Submitted:
09 December 2023
Posted:
11 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Silage preparation
2.2. Fermentation Quality Analysis
2.3. Chemical Composition Analysis
2.4. Microbiological Analysis
2.5. Measurement of Rumen Degradation Characteristics
2.6. Microbial diversity analysis
2.7. Statistical analyses
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Characteristics of Chinese water chestnut residue and Corn gluten meal upon Mixed Silage
3.2. Analysis of Malic acid and Citric acid, Chemical Composition and In Situ Effective Degradability of Chinese water chestnut residue and Corn gluten meal upon Mixed Silage
3.3. The Analysis of Malic acid and Citric acid, Fermentation Characteristics and Microbiological Analysis of Chinese water chestnut residue and Corn gluten meal upon Mixed Silage
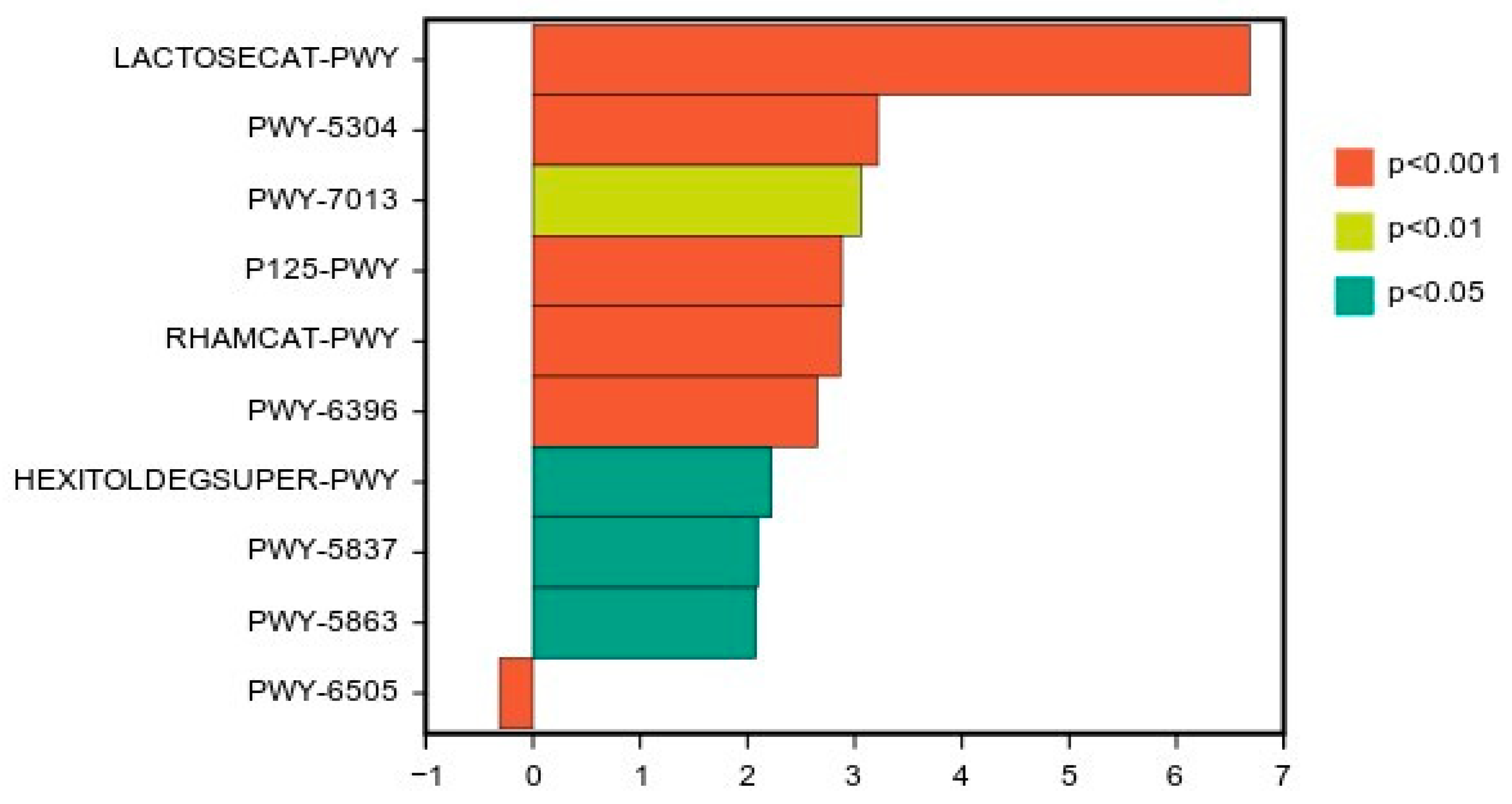
3.6. Analysis of Malic acid and Citric acid in the Microbial Communities of Chinese water chestnut residue and Corn gluten meal upon Mixed Silage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- F. Li, Y. Hu, Y. Shan, J. Liu, X. Ding, X. Duan, J. Zeng, Y. Jiang, Hydrogen-rich water maintains the color quality of fresh-cut Chinese water chestnut, Postharvest Biology and Technology. 2022, 183,111743. [CrossRef]
- Y. You, X. Duan, X. Wei, X. Su, M. Zhao, J. Sun, N. Ruenroengklin, Y. Jiang, Identification of major phenolic compounds of Chinese water chestnut and their antioxidant activity, Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). 2007,12(4), 842-52.
