Submitted:
17 December 2023
Posted:
18 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
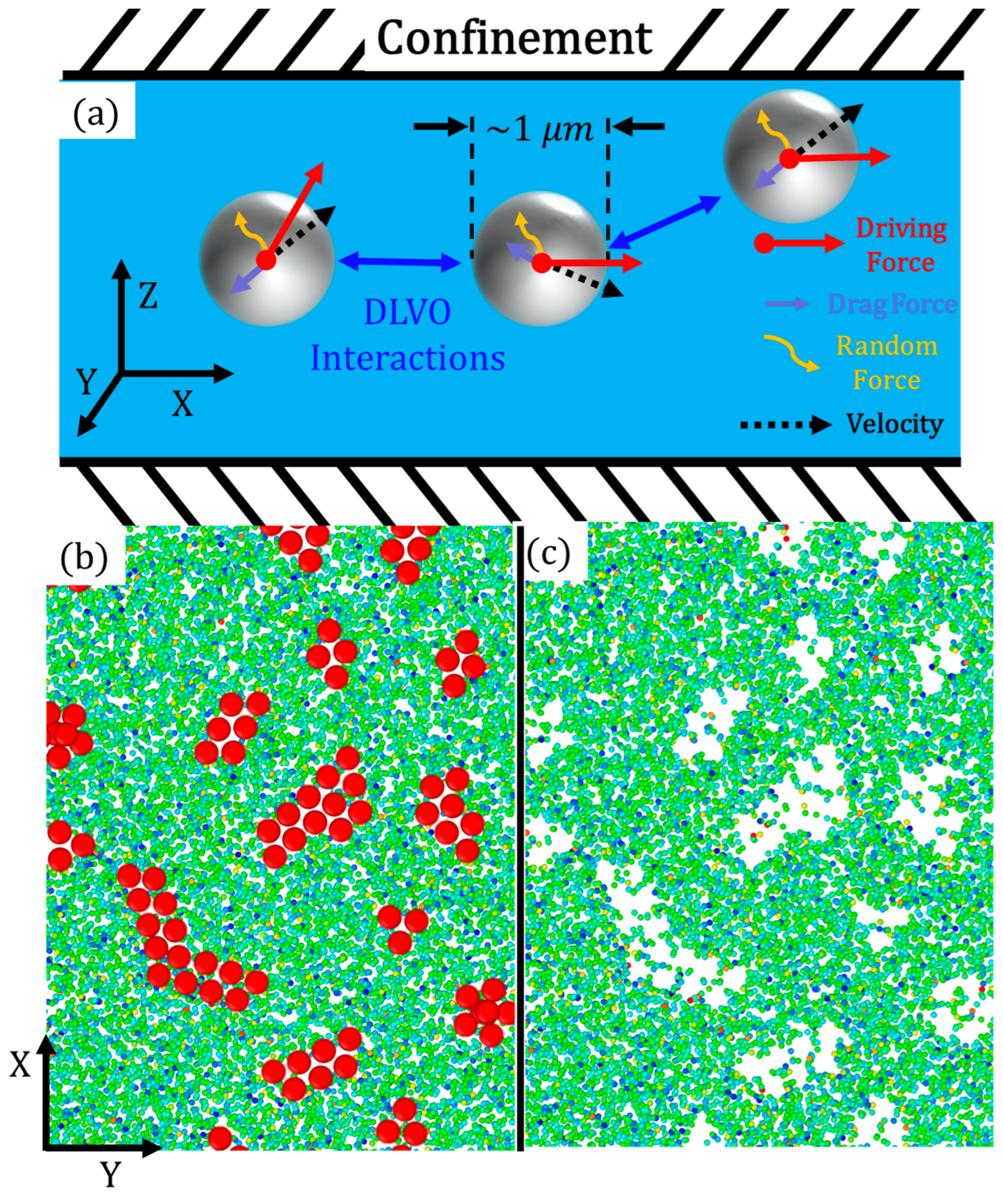
2. Methods and Models
2.1. SRD explicit hydrodynamic solvent
2.2. Coarse-grained molecular dynamic (CGMD) active particles and DLVO potential
3. Results and Discussion
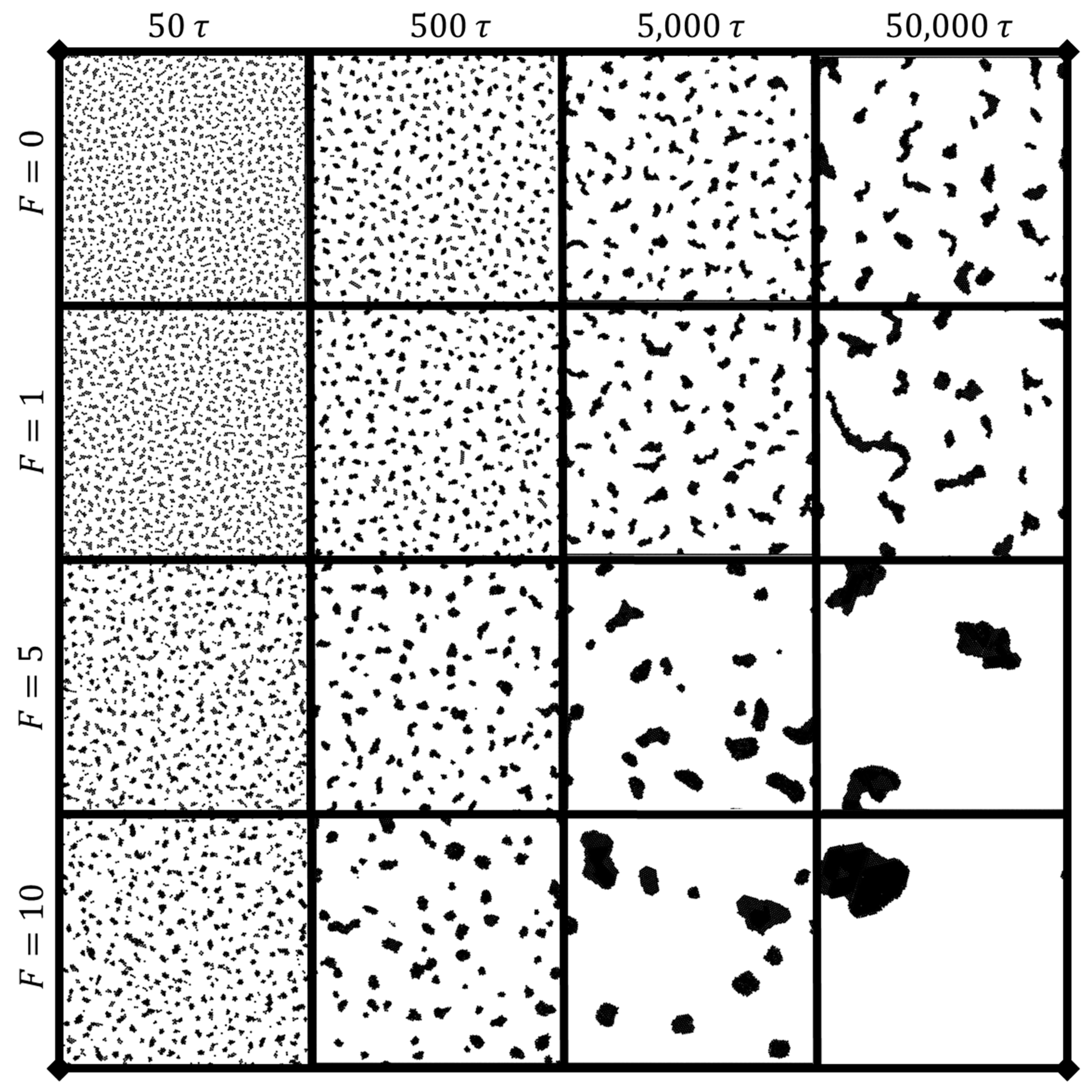
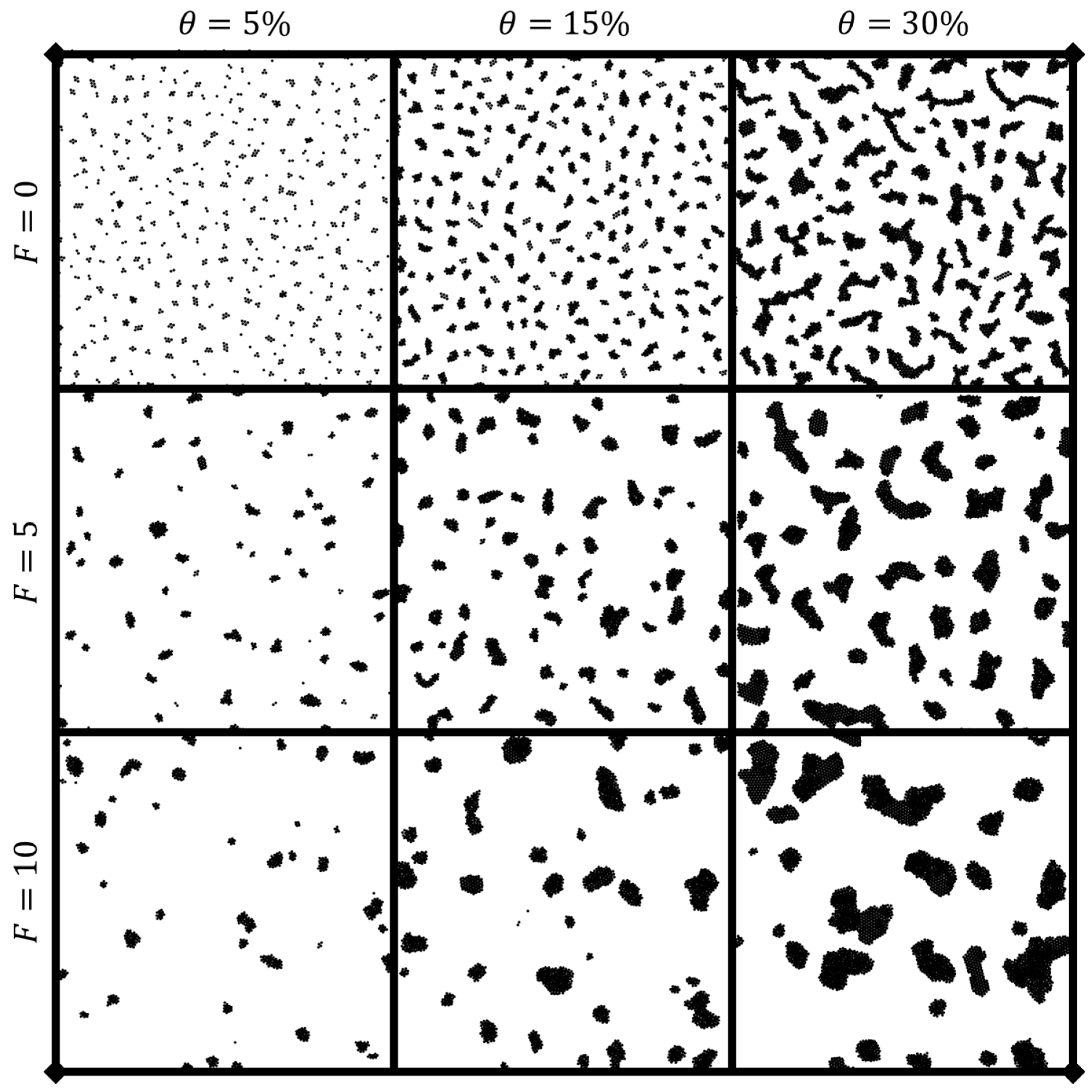
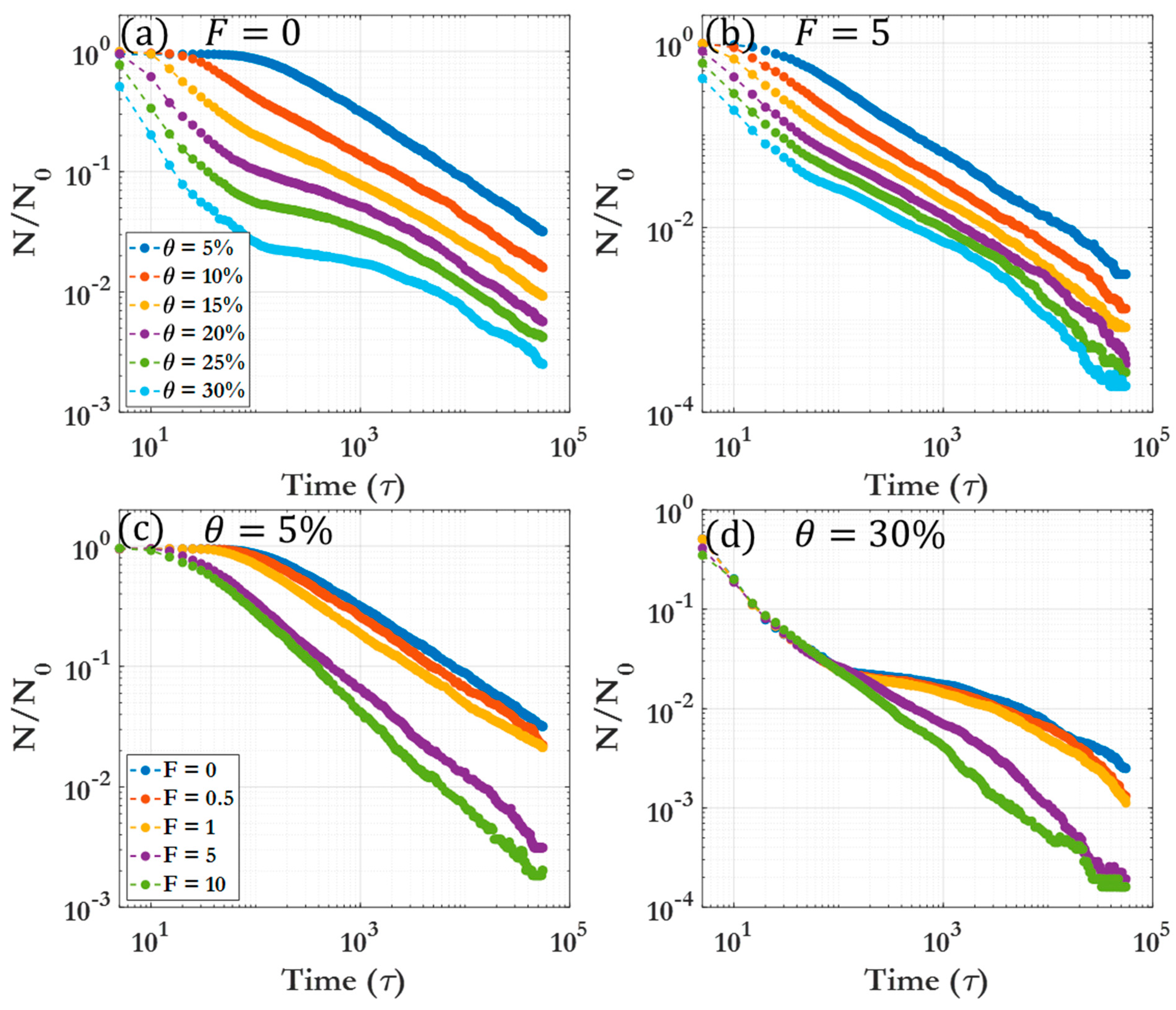
3.1. Dynamic clustering behavior
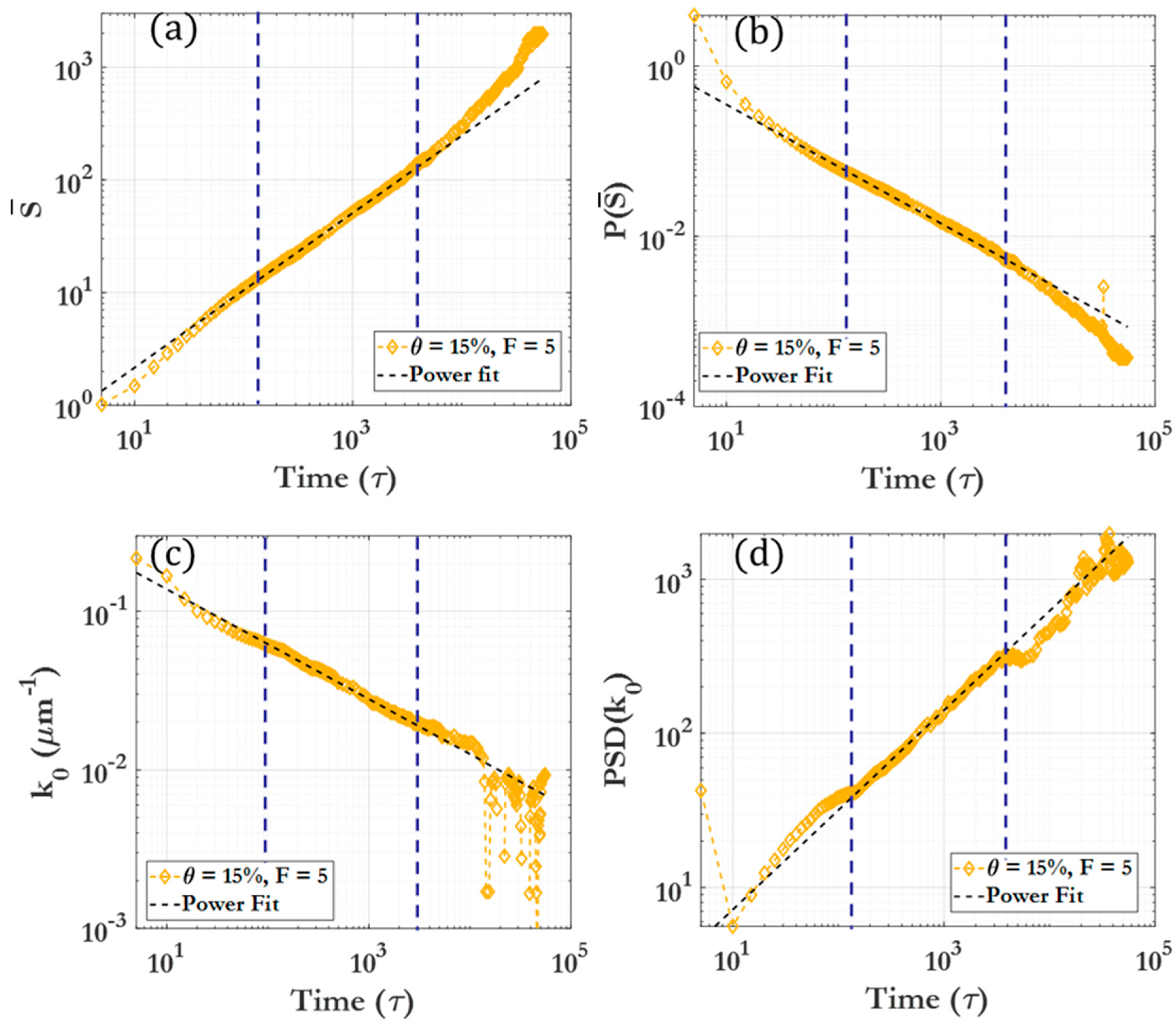
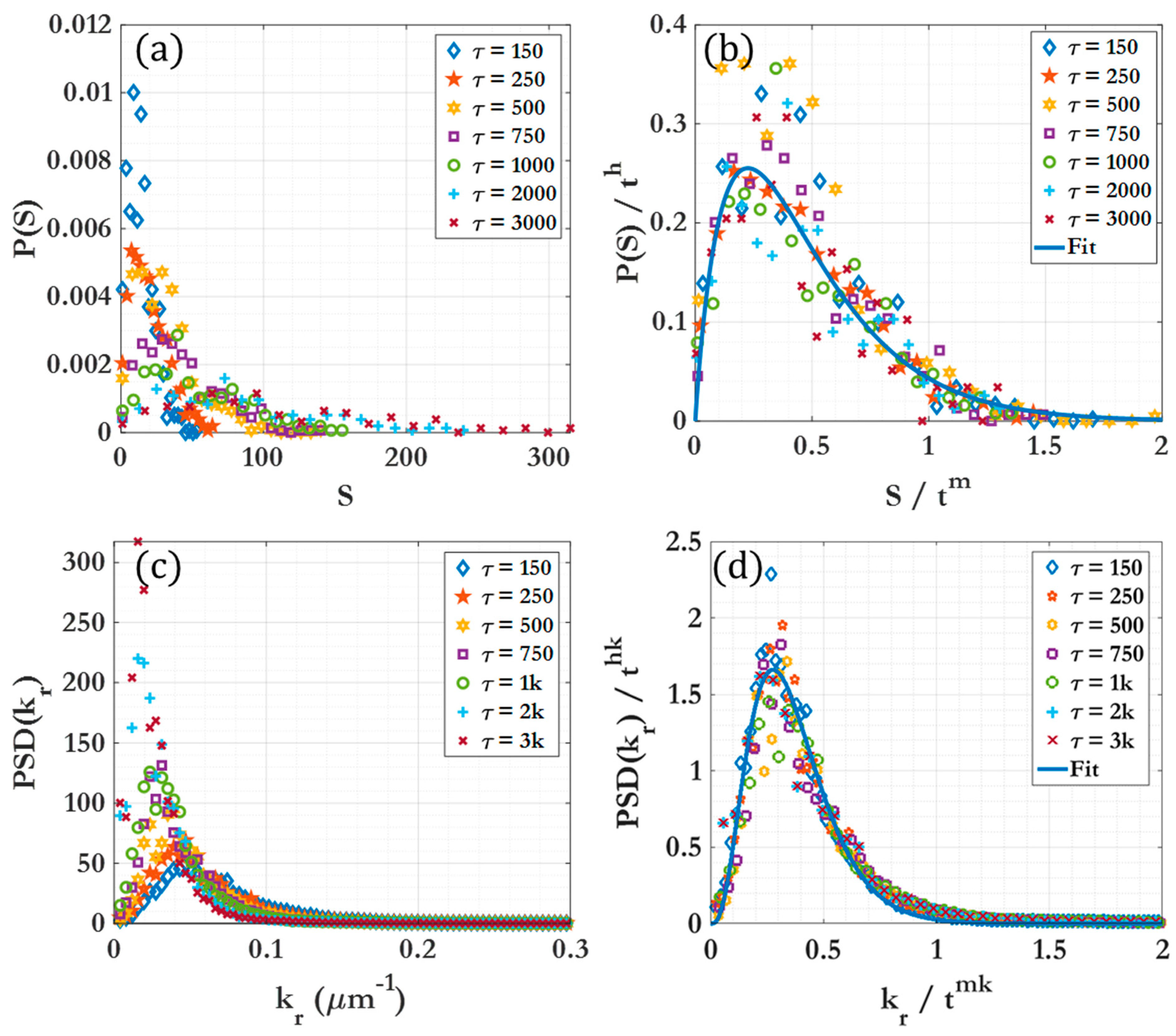
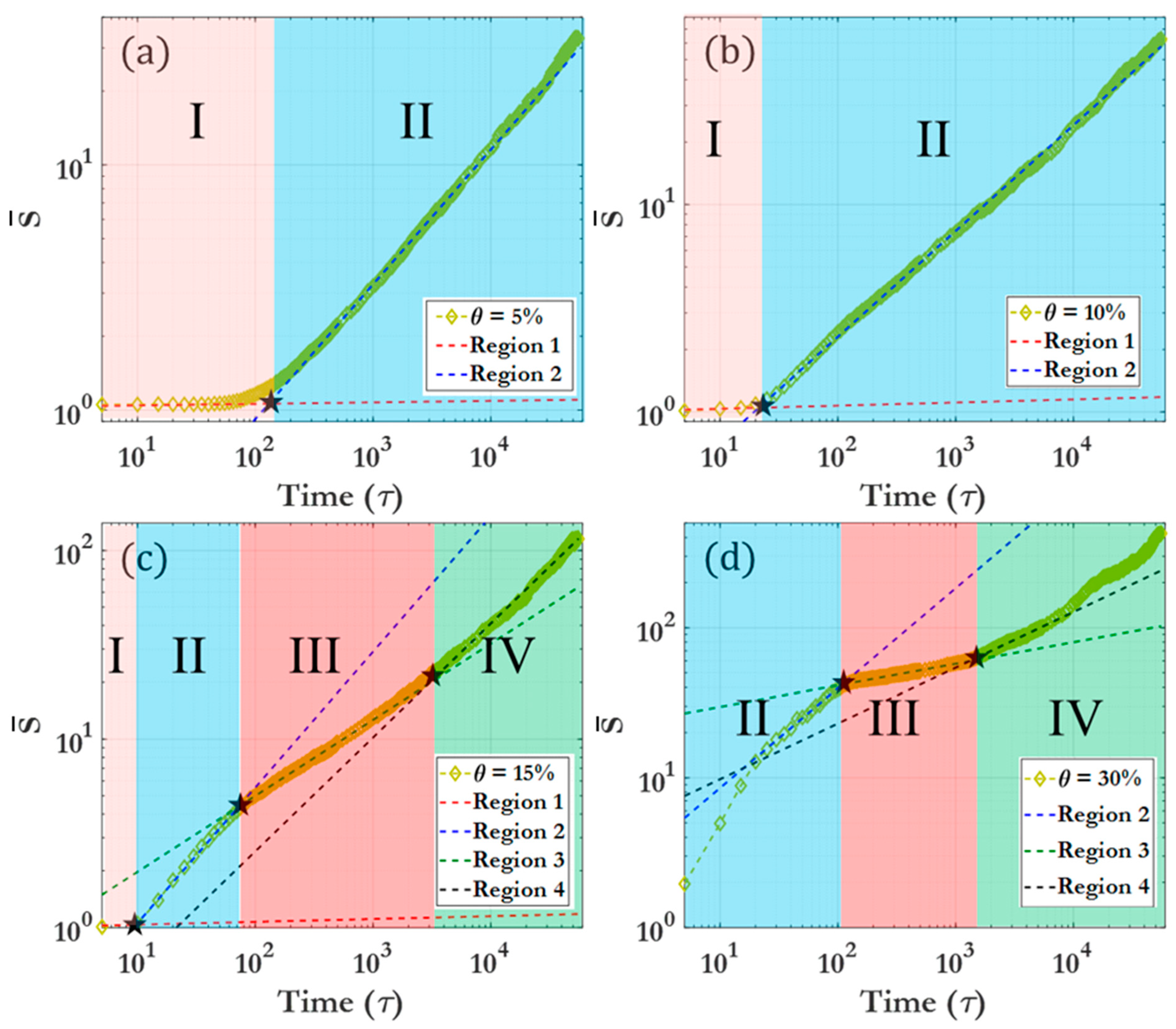
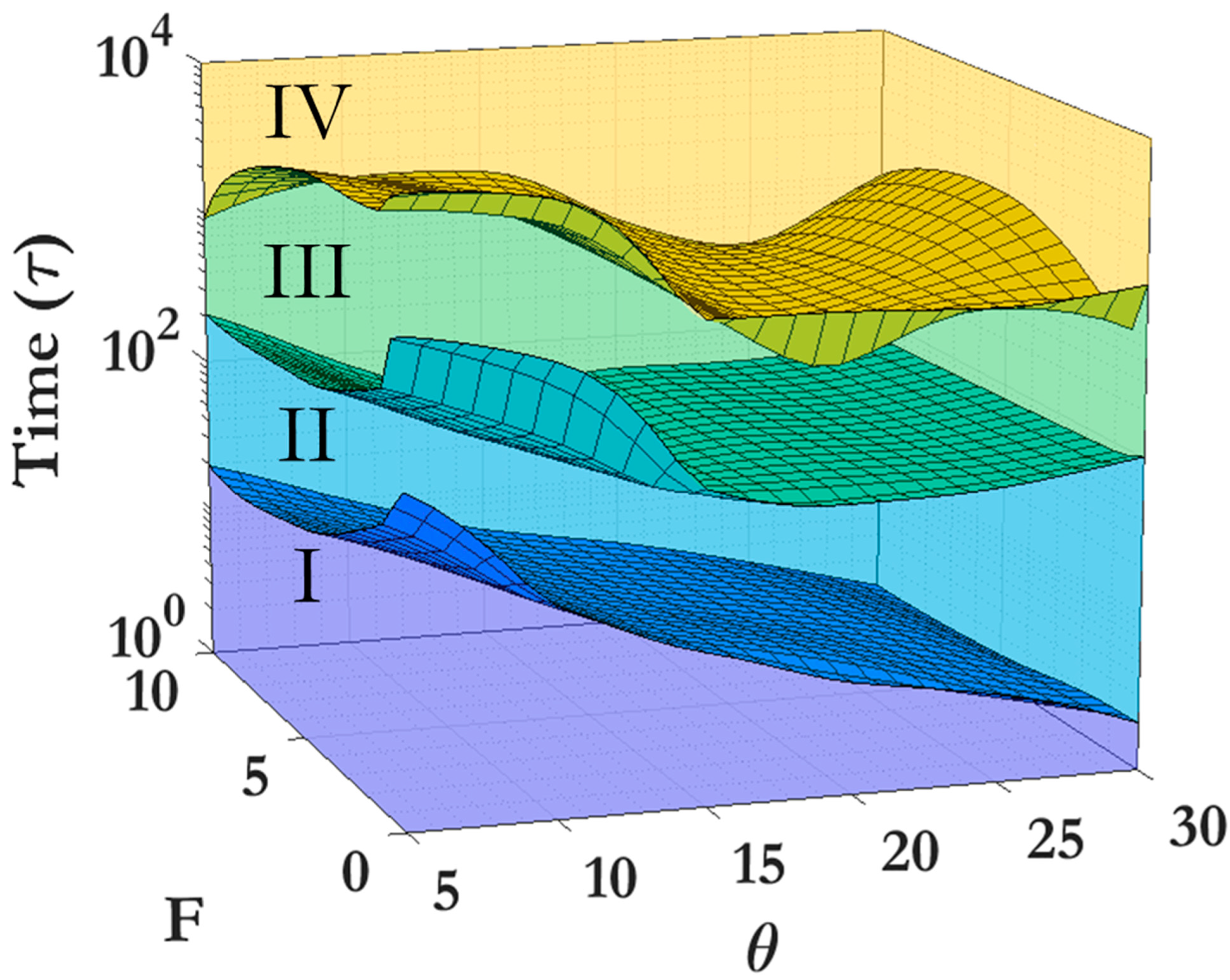
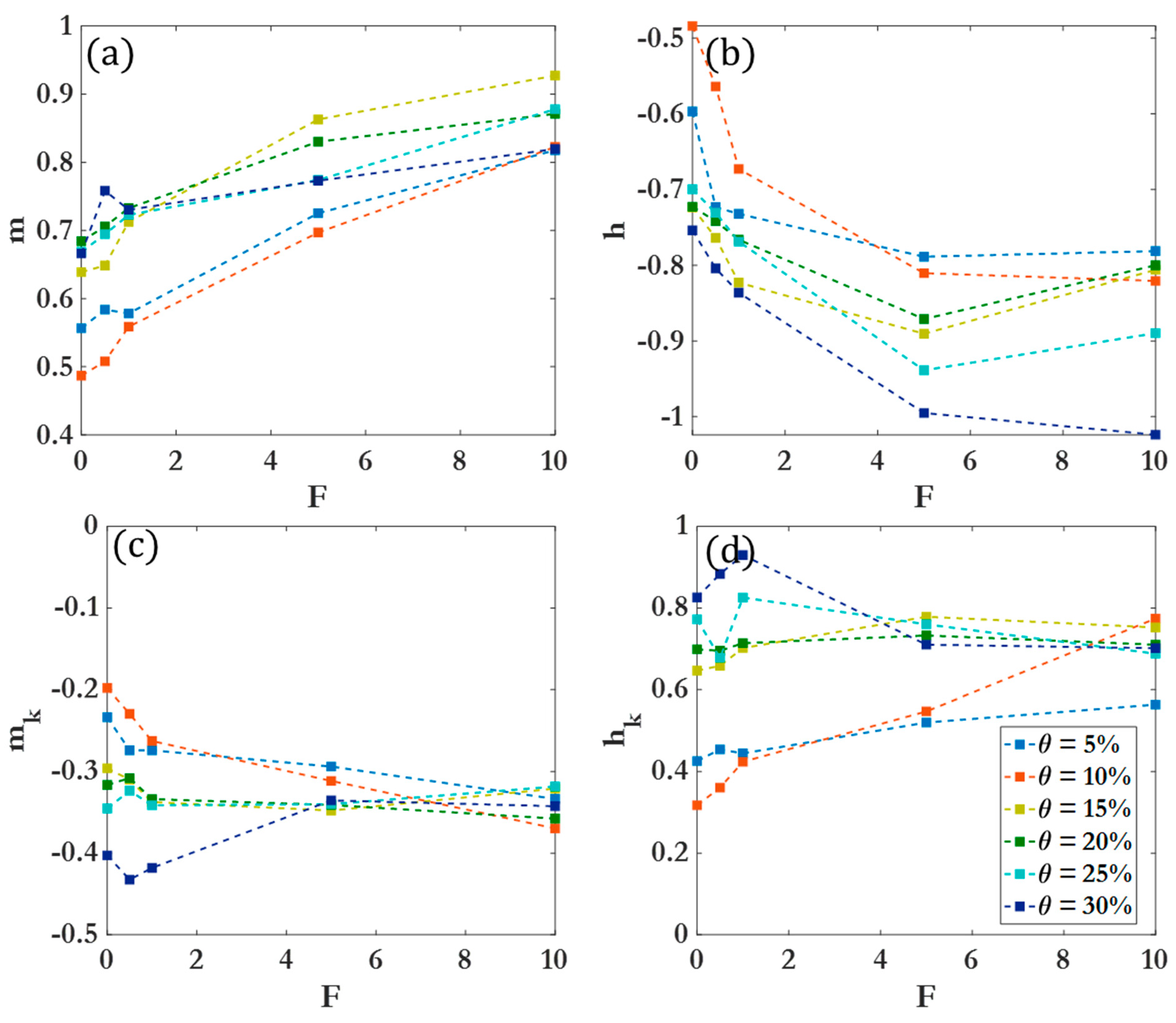
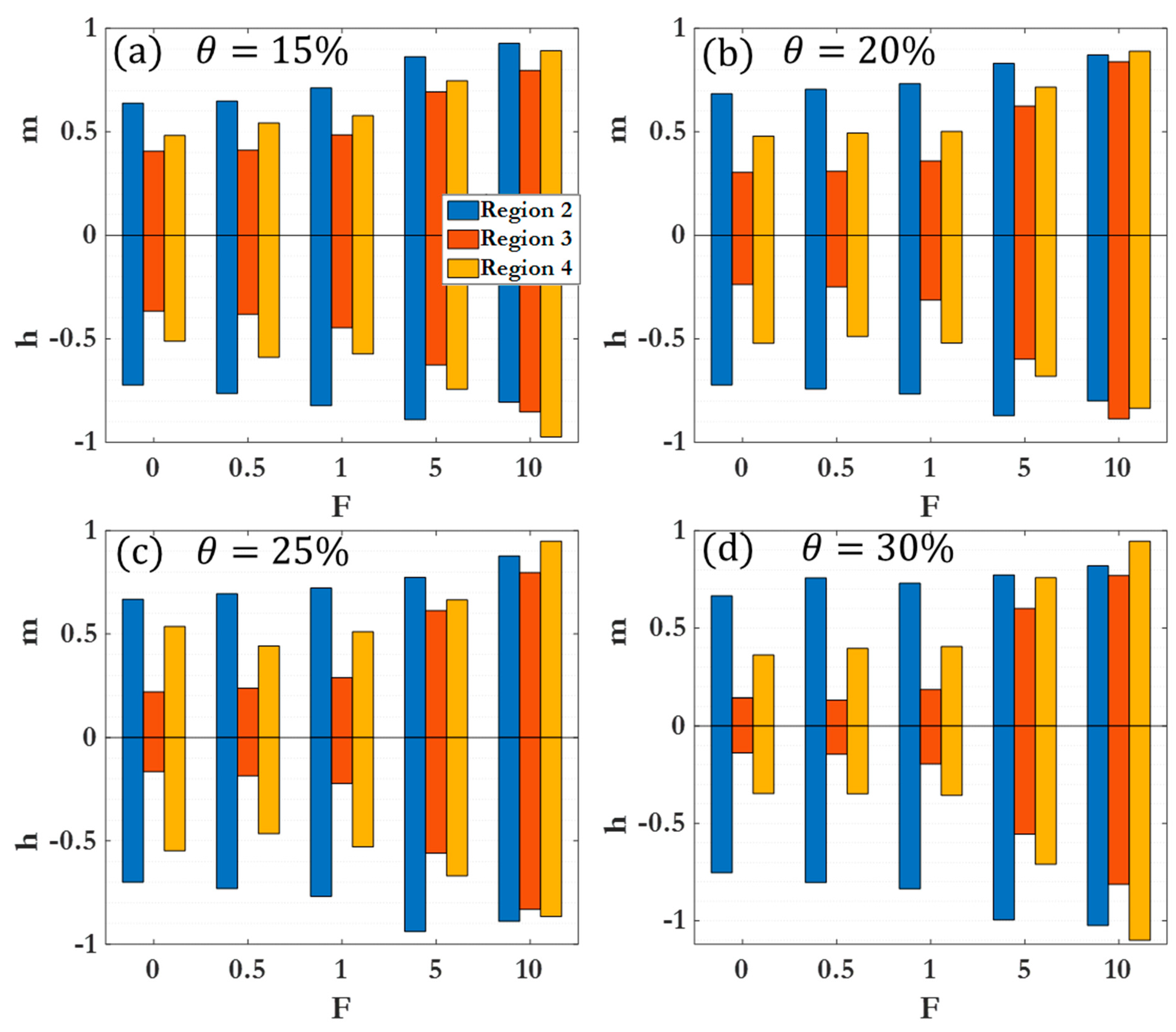
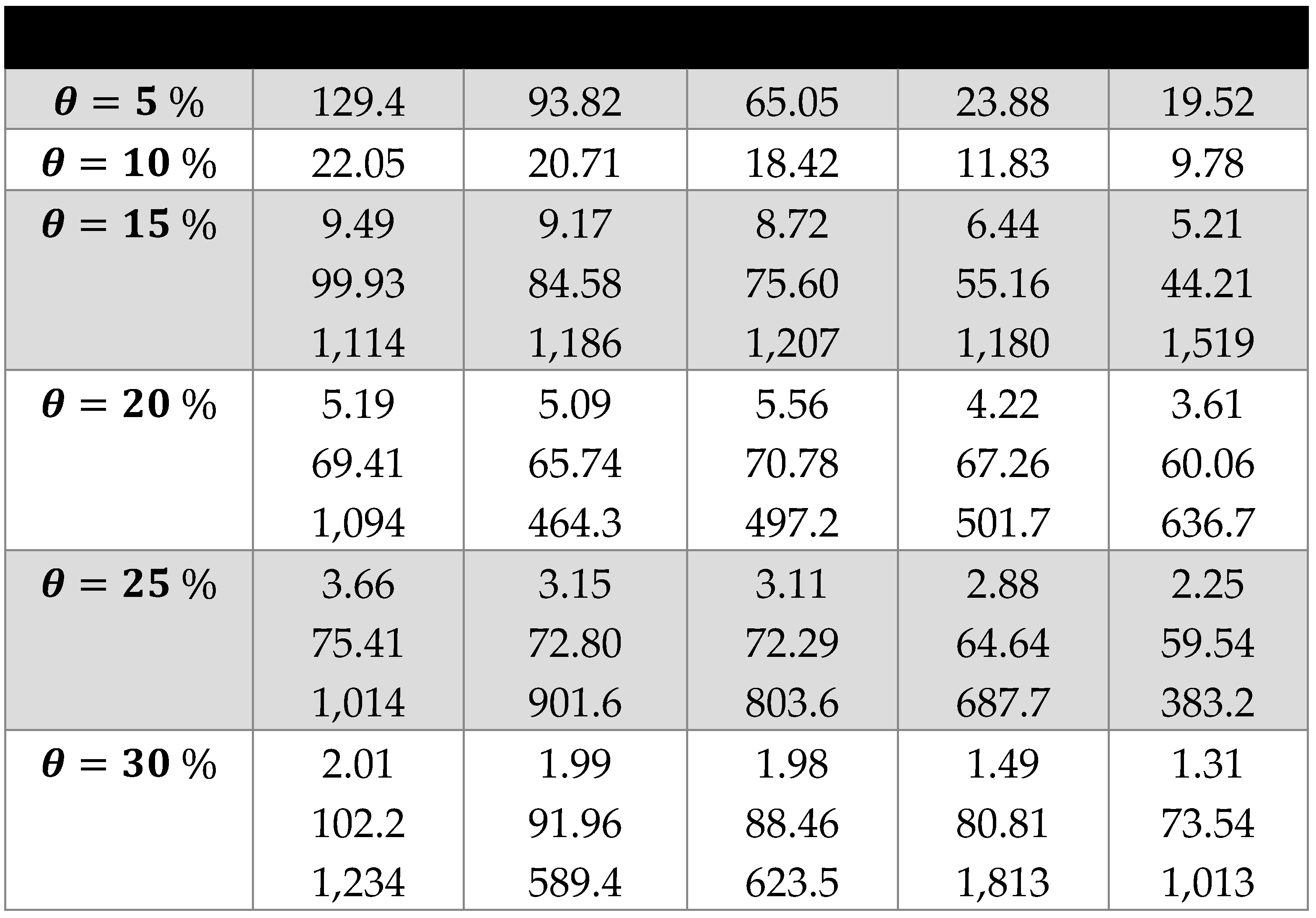
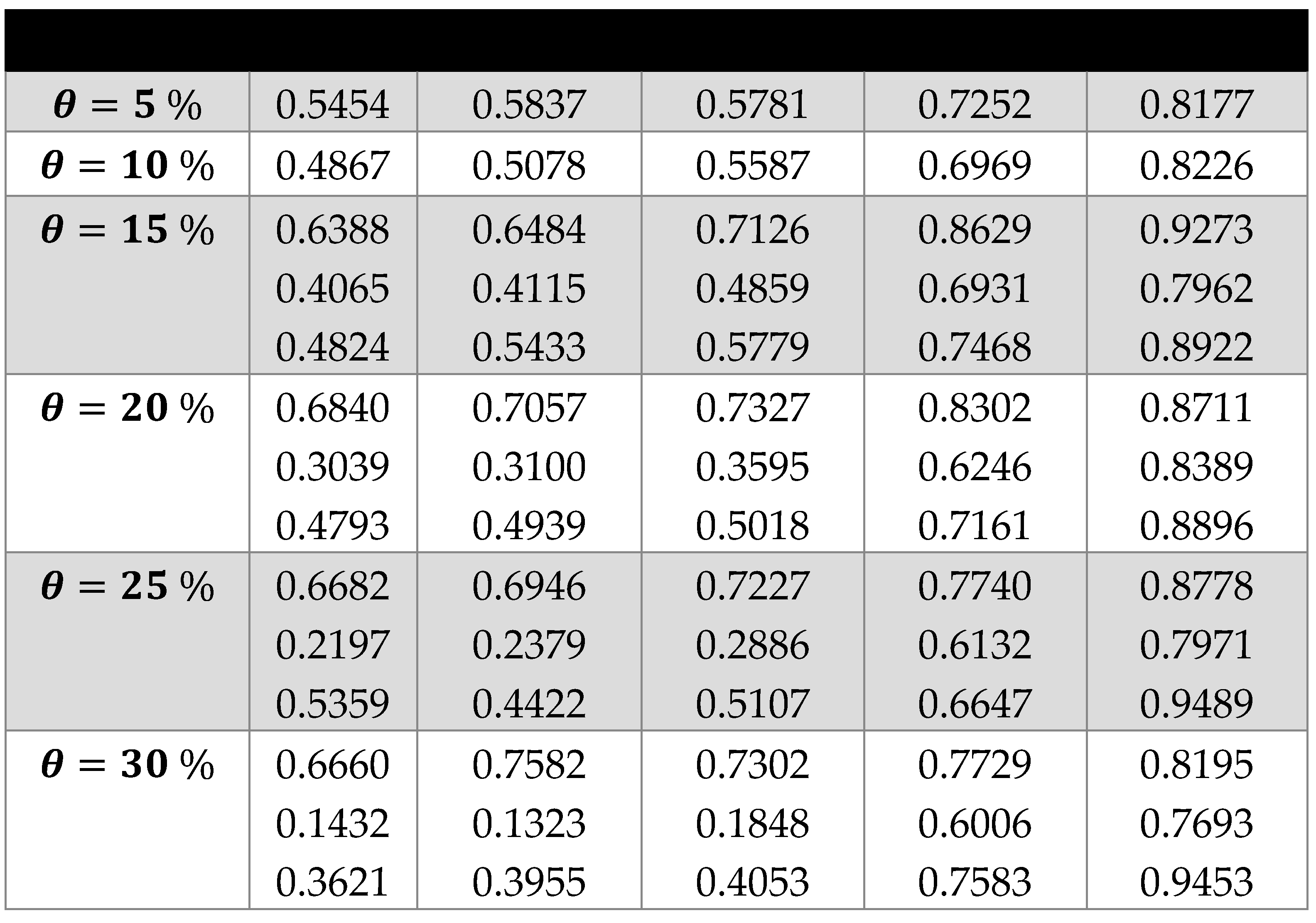
3.2. Scaling laws and relationships
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Cui, X.L.; Li, J.; Ng, D.H.L.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.N. 3D hierarchical ACFs-based micromotors as efficient photo-Fentonlike catalysts. Carbon 2020, 158, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Sanchez, B.; Pacheco, M.; Rojo, J.; Escarpa, A. Magnetocatalytic Graphene Quantum Dots Janus Micromotors for Bacterial Endotoxin Detection. Angew Chem Int Edit 2017, 56, 6957–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Avila, B.E.F.; Lopez-Ramirez, M.A.; Baez, D.F.; Jodra, A.; Singh, V.V.; Kaufmann, K.; Wang, J. Aptamer-Modified Graphene-Based Catalytic Micromotors: Off-On Fluorescent Detection of Ricin. Acs Sensors 2016, 1, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.J.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.R.; Bian, F.K.; Wang, Y.; Shi, K.Q.; Ye, F.F.; Zhao, Y.J. Stomatocyte structural color-barcode micromotors for multiplex assays. Natl Sci Rev 2020, 7, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mou, F.Z.; Chen, C.R.; You, M.; Yin, Y.X.; Xu, L.L.; Guan, J.G. Light-controlled bubble propulsion of amorphous TiO2/Au Janus micromotors. Rsc Adv 2016, 6, 10697–10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, D.; Jurado-Sanchez, B.; Escarpa, A. "Shoot and Sense" Janus Micromotors-Based Strategy for the Simultaneous Degradation and Detection of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Food and Biological Samples. Anal Chem 2016, 88, 4153–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Zhao, A.D.; Wang, F.M.; Ren, J.S.; Qu, X.G. Design of a plasmonic micromotor for enhanced photo-remediation of polluted anaerobic stagnant waters. Chem Commun 2016, 52, 5550–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delezuk, J.A.M.; Ramirez-Herrera, D.E.; de Avila, B.E.F.; Wang, J. Chitosan-based water-propelled micromotors with strong antibacterial activity. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2195–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Guix, M.; Schmidt, O.G. Wastewater Mediated Activation of Micromotors for Efficient Water Cleaning. Nano Lett 2016, 16, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wybieralska, K.; Wajda, A. Removal of organic dyes from aqueous solutions with surfactant-modified magnetic nanoparticles. Pol J Chem Technol 2014, 16, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Yeom, J. Pollutant-Degrading Multifunctional Micromotors. Int Conf Nano Micro 2017, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.S.; Gong, J.Y.; Oh, D.S.; Jeon, J.R.; Chang, Y.S. Zerovalent-Iron/Platinum Janus Micromotors with Spatially Separated Functionalities for Efficient Water Decontamination. Acs Appl Nano Mater 2018, 1, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygun, M.; Singh, V.V.; Kaufmann, K.; Uygun, D.A.; de Oliveira, S.D.S.; Wang, J. Micromotor-Based Biomimetic Carbon Dioxide Sequestration: Towards Mobile Microscrubbers. Angew Chem Int Edit 2015, 54, 12900–12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.V.; Wang, J. Nano/micromotors for security/defense applications. A review. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19377–19389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.V.; Martin, A.; Kaufmann, K.; de Oliveira, S.D.S.; Wang, J. Zirconia/Graphene Oxide Hybrid Micromotors for Selective Capture of Nerve Agents. Chem Mater 2015, 27, 8162–8169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.V.; Jurado-Sanchez, B.; Sattayasamitsathit, S.; Orozco, J.; Li, J.X.; Galarnyk, M.; Fedorak, Y.; Wang, J. Multifunctional Silver-Exchanged Zeolite Micromotors for Catalytic Detoxification of Chemical and Biological Threats. Adv Funct Mater 2015, 25, 2147–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.V.; Kaufmann, K.; Orozco, J.; Li, J.X.; Galarnyk, M.; Arya, G.; Wang, J. Micromotor-based on-off fluorescence detection of sarin and soman simulants. Chem Commun 2015, 51, 11190–11193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Ajalloueian, F.; Boisen, A. Thread-Like Radical-Polymerization via Autonomously Propelled (TRAP) Bots. Adv Mater 2019, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.C.; Chen, C.R.; Li, J.X.; Lu, X.L.; Liang, Y.Y.; Zhou, D.K.; Wang, H.C.; Zhang, G.Y.; Li, T.L.; Wang, J.; et al. Motile Micropump Based on Synthetic Micromotors for Dynamic Micropatterning. Acs Appl Mater Inter 2019, 11, 28507–28514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.V.; Soto, F.; Kaufmann, K.; Wang, J. Micromotor-Based Energy Generation. Angew Chem Int Edit 2015, 54, 6896–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotariu, O.; Udrea, L.E.; Strachan, N.J.C.; Heys, S.D.; Schofield, A.C.; Gilbert, F.J.; Badescu, V. Studies of magnetic carrier particles capture for blood vessel embolization. J Optoelectron Adv M 2006, 8, 1758–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Udrea, L.E.; Rotariu, O.; Popa, M.I. Magnetic Support Nanoparticles for the Targeting of Drugs: Physical Characterization and Manipulation in Magnetic Field. Sci Study Res-Chem C 2006, 7, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Alexiou, C.; Tietze, R.; Schreiber, E.; Lyer, S. Nanomedicine. Bundesgesundheitsbla 2010, 53, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, R.; Tosi, G.; Grabrucker, A.M. Emerging Use of Nanotechnology in the Treatment of Neurological Disorders. Curr Pharm Design 2015, 21, 3111–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talelli, M.; Aires, A.; Marciello, M. Protein-modified Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Curr Org Chem 2016, 20, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.; Seo, K.D.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, B.C.; Kim, D.S. Recent advances in engineering microparticles and their nascent utilization in biomedical delivery and diagnostic applications. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 591–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karshalev, E.; de Avila, B.E.F.; Beltran-Gastelum, M.; Angsantikul, P.; Tang, S.S.; Mundaca-Uribe, R.; Zhang, F.Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.F.; Wang, J. Micromotor Pills as a Dynamic Oral Delivery Platform. Acs Nano 2018, 12, 8397–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, X.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, J.; Ng, D.H.L.; Yang, W.N.; Yang, J. 3D hierarchical tubular micromotors with highly selective recognition and capture for antibiotics. J Mater Chem A 2020, 8, 2809–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.R.; Guo, J.H.; Wang, Y.T.; Shao, C.