Submitted:
12 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Motivations and Contributions
- Detailed theoretical finite element modelling and simulation using Flux by Cedrat. The magnetic flux within and between the stator and mover cores was modelled to analyse machine reluctance. Air gap reluctance was reduced through the use of flanges on the stator teeth.
- Simulation studies were performed for various excitation modes in both static and parametric analysis. The modes studied include no mover coil excitation, a DC excited mover coil, and an AC excited mover coil.
- Construction and design of a practical linear generator were performed once the proposed design was verified. Calculations for the mechanical properties of the machine were undertaken to obtain the spring rate which would provide the desired resonant frequency.
- Verification and analysis of the hardware through the use of empirical testing with the use of a pneumatic actuator.
1.3. Paper Structure
2. Theoretical Aspects
2.1. Electromagnetism
2.2. Mechanics
3. Machine design
4. Simulations
4.1. Modelling of the generator
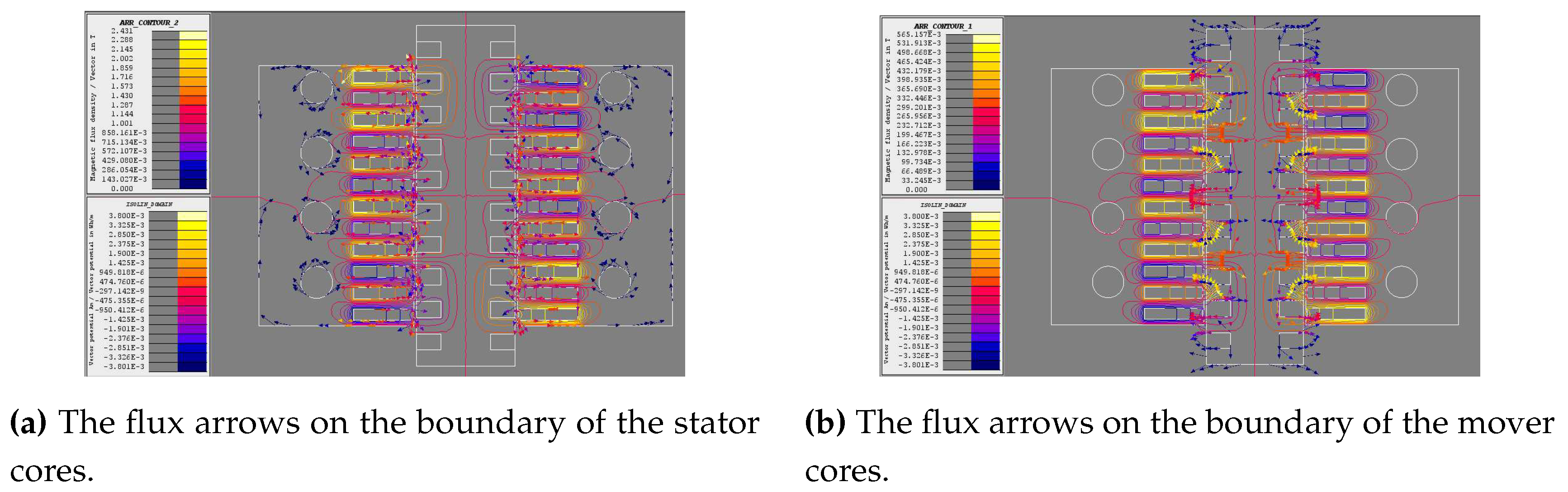
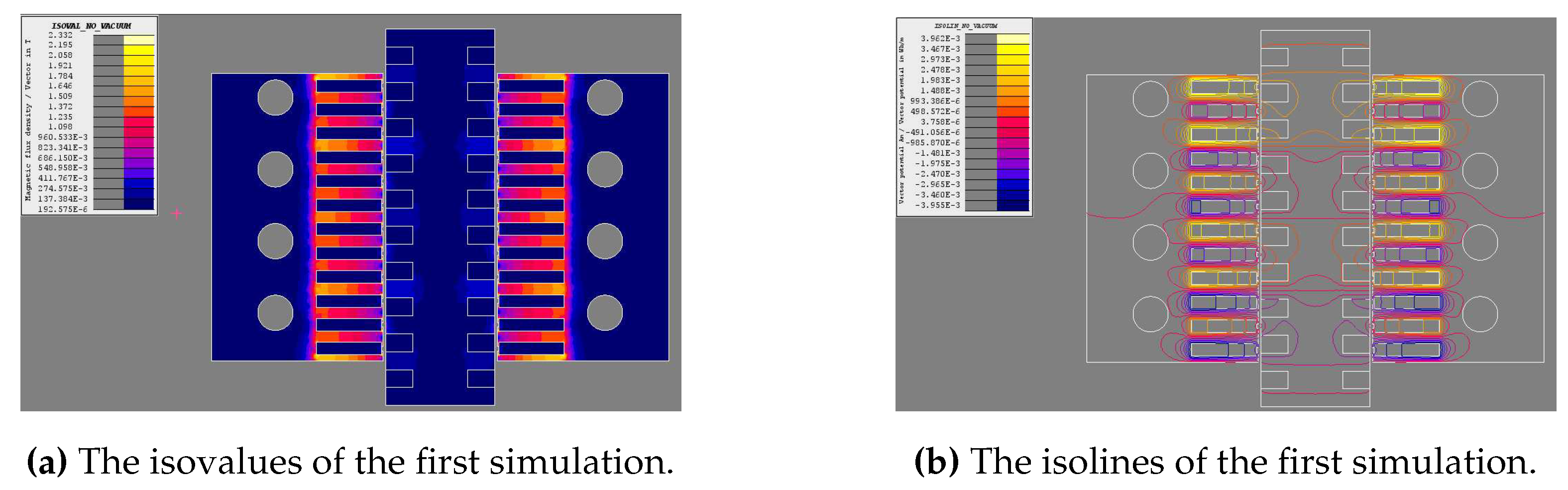
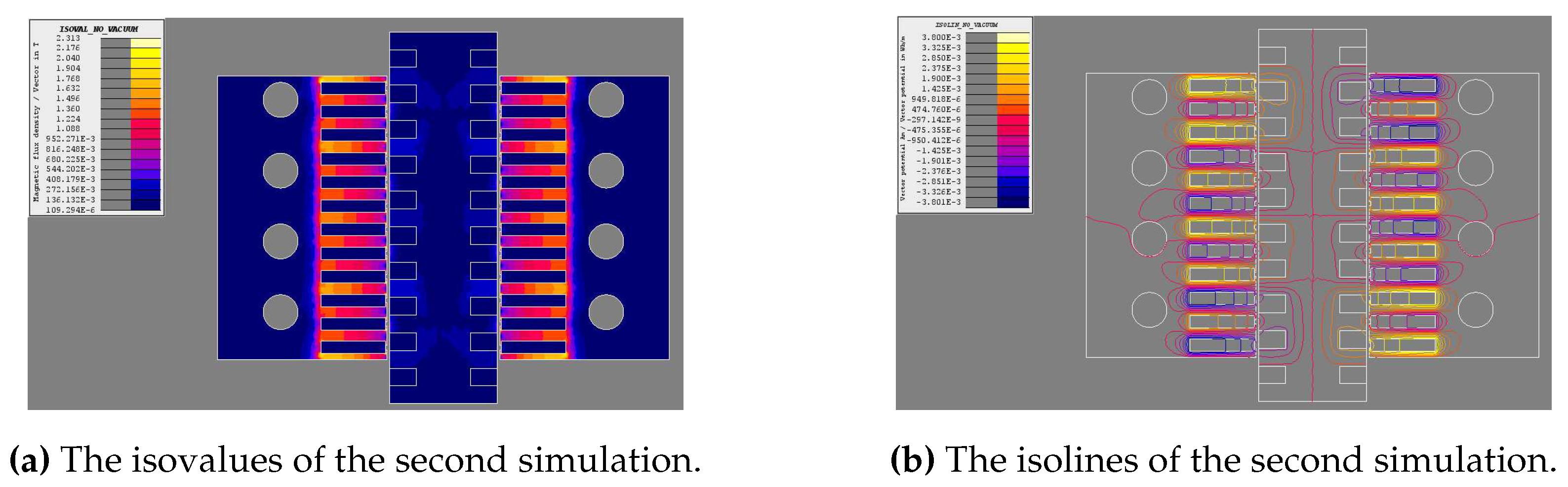