- W.H. Hodge, Chinese water chestnut or matai— A Paddy Crop of China, Economic Botany. 1956,10(1), 49-65. [CrossRef]
- L. Xu, W. He, M. Lu, B. Yuan, M. Zeng, G. Tao, F. Qin, J. Chen, Y. Guan, Z. He, Enzyme-assisted ultrasonic-microwave synergistic extraction and UPLC-QTOF-MS analysis of flavonoids from Chinese water chestnut peels, Industrial Crops and Products. 2018,117,179-186. [CrossRef]
- T.A. Khan, M. Nazir, E.A. Khan, Adsorptive removal of rhodamine B from textile wastewater using water chestnut (Trapa natans L.) peel: adsorption dynamics and kinetic studies, Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry. 2013,95(6),919-931.
- C. Nie, P. Zhu, S. Ma, M. Wang, Y. Hu, Purification, characterization and immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides from stem lettuce, Carbohydrate Polymers. 2018,188,236-242. [CrossRef]
- C. Zhao, L. Wang, G. Ma, X. Jiang, J. Yang, J. Lv, Y. Zhang, Cellulase Interacts with Lactic Acid Bacteria to Affect Fermentation Quality, Microbial Community, and Ruminal Degradability in Mixed Silage of Soybean Residue and Corn Stover, Animals, 2021. [CrossRef]
- D.D. Loy, E.L. Lundy, Chapter 23 - Nutritional Properties and Feeding Value of Corn and Its Coproducts, in: S.O. Serna-Saldivar (Ed.), Corn (Third Edition), AACC International Press, Oxford, 2019, pp. 633-659.
- R. Gümü, N. Ercan, H. Mik, The Effect of High Amounts of Wheat Gluten Meal and Corn Gluten Meal Added to the Diets on Some Serum Parameters in Rats, Turkish Journal of Agriculture - Food Science and Technology. 2020,8(3),698.
- S.L.C.d. VILA, C.O.D. Oliveira, T.A. RODRIGUES, A.T. Tavares, D.C. Bongalhardo, Replacement of corn and soybean meal with corn gluten meal on rooster's diet, Turkish Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences. 2020,44(4),798-804. [CrossRef]
- R. Hu, K.M. Dunmire, C.N. Truelock, C.B. Paulk, G. Aldrich, Y. Li, Antioxidant performances of corn gluten meal and DDGS protein hydrolysates in food, pet food, and feed systems, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research. 2020,2,100030. [CrossRef]
- A.T. Brown, J. Lee, R. Adhikari, K. Haydon, K.G.S. Wamsley, Determining the optimum digestible isoleucine to lysine ratio for Ross 708 x Ross YP male broilers from 0 to 18 d of age, Journal of Applied Poultry Research. 2022,31(1),100217. [CrossRef]
- L.C.A. da Silva, T.L. Honorato, R.S. Cavalcante, T.T. Franco, S. Rodrigues, Effect of pH and Temperature on Enzyme Activity of Chitosanase Produced Under Solid Stated Fermentation by Trichoderma spp, Indian Journal of Microbiology. 2012,52(1),60-65. [CrossRef]
- X. Guo, H. Zhou, Z. Yu, Y. Zhang, Changes in the distribution of nitrogen and plant enzymatic activity during ensilage of lucerne treated with different additives, Grass and Forage Science. 2007,62(1),35-43. [CrossRef]
- W.C. Ke, W.R. Ding, D.M. Xu, L.M. Ding, P. Zhang, F.D. Li, X.S. Guo, Effects of addition of malic or citric acids on fermentation quality and chemical characteristics of alfalfa silage, Journal of Dairy Science. 2017,100(11),8958-8966. [CrossRef]
- W. Ke, W. Ding, D. Xu, M.N. Shah, P. Zhang, X. Guo, Influences of addition of malic acid or citric acid, Lactobacillus plantarum and their mixtures on fermentation quality, proteolysis and fatty acid composition of ensiled alfalfa, Archives of Animal Nutrition. 2018,72(6),492-502.
- M.T. Hasan, AOAC. (1990). Official Methods of Analysis. 15th ed., Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Artington, Virginia, USA, 2015.
