1. Introduction
Currently, with the development of machine learning, deep learning, computer vision, and 5G mobile communication technologies, the Internet of Things (IoT) techniques [
1] have made tremendous progress and become a closely related part of people’s lives. Consequently, the intelligent transportation technology represented by Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) and autonomous driving technology has achieved tremendous development due to a growing demand for smart cities and IoT technologies in modern society. As one of the most important popular applications of IoT technologies, the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) [
2] technique has become an essential data transmission and resource scheduling framework in ITS and has attracted the attention of many researchers. Although the IoT and IoV technologies have become very hot research fields and achieved tremendous development, they have to face with some challenges because of their known limitations, such as restricted storage, real time critical, load-balancing, energy consumption, and so on. Artificial Intelligence (AI) [
3] technologies such as Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning [
4] and deep neural networks, that are popular and have shown significant influence, are more and more applied in IoT and IoV fields and dramatically improve the effectiveness of IoT devices [
5,
6].
Generally, the IoVs are regard as data transmission platform that provide information exchange service between the vehicle, or vehicle and other surrounding devices through different communication media [
7]. Through deep integration with the ITs, the IoV builds an intelligent network to provide essential functions for transportation systems,such as intelligent traffic management, dynamic information services, intelligent vehicle control, among others [
8]. The architecture of IoV shown in
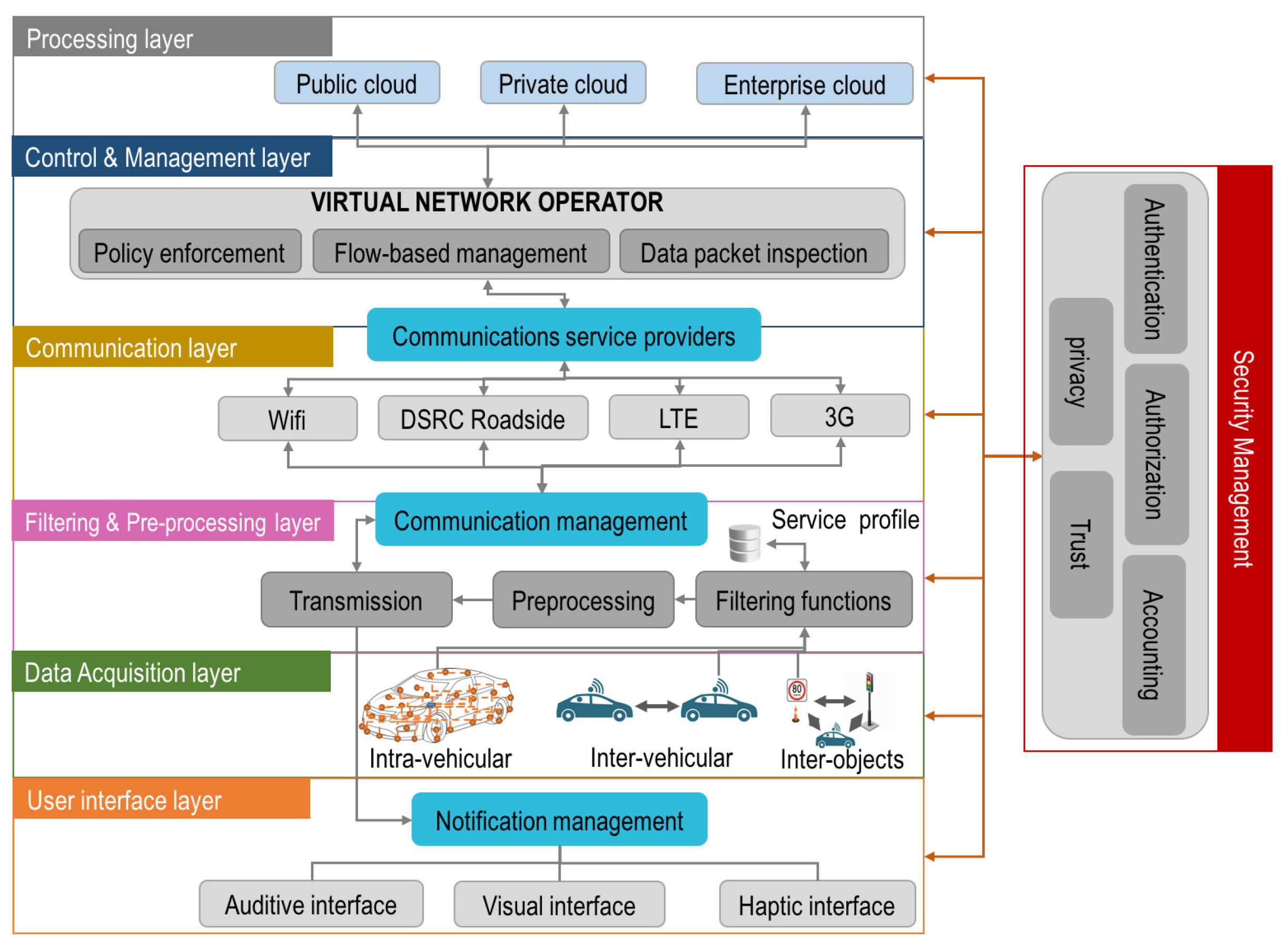
Figure 1 is composed of three fundamental components: the inter-vehicular network (V2V), intra-vehicular network (V2I), and vehicular mobile Internet. Every vehicle in the IoV is connected with other vehicles and devices through Mobile Internet all time. The IoV creates an interconnected network for all vehicles to enable the exchange of information passengers, drivers, sensors and electric actuators, and the Internet by using advanced communication technique, such as IEEE 802.11p, cellular data networks (4G/5G) directional medium access control (DMAC), vehicular cooperative media access control (VC-MAC), and others.
