Submitted:
08 December 2023
Posted:
11 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mathematical Model Development
2.2. Main Assumptions and Considerations
2.3. Mathematical Model Equations
2.3.1. The Standard k-ε realizable Turbulence Model
2.3.2. The Lagrangian Discrete Phase Model
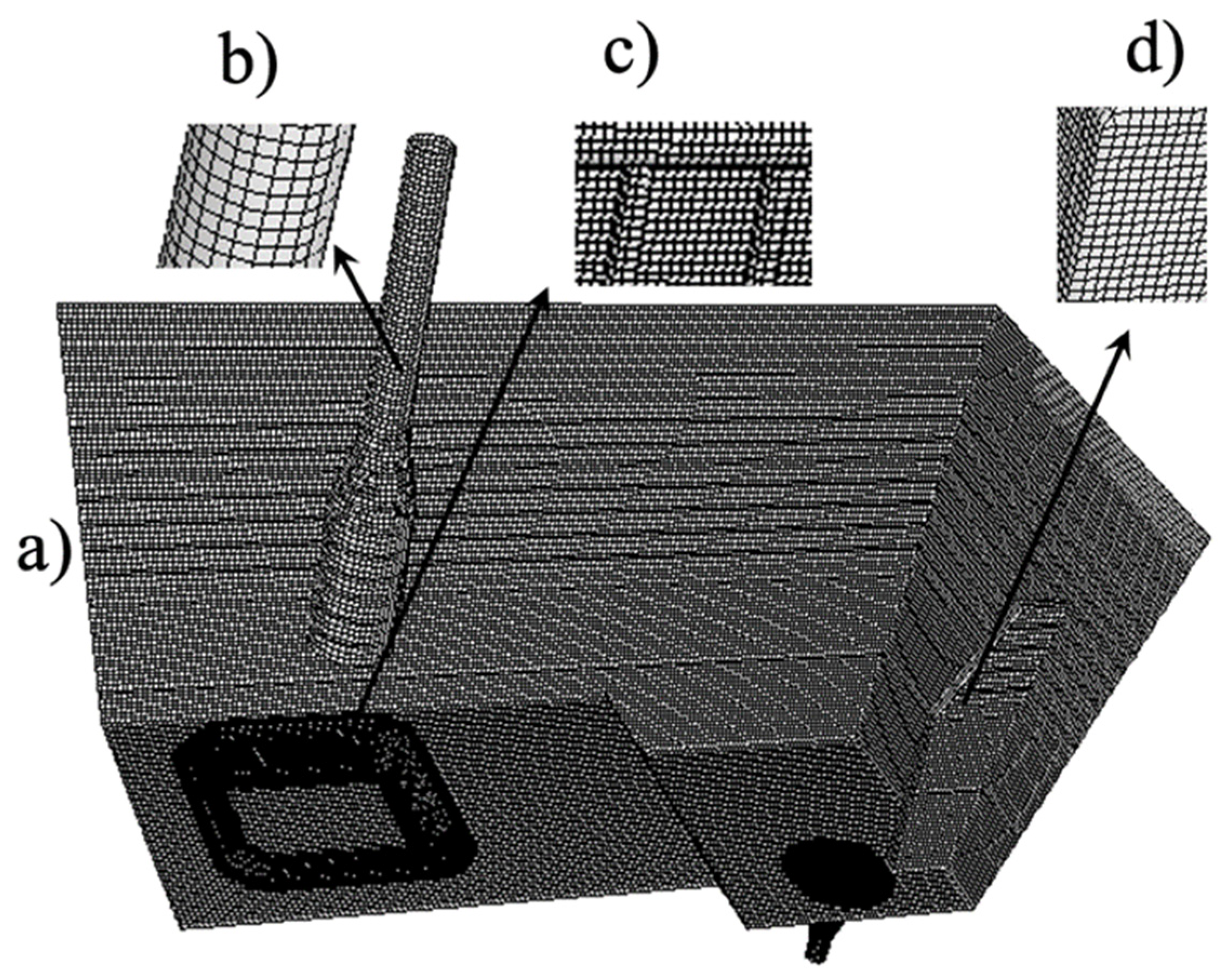
2.4. Numerical Procedure
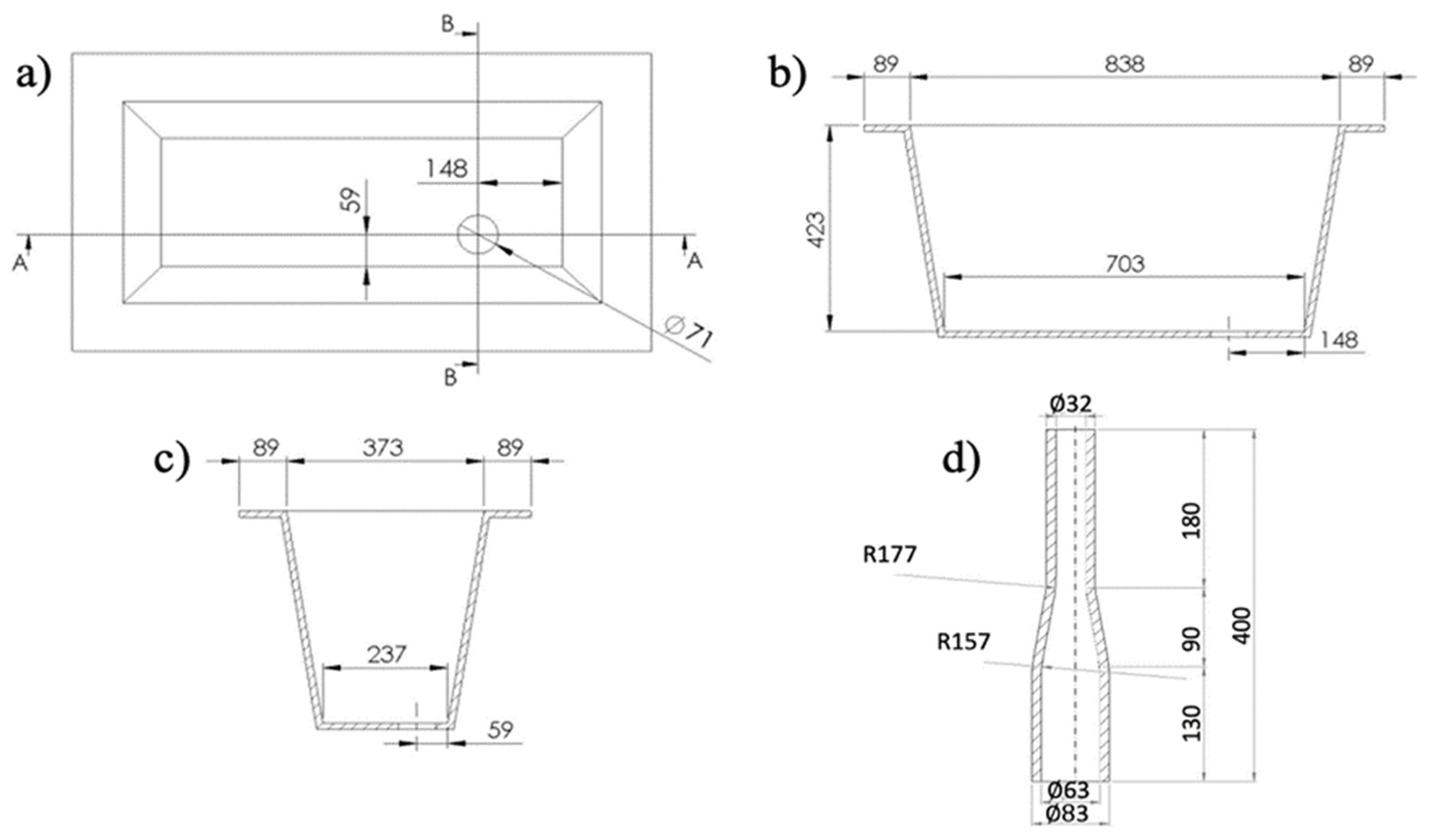
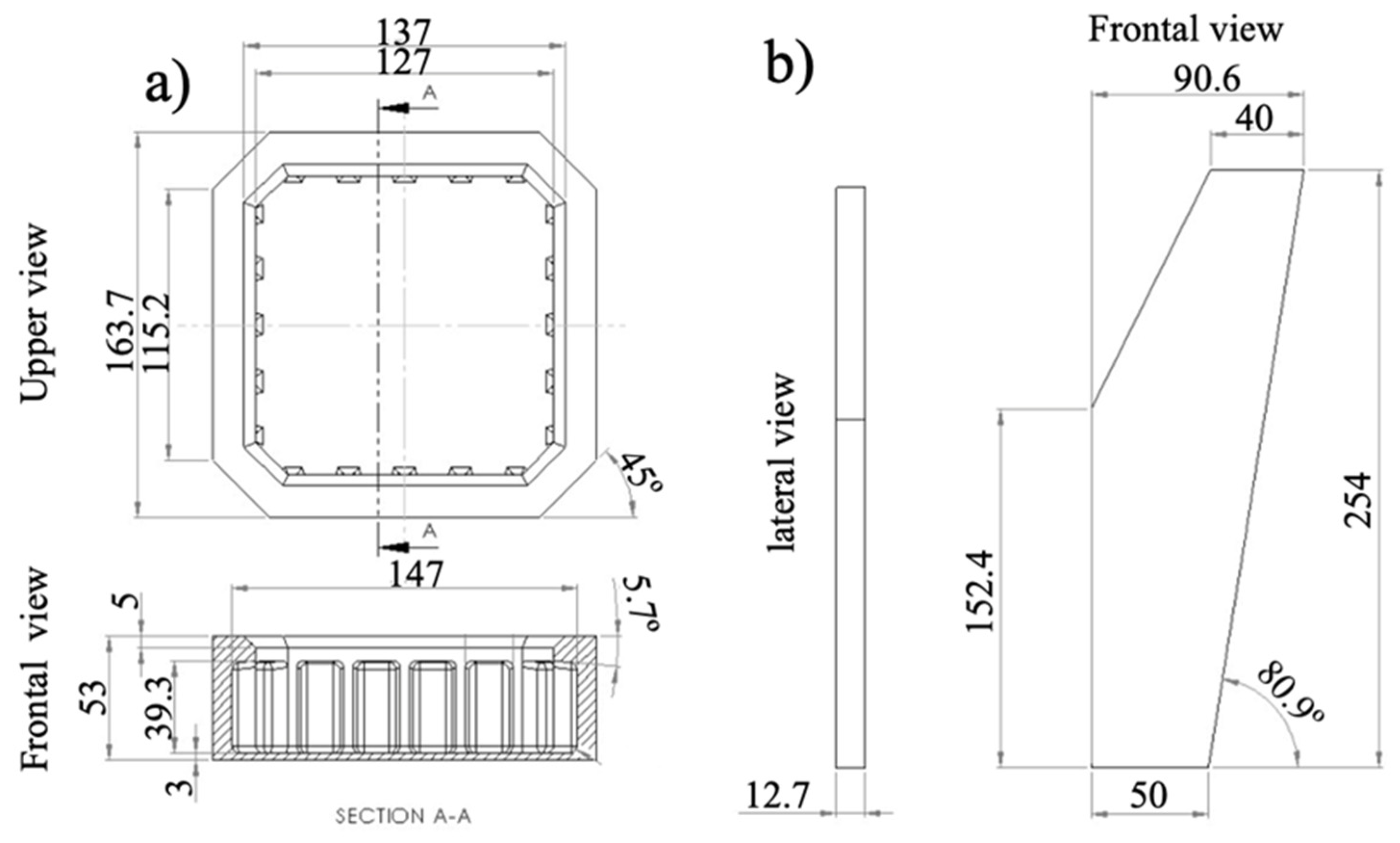
2.5. Physical model
3. Results and discussion
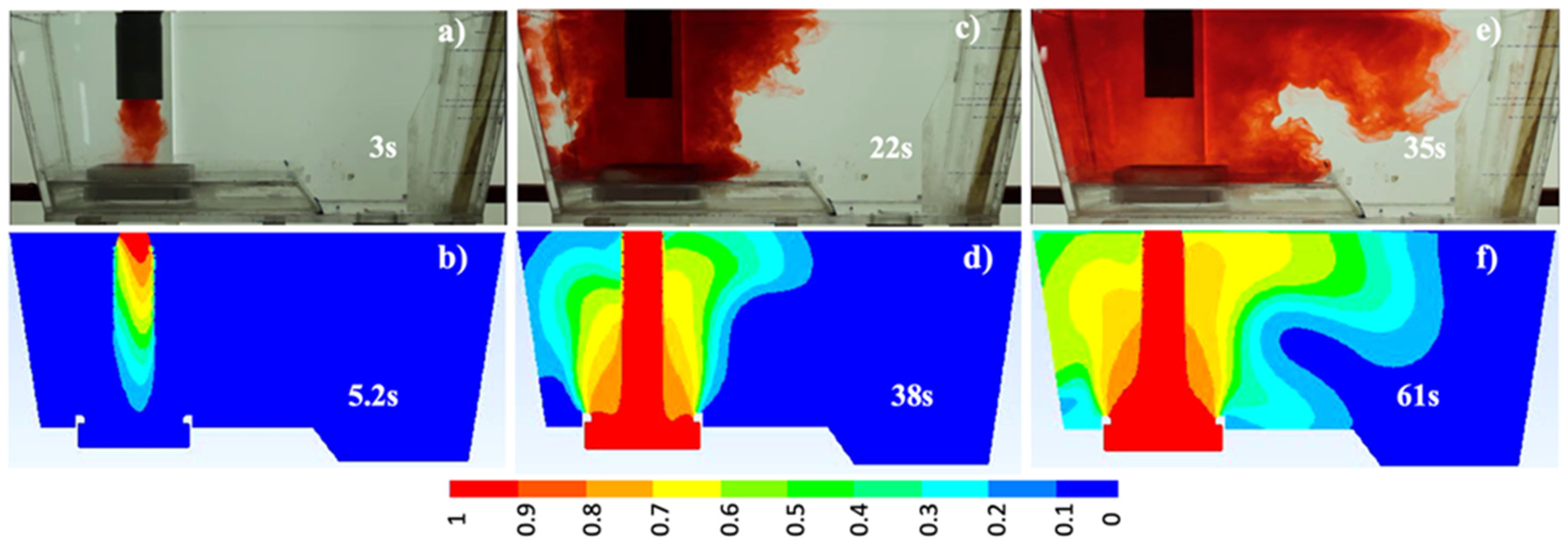
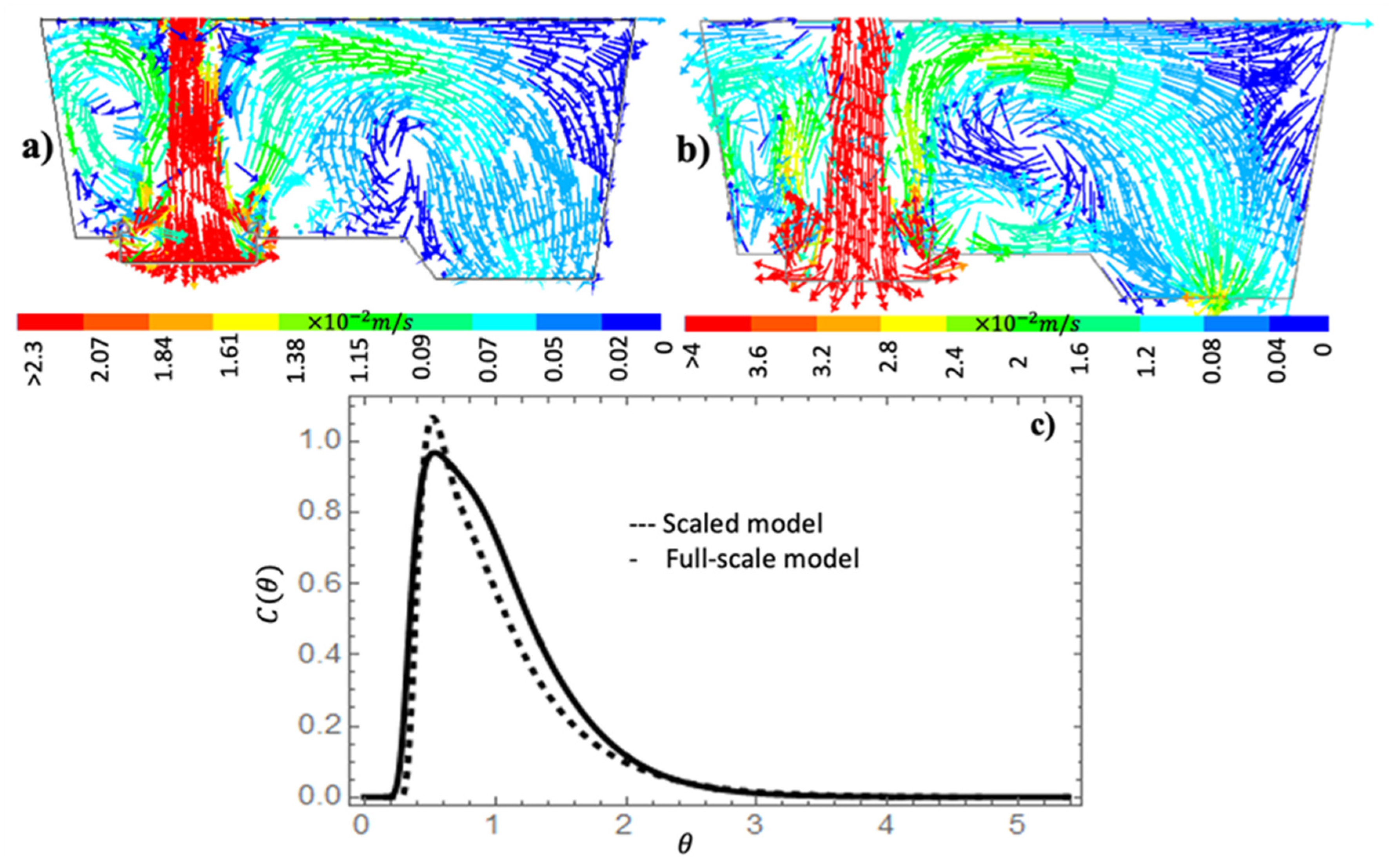
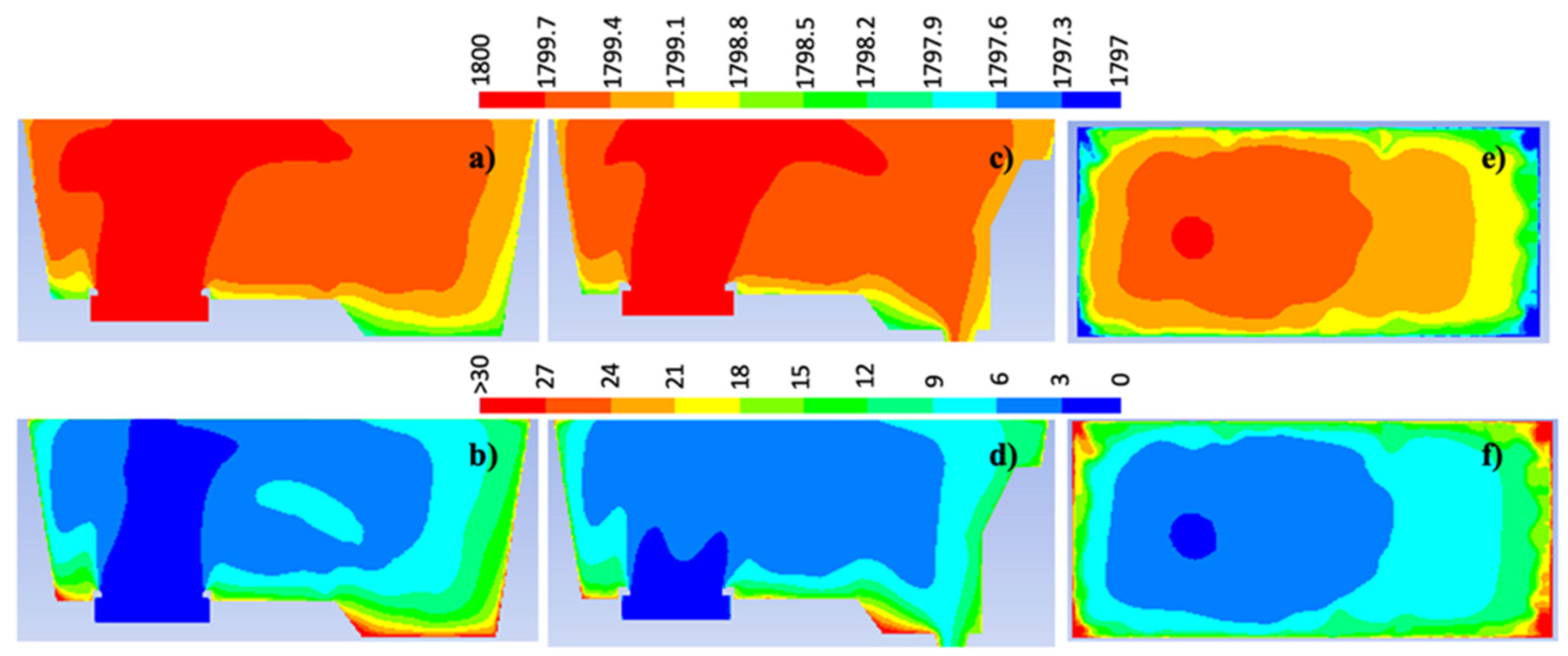