- T.A. Thomas, An Automated Procedure For The Determination Of Soluble Carbohydrate In Herbage, 1977. [CrossRef]
- G.A. Broderick, J.H. Kang, Automated Simultaneous Determination of Ammonia and Total Amino Acids in Ruminal Fluid and In Vitro Media1, Journal of Dairy Science. 1980,63(1),64-75. [CrossRef]
- R.A. Olsen, L.R. Bakken, Viability of soil bacteria: Optimization of plate-counting technique and comparison between total counts and plate counts within different size groups, Microbial Ecology. 1987,13(1),59-74. [CrossRef]
- M.M. Chen, Q.H. Liu, G.R. Xin, J.G. Zhang, Characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their inoculating effects on the silage fermentation at high temperature, Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Y. Cai, J. Yang, H. Pang, M. Kitahara, Lactococcus fujiensis sp. nov., a lactic acid bacterium isolated from vegetable matter, International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 2011,61(8),2023-2023.
- F. Hassanat, R. Gervais, C. Julien, D.I. Massé, A. Lettat, P.Y. Chouinard, H.V. Petit, C. Benchaar, Replacing alfalfa silage with corn silage in dairy cow diets: Effects on enteric methane production, ruminal fermentation, digestion, N balance, and milk production, Journal of Dairy Science. 2013,96(7),4553-4567.
- J.R. White, N. Nagarajan, M. Pop, Statistical Methods for Detecting Differentially Abundant Features in Clinical Metagenomic Samples, PLOS Computational Biology. 2009,5(4),e1000352. [CrossRef]
- W. Hu, R.J. Schmidt, E.E. McDonell, C.M. Klingerman, L. Kung, The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 or Lactobacillus plantarum MTD-1 on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silages ensiled at two dry matter contents, Journal of Dairy Science. 2009,92(8),3907-3914. [CrossRef]
- G. Colombari, G. Borreani, G.M. Crovetto, Effect of Ensiling Alfalfa at Low and High Dry Matter on Production of Milk Used to Make Grana Cheese, Journal of Dairy Science. 2001,84(11),2494-2502. [CrossRef]
- R.E. Muck, Dry Matter Level Effects on Alfalfa Silage Quality I. Nitrogen Transformations, Transactions of the Asae. 1987,30(1),7-14. [CrossRef]
- Z. Liao, S. Chen, L. Zhang, S. Li, Y. Zhang, X. Yang, Microbial assemblages in water hyacinth silages with different initial moistures, Environmental Research. 2023,231,116199.
- K. Ni, F. Wang, B. Zhu, J. Yang, G. Zhou, Y. Pan, Y. Tao, J. Zhong, Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses additives on the microbial community and fermentation quality of soybean silage, Bioresource Technology. 2017,238,706-715. [CrossRef]
- W. Hu, W.-j. Li, H.-q. Yang, J.-h. Chen, Current strategies and future prospects for enhancing microbial production of citric acid, Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2019,103(1),201-209. [CrossRef]
- M. Melaku, R. Zhong, H. Han, F. Wan, B. Yi, H. Zhang, Butyric and Citric Acids and Their Salts in Poultry Nutrition: Effects on Gut Health and Intestinal Microbiota, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R.E. Muck, Recent advances in silage microbiology, AGRICULTURAL AND FOOD SCIENCE. 2013,22(1),3-15. [CrossRef]
- X.S. Guo, J. Bai, F.H. Li, D.M. Xu, Y.X. Zhang, D.P. Bu, L.S. Zhao, Effects of malate, citrate, succinate and fumarate on fermentation, chemical composition, aerobic stability and digestibility of alfalfa silage, Animal Feed Science and Technology. 2020,268,114604. [CrossRef]
- Q.-h. Liu, X.-y. Li, S.T. Desta, J.-g. Zhang, T. Shao, Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and fibrolytic enzyme on the fermentation quality and in vitro digestibility of total mixed rations silage including rape straw, Journal of Integrative Agriculture. 2016,15(9),2087-2096. [CrossRef]
- İ. Ertekin, M. Kızılşimşek, Effects of lactic acid bacteria inoculation in pre-harvesting period on fermentation and feed quality properties of alfalfa silage, Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2020,33(2),245-253.
- L. Chen, X.-j. Yuan, J.-f. Li, S.-r. Wang, Z.-h. Dong, T. Shao, Effect of lactic acid bacteria and propionic acid on conservation characteristics, aerobic stability and in vitro gas production kinetics and digestibility of whole-crop corn based total mixed ration silage, Journal of Integrative Agriculture. 2017,16(7),1592-1600. [CrossRef]
- D.H. Kleinschmit, R.J. Schmidt, L. Kung, The Effects of Various Antifungal Additives on the Fermentation and Aerobic Stability of Corn Silage, Journal of Dairy Science. 2005,88(6),2130-2139. [CrossRef]
- B.F. Carvalho, C.L.S. Ávila, J.C. Pinto, M.N. Pereira, R.F. Schwan, Effects of propionic acid and Lactobacillus buchneri (UFLA SIL 72) addition on fermentative and microbiological characteristics of sugar cane silage treated with and without calcium oxide, Grass and Forage Science. 2012,67(4),462-471. [CrossRef]
- W.C. Meteer, L.M. Shoup, W.P. Chapple, W.T. Meteer, D.W. Shike, Effects of feeding high-moisture corn stover to gestating and lactating beef cows as an alternative to hay and corn silage on performance and reproduction, The Professional Animal Scientist. 2018,34(2),210-217. [CrossRef]
- H. Lv, R. Pian, Y. Xing, W. Zhou, F. Yang, X. Chen, Q. Zhang, Effects of citric acid on fermentation characteristics and bacterial diversity of Amomum villosum silage, Bioresource Technology. 2020,307,123290. [CrossRef]
- F. Li, W. Ke, Z. Ding, J. Bai, Y. Zhang, D. Xu, Z. Li, X. Guo, Pretreatment of Pennisetum sinese silages with ferulic acid esterase-producing lactic acid bacteria and cellulase at two dry matter contents: Fermentation characteristics, carbohydrates composition and enzymatic saccharification, Bioresource Technology. 2020,295,122261. [CrossRef]
