Submitted:
13 December 2023
Posted:
14 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
| Abbreviation | Description | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3DQN | Double Dueling Deep Q Network | LTE | Long Term Evolution |
| 3GPP | 3rd Generation Partnership Program | MACEL | Multi-Agent Collaborative Environment Learning |
| 5G | 5th Generation | MAC | Medium Access Control |
| A3C | Asynchronous Actor Citric | MARL | Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning |
| AEC | Average Energy Constraint | MDP | Markov Decision Process |
| ASR-CUMS | Automated Slice Resource Control and Update Management System | MJDDPG | Multi-objective Joint Optimization-Oriented DDPG Algorithm |
| ARdeep | Adoptive Reliable Deep | MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| BT-MP-DQN | Beam-forming Control and Trajectory-Multi-Pass Deep Q Network | mmWAVE | Millimeter Wave |
| CA-MOEA | Clustering based Adoptive Multi Objective Evolutionary Algorithm | MOEA/D | A Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithm Based on Decomposition |
| CCSRL | Cluster-enabled Cooperative Scheduling based on Reinforcement Learning | MSA-LS | Mobile Service Amount based Link scheduling |
| CEPF | Context Aware Packet Forwarding | NGSIM | Next generation Simulation |
| CKF | Constant Kalman Filter | QAGR | Geographic Routing with Q-Learning |
| CSMA | Carrier Sense Multiple Access | QFHR | Q-learning and Fuzzy-based Hierarchical Routing Solution |
| DDPG | Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient | QLBR | Q-Learning based Load Balancing Routing |
| DFS | Depth First Search | QLFMOR | Q-Learning based Fuzzy Logic for Multi Objective Routing Algorithm |
| DGCIM | Dual Graph Coloring based Interference Management | QTAR | Q-Learning based Traffic Aware Routing |
| DQL | Deep Q-Learning | RRB | Radio Resource Block |
| DQN | Deep Q-Network | RRPV | Reinforcement Learning Routing Protocol for Vehicles |
| DRL | Deep Reinforcement Learning | SGD | Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| DRQN | Deep Recurrent Object Networks | SUMO | Simulation of Urban Mobility |
| EED | End-to-End Delay | SWIPT | Simultaneous Wireless and power Transfer |
