1. Introduction
The yield of plants is directly dependent on the productivity of the interaction between soil, plants, and microorganisms. Through microorganisms, plants not only fulfill their nutrient requirements (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.) but also gain protection from phytopathogens. This effect is achieved through various mechanisms, including: (a) increased mobilization of insoluble nutrients, subsequently enhancing assimilation by plants [
1], (b) production of plant growth hormones like auxins [
2], cytokinins [
3], gibberellins [
4], and (c) antagonism against phytopathogenic microorganisms by producing siderophores [
5]. Consequently, microbial preparations can significantly reduce the need for mineral fertilizers, thereby enhancing their efficiency of use. The amalgamation of mineral and targeted bacterial preparations represents a new generation of agricultural technology.
It has been reported that inoculation with combined preparations of microorganisms is more effective than inoculation with a single microorganism in stimulating plant growth by providing a more balanced diet for various crops [
6,
7]. Zhang Yi et al. demonstrated that the co-inoculation of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) and phosphate-accumulating bacteria led to higher levels of microbial biomass phosphorus and polyphosphate [
8]. The synergistic effect of
Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110 and
Pseudomonas putida NUU8 for soybeans in arid field conditions exhibited a significant increase in root length by 56%, shoot length by 33%, dry root mass by 47%, dry shoot mass by 48%, and the number of nodules by 17% compared to the control [
9]. The synergistic effect of microorganisms is observed even if each of them individually exhibits different properties. For example, Wang showed the effect of combined treatment of PSB (
Bacillus megaterium and
Pseudomonas fluorescens) and N2-fixing bacteria (
Azotobacter chroococcum and
Azospirillum brasilence) on the availability of nitrogen and phosphorus within the first 60 days after the addition of bacteria [
10]. In addition, the beneficial effect of PSB on the survival of
Azotobacter in the rhizosphere was observed [
11]. Belimov et al., using the 15N isotope dilution method, showed that combined inoculation significantly increased the accumulation of nitrogen fertilizers in plants. Consequently, N2 fixation is not the main mechanism affecting plant growth reactions, and the effect of joint inoculation on their nitrogen nutrition can be explained by an increase in the extraction of nitrogen fertilizers. It is possible that the effect of bacterial mixtures on the mineral nutrition of plants is due to growth-stimulating substances secreted by bacteria [
12]. Thus, microorganisms play an important role in agriculture, promoting the circulation of nutrients in plants and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers, although many questions still remain unanswered.
Do the same bacteria have the same effect on different plants? Do microorganisms exhibit properties predicted by laboratory tests in an open field? To address these questions, an experiment was conducted with 20 consortia composed of phosphate-immobilizing and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The experiment involved three plants belonging to the main agricultural areas of plant cultivation in Western Siberia: cereals – wheat, cereals – buckwheat, and green biomass – corn.
2. Results
2.1. Yield of buckwheat, wheat, and corn
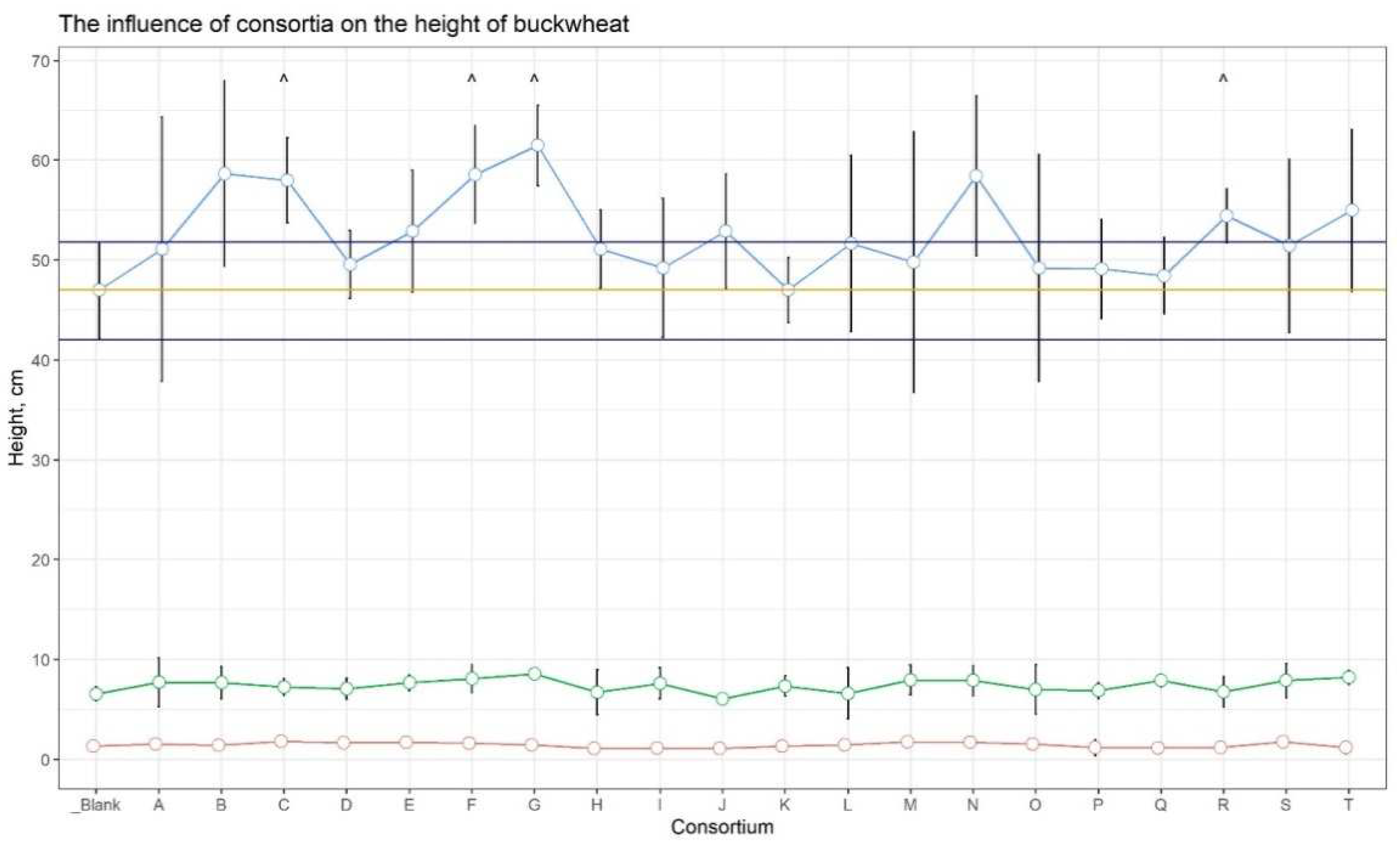
In the initial weeks of growth, buckwheat plants were approximately the same height in all plots, but after 6 weeks, plants from plots C (23.4%), F (24.6%), G (30.9%), and R (15.8%) showed a noticeable increase in height versus the control (
Figure 1, Suppl.
Table 1).