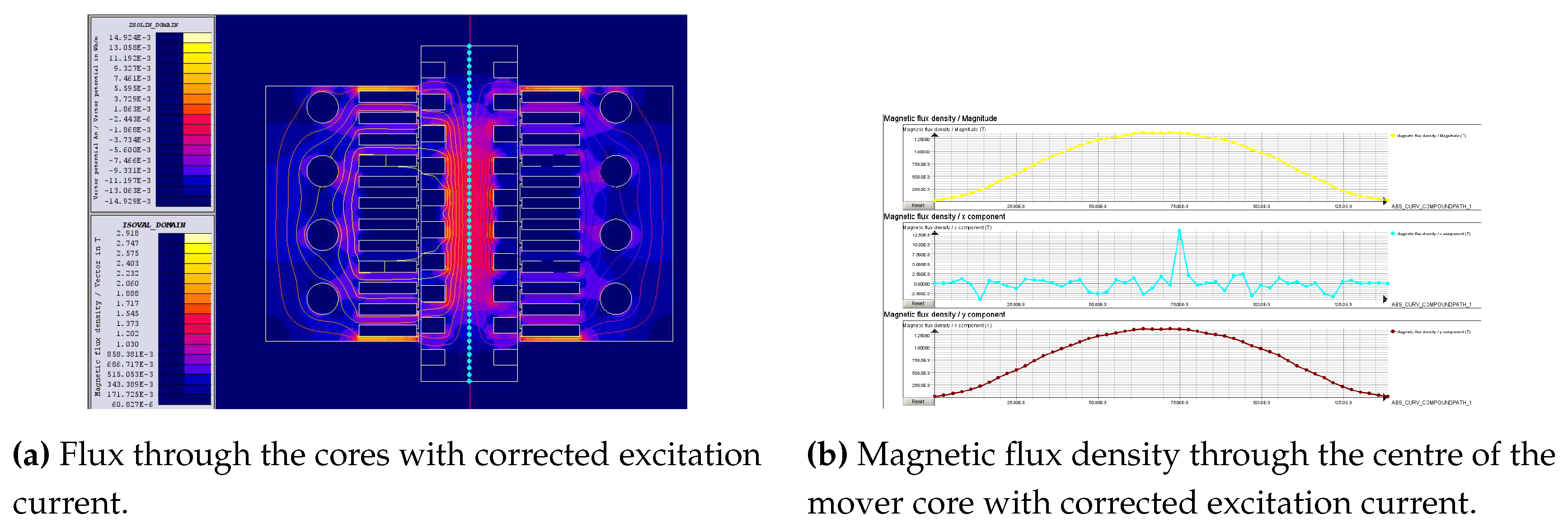
4.2. Magnetostatic analysis
4.3. Parametric analysis
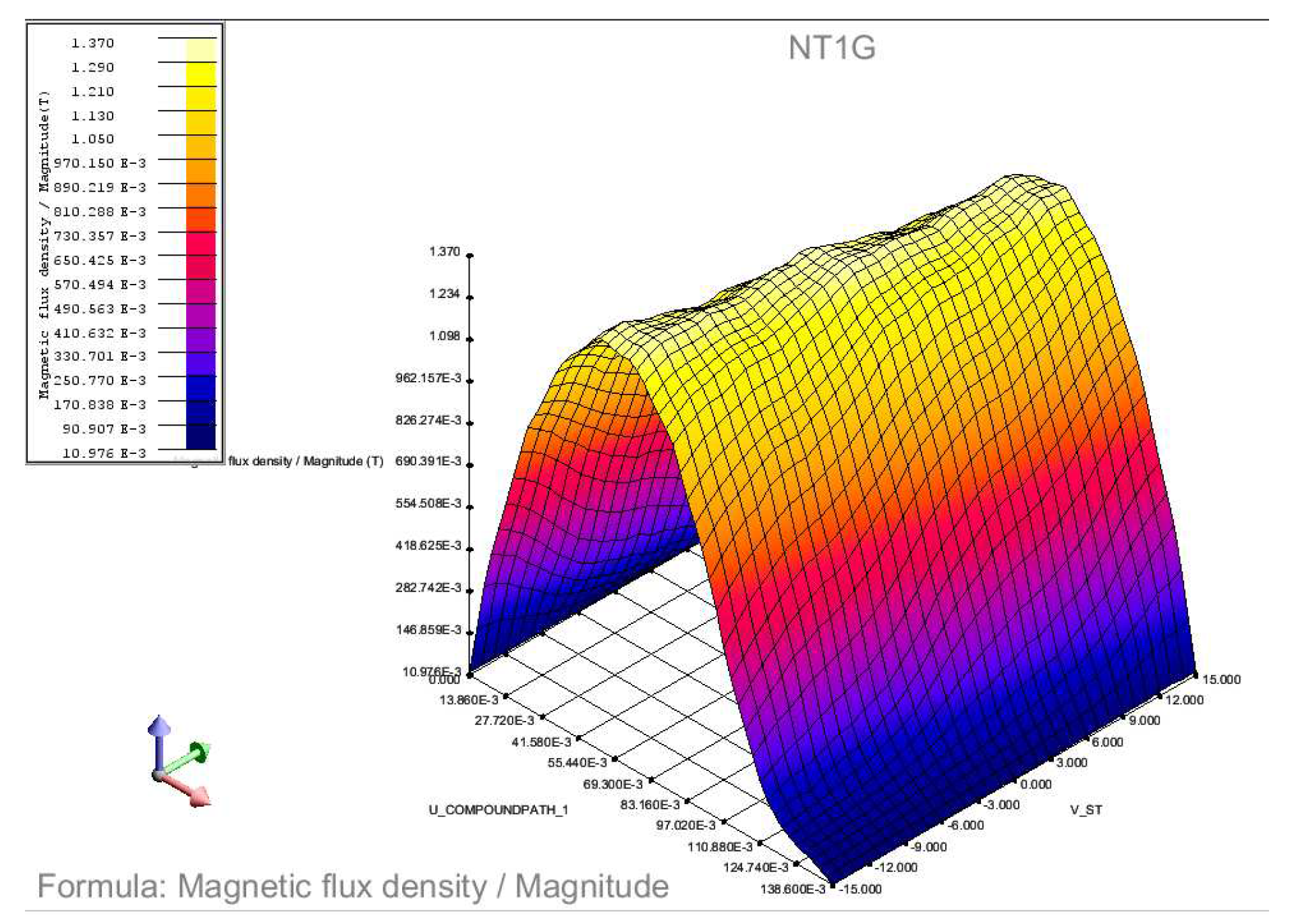
4.3.1. No mover excitation
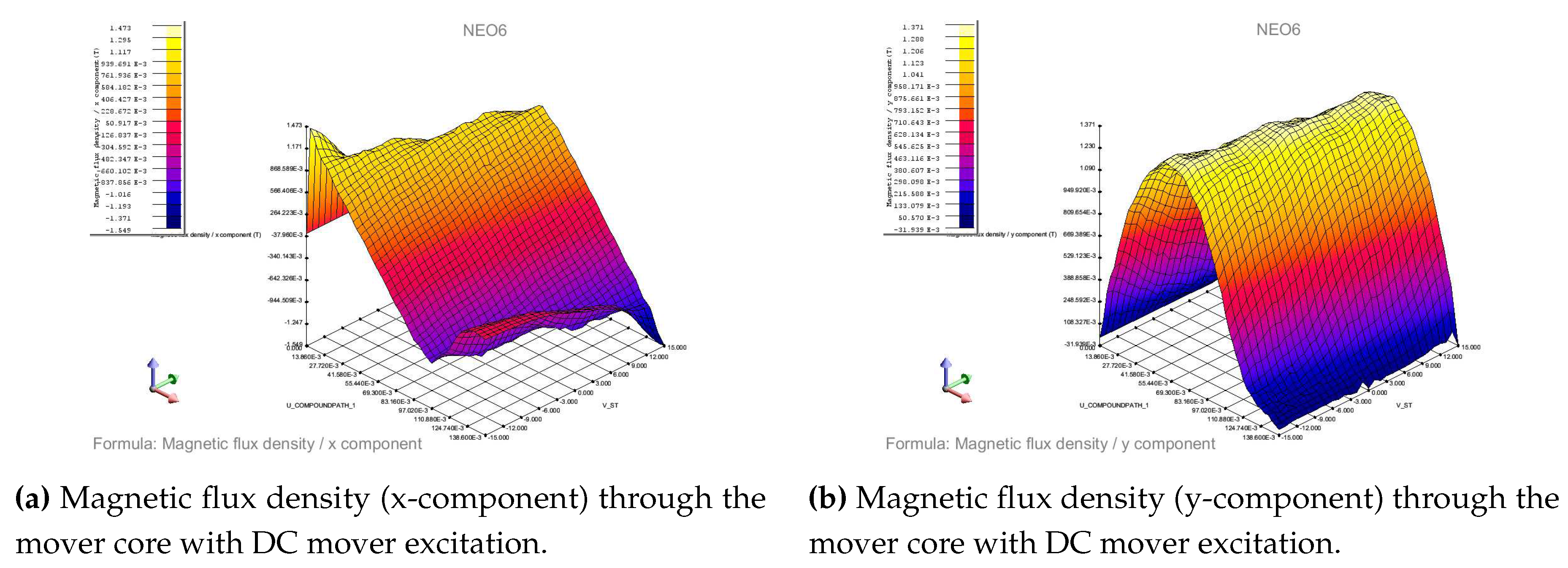
4.3.2. DC excited mover
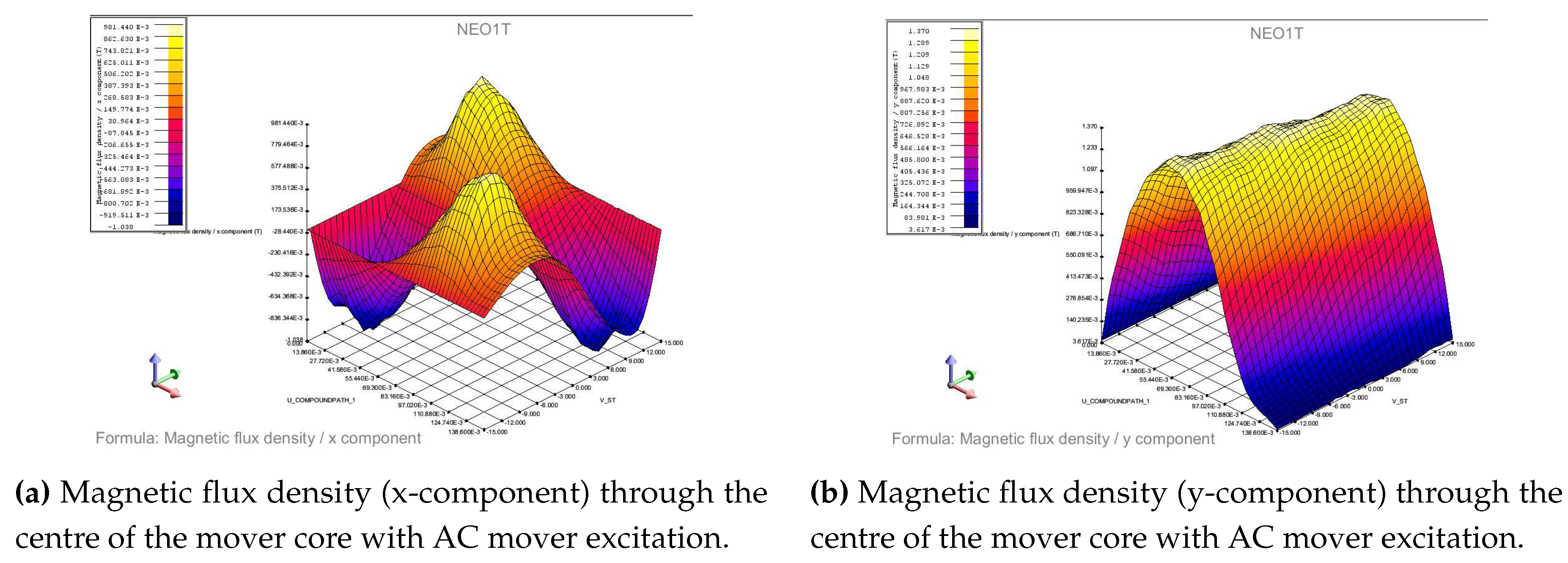
4.3.3. AC excited mover