However, this early proposed IoV architecture faces with a challenge of real-time critical requirement. Specifically, the IoV may be susceptible to significant latency when storing or retrieving data, as when multiple vehicles access data simultaneously, it is limited by the data storage and processing capabilities of the vehicular cloud layer, resulting in significant latency. Under this situation, the problem of network congestion often appear in IoV networks, which can cause many issues that influence the operation of network, such as reduction of QoS and long time delay in data transmission [
9]. From the view of this point, therefore, the IoV networks are time-critical systems [
1,
10].
The main challenge of time-critical systems is to ensure that tasks with real-time constraints in the system meet their respective deadlines. This problem presents an astonishing number of challenges and research opportunities for modern computing systems, which are not specifically designed to support time criticality [
10]. However, the significant latency is the main challenge of current IoV architecture. In cloud computing-based IoV architecture, the data sources are often far away data process and store server, which are main reason to cause long time latency and lead to slow response times [
11]. Therefore, these features limit the application of these frameworks to apply in many cases with less stringent functional requirements of real-time or timely intervention, thereby limiting the scope of vehicle services that cloud-based IoT frameworks may provide [
11,
12,
13]. In responding to these concerns and limitations, the Edge and Fog Computing based IoV application frameworks offering better response time and privacy preservation [
14] by moving data process and store to fog or edge layer to reduce distances and significant latency. In building Edge/Fog Computing infrastructures, the popular AI techniques including ML, DL, or Reinforcement Learning (RL) [
15] algorithms are widely applied, which makes the intelligent data processing possible at the edge of network. This novel technique of edge/fog computing greatly reduces the application latency and improves the privacy offered to each vehicle.
Based on the fog computing, the reference of [
14] proposed a new paradigm for IoV called Vehicular Fog Computing (VFC), in which the end-to-end latency is deeply investigated. Based on early architecture shown in
Figure 1, a special layer called fog computing is introduced to reduces the delays and improves QoS. The fog layer consists of a large number of interconnected fog nodes which are data processing servers. Many IoV cloud-like services are provided by fog nodes using FC technique. However, the study of VFC in IoV is still in its early stage and there are several problem required to research deeply, such as congestion avoidance, guaranteed end-to-end delay, resources and tasks offloading, fault tolerance, security, and so on [
16,
17].
To reduce time delay and reach time-crucial requirement, the proposed architectures [
18,
19,
20,
21] applied some effective methods by reducing energy consumption, end-to-end delay, and communication resources in IoV networks. However, there are several important issues such as dynamic computational costs for load balancing and minimizing IoV networks’ delay, and dynamic IoV topologies that are still at early stage of research, and required to study deeply [
14].
Focusing on these issues, we propose a new IoV architecture in this paper by combining the advantages of AI based time-critical system, deep learning approaches, and edge(fog)/ cloud-based IoT technologies. Benefiting from the advantages of AI and fog computing-based vehicle network, the proposed architecture guarantees reliable and low latency communication in a highly dynamic environment. As the edge node, the processers in each vehicle need process large data collected from sensors and implement many task. In this paper, we propose a task allocation and offloading algorithm based on the SDV-F framework by applying deep learning technique to distribute tasks and computation resource efficiently and minimize the end-to-end delay.
The main contributions of this article are as follows:
We propose a novel AI-based architecture for IoV network based on SDV-F framework, which can help to minimize end-to-end delay in data transmission.
We propose an AI-based time-critical task allocation approach in IoV network, in which the AI algorithms such as DL and RL are applied to implement task offloading and resource allocation.
We propose deep network-based Reinforcement Learning framework for resource allocation and task offloading approach in IoV network.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 introduces the background and challenges of this study.
Section 3 describes the framework of the proposed model. The evaluation criterion simulation results are presented in
Section 4 and, finally,
Section 5 gives the conclusions.
2. Background and Challenging
Over the last decade, many researchers have presented various architectural configurations for IoV service. The main targets of these paradigms are to reduce end-to-end delay by applying advanced technologies or proposing novel architectures.
The early IoV service architecture is proposed in [
22,
23], the basic architecture of which is shown in
Figure 1. In [
22,
23], the researchers combined IoT-aware technique with ML and cloud computing techniques for IoV architecture. In this kind of early architectures, the devices of vehicles accessed to connect internet by the managements from anywhere send data to a cloud computing server which implements data processing, storage, transmission, and other facilities. To ensure seamless connectivity, the communication layer needs to apply advanced wireless communication technologies such as GSM, WiFi, 3G/4G mobile network, or others. Although various technological alternatives have been adopted to meet specific needs or application scenarios and improve the efficiency and reliability of the cloud-based IoV infrastructure, the limitations of cloud-based architecture configuration are privacy and latency issues. These were mainly related to the centralized cloud server location and network infrastructure for communication and data transmission. As a result, on responding to the requirement of speed, accuracy, and reliability, this kind of approaches can not achieve satisfied time-critical solution.
