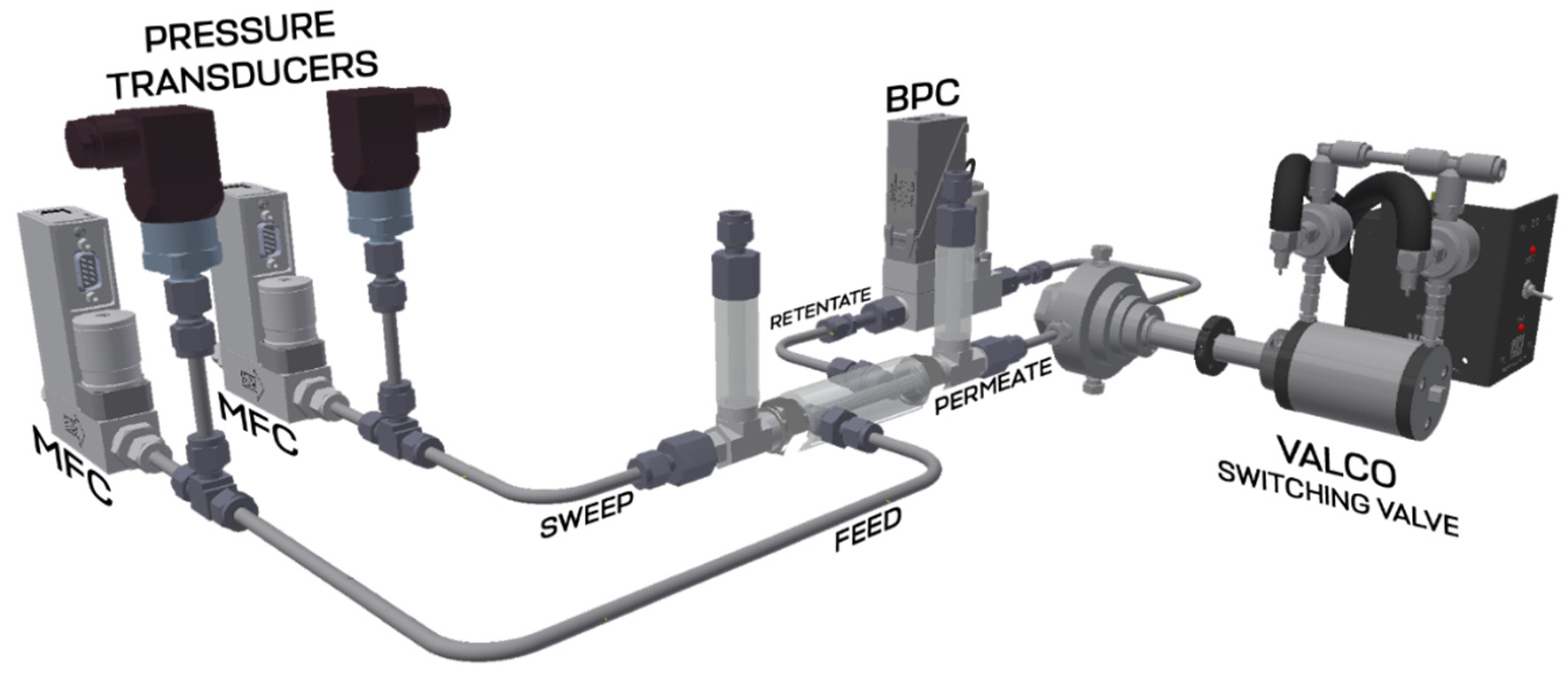
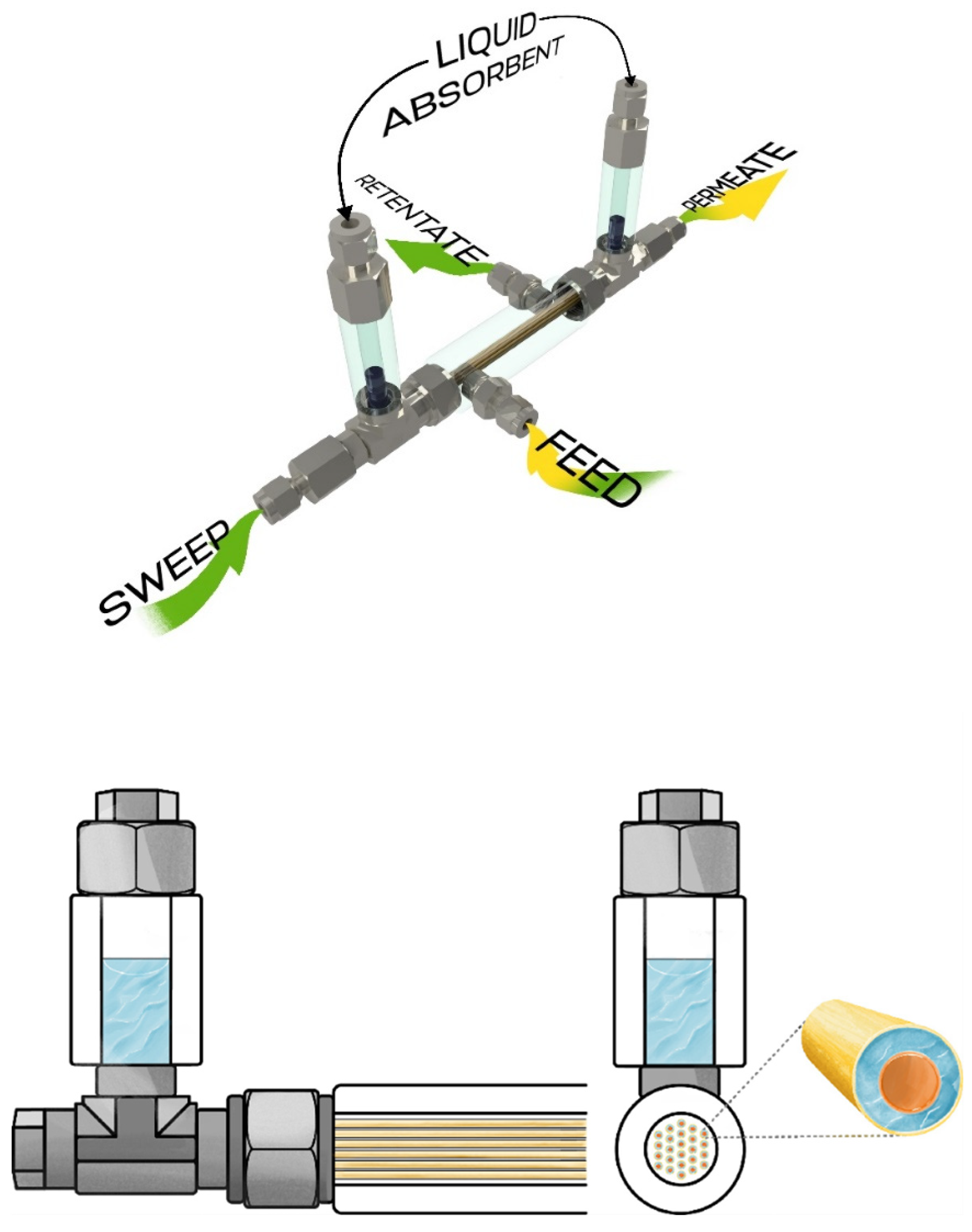
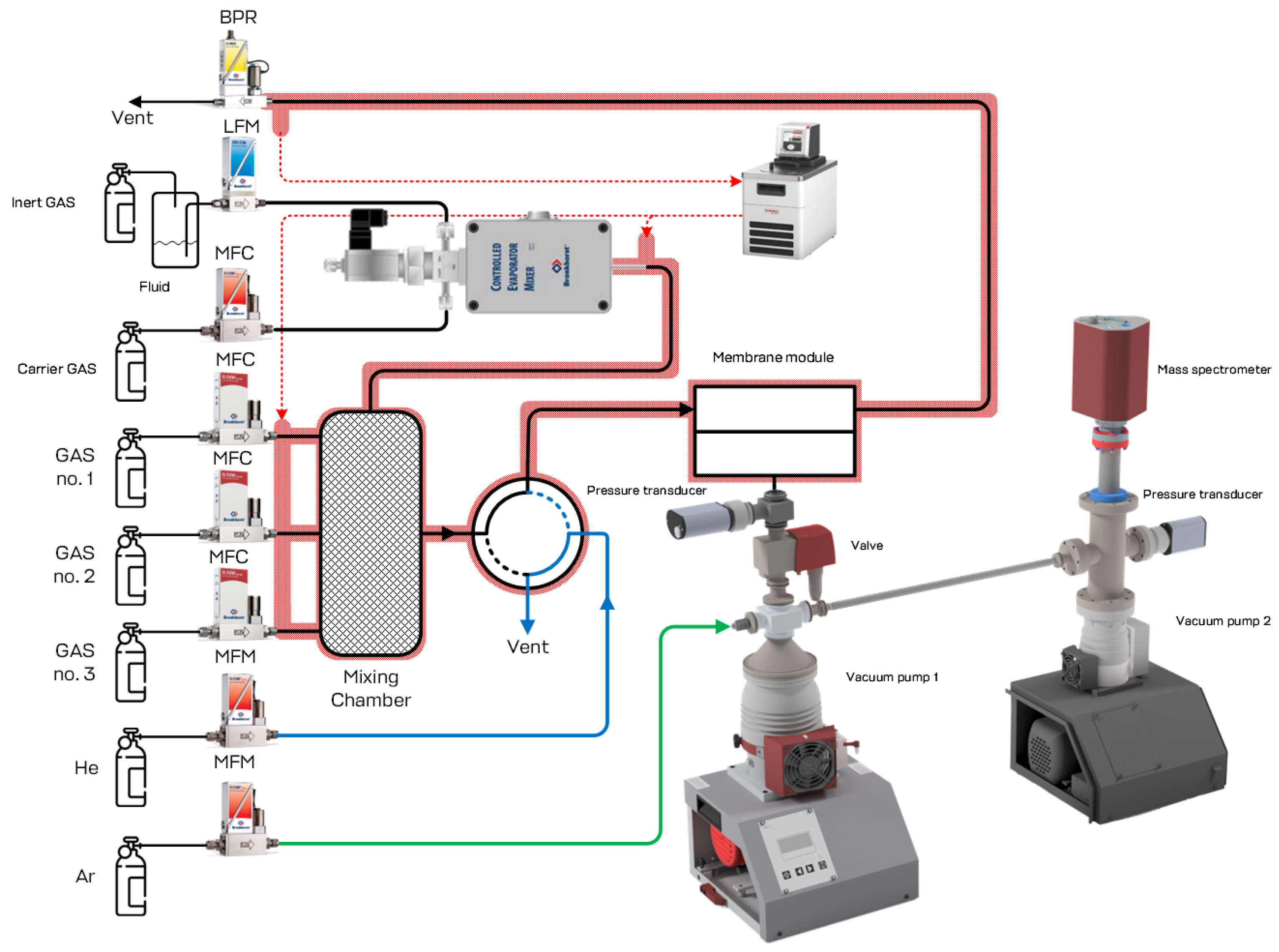
Performance test of the developed membrane-assisted gas absorption unitSeparation of the model gas mixture
The efficiency of the proposed technique during the natural gas processing was evaluated on the example of two gas mixtures: three-component, containing methane, carbon dioxide and xenon in the ratio 94. 5/5.35/0.15 vol.% and an eight-component mixture containing methane, ethane, carbon dioxide, propane, nitrogen, butane, hydrogen sulfide and xenon at a ratio of 75.677/7.41/5.396/4.534/3.013/2.469/1.389/0.113 vol.%. A 30 wt.% aqueous solution of amino alcohol - methyldiethanolamine was used as an absorbent. The results obtained for the separation process of the three-component gas mixture are shown in
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7 and
Figure 8.
Figure 4,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6 contain data on the dependences of the content of the components of the ternary gas mixture in the retentate flow on the stage-cut.
Figure 7 and
Figure 8 show the dependences of methane and carbon dioxide content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut. The dependence of xenon content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut is not shown, as in the whole range of stage-cut value its content was below the detection limit of the gas chromatograph equipped with a thermal conductivity detector with increased sensitivity. This allows us to conclude that the xenon content in the permeate stream did not exceed 10 ppm.
