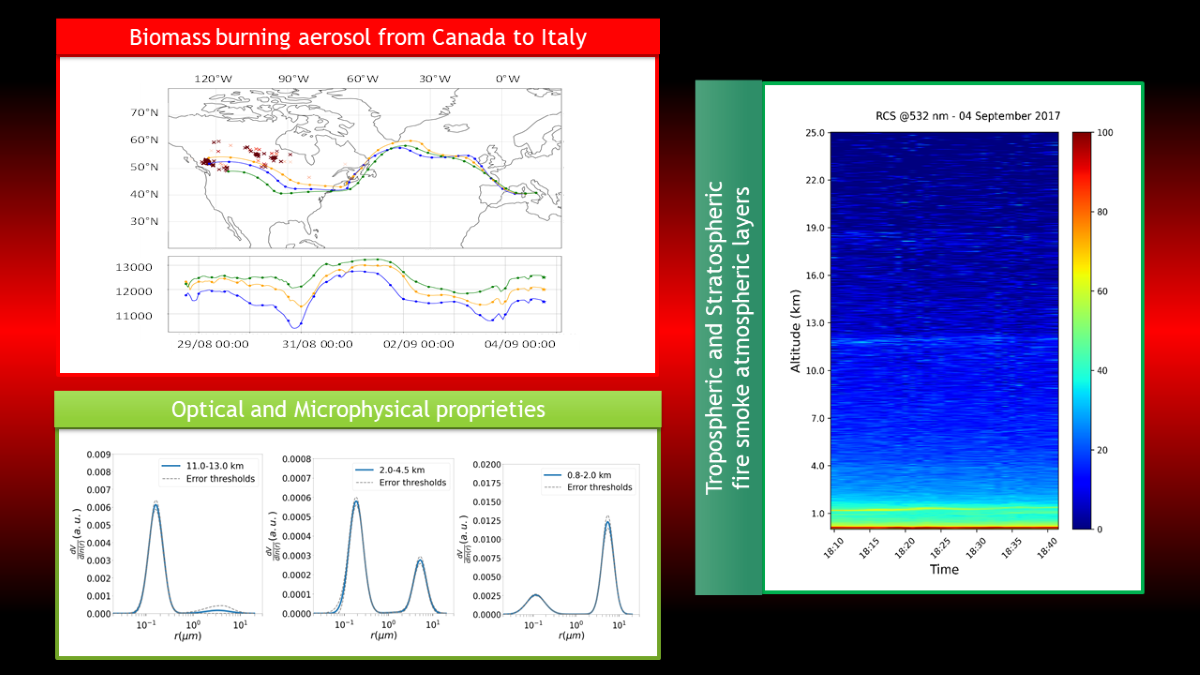
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MALIA multi-wavelength lidar
2.2. AERONET sun-photometer
2.3. Fire aerosol identification
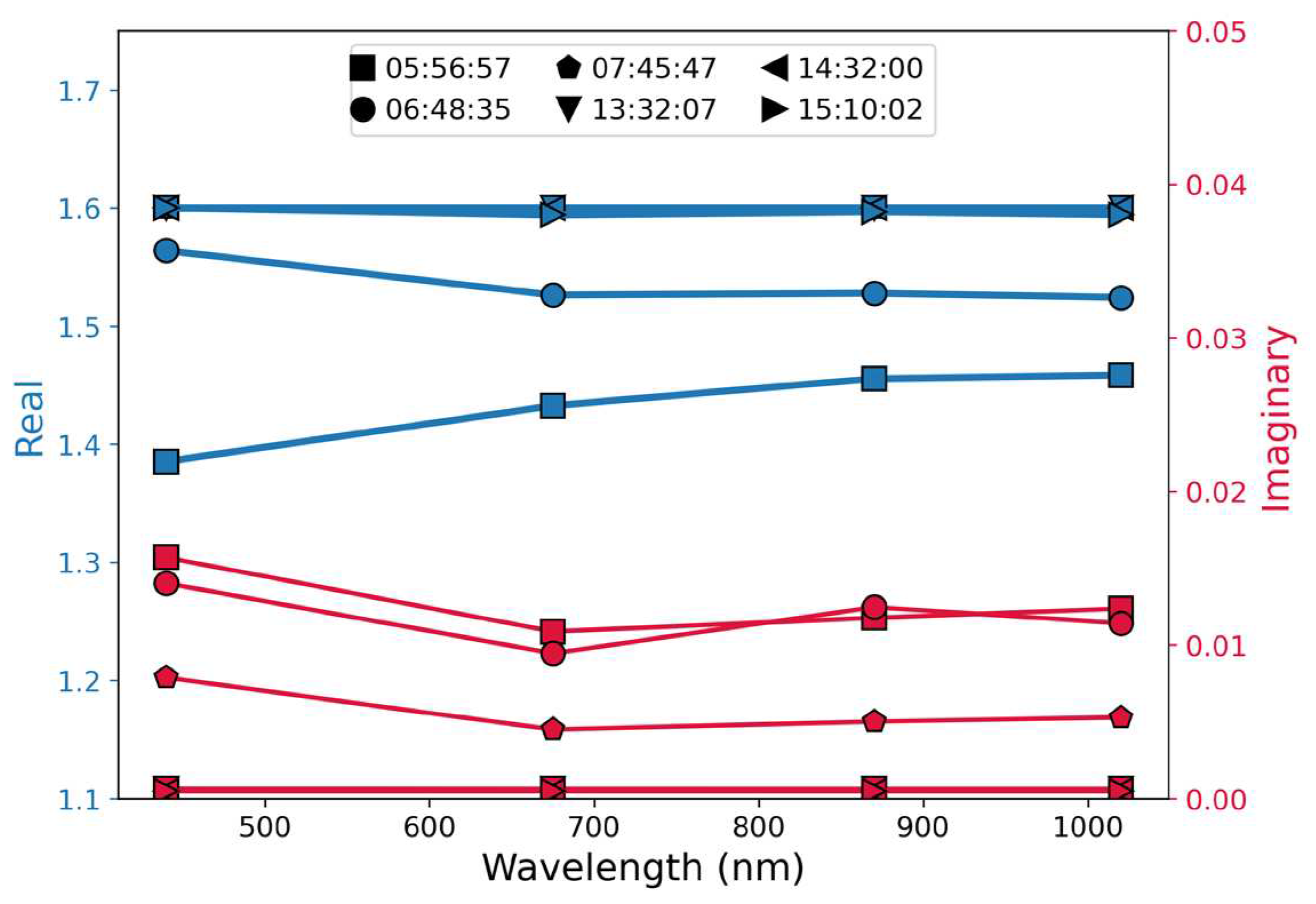
3. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linares, C.; Carmona, R.; Salvador, P.; Díaz, J. Impact on Mortality of Biomass Combustion from Wildfires in Spain: A Regional Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Blanco, E.; Castro, A.; Calvo, A.I.; Pont, V.; Mallet, M.; Fraile, R. Wildfire Smoke Plumes Transport under a Subsidence Inversion: Climate and Health Implications in a Distant Urban Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 988–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, J.S.; Koppmann, R.; Eck, T.F.; Eleuterio, D.P. A Review of Biomass Burning Emissions Part II: Intensive Physical Properties of Biomass Burning Particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 799–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebig, M.; Petzold, A.; Wandinger, U.; Wendisch, M.; Kiemle, C.; Stifter, A.; Ebert, M.; Rother, T.; Leiterer, U. Optical Closure for an Aerosol Column: Method, Accuracy, and Inferable Properties Applied to a Biomass-Burning Aerosol and Its Radiative Forcing. J. Geophys. Res. : Atmos. 2002, 107, LAC–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodshire, A.L.; Akherati, A.; Alvarado, M.J.; Brown-Steiner, B.; Jathar, S.H.; Jimenez, J.L.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Lonsdale, C.R.; Onasch, T.B.; Ortega, A.M.; et al. Aging Effects on Biomass Burning Aerosol Mass and Composition: A Critical Review of Field and Laboratory Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10007–10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Baars, H.; Chudnovsky, A.; Mattis, I.; Veselovskii, I.; Haarig, M.; Seifert, P.; Engelmann, R.; Wandinger, U. Extreme Levels of Canadian Wildfire Smoke in the Stratosphere over Central Europe on 21–22 August 2017. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11831–11845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaykin, S.M.; Godin-Beekmann, S.; Hauchecorne, A.; Pelon, J.; Ravetta, F.; Keckhut, P. Stratospheric Smoke With Unprecedentedly High Backscatter Observed by Lidars Above Southern France. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, M.; Granados-Muñoz, M.J.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Barragán, R.; Bedoya-Velásquez, A.E.; Benavent-Oltra, J.A.; Bortoli, D.; Comerón, A.; Córdoba-Jabonero, C.; Costa, M.J.; et al. Ground/Space, Passive/Active Remote Sensing Observations Coupled with Particle Dispersion Modelling to Understand the Inter-Continental Transport of Wildfire Smoke Plumes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Goloub, P.; Veselovskii, I.; Bravo-Aranda, J.-A.; Popovici, I.E.; Podvin, T.; Haeffelin, M.; Lopatin, A.; Dubovik, O.; Pietras, C.; et al. Long-Range-Transported Canadian Smoke Plumes in the Lower Stratosphere over Northern France. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1173–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohneiser, K.; Ansmann, A.; Witthuhn, J.; Deneke, H.; Chudnovsky, A.; Walter, G.; Senf, F. Self-Lofting of Wildfire Smoke in the Troposphere and Stratosphere: Simulations and Space Lidar Observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 2901–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Fromm, M.; Trentmann, J.; Luderer, G.; Andreae, M.O.; Servranckx, R. The Chisholm Firestorm: Observed Microstructure, Precipitation and Lightning Activity of a Pyro-Cumulonimbus. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Ohneiser, K.; Chudnovsky, A.; Knopf, D.A.; Eloranta, E.W.; Villanueva, D.; Seifert, P.; Radenz, M.; Barja, B.; Zamorano, F.; et al. Ozone Depletion in the Arctic and Antarctic Stratosphere Induced by Wildfire Smoke. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 11701–11726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alados-Arboledas, L.; Müller, D.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Navas-Guzmán, F.; Pérez-Ramírez, D.; Olmo, F.J. Optical and Microphysical Properties of Fresh Biomass Burning Aerosol Retrieved by Raman Lidar, and Star-and Sun-Photometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, B.; Amato, F.; Amodeo, A.; D’Amico, G.; Dema, C.; Falconieri, A.; Giunta, A.; Gumà-Claramunt, P.; Kampouri, A.; Solomos, S.; et al. Characterization of Extremely Fresh Biomass Burning Aerosol by Means of Lidar Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Ohneiser, K.; Mamouri, R.