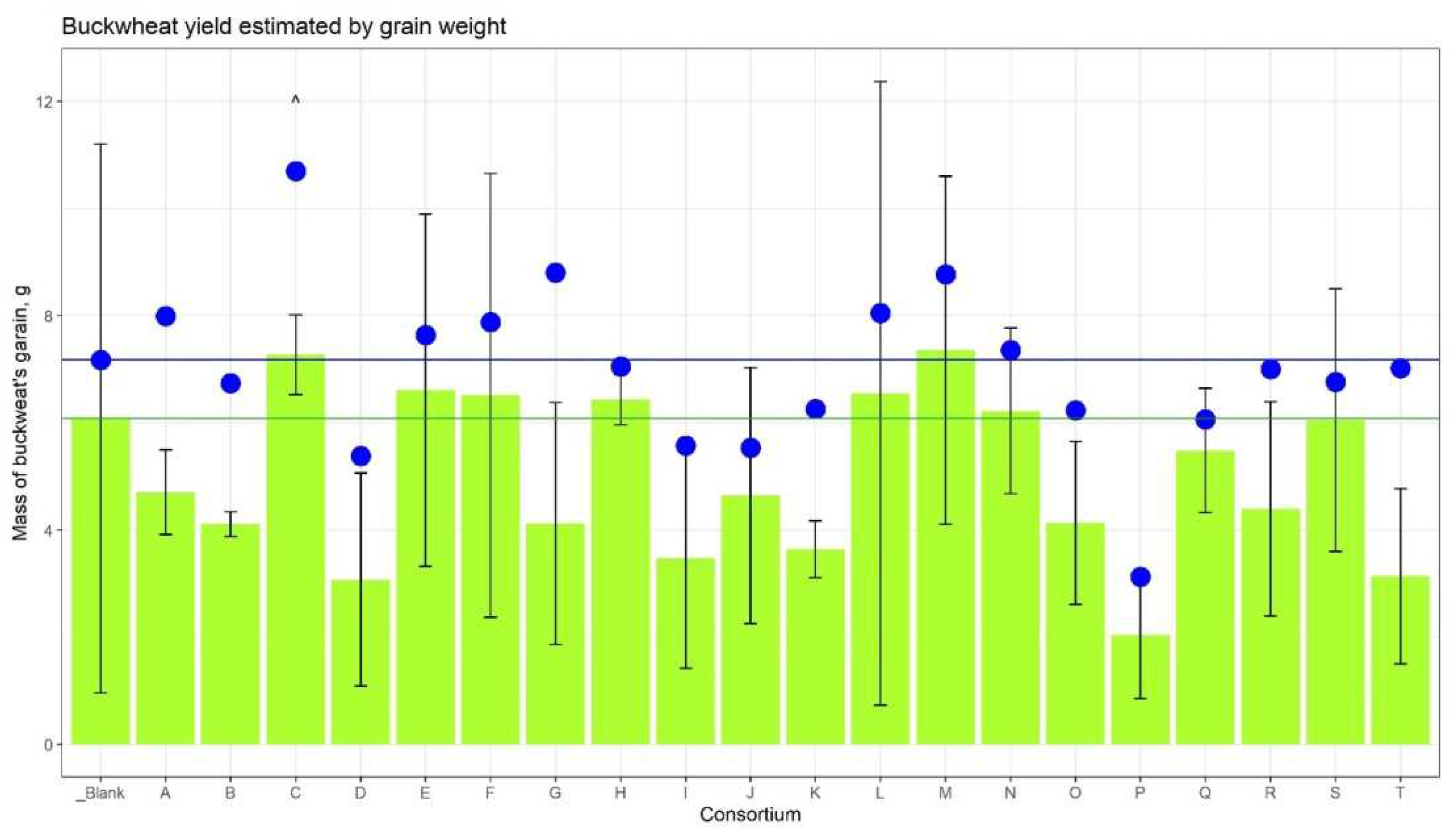
The amount of ripened grain compared to the control plot was greater in the plots corresponding to Consortia C, E, F, H, L, M, and N (
Figure 2). In comparison, only grain harvested from ears showed the maximum yield for Consortia C and M (+19.6% and +20.9%, respectively). Taking into account the fallen grain, the increase in yield for Consortium C was 49.2% (Suppl. Table 2).
Figure 2.
Buckwheat’s grain yield. The height of the green columns corresponds to the mean weight of grain from three plots, the whiskers are SD. The green horizontal line shows the mean weight from the control plot. The blue dots represent the average weight of the grain from the plot, taking into account the grain fallen to the ground. The blue horizontal line corresponds to the dot of the control plot.
Figure 2.
Buckwheat’s grain yield. The height of the green columns corresponds to the mean weight of grain from three plots, the whiskers are SD. The green horizontal line shows the mean weight from the control plot. The blue dots represent the average weight of the grain from the plot, taking into account the grain fallen to the ground. The blue horizontal line corresponds to the dot of the control plot.
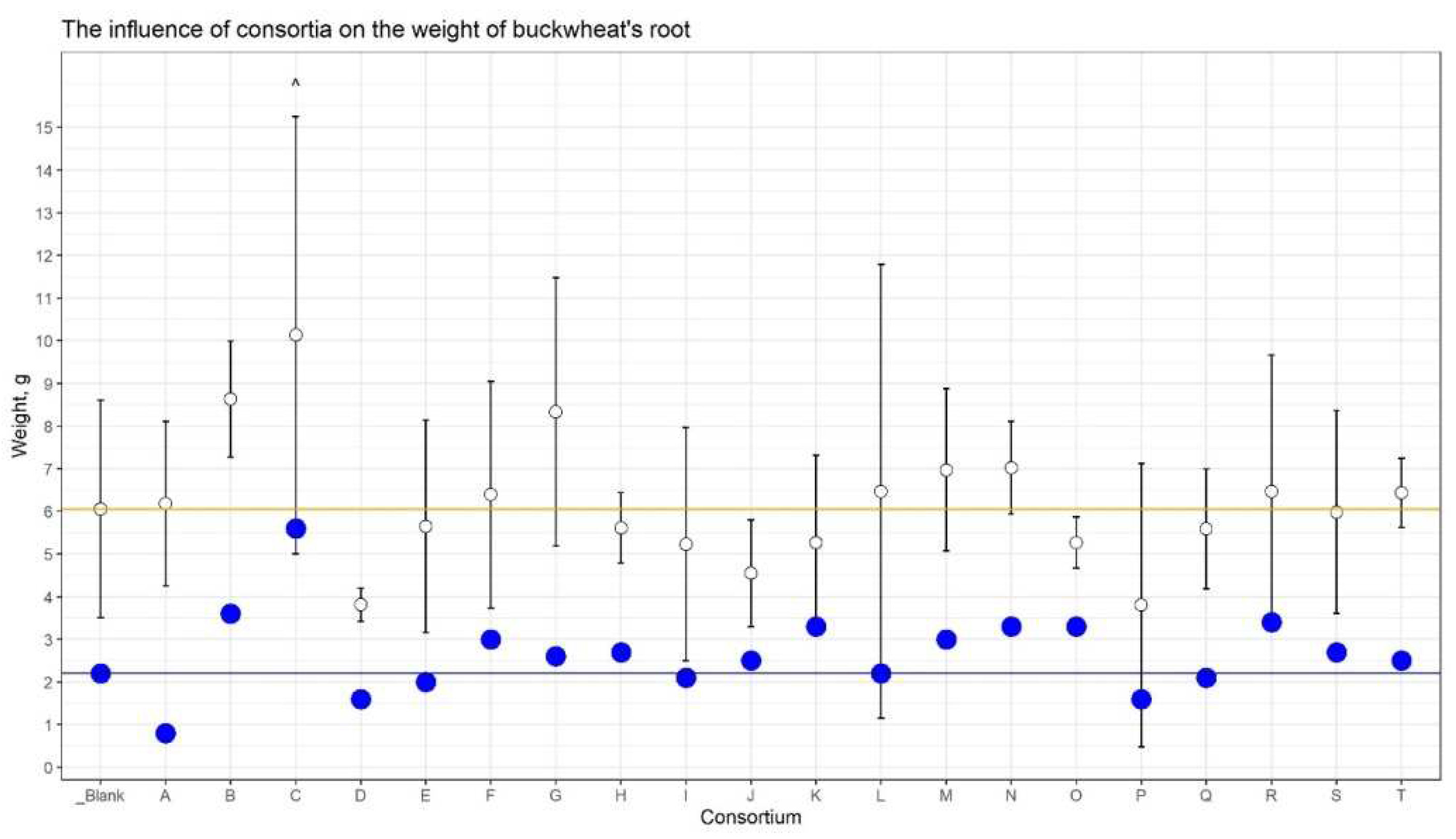
The consortium’s influence on the weight of straw and dry roots was also revealed (
Figure 3). The increase in straw weight was detected for Consortia B, C, and G. The weight of dry roots was dramatically strong for consortium C (+152%) versus control plants.