As the mobile communication networks used in SDV-F are more and more intelligent and efficient, one of effective way to solve the shortcomings of time-critical system is to apply advanced data transmitting technologies or proposed efficient IoV architectures or approaches. With the development and popular application of 5G cellular mobile communication, Huang et.al [
24] proposed a 5G-enabled SDV Network (5G-SDVNs) to provide communication service in IoV. In improving performance of data transmission in dynamic vehicular networking environments, the reference of [
25] proposes novel approach which is under the framework of SDN-based Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol. At the same time, further work is being carried out in [
26], in which the authors proposed the MCH framework. This MCH (Mobile Cloud Hybrid) framework are often applied to decrease the power consumption of mobile terminal or robotics. At the same time, Chen et.al. [
18] proposed another cloud computing framework for mobile systems framework. By mean of these approaches, each mobile user’s independent task can be processed locally in the Computing Access Point or on a remote cloud server.
The emerging autonomous driving technology for vehicles requires many applications, such as real-time situational awareness, collaborative lane changing, and vehicle stability control. These applications need edge computing technology to provide sufficient computing resources at edge nodes to perform time critical and data intensive activities. To meet these requirements, Zhu et.al. [
27] did deeply research on the latency issues and task allocation in vehicular fog computing and proposed a novel approach called Folo. Moreover, the Folo approach is improved to support vehicles’ mobility by creating edge computing layer for IoV, in which the producing tasks acting are as fog nodes. However, the optimization in Folo is an NP-hard problem, which is approximately solved by applying the Linear Programming technique only.
Applying fog computing is a great improvement to decrease the time delay in data processing and transmission. The fog nodes are designed closer to the bottom nodes, i.e. vehicles, to process and transmit the data produced by vehicles in the fog computing-based IoV network,. The research work of [
5,
28] investigated the applications of SDN on large-scale usage of Vehicle Networks (VN) services base on fog computing framework. The study on management of each wireless network composing VN is still in its early stage, however, which limits the development of fog infrastructures.
Undoubtedly, some recent research work offer good models or approaches to minimize latency, build time-critical system to manage the task offloading issues in the SDV-F architecture. However, most of these works are limited in using the multi-agent system and the horizontal fog layer resource pooling, which are demonstrated to substantially decrease the data respond latency [
5]. Focusing on the time-critical computation applied in VSDN of IoV service architectures, in this article, we present AI-based hierarchical framework for SDN-F. We propose a AI-based time-critical system to manage task allocation and offloading to fit real-time requirement. We also present a AI (ML,DL) based fog computing network supporting between fog nodes, vehicles-to-fog nodes, and fog layer to cloud layer tasks and traffic offloading to attain intelligent resource allocation and minimize the end-to-end latency.
3. Proposed System Architecture
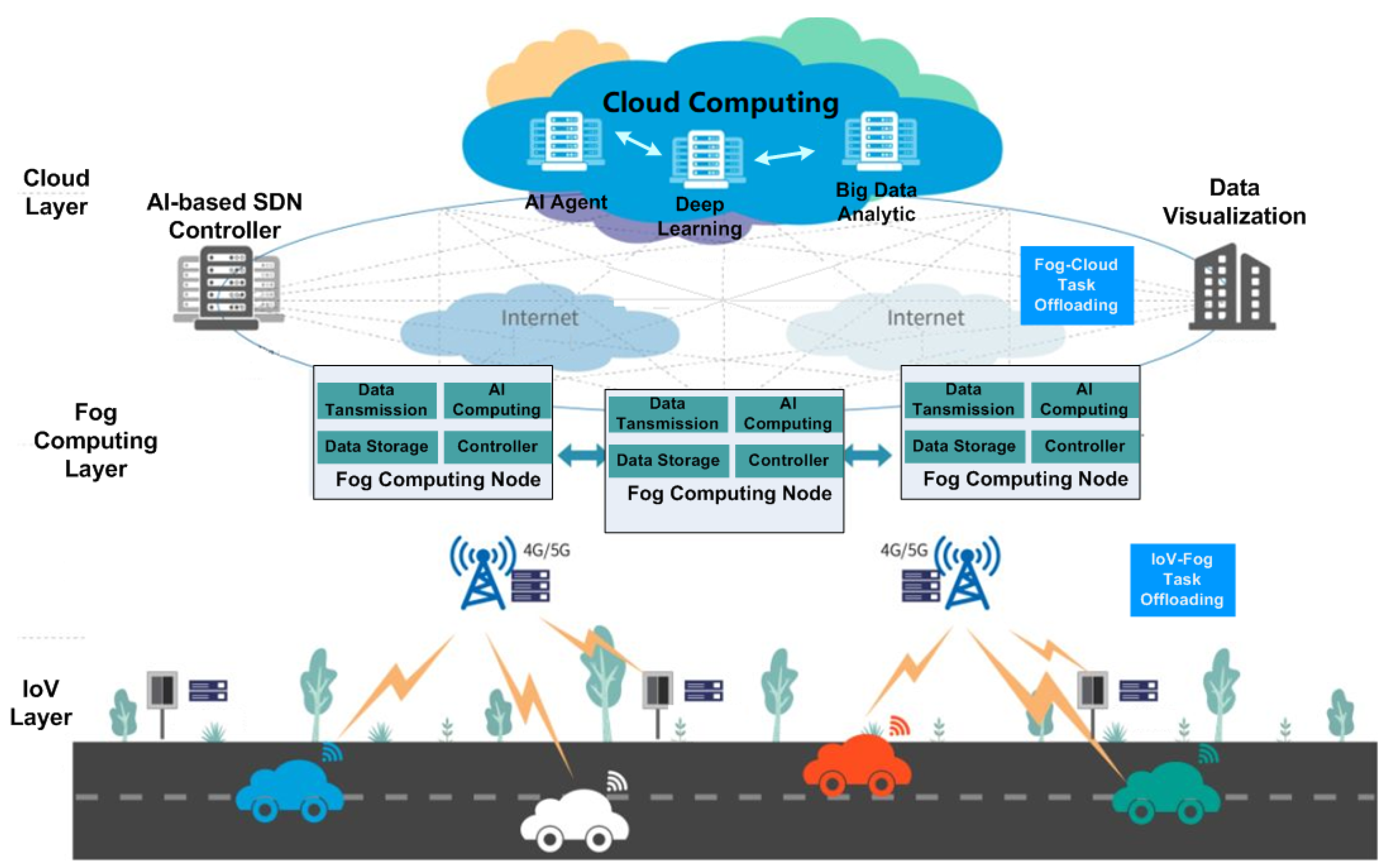
Based on the analysis reported in the literature review and inspired by the solutions proposed in the previous papers, in this section, we present the architecture for a IoV service system that incorporates advanced AI-based time-critical technologies, fog computing, and deep learning approaches. The proposed architecture contains three main layers: Intelligent Data Acquisition Layer or IoV Layer, Fog Computing Layer, and Data Visualisation and AI-based SDN Controller Layer, as illustrated in
Figure 2.