-E.; Knopf, D.A.; Veselovskii, I.; Baars, H.; Engelmann, R.; Foth, A.; Jimenez, C.; Seifert, P.; et al. Tropospheric and Stratospheric Wildfire Smoke Profiling with Lidar: Mass, Surface Area, CCN, and INP Retrieval. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9779–9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, H.; Radenz, M.; Floutsi, A.A.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D.; Heese, B.; Ansmann, A.; Flament, T.; Dabas, A.; Trapon, D.; et al. Californian Wildfire Smoke Over Europe: A First Example of the Aerosol Observing Capabilities of Aeolus Compared to Ground-Based Lidar. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL092194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.; Pahlow, M.; Kovalev, V.A.; Ondov, J.M.; Parlange, M.B.; Nair, N. Aerosol Optical Characterization by Nephelometer and Lidar: The Baltimore Supersite Experiment during the Canadian Forest Fire Smoke Intrusion. J. Geophys. Res. : Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloss, C.; Berthet, G.; Sellitto, P.; Ploeger, F.; Bucci, S.; Khaykin, S.; Jégou, F.; Taha, G.; Thomason, L.W.; Barret, B.; et al. Transport of the 2017 Canadian Wildfire Plume to the Tropics via the Asian Monsoon Circulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13547–13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarig, M.; Ansmann, A.; Baars, H.; Jimenez, C.; Veselovskii, I.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D. Depolarization and Lidar Ratios at 355, 532, and 1064 nm and Microphysical Properties of Aged Tropospheric and Stratospheric Canadian Wildfire Smoke. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11847–11861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baars, H.; Ansmann, A.; Ohneiser, K.; Haarig, M.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D.; Hanssen, I.; Gausa, M.; Pietruczuk, A.; Szkop, A.; et al. The Unprecedented 2017–2018 Stratospheric Smoke Event: Decay Phase and Aerosol Properties Observed with the EARLINET. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 15183–15198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.A.; Fromm, M.D.; McRae, R.H.D.; Campbell, J.R.; Hyer, E.J.; Taha, G.; Camacho, C.P.; Kablick, G.P.; Schmidt, C.C.; DeLand, M.T. Australia’s Black Summer Pyrocumulonimbus Super Outbreak Reveals Potential for Increasingly Extreme Stratospheric Smoke Events. npj Clim Atmos Sci 2021, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohneiser, K.; Ansmann, A.; Baars, H.; Seifert, P.; Barja, B.; Jimenez, C.; Radenz, M.; Teisseire, A.; Floutsi, A.; Haarig, M.; et al. Smoke of Extreme Australian Bushfires Observed in the Stratosphere over Punta Arenas, Chile, in January 2020: Optical Thickness, Lidar Ratios, and Depolarization Ratios at 355 and 532 nm. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 8003–8015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohneiser, K.; Ansmann, A.; Kaifler, B.; Chudnovsky, A.; Barja, B.; Knopf, D.A.; Kaifler, N.; Baars, H.; Seifert, P.; Villanueva, D.; et al. Australian Wildfire Smoke in the Stratosphere: The Decay Phase in 2020/2021 and Impact on Ozone Depletion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 7417–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandinger, U.; Nicolae, D.; Pappalardo, G.; Mona, L.; Comerón, A. ACTRIS and Its Aerosol Remote Sensing Component. EPJ Web Conf. 2020, 237, 05003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenthaler, V.; Linné, H.; Chaikovski, A.; Rabus, D.; Groß, S. EARLINET Lidar Quality Assurance Tools. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2018, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandinger, U.; Freudenthaler, V.; Baars, H.; Amodeo, A.; Engelmann, R.; Mattis, I.; Groß, S.; Pappalardo, G.; Giunta, A.; D’Amico, G.; et al. EARLINET Instrument Intercomparison Campaigns: Overview on Strategy and Results. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1001–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, A.; Sannino, A.; Spinelli, N.; Piana, M.; Boselli, A.; Tontodonato, V.; Castellano, P.; Wang, X. A Bayesian Parametric Approach to the Retrieval of the Atmospheric Number Size Distribution from Lidar Data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2022, 15, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilova, S.V. Simultaneous Reconstruction of the Complex Refractive Index and the Particle Size Distribution Function from Lidar Measurements: Testing the Developed Algorithms. Atmos Ocean Opt 2019, 32, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klett, J.D. Stable Analytical Inversion Solution for Processing Lidar Returns. Appl. Opt., AO 1981, 20, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernald, F.G. Analysis of Atmospheric Lidar Observations: Some Comments. Appl. Opt., AO 1984, 23, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansmann, A.; Riebesell, M.; Wandinger, U.; Weitkamp, C.; Voss, E.; Lahmann, W.; Michaelis, W. Combined Raman Elastic-Backscatter LIDAR for Vertical Profiling of Moisture, Aerosol Extinction, Backscatter, and LIDAR Ratio. Appl. Phys. B 1992, 55, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böckmann, C.; Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A.; Bösenberg, J.; Amiridis, V.; Boselli, A.; Delaval, A.; Tomasi, F.D.; Frioud, M.; Grigorov, I.V.; et al. Aerosol Lidar Intercomparison in the Framework of the EARLINET Project. 2. Aerosol Backscatter Algorithms. Appl. Opt., AO 2004, 43, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, G.; Amodeo, A.; Pandolfi, M.; Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A.; Bösenberg, J.; Matthias, V.; Amiridis, V.; De Tomasi, F.; Frioud, M.; et al. Aerosol Lidar Intercomparison in the Framework of the EARLINET Project. 3. Raman Lidar Algorithm for Aerosol Extinction, Backscatter, and Lidar Ratio. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 5370–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biele, J.; Beyerle, G.; Baumgarten, G. Polarization Lidar: Corrections of Instrumental Effects. Opt. Express OE 2000, 7, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenthaler, V.; Esselborn, M.; Wiegner, M.; Heese, B.; Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; Müller, D.; Althausen, D.; Wirth, M.; Fix, A.; et al. Depolarization Ratio Profiling at Several Wavelengths in Pure Saharan Dust during SAMUM 2006. Tellus B 2009, 61, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N. Angstrom Exponent and Bimodal Aerosol Size Distributions. J. Geophys. Res. : Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, B.; Shi, G.; Li, S.; Di, H.; Yan, Q.; Hua, D. Correlation between the Lidar Ratio and the Ångström Exponent of Various Aerosol Types. Particuology 2018, 40, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, Á.; Cuevas, E.; Granados-Muñoz, M.-J.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Romero, P.M.; Gröbner, J.; Kouremeti, N.; Almansa, A.F.; Stone, T.; Toledano, C.; et al. The New Sun-Sky-Lunar Cimel CE318-T Multiband Photometer – a Comprehensive Performance Evaluation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 631–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Stunder, B. Real-Time Environmental Applications and Display sYstem: READY. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 95, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M. A Flexible Inversion Algorithm for Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Properties from Sun and Sky Radiance Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105696, 673–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Tanré, D.; Smirnov, A.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Abuhassan, N.; Newcomb, W.W.; Schafer, J.S.; Chatenet, B.; Lavenu, F.; et al. An Emerging Ground-Based Aerosol Climatology: Aerosol Optical Depth from AERONET. J. Geophys. Res. : Atmos. 2001, 106, 12067–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Fu, J.S.; Lin, N.-H.; Wang, S.-H.; Dong, X.; Wang, G. Superposition of Gobi Dust and Southeast Asian Biomass Burning: The Effect of Multisource Long-Range Transport on Aerosol Optical Properties and Regional Meteorology Modification. J. Geophys. Res. : Atmos. 2019, 124, 9464–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, R.W.; Pilewskie, P.; Russell, P.B.; Redemann, J.; Bond, T.C.; Quinn, P.K.; Sierau, B. Spectral Absorption Properties of Atmospheric Aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 5937–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Lin, N.-H.; Chou, M.-D.; Woo, J.-H. Estimate of Radiative Forcing of Asian Biomass-Burning Aerosols during the Period of TRACE-P. J. Geophys. Res. : Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Neill; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength Dependence of the Optical Depth of Biomass Burning, Urban, and Desert Dust Aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104349, 333–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, C.; Cachorro, V.E.; Berjon, A.; de Frutos, A.M.; Sorribas, M.; de la Morena, B.A.; Goloub, P. Aerosol optical depth and Ångström exponent climatology at El Arenosillo AERONET site (Huelva, Spain). Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 133, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I. Accuracy Assessments of Aerosol Optical Properties Retrieved from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Sun and Sky Radiance Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. : Atmos. 2000, 105, 9791–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.K.; Ilavajhala, S.; Wong, M.M.; Justice, C.O. Fire Information for Resource Management System: Archiving and Distributing MODIS Active Fire Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiridis, V.; Balis, D.S.; Giannakaki, E.; Stohl, A.; Kazadzis, S.; Koukouli, M.E.; Zanis, P. Optical Characteristics of Biomass Burning Aerosols over Southeastern Europe Determined from UV-Raman Lidar Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicka, L.; Davuliene, L.; Bycenkiene, S.; Stachlewska, I.S. Long Term Observations of Biomass Burning Aerosol over Warsaw by Means of Multiwavelength Lidar. Opt. Express OE 2023, 31, 33150–33174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, A.; Amoruso, S.; Damiano, R.; Scollo, S.; Sellitto, P.; Boselli, A. Optical and Microphysical Characterization of Atmospheric Aerosol in the Central Mediterranean during Simultaneous Volcanic Ash and Desert Dust Transport Events. Atmos. Res. 2022, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.A.; Cappa, C.D. Impact of Brown and Clear Carbon on Light Absorption Enhancement, Single Scatter Albedo and Absorption Wavelength Dependence of Black Carbon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4207–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonovas, T.; North, P.R.J.; Doerr, S.H. Smoke Aerosol Properties and Ageing Effects for Northern Temperate and Boreal Regions Derived from AERONET Source and Age Attribution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7929–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowicz, K.M.; Chilinski, M.T.; Lisok, J.; Zawadzka, O.; Stachlewska, I.S.; Janicka, L.; Rozwadowska, A.; Makuch, P.; Pakszys, P.; Zielinski, T.; et al. Study of Aerosol Optical Properties during Long-Range Transport of Biomass Burning from Canada to Central Europe in July 2013. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 101, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Amezcua, P.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Granados-Muñoz, M.J.; Benavent-Oltra, J.A.; Böckmann, C.; Samaras, S.; Stachlewska, I.S.; Janicka, Ł.; Baars, H.; Bohlmann, S.; et al. Microphysical Characterization of Long-Range Transported Biomass Burning Particles from North America at Three EARLINET Stations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5931–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Sinyuk, A.; Hyer, E.J.; O’Neill, N.T.; Shaw, G.E.; Castle, J.R.V.; Chapin, F.S.; Dubovik, O.; et al. Optical Properties of Boreal Region Biomass Burning Aerosols in Central Alaska and Seasonal Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth at an Arctic Coastal Site. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D11201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T.; Hobbs, P.V. Evidence That the Spectral Dependence of Light Absorption by Aerosols Is Affected by Organic Carbon. J. Geophys. Res. : Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womack, C.C.; Manfred, K.M.; Wagner, N.L.; Adler, G.; Franchin, A.; Lamb, K.D.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Schwarz, J.P.; Brock, C.A.; Brown, S.S.; et al. Complex Refractive Indices in the Ultraviolet and Visible Spectral Region for Highly Absorbing Non-Spherical Biomass Burning Aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 7235–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Kuang, Y.; Huang, S.; Song, Q.; Hu, W.; Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Chen, D.; Yue, D.; Yuan, B.; et al. Parameterizations of Size Distribution and Refractive Index of Biomass Burning Organic Aerosol with Black Carbon Content. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 12401–12415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, A.; Damiano, R.; Sorrentino, A.; Spinelli, N.; Wang, X.; Boselli, A. Retrieving Atmospheric Number Size Distribution and Complex Refractive Index from Lidar Data. 2024. To be submitted.