Thus, based on agronomic measurements, it was found that buckwheat plants grown from seeds inoculated with Consortium C consistently outperformed control plants in their indicators: the growth rate, the mass of the vegetative part, and the mass of the grain.
There was no difference between the height of wheat plants in different consortia compared to the control after either 4 weeks or 6 weeks (Suppl. Table 3, Suppl.
Figure 1). Despite the fact that the stems of plants from the consortium at the site were statistically significantly longer than in the control, after 3 months (Suppl.
Figure 2), the influence of consortia on the length of the wheat ear, as well as on the ratio of the length of the stem to the length of the ear, was not evident (Suppl. Table 4). Also, no effect was found on such yield characteristics as the weight of the ear and the weight of grain without a floor (Suppl.
Figure 3).
To assess the effect of inoculation of corn seeds in bacterial consortia, plant height was measured after 4 and 6 weeks, also the weight of wet and dry ears and the weight of dry roots were measured after 3 months. However, none of these indicators were statistically significantly different compared to the control plot (Suppl. Table 4, Suppl.
Figure 4 and
Figure 5).
2.2. Soil nutrient status
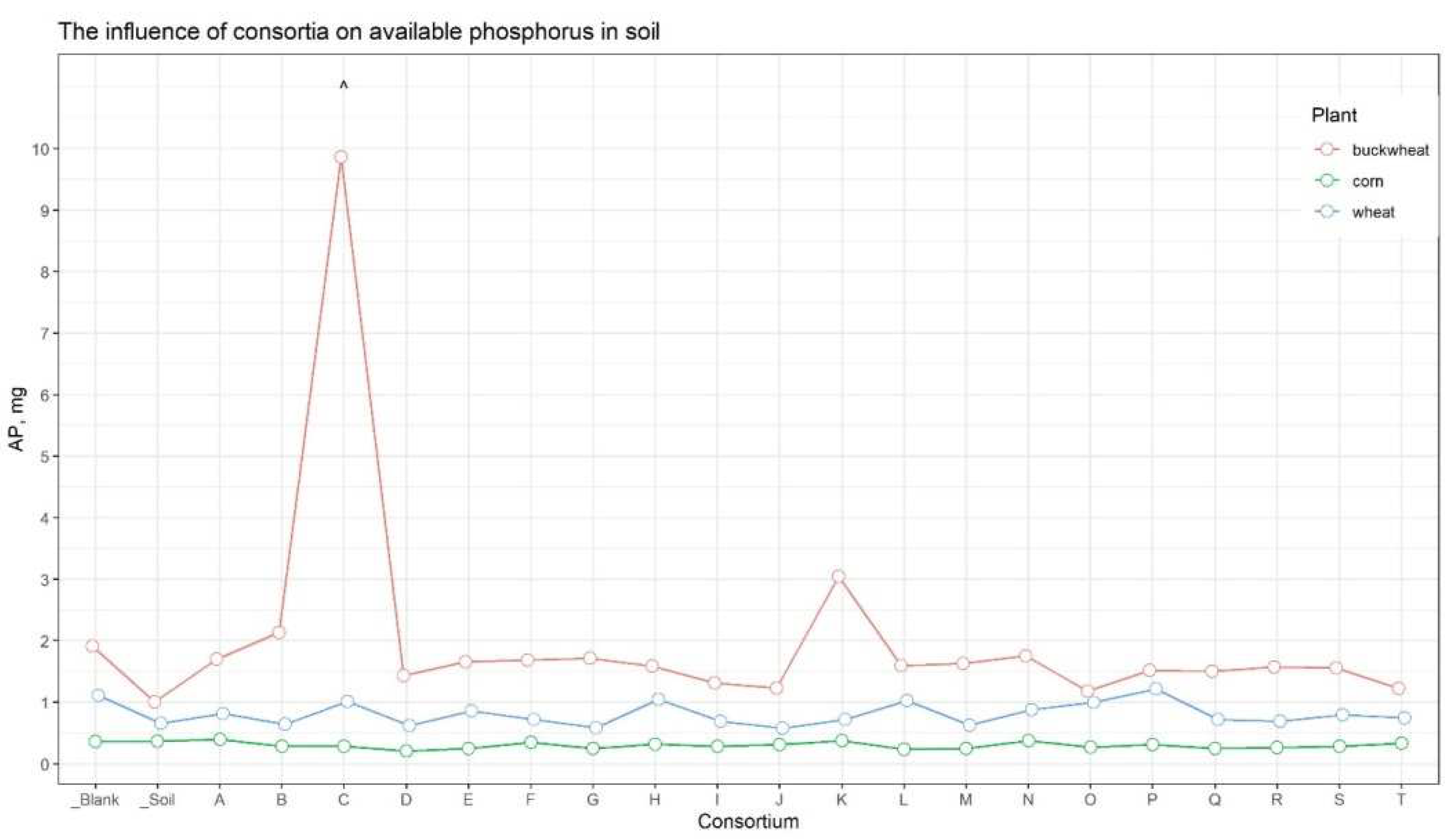
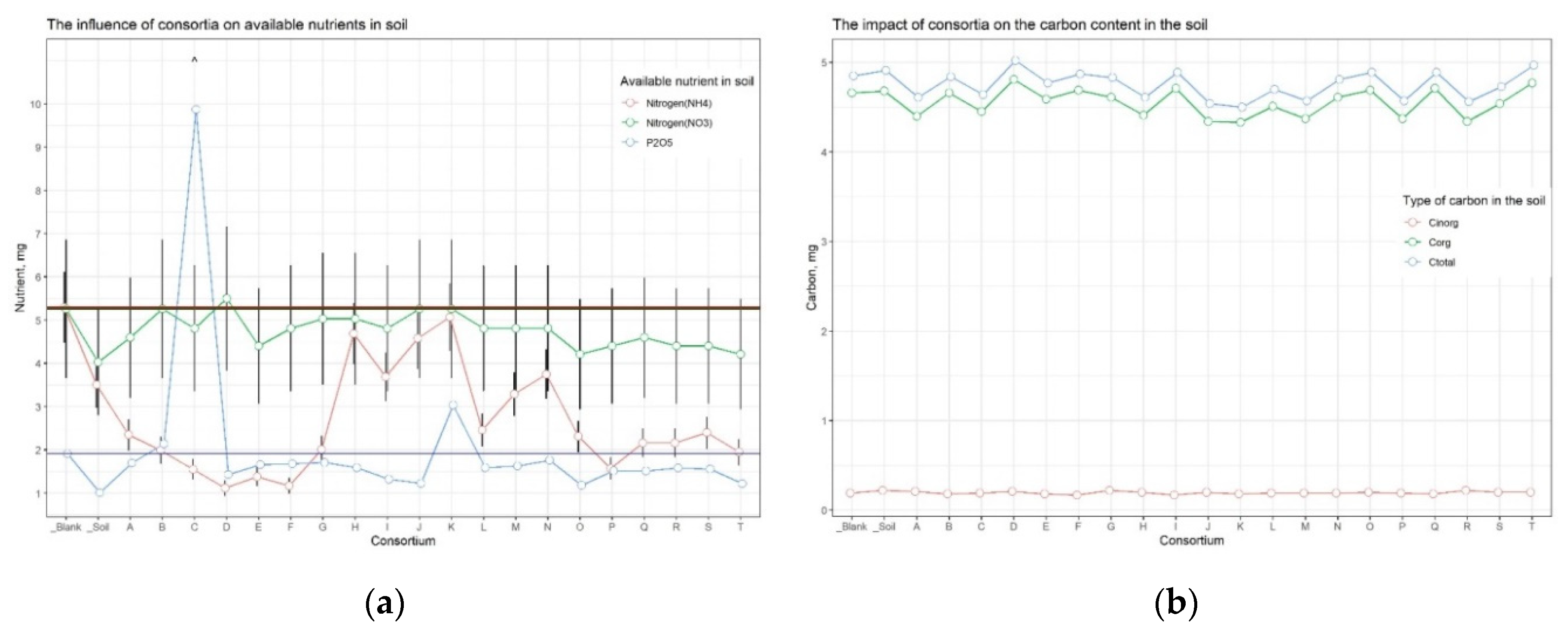
The analysis of soil nutrients indicated that the content of available forms of nitrogen, potassium, and carbon (organic, inorganic, and total) was approximately consistent across all samples (Suppl. Table 5). At the same time, for the soil sample from the plot with buckwheat inoculated in Consortium C, the amount of available phosphorus was significantly compared to the other samples (
Figure 4).