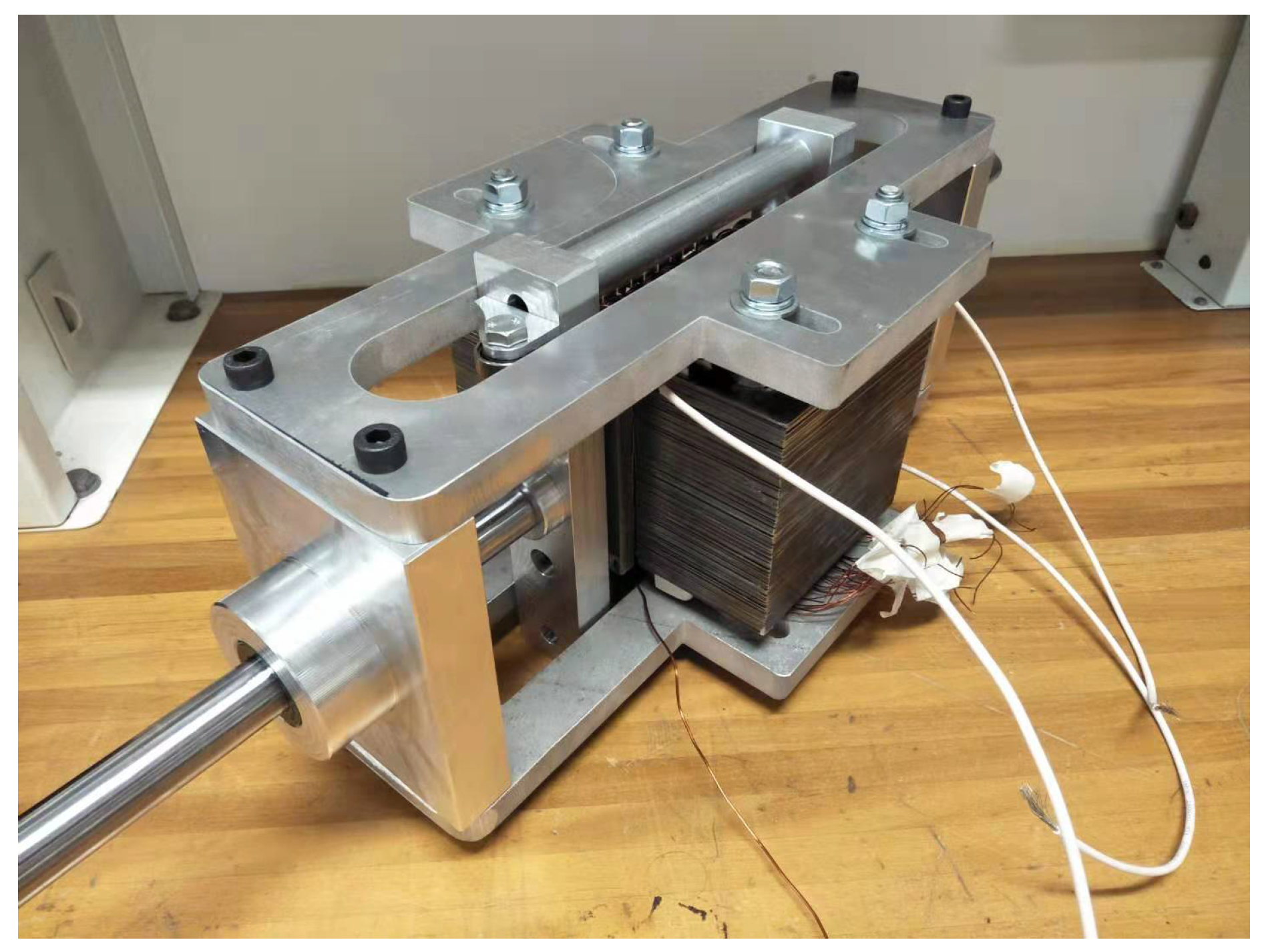
5. Hardware tests
6. Conclusion
References
- A. Ball, J. Billing, C. McCluskey, P. Pham, O. Pittman, S. Lawson, S. Ahmad, A. Starr, J. Rousseau and N. Lambert, “Australian Energy Statistics,” Australian Government Department of Environment and Energy, 2018.
