Submitted:
13 December 2023
Posted:
13 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
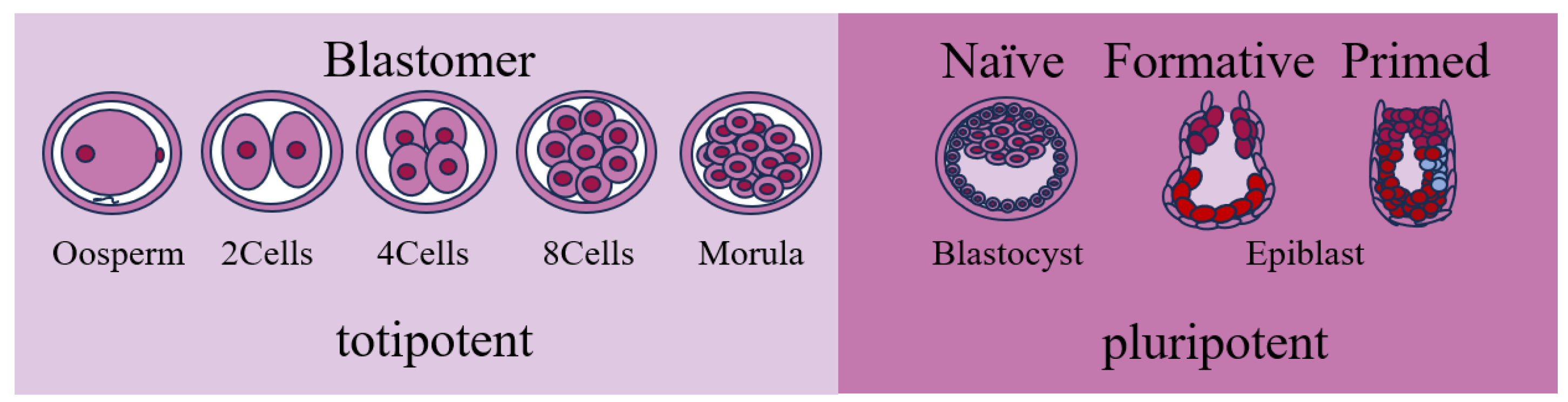
2. Sources of PSCs
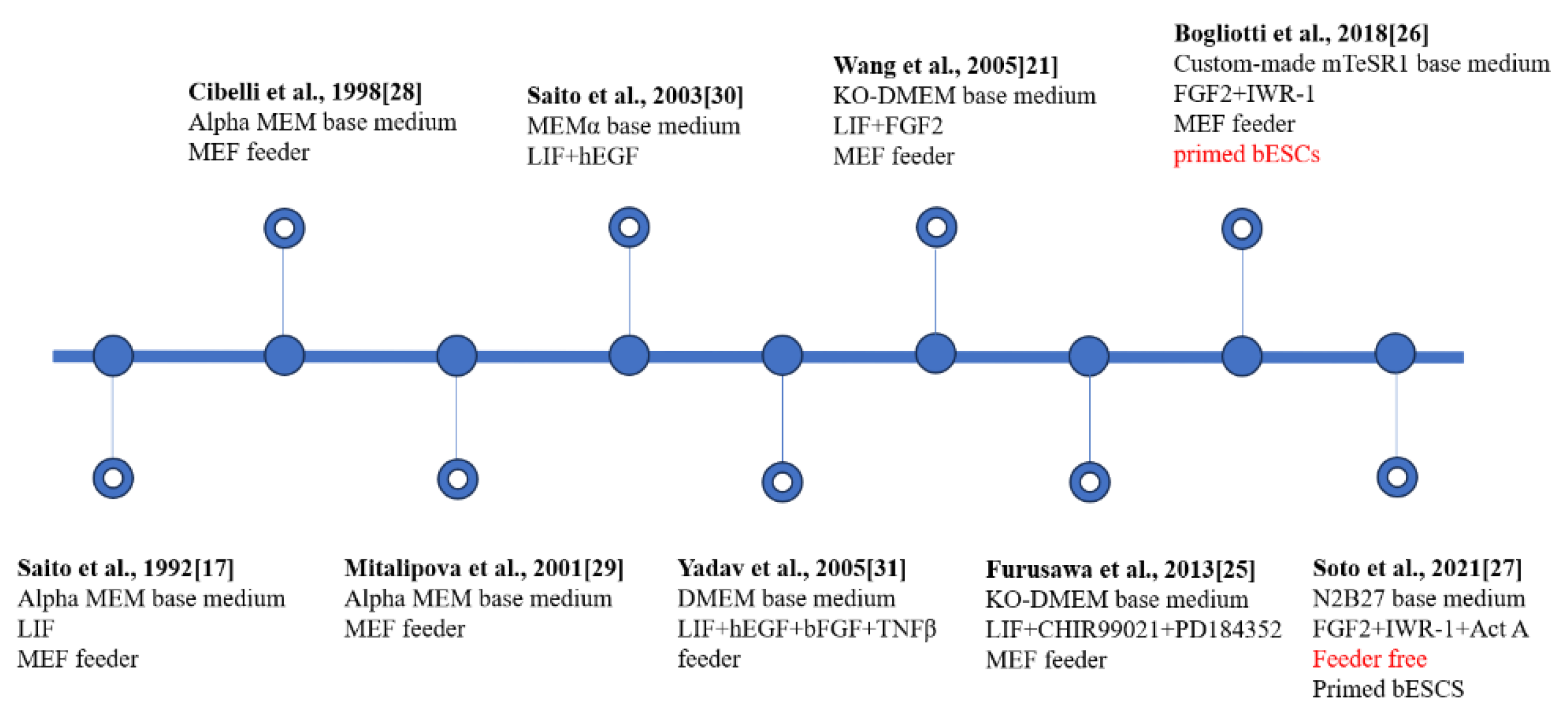
3. Establishment of bESCs
4. Establishment of biPSCs
5. Establishment of bovine expanded potential stem cells
6. Challenge
7. Conclusion and outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheng, C.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, C.; Wu, H.-J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; He, S.; Wang, X.-J.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Q. Direct Reprogramming of Sertoli Cells into Multipotent Neural Stem Cells by Defined Factors. Cell Res 2012, 22 (1), 208–218. [CrossRef]
- Wolf, D. P.; Morey, R.; Kang, E.; Ma, H.; Hayama, T.; Laurent, L. C.; Mitalipov, S. Concise Review: Embryonic Stem Cells Derived by Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer: A Horse in the Race? Stem Cells 2017, 35 (1), 26–34. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Izpisua Belmonte, J. C. Dynamic Pluripotent Stem Cell States and Their Applications. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17 (5), 509–525. [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.; Piedrahita, J. A. From “ES-like” Cells to Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: A Historical Perspective in Domestic Animals. Theriogenology 2014, 81 (1), 103–111. [CrossRef]
- De Los Angeles, A.; Ferrari, F.; Xi, R.; Fujiwara, Y.; Benvenisty, N.; Deng, H.; Hochedlinger, K.; Jaenisch, R.; Lee, S.; Leitch, H. G.; Lensch, M. W.; Lujan, E.; Pei, D.; Rossant, J.; Wernig, M.; Park, P. J.; Daley, G. Q. Hallmarks of Pluripotency. Nature 2015, 525 (7570), 469–478. [CrossRef]
- Scarfone, R. A.; Pena, S. M.; Russell, K. A.; Betts, D. H.; Koch, T. G. The Use of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in Domestic Animals: A Narrative Review. BMC Vet Res 2020, 16 (1), 477. [CrossRef]
- Pieri, N. C. G.; de Souza, A. F.; Botigelli, R. C.; Machado, L. S.; Ambrosio, C. E.; Dos Santos Martins, D.; de Andrade, A. F. C.; Meirelles, F. V.; Hyttel, P.; Bressan, F. F. Stem Cells on Regenerative and Reproductive Science in Domestic Animals. Vet Res Commun 2019, 43 (1), 7–16. [CrossRef]
- Chehelgerdi, M.; Behdarvand Dehkordi, F.; Chehelgerdi, M.; Kabiri, H.; Salehian-Dehkordi, H.; Abdolvand, M.; Salmanizadeh, S.; Rashidi, M.; Niazmand, A.; Ahmadi, S.; Feizbakhshan, S.; Kabiri, S.; Vatandoost, N.; Ranjbarnejad, T. Exploring the Promising Potential of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in Cancer Research and Therapy. Mol Cancer 2023, 22 (1), 189. [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Mazid, M. A.; Li, C.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, W.; Wu, L.; Liao, Z.; Sun, S.; Song, W.; Fu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Nie, Y.; Bian, X.; Gao, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Shang, S.; Li, Y.; Fu, L.; Liu, H.; Lai, J.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Jin, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Lai, Y.; Shi, X.; Maxwell, P. H.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Poo, M.; Wang, X.; Sun, Q.; Esteban, M. A.; Liu, Z. Live Birth of Chimeric Monkey with High Contribution from Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell 2023, 186 (23), 4996-5014.e24. [CrossRef]
- Bissiere, S.; Hernandez, B.; Rubio, C.; Simón, C.; Plachta, N. Updates on Preimplantation Embryo Research. Fertil Steril 2023, 120 (3 Pt 1), 467–472. [CrossRef]
- White, M. D.; Zenker, J.; Bissiere, S.; Plachta, N. Instructions for Assembling the Early Mammalian Embryo. Developmental Cell 2018, 45 (6), 667–679. [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Suo, S.; Cui, G.; Yu, F.; Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, G.; Qian, Y.; Tam, P. P. L.; Han, J.-D. J.; Jing, N. Molecular Architecture of Lineage Allocation and Tissue Organization in Early Mouse Embryo. Nature 2019, 572 (7770), 528–532. [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J. H.; Saha, K.; Jaenisch, R. Pluripotency and Cellular Reprogramming: Facts, Hypotheses, Unresolved Issues. Cell 2010, 143 (4), 508–525. [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, M.; Barber, M.; Mansfield, W.; Cui, Y.; Spindlow, D.; Stirparo, G. G.; Dietmann, S.; Nichols, J.; Smith, A. Capture of Mouse and Human Stem Cells with Features of Formative Pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28 (3), 453-471.e8. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, J.; Yu, L.; Sun, H.-X.; Li, J.; Dong, G.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wu, J.; Gu, Y. Cross-Species Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Pre-Gastrulation Developmental Differences among Pigs, Monkeys, and Humans. Cell Discov 2021, 7 (1), 8. [CrossRef]
- Evans, M. J.; Kaufman, M. H. Establishment in Culture of Pluripotential Cells from Mouse Embryos. Nature 1981, 292 (5819), 154–156. [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Strelchenko, N.; Niemann, H. Bovine Embryonic Stem Cell-like Cell Lines Cultured over Several Passages. Rouxs Arch Dev Biol 1992, 201 (3), 134–141. [CrossRef]
- Soto, D. A.; Ross, P. J. Pluripotent Stem Cells and Livestock Genetic Engineering. Transgenic Res 2016, 25 (3), 289–306. [CrossRef]
- Diamante, L.; Martello, G. Metabolic Regulation in Pluripotent Stem Cells. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2022, 75, 101923. [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J. A.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Shapiro, S. S.; Waknitz, M. A.; Swiergiel, J. J.; Marshall, V. S.; Jones, J. M. Embryonic Stem Cell Lines Derived from Human Blastocysts. Science 1998, 282 (5391), 1145–1147. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Duan, E.; Sung, L.; Jeong, B.-S.; Yang, X.; Tian, X. C. Generation and Characterization of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Cloned Bovine Embryos. Biol Reprod 2005, 73 (1), 149–155. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.; Jiao, C.; Wang, J.; Bai, C.; Su, G.; Liu, X.; Li, G. Establishment of Bovine Embryonic Stem Cells after Knockdown of CDX2. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 28343. [CrossRef]
- Nicola, N. A.; Babon, J. J. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF). Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2015, 26 (5), 533–544. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Jung, Y.-G.; Roh, S. Microarray Analysis of Embryo-Derived Bovine Pluripotent Cells: The Vulnerable State of Bovine Embryonic Stem Cells. PLoS One 2017, 12 (3), e0173278. [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, T.; Ohkoshi, K.; Kimura, K.; Matsuyama, S.; Akagi, S.; Kaneda, M.; Ikeda, M.; Hosoe, M.; Kizaki, K.; Tokunaga, T. Characteristics of Bovine Inner Cell Mass-Derived Cell Lines and Their Fate in Chimeric Conceptuses. Biol Reprod 2013, 89 (2), 28. [CrossRef]
- Bogliotti, Y. S.; Wu, J.; Vilarino, M.; Okamura, D.; Soto, D. A.; Zhong, C.; Sakurai, M.; Sampaio, R. V.; Suzuki, K.; Izpisua Belmonte, J. C.; Ross, P. J. Efficient Derivation of Stable Primed Pluripotent Embryonic Stem Cells from Bovine Blastocysts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115 (9), 2090–2095. [CrossRef]
- Soto, D. A.; Navarro, M.; Zheng, C.; Halstead, M. M.; Zhou, C.; Guiltinan, C.; Wu, J.; Ross, P. J. Simplification of Culture Conditions and Feeder-Free Expansion of Bovine Embryonic Stem Cells. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 11045. [CrossRef]
- Cibelli, J. B.; Stice, S. L.; Golueke, P. J.; Kane, J. J.; Jerry, J.; Blackwell, C.; Ponce de León, F. A.; Robl, J. M. Transgenic Bovine Chimeric Offspring Produced from Somatic Cell-Derived Stem-like Cells. Nat Biotechnol 1998, 16 (7), 642–646. [CrossRef]
- Mitalipova, M.; Beyhan, Z.; First, N. L. Pluripotency of Bovine Embryonic Cell Line Derived from Precompacting Embryos. Cloning 2001, 3 (2), 59–67. [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Sawai, K.; Ugai, H.; Moriyasu, S.; Minamihashi, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hirayama, H.; Kageyama, S.; Pan, J.; Murata, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Obata, Y.; Yokoyama, K. K. Generation of Cloned Calves and Transgenic Chimeric Embryos from Bovine Embryonic Stem-like Cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003, 309 (1), 104–113. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P. S.; Kues, W. A.; Herrmann, D.; Carnwath, J. W.; Niemann, H. Bovine ICM Derived Cells Express the Oct4 Ortholog. Mol Reprod Dev 2005, 72 (2), 182–190. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Fibroblast Cultures by Defined Factors. Cell 2006, 126 (4), 663–676. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Fibroblasts by Defined Factors. Cell 2007, 131 (5), 861–872. [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Feng, T.; Yu, D.; Wu, Y.; Zou, H.; Ma, S.; Feng, C.; Huang, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Hu, X.; Pan, D.; Li, N.; Wu, S. Barriers for Deriving Transgene-Free Pig iPS Cells with Episomal Vectors. Stem Cells 2015, 33 (11), 3228–3238. [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Han, J.; Ding, F.; Cao, S.; Lim, S. S.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Lim, B.; Li, N. Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Bovine Embryonic Fibroblast Cells. Cell Res 2011, 21 (10), 1509–1512. [CrossRef]