Figure 4.
The amount of soluble phosphorus in soils. The red line corresponding on soil samples under buckwheat, the green one – under corn, and the blue one – under wheat. Dots are the mean equal. ^ - marked plot of consortia, which has shown maximal additional growing versus control.
Figure 4.
The amount of soluble phosphorus in soils. The red line corresponding on soil samples under buckwheat, the green one – under corn, and the blue one – under wheat. Dots are the mean equal. ^ - marked plot of consortia, which has shown maximal additional growing versus control.
2.3. Effect of Different Consortium on Soil Microbial Community and Diversity
The dependence of the number of identified taxa on the number of sequences was estimated by constructing rarefaction curves (Suppl.
Figure 6). The analysis showed a complete determination of the taxonomic composition even with 700 sequences in all soil samples, as the curves reached a plateau. The sequencing depth proved adequate to assess alpha diversity.
Estimates of the alpha diversity (Observed, Chao1, ACE, Shannon) of microbial communities of soil samples were calculated depending on the type of consortium that seeds were inoculated with before planting (Suppl. Table 6). Box and whisker diagrams were constructed for comparison (Suppl.
Figure 7).
A pairwise comparison of alpha-diversity indices (observed and Shannon) by the Wilcoxon test did not show a significant difference between soil samples from seeds inoculated with different consortia.
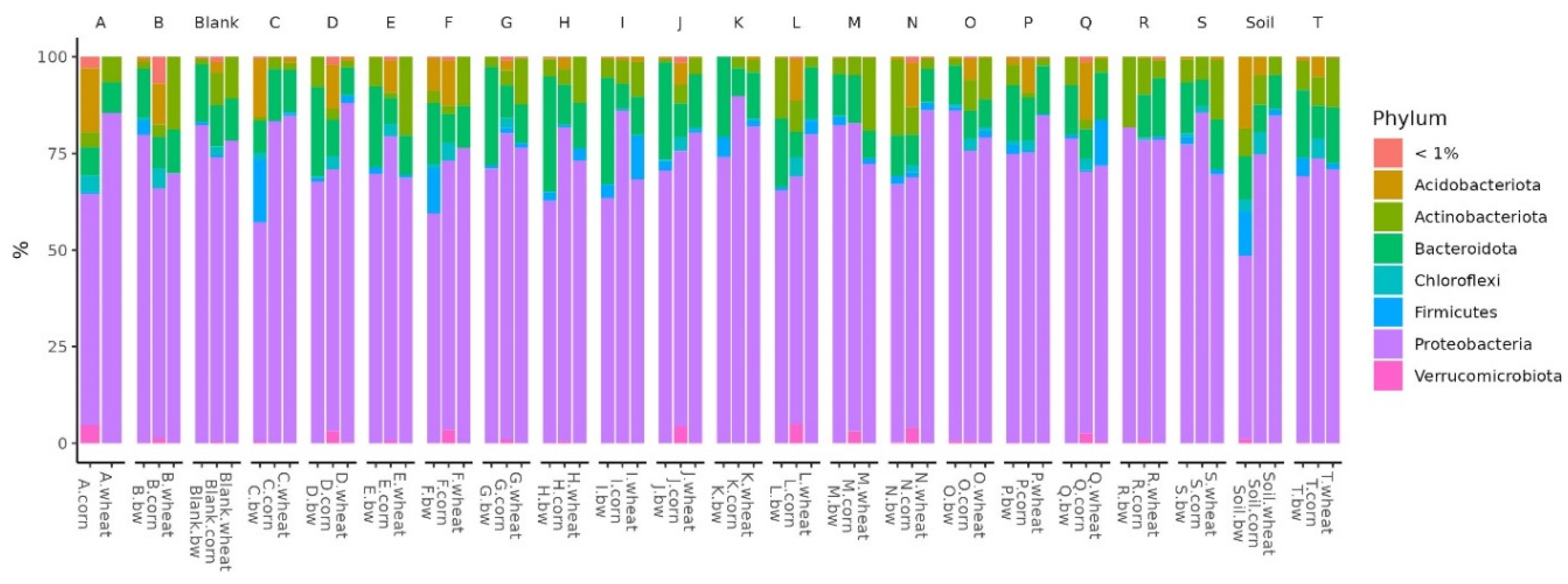
In all the studied soil samples, the dominant bacterial filaments were Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidota, Actinobacteroidota, and Acidobactoroidota. It is noteworthy that the proportion of Firmicutes increased in the three soil samples. All these samples belonged to plots with buckwheat, two had plants whose seeds were inoculated by Consortia C and F, and the third was a control plot of soil on which plants were not grown.
Figure 5.
Relative abundance histograms of dominant bacteria phyla in each soil sample.
Figure 5.
Relative abundance histograms of dominant bacteria phyla in each soil sample.
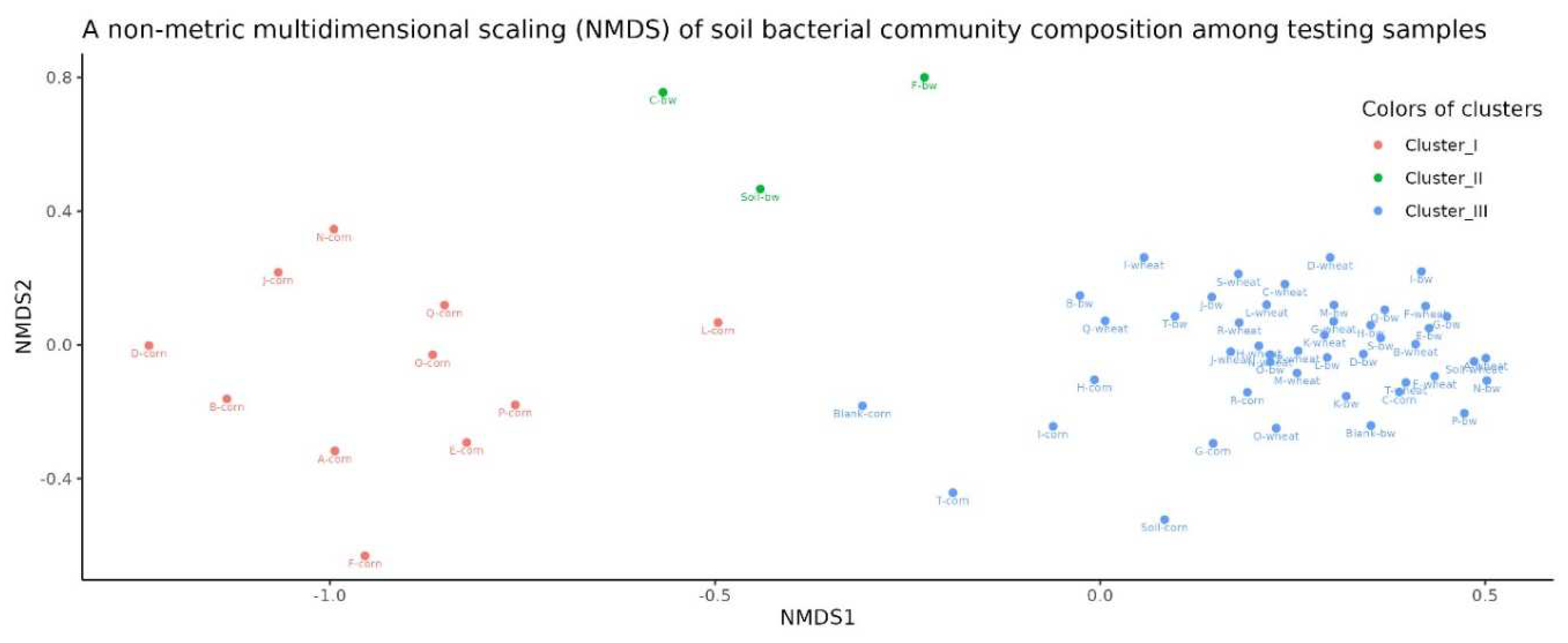
Beta diversity analysis using non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) showed that the samples were clearly divided into three clusters. The first cluster predominantly included samples from corn plots, the second from the C, F and Soil from buckwheat plots, and the third included the remaining samples.
Figure 6.
A non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) of soil bacterial community composition among testing samples.
Figure 6.
A non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) of soil bacterial community composition among testing samples.
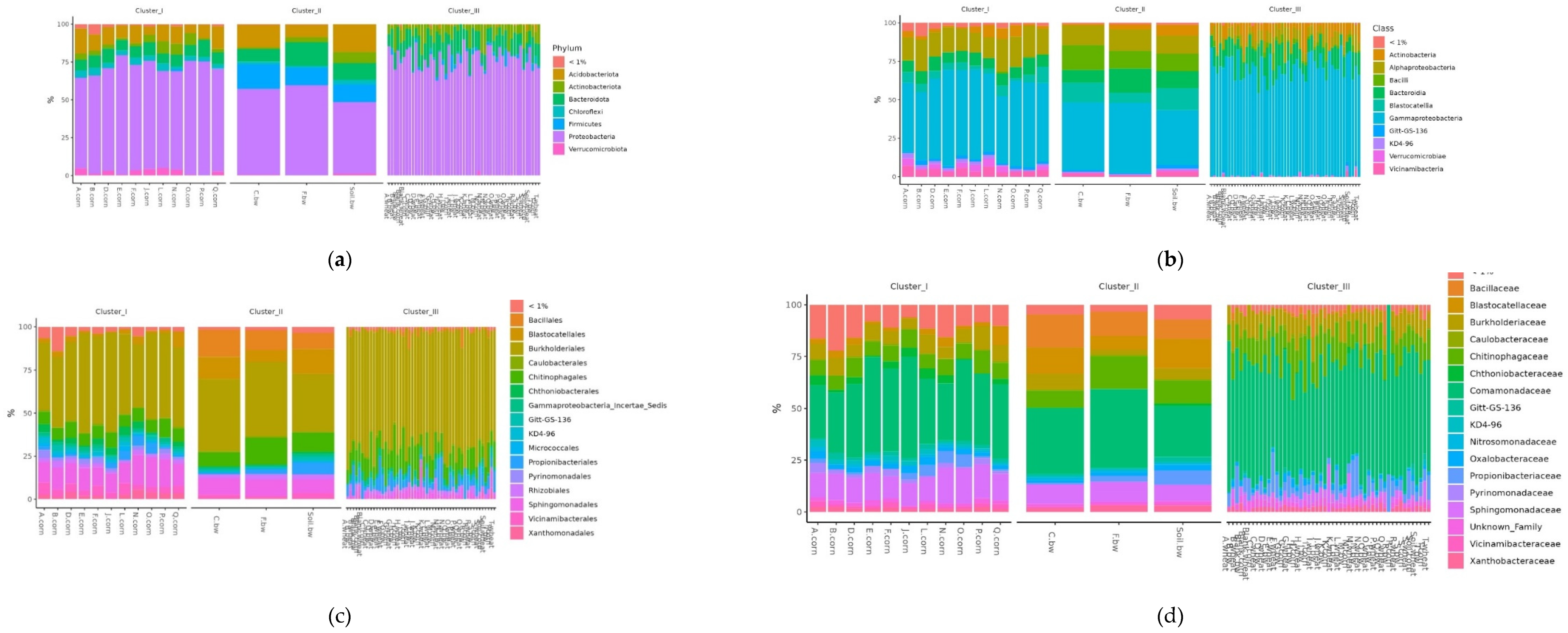
To assess the differences in the representation of different bacteria between the clusters defined by the analysis, several additional relative abundance histograms were built (
Figure 7 A-D).
Figure 7.
Relative abundance histograms of dominant bacteria Phyla (a), Class (b), Order (c), Family (d) in each soil sample grouped by clusters from NMDS.
Figure 7.
Relative abundance histograms of dominant bacteria Phyla (a), Class (b), Order (c), Family (d) in each soil sample grouped by clusters from NMDS.