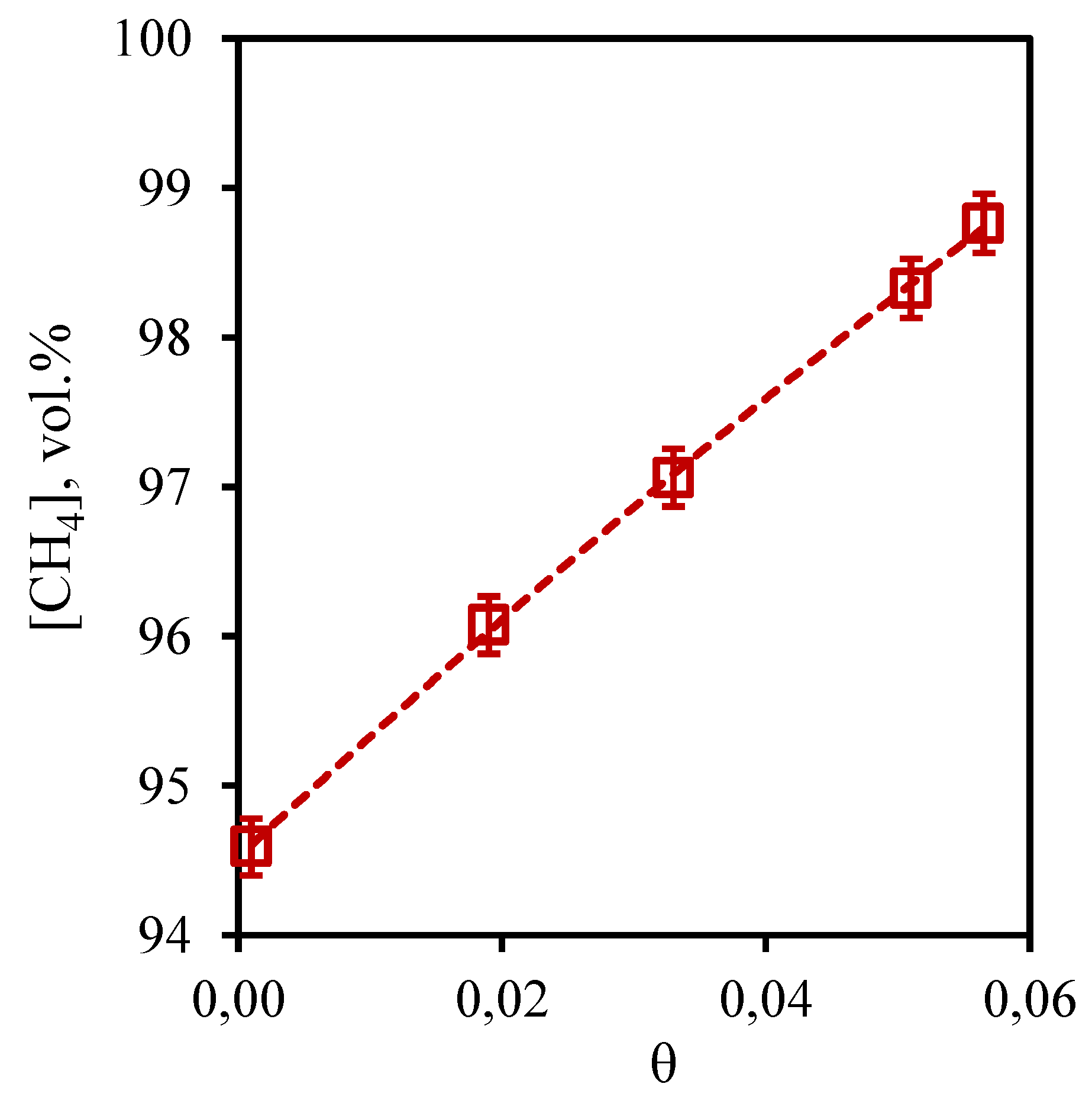
From the presented dependence of methane concentration on the stage-cut (
Figure 4) it can be seen that when the process is carried out with the minimum value of the stage-cut, no change in the composition of the separated mixture is observed. So, methane concentration in a retentate stream is 94.59 vol.% thus, that its initial concentration in a mix was equal 94.5 vol.%. However, maximum achieved concentration of this component in the retentate flow is 98.8 vol.%. It is evident from the presented dependence that the growth of stage-cut is accompanied by a significant growth of methane content in the retentate flow. Such dependence is explained by the fact that methane is a low-soluble component in the used absorption system, as well as by the fact that the membrane permeability value for this component is significantly lower than the same value for carbon dioxide. Since the stage-cut is determined by the ratio of the permeate flow rate to the feed flow rate, increasing the stage-cut means increasing the permeate flow rate (if the feed flow rate is constant). Thus, when the stage-cut increases, a more soluble component - carbon dioxide permeates the combined membrane-absorbent system, which allows to obtain more concentrated methane in the retentate flow.
Figure 4.
- Dependence of methane content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of a three-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 4.
- Dependence of methane content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of a three-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
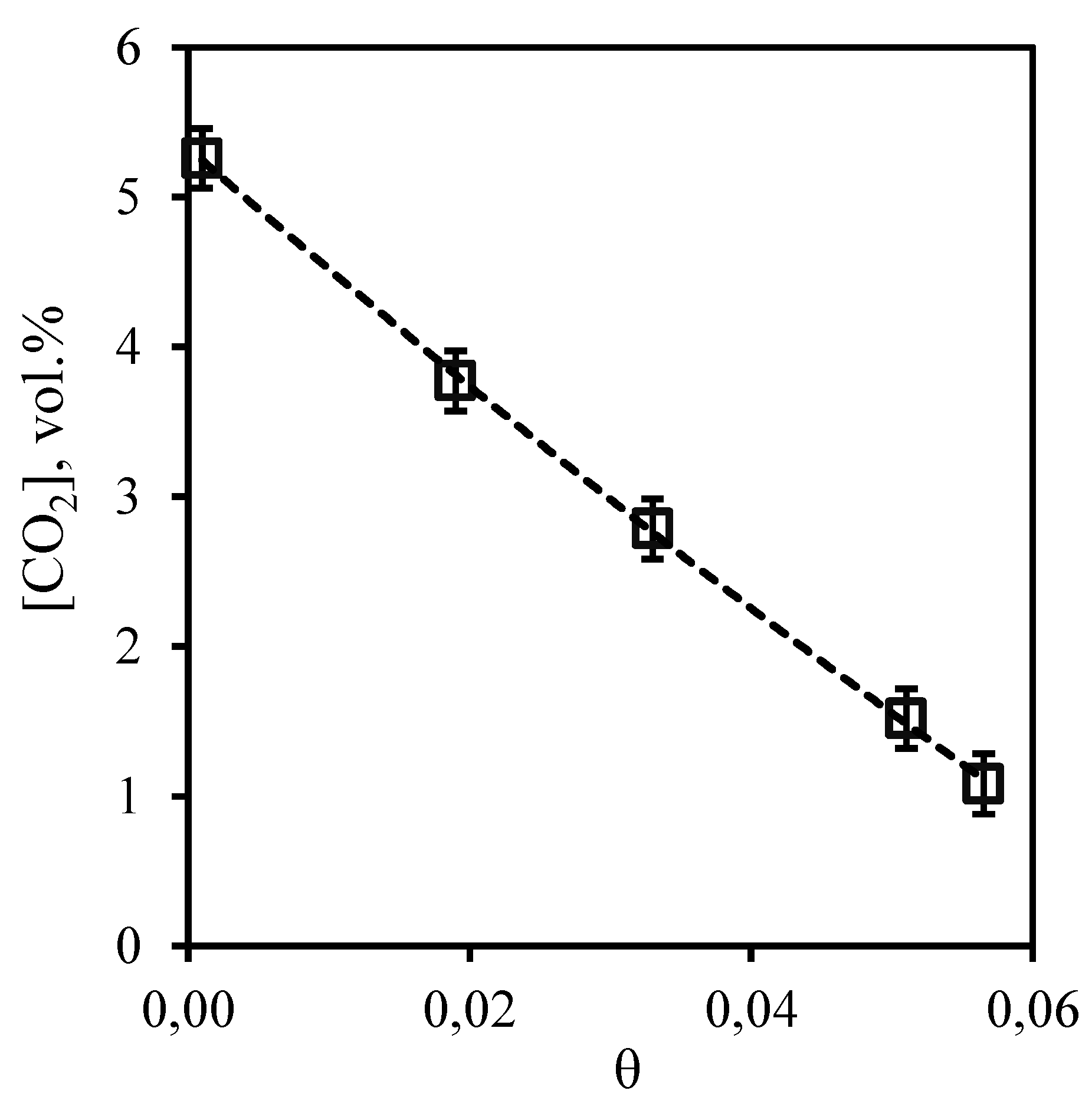
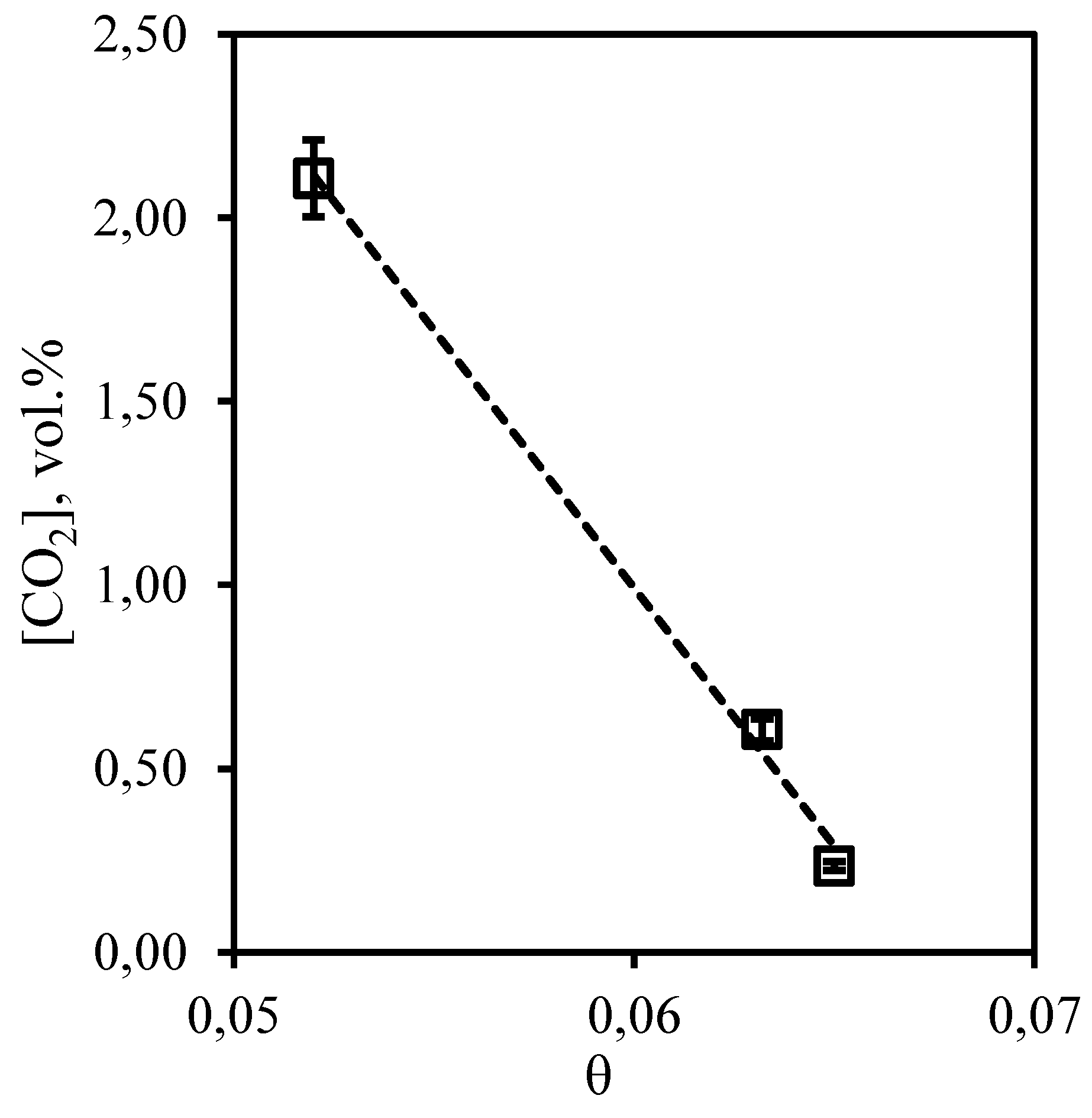
Dependence of carbon dioxide content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut, presented in
Figure 5 is in good agreement with the conclusions described above. It can be seen that the growth of the stage-cut is accompanied by a sharp decrease in carbon dioxide content in the retentate stream. So, at the minimum value of the stage-cut, the concentration of carbon dioxide is equal to 5.26 vol.% at its initial content of 5.35 vol.%. Thus, carrying out the process at the maximum value of stage-cut allows to lower concentration of carbon dioxide in the retentate flow to 1.08 vol.%. Such dependence is explained by the fact that carbon dioxide is soluble in the used absorption system, and its efficient removal from the system at a higher flow rate of permeate allows to remove most of it from the separated gas mixture.
Figure 5.
- Dependence of carbon dioxide content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of a three-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 5.
- Dependence of carbon dioxide content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of a three-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
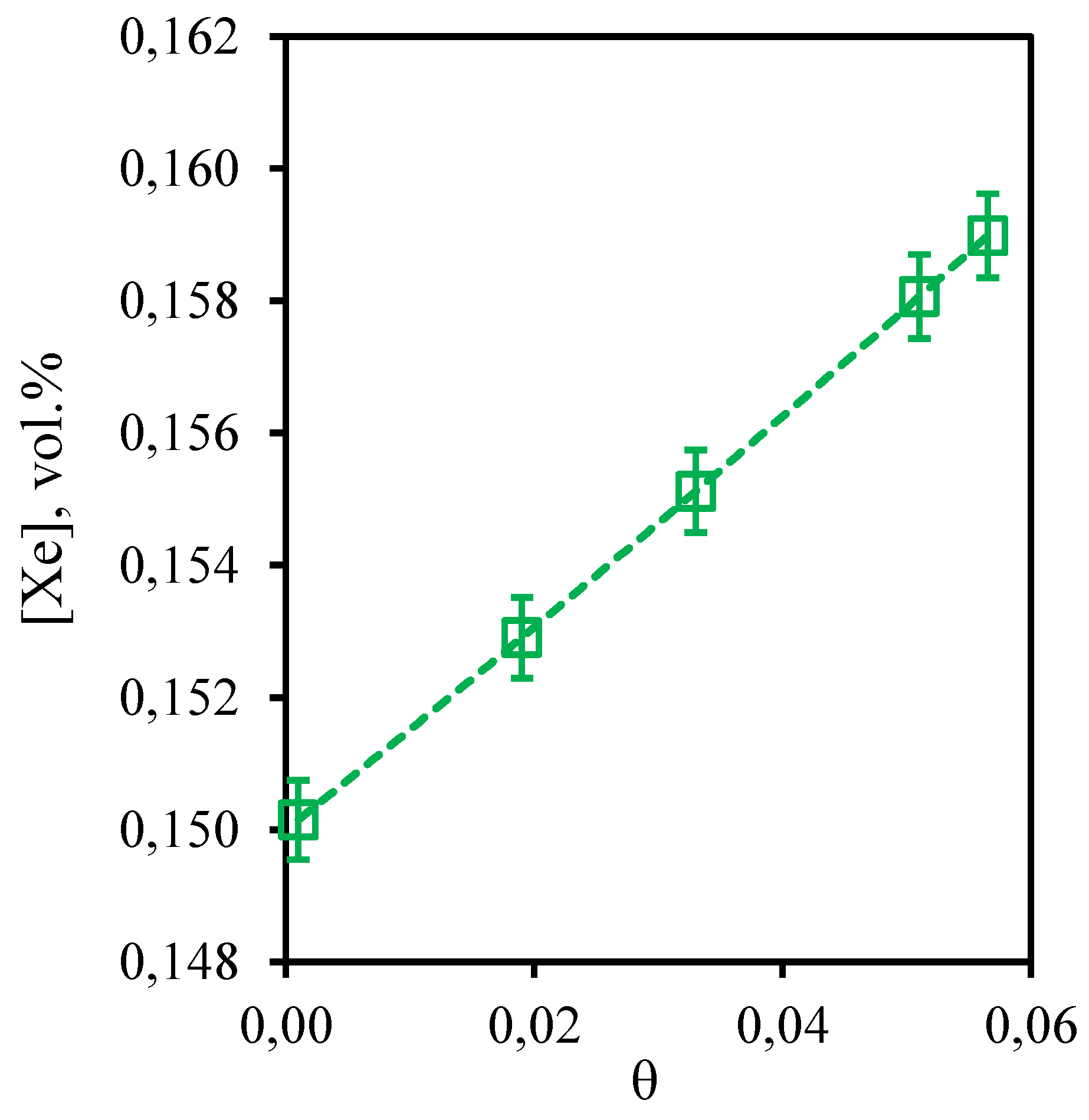
Figure 6 shows the dependence of xenon content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut. From the obtained curve describing this dependence it can be seen that the growth of the stage-cut value is accompanied by slow increase in xenon concentration in the withdrawn flow. In this case, carrying out the process at the lowest value of the stage-cut maintain the initial concentration of xenon. However, a further increase in the stage-cut practically does not affect the change in xenon concentration in the retentate flow. This dependence is explained by two factors: the ability of xenon to dissolve in water, low permeability of the membrane used and relatively large kinetic diameter of the xenon molecule. Thus, the reduction of xenon concentration in the retentate flow compared to its content in feed is most likely due to the fact that some of it is dissolved in the water contained in the liquid absorbent. At the same time, low membrane permeability to this component and large size of the molecule do not allow xenon to permeate through the combined membrane-absorbent system. This explains the fact that in the permeate stream the xenon content was below the GC detection limit. The increase in the xenon concentration observed with the increase of the stage-cut is due to the fact that the solubility limit for this component is reached in the membrane-absorber module, which, at the same time, leads to some loss of this component in the absorbent. However, the xenon is not permeated to the submembrane space, which indicates that these losses are not irreversible. Thus, regeneration of the absorbent used will allow the extraction of the dissolved xenon. This effect should be taken into account in further optimization of the proposed technique.
Figure 6.
- Dependence of xenon content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of a three-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 6.
- Dependence of xenon content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of a three-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
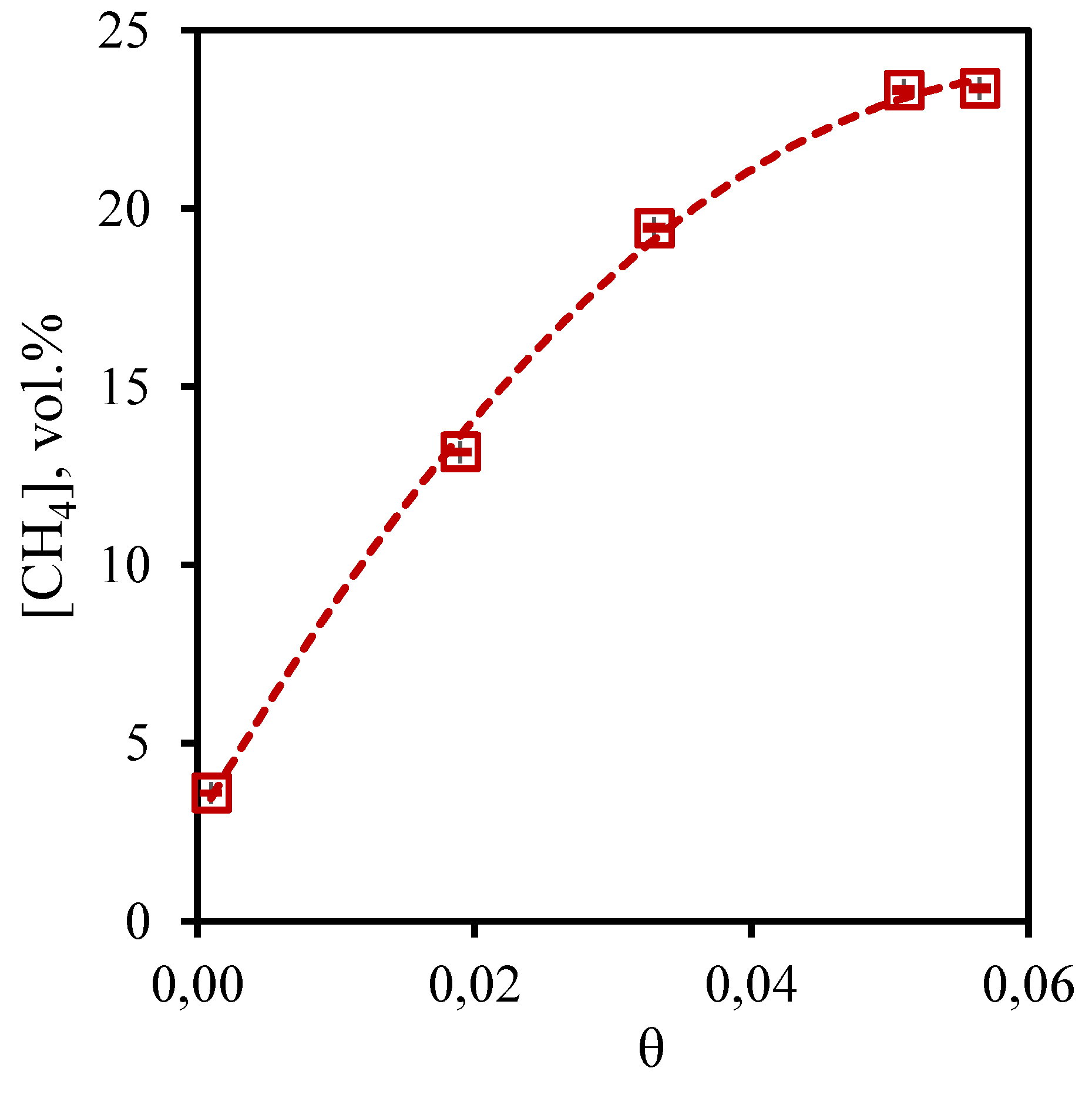
Figure 7 shows the dependence of methane concentration in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during separation of a three-component gas mixture. From the presented curve it is seen that the growth of the stage-cut is accompanied by an increase in the methane concentration in the permeate stream. So, at the lowest value of the stage-cut, the methane concentration is equal to 3.6 vol.%, and at the stage-cut value of 0.05 and 0.06, the methane content in the permeate stream is 23.32 and 23.37 vol.%, respectively. It is seen that a change in the stage-cut from 0.05 to 0.06, is not accompanied by a significant change in the concentration of methane in the permeate stream, while the change in the stage-cut from 0.02 to 0.03 causes a sharp increase in the methane content in this stream. The dependence obtained for the permeate flow agrees well with the data obtained for the retentate flow. Thus, an increase in the stage-cut and, consequently, an increase in the permeate flow rate leads to an increase in the fraction of methane permeating through the combined membrane-absorbent system. Since methane is practically insoluble in the absorbent used, its transfer through this system is most likely caused by diffusion processes. Such an effect requires an additional study aimed at determining the diffusion coefficients of the gases included in the mixtures.
Figure 7.
- Dependence of methane content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of a three-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 7.
- Dependence of methane content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of a three-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
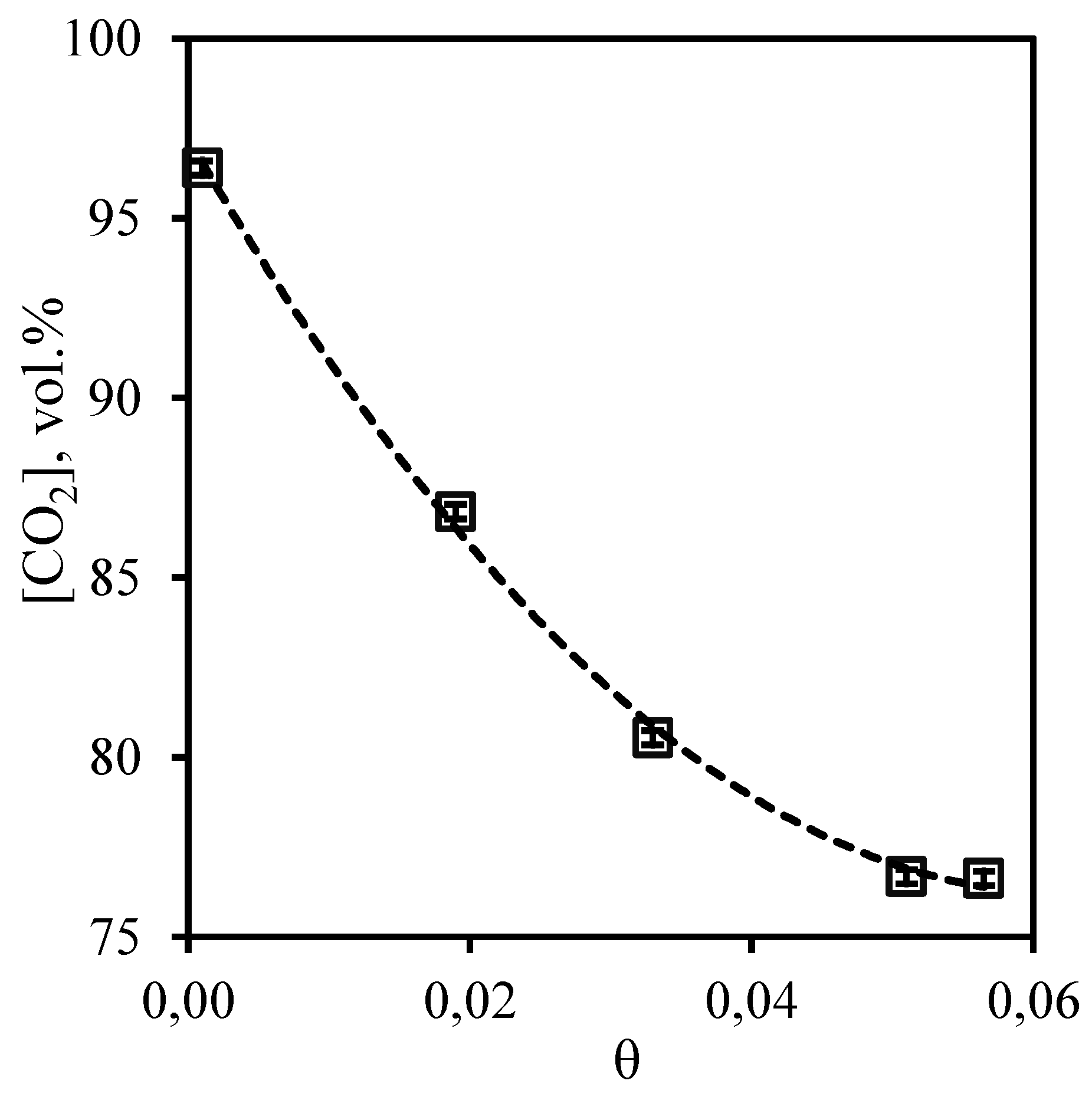
Figure 8 illustrates the dependence of carbon dioxide content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut, at which the separation process in membrane-assisted gas absorption unit is realized. From the curve shown in the figure is seen that increase of the stage-cut in the whole observed range is accompanied by change of a content of carbon dioxide from 96.4 to 76.6 vol.%. At the same time, the concentration of carbon dioxide does not fall below 76.6 vol.%, which allows to make a conclusion about high efficiency of the proposed technique, because the conventional membrane gas separation rarely allows to obtain a carbon dioxide concentrate of more than 50 - 65 vol.% in one stage even when using a highly selective membrane [
42].
Figure 8.
- Dependence of carbon dioxide content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of a three-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 8.
- Dependence of carbon dioxide content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of a three-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
As a result of the cumulative analysis of the obtained results on the example of separation of a three-component gas mixture, it may be concluded that the proposed technique is promising for the task of removing acid gases from the natural gas flow. Thus, the maximum purity of methane, withdrawn in the form of retentate flow is 98.8 vol.%, at its same content in the permeate flow at a level ~ 24 vol.%. To reduce methane losses in the permeate stream, optimization of the process is required, aimed at selection of the most effective absorbent solution. Its selective adsorption will reduce the transfer of methane into the submembrane space.
Separation of quasi-real mixture
For more detailed and approbation of the proposed technique, a similar study for an eight-component gas mixture containing methane, ethane, carbon dioxide, propane, nitrogen, butane, hydrogen sulfide and xenon in the ratio: 75.677/7.41/5.396/4.534/3.013/2.469/1.389/0.113 mol% was conducted. The results obtained for the separation process of the eight-component gas mixture are shown in
Figure 9,
Figure 10,
Figure 11,
Figure 12,
Figure 13,
Figure 14,
Figure 15,
Figure 16,
Figure 17,
Figure 18,
Figure 19,
Figure 20,
Figure 21,
Figure 22 and
Figure 23,
Figure 9,
Figure 10,
Figure 11,
Figure 12,
Figure 13,
Figure 14,
Figure 15 and
Figure 16 contain data on the dependences of the components content of the eight-component gas mixture in the retentate flow on the stage-cut, and in
Figure 17 and
Figure 23 dependences of the methane, ethane, propane, n-butane, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut are presented. Also, as in the previous case, the dependence of xenon content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut is not presented, because in the whole considered range of the stage-cut its content was below the detection limit of the gas chromatograph, equipped with a thermal conductivity detector with increased sensitivity, which allows us to conclude that the xenon content in the permeate flow did not exceed 10 ppm.
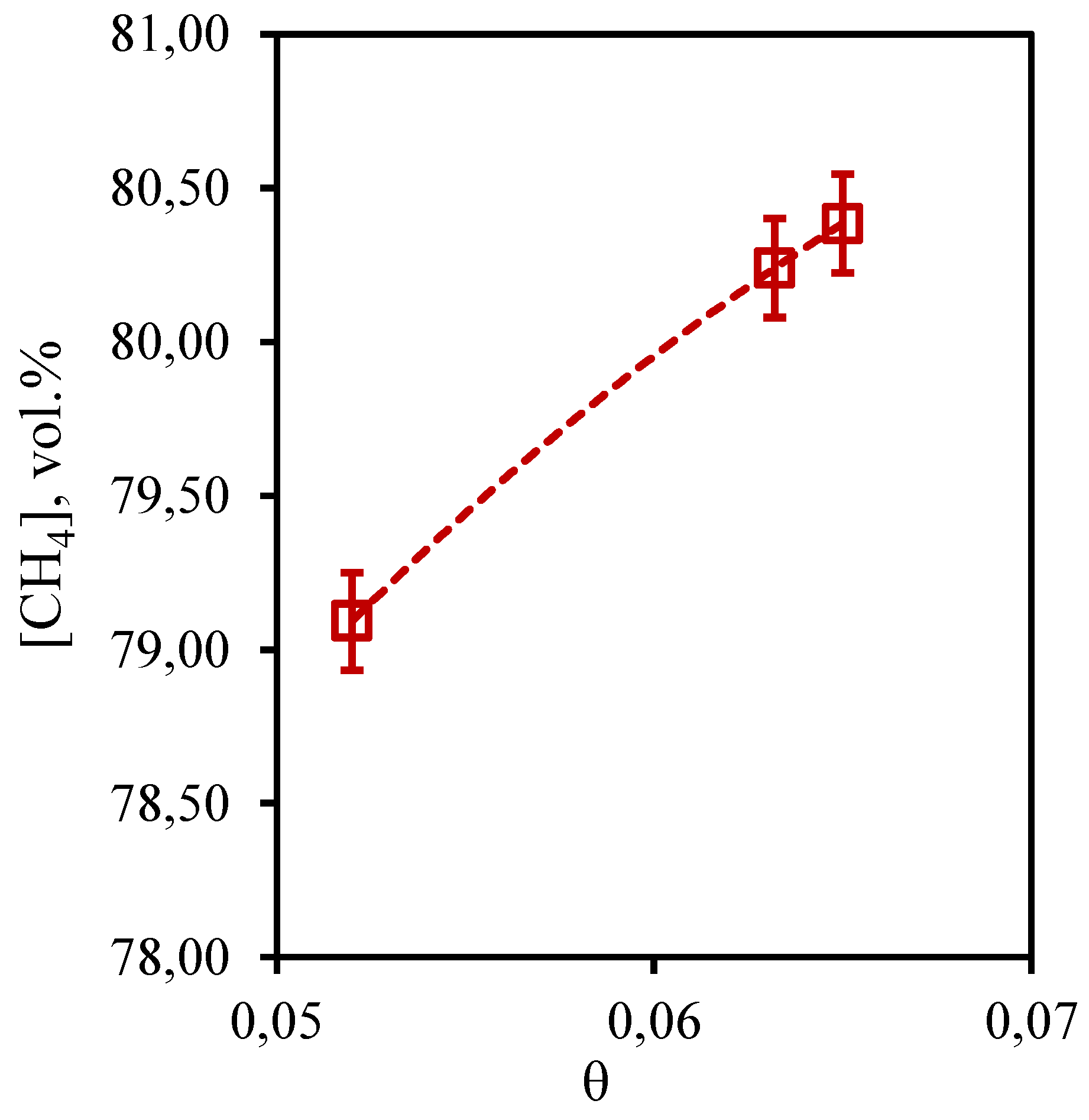
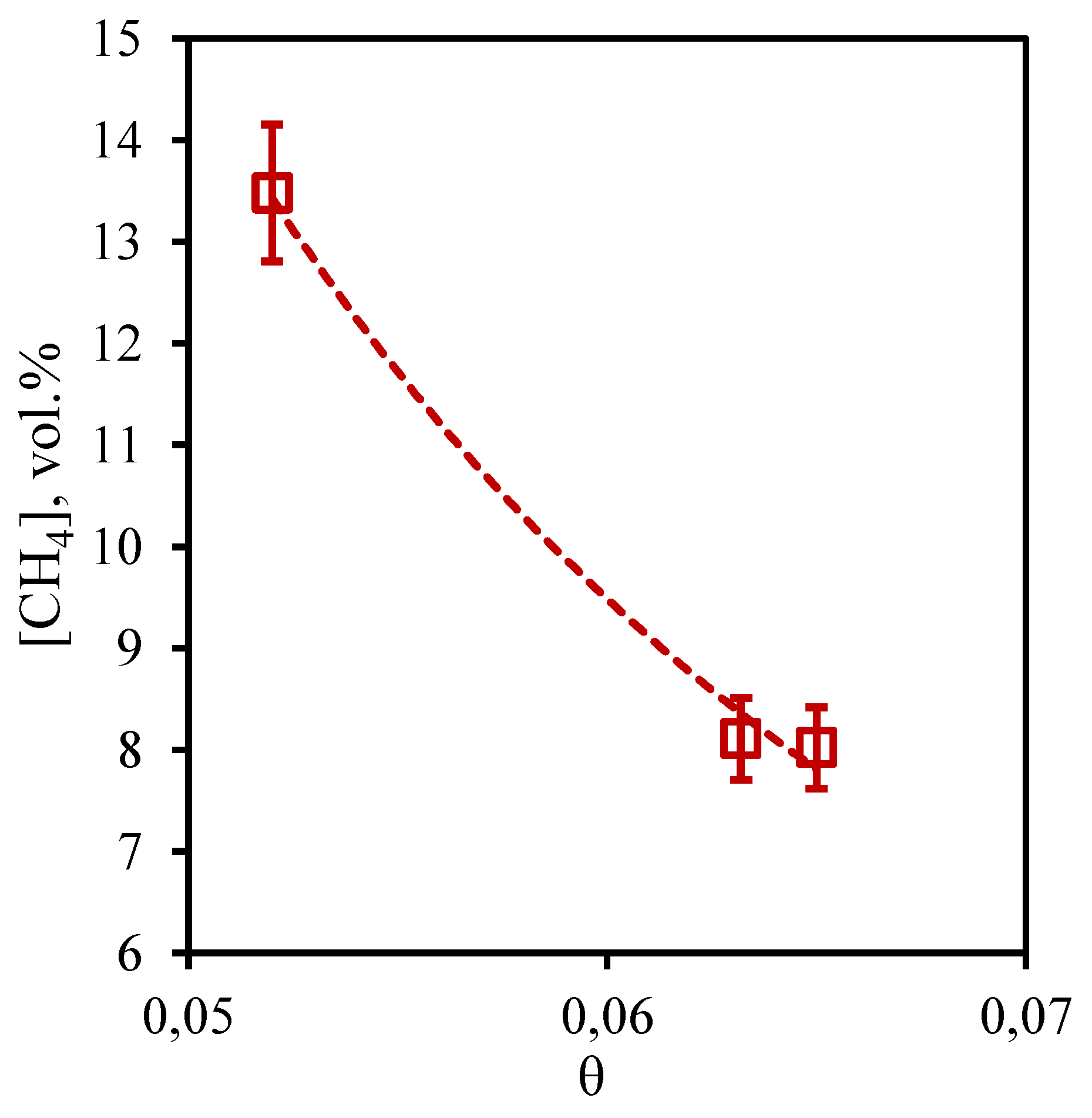
In
Figure 9 the dependence of methane concentration in the retentate flow on the stage-cut is presented. From the presented curve it is visible that change of methane content is in a range from 79.1 to 80.4 vol.% that speaks about insignificant change of this value from the stage-cut at which process is realized. Given the initial content of this component in the mixture (75.677 vol.%), it can be concluded that the membrane-assisted gas absorption process contributes to an insignificant concentration of methane in the withdrawn flow. In this case, an increase in the stage-cut is accompanied by an increase in the methane concentration value, which agrees well with the data obtained earlier for the three-component gas mixture. The obtained dependence is explained by the fact that the growth of the stage-cut is caused by an increase in the permeate flow rate. This, in turn, contributes to a more efficient removal of soluble components to the permeate side. Since methane is practically insoluble in the selected absorbent, its buildup in the retentate flow occurs.
Figure 9.
- Dependence of methane content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 9.