- Talluri, T. R.; Kumar, D.; Glage, S.; Garrels, W.; Ivics, Z.; Debowski, K.; Behr, R.; Niemann, H.; Kues, W. A. Derivation and Characterization of Bovine Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells by Transposon-Mediated Reprogramming. Cell Reprogram 2015, 17 (2), 131–140. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Gao, X.; Wu, B.; Zhao, G.; Bao, S.; Hu, S.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Characterization of the Single-Cell Derived Bovine Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Tissue and Cell 2017, 49 (5), 521–527. [CrossRef]
- Rony, I. K.; Baten, A.; Bloomfield, J. A.; Islam, M. E.; Billah, M. M.; Islam, K. D. Inducing Pluripotency in Vitro: Recent Advances and Highlights in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Generation and Pluripotency Reprogramming. Cell Prolif 2015, 48 (2), 140–156. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Anand, T.; Talluri, T. R.; Kues, W. A. Potential of Transposon-Mediated Cellular Reprogramming towards Cell-Based Therapies. World J Stem Cells 2020, 12 (7), 527–544. [CrossRef]
- Liuyang, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; He, H.; Lyu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yang, Z.; Guan, J.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhong, X.; Sun, S.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Deng, H. Highly Efficient and Rapid Generation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells by Chemical Reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 2023, 30 (4), 450-459.e9. [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Guan, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, T.; Ye, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, K.; Ge, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, H. Pluripotent Stem Cells Induced from Mouse Somatic Cells by Small-Molecule Compounds. Science 2013, 341 (6146), 651–654. [CrossRef]
- Canizo, J. R.; Vazquez Echegaray, C.; Klisch, D.; Aller, J. F.; Paz, D. A.; Alberio, R. H.; Alberio, R.; Guberman, A. S. Exogenous Human OKSM Factors Maintain Pluripotency Gene Expression of Bovine and Porcine iPS-like Cells Obtained with STEMCCA Delivery System. BMC Res Notes 2018, 11 (1), 509. [CrossRef]
- Sumer, H.; Liu, J.; Malaver-Ortega, L. F.; Lim, M. L.; Khodadadi, K.; Verma, P. J. NANOG Is a Key Factor for Induction of Pluripotency in Bovine Adult Fibroblasts. J Anim Sci 2011, 89 (9), 2708–2716. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Kuo, K.-K.; Wuputra, K.; Lin, S.-H.; Ku, C.-C.; Yang, Y.-H.; Wang, S.-W.; Wang, S.-W.; Wu, D.-C.; Wu, C.-C.; Chai, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-L.; Lin, C.-S.; Kajitani, M.; Miyoshi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Matsushima, K.; Jin, C.; Huang, S.-K.; Saito, S.; Yokoyama, K. K. Bovine Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Are More Resistant to Apoptosis than Testicular Cells in Response to Mono-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate. Int J Mol Sci 2014, 15 (3), 5011–5031. [CrossRef]
- Pillai, V. V.; Koganti, P. P.; Kei, T. G.; Gurung, S.; Butler, W. R.; Selvaraj, V. Efficient Induction and Sustenance of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Bovine Somatic Cells. Biol Open 2021, 10 (10), bio058756. [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, L.; Fan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Kaback, D.; Oudiz, J.; Patrick, T.; Yee, S. P.; Tian, X. C.; Polejaeva, I.; Tang, Y. Establishment of Bovine-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22 (19), 10489. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, Y.; Huang, H.; Xu, K.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, S.; Tao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Cai, T.; Gao, S. The Combination of Tet1 with Oct4 Generates High-Quality Mouse-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2015, 33 (3), 686–698. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, K.; Wu, T.; Huang, B.; Liu, W.; Kou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yao, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Kang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Cai, T.; Gao, S. Replacement of Oct4 by Tet1 during iPSC Induction Reveals an Important Role of DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation in Reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12 (4), 453–469. [CrossRef]
- Kidder, B. L.; Hu, G.; Yu, Z.-X.; Liu, C.; Zhao, K. Extended Self-Renewal and Accelerated Reprogramming in the Absence of Kdm5b. Mol Cell Biol 2013, 33 (24), 4793–4810. [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Zhang, H.; Wei, R.; Li, Q.; Weng, X.; Kong, Q.; Liu, Z. Histone H3 Lysine 27 Trimethylation Acts as an Epigenetic Barrier in Porcine Nuclear Reprogramming. Reproduction 2016, 151 (1), 9–16. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, J.; An, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. H3K27me3 Is an Epigenetic Barrier While KDM6A Overexpression Improves Nuclear Reprogramming Efficiency. FASEB J 2019, 33 (3), 4638–4652. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hu, G.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, R.; Dong, X.; Babarinde, I. A.; Ping, W.; Sheng, Y.-L.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Gao, M.; Chen, Y.; Shan, G.; Zhang, M. Q.; Hutchins, A. P.; Fu, X.-D.; Yao, H. CTCF Functions as an Insulator for Somatic Genes and a Chromatin Remodeler for Pluripotency Genes during Reprogramming. Cell Rep 2022, 39 (1), 110626. [CrossRef]
- Fan, A.; Ma, K.; An, X.; Ding, Y.; An, P.; Song, G.; Tang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, P.; Tan, W.; Tang, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Effects of TET1 Knockdown on Gene Expression and DNA Methylation in Porcine Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Reproduction 2013, 146 (6), 569–579. [CrossRef]