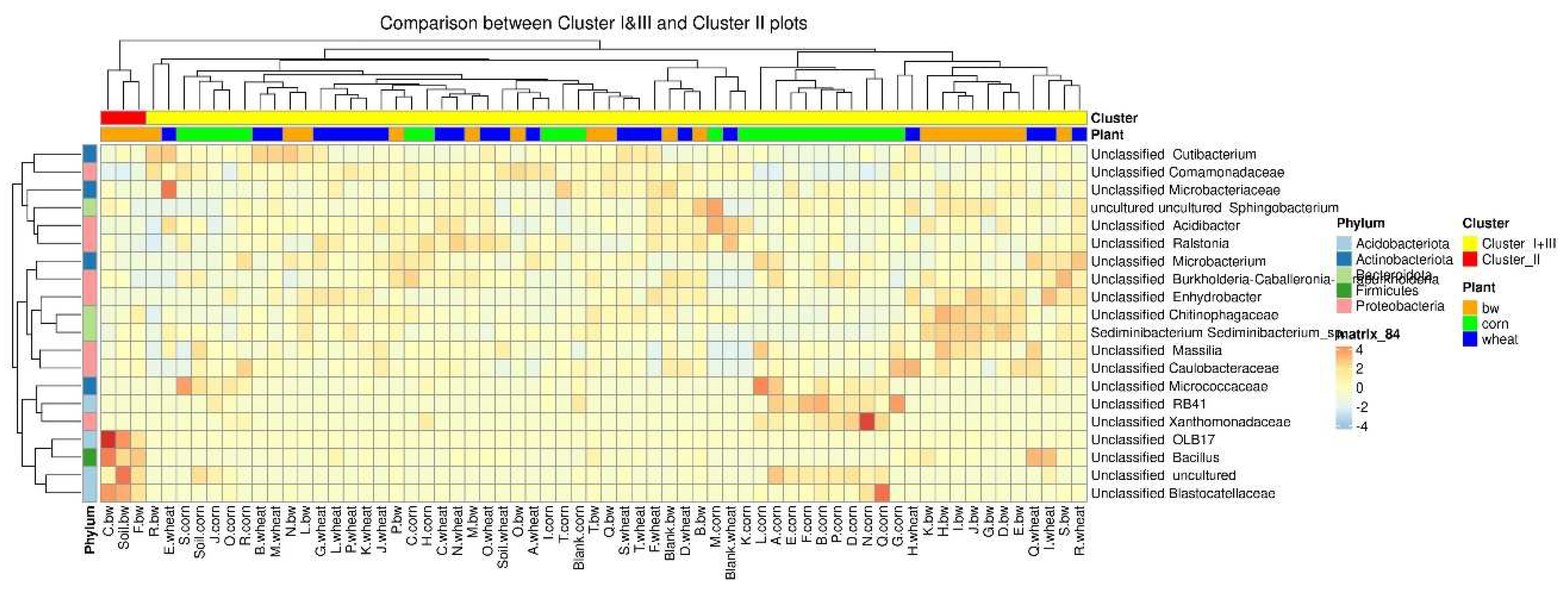
Histograms show the difference in the representation of bacteria between clusters at different levels of classification: phylum, class, order, and family. At the phylum level in the samples of Cluster 2, the amount of Proteobacteria was significantly reduced, while Firmicutes and Acidobacteriota were increased. At the class level in Cluster 2, the content of Bacilli was increased, and Gammaproteobacteria was reduced. At the level of orders in class 2, Bacillales was elevated, and at the level of the family – Bacillaceae was increased.
To estimate the differential abundance of taxa between the groups, a differential abundance analysis was carried out. Cluster 2, containing a sample of C.bw, and the union of Clusters 1 and 3 were initially taken as comparison groups (
Figure 8). In the heat map, the red square marks OTUs, the representation of which is significantly higher in this group compared to the rest. The samples of Cluster II 4 OTUs are more abundant:
Unclassified OBL17,
Unclassified Bacillus,
Unclassified Blastocatellaceae, and
Unclassified uncultured.
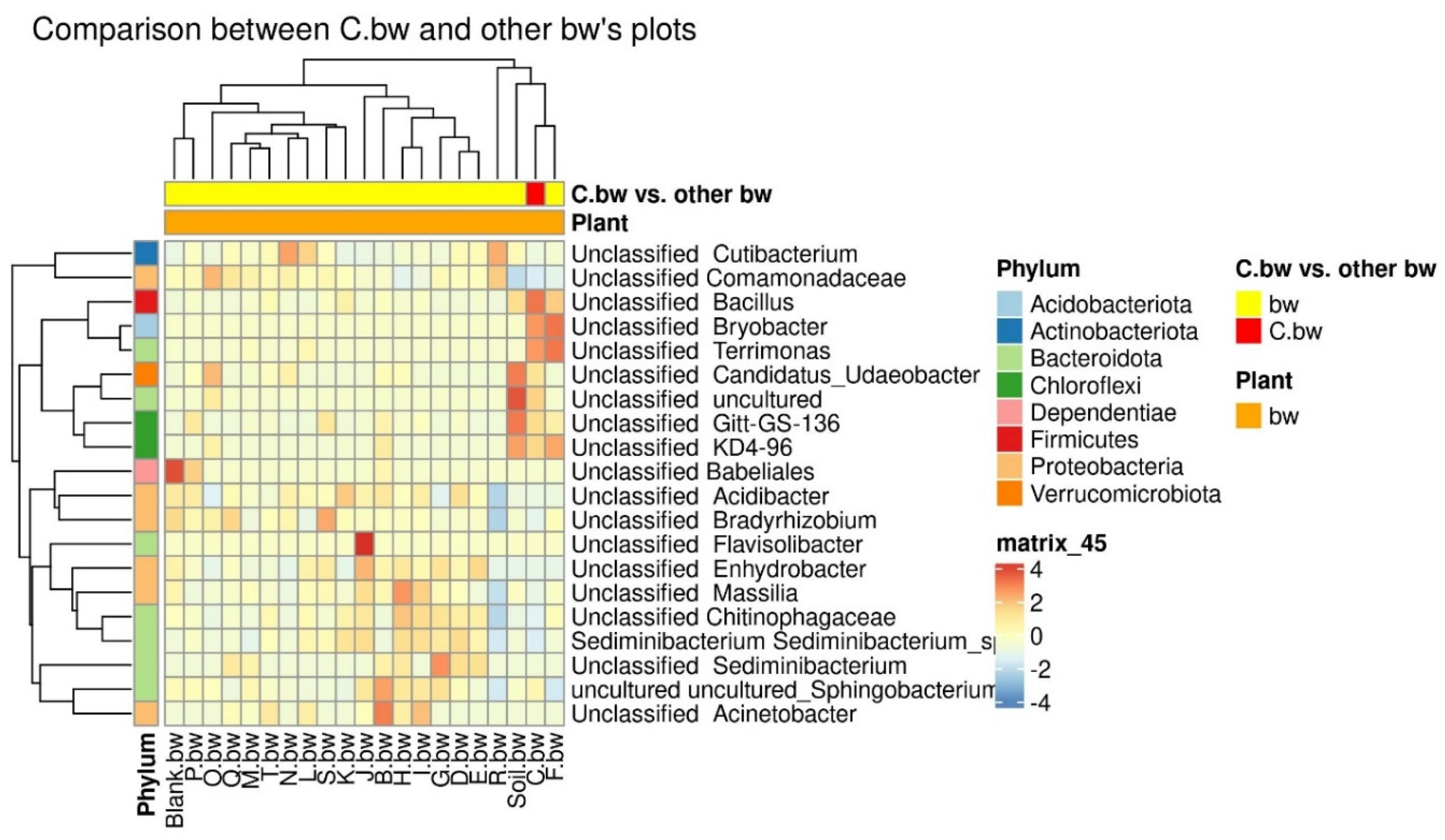
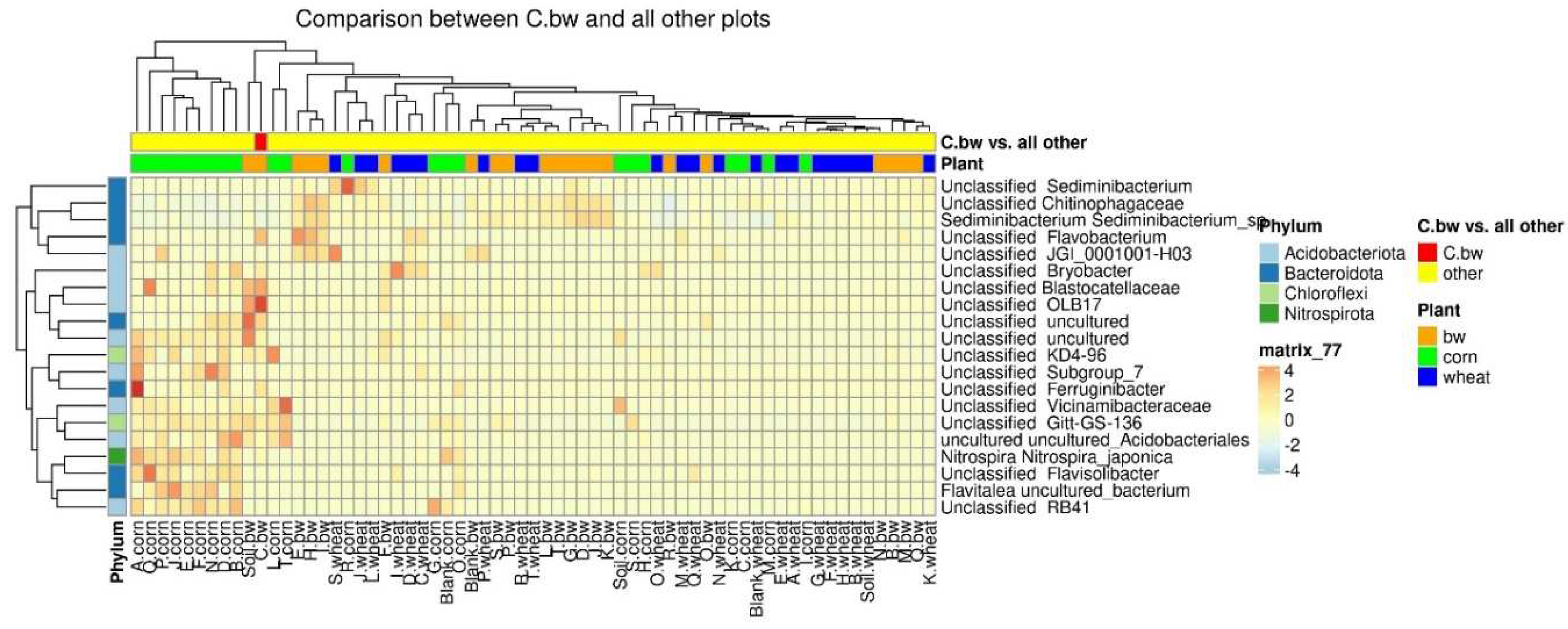
Due to the fact that the plants and the composition of the soil from the C.bw plot showed the highest agrotechnical indicators in this experiment, two comparisons were carried out: C.bw against all other samples (
Figure 9) and C.bw against all samples from plots with buckwheat (
Figure 10).