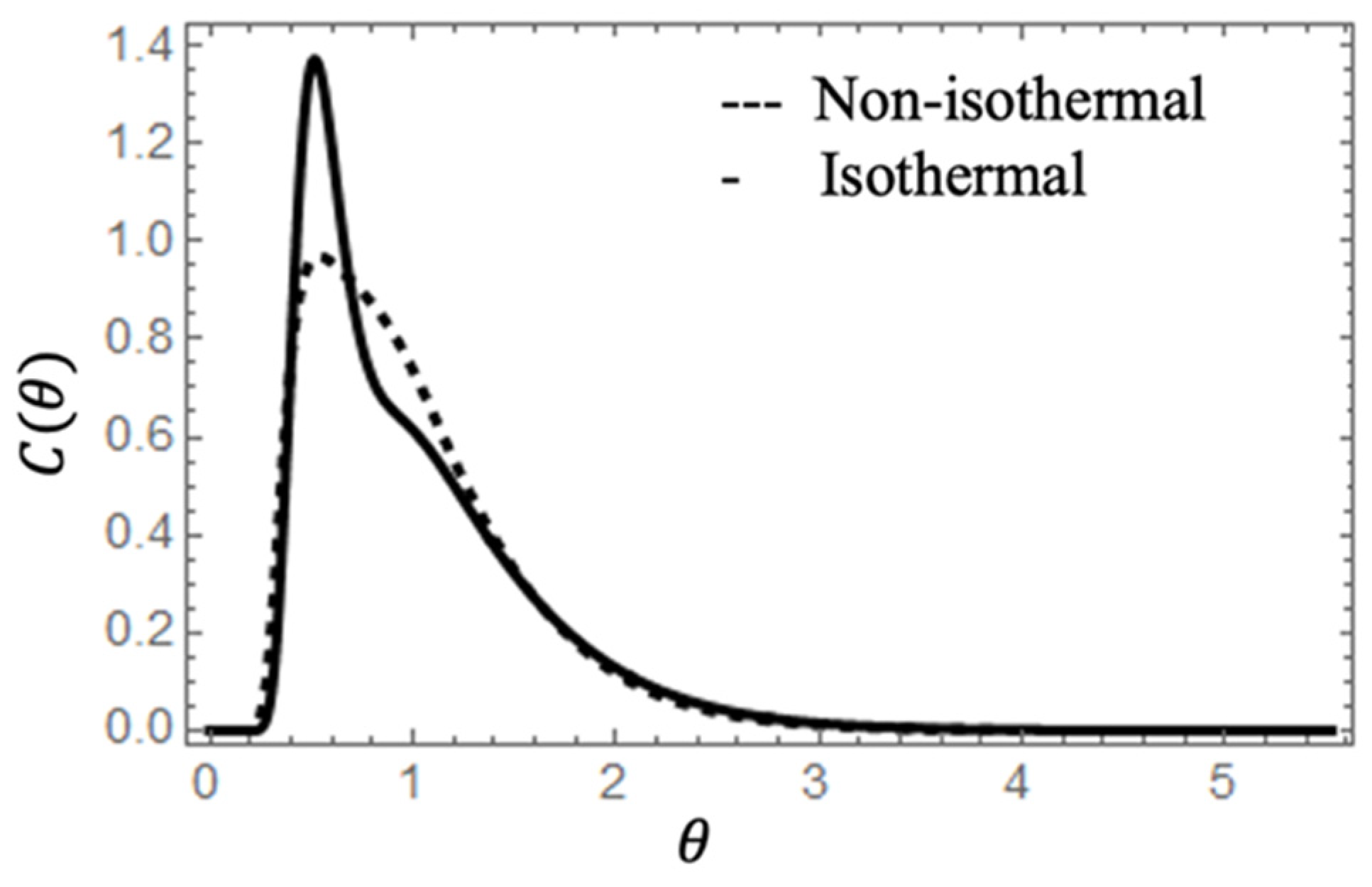
3.1. Mathematical model validation
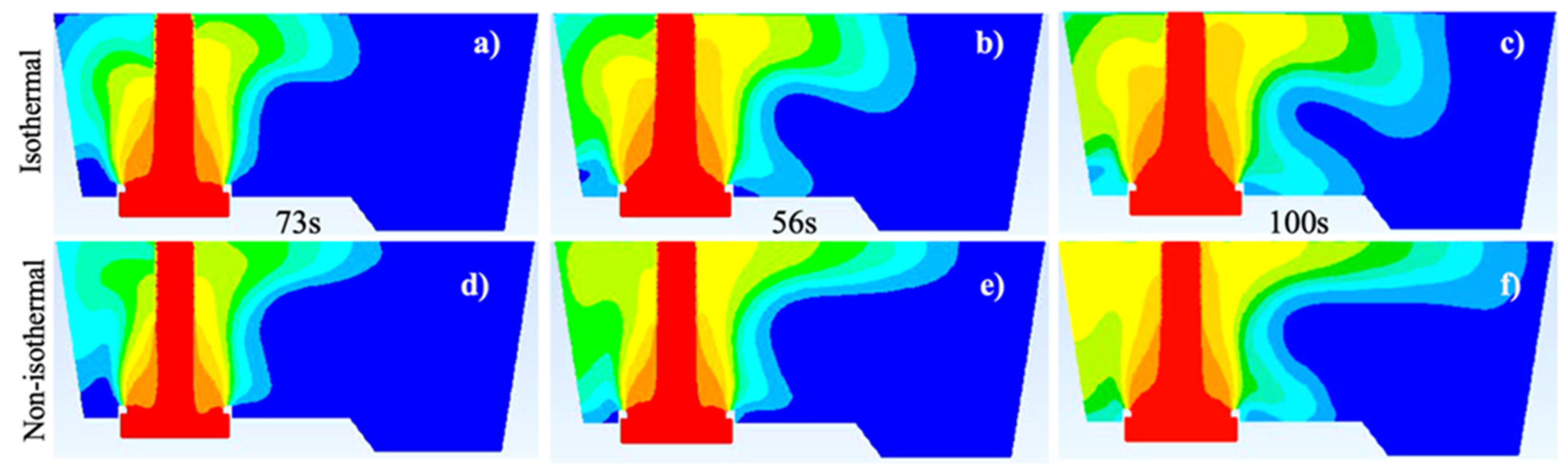
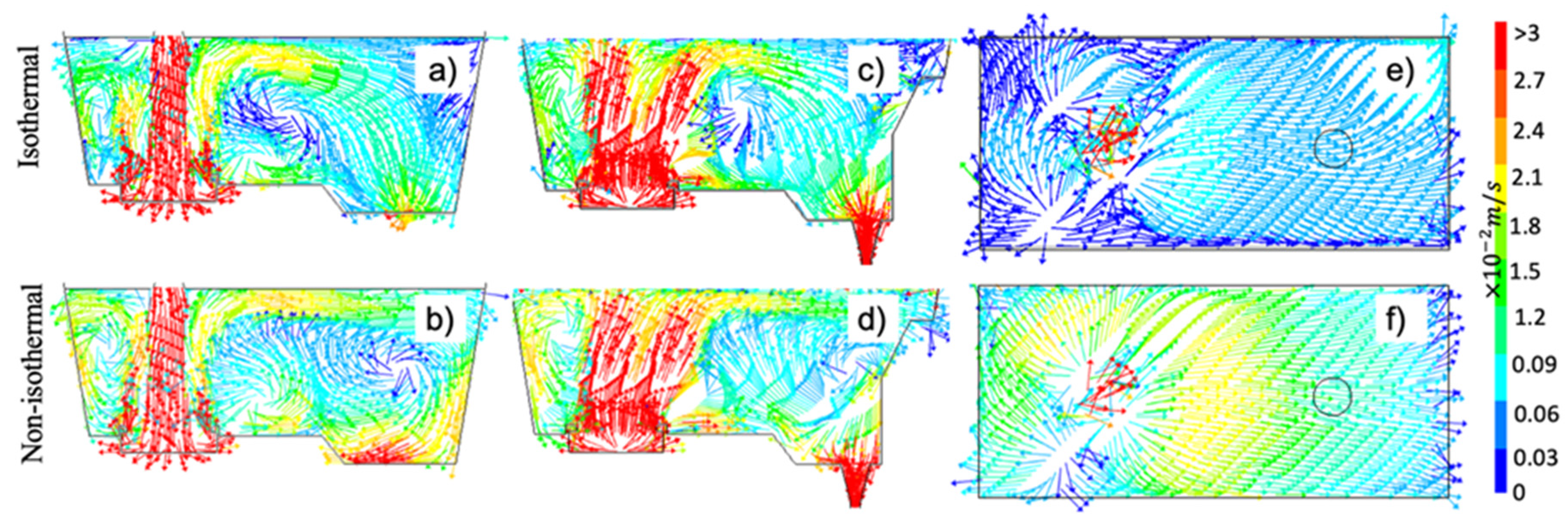
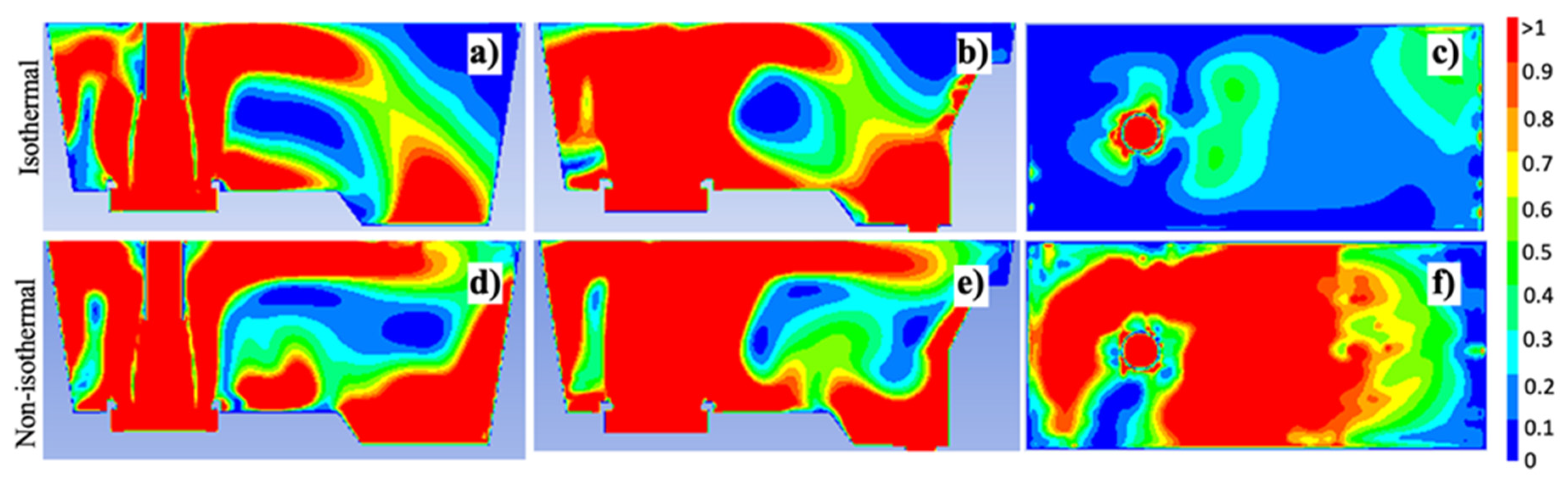
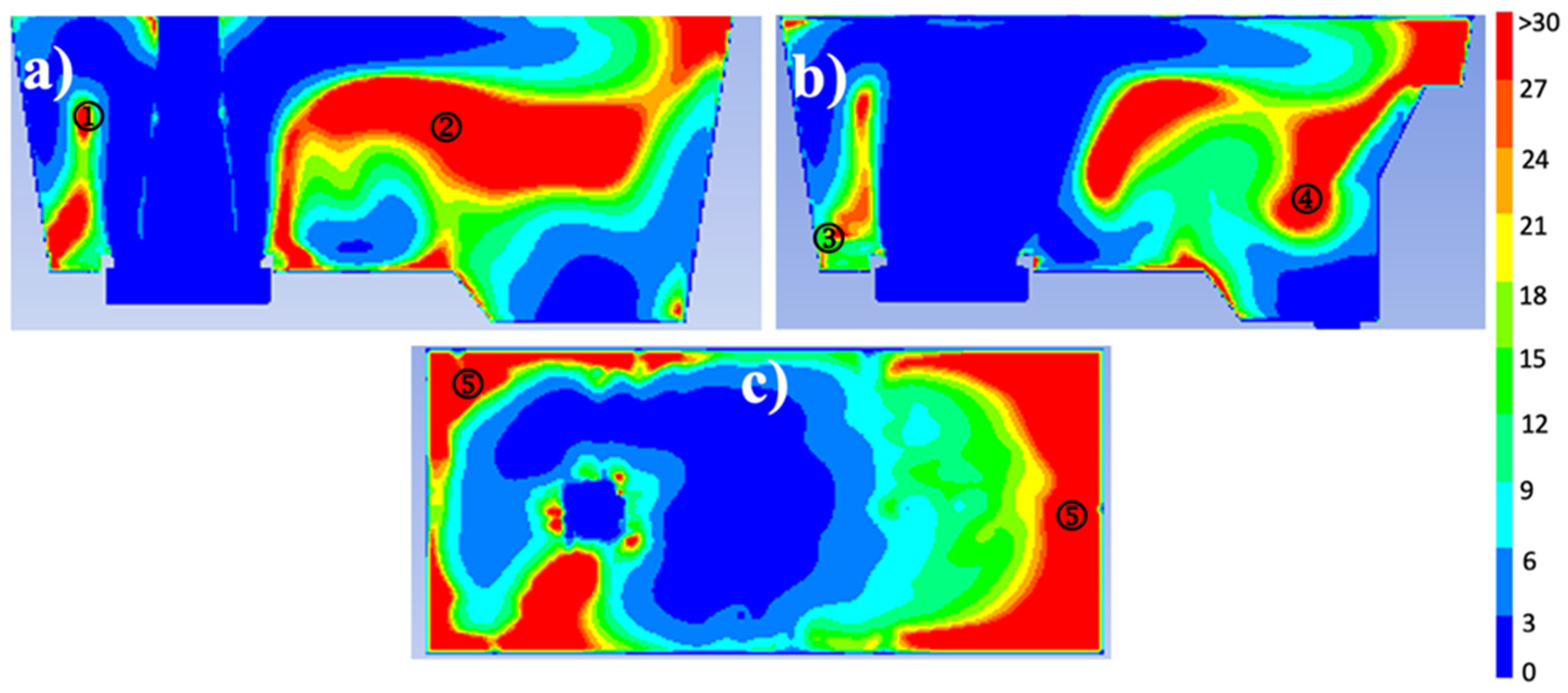
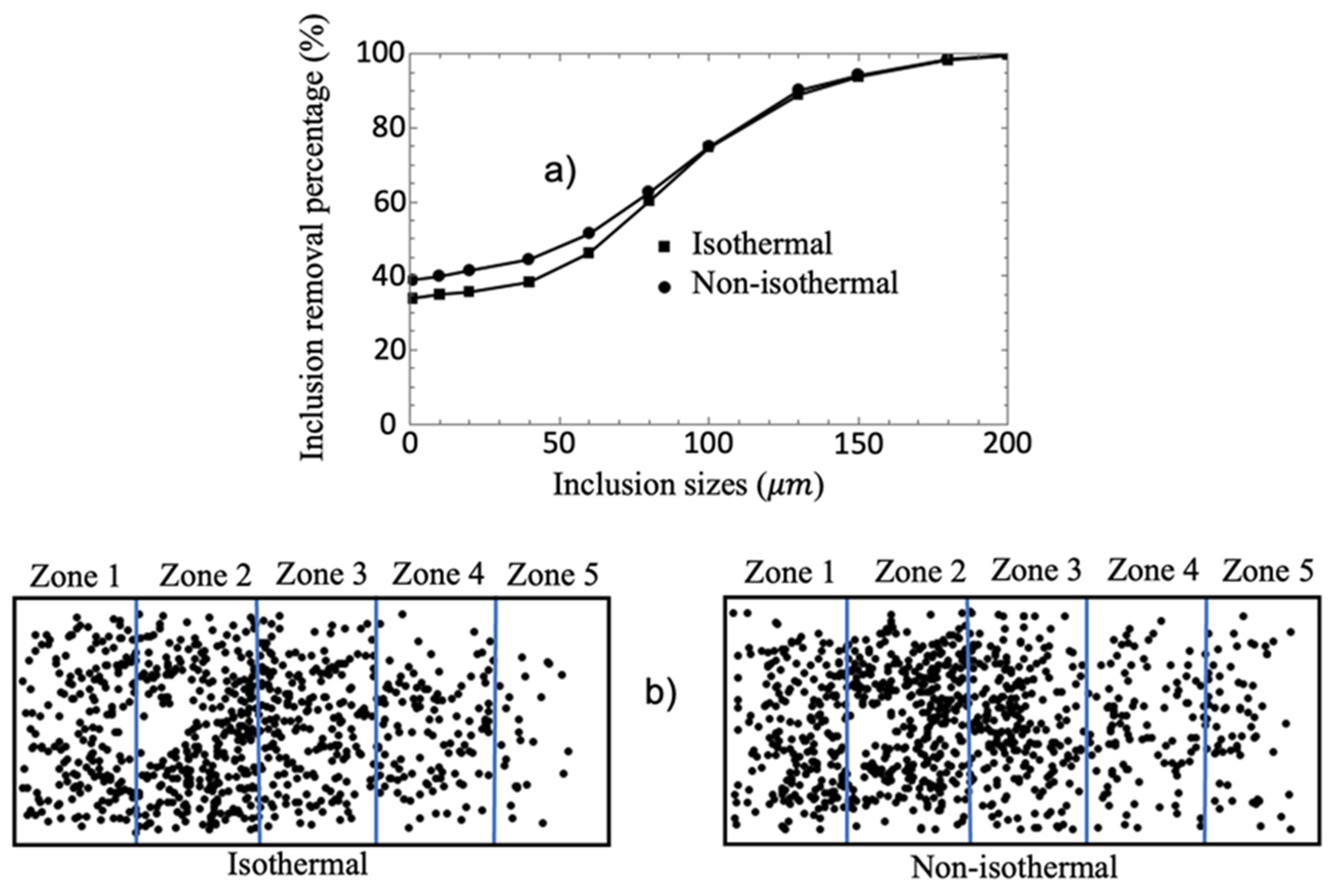
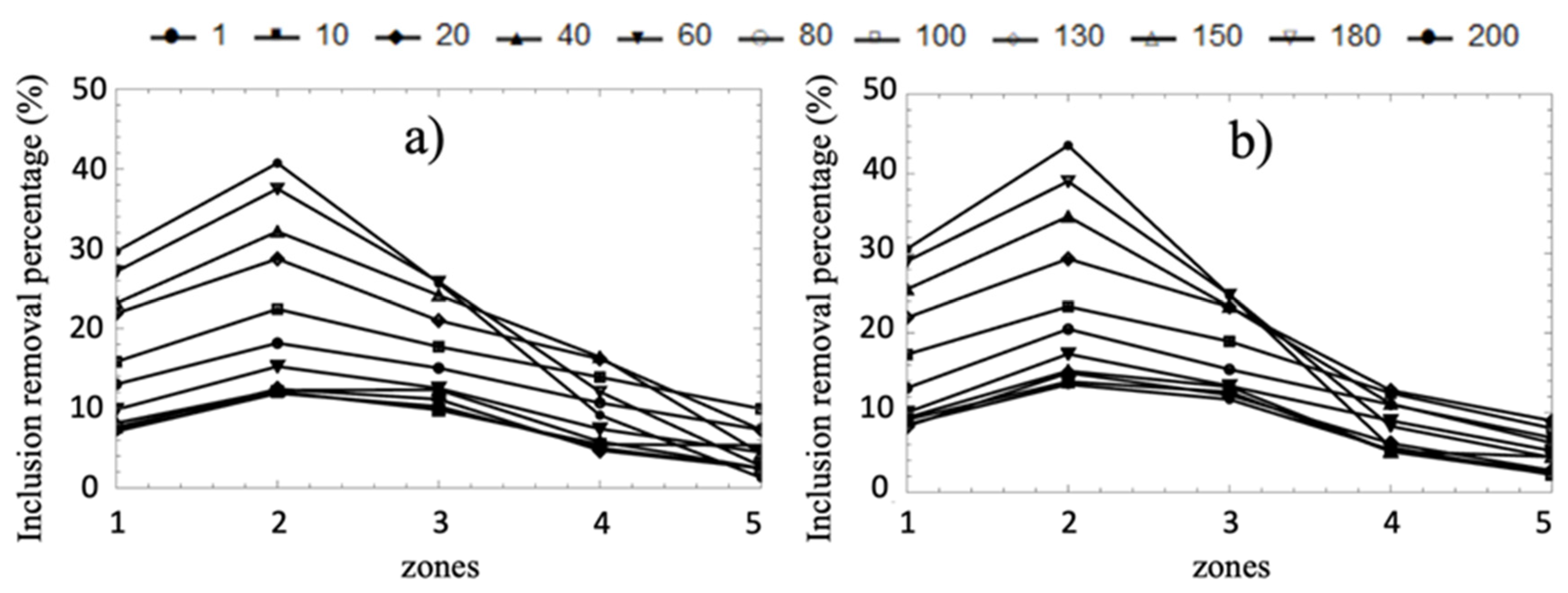