- M. Höök and X. Tang, “Depletion of fossil fuels and anthropogenic climate change—A review,” Energy Policy, vol. 52, pp. 797–809, 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. S. Kulkarni and R. K., “A Comprehensive Review of Energy Harvesting Techniques and its Potential Applications,” International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 139, pp. 14–19, 2016.
- A. Ballo, M. Bottaro and A. D. Grasso, “A Review of Power Management Integrated Circuits for Ultrasound-Based Energy Harvesting in Implantable Medical Devices," Applied Sciences, vol. 11, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Z. Hadas, V. Vetiska, J. Vetiska and J. Krejsa, “Analysis and efficiency measurement of electromagnetic vibration energy harvesting system,” Microsystem Technologies, vol. 22, pp. 1767–1779, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Aliabadi, S. H. Hosseinian, S. J. Moghani and M. Abedi, “Multisided linear induction generator, analytical modeling, 3-D finite element analysis and experimental test,” Elektronika ir Elektrotechnika, vol. 19, pp. 8–14, 2013.
- Z. Li, Z. Yang, H. Naguib and J. Zu, “Design and Studies on a Low-Frequency Truss-Based Compressive-Mode Piezoelectric Energy Harvester,” IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 23, pp. 2849–2858, 2018. [CrossRef]
- C. K. Thein, F. M. Foong and Y. C. Shu, “Damping ratio and power output prediction of an electromagnetic energy harvester designed through finite element analysis,” Sensors and Actuators, A Physical, vol. 286, pp. 220–231, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhou, J. Cao, D.J. Inman, J. Lin, S. Liu and Z. Wang, “Broadband tristable energy harvester: Modeling and experiment verification,” Applied Energy, vol. 133, pp. 33–39, 2014. [CrossRef]
- C. K. Thein, F. M. Foong and Y. C. Shu, “Spring amplification and dynamic friction modelling of a 2DOF/2SDOF system in an electromagnetic vibration energy harvester – Experiment, simulation, and analytical analysis,” Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, vol. 132, pp. 232–252, 2019.
- N. Y. P. Vo, and T. D. Le, “Adaptive pneumatic vibration isolation platform,” Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, vol. 133, 2019. [CrossRef]
- H. Tri Nguyen, D.A. Genov, H. Bardaweel, “Vibration energy harvesting using magnetic spring based nonlinear oscillators: Design strategies and insights," Applied Energy, vol. 269, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Gu, W. Liu, C. Zhao, P. Wang, “A goblet-like non-linear electromagnetic generator for planar multi-directional vibration energy harvesting,” Applied Energy, vol. 266, 2020. [CrossRef]
- W. R. Cawthorne, P. Famouri, J. Chen, N. N. Clark, T. I. McDaniel, R. J. Atkinson, S. Nandkumar, C. M. Atkinson and S. Petreanu, “Development of a linear alternator-engine for hybrid electric vehicle applications,” IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 48, pp. 1797–1802, 1999. [CrossRef]
- U. Ngwaka, B. Jia, C. Lawrence, D. Wu, A. Smallbone and A. P. Roskilly, “The characteristics of a Linear Joule Engine Generator operating on a dry friction principle,” Applied Energy, vol. 237, pp. 49–59, 2019. [CrossRef]
- I. Boldea, S. A. Nasar, Linear Electric Actuators and Generators, 1997. [CrossRef]
- J. Prudell, M. Stoddard, E. Amon, T. K. A. Brekken and A. Von Jouanne, “A permanent-magnet tubular linear generator for ocean wave energy conversion,” IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 46, pp. 2392–2400, 2010. [CrossRef]
- J. S. Shin, R. Watanabe, T. Koseki, and H. J. Kim, “Practical design approach of a transverse flux linear synchronous motor for compact size, small mover weight, high efficiency, and low material cost," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 51, 2015.