The results of the comparison confirmed the previously identified Unclassified OBL17 and Unclassified Bacillus.
Figure 10.
The heatmap of differentially abundant taxa between the C.bw sample and all other samples.
Figure 10.
The heatmap of differentially abundant taxa between the C.bw sample and all other samples.
The plot C.bw was distinguished from all other plots (except for F.bw) with buckwheat by Unclassified Bacillus (Firmicutes), Unclassified Bryobacter (Acidobacteriota), Unclassified Terrimonas (Bacteroidota). Also, the content of Unclassified Candidatus_Udaeobacter, Unclassified Gitt-GS-136, Unclassified KD4-96, and Unclassified uncultured was increased. It is noteworthy that an increased content of KD4-96 was detected for all three samples included in Cluster II (C.bw, F.bw, and Soil.bw).
Since Cluster 2 contained only samples from plots allocated for buckwheat, the available soil nutrients and carbon content were separately compared between only buckwheat plots, in order to neutralize the influence of different crops on soil nutrients (
Figure 11).
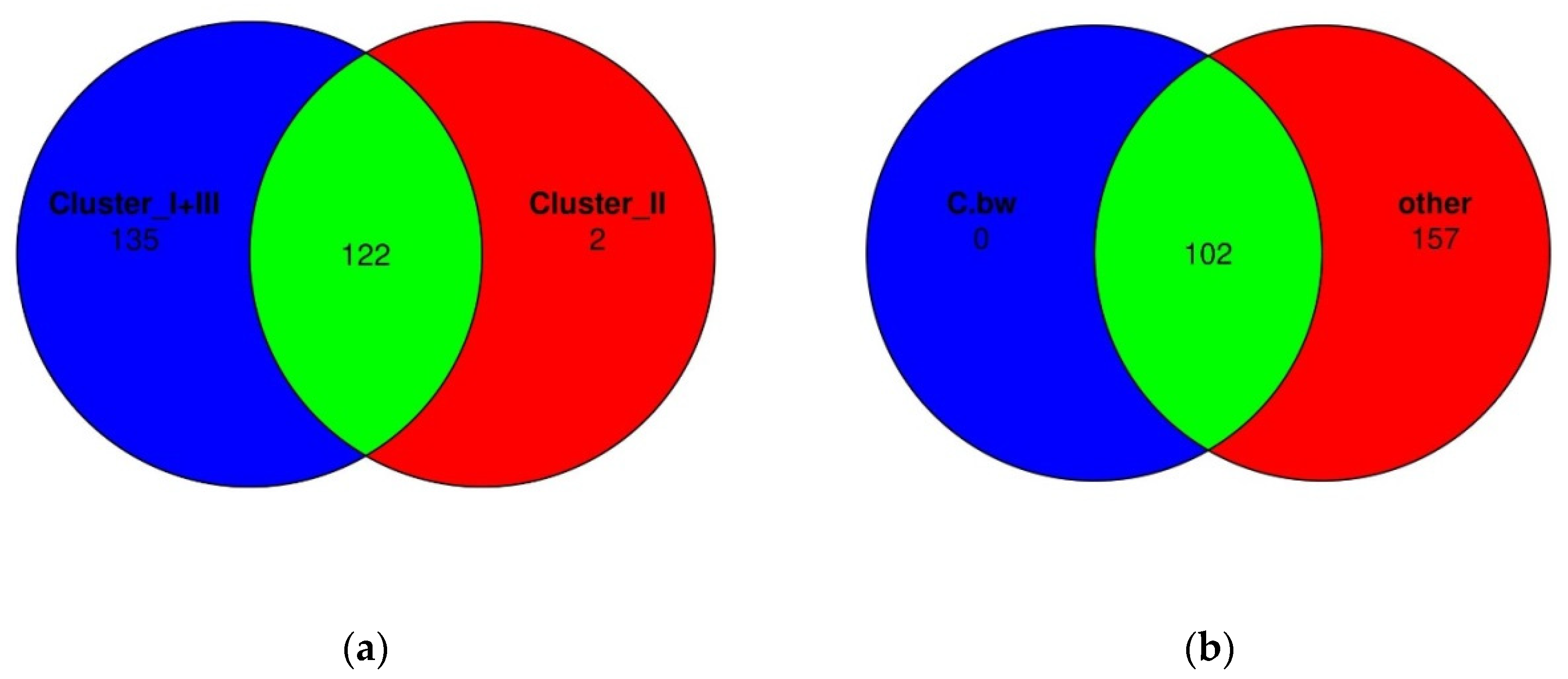
Finally, Venn diagrams were constructed in order to assess whether there were unique bacterial taxa in Cluster II or in the soil of the plot from C.bw (
Figure 12).
According to Venn diagrams, Cluster 2 had two unique OTUs. Both OTUs are defined to the family level, moreover, both belong to the same family: domain Bacteria, phylum Acidobacteriota, class Blastocatellia, order Blastocatellales, family Blastocatellaceae. Both OTUs are not unique to C.bw; they were identified in two samples C.bw and Soil.bw. Since the Soil.bw sample represents the soil microbiome before the experiment, it can be argued that these OTUs were likely present initially, and were preserved only in plot C.bw. Other taxa, which exhibited increased content in the soil sample of the C.bw plot, were likely present in the soil before planting. However, under the influence of external factors, these taxa gained a selective advantage in reproduction.