- Botigelli, R. C.; Pieri, N. C. G.; Bessi, B. W.; Machado, L. S.; Bridi, A.; de Souza, A. F.; Recchia, K.; Neto, P. F.; Ross, P. J.; Bressan, F. F.; Nogueira, M. F. G. Acquisition and Maintenance of Pluripotency Are Influenced by Fibroblast Growth Factor, Leukemia Inhibitory Factor, and 2i in Bovine-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10, 938709. [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M. Therapeutics Targeting FGF Signaling Network in Human Diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2016, 37 (12), 1081–1096. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H. T. MAPK Signal Pathways in the Regulation of Cell Proliferation in Mammalian Cells. Cell Res 2002, 12 (1), 9–18. [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Tsukiyama, T.; Kimura, K.; Matsuyama, S.; Minami, N.; Yamada, M.; Imai, H. Generation of Naïve Bovine Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Using PiggyBac Transposition of Doxycycline-Inducible Transcription Factors. PLoS One 2015, 10 (8), e0135403. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Ma, Z.; Yu, T.; Ling, M.; Wang, H. Methanol Fixed Fibroblasts Serve as Feeder Cells to Maintain Stem Cells in the Pluripotent State in Vitro. Sci Rep 2018, 8 (1), 7780. [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Cao, G.; Liu, D. Effects of Different Feeder Layers on Culture of Bovine Embryonic Stem Cell-like Cells in Vitro. Cytotechnology 2014, 66 (6), 995–1005. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Cai, N.-N.; An, X.-L.; Zhu, W.-Q.; Yang, R.; Tang, B.; Li, Z.-Y.; Zhang, X.-M. Naïve-like Conversion of Bovine Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Sertoli Cells. Theriogenology 2023, 196, 68–78. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, B.; Xiao, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Yu, J.; Shao, Z.; Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, S. Long Noncoding RNA CCDC144NL-AS1 Knockdown Induces Naïve-like State Conversion of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 2019, 10 (1), 220. [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Liu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, D.; Du, Y.; Xiang, C.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Yang, W.; Xu, J.; Deng, H. Generation of Naive Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Rhesus Monkey Fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 15 (4), 488–497. [CrossRef]
- Bessi, B. W.; Botigelli, R. C.; Pieri, N. C. G.; Machado, L. S.; Cruz, J. B.; de Moraes, P.; de Souza, A. F.; Recchia, K.; Barbosa, G.; de Castro, R. V. G.; Nogueira, M. F. G.; Bressan, F. F. Cattle In Vitro Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Generated and Maintained in 5 or 20% Oxygen and Different Supplementation. Cells 2021, 10 (6), 1531. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Park, J.; Dai, A.; Roberts, R. M.; Liu, Y.; Han, X. Efficient Long-Term Cryopreservation of Pluripotent Stem Cells at -80 °C. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 34476. [CrossRef]