- López-Cayuela, M.-Á.; Herrera, M.E.; Córdoba-Jabonero, C.; Pérez-Ramírez, D.; Carvajal-Pérez, C.V.; Dubovik, O.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L. Retrieval of Aged Biomass-Burning Aerosol Properties by Using GRASP Code in Synergy with Polarized Micro-Pulse Lidar and Sun/Sky Photometer. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
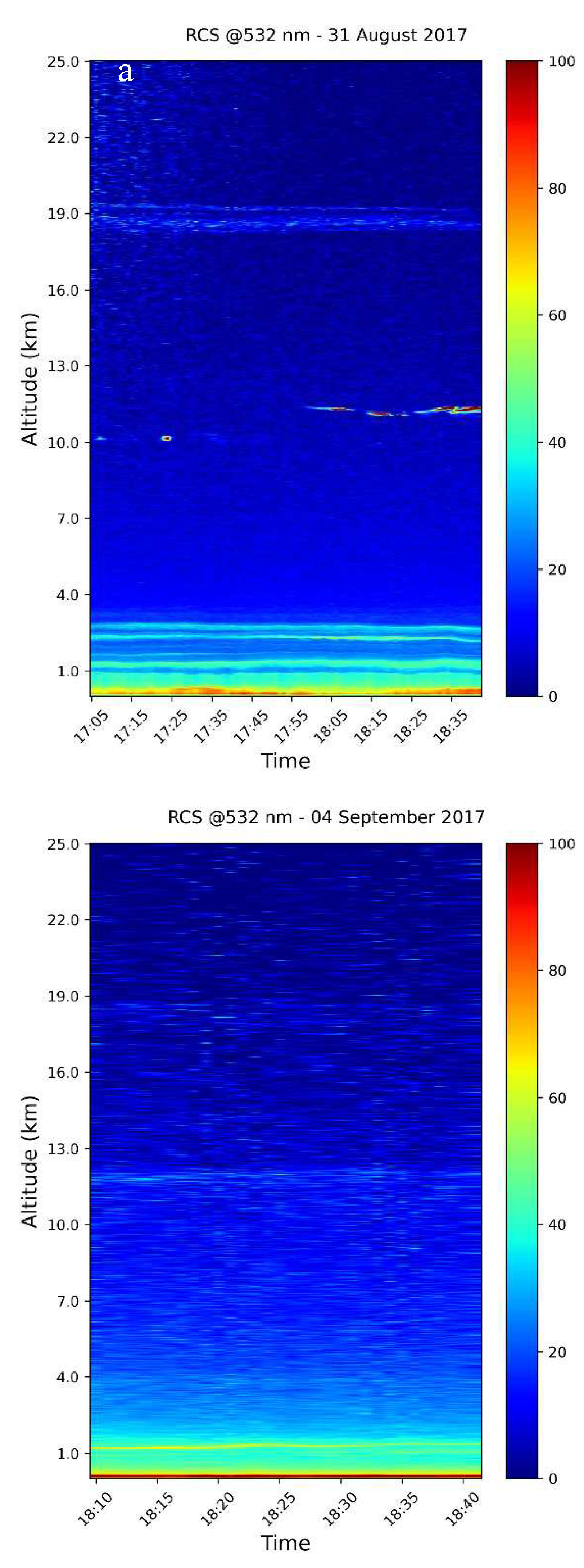
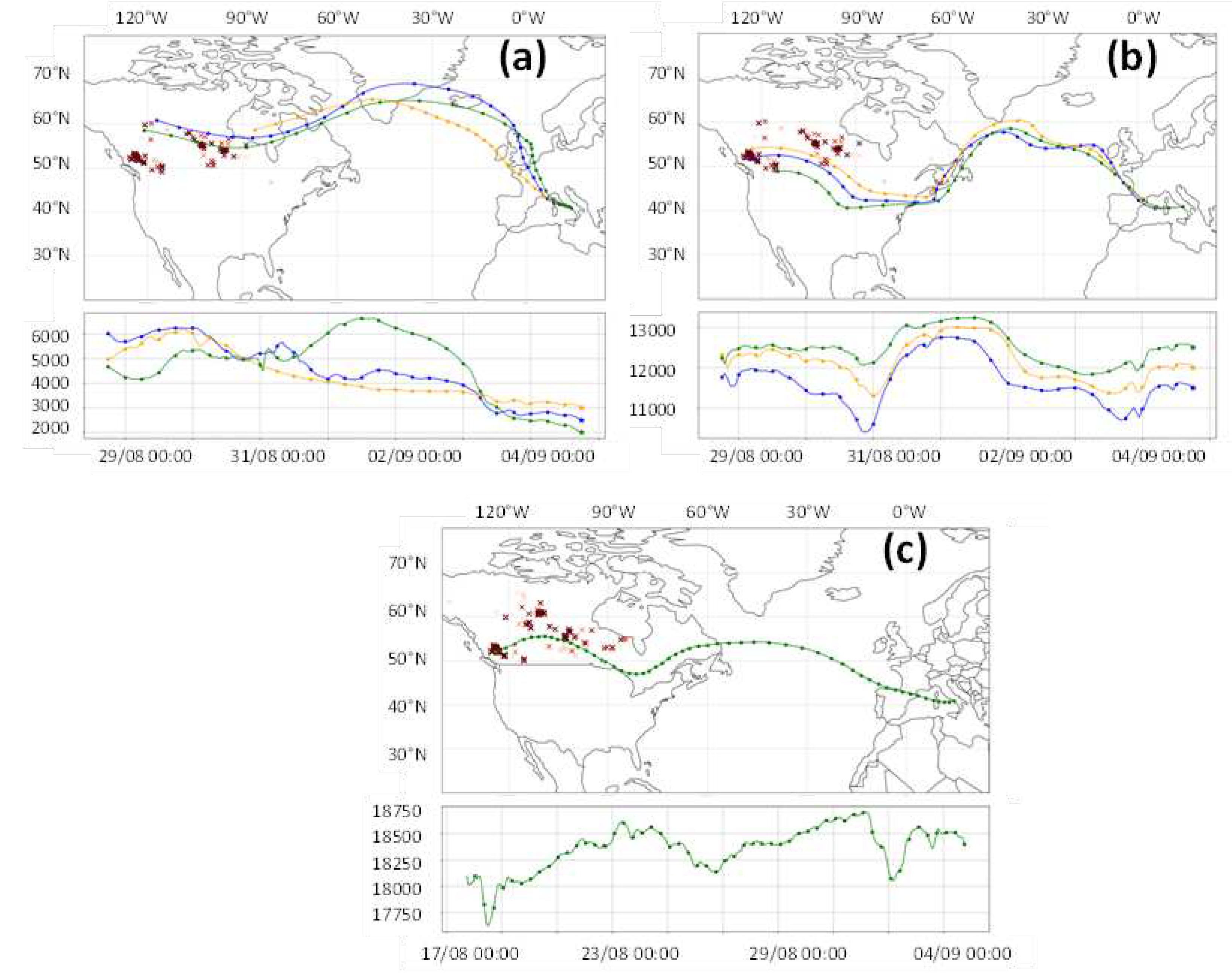
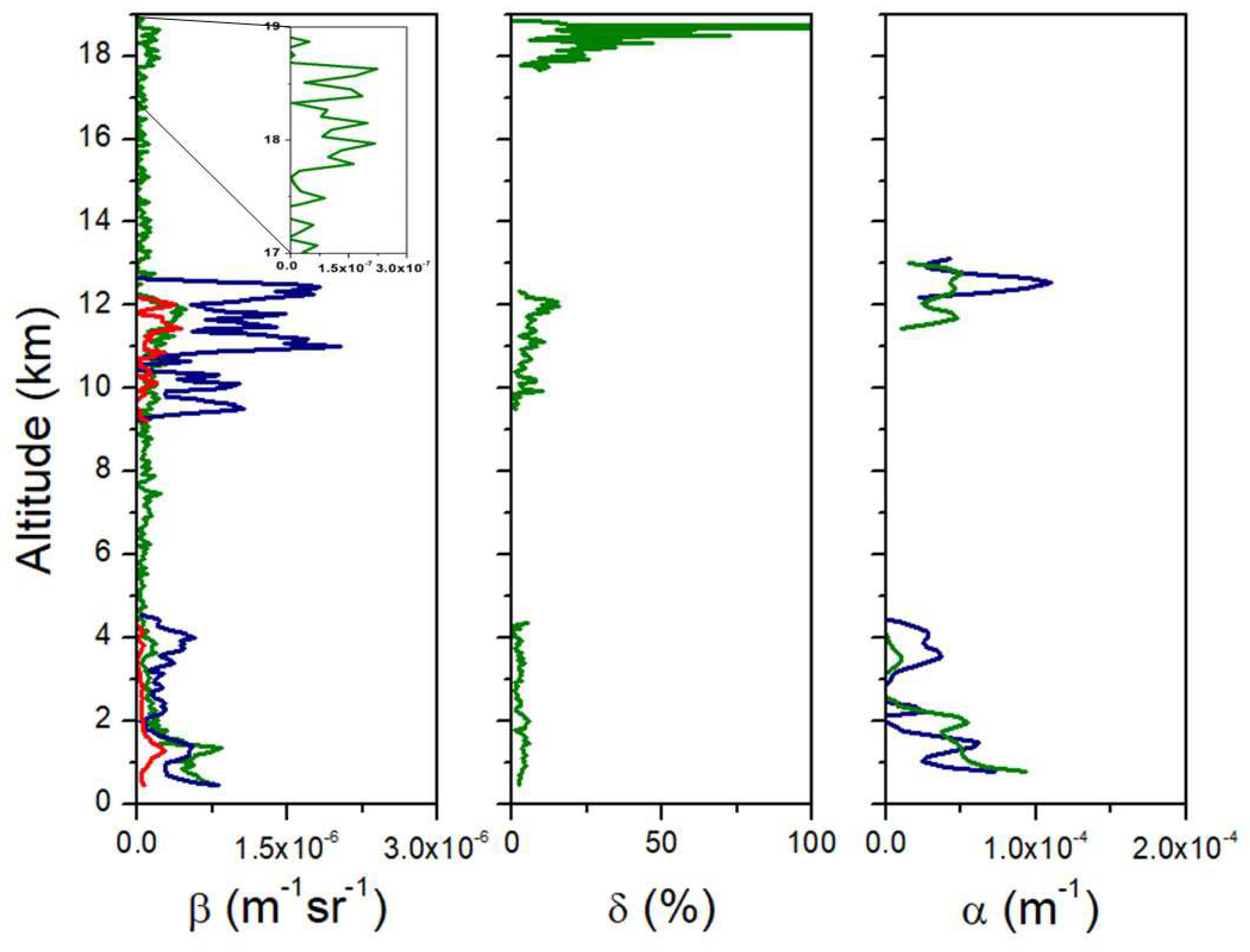
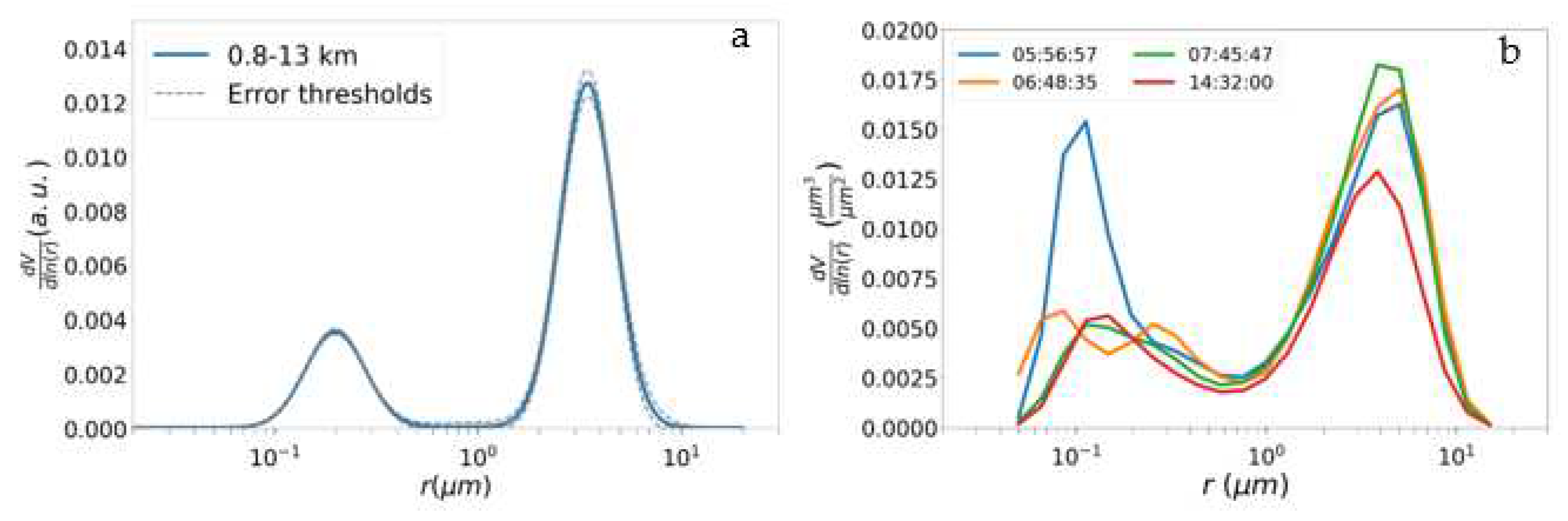
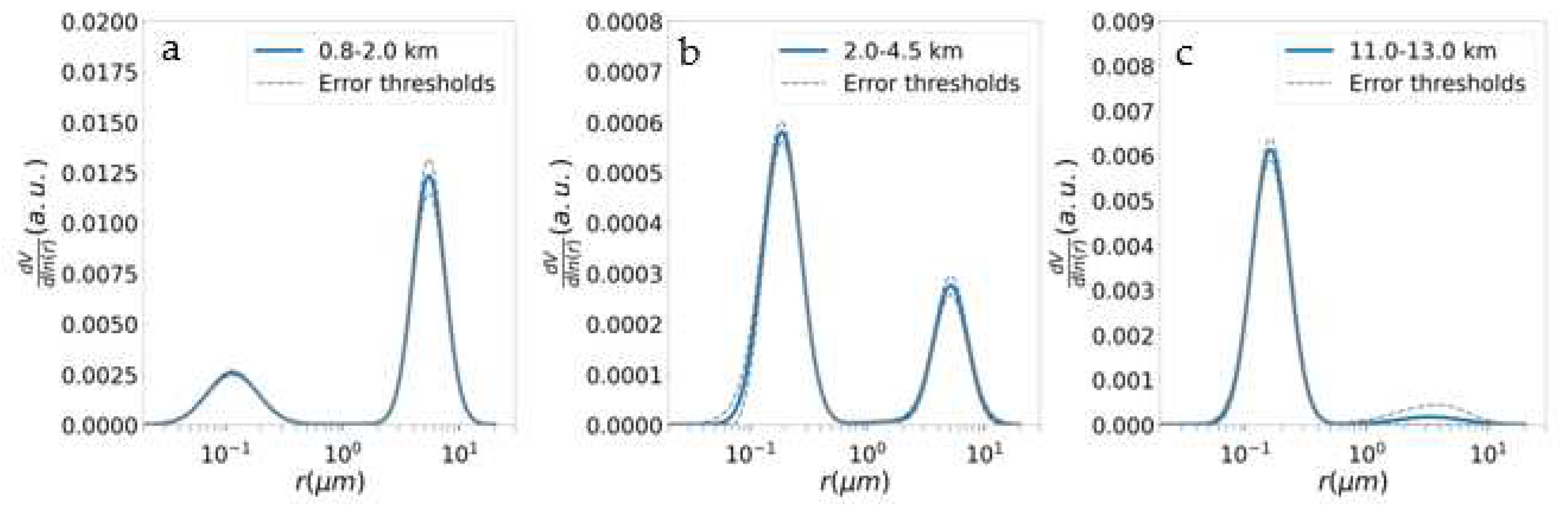