| FANET | Flying Ad-hoc Network | UAS | Unmanned Aerial System |
| FLRLR | Fuzzy Logic Reinforcement Learning based Routing | UE | User Equipment |
| GCS | Ground Control Station | UCPA | UAV based Clustering and Positioning Protocol |
| GMM | Gaussian Mixture Model | URLLC | Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications |
| GPGC-RLF | Grouping Graph Coloring with Recursive Largest First | V2N | Vehicle-to-Network |
| GYGC | Greedy Graph Coloring | V2P | Vehicle-to-Pedestrian |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit | V2R | Vehicle-to-Roadside Infrastructure |
| iProPHET | Improved Probability Routing Protocol using History of Encounters and Transitivity | VANET | Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network |
| ITS | Intelligent Transport Systems | VEC | Vehicular Edge Computing |
| JTSM | Joint Time Series Modeling | VUE | Vehicle User Equipment |
| LBTO | Load Balancing and Task Offloading | WPT | Wireless Power Transfer |
| LIDAR | Light Detection and Ranging | WMMSE | Weighted Minimum Mean Square Error |
| LPA | Long Prediction Algorithm | WSN | Wireless Sensor Network |
2. Related Work and Survey Contribution
3. Overview of IoV and UAV Networks
3.1. IoV Communication Technologies
3.2. UAV
3.2.1. Components of UAV
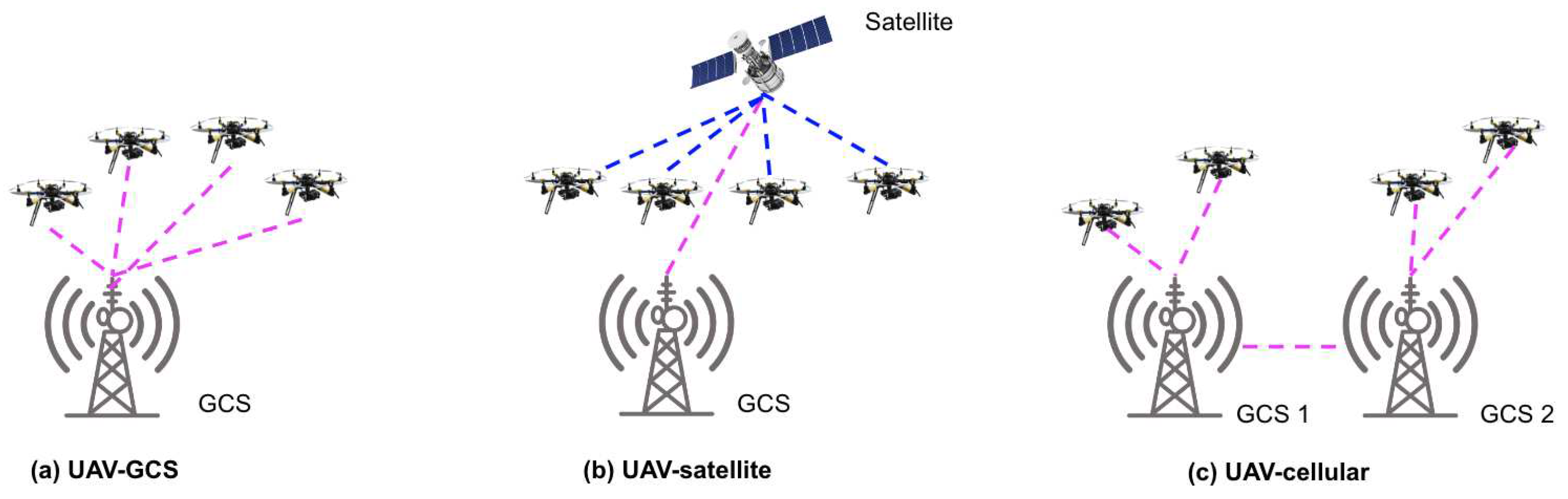
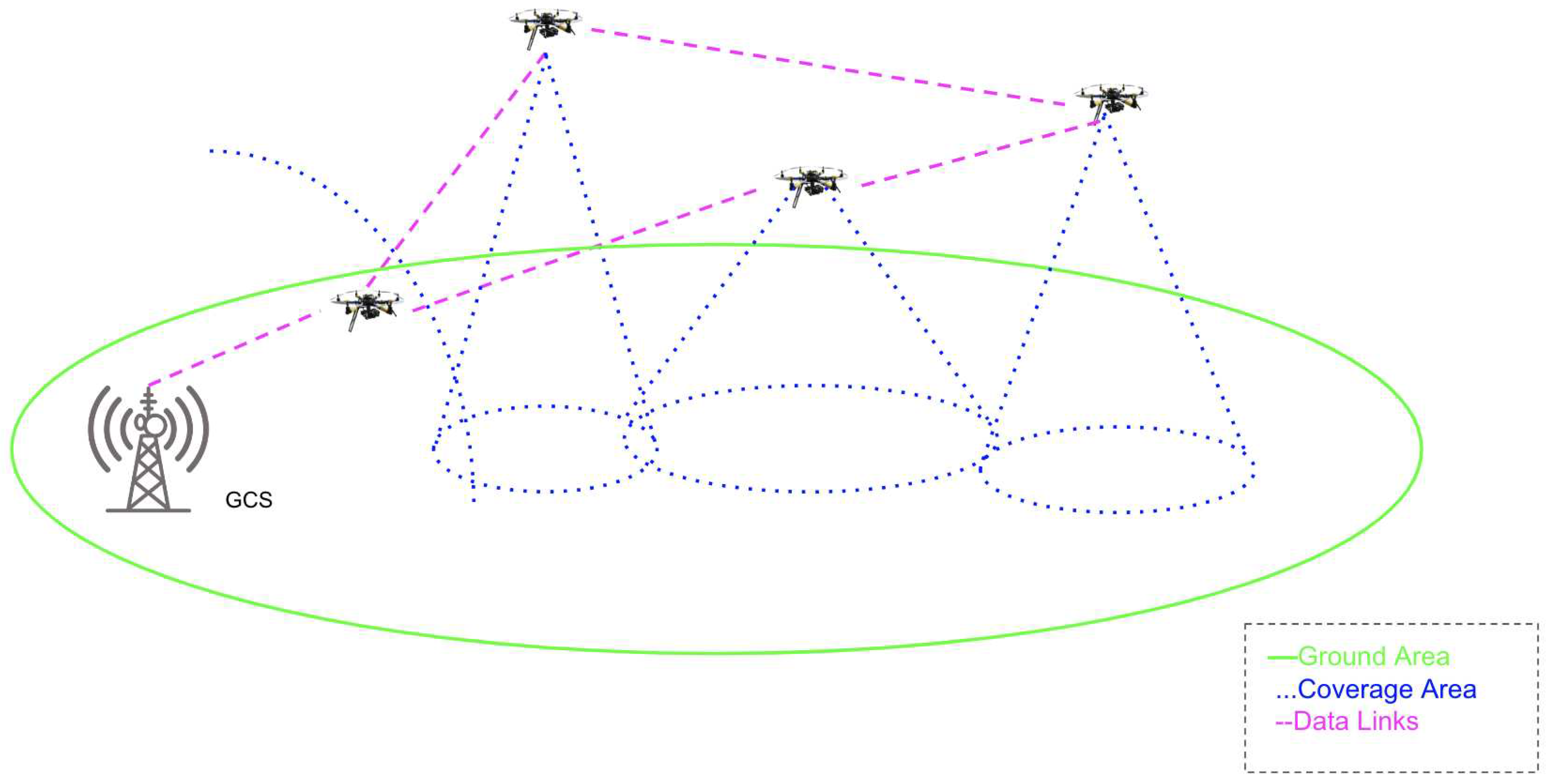
3.2.2. UAV Communication Architecture
4. AI based Resource Allocation in UAV and IoV Networks
4.1. AI for Resource Allocation in IoV Network
4.2. AI for Resource Allocation in UAV Network
4.3. AI for Resource Allocation in UAV-IoV Network
5. AI based Routing in UAV and IoV Networks
5.1. AI for Routing in IoV Network
5.2. AI for Routing in UAV Network
5.3. AI for Routing in UAV-IoV Network
6. Challenges and Open Issues with Future Directions
6.1. Major Limitations and Challenges of AI/ML
- Application Specific ML based models are application specific. It means if we train a DL model on certain vehicular application such as network data congestion prediction or classification, the model would be able to provide high quality results in same area, but it would not predict or classify the vehicular traffic congestion in a different area.
- Noisy and Incomplete Data: ML agents may have to deal with noisy and incomplete data, which can impact their learning and decision-making processes.
6.2. Testbed and Datasets
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashemi, S., and Zarei, M. (2021). "Internet of Things backdoors: resource management issues, security challenges, and detection methods". Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 32, e4142.
- Gillis, Alexander (2021). "What is internet of things (IoT)?". IOT Agenda. Retrieved 03 August 2023.
- Tang, C., Wei, X., Liu, C., Jiang, H., Wu, H., Li, Q. (2020). UAV-Enabled Social Internet of Vehicles: Roles, Security Issues and Use Cases. In: Xiang, Y., Liu, Z., Li, J. (eds) Security and Privacy in Social Networks and Big Data. SocialSec 2020. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1298. Springer, Singapore.
- Jamalzadeh, Melody, Mohsen Maadani, and Mojdeh Mahdavi. "EC-MOPSO: an edge computing-assisted hybrid cluster and MOPSO-based routing protocol for the Internet of Vehicles." Annals of Telecommunications 77.7-8 (2022): 491-503. [CrossRef]
- Krishna, M. "A Survey UAV-Assisted VANET Routing Protocol." International Journal of Computer Science Trends and Technology (IJCST)–Vol 8 (2020).
- Guerna, A.; Bitam, S.; Calafate, C.T. "Roadside Unit Deployment in Internet of Vehicles Systems: A Survey". Sensors 2022, 22, 3190. [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, T.M.; Hasan, M.K.; Alshurideh, M.T.; Alzoubi, H.M.; Ahmad, M.; Akbar, S.S.; Al Kurdi, B.; Akour, I.A. IoT for Smart Cities: Machine Learning Approaches in Smart Healthcare—A Review. Future Internet 2021, 13, 218. [CrossRef]
- S. Yaqoob, A. Ullah, M. Awais, I. Katib, A. Albeshri, R. Mehmood , et al . 2021. Novel congestion avoidance scheme for Internet of Drones. Computer Communications 169 (2021), 202–210. [CrossRef]
- Nina Mazyavkina, Sergey Sviridov, Sergei Ivanov, Evgeny Burnaev, Reinforcement learning for combinatorial optimization: A survey, Computers and Operations Research, Volume 134, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, M.; Ganeshkumar, P. Routing using reinforcement learning in vehicular ad hoc networks. Comput. Intell. 2020, 36, 682–697. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y., Lin, Y., Tang, Y. (2019). A Reinforcement Learning-Based Routing Protocol in VANETs. In: Liang, Q., Mu, J., Jia, M., Wang, W., Feng, X., Zhang, B. (eds) Communications, Signal Processing, and Systems. CSPS 2017. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 463.
- L. Liang, H. Ye and G. Y. Li, "Toward Intelligent Vehicular Networks: A Machine Learning Framework," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 124-135, Feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- W. Tong, A. Hussain, W. X. Bo and S. Maharjan, "Artificial Intelligence for Vehicle-to-Everything: A Survey," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 10823-10843, 2019. [CrossRef]
- F. Tang, Y. Kawamoto, N. Kato and J. Liu, "Future Intelligent and Secure Vehicular Network Toward 6G: Machine-Learning Approaches," in Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 108, no. 2, pp. 292-307, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. Tang, B. Mao, N. Kato and G. Gui, "Comprehensive Survey on Machine Learning in Vehicular Network: Technology, Applications and Challenges," in IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 2027-2057, thirdquarter 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Hossain, R. M. Noor, K. -L. A. Yau, S. R. Azzuhri, M. R. Z’aba and I. Ahmedy, "Comprehensive Survey of Machine Learning Approaches in Cognitive Radio-Based Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 78054-78108, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Z. Du, C. Wu, T. Yoshinaga, K. -L. A. Yau, Y. Ji and J. Li, "Federated Learning for Vehicular Internet of Things: Recent Advances and Open Issues," in IEEE Open Journal of the Computer Society, vol. 1, pp. 45-61, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Elmustafa Sayed Ali, Mohammad Kamrul Hasan, Rosilah Hassan, Rashid A. Saeed, Mona Bakri Hassan, Shayla Islam, Nazmus Shaker Nafi, Savitri Bevinakoppa, "Machine Learning Technologies for Secure Vehicular Communication in Internet of Vehicles: Recent Advances and Applications", Security and Communication Networks, vol. 2021, Article ID 8868355, 23 pages, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Nurcahyani, I.; Lee, J.W. Role of Machine Learning in Resource Allocation Strategy over Vehicular Networks: A Survey. Sensors 2021, 21, 6542. [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader Mekrache, Abbas Bradai, Emmanuel Moulay, Samir Dawaliby, Deep reinforcement learning techniques for vehicular networks: Recent advances and future trends towards 6G, Vehicular Communications, Volume 33, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Gillani, Maryam, Hafiz Adnan Niaz, and Muhammad Tayyab. "Role of machine learning in WSN and VANETs." International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering Research 1.1 (2021): 15-20.
- Abir Mchergui, Tarek Moulahi, Sherali Zeadally, Survey on Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques for Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs), Vehicular Communications, Volume 34, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Noor-A-Rahim, Z. Liu, H. Lee, G. G. M. N. Ali, D. Pesch and P. Xiao, "A Survey on Resource Allocation in Vehicular Networks," in IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 701-721, Feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Lansky, J.; Rahmani, A.M.; Hosseinzadeh, M. Reinforcement Learning-Based Routing Protocols in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks for Intelligent Transport System (ITS): A Survey. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4673. [CrossRef]
- Javed, A.R.; Hassan, M.A.; Shahzad, F.; Ahmed, W.; Singh, S.; Baker, T.; Gadekallu, T.R. Integration of Blockchain Technology and Federated Learning in Vehicular (IoT) Networks: A Comprehensive Survey. Sensors 2022, 22, 4394. [CrossRef]
- Maria Christopoulou, Sokratis Barmpounakis, Harilaos Koumaras, Alexandros Kaloxylos, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning as key enablers for V2X communications: A comprehensive survey, Vehicular Communications, Volume 39, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Atefeh Hemmati, Mani Zarei, Alireza Souri, UAV-based Internet of Vehicles: A systematic literature review, Intelligent Systems with Applications, Volume 18, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Arash Heidari, Nima Jafari Navimipour, Mehmet Unal, and Guodao Zhang. 2023. Machine Learning Applications in Internet-of-Drones: Systematic Review, Recent Deployments, and Open Issues. ACM Comput. Surv. 55, 12, Article 247 (December 2023), 45 pages. [CrossRef]
- "IEEE Draft Guide for Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments (WAVE) - Architecture," in IEEE P1609.0/D9, July 2017 , vol., no., pp.1-104, 14 July 2017.
- "IEEE Standard for Information Technology-Telecommunications and information exchange between systems-Local and Metropolitan networks-specific requirements-Part II: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) specifications: Amendment 9: Interworking with External Networks," in Amendment to IEEE Std 802.11-2007 as amended by IEEE Std 802.11k-2008, IEEE Std 802.11r-2008, IEEE Std 802.11y-2008, IEEE Std 802.11w-2009, IEEE Std 802.11n-2009, IEEE Std 802.11p-2010, IEEE Std 802.11z-2010, and IEEE Std 802.11v-2011 , vol., no., pp.1-208, 25 Feb. 2011. [CrossRef]
- J. Li, M. Shi, J. Li and D. Yao, "Media Access Process Modeling of LTE-V-Direct Communication Based on Markov Chain," 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Changshu, China, 2018, pp. 61-66. [CrossRef]
- L. U. Khan, “Visible light communication: Applications, architecture, standardization and research challenges,” Digit. Commun. Netw., vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 78-88, May 2017.
- N. Cen, J. Jagannath, S. Moretti, Z. Guan, and T. Melodia, "LANET:Visible-light ad hoc networks," Ad Hoc Netw., vol. 84, pp. 107-123, Mar. 2019. [CrossRef]
- G. Araniti, C. Campolo, M. Condoluci, A. Iera, and A. Molinaro, “LTE for vehicular networking: A survey,” IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 51, no. 5, pp. 148-157, May 2013. [CrossRef]
- J. Choi, V. Va, N. Gonzalez-Prelcic, R. Daniels, C. R. Bhat, and R. W. Heath, Jr., “Millimeter-wave vehicular communication to support massive automotive sensing,” IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 54, no. 12, pp. 160-167, Dec. 2016. [CrossRef]
- V. Va, T. Shimizu, G. Bansal, and R. W. Heath, Jr., Millimeter Wave Vehicular Communications: A Survey. Hanover, MA, USA: Now, 2016.
- Apostolos (Tolis) Papathanassiou and Alexey Khoryaev, "Cellular V2X as the essential enabler of superior global connected transportation services,” IEEE 5G Tech Focus, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 1-2, Jun. 2017.
- PC5. Initial Cellular V2X Standard Completed. Accessed: Aug. 08, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.3gpp.org/news-events/3gpp-news/v2x-r14.
- S. Husain, A. Kunz, A. Prasad, E. Pateromichelakis, K. Samdanis and J. Song, "The Road to 5G V2X: Ultra-High Reliable Communications," 2018 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN), Paris, France, 2018, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- D. P. Moya Osorio et al., "Towards 6G-Enabled Internet of Vehicles: Security and Privacy," in IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, vol. 3, pp. 82-105, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Commission delegated regulation (EU) 2019/945, 2019, Official Journal of the European Union, 12th, Mar.2019, URL https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32019R0945.
- Altawy, Riham, and Amr M. Youssef. "Security, privacy, and safety aspects of civilian drones: A survey." ACM Transactions on Cyber-Physical Systems 1.2 (2016): 1-25.
- Villa, T.F.; Salimi, F.; Morton, K.; Morawska, L.; Gonzalez, F. Development and Validation of a UAV Based System for Air Pollution Measurements. Sensors 2016, 16, 2202. [CrossRef]
- Vasylenko M. P. "Telemetry System of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles" Electronics and control systems. (2018) 95-100.
- Chao, H., Cao, Y. and Chen, Y. Autopilots for small unmanned aerial vehicles: A survey. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 8, 36–44 (2010). [CrossRef]
- F. Hoflinger, J. Muller, R. Zhang, L. M. Reindl and W. Burgard, "A Wireless Micro Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)," in IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, vol. 62, no. 9, pp. 2583-2595, Sept. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Yalin Liu, Hong-Ning Dai, Qubeijian Wang, Mahendra K. Shukla, Muhammad Imran, Unmanned aerial vehicle for internet of everything: Opportunities and challenges, Computer Communications, Volume 155, 2020, Pages 66-83, ISSN 0140-3664. [CrossRef]
- Amira Chriki, Haifa Touati, Hichem Snoussi, Farouk Kamoun, FANET: Communication, mobility models and security issues, Computer Networks, Volume 163, 2019, 106877, ISSN 1389-1286, (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1389128618309034). [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S., and Kaushik, B. (2019). A survey on internet of vehicles: Applications, security issues and solutions. Vehicular Communications, 20, Article 100182.
- Chaurasia, R., and Mohindru, V. (2021). Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV): A comprehensive survey. Unmanned aerial vehicles for Internet of Things (IoT) (pp.1–27).
- Ad Hoc Network, NIST. https://csrc.nist.gov/glossary.
- Cao, H., Garg, S., Kaddoum, G., Hassan, M. M., and AlQahtani, S. A. (2022)" Intelligent virtual resource allocation of QoS-guaranteed slices in B5G-Enabled VANETs for intelligent transportation systems"IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 23(10), 19704-19713.
- L. Liang, H. Ye and G. Y. Li, "Spectrum Sharing in Vehicular Networks Based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning," in IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 37, no. 10, pp. 2282-2292, Oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A. H., and Anpalagan, A. (2022, May). AI Empowered Computing Resource Allocation in Vehicular Ad-hoc NETworks. In 2022 7th International Conference on Business and Industrial Research (ICBIR) (pp. 221-226). IEEE.
- Pan, Q., Wu, J., Nebhen, J., Bashir, A. K., Su, Y., and Li, J. (2022)." Artificial intelligence-based energy efficient communication system for intelligent reflecting surface-driven vanets". IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 23(10), 19714-19726. [CrossRef]
- Ibrar, M., Akbar, A., Jan, S. R. U., Jan, M. A., Wang, L., Song, H., and Shah, N. (2020). "Artnet: Ai-based resource allocation and task offloading in a reconfigurable internet of vehicular networks".IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 9(1), 67-77. [CrossRef]
- Qafzezi, E., Bylykbashi, K., Ampririt, P., Ikeda, M., Matsuo, K., and Barolli, L. (2022). "An intelligent approach for cloud-fog-edge computing SDN-VANETs based on fuzzy logic: effect of different parameters on coordination and management of resources".Sensors, 22(3), 878. [CrossRef]
- Haris, Muhammad, Munam Ali Shah, and Carsten Maple. "Internet of intelligent vehicles (IoIV): an intelligent VANET based computing via predictive modeling." IEEE Access (2023). [CrossRef]
- Xing, Yang, Chen Lv, and Dongpu Cao. "Personalized vehicle trajectory prediction based on joint time-series modeling for connected vehicles." IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 69.2 (2019): 1341-1352. [CrossRef]
- L. Hou, L. Lei, K. Zheng and X. Wang, "A Q -Learning-Based Proactive Caching Strategy for Non-Safety Related Services in Vehicular Networks," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 4512-4520, June 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. -S. Lee and S. Lee, "Resource Allocation for Vehicular Fog Computing Using Reinforcement Learning Combined With Heuristic Information," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 7, no. 10, pp. 10450-10464, Oct. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Xia, L. Wu, Z. Wang, X. Zheng and J. Jin, "Cluster-Enabled Cooperative Scheduling Based on Reinforcement Learning for High-Mobility Vehicular Networks," in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 69, no. 11, pp. 12664-12678, Nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- X. Zhang, M. Peng, S. Yan and Y. Sun, "Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Based Mode Selection and Resource Allocation for Cellular V2X Communications," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 7, no. 7, pp. 6380-6391, July 2020. [CrossRef]
- Q. Yan, B. -J. Hu and Q. Wen, "Joint Resource Allocation and Power Control for V2V Communication of High-density Vehicle Network," 2021 IEEE 93rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2021-Spring), Helsinki, Finland, 2021, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- S. Song, C. Lee, H. Cho, G. Lim and J. -M. Chung, "Clustered Virtualized Network Functions Resource Allocation based on Context-Aware Grouping in 5G Edge Networks," in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 1072-1083, 1 May 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Khan, S. Samarakoon and M. Bennis, "Enhancing Video Streaming in Vehicular Networks via Resource Slicing," in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 69, no. 4, pp. 3513-3522, April 2020. [CrossRef]
- B. Cao, Z. Sun, J. Zhang and Y. Gu, "Resource Allocation in 5G IoV Architecture Based on SDN and Fog-Cloud Computing," in IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 3832-3840, June 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Cui, Y. Liang and R. Wang, "Resource Allocation Algorithm With Multi-Platform Intelligent Offloading in D2D-Enabled Vehicular Networks," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 21246-21253, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Z. Lyu, Y. Wang, M. Liu and Y. Chen, "Service-Driven Resource Management in Vehicular Networks Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning," 2020 IEEE 31st Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, London, UK, 2020, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Y. -H. Xu, C. -C. Yang, M. Hua and W. Zhou, "Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG)-Based Resource Allocation Scheme for NOMA Vehicular Communications," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 18797-18807, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Ye, G. Y. Li and B. -H. F. Juang, "Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Resource Allocation for V2V Communications," in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 68, no. 4, pp. 3163-3173, April 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Khan Tayyaba et al., "5G Vehicular Network Resource Management for Improving Radio Access Through Machine Learning," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 6792-6800, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Muhammad, T. A. Khan, K. Abbass and W. -C. Song, "An End-to-end Intelligent Network Resource Allocation in IoV: A Machine Learning Approach," 2020 IEEE 92nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Fall), Victoria, BC, Canada, 2020, pp. 1-5. [CrossRef]
- H. Khan, M. M. Butt, S. Samarakoon, P. Sehier and M. Bennis, "Deep Learning Assisted CSI Estimation for Joint URLLC and eMBB Resource Allocation," 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Dublin, Ireland, 2020, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- J. Gao, M. R. A. Khandaker, F. Tariq, K. -K. Wong and R. T. Khan, "Deep Neural Network Based Resource Allocation for V2X Communications," 2019 IEEE 90th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall), Honolulu, HI, USA, 2019, pp. 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li and A. H. Aghvami, "Radio Resource Management for Cellular-Connected UAV: A Learning Approach," in IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 71, no. 5, pp. 2784-2800, May 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Dai, Y. Zhang, W. Zhang, X. Luo and Z. He, "A Multi-Agent Collaborative Environment Learning Method for UAV Deployment and Resource Allocation," in IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, vol. 8, pp. 120-130, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Alfaia, R.D.; Souto, A.V.d.F.; Cardoso, E.H.S.; Araújo, J.P.L.d.; Francês, C.R.L. Resource Management in 5G Networks Assisted by UAV Base Stations: Machine Learning for Overloaded Macrocell Prediction Based on Users’ Temporal and Spatial Flow. Drones 2022, 6, 145. [CrossRef]
- C. Deng, X. Fang and X. Wang, "UAV-Enabled Mobile-Edge Computing for AI Applications: Joint Model Decision, Resource Allocation, and Trajectory Optimization," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 10, no. 7, pp. 5662-5675, 1 April1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Khalili, E. M. Monfared, S. Zargari, M. R. Javan, N. M. Yamchi and E. A. Jorswieck, "Resource Management for Transmit Power Minimization in UAV-Assisted RIS HetNets Supported by Dual Connectivity," in IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 1806-1822, March 2022. [CrossRef]
- 2023; Pengshuo Ji, Jie Jia, Jian Chen, Liang Guo, An Du, Xingwei Wang, Reinforcement learning based joint trajectory design and resource allocation for RIS-aided UAV multicast networks, Computer Networks, Volume 227, 2023,109697, ISSN 1389-1286. [CrossRef]
- Munaye, Y.Y.; Juang, R.-T.; Lin, H.-P.; Tarekegn, G.B.; Lin, D.-B. Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Resource Management in UAV-Assisted IoT Networks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2163. [CrossRef]
- Ting Lyu, Haiwang Zhang, Haitao Xu, "Resource Allocation in UAV-Assisted Wireless Powered Communication Networks for Urban Monitoring", Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, vol. 2022, Article ID 7730456, 15 pages, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Lin, M. Wang, X. Zhou, G. Ding, and S. Mao, “Dynamic spectrum interaction of UAV flight formation communication with priority: A deep reinforcement learning approach,” IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw., vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 892–903, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhu, L. Gui, N. Cheng, Q. Zhang, F. Sun, and X. Lang, “UAV-enabled computation migration for complex missions: A reinforcement learning approach,” IET Commun., vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 2472–2480, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Kim, Y. M. Park, and C. S. Hong, “Machine learning based edge assisted UAV computation offloading for data analyzing,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Inf. Netw. (ICOIN), 2020, pp. 117–120.
- J. Cui, Y. Liu, and A. Nallanathan, “Multi-agent reinforcement learning-based resource allocation for UAV networks,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 729–743, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- O. Anicho, P. B. Charlesworth, G. S. Baicher, A. Nagar, and N. Buckley, “Comparative study for coordinating multiple unmanned HAPS for communications area coverage,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Unmanned Aircraft Syst. (ICUAS), 2019, pp. 467–474.
- Liu, C.; Zhu, Q. Joint Resource Allocation and Learning Optimization for UAV-Assisted Federated Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3771. [CrossRef]
- T. Zeng, O. Semiari, M. Mozaffari, M. Chen, W. Saad and M. Bennis, "Federated Learning in the Sky: Joint Power Allocation and Scheduling with UAV Swarms," ICC 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 2020, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- S. Wang et al., “Federated learning for task and resource allocation in wireless high altitude balloon networks,” [Online]. Available: arxiv.abs/2003.09375. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, X. Zhang, X. He and Y. Sun, "Bandwidth Allocation and Trajectory Control in UAV-Assisted IoV Edge Computing Using Multiagent Reinforcement Learning," in IEEE Transactions on Reliability, vol. 72, no. 2, pp. 599-608, June 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Zhang, X. Xie, C. Xu and R. Wu, "Energy Harvesting-Based UAV-Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach," 2022 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC Workshops), Sanshui, Foshan, China, 2022, pp. 199-204. [CrossRef]
- N. Hu, X. Qin, N. Ma, Y. Liu, Y. Yao and P. Zhang, "Energy-efficient Caching and Task offloading for Timely Status Updates in UAV-assisted VANETs," 2022 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Sanshui, Foshan, China, 2022, pp. 1032-1037. [CrossRef]
- C. Yang, B. Liu, H. Li, B. Li, K. Xie and S. Xie, "Learning Based Channel Allocation and Task Offloading in Temporary UAV-Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing Networks," in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 71, no. 9, pp. 9884-9895, Sept. 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Y. Bryan Lim et al., "Multi-Dimensional Contract-Matching for Federated Learning in UAV-Enabled Internet of Vehicles," GLOBECOM 2020 - 2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 2020, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y., Xu, S., Cao, Y., He, Y., Xiao, K. (2022). SBA-GT: A Secure Bandwidth Allocation Scheme with Game Theory for UAV-Assisted VANET Scenarios. In: Wang, L., Segal, M., Chen, J., Qiu, T. (eds) Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications. WASA 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13472. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhai, D.; Huang, F.; Wang, D.; Tang, X.; Zhang, R. Joint Task Offloading, Resource Allocation, and Security Assurance for Mobile Edge Computing-Enabled UAV-Assisted VANETs. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1547. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu et al., "Joint Communication and Computation Resource Scheduling of a UAV-Assisted Mobile Edge Computing System for Platooning Vehicles," in IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 23, no. 7, pp. 8435-8450, July 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Samir, D. Ebrahimi, C. Assi, S. Sharafeddine and A. Ghrayeb, "Leveraging UAVs for Coverage in Cell-Free Vehicular Networks: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach," in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 20, no. 9, pp. 2835-2847, 1 Sept. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Jer Shyuan Ng and Wei Yang Bryan Lim and Hong-Ning Dai and Zehui Xiong and Jianqiang Huang and Dusit Niyato and Xian-Sheng Hua and Cyril Leung and Chunyan Miao. "Joint Auction-Coalition Formation Framework for Communication-Efficient Federated Learning in UAV-Enabled Internet of Vehicles." IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 22, 2326–2344.
- Lim, W. Y. B., Huang, J., Xiong, Z., Kang, J., Niyato, D., Hua, X. S., et al. (2021). Towards federated learning in UAV-enabled internet of vehicles: A multi-dimensional contract-matching approach. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 22, 5140–5154. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K., Sun, Y., Lin, Z., and Tang, Y. (2020). UAV-assisted online video downloading in vehicular networks: A reinforcement learning approach. In 2020 IEEE 91st vehicular technology conference (VTC2020-Spring) (pp. 1–5).
- Srinidhi, N. N., Sagar, C. S., Shreyas, J., and SM, D. K. (2020). "An improved PRoPHET-Random forest based optimized multi-copy routing for opportunistic IoT networks". Internet of Things, 11, 100203. [CrossRef]
- Nadarajan, J., Kaliyaperumal, J. "QOS aware and secured routing algorithm using machine intelligence in next generation VANET". Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag (2021). [CrossRef]
- L. Luo, L. Sheng, H. Yu and G. Sun, "Intersection-Based V2X Routing via Reinforcement Learning in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks," in IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 5446-5459, June 2022. [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Wu, C.; Yoshinaga, T.; Chen, X.; Ji, Y. A Context-Aware Edge-Based VANET Communication Scheme for ITS. Sensors 2018, 18, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, O., Dehghan, M., Sargolzaey, H. et al. A Model-Based Reinforcement Learning Protocol for Routing in Vehicular Ad hoc Network. Wireless Pers Commun 123, 975–1001 (2022). [CrossRef]
- J. Wu, M. Fang, H. Li and X. Li, "RSU-Assisted Traffic-Aware Routing Based on Reinforcement Learning for Urban Vanets," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 5733-5748, 2020. [CrossRef]
- X. Bi, D. Gao and M. Yang, "A Reinforcement Learning-Based Routing Protocol for Clustered EV-VANET," 2020 IEEE 5th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China, 2020, pp. 1769-1773. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X. Novel self-adaptive routing service algorithm for application in VANET. Appl. Intell. 2019, 49, 1866–1879. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Mosavi, A. An Intersection-Based Routing Scheme Using Q-Learning in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks for Traffic Management in the Intelligent Transportation System. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3731. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.M.; Naqvi, R.A.; Yousefpoor, E.; Yousefpoor, M.S.; Ahmed, O.H.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Siddique, K. A Q-Learning and Fuzzy Logic-Based Hierarchical Routing Scheme in the Intelligent Transportation System for Smart Cities. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4192. [CrossRef]
- Daniel Fuertes, Carlos R. del-Blanco, Fernando Jaureguizar, Juan José Navarro, Narciso García, Solving routing problems for multiple cooperative Unmanned Aerial Vehicles using Transformer networks, Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Volume 122, 2023, 106085, ISSN 0952-1976. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, L.; Cheng, N.; Sun, R.; Luan, T.; Quan, W.; Aldubaikhy, K. Joint Flying Relay Location and Routing Optimization for 6G UAV–IoT Networks: A Graph Neural Network-Based Approach. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4377. [CrossRef]
- Sadoon Hussain, Ahmed Sami, Abida Thasin, Redhwan M. A. Saad, "AI-Enabled Ant-Routing Protocol to Secure Communication in Flying Networks", Applied Computational Intelligence and Soft Computing, vol. 2022, Article ID 3330168, 9 pages, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Wang, Y. Liu, R. Srikant and L. Ying, "3M-RL: Multi-Resolution, Multi-Agent, Mean-Field Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous UAV Routing," in IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 23, no. 7, pp. 8985-8996, July 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. Sliwa, C. Schuler, M. Patchou, C. Wietfeld, "PARRoT: Predictive Ad-hoc Routing fueled by reinforcement learning and trajectory knowledge," 2020, arXiv:2012.05490.
- C. He, S. Liu and S. Han, "A Fuzzy Logic Reinforcement Learning-Based Routing Algorithm For Flying Ad Hoc Networks," 2020 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Big Island, HI, USA, 2020, pp. 987-991. [CrossRef]
- J. LIU, Q. WANG, C. HE and Y. XU, "ARdeep: Adaptive and Reliable Routing Protocol for Mobile Robotic Networks with Deep Reinforcement Learning," 2020 IEEE 45th Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2020, pp. 465-468. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q., Jang, SJ. and Yoo, SJ. Q-Learning-Based Fuzzy Logic for Multi-objective Routing Algorithm in Flying Ad Hoc Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 113, 115–138 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Roh, B.-S.; Han, M.-H.; Ham, J.-H.; Kim, K.-I. Q-LBR: "Q-Learning Based Load Balancing Routing for UAV-Assisted VANET". Sensors 2020, 20, 5685. [CrossRef]
- H. Fatemidokht, M. K. Rafsanjani, B. B. Gupta and C. -H. Hsu, "Efficient and Secure Routing Protocol Based on Artificial Intelligence Algorithms With UAV-Assisted for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks in Intelligent Transportation Systems," in IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 22, no. 7, pp. 4757-4769, July 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Jiang, Z. Huang and Y. Ji, "Adaptive UAV-Assisted Geographic Routing With Q-Learning in VANET," in IEEE Communications Letters, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 1358-1362, April 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. He, D. Zhai, Y. Jiang and R. Zhang, "Relay Selection for UAV-Assisted Urban Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks," in IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol. 9, no. 9, pp. 1379-1383, Sept. 2020. [CrossRef]
- O. S. Oubbati, N. Chaib, A. Lakas, P. Lorenz and A. Rachedi, "UAV-Assisted Supporting Services Connectivity in Urban VANETs," in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 68, no. 4, pp. 3944-3951, April 2019. [CrossRef]
| Reference | Main Research Area | Domain | AI Technique Covered |
|---|---|---|---|
| [12] | Resource management, security and congestion control | VANET | ML and RL |
| [13] | Mobile edge offloading, security, transportation | VANET | ML and RL |
| [14] | Resource allocation, security, cognitive radio | VANET | ML and DL |
| [15] | Spectrum allocation | CR-VANET | ML and DL |
| [16] | Security, traffic safety and congestion | CR-VANET | ML, DL and RL |
| [17] | FL based wireless IoT applications | CR-IoT | FL |
| [18] | MEC decisions based offloading | VANET | ML and DRL |
| [19] | Resource allocation scenarios | VANET | ML and DRL |
| [20] | Caching, resource and infrastructure management | IoV | DRL |
| [21] | Wireless sensor networks | VANET | ML |
| [22] | Security, routing, resource and mobility management | VANET | ML and DL |
| [23] | Resource allocation techniques | C-V2X | ML |
| [24] | Position, cluster and topology-based routing algorithms | VANET | RL and DRL |
| [25] | FL based security and privacy applications | VANET | FL |
| [26] | Handover, caching and resource management, routing | V2X Communication | ML, DL, DRL, FL |
| [27] | Privacy, security, congestion and network delays in fog computing | UAV-IoV | None |
| [28] | Resource, mobility and security management and object detection | IoD | ML, DL, DRL |
| Reference | Learning Mechanism | Contribution | Evaluation |
| [92] | Bandwidth allocation, location control deployment and trajectory of UAVs | Multi-attentive agent deep deterministic policy gradient (MA2DDPG) | Improved convergence velocity of AC-Mix and MA2DDPG by 30.0% and 63.3% |
| [93] | Energy harvesting based UAV-assisted vehicular edge computing framework to maximize the amount of data offloaded to the UAV | DRL-based resource allocation and speed optimization (DRL-RASO) model | Reward and offloading amount 5.79% and 7.645% higher |
| [94] | Energy minimization by considering cache refreshing, computation offloading and aging of status updates | RL based DDPG | Not Reported |
| [95] | Auction-coalition building method to allocate UAV coalitions to various IoV component groups | FL | Decreased FL communication latency |
| [96] | Traffic prediction and car park occupancy management | FL | Not Reported |
| [97] | bandwidth allocation scheme based on the game theory | blockchain-based system | Throughput of about %95 |
| [98] | Task offloading and security assurance | LBTO | at 5s and 20s latency highest task processing ratio |
| [99] | Capacity maximization using vehicle platooning | quadratic programming sub-problems | Not Reported |
| [100] | Efficient communication coverage via trajectories decisions making of UAVs | DRL | convergence improvement of 40% |
| [101] | Combined auction-integration formations for AV integration with IoV elements | FL | highest profit of 102 |
| [102] | IoV applications for confidentiality via cooperative ML | FL | Not Reported |
| [103] | Q network to select best UAV advice | RL | No exact number reported |
| Reference | Learning Mechanism | Contribution | Evaluation |
| [122] | a Q-learning based load balancing routing (Q-LBR) | Q-Learning | Improved PDR, network utilization and latency by more than 8%, 28% and 30%. |
| [123] | VRU based routing to handle frequent topology changes | Linux Ubuntu 12.04 for routing protocol, VanetMobiSim, MobiSim | Improved PDR 16%, detection ratio 7%, decreases end-to-end delay 13% and overhead by 40%. |
| [124] | UAV assisted QAGR algorithm | Simulated in NS-3, Q-Learning | 90% PDR achieved |
| [125] | Relay selection for A2G VANETs | Q- Learning | 96% PDR achieved |
| [126] | Traffic prediction and car park occupancy management | NS2 and SUMO | PDR 90% more than compared protocols |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