3.1. Layers of System Architecture
The Intelligent Data Acquisition Layer is also called IoV layer which includes a large number of IoV devices. Each vehicle contains a complex computer system which processes large scale of data from many sensors, implements and allocates multiple tasks. The vehicles are edge-nodes of edge computing network to communicate with Base Station (BS) by using 4G/5G mobile communication.
The fog computing layer is a fog computing networks which consists of many fog computing servers providing network communications, data storages, data processing and computing to IoV devices. These many servers are also called fog nodes. In real-world applications, the vehicles in motion will generate a large scale of data representing their real-time status all time. The mainly function of the fog nodes is to process and upload so large scale of data to the control servers. Moreover, these implementations of fog nodes have to meet the requirements of real-time critical and low latency. Obviously, it is very difficult for fog nodes to complete these tasks successfully. Therefore, it is significant important for IoV system to enable to perform distributed computing and implement a load balancing technique to control load and reduce latency. More deeply, besides fog computing-based network architecture, the efficient AI-based algorithm for task and resource offloading is also essential. Other target of this paper is to propose task and resource offloading approach by applying AI algorithms.
The high-lever of the architecture is cloud computing layer which provides AI-based SDN controlling and data visualisation functions. In designing AI-based SDN controller, we adopt two-layer structure, i.e. the data process unit is separated from control unit. This structure helps to improve the evolution of the system and facilitates network management. The intelligent unit implements big data analysis and process, and make decision. The intelligent unit consists of three intelligent modules: intelligent agent module, big data analysis, and deep learning module. By taking into account the available computing resources and combining data analytic results provided by the big data analytic module, the deep learning module offers the best model for the fog node to execute on each fog node. By using the intelligent techniques, the AI unit can make intelligent decisions adaptively.