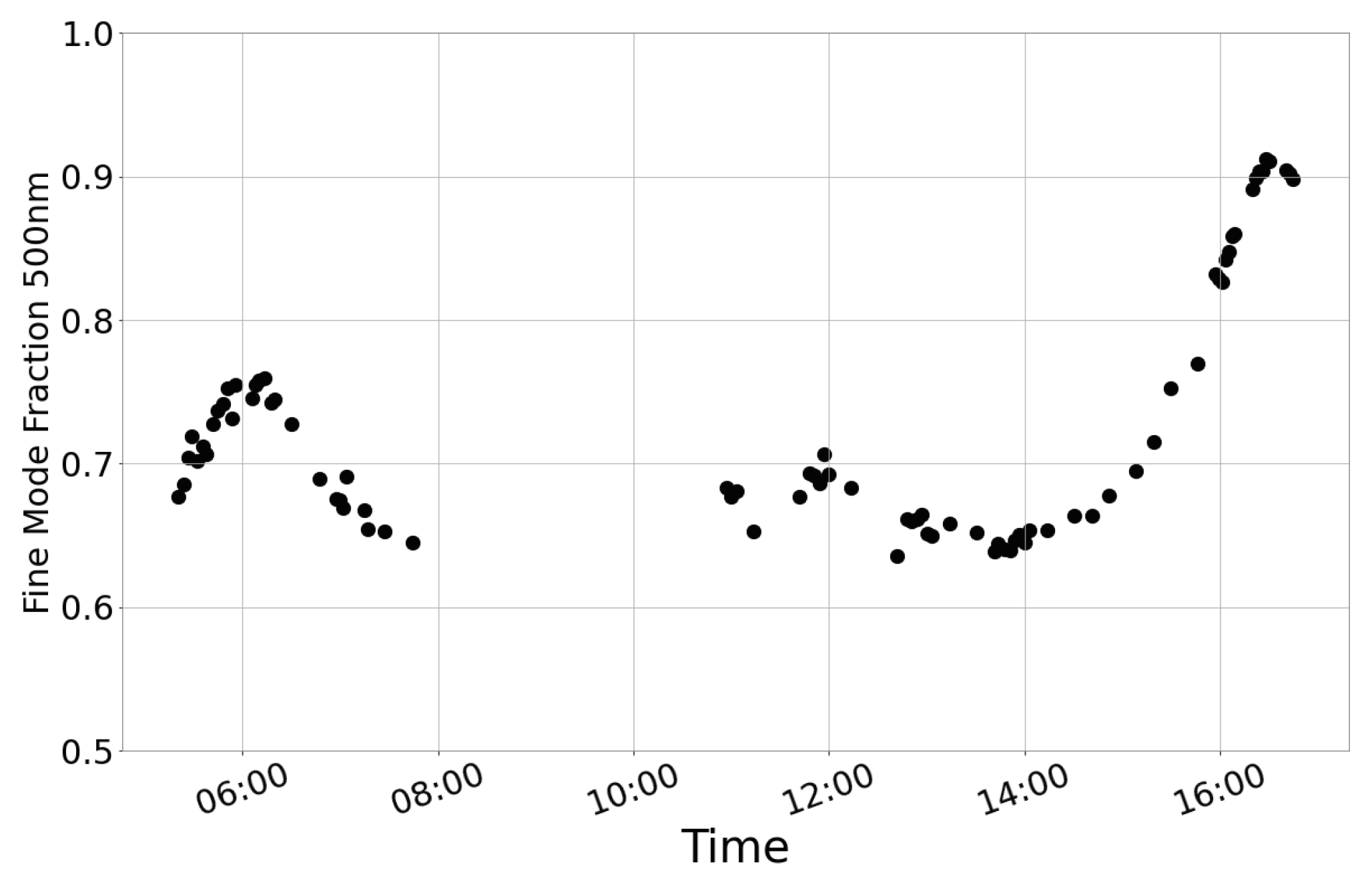
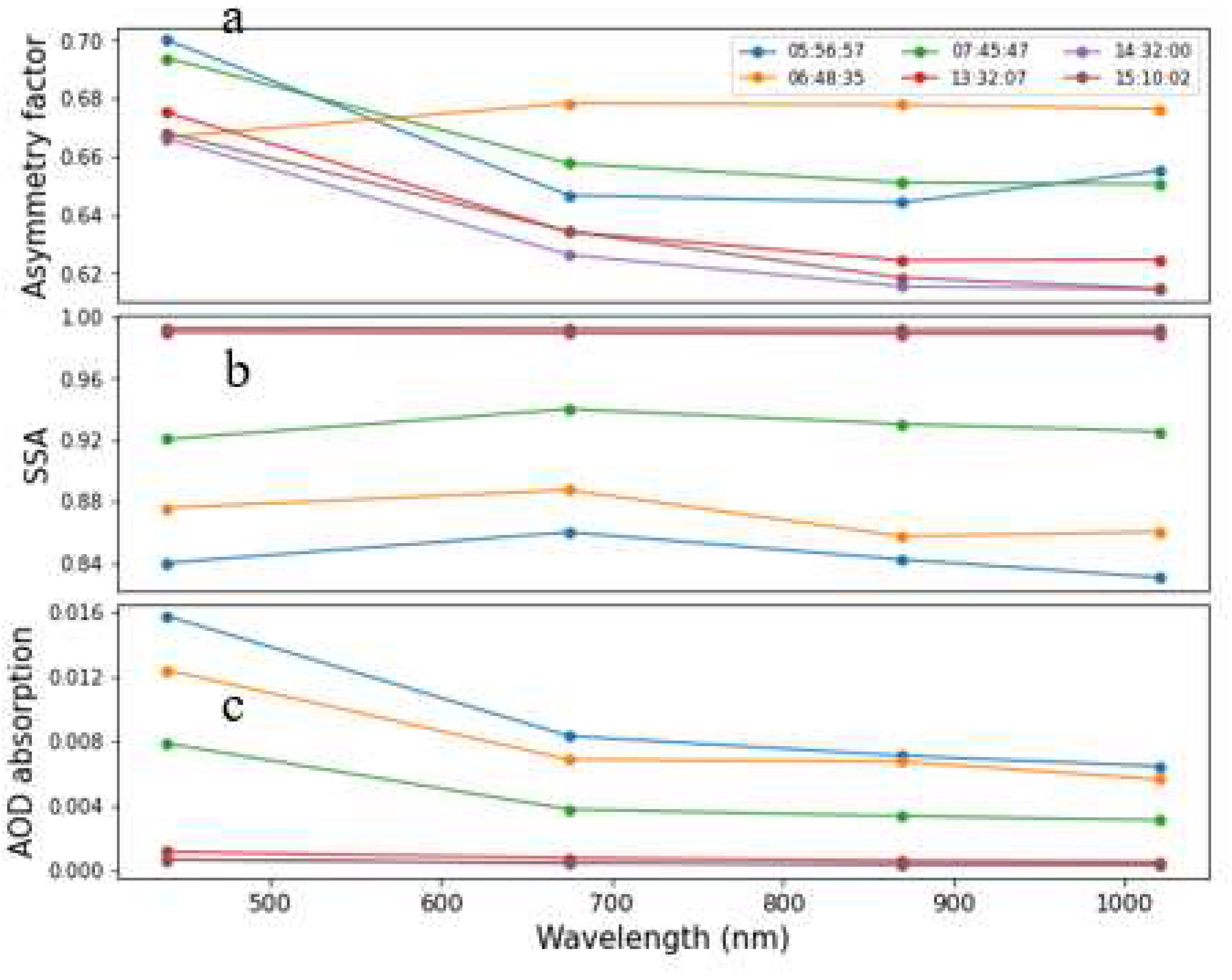
| Range (km) | δ (%) | LR355 | LR532 | BAE | EAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 (0.8-2.0) | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 32 ± 10 | 82 ± 17 | 1.1 ± 0.7 | -1.0 ± 0.5 |
| R2 (2.0-4.5) | 2.5 ± 0.3 | 20 ± 17 | 32 ± 9 | 3.4 ± 2.1 | -0.5 ± 3.0 |
| R3 (11.0-13.0) | 6.6 ± 1.8 | 65 ± 35 | 82 ± 47 | 4.4 ± 4.9 | 2.9 ± 4.0 |
| R4 (17.0-19.0) | 29.8 ± 7.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