- M. Nazar, S. Wang, J. Zhao, Z. Dong, J. Li, N. Ali Kaka, T. Shao, Effects of various epiphytic microbiota inoculation on the fermentation quality and microbial community dynamics during the ensiling of sterile Napier grass, Journal of Applied Microbiology. 2021,130(5),1466-1480. [CrossRef]
- H. Ren, Y. Feng, T. Liu, J. Li, Z. Wang, S. Fu, Y. Zheng, Z. Peng, Effects of different simulated seasonal temperatures on the fermentation characteristics and microbial community diversities of the maize straw and cabbage waste co-ensiling system, Science of The Total Environment. 2020,708,135113. [CrossRef]
- W.G. Nuez-Ortín, P. Yu, Estimation of ruminal and intestinal digestion profiles, hourly effective degradation ratio and potential N to energy synchronization of co-products from bioethanol processing, Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 2010,90(12),2058-2067. [CrossRef]
- P. Yu, D.A. Christensen, J.J. McKinnon, In situ rumen degradation kinetics of timothy and alfalfa as affected by cultivar and stage of maturity, Canadian Journal of Animal Science. 2004,84(2),255-263. [CrossRef]
- Ke, Chen, Erchao, Li, Zhixin, Xu, Tongyu, Li, Chang, X.J.P. ONE, Comparative Transcriptome Analysis in the Hepatopancreas Tissue of Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Fed Different Lipid Sources at Low Salinity. 2015,10(12),e0144889.
- C.E. Polan, K.A. Cummins, C.J. Sniffen, T.V. Muscato, J.L. Vicini, B.A. Crooker, J.H. Clark, D.G. Johnson, D.E. Otterby, B. Guillaume, L.D. Muller, G.A. Varga, R.A. Murray, S.B. Peirce-Sandner, Responses of Dairy Cows to Supplemental Rumen-Protected Forms of Methionine and Lysine, Journal of Dairy Science. 1991,74(9),2997-3013. [CrossRef]
