Submitted:
04 December 2023
Posted:
05 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
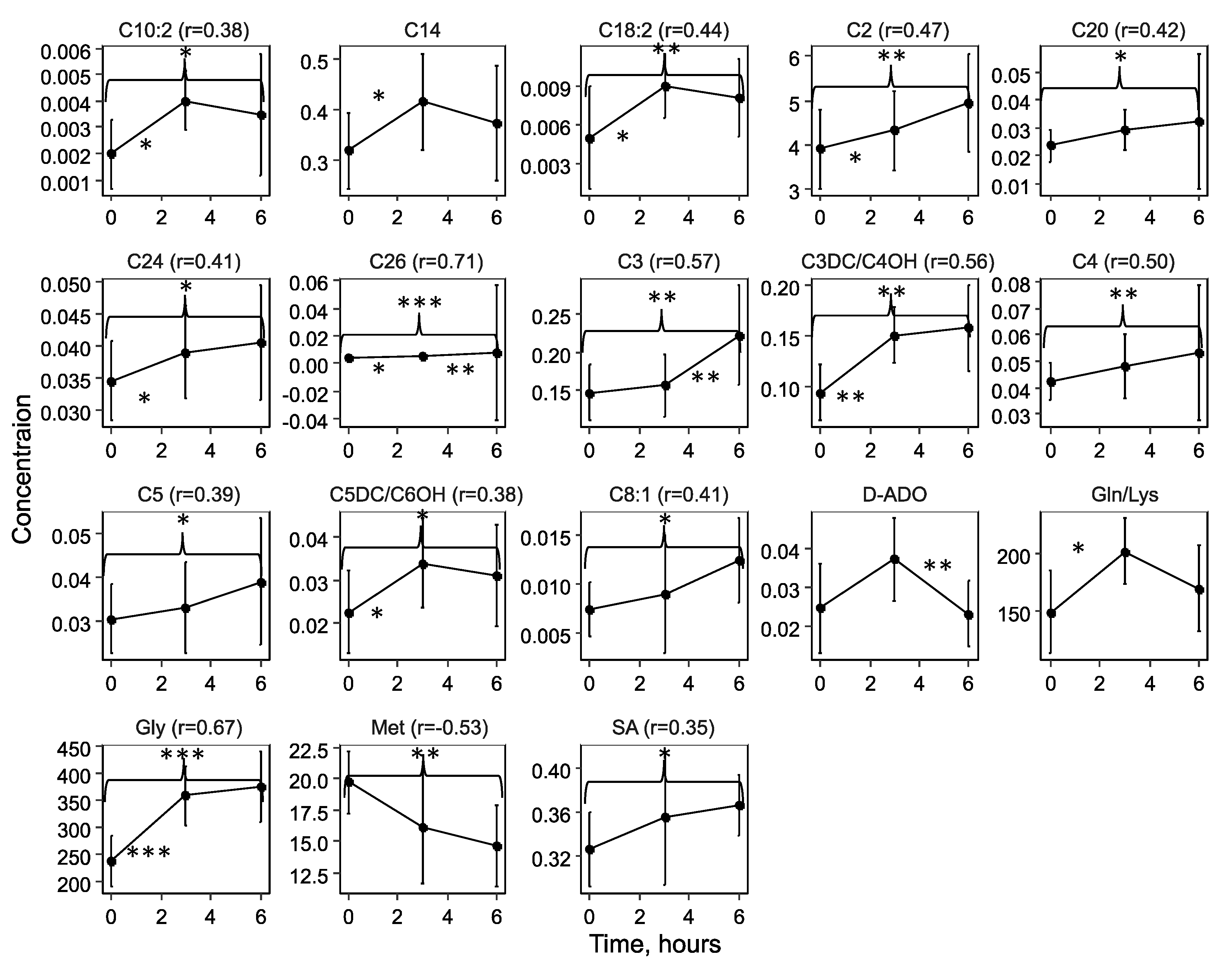
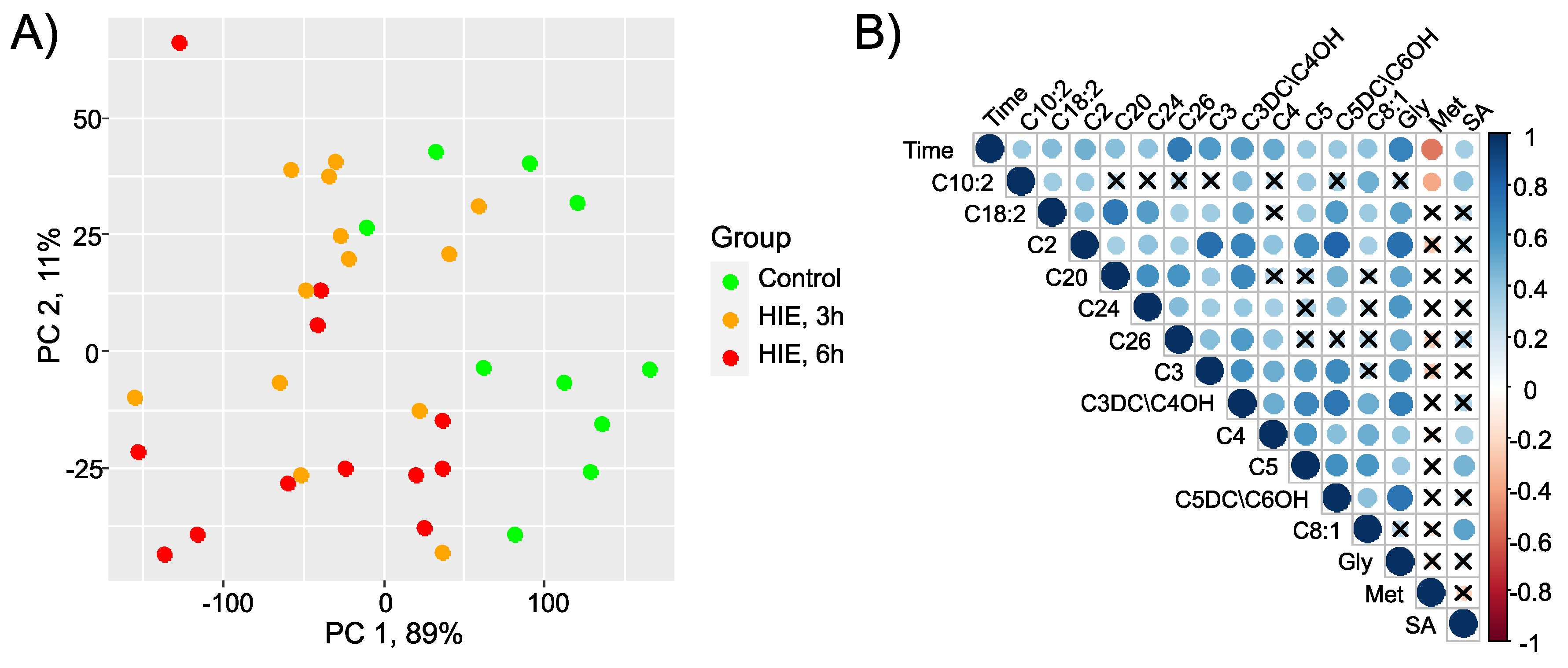
2.1. Time-Related Changes in DBS after Hypoxia-Ischemia
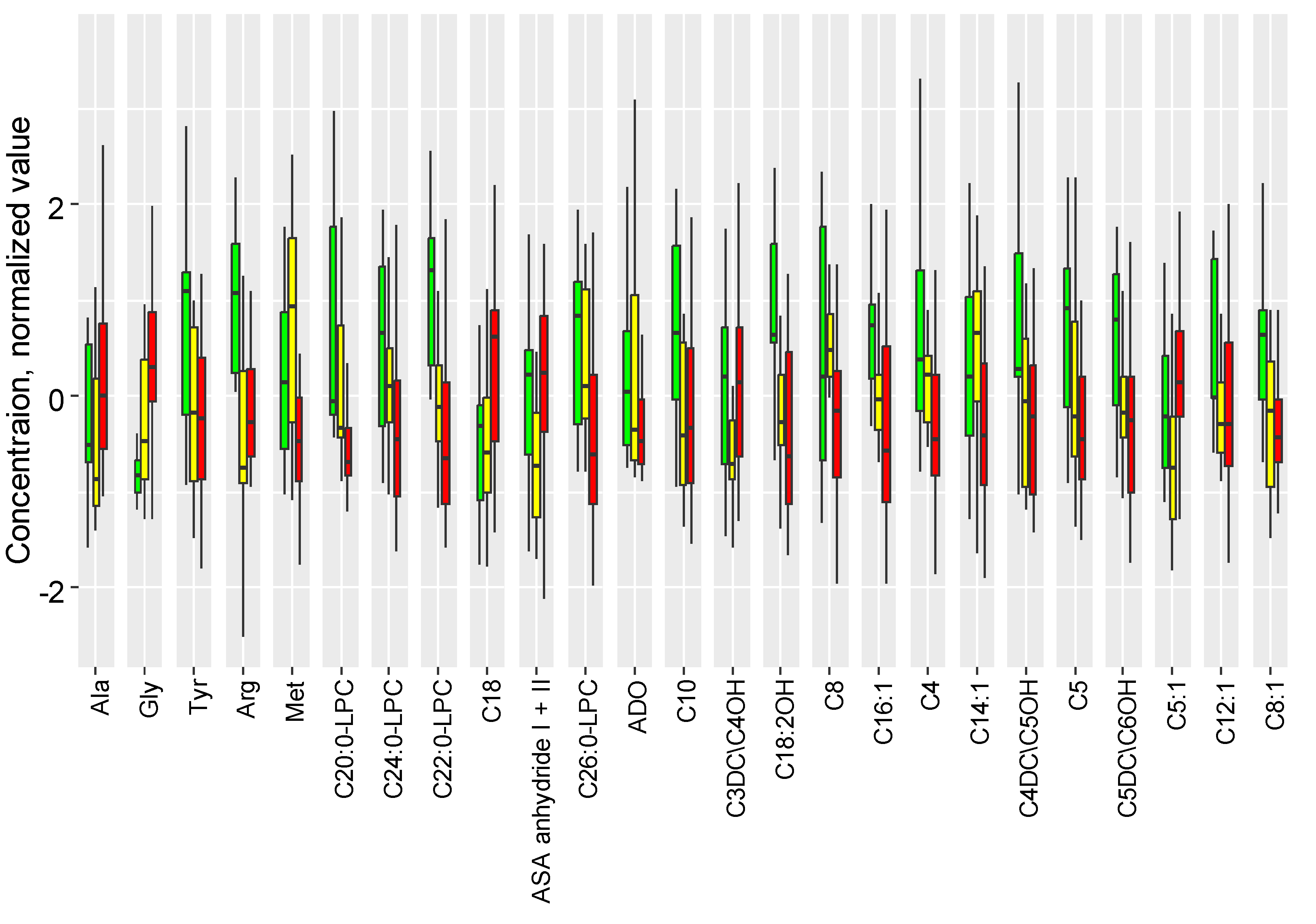
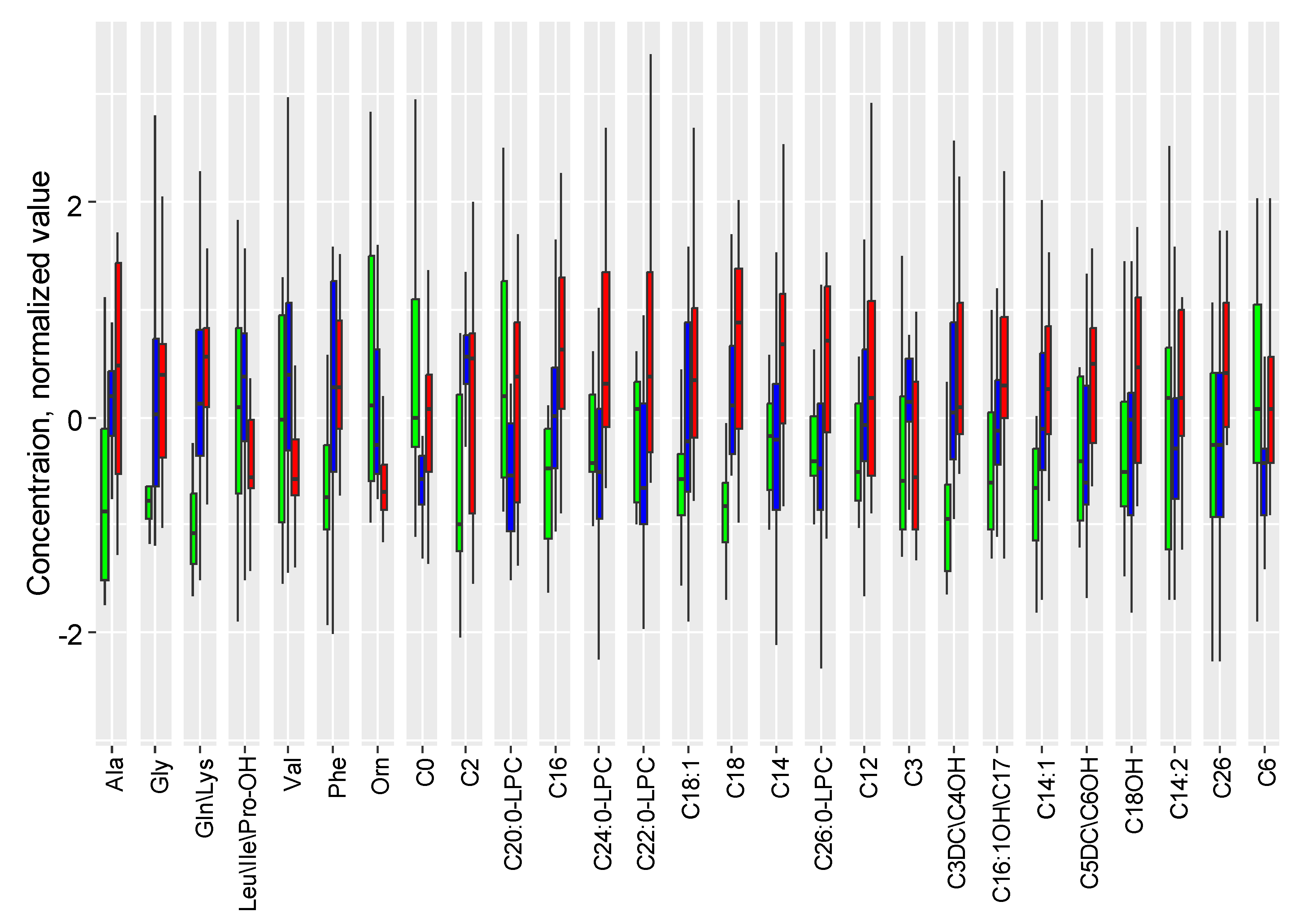
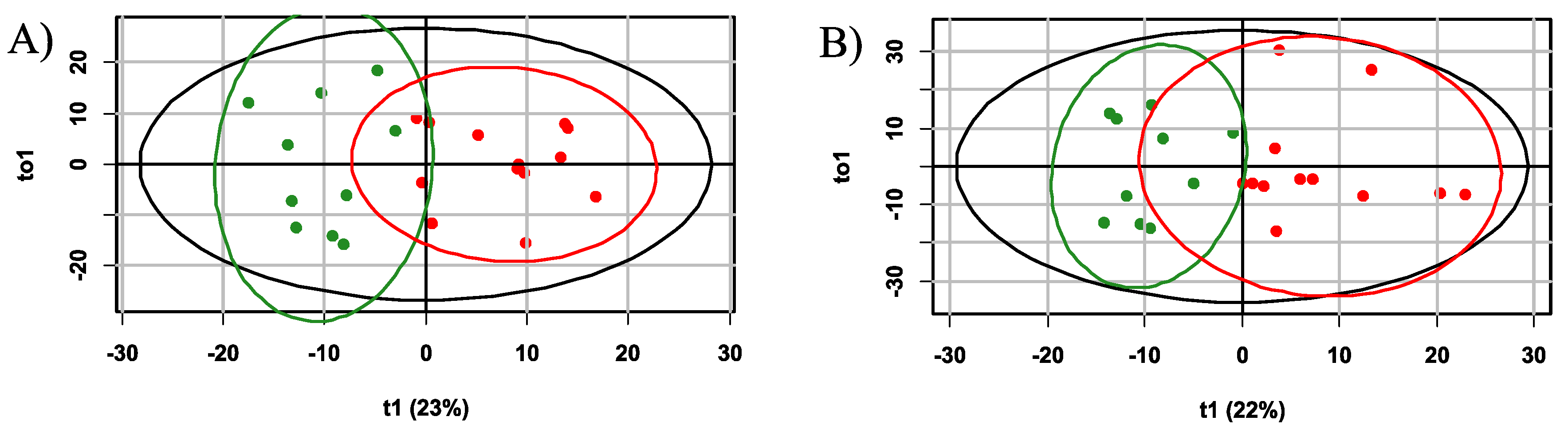
2.2. The Influence of Accute Inflammation (LPS-Induced) and Hypoxia-Ischemia on DBS Metabolome
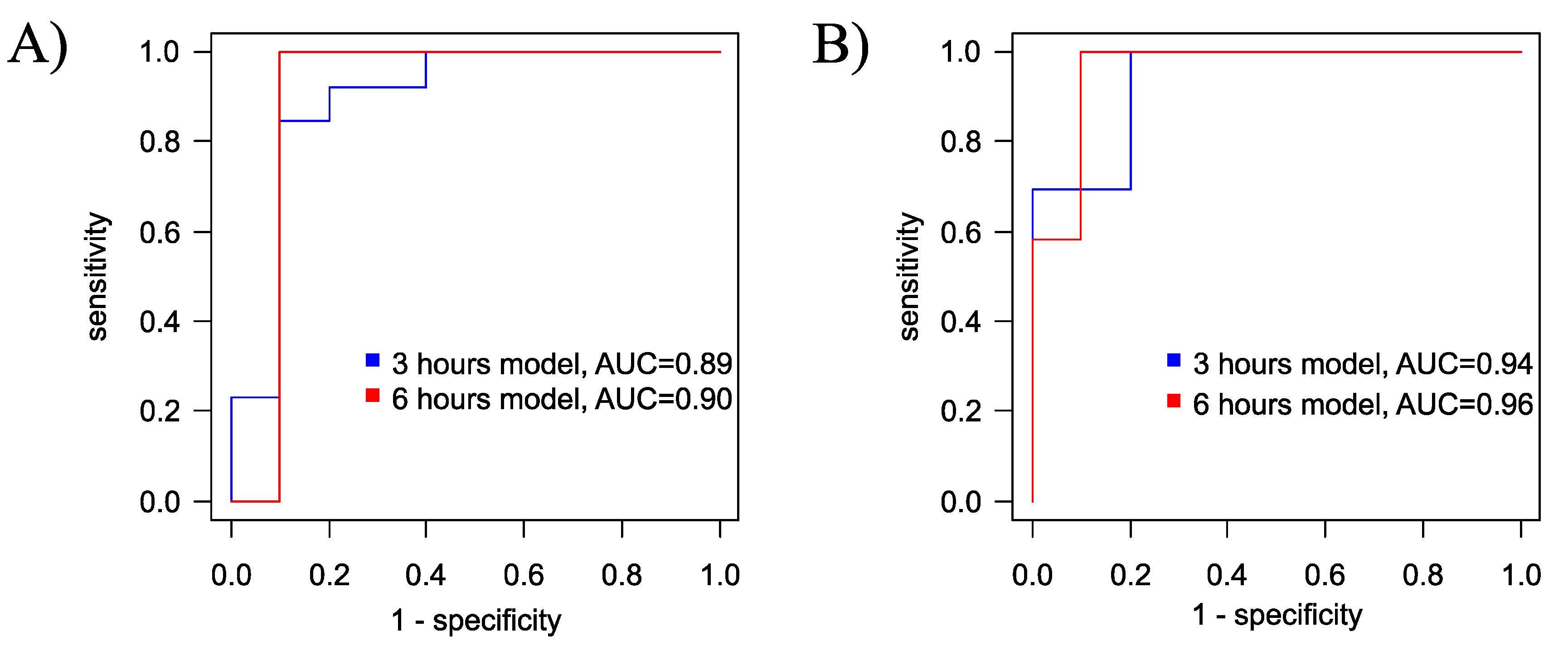
2.3. Therapeutic Effect of Hypotermia in Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1 Animals
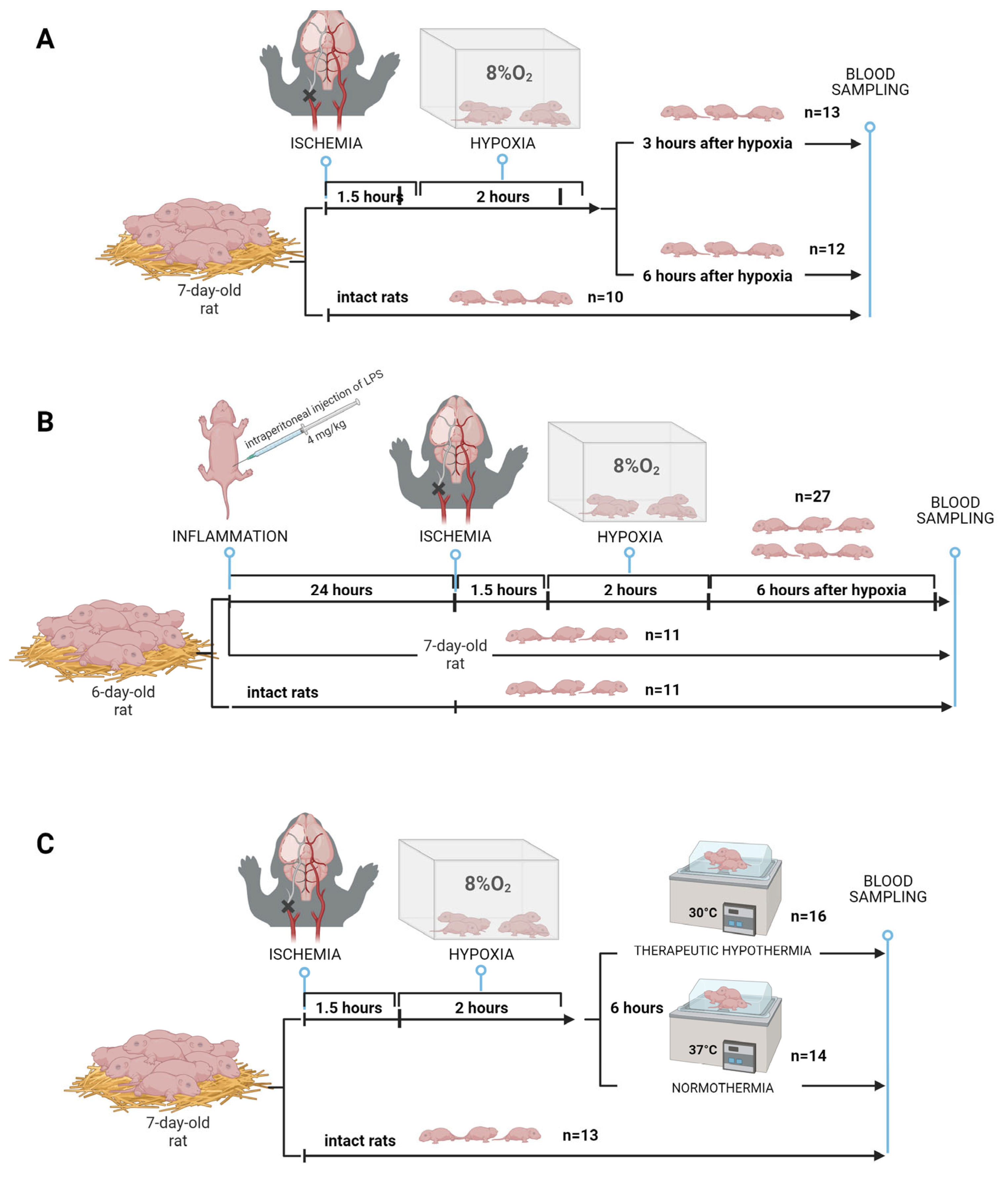
4.2. HIE Modeling
4.2.1.HIE with Sampling at Different Times
4.2.2. HIE Model with LPS-Induced Inflammation
4.2.3. Modeling of therapeutic hypothermia
4.3. Dried Blood Spot metabolome analysis (FIA-MRM-MS)
4.4. Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurinczuk, J.J.; White-Koning, M.; Badawi, N. Epidemiology of neonatal encephalopathy and hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuck, T.; Rice, M.; Bailit, J.; Grobman, W.A.; Reddy, U.M.; Wapner, R.J.; et al. Preterm Neonatal Morbidity and Mortality by Gestational Age: A Contemporary Cohort. Am J Obs. Gynecol 2016, 215, 103.e1–103.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, J.J. Neonatal encephalopathy: An inadequate term for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, A.; Korzeniewski, S.J. Long-Term Cognitive Outcomes of Birth Asphyxia and the Contribution of Identified Perinatal Asphyxia to Cerebral Palsy. Clin. Perinatol. 2016, 43, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, M.; Ramenghi, L.A.; Edwards, A.D.; Brocklehurst, P.; Halliday, H.; Levene, M.; Strohm, B.; Thoresen, M.; Whitelaw, A.; Azzopardi, D. Assessment of brain tissue injury after moderate hypothermia in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy: a nested substudy of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankaran, S.; McDonald, S.A.; Laptook, A.R.; Hintz, S.R.; Barnes, P.D.; Das, A.; Pappas, A.; Higgins, R.D. Neonatal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Pattern of Brain Injury as a Biomarker of Childhood Outcomes following a Trial of Hypothermia for Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 987–93.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankaran, S.; Barnes, P.D.; Hintz, S.R.; Laptook, A.R.; Zaterka-Baxter, K.M.; McDonald, S.A.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Walsh, M.C.; Tyson, J.E.; Donovan, E.F.; et al. Brain injury following trial of hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, J.L.Y.; Coleman, L.; Hunt, R.W.; Lee, K.J.; Doyle, L.W.; Inder, T.E.; Jacobs, S.E. Prognostic utility of magnetic resonance imaging in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: Substudy of a randomized trial. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2012, 166, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassink, G.; Gunn, E.R.; Drury, P.P.; Bennet, L.; Gunn, A.J. The mechanisms and treatment of asphyxial encephalopathy. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, G.; Zhou, W.; Sun, J.; Cao, Y.; Shao, X. [Meta-analysis of mild hypothermia for gestational age over 35-week newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2012, 92, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, A.D.; Brocklehurst, P.; Gunn, A.J.; Halliday, H.; Juszczak, E.; Levene, M.; Strohm, B.; Thoresen, M.; Whitelaw, A.; Azzopardi, D. Neurological outcomes at 18 months of age after moderate hypothermia for perinatal hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: synthesis and meta-analysis of trial data. BMJ 2010, 340, c363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, H.; Tomimatsu, T.; