3.4. Data Analysis
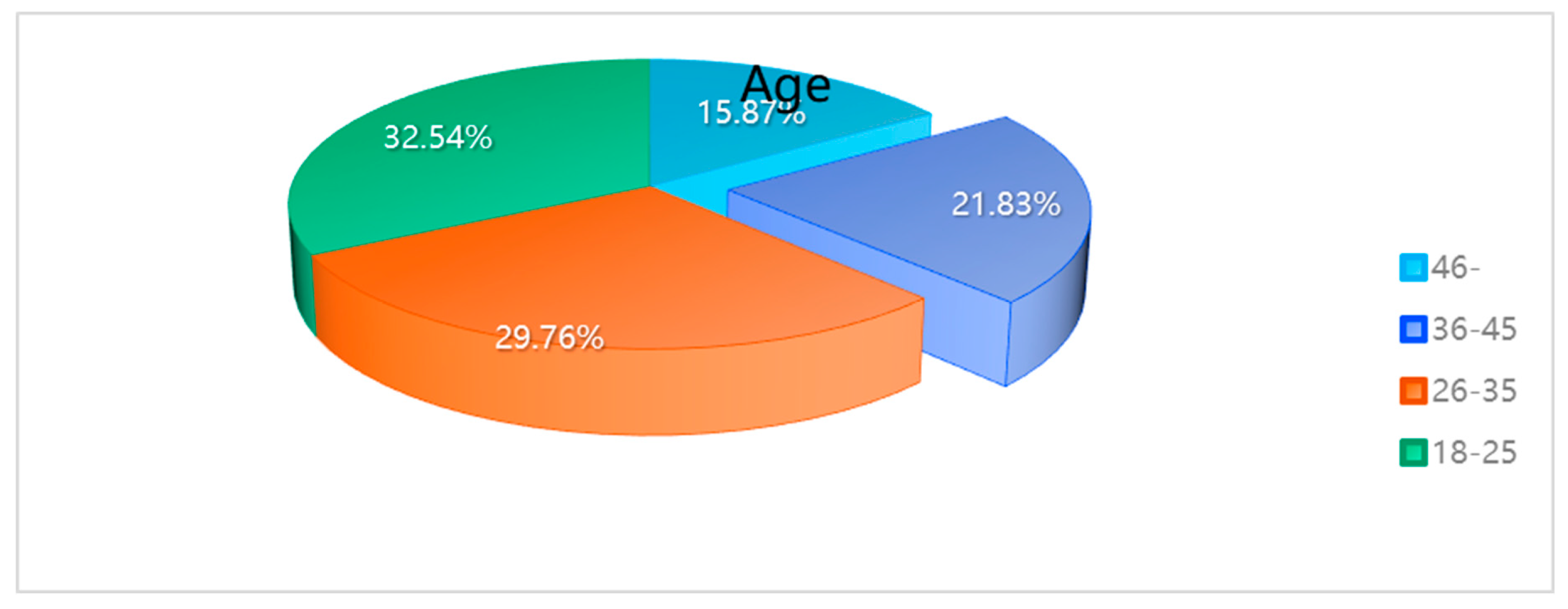
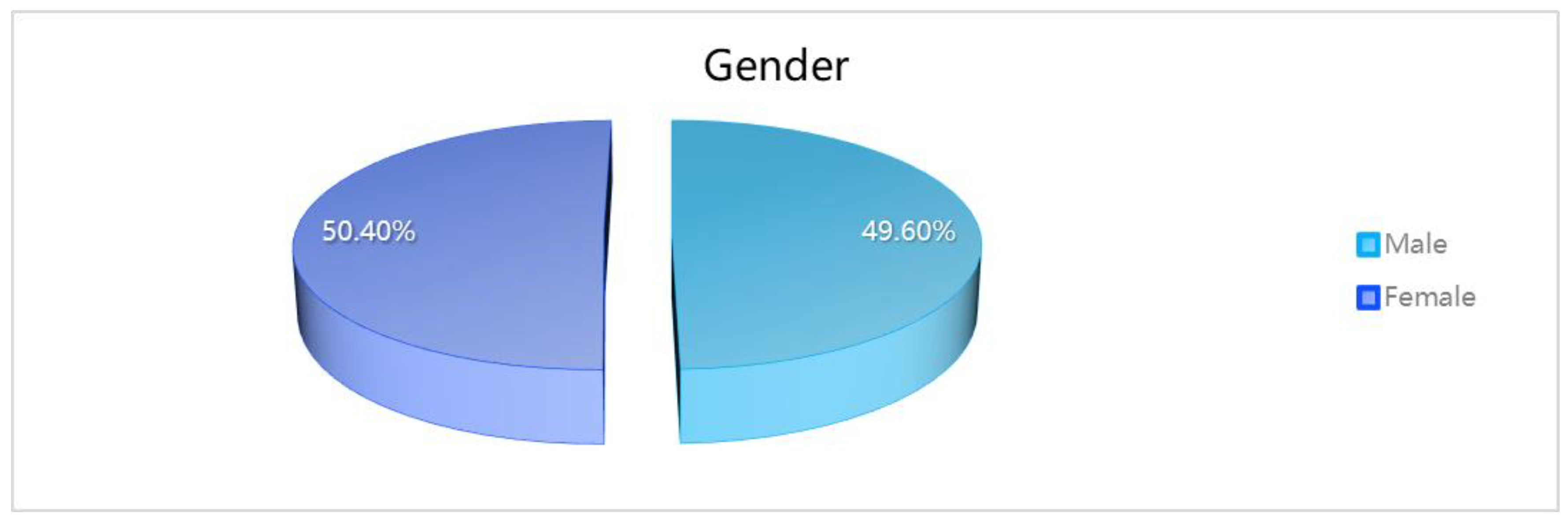
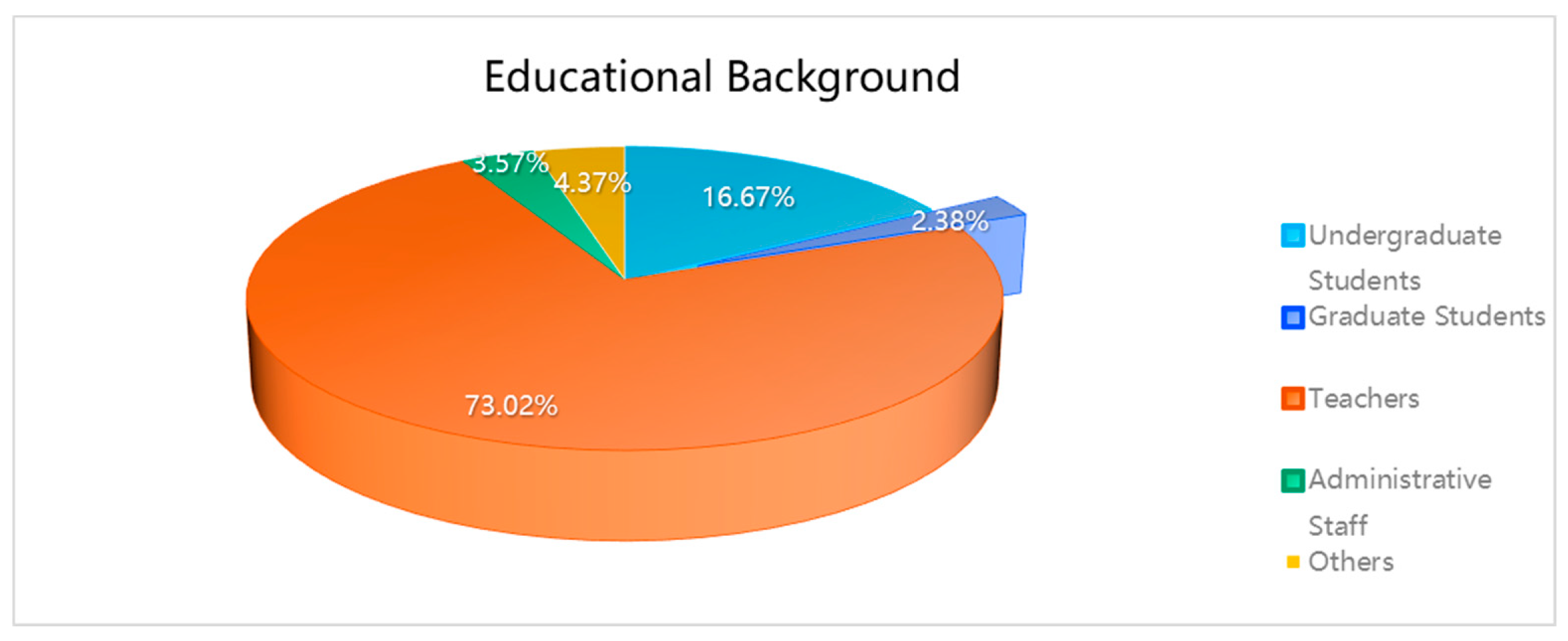
From the table presented,, it can be discerned that within the age range of the sample, the “18-25” category is the most represented, constituting 32.54%. The gender distribution within the sample is relatively balanced, with females comprising 50.40% and males 49.60%. A significant majority of the sample, 73.02%, identified themselves as “teachers.”
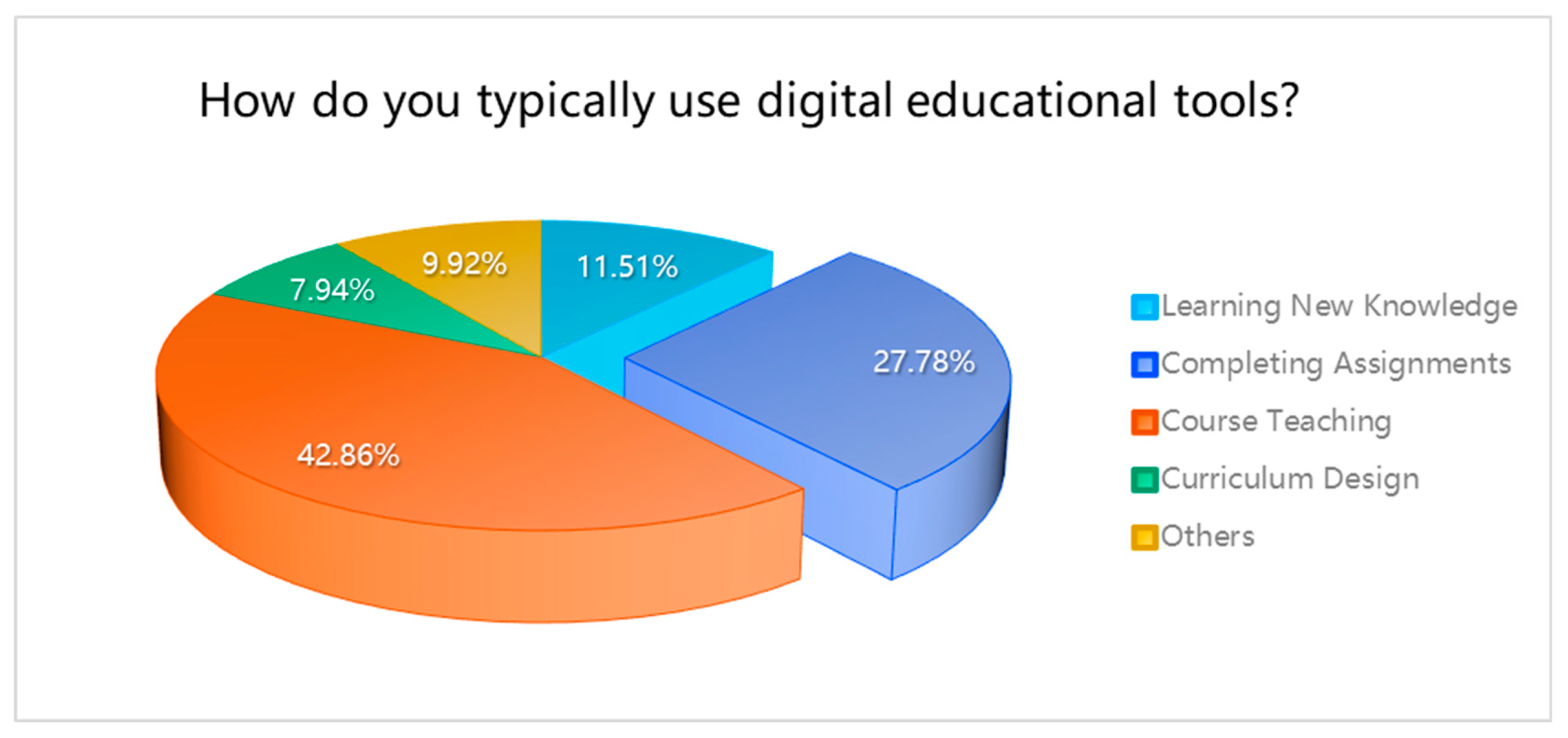
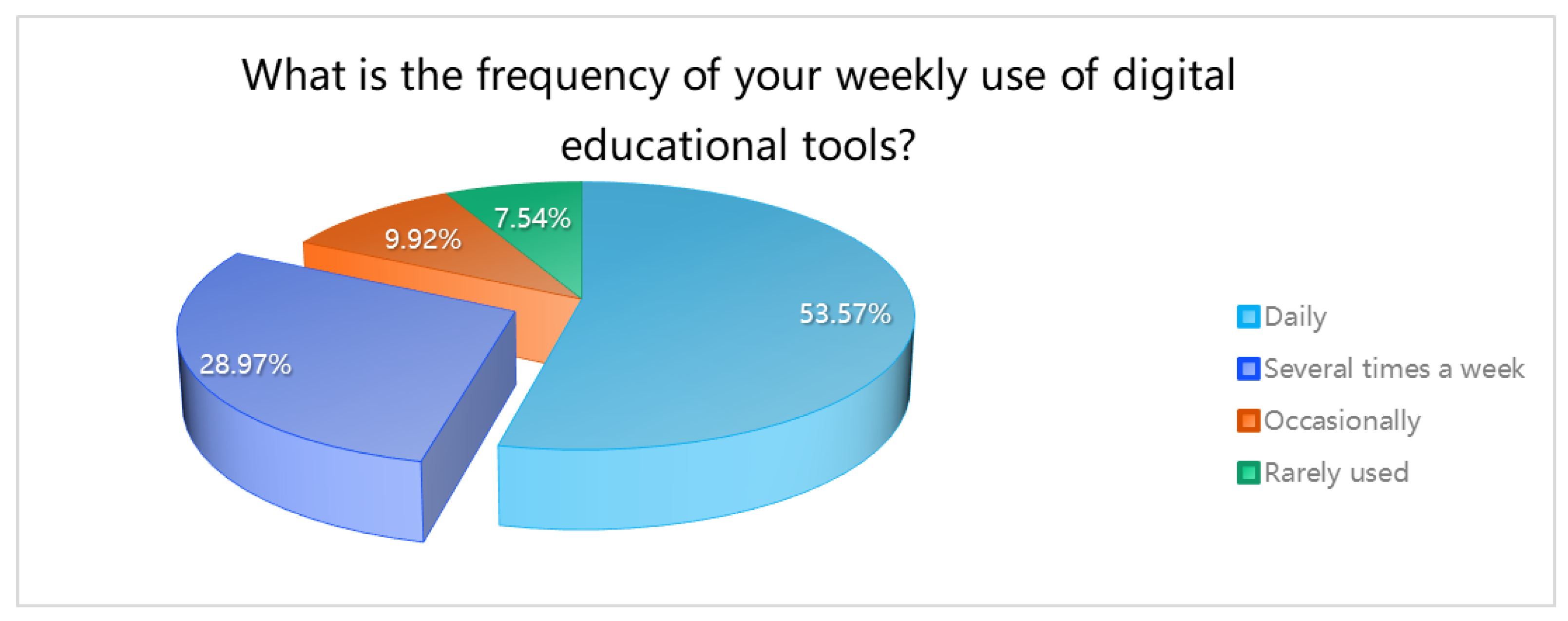
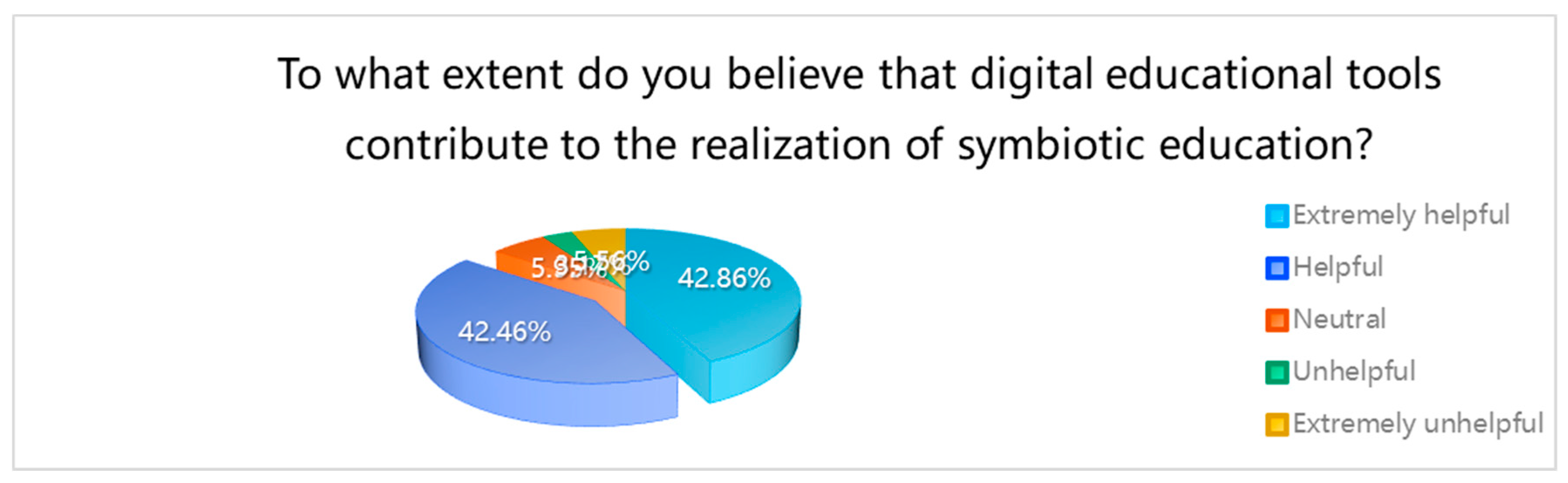
Regarding the typical use of digital educational tools, “course teaching” was the prevalent application, reported by 42.86% of the sample. Daily usage of digital tools was noted by 53.57% of the respondents. When asked to what extent digital educational tools are considered helpful in facilitating symbiotic education, over 40% of the sample indicated “very helpful,” with an additional 42.46% deeming them “helpful.”
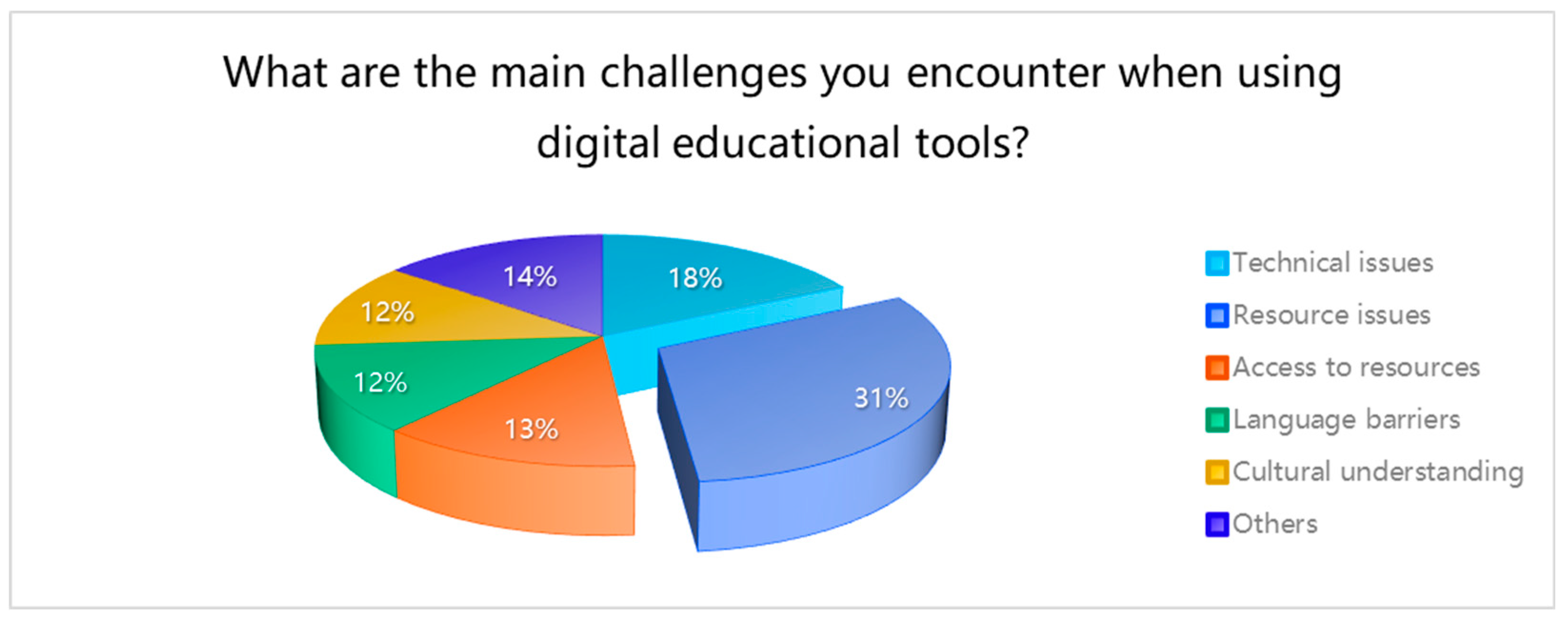
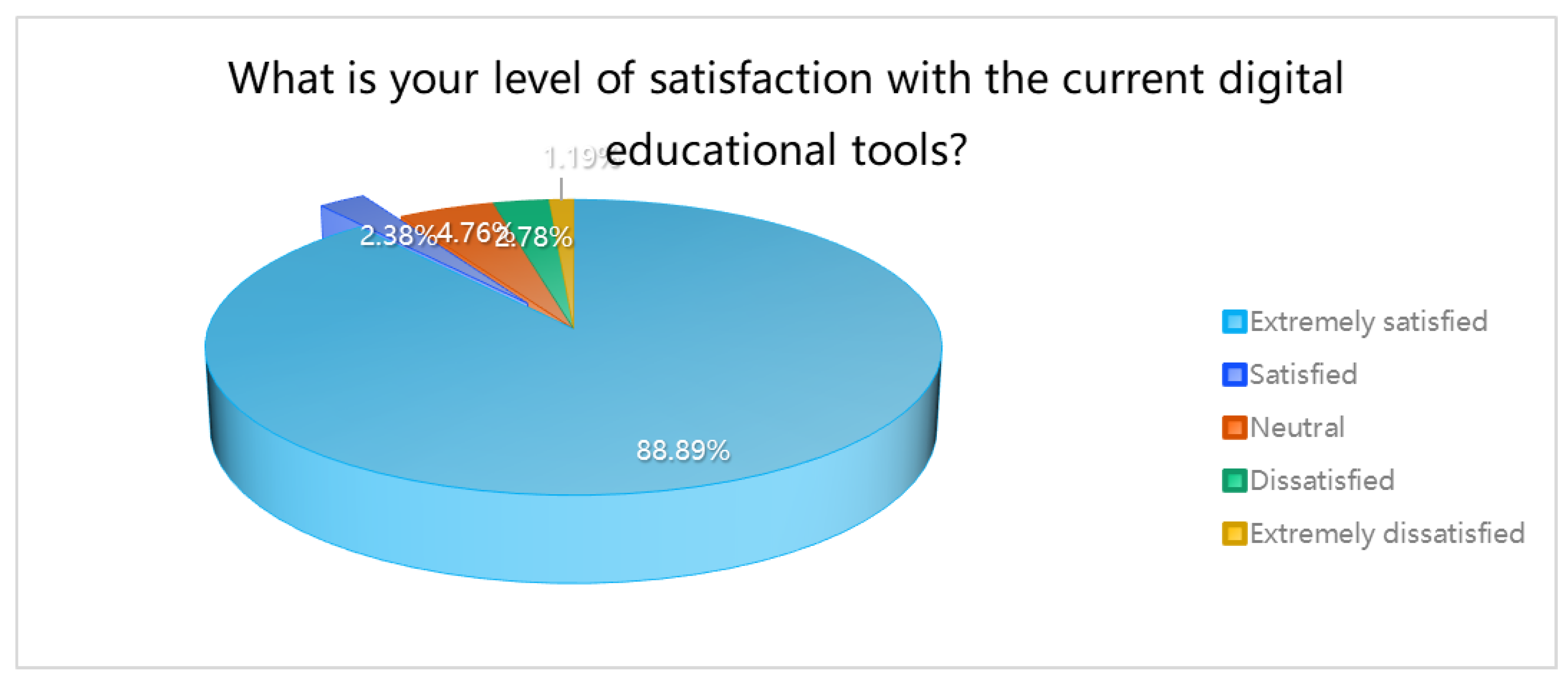
Concerning the main challenges encountered when using digital educational tools, more than 30% of the sample identified “resource issues.” A substantial majority, 88.89%, expressed “very satisfaction” with the current digital educational tools.
Table 2.
This is a table.Age.
Table 2.
This is a table.Age.
| Age |
| Category |
Frequency |
Percentage (%) |
Cumulative Percentage (%) |
| 18-25 |
82 |
32.54% |
32.54% |
| 26-35 |
75 |
29.76% |
62.30% |
| 36-45 |
55 |
21.83% |
84.13% |
| 46- |
40 |
15.87% |
100.00% |
| Total |
252 |
100.0% |
|
Figure 1.
This is a figure. Age.
Figure 1.
This is a figure. Age.
Table 3.
This is a table.Gender.
Table 3.
This is a table.Gender.
| Gender |
| Category |
Frequency |
Percentage (%) |
Cumulative Percentage (%) |
| Male |
125 |
49.60% |
49.60% |
| Female |
127 |
50.40% |
100.00% |
| Total |
252 |
100.0% |
|
Figure 2.
This is a figure. Gender.
Figure 2.
This is a figure. Gender.
Table 4.
This is a table.Educational Background.
Table 4.
This is a table.Educational Background.
| Educational Background |
| Category |
Frequency |
Percentage (%) |
Cumulative Percentage (%) |
| Undergraduate Students |
42 |
16.67% |
16.67% |
| Graduate Students |
6 |
2.38% |
19.05% |
| Teachers |
184 |
73.02% |
92.06% |
| Administrative Staff |
9 |
3.57% |
95.63% |
| Others |
11 |
4.37% |
100.00% |
| Total |
252 |
100.0% |
|
Figure 3.
This is a figure.Educational Background.
Figure 3.
This is a figure.Educational Background.
Table 5.
This is a table. How do you typically use digital educational tools?
Table 5.
This is a table. How do you typically use digital educational tools?
| How do you typically use digital educational tools? |
| Category |
Frequency |
Percentage (%) |
Cumulative Percentage (%) |
| Learning New Knowledge |
29 |
11.51% |
11.51% |
| Completing Assignments |
70 |
27.78% |
39.29% |
| Course Teaching |
108 |
42.86% |
82.14% |
| Curriculum Design |
20 |
7.94% |
90.08% |
| Others |
25 |
9.92% |
100.00% |
| Total |
252 |
100.0% |
|
Figure 4.
This is a figure. How do you typically use digital educational tools?
Figure 4.
This is a figure. How do you typically use digital educational tools?
Table 6.
This is a table. What is the frequency of your weekly use of digital educational tools?
Table 6.
This is a table. What is the frequency of your weekly use of digital educational tools?
| What is the frequency of your weekly use of digital educational tools? |
| Category |
Frequency |
Percentage (%) |
Cumulative Percentage (%) |
| Daily |
135 |
53.57% |
53.57% |
| Several times a week |
73 |
28.97% |
82.54% |
| Occasionally |
25 |
9.92% |
92.46% |
| Rarely used |
19 |
7.54% |
100.00% |
| Total |
252 |
100.0% |
|
Figure 5.
This is a figure. What is the frequency of your weekly use of digital educational tools?
Figure 5.
This is a figure. What is the frequency of your weekly use of digital educational tools?
Table 7.
This is a table. To what extent do you believe that digital educational tools contribute to the realization of symbiotic education?
Table 7.
This is a table. To what extent do you believe that digital educational tools contribute to the realization of symbiotic education?
| To what extent do you believe that digital educational tools contribute to the realization of symbiotic education? |
| Category |
Frequency |
Percentage (%) |
Cumulative Percentage (%) |
| Extremely helpful |
108 |
42.86% |
42.86% |
| Helpful |
107 |
42.46% |
85.32% |
| Neutral |
15 |
5.95% |
91.27% |
| Unhelpful |
8 |
3.17% |
94.44% |
| Extremely unhelpful |
14 |
5.56% |
100.00% |
| Total |
252 |
100.0% |
|
Figure 6.
This is a figure. To what extent do you believe that digital educational tools contribute to the realization of symbiotic education?
Figure 6.
This is a figure. To what extent do you believe that digital educational tools contribute to the realization of symbiotic education?
Table 8.
This is a table. What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools?
Table 8.
This is a table. What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools?
| What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools? |
| Category |
Frequency |
Percentage (%) |
Cumulative Percentage (%) |
| Technical issues |
44 |
17.46% |
17.46% |
| Resource issues |
78 |
30.95% |
48.41% |
| Access to resources |
33 |
13.10% |
61.51% |
| Language barriers |
31 |
12.30% |
73.81% |
| Cultural understanding |
30 |
11.90% |
85.71% |
| Others |
36 |
14.29% |
100.00% |
| Total |
252 |
100.0% |
|
Figure 7.
This is a figure. What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools?
Figure 7.
This is a figure. What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools?
Table 9.
This is a table. What is your level of satisfaction with the current digital educational tools?
Table 9.
This is a table. What is your level of satisfaction with the current digital educational tools?
| What is your level of satisfaction with the current digital educational tools? |
| Category |
Frequency |
Percentage (%) |
Cumulative Percentage (%) |
| Extremely satisfied |
224 |
88.89% |
88.89% |
| Satisfied |
6 |
2.38% |
91.27% |
| Neutral |
12 |
4.76% |
96.03% |
| Dissatisfied |
7 |
2.78% |
98.81% |
| Extremely dissatisfied |
3 |
1.19% |
100.00% |
| Total |
252 |
100.0% |
|
Figure 8.
This is a figure. What is your level of satisfaction with the current digital educational tools? .
Figure 8.
This is a figure. What is your level of satisfaction with the current digital educational tools? .
Table 10.
This is a table.ANOVA results.
Table 10.