- Dependence of methane content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
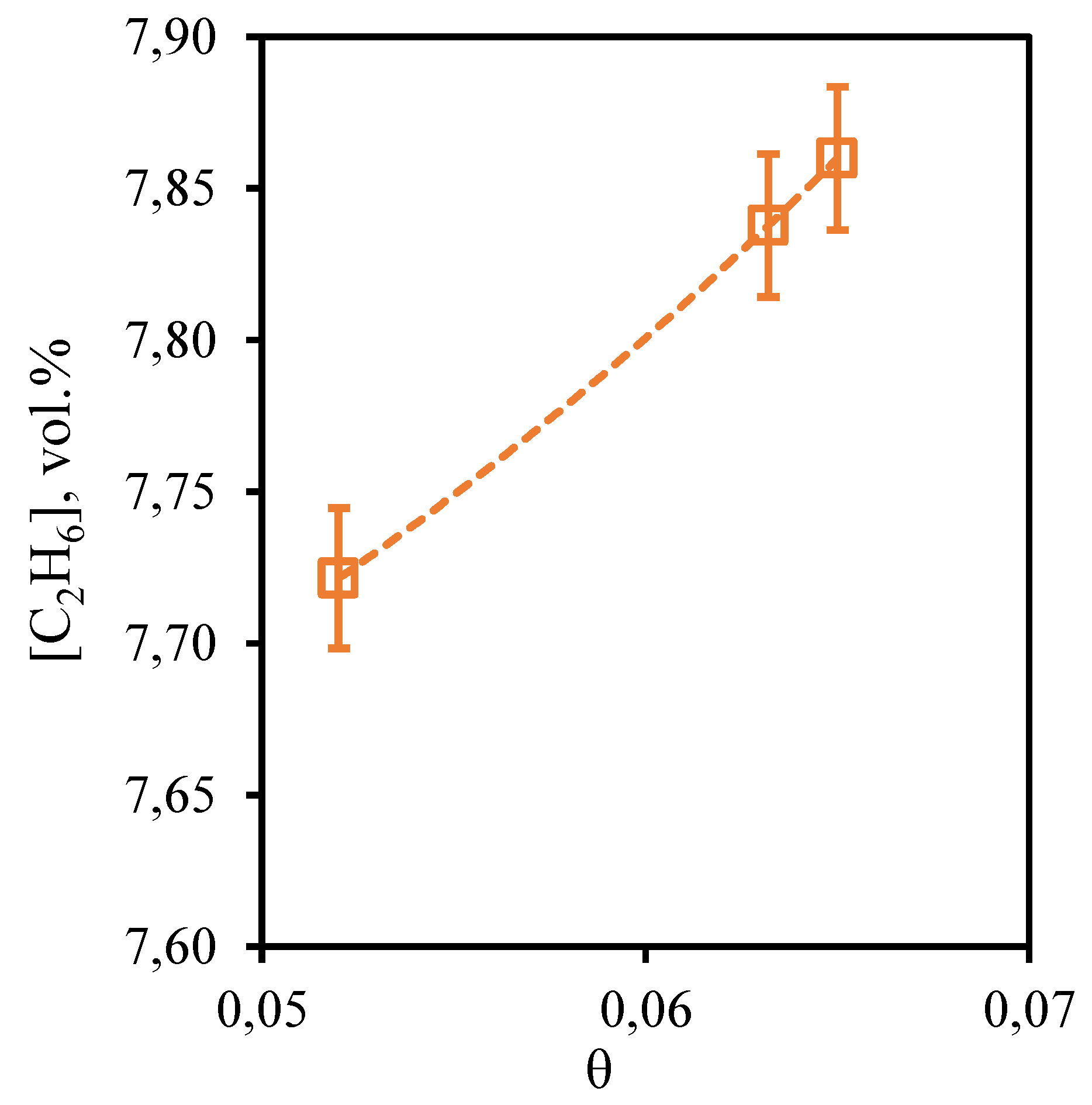
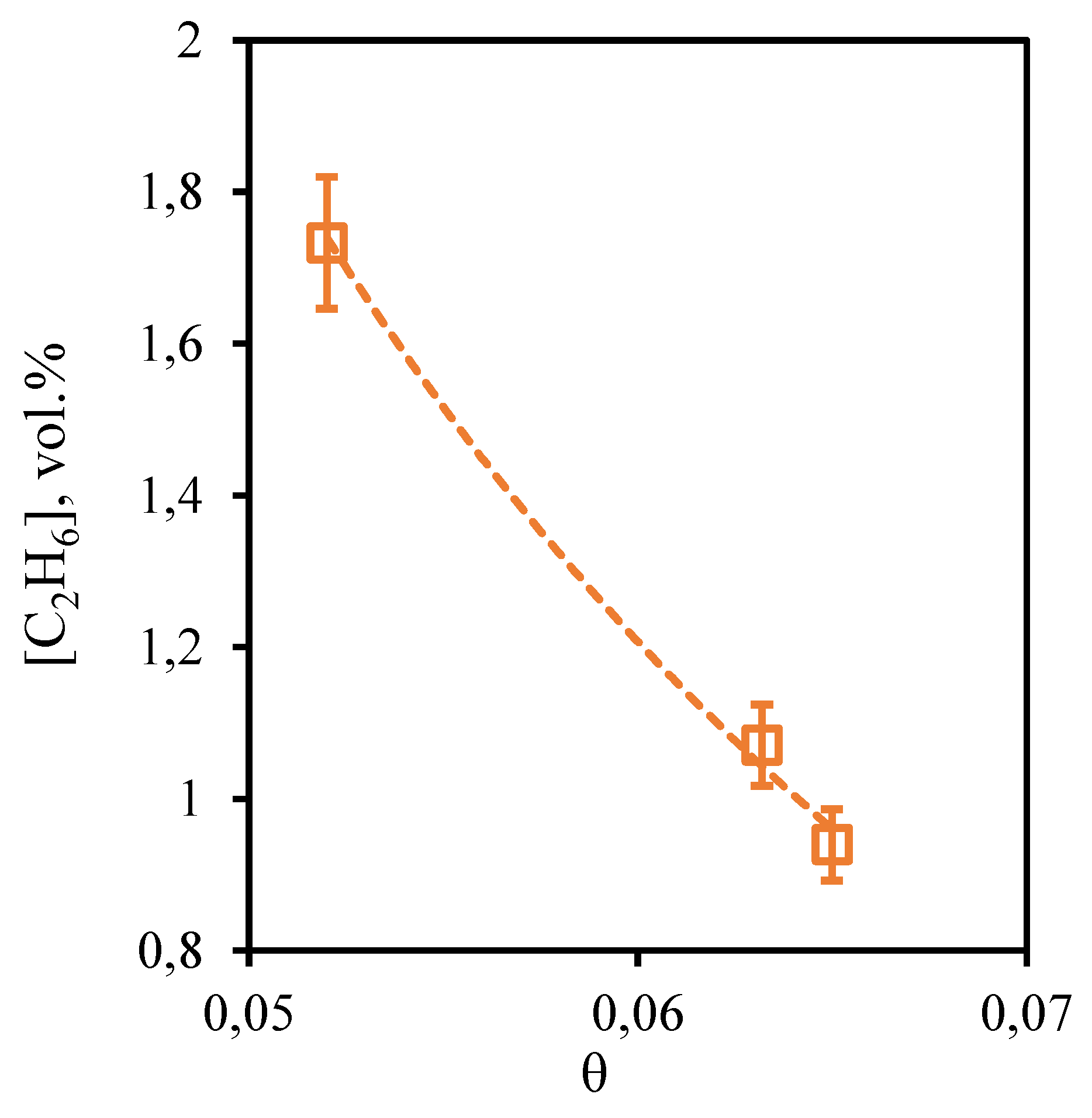
Figure 10 shows the dependence of ethane content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut, at which the gas separation process is realized. From the presented dependence it can be seen that the concentration of ethane, as well as in the case of methane, practically does not depend on the value of the stage-cut. Thus, as the stage-cut growth, the content of this component in the retentate stream is observed very insignificantly, namely, the ethane concentration increases from 7.72 to 7.86 vol. % when changing the stage-cut from 0.05 to 0.065. Since ethane also is a low-soluble component, its concentration depends on the gas flow rate passing through the combined membrane-absorbent system insignificantly. Comparing the concentration of ethane in the feed flow with its initial content in the mixture (7.41 vol.%), we can see that there is an insignificant concentration of this component.
Figure 10.
- Dependence of ethane content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 10.
- Dependence of ethane content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
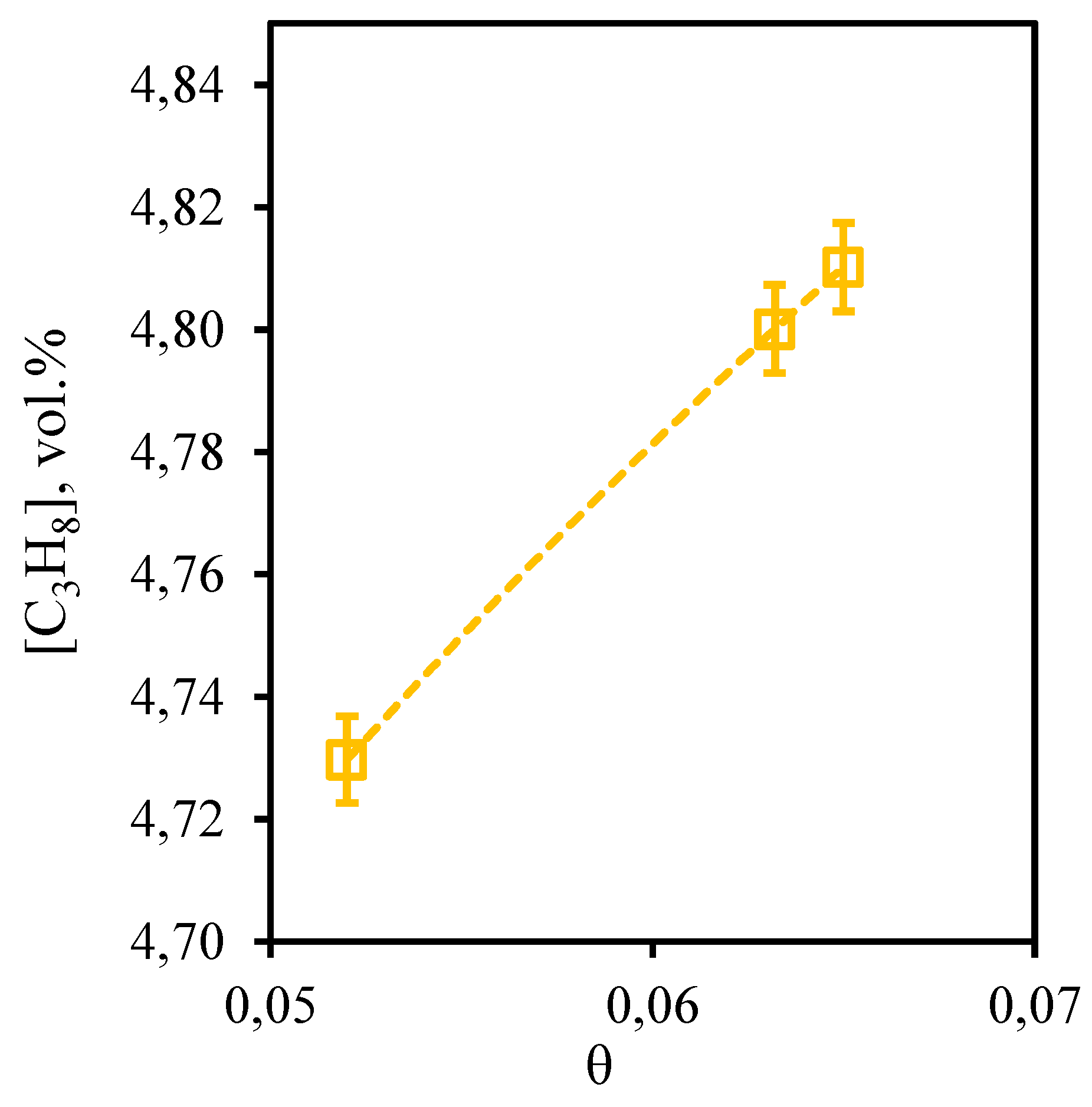
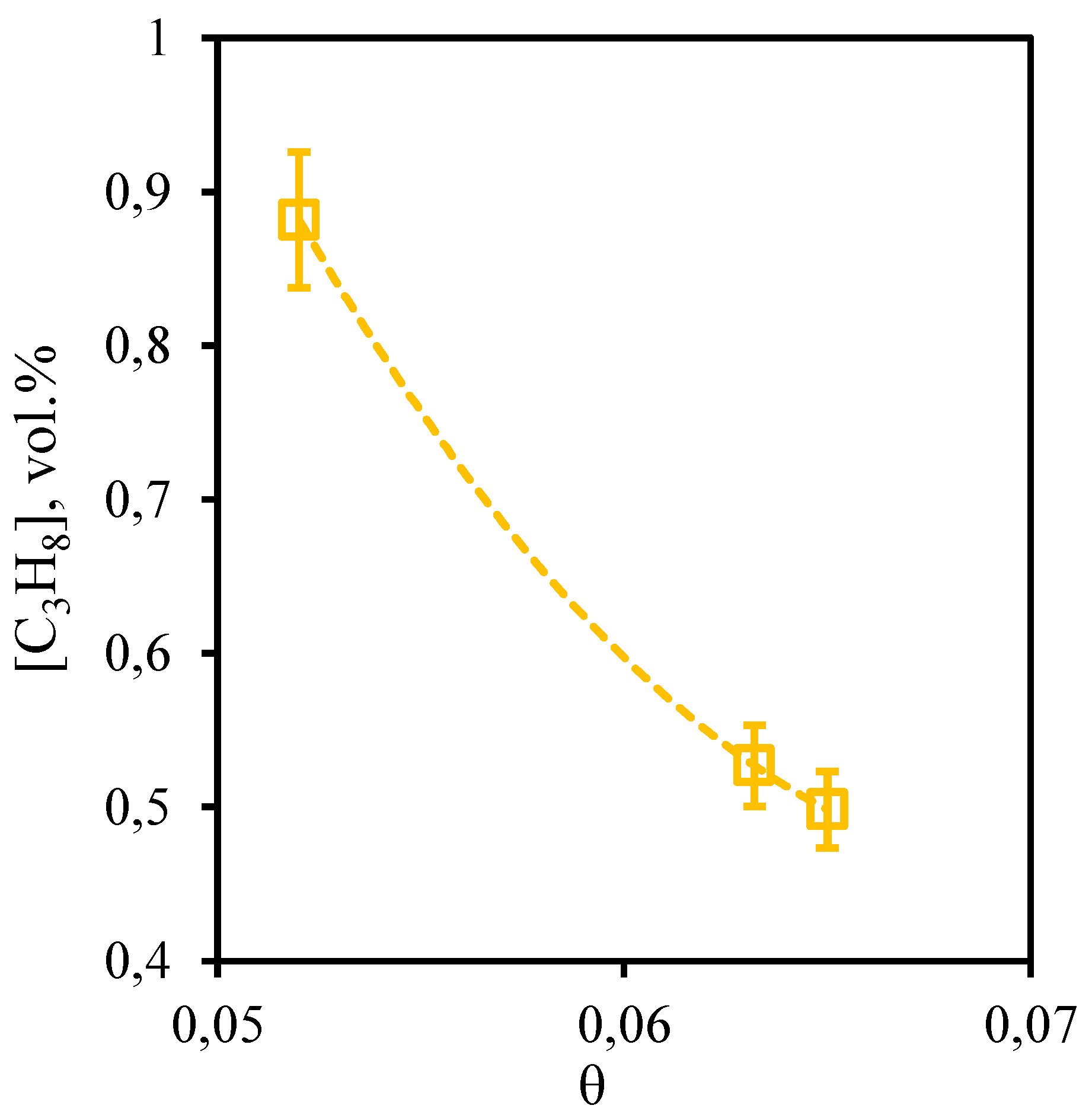
Figure 11 shows the dependence of propane content in the retentate stream on the stage-cut. From this curve it can be seen that the tendency described above for other hydrocarbons is also observed for propane. So, at the stage-cut value of 0.05 the propane content in the permeate stream is at a level of 4.73 vol.%. At the maximum value of the stage-cut (0.065) its concentration is 4.81 vol.%. Here it is necessary to note, that as a result of carrying out of process even at the lowest value of the stage-cut, which promotes the least concentration of hardly permeable and low-soluble components, the growth of the propane content equal to 0.2 vol.%, in comparison with its initial content is observed.
Figure 11.
- Dependence of propane content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 11.
- Dependence of propane content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
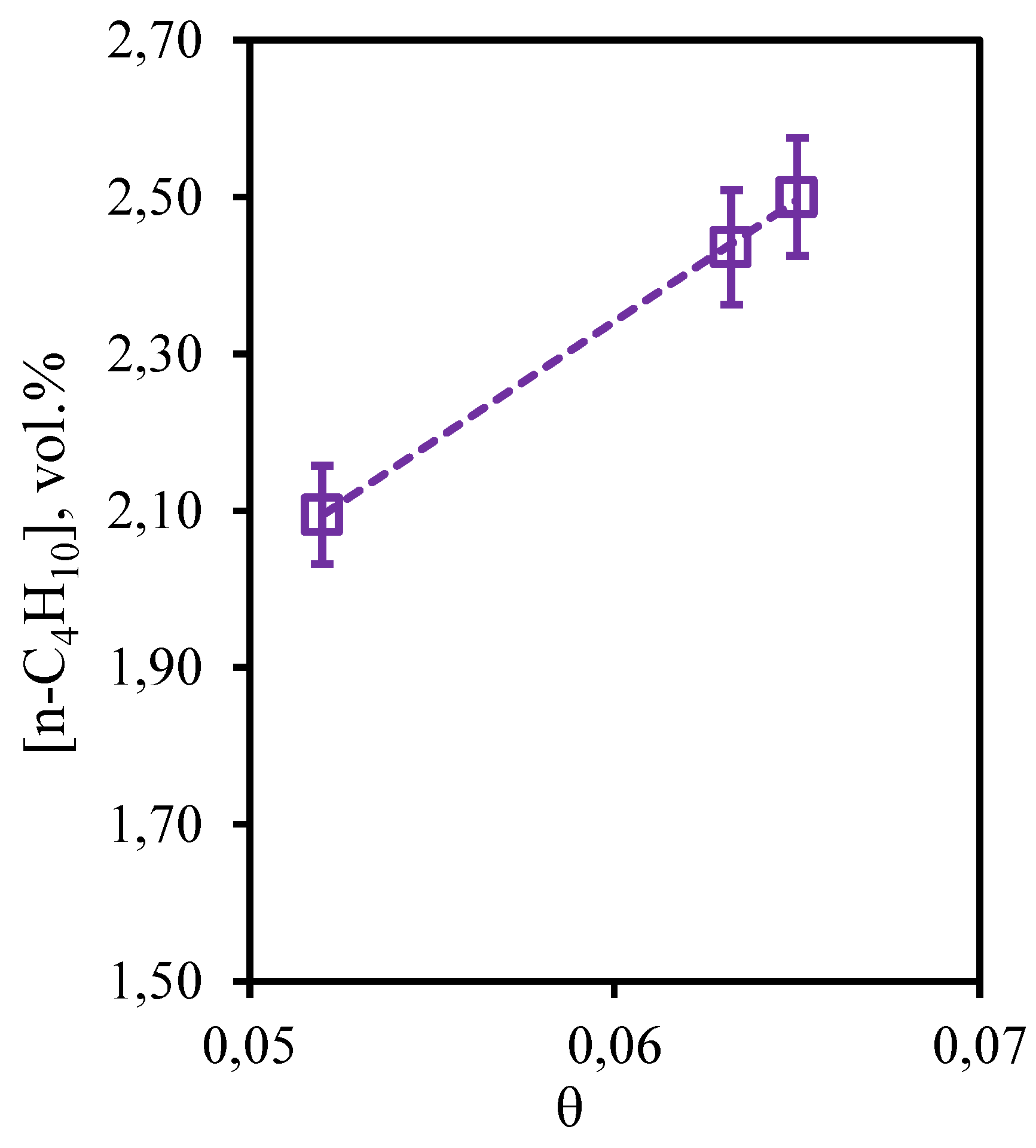
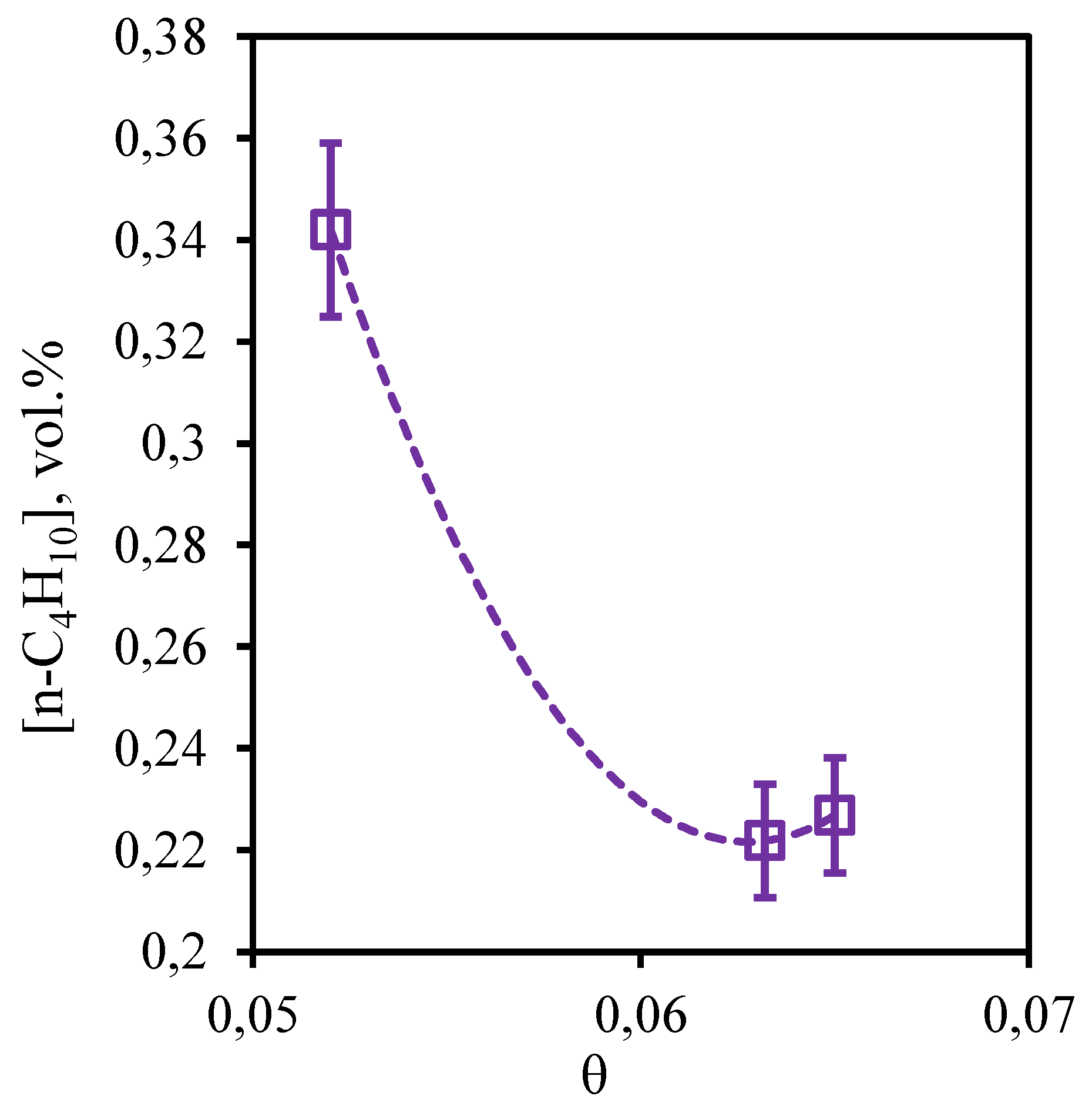
Figure 12 illustrates the dependence of n-butane concentration in the retentate flow on the stage-cut. From the obtained dependence it can be seen that in this case, the change of stage-cut causes more pronounced change in the content of this component in the retentate flow than in the case of ethane and propane. Thus, carrying out the process at the stage-cut equal to 0.05, a decrease in the n-butane concentration value (~ 2.1 vol.%) is observed in comparison with its initial content in the mixture (2.469 vol.%). However, an increase in the stage-cut to 0.065 is accompanied by an increase in the n-butane concentration to 2.5 vol.%, which is equal to its initial content. Thus, the cumulative analysis of dependencies of concentrations of hydrocarbons on value of the stage-cut shows that on all these components insignificant concentration change is observed at carrying out the process with the stage-cut value ≥0.06. Thus, application of a hybrid method - membrane-assisted gas absorption allows to concentrate these components in the retentate stream.
Figure 12.
- Dependence of n-butane content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 12.
- Dependence of n-butane content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
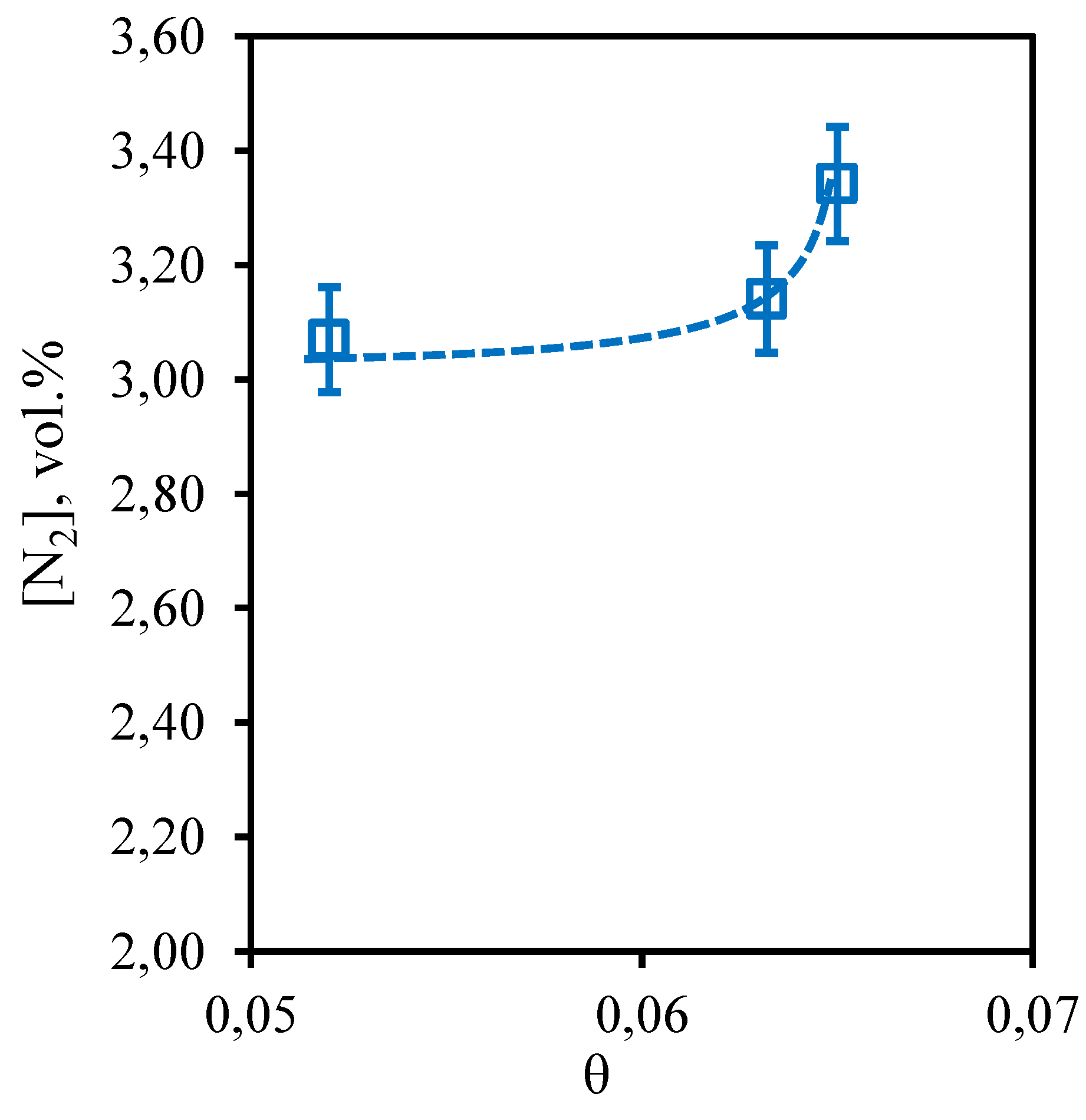
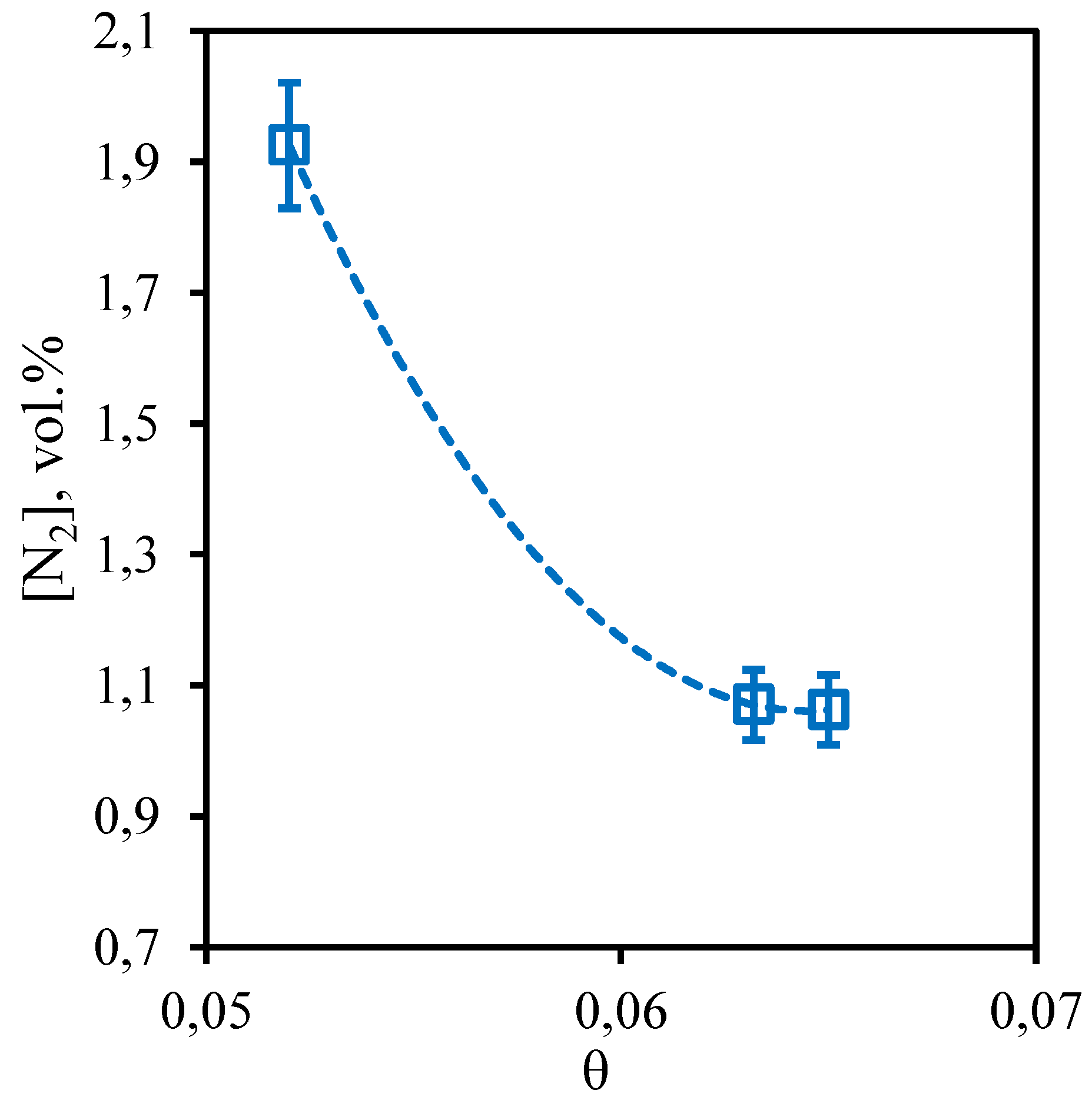
Figure 13 shows the dependence of nitrogen content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut. The obtained dependence shows that the nitrogen content in the captured retentate stream does not depend on the value of the stage-cut, at which the gas separation process is implemented. Thus, the concentration of nitrogen in the whole considered range of stage-cut values varies from 3.1 to 3.34 vol.%. At the same time, comparing the achieved nitrogen concentration with its initial content in the separated gas mixture, it can be seen that its content increased by 0.33 vol.%. Thus, we can conclude that the implementation of the membrane-assisted gas absorption process allows to slightly concentrate nitrogen, which is also a low-soluble component unable to permeate and concentrate on the permeate side.
Figure 13.
- Dependence of nitrogen content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 13.
- Dependence of nitrogen content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
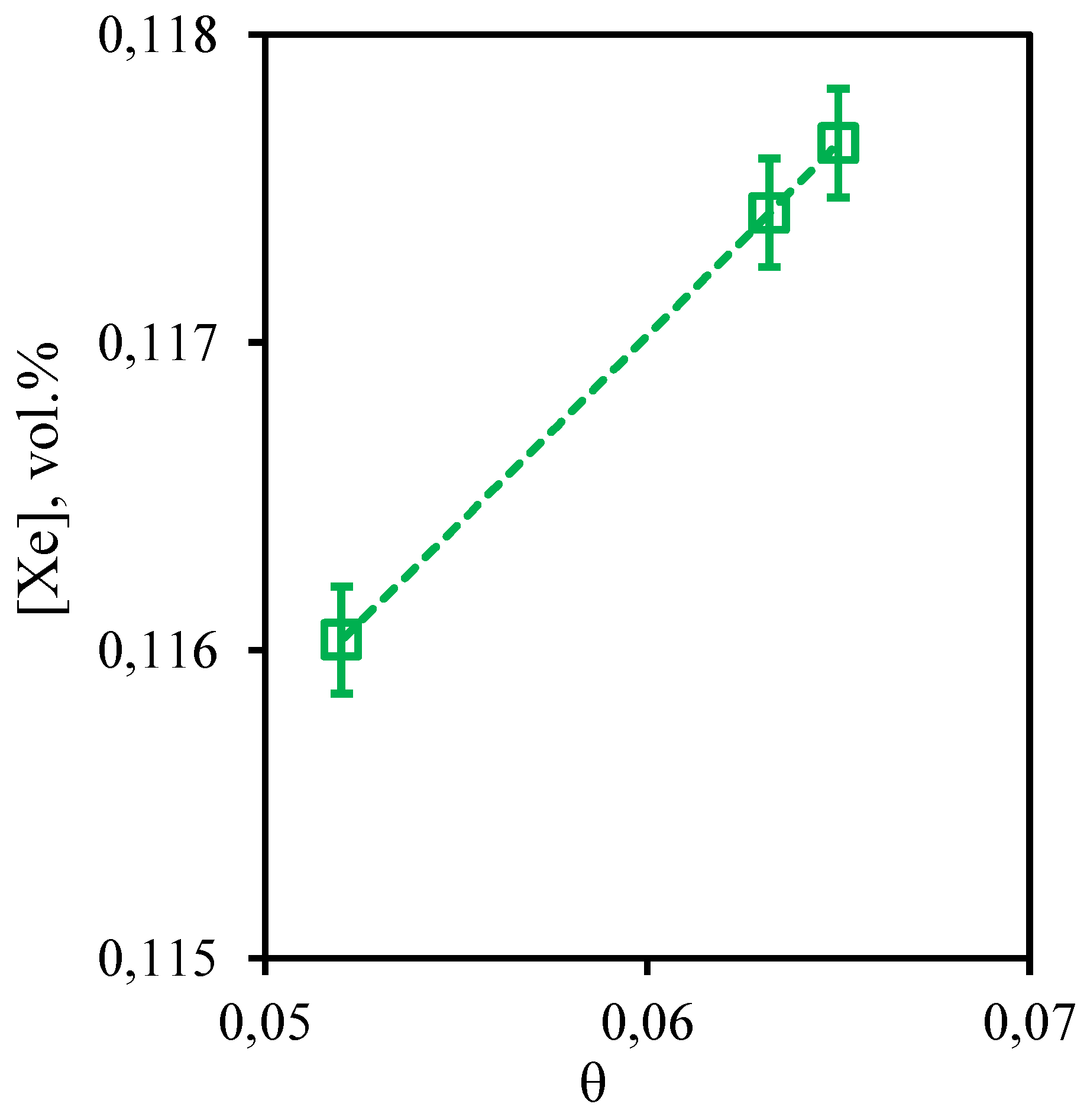
Figure 14 illustrates the dependence of xenon content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut value. In general, for xenon a dependence similar to nitrogen is observed. In the whole considered range of the stage-cut, the xenon concentration value varies from 0.116 to 0.117 vol.%. However, there is a weak tendency of increase in xenon concentration with increase in the stage-cut, at which gas separation process is realized. Thus, at the stage-cut equal to 0.05, xenon concentration is equal to 0.116 vol.%, and at the stage-cut equal to 0.065, xenon concentration decreases to 0.117 vol.%. As is seen, there is a linear dependence of Xe content on stage-cut. The dependence obtained for the eight-component mixture is in well agreement with the same dependence obtained for the ternary mixture. Despite the fact that xenon is able to dissolve in the water contained in the liquid absorbent used, this does not occur in the presence of other components (nitrogen, ethane, propane, n-butane, hydrogen sulfide) that are absent in the triple mixture. Most likely, this dependence can be explained by a specific sorption realized in the presence of an even more soluble gas - hydrogen sulfide. Presumably, the solubility limit is reached in the membrane-assisted gas absorption unit, which does not allow xenon to sorb in a liquid saturated with more soluble components - carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide.