- Eminli, S.; Foudi, A.; Stadtfeld, M.; Maherali, N.; Ahfeldt, T.; Mostoslavsky, G.; Hock, H.; Hochedlinger, K. Differentiation Stage Determines Reprogramming Potential of Hematopoietic Cells into iPS Cells. Nat Genet 2009, 41 (9), 968–976. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Y.; Sun, Y. X.; Wang, A. B.; Che, G. Y.; Hu, T. J.; Zhang, X. M. Effect of Newborn Bovine Serum on Cryopreservation of Adult Bovine Testicular Tissue. Andrologia 2014, 46 (3), 308–312. [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, J. Y.; Zhao, X. X.; Wang, Z. Z.; An, X. L.; Lai, L. X.; Li, Z. Y.; Zhang, X. M. Enrichment and in Vitro Features of the Putative Gonocytes from Cryopreserved Testicular Tissue of Neonatal Bulls. Andrology 2016, 4 (6), 1150–1158. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wen, L.; Yuan, Q.; Sun, M.; Niu, M.; He, Z. Establishment and Applications of Male Germ Cell and Sertoli Cell Lines. Reproduction 2016, 152 (2), R31-40. [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, G.; Dong, F.; Wang, F.; Cao, W. Reprogramming Sertoli Cells into Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Reprogram 2014, 16 (3), 196–205. [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, P.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Guan, W.; Ma, Y. Melatonin Improves Reprogramming Efficiency and Proliferation of Bovine-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. J Pineal Res 2016, 61 (2), 154–167. [CrossRef]
- Mascetti, V. L.; Pedersen, R. A. Contributions of Mammalian Chimeras to Pluripotent Stem Cell Research. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19 (2), 163–175. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Gao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Ren, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, B.; Chen, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Su, J.; Ding, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, M.; Bai, X.; Sun, L.; Cao, G.; Tang, F.; Bao, S.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Establishment of Bovine Expanded Potential Stem Cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2021, 118 (15), e2018505118. [CrossRef]
- Pillai, V. V.; Kei, T. G.; Reddy, S. E.; Das, M.; Abratte, C.; Cheong, S. H.; Selvaraj, V. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Generation from Bovine Somatic Cells Indicates Unmet Needs for Pluripotency Sustenance. Anim Sci J 2019, 90 (9), 1149–1160. [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.; Zhang, S.-M.; Ellis, M. W.; Luo, J. Large Animal Models for the Clinical Application of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells Dev 2019, 28 (19), 1288–1298. [CrossRef]
- Ho, R.; Chronis, C.; Plath, K. Mechanistic Insights into Reprogramming to Induced Pluripotency. J Cell Physiol 2011, 226 (4), 868–878. [CrossRef]
- Brosh, R.; Assia-Alroy, Y.; Molchadsky, A.; Bornstein, C.; Dekel, E.; Madar, S.; Shetzer, Y.; Rivlin, N.; Goldfinger, N.; Sarig, R.; Rotter, V. P53 Counteracts Reprogramming by Inhibiting Mesenchymal-to-Epithelial Transition. Cell Death Differ 2013, 20 (2), 312–320. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R. A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The next Generation. Cell 2011, 144 (5), 646–674. [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, M. A.; Knoblich, J. A. Organogenesis in a Dish: Modeling Development and Disease Using Organoid Technologies. Science 2014, 345 (6194), 1247125. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