- Y. Tang, J. J. H. Paulides, T. E. Motoasca and E. A. Lomonova, “Flux-switching machine with DC excitation," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 48, pp. 3583–3586. 2012. [CrossRef]
- J. Li, W. Li, R. Li and Z. Ming, “A Five-Phase Doubly Fed Doubly Salient HTS Linear Motor for Vertical Transportation," IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, vol. 28, 2018. [CrossRef]
- O. Farrok, M. R. Islam, Y. Guo, J. Zhu and W. Xu, “A Novel Design Procedure for Designing Linear Generators," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 65, pp. 1846–1854, 2018. [CrossRef]
- O. Farrok, M. R. Islam, M. R. I. Sheikh, Y. Guo and J. G. Zhu, “Design and Analysis of a Novel Lightweight Translator Permanent Magnet Linear Generator for Oceanic Wave Energy Conversion," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 53, pp. 1–4, 2017. [CrossRef]
- O. Farrok, M. R. Islam, M. R. I. Sheikh, Y. Guo and J. G. Zhu, “A Split Translator Secondary Stator Permanent Magnet Linear Generator for Oceanic Wave Energy Conversion," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 65, pp. 7600–7608, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Jun, Y. Shin and J. H. Kim, “Linear electric generator with Halbach array to self-charge a smartphone," Journal of Vibroengineering, vol. 18, pp. 587–594, 2016.
- U. J. Seo, B. Riemer, R. Appunn and K. Hameyer, “Design considerations of a linear generator for a range extender application," Archives of Electrical Engineering, vol. 64, pp. 581–592, 2015. [CrossRef]
- M. F. Iacchetti, R. Shuttleworth and M. Zhang, “Volt-ampere ratings in electronically tuned linear alternators for thermoacoustic engines," IET Renewable Power Generation, vol. 12, pp. 1256–1262, 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. Benamor, M. T. Benchouia, K. Srairi and M. E. H. Benbouzid, “A novel rooted tree optimization apply in the high order sliding mode control using super-twisting algorithm based on DTC scheme for DFIG," International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, vol. 108, pp. 293–302, 2019. [CrossRef]
- T. S. L. V. Ayyarao, “Modified vector controlled DFIG wind energy system based on barrier function adaptive sliding mode control,” Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, vol. 4, 2019. [CrossRef]
- H. M. Jabr, D. Lu and N. C. Kar, “Design and implementation of neuro-fuzzy vector control for wind-driven doubly-fed induction generator,” IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, vol. 2, pp. 404–413, 2011. [CrossRef]
- S. J. Cho and J. H. Kim, “ Linear electromagnetic electric generator for harvesting vibration energy at frequencies more than 50 Hz," Advances in Mechanical Engineering, vol. 9, 2017. [CrossRef]
- N. M. Kimoulakis, A. G. Kladas and J. A. Tegopoulos, “Cogging force minimization in a coupled permanent magnet linear generator for sea wave energy extraction applications,” IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 45, pp. 1246–1249, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang, K. Zhang and M. Zhou, “Suppression of thrust fluctuation of doubly-fed linear motor,” Journal of Modern Transportation, vol. 20, pp. 103–107, 2012. [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Number of stator teeth | 13 | |
| Number of stator slots | 12 | |
| Stator pole pitch | 8.8 | mm |
| Depth of stator slot | 24 | mm |
| Number of mover teeth | 11 | |
| Number of mover slots | 10 | |
| Mover pole pitch | 13.2 | mm |
| Width of mover tooth | 6.6 | mm |
| Width of mover slot | 6.6 | mm |
| Depth of mover slot | 10 | mm |
| Mover length | 138.6 | mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