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.J. Bioinspired Helical Micromotors as Dynamic Cell Microcarriers. Acs Appl Mater Inter 2020, 12, 16097–16103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.S.; Zhang, F.Y.; Gong, H.; Wei, F.N.; Zhuang, J.; Karshalev, E.; de Avila, B.E.F.; Huang, C.Y.; Zhou, Z.D.; Li, Z.X.; et al. Enzyme-powered Janus platelet cell robots for active and targeted drug delivery. Sci Robot 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.S.; Ma, L.; Xu, X.B. Recent progress on the design and fabrication of micromotors and their biomedical applications. Bio-Des Manuf 2018, 1, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.H.; Le, T.H.; Lin, Y.J.; Miao, Y.B.; Sung, I.T.; Tsai, W.B.; Chan, H.Y.; Lin, Z.H.; Sung, H.W. A self-powered battery-driven drug delivery device that can function as a micromotor and galvanically actuate localized payload release. Nano Energy 2019, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.L.; Brinkmann, M.; Pagonabarraga, I.; Seemann, R.; Fleury, J.B. Spatiotemporal control of cargo delivery performed by programmable self-propelled Janus droplets. Commun Phys-Uk 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yi, C.; Yang, S.S.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Du, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, B.F. A substrate-free graphene oxide-based micromotor for rapid adsorption of antibiotics. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4562–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.; Borrmann, P.; Tomanek, D. Targeted medication delivery using magnetic nanostructures. J Phys-Condens Mat 2007, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ji, F.; Ng, D.H.L.; Liu, J.; Bing, X.M.; Wang, P. Bioinspired Pt-free molecularly imprinted hydrogel-based magnetic Janus micromotors for temperature-responsive recognition and adsorption of erythromycin in water. Chem Eng J 2019, 369, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, R.; Lyer, S.; Schreiber, E.; Mann, J.; Durr, S.; Alexiou, C. Local Cancer Therapy with Magnetic Nanoparticles. Else Kroner Fresen S 2011, 2, 154. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.N.; Huang, S.W.; Zhu, L.; Huang, W.J.; Zhao, Y.P.; Jin, K.L.; ZhuGe, Q.C. Tissue Plasminogen Activator-Porous Magnetic Microrods for Targeted Thrombolytic Therapy after Ischemic Stroke. Acs Appl Mater Inter 2018, 10, 32988–32997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.M.; Fan, X.J.; Meng, X.H.; Song, J.M.; Chen, W.N.; Sun, L.N.; Xie, H. Magnetic biohybrid micromotors with high maneuverability for efficient drug loading and targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 18382–18392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridjonsson, E.O.; Seymour, J.D. Colloid particle transport in a microcapillary: NMR study of particle and suspending fluid dynamics. Chem Eng Sci 2016, 153, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udrea, L.E.; Strachan, N.J.C.; Badescu, V.; Rotariu, O. An in vitro study of magnetic particle targeting in small blood vessels. Phys Med Biol 2006, 51, 4869–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.W. Anomalous Diffusion of Active Brownian Particles in Crystalline Phases. Iop C Ser Earth Env 2019, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, E.; Nemoto, T.; Vaikuntanathan, S. Dissipation controls transport and phase transitions in active fluids: mobility, diffusion and biased ensembles. New J Phys 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, R.C.; Liao, G.J.; Klapp, S.H.L.; Hall, C.K. Clustering and phase separation in mixtures of dipolar and active particles. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 3779–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czirok, A.; Vicsek, T. Collective behavior of interacting self-propelled particles. Physica A 2000, 281, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, A.; Theraulaz, G.; Vicsek, T. Collective motion in biological systems. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehes, E.; Vicsek, T. Collective motion of cells: from experiments to models. Integr Biol-Uk 2014, 6, 831–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdinandy, B.; Ozogany, K.; Vicsek, T. Collective motion of groups of self-propelled particles following interacting leaders. Physica A 2017, 479, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czirok, A.; Vicsek, M.; Vicsek, T. Collective motion of organisms in three dimensions. Physica A 1999, 264, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czirok, A.; Barabasi, A.L.; Vicsek, T. Collective motion of self-propelled particles: Kinetic phase transition in one dimension. Phys Rev Lett 1999, 82, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, Z.M.; Swan, J.W. Transmutable Colloidal Crystals and Active Phase Separation via Dynamic, Directed Self-Assembly with Toggled External Fields. Acs Nano 2019, 13, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alapan, Y.; Yigit, B.; Beker, O.; Demirors, A.F.; Sitti, M. Shape-encoded dynamic assembly of mobile micromachines. Nat Mater 2019, 18, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soheilian, R.; Abdi, H.; Maloney, C.E.; Erb, R.M. Assembling particle clusters with incoherent 3D magnetic fields. J Colloid Interf Sci 2018, 513, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallory, S.A.; Valeriani, C.; Cacciuto, A. An Active Approach to Colloidal Self-Assembly. Annu Rev Phys Chem 2018, 69, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Wurger, A.; Lintuvuori, J.S. Hydrodynamic self-assembly of active colloids: chiral spinners and dynamic crystals. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 1508–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspard, P.; Kapral, R. Active Matter, Microreversibility, and Thermodynamics. Research-China 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Adhikari, R. Generalized Stokes laws for active colloids and their applications. J Phys Commun 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theurkauff, I.; Cottin-Bizonne, C.; Palacci, J.; Ybert, C.; Bocquet, L. Dynamic Clustering in Active Colloidal Suspensions with Chemical Signaling. Phys Rev Lett 2012, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskar, A.; Manna, R.K.; Shklyaev, O.E.; Balazs, A.C. Modeling the biomimetic self-organization of active objects in fluids. Nano Today 2019, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theers, M.; Westphal, E.; Qi, K.; Winkler, R.G.; Gompper, G. Clustering of microswimmers: interplay of shape and hydrodynamics. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 8590–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanso, E.; Michelin, S. Phoretic and hydrodynamic interactions of weakly confined autophoretic particles. J Chem Phys 2019, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, M.N.; Uspal, W.E.; Eskandari, Z.; Tasinkevych, M.; Dietrich, S. Effective squirmer models for self-phoretic chemically active spherical colloids. Eur Phys J E 2018, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuron, M.; Kreissl, P.; Holm, C. Toward Understanding of Self-Electrophoretic Propulsion under Realistic