- K. Ni, J. Zhao, B. Zhu, R. Su, Y. Pan, J. Ma, G. Zhou, Y. Tao, X. Liu, J. Zhong, Assessing the fermentation quality and microbial community of the mixed silage of forage soybean with crop corn or sorghum, Bioresource Technology. 2018,265,563-567. [CrossRef]
- M. du Toit, L. Engelbrecht, E. Lerm, S. Krieger-Weber, Lactobacillus: the Next Generation of Malolactic Fermentation Starter Cultures—an Overview, Food and Bioprocess Technology. 2011,4(6),876-906. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li, N. Nishino, Bacterial and fungal communities of wilted Italian ryegrass silage inoculated with and without Lactobacillus rhamnosus or Lactobacillus buchneri, Letters in Applied Microbiology. 2011,52(4),314-321. [CrossRef]
- B. Liu, H. Huan, H. Gu, N. Xu, Q. Shen, C. Ding, Dynamics of a microbial community during ensiling and upon aerobic exposure in lactic acid bacteria inoculation-treated and untreated barley silages, Bioresource Technology. 2019,273,212-219. [CrossRef]
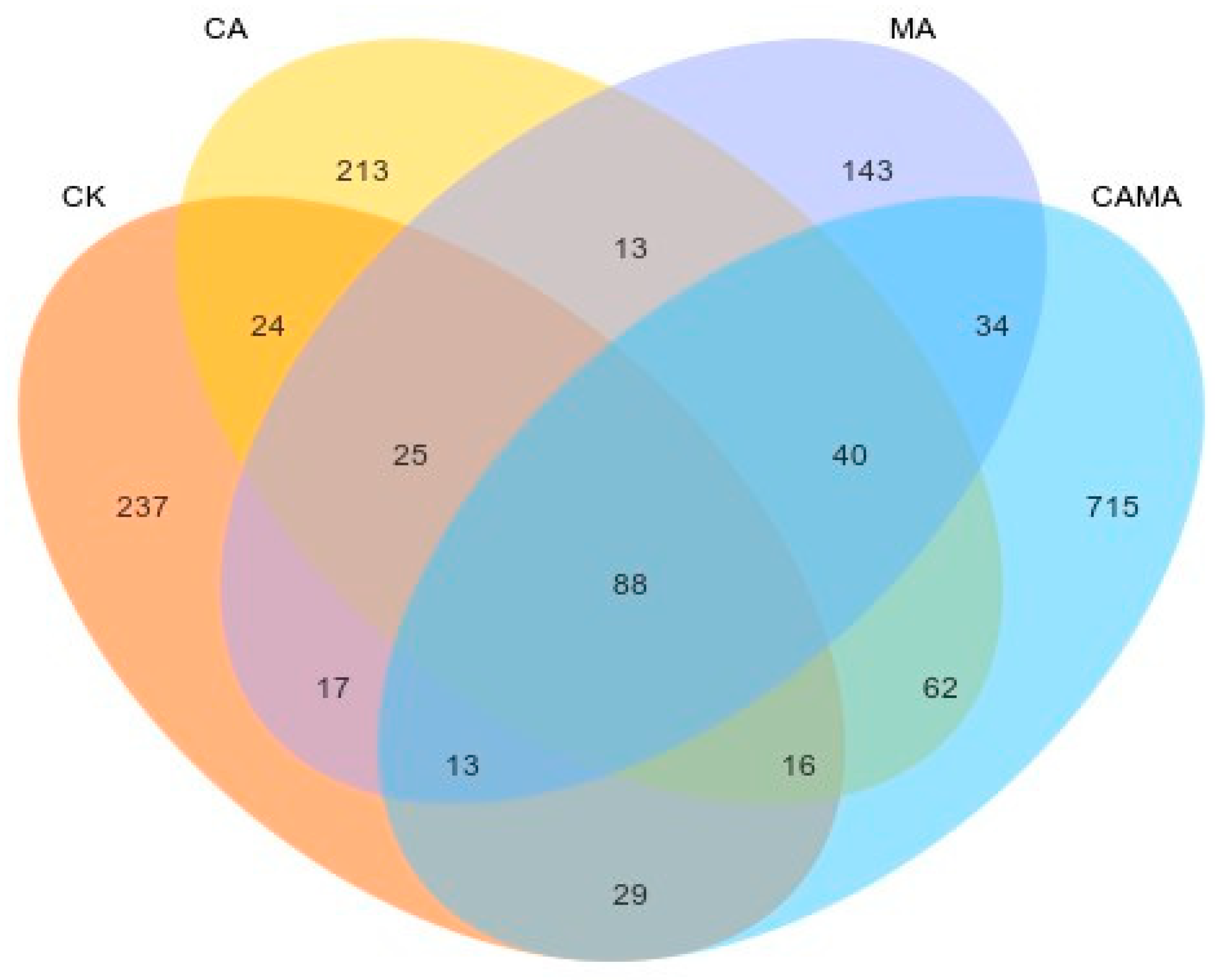
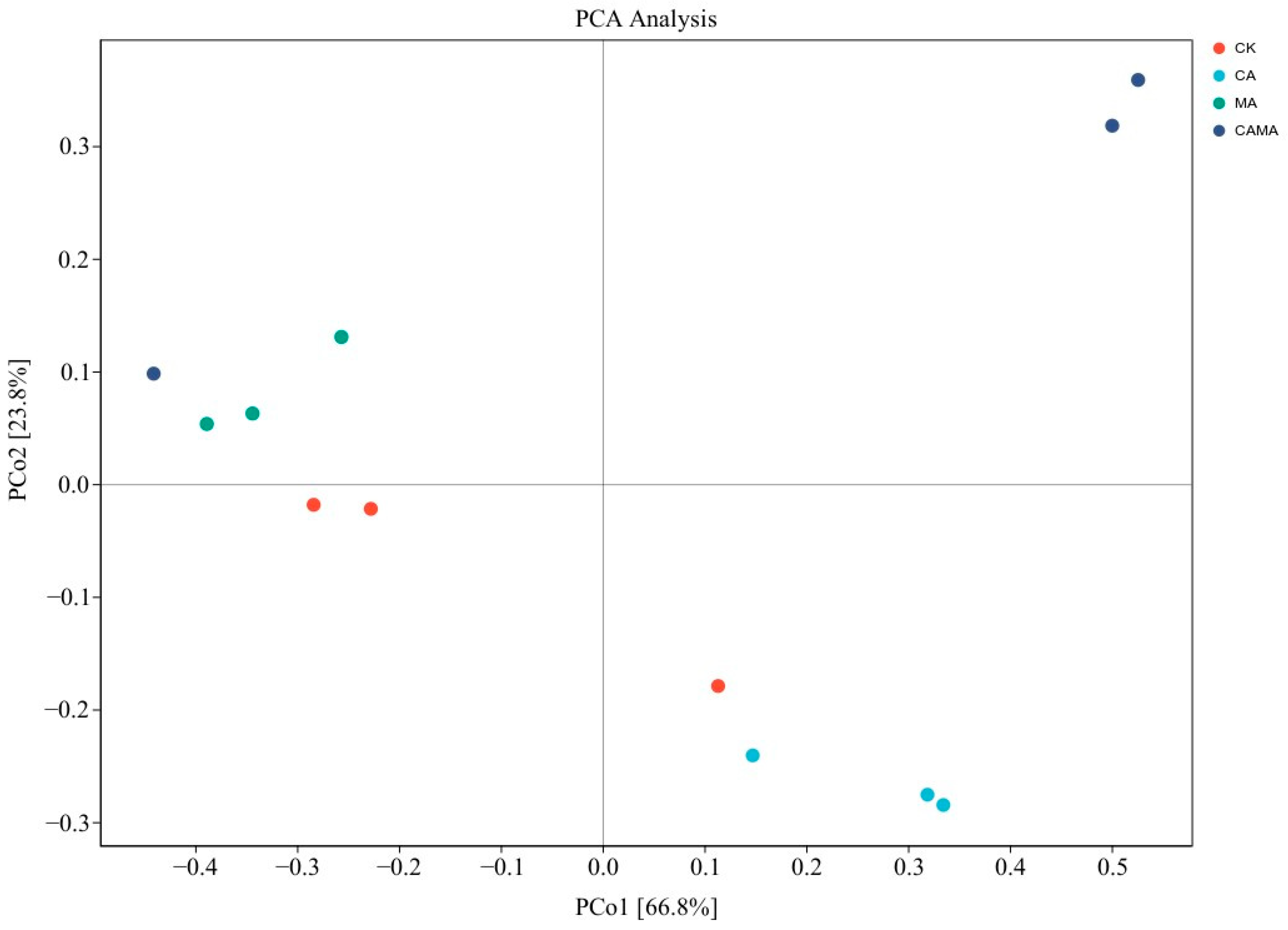
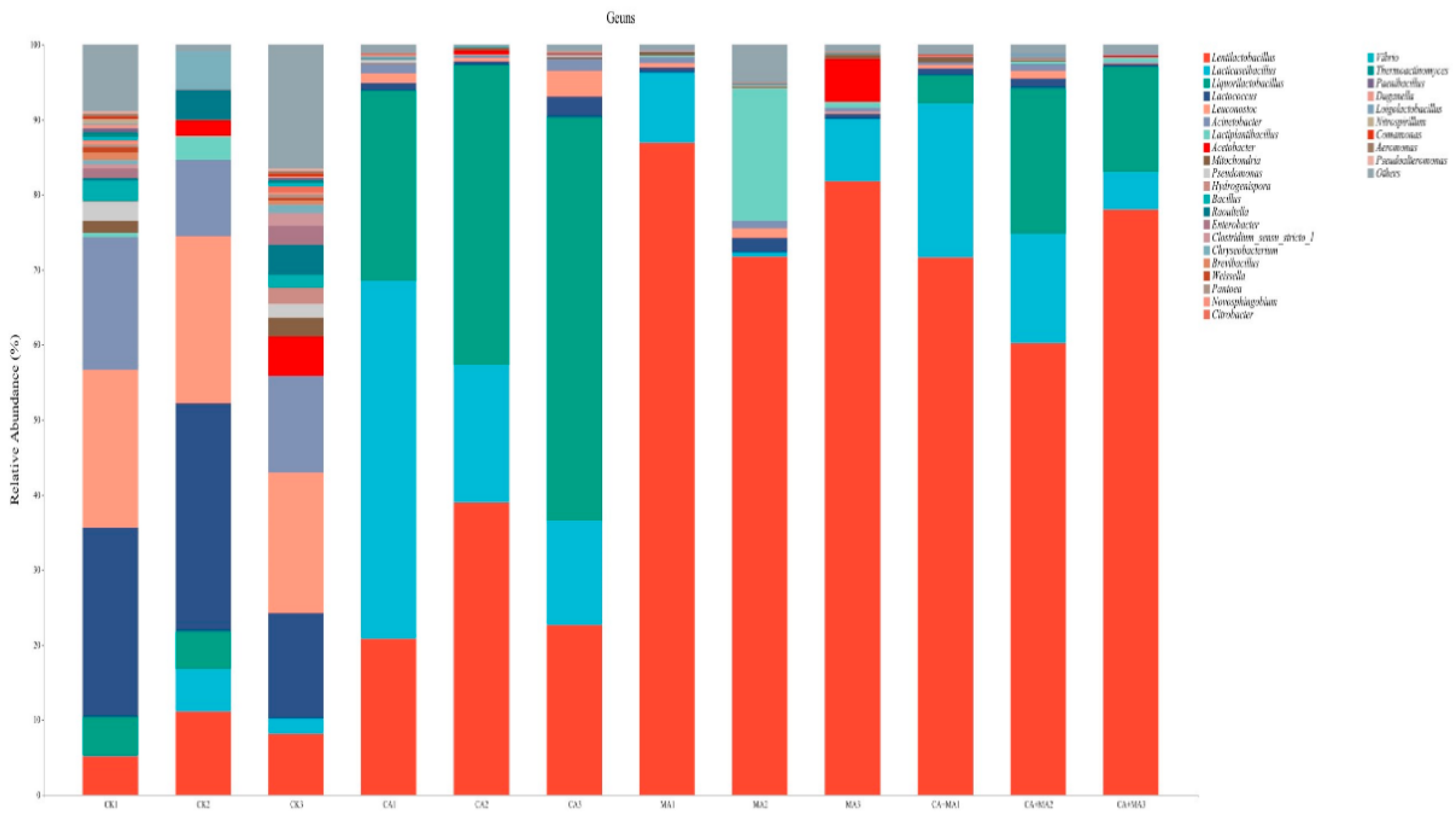
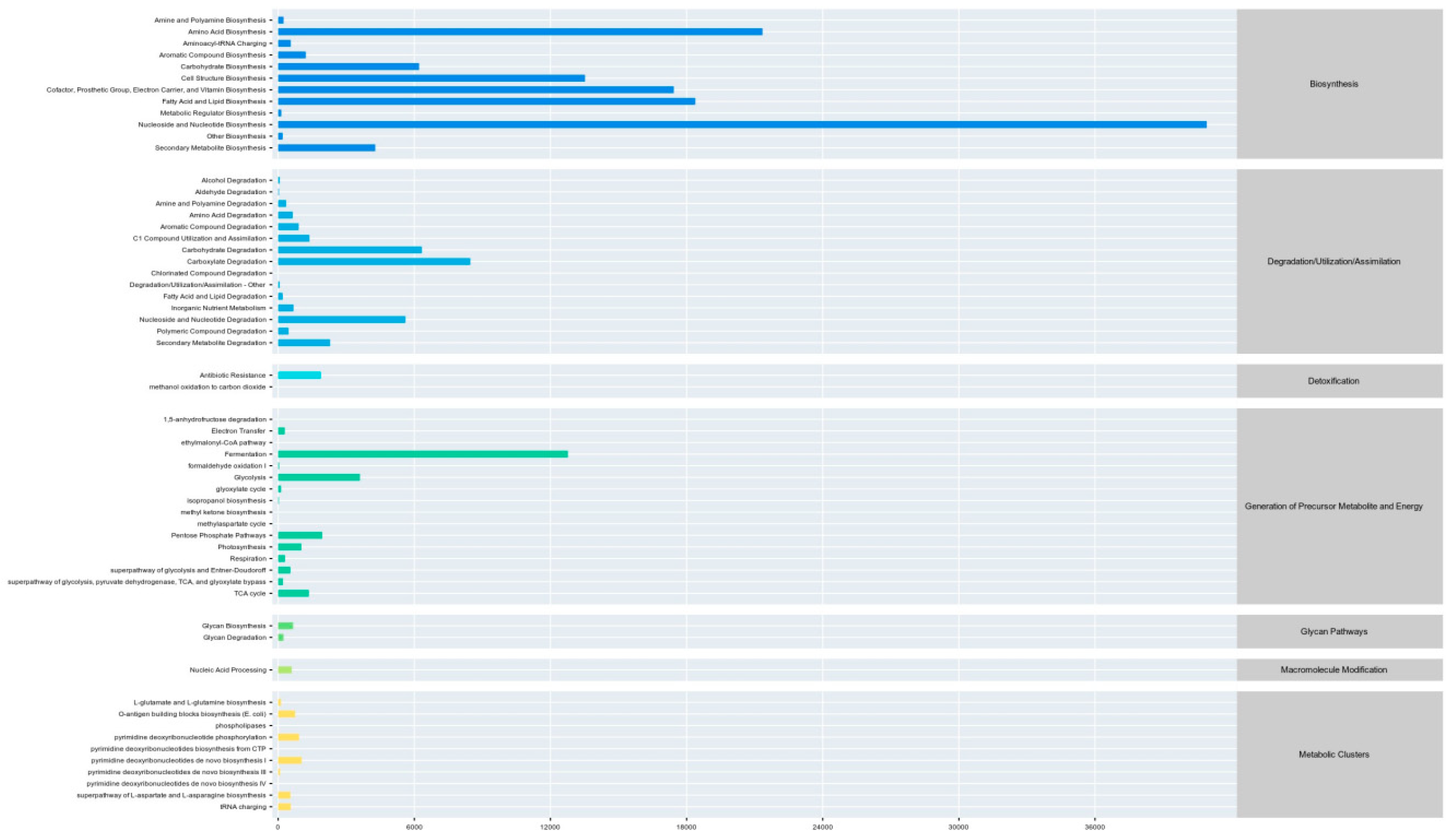
| Items | Content |
|---|---|
| Ingredients | |
| Corn, % of DM | 13.31 |
| Wheat bran, % of DM | 3.67 |
| Molasses, % of DM | 0.98 |
| Soybean meal, % of DM | 3.17 |
| Distillers dried grains with solubles, % of DM | 5.61 |
| Cottonseed meal, % of DM | 2.16 |
| Corn gluten feed, % of DM | 7.31 |
| Corn germ meal, % of DM | 4.62 |
| Premix1, % of DM | 0.49 |
| Corn silage, % of DM | 15.70 |
| Leymus chinensis, % of DM | 42.98 |
| Total | 100.00 |
| Nutrient levels2 | |
| Net Energy for Lactating /(MJ/kg) | 5.44 |
| CP | 14.28 |
| NDF | 39.17 |
| ADF | 20.12 |
| Ca | 0.60 |
| P | 0.40 |