3.2. Intelligent Data Acquisition Layer (IoV Layer)
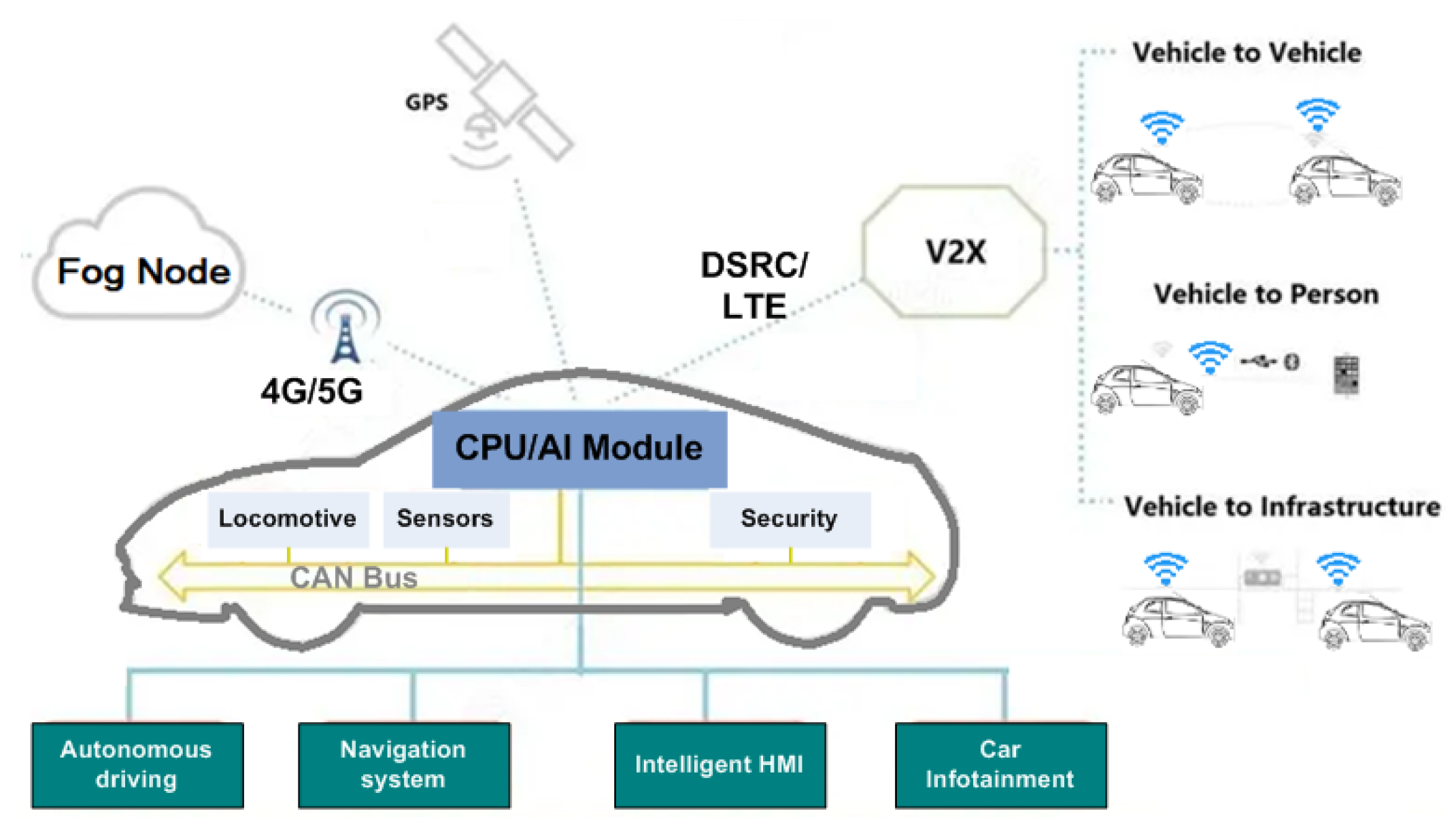
The Intelligent Data Acquisition Layer includes a large number of IoV devices. Each node of IoV layer is a complex computer system which is also divided into three layers: advanced sensors and sub-system layer; computational, storage and process unit, and Artificial Intelligence module, as shown in
Figure 3.
3.2.1. AI-Based Task-Allocation Algorithm in IoV Node
The advanced sensing technologies are used to collect data related to real-time status of vehicles on motion. The multiple-sensor techniques allow the system to collect important correlating data that can be used by AI module to make meaningful decision ensuring IoV frameworks more robust and trustworthy. The computation and data processing unit is key part in this system. To achieve real-time response and forwarding of processed data to upper layers, it is necessary to equip AI-based algorithm to central processing unit (CPU). By applying AI techniques such as deep learning, machine learning, or reinforcement learning, the AI based algorithms can make intelligent decisions based on data analysis. In this subsection, we propose a Reinforcement Learning (RL) [
29] and deep neural network (DNN) based algorithm to fulfil task allocation with time critical-aware.
The CPU is central processing unit which manages many tasks of multiple sub-systems and makes decisions to provide distributed and efficient resource management. The responding algorithm is based on the framework of Markov Decision Process (MDP) [
30] and RL and embedding deep neural network to enable the servers make effective decisions adaptively.
3.2.2. MDP-Based Reinforcement Learning
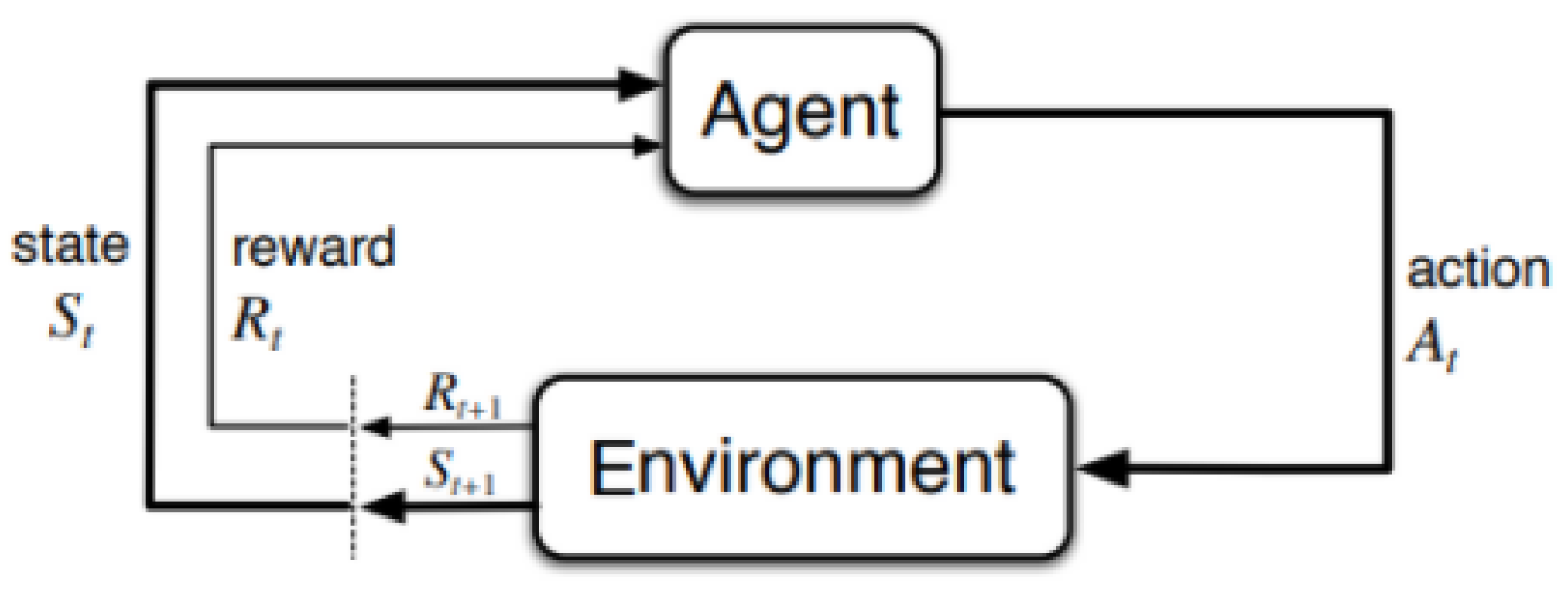
In this on board system, we assume the central CPU as main agent, and other sub-systems as general agent. In RL algorithm, three components are needed: States, Actions, and Rewards.