This is a table.ANOVA results.
| ANOVA results (normal format) |
| Analysis item |
Item |
Sample size |
Average |
Standard deviation |
F |
P |
| How do you typically use digital educational tools? |
18-25 |
82 |
2.40 |
0.73 |
5.337 |
0.001** |
| 26-35 |
75 |
3.03 |
1.08 |
| 36-45 |
55 |
2.95 |
1.46 |
| 46- |
40 |
2.80 |
0.88 |
| Total |
252 |
2.77 |
1.08 |
| What is the frequency of your weekly use of digital educational tools? |
18-25 |
82 |
1.72 |
0.57 |
47.145 |
0.000** |
| 26-35 |
75 |
1.28 |
0.76 |
| 36-45 |
55 |
2.69 |
0.96 |
| 46- |
40 |
1.18 |
0.68 |
| Total |
252 |
1.71 |
0.93 |
| To what extent do you believe that digital educational tools contribute to the realization of symbiotic education? |
18-25 |
82 |
2.13 |
0.52 |
22.215 |
0.000** |
| 26-35 |
75 |
1.36 |
0.48 |
| 36-45 |
55 |
2.51 |
1.62 |
| 46- |
40 |
1.35 |
0.98 |
| Total |
252 |
1.86 |
1.05 |
| What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools? |
18-25 |
82 |
3.50 |
1.75 |
3.686 |
0.013* |
| 26-35 |
75 |
2.63 |
1.36 |
| 36-45 |
55 |
3.24 |
1.69 |
| 46- |
40 |
3.17 |
1.99 |
| Total |
252 |
3.13 |
1.70 |
| What is your level of satisfaction with the current digital educational tools? |
18-25 |
82 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
104.912 |
0.000** |
| 26-35 |
75 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
| 36-45 |
55 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
| 46岁以上 |
40 |
2.58 |
1.30 |
| Total |
252 |
1.25 |
0.77 |
| * p<0.05 ** p<0.01 |
Variance:
Age demonstrated significant differences at the 0.01 level (F=5.337, p=0.001) concerning the usual use of digital educational tools. Specific comparative differences revealed that the mean scores of age groups “26-35 > 18-25; 36-45 > 18-25” were notably different, which can also be visually displayed using line graphs. As for the frequency of digital educational tool usage each week, significant differences were again apparent at the 0.01 level (F=47.145, p<0.001), with the mean score comparisons indicating substantial differences: “18-25 > 26-35; 36-45 > 18-25; 18-25 > over 46; 36-45 > 26-35; 36-45 > over 46,” which can also be represented using line graphs for intuitive presentation.
Furthermore, age showed significant differences at the 0.01 level (F=22.215, p<0.001) in perceptions of the extent to which digital educational tools facilitate symbiotic education. The mean score comparisons revealed significant differences, with “18-25 > 26-35; 36-45 > 18-25; 18-25 > over 46; 36-45 > 26-35; 36-45 > over 46,” and these relationships can also be depicted using line graphs.
In terms of the main challenges encountered when using digital educational tools, significant differences emerged at the 0.05 level (F=3.686, p=0.013), with mean score comparisons indicating that “18-25 > 26-35; 36-45 > 26-35,” which can also be illustrated through line graphs.
Regarding satisfaction with current digital educational tools, age showed significant differences at the 0.01 level (F=104.912, p<0.001), with the mean score comparisons showing distinct disparities: “over 46 > 18-25; over 46 > 26-35; over 46 > 36-45,” which can also be visually presented using line graphs.
In summary, significant differences were observed across all age samples concerning the usual use of digital educational tools, the weekly frequency of using digital educational tools, perceptions of digital tools’ contribution to symbiotic education, the main challenges encountered, and satisfaction with current digital educational tools.
Table 11.
This is a table.ANOVA results.
Table 11.
This is a table.ANOVA results.
| ANOVA results (normal format) |
| Analysis item |
Item |
Sample size |
Average |
Standard deviation |
F |
p |
| How do you typically use digital educational tools? |
Male |
125 |
2.78 |
1.10 |
0.042 |
0.837 |
| Female |
127 |
2.76 |
1.07 |
| Total |
252 |
2.77 |
1.08 |
| What is your frequency of digital educational tools usage per week? |
Male |
125 |
1.80 |
1.01 |
2.133 |
0.145 |
| Female |
127 |
1.63 |
0.83 |
| Total |
252 |
1.71 |
0.93 |
| To what extent do you think digital educational tools contribute to the realization of symbiotic education? |
Male |
125 |
1.84 |
1.00 |
0.100 |
0.752 |
| Female |
127 |
1.88 |
1.10 |
| Total |
252 |
1.86 |
1.05 |
| What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools? |
Male |
125 |
2.82 |
1.55 |
8.331 |
0.004** |
| Female |
127 |
3.43 |
1.79 |
| Total |
252 |
3.13 |
1.70 |
| How satisfied are you with the current digital educational tools? |
Male |
125 |
1.17 |
0.68 |
2.825 |
0.094 |
| Female |
127 |
1.33 |
0.85 |
| Total |
252 |
1.25 |
0.77 |
| * p<0.05 ** p<0.01 |
Gender For 7 WhGender For 7 What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools? It shows significance at the 0.01 level (F=8.331, p=0.004), and the specific comparison shows that the average value of men (2.82) is significantly lower than the average value of women (3.43).
In summary, we can know: How do you usually use digital educational tools for different gender samples? How often do you use digital educational tools every week? To what extent do you think digital educational tools help achieve symbiotic education?, how satisfied are you with current digital education tools? A total of 4 items will not show significant differences. In addition, gender samples have 7 What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools? A total of 1 item showed a significant difference.
Table 12.
This is a table.ANOVA results.
Table 12.