Figure 14.
- Dependence of xenon content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 14.
- Dependence of xenon content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 15 shows the dependence of carbon dioxide content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut. The obtained dependence shows that an increase in the stage-cut is accompanied by a decrease in carbon dioxide content in the retentate stream, withdrawn from the membrane-assisted gas absorption module. Thus, the maximum concentration of carbon dioxide is 2.1 vol.% at the stage-cut equal to 0.05. Performing the separation process at the stage-cut of 0.065, the carbon dioxide content decreases to 0.23 vol.%. At the same time, there is a significant decrease in the concentration of carbon dioxide compared with its initial content in the mixture (5.396 vol.%). Thus, at the stage-cut of 0.05, the concentration of carbon dioxide decreases by 3.3 vol.%, and at the process stage-cut value of 0.065, the concentration of carbon dioxide decreases by 5.17 vol.%. The obtained dependence is explained by the fact that carbon dioxide, firstly, is well dissolved in the used liquid absorbent, and secondly, the membrane is characterized by the highest permeability by this component (among the components of the mixture). Thus, in the process under consideration, carbon dioxide is able to dissolve effectively in the liquid absorbent layer and move into the submembrane space of the membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 15.
- Dependence of carbon dioxide content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 15.
- Dependence of carbon dioxide content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
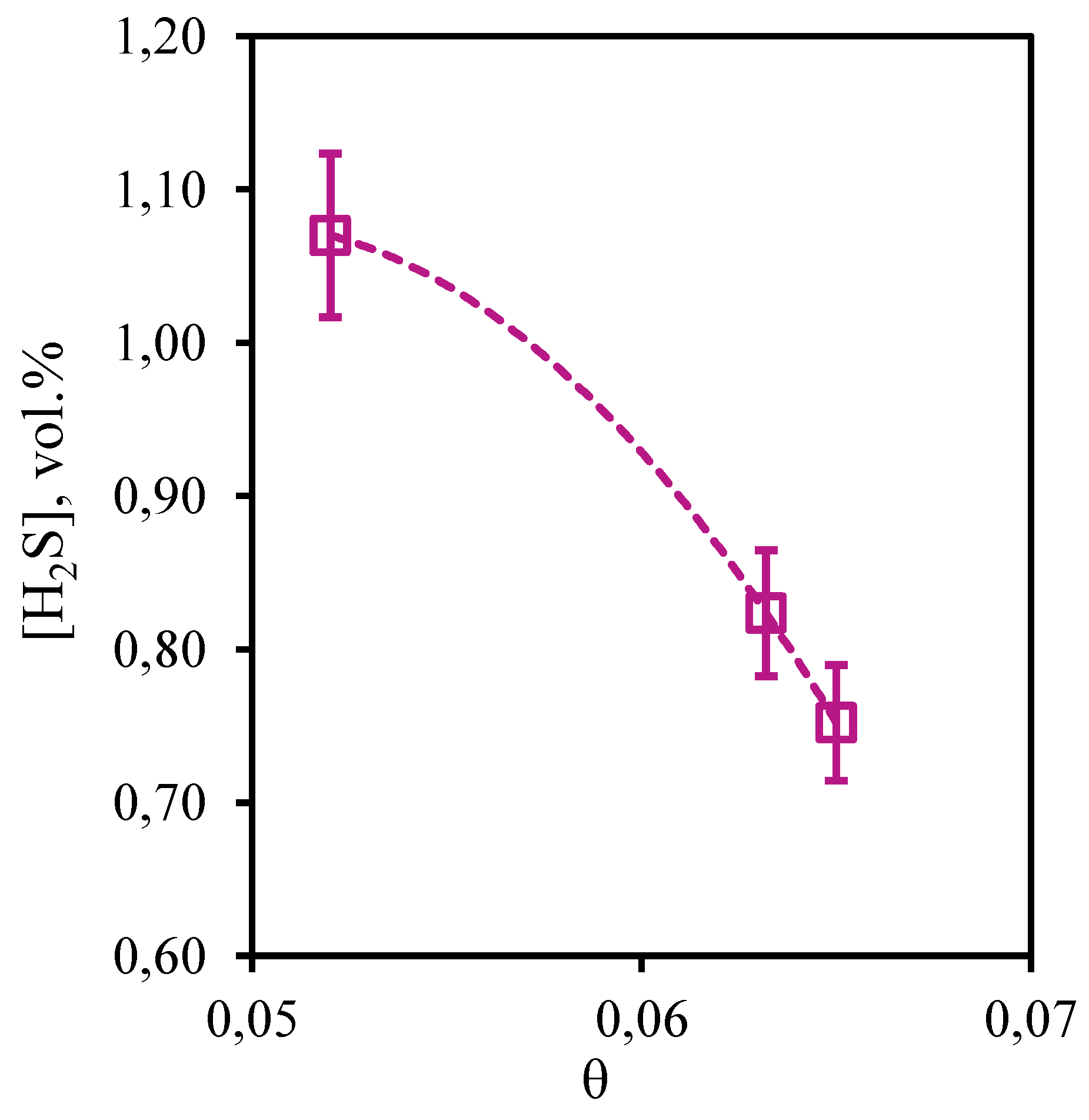
In
Figure 16 the dependence of hydrogen sulfide concentration on the stage-cut value, at which the separation process is carried out, is presented. From the received curve it is visible that growth of the stage-cut is accompanied by decrease in hydrogen sulfide content in a retentate stream. So, at the stage-cut equal to 0.05 the hydrogen sulfide concentration makes 1.07 vol.%, and at the stage-cut equal to 0.065 the hydrogen sulfide concentration is equal to 0.75 vol.%. Thus, as a result of this process decrease in the hydrogen sulfide content in comparison with its initial concentration in a mix from 0.32 to 0.64 vol.% is observed. Like in the case of carbon dioxide, the obtained dependence is explained by the absorbent ability to effectively dissolve this component and relatively high membrane permeance to hydrogen sulfide, which provides effective transfer of this gas to the permeate side. Thus, implementation of the process at the stage-cut value equal to 0.65, the gas stream withdrawn as retentate consists of methane, ethane, carbon dioxide, propane, nitrogen, n-butane, hydrogen sulfide and xenon in the ratio 80. 39/7.86/0.23/4.81/3.34/2.50/0.75/0.12 vol.%, which corresponds to an increase in the concentration of all components except impurities of acid gases, and, equally importantly, preservation and a slight increase in xenon content.