3. Discussion
Inoculation of seeds from important agricultural crops (wheat, buckwheat, corn) with bacterial consortia followed by cultivation in the open field, improved the agrotechnical indicators for buckwheat treated by Consortium C. While for other variants of the culture-consortium interaction, the agrotechnical indicators either did not differ from the control or exhibited variations in just one indicator, for the combination “Consortium C – buckwheat” there was a systemic positive improvement in all growth and yield indicators. The height of plants after six weeks (+23.4%), a large amount of grain from the plot (+19.6%, taking into account the fallen +49.2%), a more developed root system (weight of dry roots +152%) exceeded those of the control plants, the seeds of which were not inoculated with any bacterial consortia. The soil of the plot where the buckwheat inoculated by Consortium C grew contained significantly more (up to 10 times) available phosphorus than all other soil samples (
Figure 4).
Consortium C was based on the
Rothia endophytica GMG9 strain, which demonstrated in a laboratory experiment a high phosphate-immobilizing ability (248.3 µg/ml). An active nitrogen fixator, the strain
Azotobacter chroococcum GMG39, was also added to Consortium C. Interestingly, another Consortium H, created on the basis of the
Rothia endophytica GMG9 strain, but with the addition of a strain with high siderophore production and antifungicidal activity (
Enterobacter amnigenus GMG288), did not demonstrate an increase in available phosphates in the soil. Also, Consortia B, D, and E, which contained
Azotobacter chroococcum GMG39 in combination with other phosphate-immobilizing bacteria, did not show any effect on the availability of phosphates in the soil and buckwheat yield. Thus, it can be assumed that in Consortium C, one can observe a synergistic effect of the strains
Rothia endophytica GMG9 and
Azotobacter chroococcum GMG39. Previously, the synergistic effects of the use of nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-immobilizing bacteria strains have already been demonstrated, both on the content of macronutrients in plants and on their availability in the soil [
6,
7]. In most cases, it is discussed that phosphate mobilizers improve nitrogen fixation by increasing the availability of phosphates for the operation of nitrogenases or the development of the root system [
13]. At the same time, it is worth noting that this synergistic effect was present only when growing buckwheat and did not manifest itself in any way either when growing wheat or when growing corn. Initially, the species
Rothia endophytica was described as isolated from superficially sterilized roots of
Dysophylla stellata (Lour.) – a plant of the family of
Lamiaceae, used as medicinal in China [
14]. Perhaps this bacterium can interact with the roots of only some plant species and one can see the effect of a successful symbiosis of bacteria and plants. Unfortunately, plant root samples were not preserved in the work, and this issue requires further research.
Analyzing microbial diversity in the soils of experimental samples three months after inoculation, no strains that formed consortia were found. This suggests that when seeds are inoculated, the main effect is 1) the initial effect of bacteria embedded in the seed peel on the seedling, 2) modification of the habitat and subsequent changes in the composition of the soil microbiome. Hypothesis 1 does not explain a serious change in soil composition 3 months after sowing seeds treated by the consortium, so it was assumed that hypothesis 2 was the most likely.
Species richness of the soil microbial community (alpha diversity) was similar for all studied samples. Beta-diversity analysis revealed that the microbial diversity of three soil samples (C.bw, F.bw and Soil.bw) differed significantly from all others and were allocated to a separate cluster by NMDS in Cluster II.
At the phylum level, the number of Acidobacteriota and Firmicutes in samples from Cluster II was increased. This is consistent with the visualization of the results of comparing the union of Clusters I and III against Cluster II on the heatmap. Cluster II samples contain an increased amount of OTUs: Unclassified OBL17 (Acidobacteriota), Unclassified Blastocatellaceae (Acidobacteriota) and Unclassified uncultured (Acidobacteriota) and Unclassified Bacillus (Firmicutes). Moreover, according to the Venn diagram, Cluster II has two unique OTUs, both of which belong to the phylum Acidobacteriota, class Blastocatellia, order Blastocatellales, and family Blastocatellaceae.
Due to the difficulties of cultivation and laboratory maintenance, many classes of
Acidobacteriota contain a limited number of well-characterized representatives. Due to approaches to the identification of bacteria that exclude cultivation, new classes of
Acidobacteriota, called subdivisions (SDs), have been identified.
Unclassified OBL17 (Acidobacteriota) [
15] and
Unclassified Blastocatellaceae (Acidobacteriota) [
16] that distinguish Cluster II from the union of Clusters I and III in this study belong to the SD4 subtype. Lauber et al. revealed a clear correlation of the representation of Acidobacteria depending on the pH of the soil. Hartman et al. observed a strong increase in the abundance of Acidobacteria with lower pH. Their results reveal shifts in the composition of whole bacterial communities and the abundance of specific taxonomic groups with environmental gradients that may reflect changes in biogeochemical cycling [
17]. Despite there are no published data on soil acidity directly for
Unclassified OLB17 (Acidobacteriota) and
Unclassified Blastocatellaceae (Acidobacteriota), the fact that a very high value of available phosphorus was recorded for a soil sample C.bw indirectly indicates that the pH of this sample was acidic.
It is noteworthy that the sample F.bw also fell into Cluster II, but the plants from this plot did not show such high agrotechnical indicators, and the soil did not have a high content of available phosphorus. C.bw and Soil.bw, as opposed to F.bw, included unique OTUs belonging to the
Blastocatellaceae family. These bacteria are known as oligotrophic [
18], demonstrate a wide range of tolerance to pH and temperature [
19], and can participate in soil bioremediation [
20].
It is possible that this genus of bacteria present in the original soil is suppressed when planting cultivated plants, since they were not found in any other samples. At the same time, the introduction of consortium C into buckwheat preserved the conditions for the favorable existence of the family Blastocatellaceae. Perhaps this factor is the acidic pH of the soil, since in laboratory studies, the Rothia endophytica GMG9 strain has demonstrated a high ability to immobilize phosphates, which in turn is often due to acid production. Unfortunately, the family Blastocatellaceae is mainly represented by uncultivated bacteria, and it is difficult to delineate their functions in the soil. Based on available data, it can be assumed that representatives of this family can participate in the elimination of some substances from the soil that inhibit plant growth or the accompanying beneficial microflora. Considering this scenario, the bacteria introduced through inoculation might have a more enduring effect in such an environment.
It is interesting to note that the soil microbiome following the introduction of consortium C aligned with a soil sample taken from a plot where no crop was grown. This suggests that the addition of Consortium C potentially conserved the original microbial community of the soil. At the same time, the buckwheat harvest was higher than in all other plots. It can be assumed that the planted plant secretes some substances into the soil that modify the microbial community, adjusting it to the needs of the plant, but at the same time suppressing the growth of some important bacteria that help enrich the soil with nutrients. In the case of consortium C, the introduced bacteria either neutralized this action or "protected" the family Blastocatellaceae bacteria from it, which allowed them (or some other bacteria) to survive and further have a beneficial effect on the plant. This may also explain the specific manifestation of the consortium C effect only on buckwheat, since different plants most likely possess their own array of such metabolites.
Therefore, this study showed that under the conditions of natural gray forest soils, the introduction of consortia of bacteria beneficial to plants did not have a significant effect on the growth and yield of wheat, corn, and buckwheat. The only successful result (consortium C for buckwheat) showed that when selecting microorganisms for the creation of microbial fertilizers, it is important to take into account not only the characteristics of the soil but also the characteristics of the plant, which can affect the survival of beneficial bacteria in the rhizosphere. It was also shown that such a favorable result was associated with a significant increase in the availability of phosphates in the soil, which can be attributed both to the direct action of a consortium of phosphate-immobilizing and nitrogen-fixing bacteria and to acidification of the medium due to an increase in phylum Acidobacteriota bacteria in the soil. Analysis of the soil microbiota after the introduction of consortia showed that the addition of consortium C during buckwheat cultivation led to the preservation of the original soil microbiome. This preservation might be the cause behind the high yield in this plot, suggesting it could be another mechanism by which beneficial bacteria contribute to plant growth.