3.2. Comparison between isothermal and non-isothermal cases
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The quantification of the differences between the results of 1:3 scaled and full-scale models, which have a maxima difference of 4% on the volume fractions percent and residence time, demonstrate that scaled and full-scale models can be used reliably to predict the flow patterns of an isothermal physical model following the Froude criteria.
- (2)
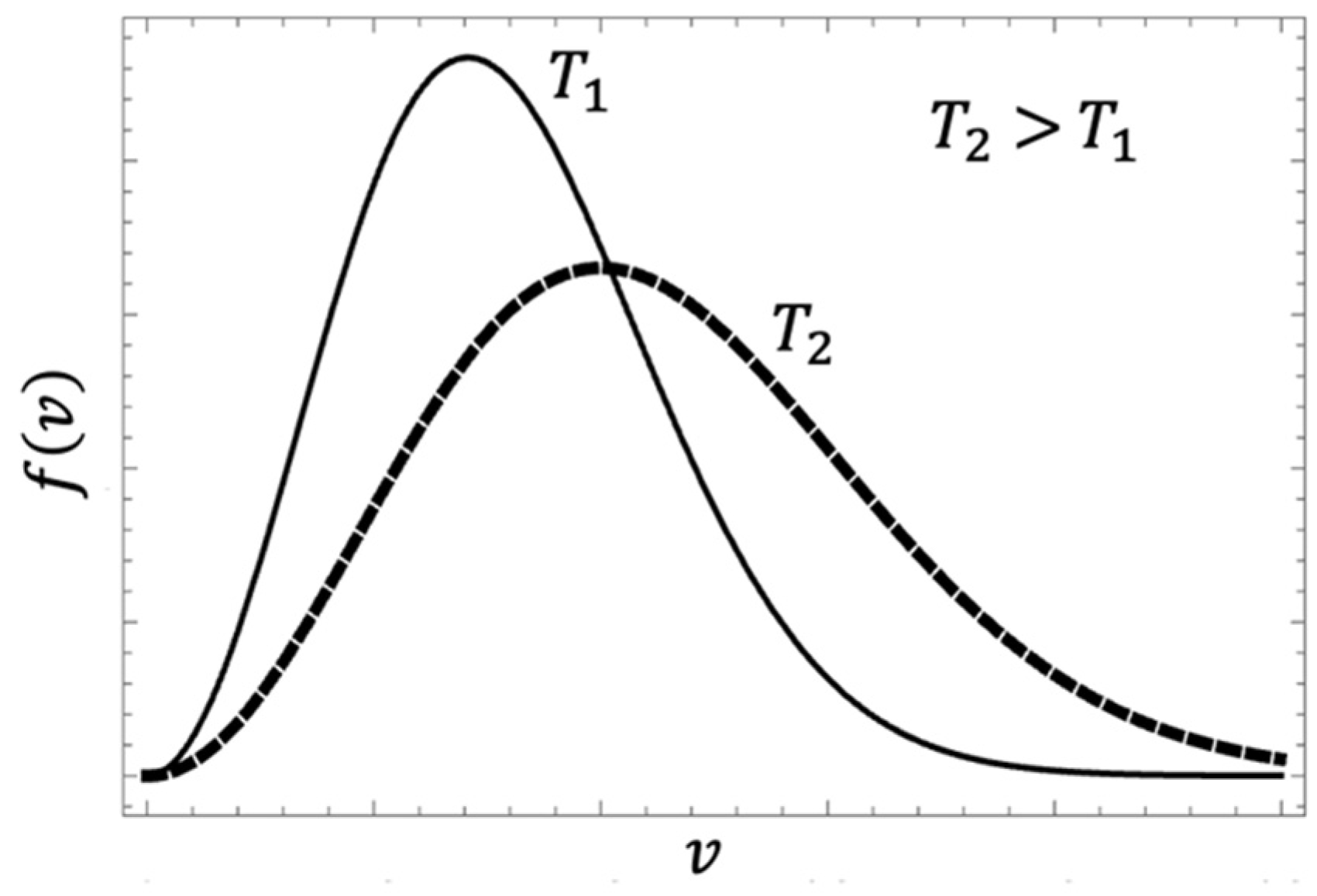
- Temperature gradients inside the tundish induce variations in the flow velocity magnitude; if the stream has a higher temperature than its surrounding flow, its velocity will increase because of the Maxwell-Boltzmann velocity distribution function; this supports why hot streams, e.g., at the bath level, under non-isothermal conditions, have bigger velocity magnitudes than the same streams but under isothermal conditions.