This is a table.ANOVA results.
| ANOVA results (normal format) |
| Analysis Item |
Item |
Sample Size |
Mean |
Standard Deviation |
F |
p |
| How do you typically use digital educational tools? |
Undergraduate Students |
42 |
2.12 |
0.71 |
6.924 |
0.000** |
| Graduate Students |
6 |
3.00 |
1.79 |
| Teachers |
184 |
2.95 |
1.04 |
| Administrative Staff |
9 |
2.00 |
1.22 |
| Others |
11 |
2.73 |
1.35 |
| Total |
252 |
2.77 |
1.08 |
| What is your frequency of digital educational tools usage per week? |
Undergraduate Students |
42 |
2.02 |
0.41 |
1.645 |
0.164 |
| Graduate Students |
6 |
1.33 |
0.52 |
| Teachers |
184 |
1.66 |
1.00 |
| Administrative Staff |
9 |
1.78 |
1.20 |
| Others |
11 |
1.64 |
0.81 |
| Total |
252 |
1.71 |
0.93 |
| To what extent do you think digital educational tools contribute to the realization of symbiotic education? |
Undergraduate Students |
42 |
2.14 |
0.57 |
1.248 |
0.291 |
| Graduate Students |
6 |
1.50 |
1.22 |
| Teachers |
184 |
1.80 |
1.08 |
| Administrative Staff |
9 |
2.11 |
1.17 |
| Others |
11 |
1.73 |
1.62 |
| Total |
252 |
1.86 |
1.05 |
| What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools? |
Undergraduate Students |
42 |
3.76 |
1.71 |
3.124 |
0.016* |
| Graduate Students |
6 |
1.83 |
0.75 |
| Teachers |
184 |
3.08 |
1.68 |
| Administrative Staff |
9 |
2.22 |
1.64 |
| Others |
11 |
3.00 |
1.73 |
| Total |
252 |
3.13 |
1.70 |
| How satisfied are you with the current digital educational tools? |
Undergraduate Students |
42 |
1.00 |
0.00 |
2.965 |
0.020* |
| Graduate Students |
6 |
1.50 |
1.22 |
| Teachers |
184 |
1.26 |
0.79 |
| Administrative Staff |
9 |
1.89 |
1.27 |
| Others |
11 |
1.36 |
0.81 |
| Total |
252 |
1.25 |
0.77 |
| * p<0.05 ** p<0.01 |
Educational background exhibited significant differences at the 0.01 level (F=6.924, p<0.001) in terms of how digital educational tools are typically used, with a notable discrepancy in mean scores indicating that “teachers > undergraduates; teachers > administrative staff.” These differences can also be visually represented through a line graph for intuitive display.
Regarding the main challenges encountered when using digital educational tools, educational background showed significant differences at the 0.05 level (F=3.124, p=0.016). The mean score comparison revealed marked differences among groups with “undergraduates > graduate students; undergraduates > teachers; undergraduates > administrative staff,” which can also be depicted using a line graph.
In terms of satisfaction with current digital educational tools, the educational background again showed significant differences at the 0.05 level (F=2.965, p=0.020), with mean score comparisons yielding “teachers > undergraduates; administrative staff > undergraduates; administrative staff > teachers,” also suitable for line graph representation.
In summary, there were no significant differences in the frequency of digital educational tool use per week and the perceived contribution of digital educational tools to facilitating symbiotic education across different educational background samples. However, three areas did present significant differences based on educational background: the typical use of digital educational tools, the main challenges encountered, and satisfaction with current digital educational tools.
Table 13.
This is a table.Correlation.
Table 13.
This is a table.Correlation.
| Pearson related-detailed format |
| |
|
To what extent do you think digital educational tools contribute to the realization of symbiotic education? |
What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools? |
How satisfied are you with the current digital educational tools? |
| To what extent do you think digital educational tools contribute to the realization of symbiotic education? |
Correlation coefficient |
1 |
|
|
| p value |
- |
|
|
| Sample size |
- |
|
|
| What are the main challenges you encounter when using digital educational tools? |
Correlation coefficient |
0.187** |
1 |
|
| p value |
0.003 |
- |
|
| Sample size |
252 |
- |
|
| How satisfied are you with the current digital educational tools? |
Correlation coefficient |
-0.218** |
-0.001 |
1 |
| p value |
0.000 |
0.990 |
- |
| Sample size |
252 |
252 |
- |
| * p<0.05 ** p<0.01 |
The table above enables us tTThe table above enables us to understand the correlations studied between the perceptions of the effectiveness of digital educational tools in facilitating symbiotic education, the main challenges encountered while using these tools, and the satisfaction with the current digital educational tools, using Pearson’s correlation coefficient to represent the strength of these relationships. The specific analysis reveals that the correlation coefficient between perceptions of the effectiveness of digital educational tools in facilitating symbiotic education and the main challenges encountered is 0.187, which is significant at the 0.01 level. This indicates a significant positive correlation between the perceived effectiveness of digital educational tools in facilitating symbiotic education and the main challenges encountered while using them. Furthermore, the correlation coefficient between the perceived effectiveness of digital educational tools in facilitating symbiotic education and satisfaction with these tools is -0.218, which is also significant at the 0.01 level, thereby indicating a significant negative correlation between the two variables. These findings suggest that while there is a recognition of the positive role of digital tools in symbiotic education, the challenges encountered in using these tools are significantly related to the overall satisfaction with the digital educational tools.