According to the principle of RL shown in
Figure 4, the CPU of servers are regard as agents (i.e., the central CPU is the primary agent) output actions to the environment based on perceived states. The environment represents the task allocation or offloading system, which evaluates the current actions and outputs the reward function and states. Based on the evaluation, a value function related to reward of actions records the value difference between the current and previous state-action pairs. Consequently, the long-term rewards represent the total rewards that the CPU (i.e., the agents) can expect to accumulate over time for each environmental state. Following this process, the RL model provides a long-term value about the future states based on their corresponding rewards. With the previous reward and value function, finally, the system model evaluates the current action to optimize a best reward and value of the next state.
The theory of the Markov decision processes provides mathematical foundation for the proposed system. We represent Markov decision processes function with a tuple of , where , , and . The symbols of S, A, and R represent the set of states, actions, and rewards. Additionally, the symbol of P is the transition probability, which represents the probability of cyclic process that the current state s produces the next state under the condition of current action. The value of the probability P is between 0 and 1. Accordingly, the is probability of a new state of the environment. This new state is generated under the environment that is represented with state s and the chosen action a. The is the reward function of new state with the current state, that is generated by environment after the action . The reward functions’ value represents with discount factor , where the value of the discount factor is .
Action Selection Policy
The policy is a necessary component in RL which defines the behavior of agents. A policy
is a distribution over action
a given state
s:
In RL, an agent attempts to seek optimal policy
that the agent achieves maximized the sum of rewards that is called utility. The utility function can be represent as follows:
where
is discount factor and
is reward function.
State-Action Quality Function
In MDP, the dynamic programming (DP) technology is applied to solve
P and
R. The DP is a optimization which seeks best choices by using a optimal value function. To realize the RL by using MDP model, there are three functions required to optimized which are he value of state (
s),
, and
. The
represents the value of action that the agent takes at the current state
. According to the principle of RL shown in
Figure 4, the agent requires to choose an new action for the current state
based on the rewards generated by environment. Specifically, before selecting a new action, the agent computing
for each possible action and then decides the new action of the current state
according to the optimal policy. In optimization,
is a optimal policy defined as optimal action selection from state
s to a new state
. In this paper, we apply the Bellman Equations as optimizing target [
14], in other word, the optimum action has to satisfy the Bellman Equations Eq.(
3).
where
and
where
represents the state-action quality pair at time
t, and
T is the time limit of the agents’ optimization problem in the proposed model.
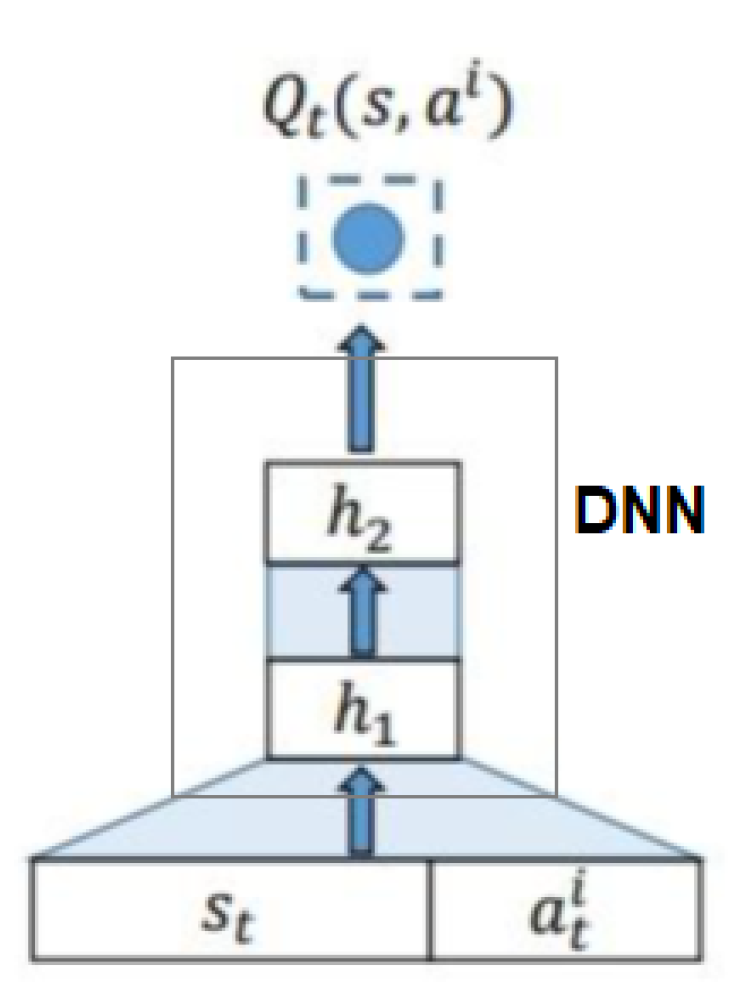
3.2.3. Deep Q-Function Learning for Task Allocation
On the base of RL, we apply DQN (deep Q-function network)) to predict the value of
. In this model, the deep neural network (DNN) is used to learn the agent’s Q-function
.
where
,
) is the state-action pair at the next time slot, and
is the set of actions at the next state
. The
Figure 5 illustrates the basic framework of DQN, in which we use convolutional neural network (CNN) as DNN. The symbol of
represents the parameter DNN.
In training model, the mean-squared error (MSE) is applied as loss function of the proposed model with the parameter CNN
, which is defined as follows:
where
is the maximal summary of future reward for the agents task allocation process.
3.3. Fog Computing Layer
The Fog Computing Layer consists of a large number of fog nodes, which frequently process and upload real-time data generated by vehicles on motion to the SDN-controller. To control the tasks load and reduce latency, the officiant algorithm is vital and essential to realize distributed computing and load balancing technique.
3.3.1. AI-Based Task-Offloading Algorithm in Fog Node Layer
The proposed task-offloading algorithm is also based on RL framework introduced in pre-subsection [
14]. But we improve the algorithm by proposing novel architecture of DNN network, reward function, and Q-function.
Task-Offloading Model for Fog Nodes
The target of the approach is to optimize the offloading operations of each agent to achieve maximum utility under the condition of minimizing time latency and optimizing the allocation of IoV tasks. Therefore, we apply the reward function is defined in [
14]:
where
represents the traffic load probability function of a fog node
, and
indicates the end-to-end delay function. Unlike Eq.(
2), the utility function is defined as:
where
is the number of tasks offloaded to fog node
, and
is the utility reward.
We apply the reward function Eq.(
9) to get the appropriate reward value of the selected fog node for task computation and a next state
in this proposed algorithm. Since the arrives of next fog node with tasks to be assigned and the task size after each node’s task are random, the Poisson random variables are used in the proposed model [
31].
Following the Eq.(
9), the probability function
of a fog node
is required to compute as follows:
where the probability of
(
) is modeled by a Poisson process and with the follows:
where
represents the weight of traffic load,
is the currently processing tasks,
indicates the tasks’ arrival rate at fog node
. The symbol of
represents the next estimated queue state of a fog node
with a given state
s and action
a,
The end-to-end delay
of task is very important in the proposed model. We compute it using the following equation.
where,
is the delay weight,
is operation delay,
is time delay of queue, and
is time delay of data transmission delay. In the proposed model,
represents the waiting time of the current node
in the queue, and
depends on the running-speed of processor in
.
Optimizing Task-Offloading Algorithm
Due to the dynamic nature of the IoV network, it is hard for controller to predict the
R and
P. Based on the fact that the reward and probability distribution are stable, we also apply DNN based RL technique. The base frame work is also shown in
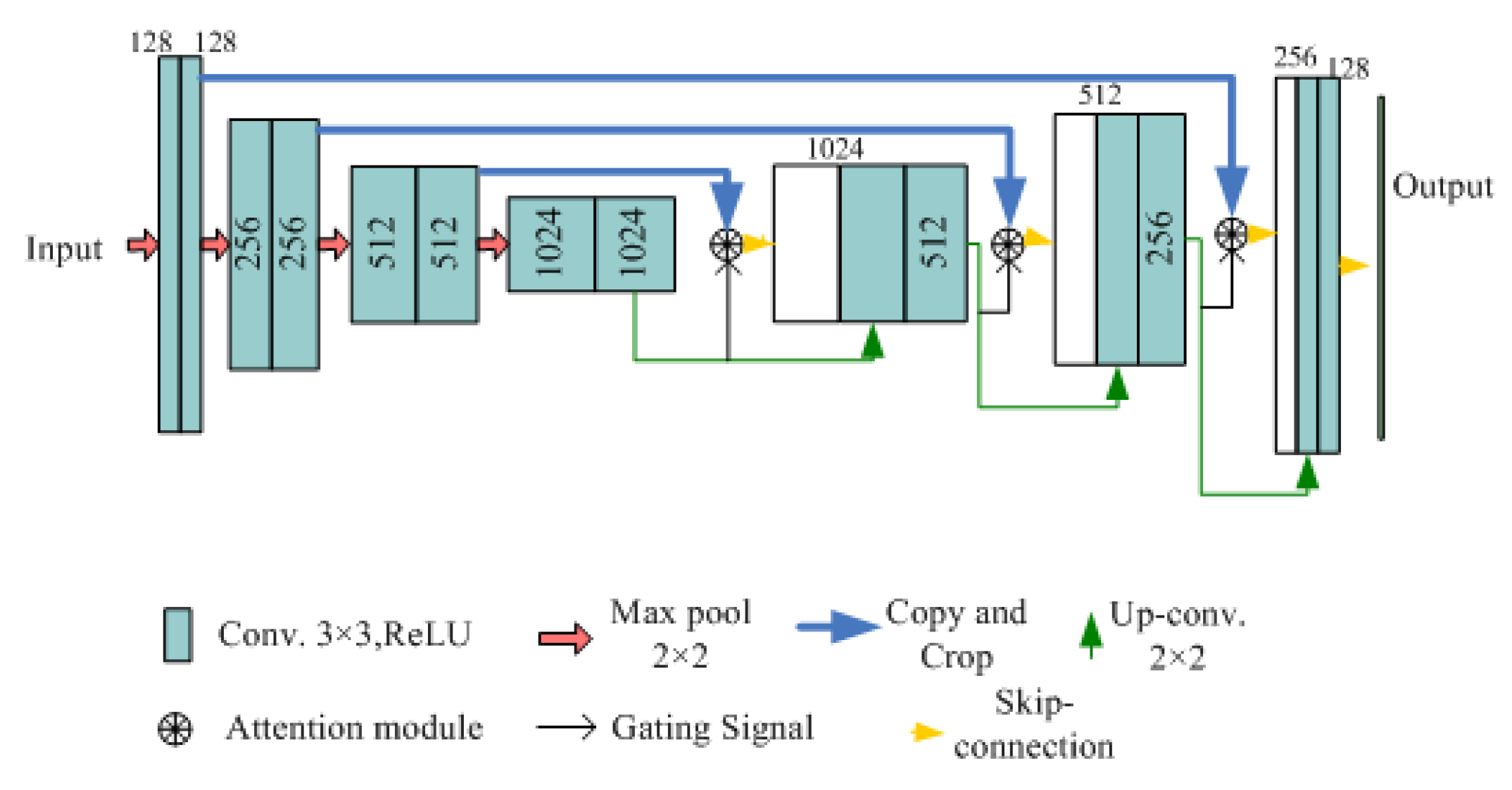
Figure 5. We use a U-Network (U-Net) [
4] shown in
Figure 6 as DNN to learn Q-function
.