- (3)
- The quantification of the ratio between inertial and buoyancy forces demonstrates that the inertial forces dominate over buoyancy forces at the entry zone because turbulence inhibitor strongly controls the fluid dynamics in such area. In contrast, the buoyancy forces take more relevance than inertial forces in the recirculation and dead flow zones, inducing noticeable changes in the fluid dynamics between isothermal and non-isothermal cases far from the entry zone.
- (4)
- Although the temperature induces substantial fluid dynamic changes between analyzed cases, this variable does not significantly impact the volume fraction percentages or the mean residence time results, and it only increases the inclusion removal percentage by 5% for the non-isothermal case.
- (5)
- The effect of the temperature on the flow patterns is not significant when the flow control devices strongly rule the fluid dynamics; nevertheless, when the flow control devices effects are not dominant, the temperature takes substantial importance by the buoyancy forces and the increment of flow velocity because the Maxwell Boltzmann velocity distribution function changing the fluid dynamics in comparison with the obtained from the isothermal conditions. Consequently, isothermal simulations can accurately describe the flow behavior in tundishes where its flow control devices control the fluid dynamic. However, the simulation of tundishes without control devices or with a weak fluid dynamic dependence on the control devices requires non-isothermal simulations.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D. Sheng and P. Jönsson. Effect of Thermal Buoyancy on Fluid Flow and Residence-Time Distribution in a Single-Strand Tundish, Materials, 2021, Volume 14, pp. 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Q. Wang, Y. Liu, A. Huang, W. Yan, H. Gu and G. Li. CFD Investigation of Effect of Multi-hole Ceramic Filter on Inclusion Removal in a Two-Strand Tundish, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2020, Volume 51, pp. 276-292. [CrossRef]
- A. Cwudzinski. Physical and mathematical simulation of liquid steel mixing zone in one strand continuous casting tundish, Int. J. Cast. Met. Res., 2017, Volume 30, pp. 50-60. [CrossRef]
- R. Agarwal, M.K Singh, R. Kumar, B. Ghosh and S. Pathak. Extensive Analysis of Multi Strand Billet Caster Tundish Using Numerical Technique, J. Mech., 2019, Volume 9, pp. 29-51. http://doi.org/10.4236/wjm.2019.92003.
- F. Xing, S. Zheng, Z. Liu and M. Zhu. Flow Field, Temperature Field, and Inclusion Removal in a New Induction Heating Tundish with Bent Channels, Metals, 2019, Volume 9, pp. 1-16. [CrossRef]
- O. Delgado Ramirez, E. Torres-Alonso, A. Ramos-Banderas, S. Arreola Villa, C. Hernández Bocanegra and J. Téllez Martínez. Thermal and Fluid-Dynamic Optimization of a Five Strand Asymmetric Delta Shaped Billet Caster Tundish, Steel Res. Int., 2018, Volume 89, pp. 1-10. [CrossRef]
- H. Tang, L. Guo, G. Wu, H. Xiao, H. Yao, and J. Zhang. Hydrodynamic Modeling and Mathematical Simulation on Flow Field and Inclusion Removal in a Seven-Strand Continuous Casting Tundish with Channel Type Induction Heating, Metals, 2018, Volume 8, pp. 1-25. [CrossRef]
- L. Neves and R. Tavares. Analysis of the mathematical model of the gas bubbling curtain injection on the bottom and the walls of a continuous casting tundish, Ironmak. Steelmak., 2017, Volume 44, pp. 559-567. [CrossRef]
- Y. Sahai. Tundish Technology for Casting Clean Steel: A Review, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, Volume 47B, pp. 2095-2106. [CrossRef]
- Q. Wang, B. Li and F. Tsukihash. Hydrodynamic Problem in Continuous Casting Tundish with Channel Type Induction Heating, ISIJ Int., 2014, Volume 54, pp. 311-320. [CrossRef]
- P. Ni, L. T. I. Jonsson, M. Ersson and P. G. Jönsson. Turbulent Flow Phenomena and Ce2O3 Behavior during a Steel Teeming Process, ISIJ Int., 2013, Volume 53, pp. 792-801. [CrossRef]
- T. Qu, C. Liu, M. Jiang and L. Zu. Numerical Simulation for Effect of Inlet Cooling Rate on Fluid Flow and Temperature Distribution in Tundish, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2012, Volume 19, pp. 12-19. [CrossRef]
- H. Ling and L. Zhang. Numerical Simulation of the Growth and Removal of Inclusions in the Molten Steel of a Two-Strand Tundish, JOM, 2013, Volume 65, pp. 1155-1163. [CrossRef]
- V. Singh, S. Ajmani, A. Pal, S. Singh and M. Denys. Single strand continuous caster tundish furniture comparison for optimal performance, Ironmak. Steelmak., 2012, Volume 39, pp. 171-179. [CrossRef]
- A. Braun, M. Warzecha and H. Pfeifer. Numerical and Physical Modeling of Steel Flow in a Two-Strand Tundish for Different Casting Conditions, Metall. Mater Trans. B, 2010, Volume 41B, pp. 549-559. [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Zamora, R. Morales, M. Díaz-Cruz, J. Palafox-Ramos, and L. García Demedices. Heat and mass transfer of a convective-stratified flow in a trough type tundish, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2003, Volume 46, pp. 3029-3039. [CrossRef]
- S. Joo, J. Han and R. Guthrie. Inclusion behavior and heat-transfer phenomena in steelmaking tundish operations: Part II. Mathematical model for liquid steel in tundishes, Metall. Mater Trans. B, 1993, Volume 24B, pp. 767-777. [CrossRef]
- S. Chakraborty and Y. Sahai. Effect of Varying Ladle Stream Temperature on the Melt Flow and Heat Transfer in Continuous Casting Tundishes, ISIJ Int., 1991, Volume 31, pp. 960-967. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/isijinternational1989/31/9/31_9_960/_pdf.