Conditions: From Bulk Reactions to Confinement Effects. Accounts Chem Res 2018, 51, 2998–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, M.N.; Uspal, W.E.; Dominguez, A.; Dietrich, S. Effective Interactions between Chemically Active Colloids and Interfaces. Accounts Chem Res 2018, 51, 2991–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zottl, A.; Stark, H. Emergent behavior in active colloids. J Phys-Condens Mat 2016, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfau, J.B.; Molina, J.; Sano, M. Collective behavior of strongly confined suspensions of squirmers. Epl-Europhys Lett 2016, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thutupalli, S.; Geyer, D.; Singh, R.; Adhikari, R.; Stone, H.A. Flow-induced phase separation of active particles is controlled by boundary conditions. P Natl Acad Sci USA 2018, 115, 5403–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theillard, M.; Alonso-Matilla, R.; Saintillan, D. Geometric control of active collective motion. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lai, W.J.; Wu, J.Y.; Gao, Y.X. Phoretic self-assembly of active colloidal molecules*. Chinese Phys B 2021, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, R.; Golestanian, R. Self-Assembly of Catalytically Active Colloidal Molecules: Tailoring Activity Through Surface Chemistry. Phys Rev Lett 2014, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, J.; Granick, S. Directed Self-Assembly Pathways of Active Colloidal Clusters. Angew Chem Int Edit 2016, 55, 5166–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbens, S.J.; Gregory, D.A. Catalytic Janus Colloids: Controlling Trajectories of Chemical Microswimmers. Accounts Chem Res 2018, 51, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, H.; Atzberger, P.J. Fluctuating hydrodynamic methods for fluid-structure interactions in confined channel geometries. Appl Math Mech-Engl 2018, 39, 125–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luijten, E.; Grzybowski, B.A.; Granick, S. Active colloids with collective mobility status and research opportunities. Chem Soc Rev 2017, 46, 5551–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaebani, M.R.; Wysocki, A.; Winkler, R.G.; Gompper, G.; Rieger, H. Computational models for active matter. Nat Rev Phys 2020, 2, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.; Winter, D.; Chaudhuri, P.; Statt, A.; Virnau, P.; Horbach, J.; Binder, K. Computer simulations of structure, dynamics, and phase behavior of colloidal fluids in confined geometry and under shear. Eur Phys J-Spec Top 2013, 222, 2787–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, A.M.; Voigtmann, T. Microrheology of colloidal systems. J Phys-Condens Mat 2014, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierno, P. Recent advances in anisotropic magnetic colloids: realization, assembly and applications. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2014, 16, 23515–23528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, D.R.; Brady, J.F. Structure, diffusion and rheology of Brownian suspensions by Stokesian Dynamics simulation. J Fluid Mech 2000, 407, 167–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malevanets, A.; Kapral, R. Mesoscopic model for solvent dynamics. J Chem Phys 1999, 110, 8605–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P.R. Hoskins, D. P.R. Hoskins, D. Hardman, Three-dimensional imaging and computational modelling for estimation of wall stresses in arteries, Brit J Radiol, 82 (2009) S3-S17.
- Plimpton, S. Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-Range Molecular-Dynamics. J Comput Phys 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M.Y. Lin, H.M. M.Y. Lin, H.M. Lindsay, D.A. Weitz, R. Klein, R.C. Ball, P. Meakin, Universal Diffusion-Limited Colloid Aggregation, J Phys-Condens Mat, 2 (1990) 3093-3113.
- P. Meakin, Models for Colloidal Aggregation, Annual Review of Physical Chemistry, 39 (1988) 237-267.
- Bostrom, M.; Deniz, V.; Franks, G.V.; Ninham, B.W. Extended DLVO theory: Electrostatic and non-electrostatic forces in oxide suspensions. Adv Colloid Interfac 2006, 123, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M. Hecht, J. M. Hecht, J. Harting, T. Ihle, H.J. Herrmann, Simulation of claylike colloids, Phys Rev E, 72 (2005).
- Padding, J.T.; Louis, A.A. Interplay between hydrodynamic and Brownian fluctuations in sedimenting colloidal suspensions. Phys Rev E 2008, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amar, J.G.; Family, F.; Lam, P.M. Dynamic Scaling of the Island-Size Distribution and Percolation in a Model of Submonolayer Molecular-Beam Epitaxy. Phys Rev B 1994, 50, 8781–8797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, D.A.; Huang, J.S.; Lin, M.Y.; Sung, J. Dynamics of Diffusion-Limited Kinetic Aggregation. Phys Rev Lett 1984, 53, 1657–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