| Items | Chinese water chestnut residu(CWCR) | Corn gluten meal (CGM) | CWCR+CGM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical composition | |||
| DM, % FW | 19.31 | 90.79 | 31.03 |
| CP, %DM | 10.43 | 41.3 | 15.06 |
| pH | 6.57 | 6.49 | 6.56 |
| EE, %DM | 2.91 | 2.41 | 2.84 |
| Starch | 18.21 | 12.7 | 17.39 |
| NDF, %DM | 47.37 | 21.3 | 43.45 |
| ADF, %DM | 28.68 | 10.8 | 26.00 |
| WSC, %DM | 8.80 | 2.41 | 7.84 |
| Microorganism | |||
| LAB, log10 cfu/g FW | 2.23 | ND | < 2.00 |
| CB, log10 cfu/g FW | < 2.00 | ND | < 2.00 |
| Yeast, log10 cfu/g FW | 2.12 | ND | < 2.00 |
| Mold, log10 cfu/g FW | ND | ND | ND |
| Items | Treatment 1 | SEM | p-Value3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | MA | CA | MA+CA | MA | CA | MA×CA | ||
| Chemical composition | ||||||||
| DM, % of FW | 30.52 | 30.61 | 30.85 | 30.91 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.92 |
| CP, % of DM | 16.06a | 17.50ab | 17.95b | 17.23ab | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.44 |
| NDFom, of DM | 36.53 | 36.41 | 35.87 | 35.92 | 1.25 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 0.42 |
| ADFom, % of DM | 22.76 | 22.35 | 22.43 | 21.98 | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.12 | 0.28 |
| ADL, % of DM | 3.56b | 3.18ab | 3.13ab | 3.06a | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.048 | 0.31 |
| Cellulose, % of DM | 19.20 | 19.17 | 19.30 | 18.92 | 0.17 | 0.41 | 0.28 | 0.29 |
| Hemicellulose, % of DM | 12.77 | 14.06 | 13.59 | 13.89 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.25 |
| WSC, % of DM | 3.21c | 2.87b | 2.64b | 2.32a | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.48 |
| In situ effective degradability | ||||||||
| ISDMD, 2 % of DM | 36.47a | 38.66b | 38.32b | 39.76b | 0.48 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.25 |
| ISNDFD, 2 % of NDF | 16.46 | 17.87 | 17.53 | 18.49 | 0.44 | 0.29 | 0.13 | 0.15 |
| ISCPD, 2 % of CP | 25.65a | 26.76b | 26.84b | 27.53b | 0.27 | 0.01 | < 0.01 | 0.36 |
| Items | Treatment 1 | SEM | p-Value | |||||
| CON | MA | CA | MA+CA | MA | CA | MA×CA | ||
| DMR, % of FW | 96.77 | 97.28 | 97.43 | 97.55 | 0.23 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.76 |
| pH | 4.14b | 3.91ab | 3.82a | 3.72a | 0.08 | < 0.01 | < 0.01 | 0.08 |
| Ammonia-N, % of DM | 2.83 | 2.49 | 2.54 | 2.24 | 0.12 | 0.35 | 0.48 | 0.92 |
| Lactic acid, % of DM | 4.72a | 6.15b | 6.02b | 6.43c | 0.55 | < 0.01 | < 0.01 | 0.42 |
| Acetic acid, % of DM | 0.73a | 0.91b | 0.89b | 0.97b | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.57 |
| Propionic acid, % of DM | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.05 | ND | - | - | - | - |
| Butyric acid, % of DM | 0.13 | ND | ND | ND | - | - | - | - |
| Microorganism | ||||||||
| LAB, log10 cfu/g FW | 5.15a | 6.54bc | 6.24b | 7.89c | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.78 |
| CB, log10 cfu/g FW | 2.33 | < 2.00 | ND | ND | - | - | - | - |
| Yeast, log10 cfu/g FW | < 2.00 | ND | < 2.00 | ND | - | - | - | - |
| Mold, log10 cfu/g FW | < 2.00 | ND | ND | ND | - | - | - | - |
| Sample ID | Treatment 1 | SEM | p-Value | |||||
| CON | MA | CA | MA+CA | MA | CA | MA×CA | ||
| Shannon Index 2 | 2.96a | 3.01a | 3.54b | 3.78b | 0.1 | 0.44 | < 0.01 | 0.71 |
| Chao1 Index 2 | 183.30 | 219.03 | 218.28 | 220.57 | 16.51 | 0.52 | 0.48 | 0.92 |
| Simpson Index 2 | 0.82b | 0.80b | 0.69a | 0.67a | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.61 |
| Good’s Coverage 2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