- Y. Miki and B. Thomas. Modeling of inclusion removal in a tundish, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, Volume 30B, pp. 639-654. [CrossRef]
- M. Alizadeh and H. Edris. Prediction of RTD Curves for Non-isotherm steel Melt Flows in Continuous Casting Tundish, Proceedings of International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, LMPC September 2007, pp. 167-172.
- H. Sun, B. Yan, J. Zhang. Effect of Thermal Buoyancy Force on the Flow, Temperature Distribution and Residence Time Distribution of Molten Steel in the Slab Casting Tundish, CFD Modeling and Simulation in Materials Processing; The Minerals, Metals, & Materials Society: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2012, pp. 327-334. [CrossRef]
- S. Chatterjee and K. Chattopadhyay. Transient steel quality under non-isothermal conditions in a multi-strand billet caster tundish: part II. Effect of a flow-control device, Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2016, Volume 44, pp. 413-420. [CrossRef]
- M. Zhu, S. Peng, K. Jiang, J. Luo, Y. Zhong and P. Tang. Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Behaviors under Non-Isothermal Conditions in a Four-Strand Tundish, Metals, 2022, Volume 12, pp. 1-15. [CrossRef]
- R. Morales, S. Lopez-Ramirez, Palafox-Ramos, and D. Zacharias. Mathematical simulation of effects of flow control devices and buoyancy forces on molten steel flow and evolution of output temperatures in tundish, Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2001, Volume 28, pp. 33-43. [CrossRef]
- K. Chattopadhyay, M. Isac and R. Guthrie. Modelling of Non-isothermal Melt Flows in a Four Strand Delta Shaped Billet Caster Tundish Validated by Water Model Experiments, ISIJ Int., 2012, Volume 52, pp. 2026-2035. http://dx.doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.52.2026.
- J. de Sousa, E. Barros, F. Marcondes and J. de Castro. Modeling and computational simulation of fluid flow, heat transfer and inclusions trajectories in a tundish of a steel continuous casting machine, Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2019, Volume 8, pp. 4209-4220. [CrossRef]
- S. Neumann, A. Asad and R. Schwarze. Numerical Simulation of an Industrial-Scale Prototypical Steel Melt Tundish Considering Flow Control and Cleaning Strategies, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2020, Volume 22, pp. 1-11. [CrossRef]
- R. Mishra and D. Mazumdar: Trans. Numerical Analysis of Turbulence Inhibitor Toward Inclusion Separation Efficiency in Tundish, Indian Inst. Met., 2019, Volume 72, pp. 889-989. [CrossRef]
- E. Gutiérrez, S. Garcia-Hernández and J. de J. Barreto. Mathematical Analysis of the Touching Inclusions Parameters at the Tundish Free Surface to Predict More Realistic Inclusion Removal Rates, Steel Res. Int,. 2019, Volume 90, pp. 1-33. [CrossRef]
- E. Gutiérrez, S. Garcia-Hernández and J. de J. Barreto. Mathematical Modeling of Inclusions Deposition at the Upper Tundish Nozzle and the Submerged Entry Nozzle, Steel Res. Int,. 2016, Volume 87, pp. 1-11. [CrossRef]
- E. Gutiérrez, S. Garcia-Hernández and J. de J. Barreto. Mathematical Analysis of the Dynamic Effects on the Deposition of Alumina Inclusions inside the Upper Tundish Nozzle, ISIJ Int., 2016, Volume 56, pp. 1394-1403. [CrossRef]
- H. Lei, Y. Zhao, and D. Geng. Mathematical Model for Cluster-Inclusion’s Collision-Growth in Inclusion Cloud at Continuous Casting Mold, ISIJ Int., 2014, Volume 54, pp. 1629-1637. [CrossRef]
- Z. Liu, B. Li and M. Jiang. Transient Asymmetric Flow and Bubble Transport Inside a Slab Continuous-Casting Mold, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, Volume 45B, pp. 675-697. [CrossRef]
- Z. Liu, B. Li, M. Jiang and F. Tsukihashi. Euler-Euler-Lagrangian Modeling for Two-Phase Flow and Particle Transport in Continuous Casting Mold, ISIJ Int., 2014, Volume 54, pp. 1314-1323. [CrossRef]
- K. Takahashi, M. Ando, and T. Ishii. Model of Gas Flow Through Porous Refractory Applied to an Upper Tundish Nozzle, ISIJ Int., 2014, Volume 54, pp. 304-405. [CrossRef]
- Z. He, K. Zhou, S. Liu, W. Xiong, and B. Li. Numerical Modeling of the Fluid Flow in Continuous Casting Tundish with Different Control Devices, A. Appl. Anal., 2013, Volume 2013, pp. 1-8. [CrossRef]
- V. Seshadri, C. da Silva, I. da Silva and E. Junior. A Physical Modelling Study Of Inclusion Removal In Tundish Using Inert Gas Curtain, Tecnol. Metal. Mater. Min., 2012, Volume 9, pp. 22-29. http://dx.doi.org/10.4322/tmm.2012.004.
- M. Long, X. Zuo, L. Zhang, and D. Chen. Kinetic Modeling on Nozzle Clogging During Steel Billet Continuous Casting, ISIJ Int., 2010, Volume 50, pp. 712-720. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhong, L. Li, B. Wang, L. Zhang, L. Zhu and Q. Zhang. Fluid flow behaviour in slab continuous casting tundish with different configurations of gas bubbling curtain, Ironmak. Steelmak., 2008, Volume 35, pp. 436-440. [CrossRef]
- A. Ramos-Banderas, R.D Morales, J. de J. Barreto and G. Solorio-Diaz. Modelling Study of Inclusions Removal by Bubble Flotation in the Tundish, Steel Res. Int., 2006, Volume 77, pp. 325-335.
- Q. Yuan, B. Thomas and S. Vanka. Study of transient flow and particle transport in continuous steel caster molds: Part II. Particle transport, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, Volume 35B, pp. 703-714. [CrossRef]
- Y. Vermeulen, B. Coletti, B. Blanpain, P. Wollants and J. Vleugels. Material Evaluation to Prevent Nozzle Clogging during Continuous Casting of Al Killed Steels, ISIJ Int., 2002, Volume 42, pp. 1234-1240. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhang, S. Taniguchi and K. Cai. Fluid flow and inclusion removal in continuous casting tundish, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, Volume 31B, pp. 253-266. [CrossRef]
- K. Sasai and Y. Mizukami. Reaction Mechanism between Alumina Graphite Immersion Nozzle and Low Carbon Steel, ISIJ Int., 1994, Volume 34, pp. 802-809. [CrossRef]
- Y. Fukuda, Y. Ueshima and S. Mizoguchi. Mechanism of Alumina Deposition on Alumina Graphite Immersion Nozzle in Continuous Caster, ISIJ Int., 1992, Volume 32, pp. 164-168. [CrossRef]
- T. Shih, W. Liou, A. Shabbir, Z. Yang and J.A. Zhu. A new k-ϵ eddy viscosity model for high reynolds number turbulent flows, Comput. Fluids, 1995, Volume 24, pp. 227-238. [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Inc. FLUENT 12.0, User’s Guide; Centerra Resource Park: Cavendish Court, Lebanon, 2009. https://www.afs.enea.it/project/neptunius/docs/fluent/html/ug/main_pre.htm.
| Property | steel | slag | air | Magnesia |
| ) | ||||
| *) | ||||
| --- |
| Wall | Heat loss |
| Bottom | |
| Back and front | |
| Right and left | |
| Control flow devices |
| Scale | ||||
| 1:3 | 46 | 40 | 14 | 0.9 |
| 1:1 | 50 | 38 | 12 | 0.92 |
| Case | ||||
| Isothermal | 50 | 38 | 12 | 0.93 |
| Non-isothermal | 46 | 39 | 15 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