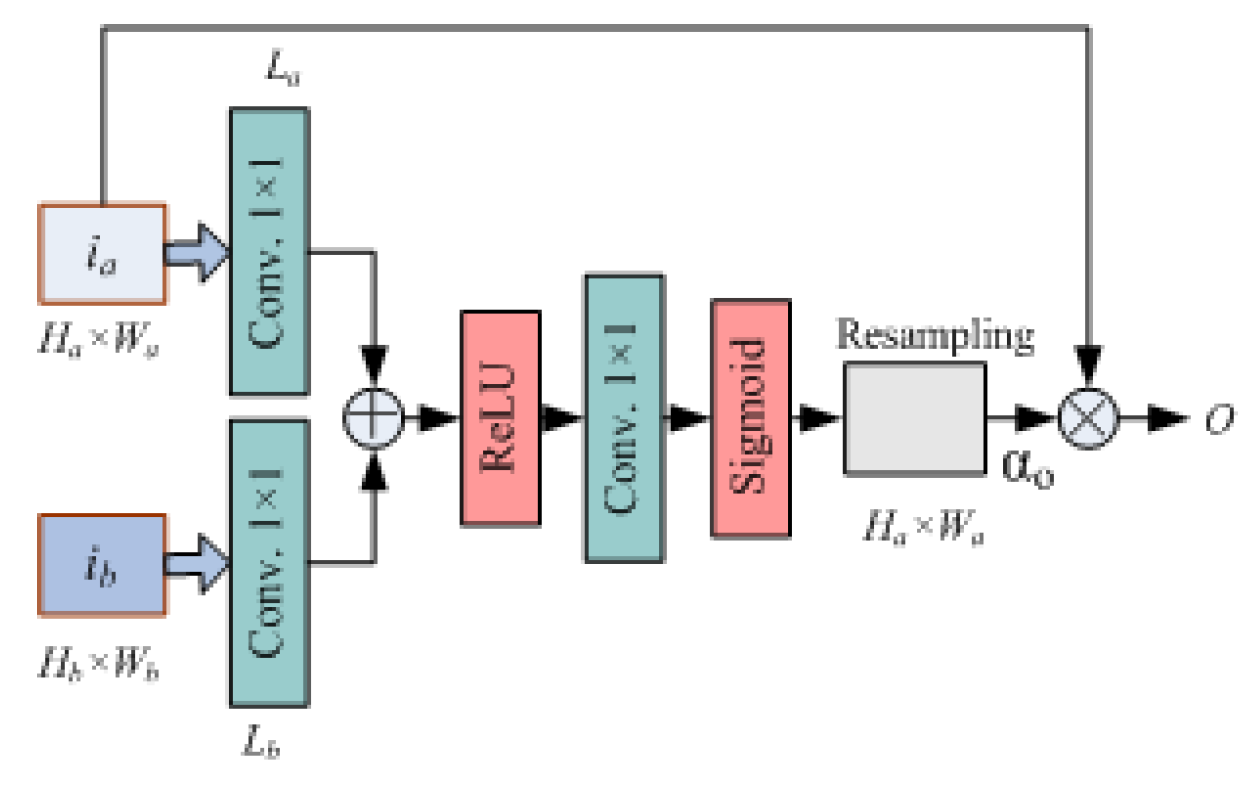
The architecture of U-Net is an autoencoder with attention module, which can make learning process focus on important agents quickly and maximize the foreseen reward function. The architecture of network consists of three downsampling layers, each of which includes two convolutional layers and a max-pooling layer with
pooling. Accordingly, there are three upsampling layers at the other side of network. Each of upsampling layer consists of two convolutional layers with
upsampling. Before input each upsampling layer, the attention module is applied to fusion and calculate a single scalar attention value. To reduce the delay and fit to real-time requirement, we use
convolutional kernel in the attention module as shown in
Figure 7.
In optimization, the target of the model is to select a optimal policy of
in the system. Specifically, based on current policy
, the system foresees the new state
and the reward by using Q-learning. The Q-learning is a continuous optimization in which the Q-function is updated with each of iterations to make the best decision for the new task. The updating equation of Q-function is as follows:
where
is the learning rate which is a factor between 0 and 1 (
), and
is the discount factor. In optimization, the reward function
R is modified based on the new learning rate.