Figure 16.
- Dependence of hydrogen sulfide content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 16.
- Dependence of hydrogen sulfide content in the retentate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Analyzing the composition of permeate flow at different values of the stage-cut it is seen that the dependences of concentrations of methane, ethane, propane, n-butane and nitrogen (
Figure 17,
Figure 18,
Figure 19,
Figure 20 and
Figure 21) on the stage-cut form the curves of similar character and similar in intensity of concentration decrease, accompanying the increase of the stage-cut value. So, in process of increase in the stage-cut from 0.05 to 0.065, decrease in concentration of these components from 54.2 to 66.3 % from the value received for the stage-cut equal to 0.05 is observed. In absolute values this corresponds to the following values: 8.02, 0.94, 0.49, 0.23, 1.06 vol.% for methane, ethane, propane, n-butane, and nitrogen when the process is conducted with the stage-cut equal to 0.065. An explanation of the obtained dependencies is given above. All these components are low-soluble components of a mixture that causes low efficiency of their transfer through the combined membrane-absorbent system, and, as consequence, their low content in a permeate stream that corresponds to small losses on these components even at high value of the stage-cut at which the considered gas separation process is realized.
Figure 17.
- Dependence of methane content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 17.
- Dependence of methane content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 18.
- Dependence of ethane content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 18.
- Dependence of ethane content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 19.
- Dependence of propane content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 19.
- Dependence of propane content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 20.
- Dependence of n-butane content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 20.
- Dependence of n-butane content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 21.
- Dependence of nitrogen content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 21.
- Dependence of nitrogen content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
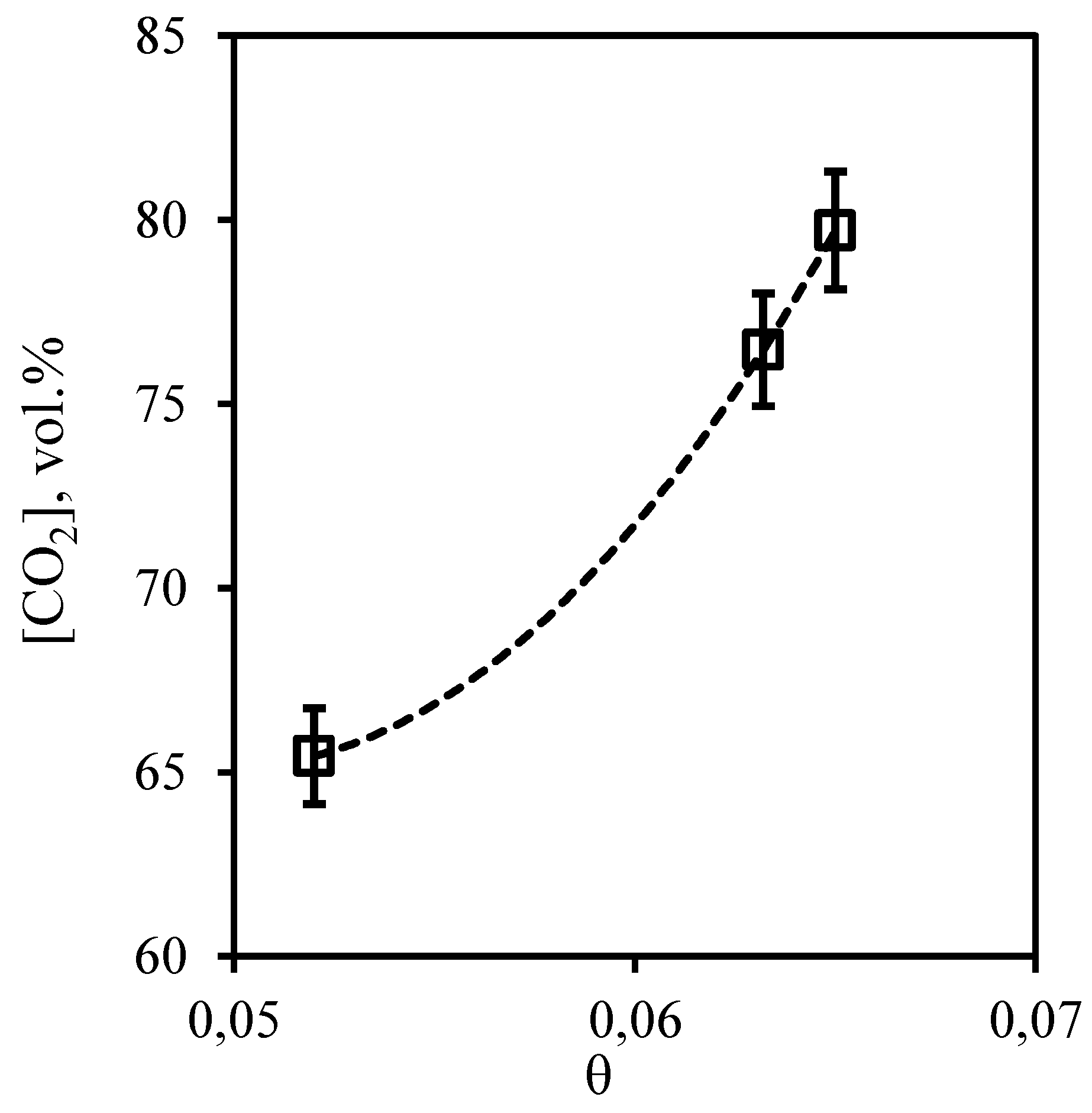
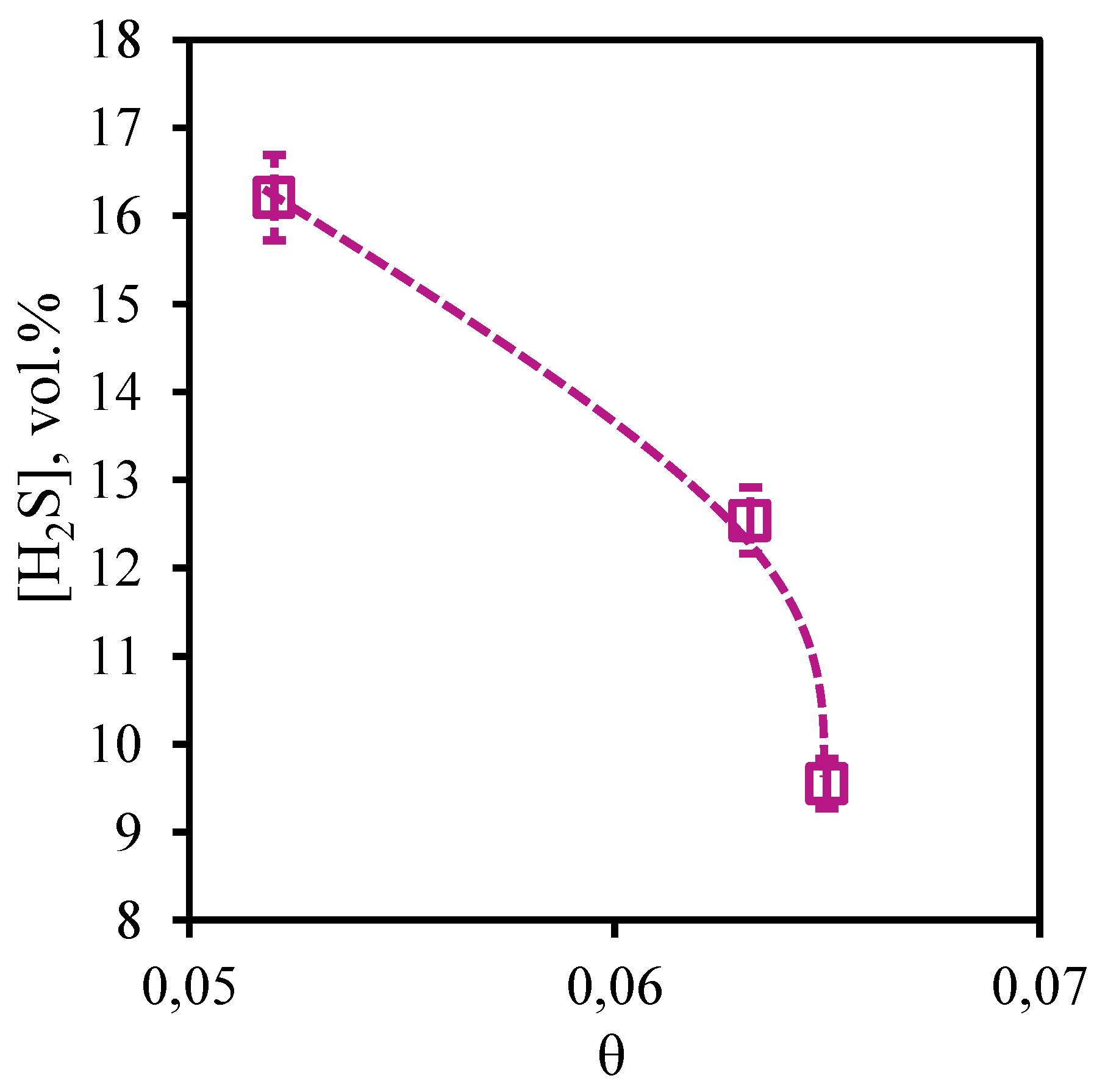
Figure 22 and
Figure 23 show the dependences of concentration of impurities of acid gases - carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide in permeate flow on the stage-cut. From the presented curves it is seen that the character of these dependences is opposite, but the values of concentrations of these components are high. So, the concentration of carbon dioxide is in a range 65.43 - 79.7 vol.%, and hydrogen sulfide content in the permeate stream is 9.55 - 16.21 vol.%. For carbon dioxide there is a significant growth of its concentration caused by growth of the stage-cut. At transition of a value of the stage-cut from 0.052 to 0.06 the concentration of carbon dioxide increases by 11 vol.% and at increase of the cut to 0.065 concentration of carbon dioxide increases by 14.27 vol.%. Decrease in hydrogen sulfide concentration in a permeate stream caused by increase of the stage-cut is less intensive and makes 3.66 and 2.99 vol.% at the same step increase of the stage-cut value. Thus, performing the membrane-assisted gas absorption process at the stage-cut equal to 0.065 (which corresponds to the most effective concentration of hydrocarbons in the retentate stream) allows to receive a permeate stream enriched with acid gases. The composition of such flow corresponds to the following proportion of methane, ethane, carbon dioxide, propane, nitrogen, n-butane, hydrogen sulfide 8.02/0.94/79.7/0.5/1.06/0.23/9.55 vol.%.
The ultimate efficiency of considered process represented as removed amount of acid gases is 96 and 61 % of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide, respectively. Under the same conditions the hydrocarbons losses were up to 0.95 %. In this way, the residual sum of acid gases content may be lowered to 0.99 vol.% from 6.79 vol.% in one stage using the heat-free hybrid membrane-assisted gas absorption technique maintaining suitable recovery rate of methane, ethane, propane and n-butane. Nevertheless, the overall efficiency of the process may be enhanced using the specific absorption agents with aqueous amino alcohol solutions.
Figure 22.
- Dependence of carbon dioxide content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 22.
- Dependence of carbon dioxide content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 23.
- Dependence of hydrogen sulfide content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.
Figure 23.
- Dependence of hydrogen sulfide content in the permeate flow on the stage-cut during the separation of an eight-component gas mixture using a membrane-assisted gas absorption unit.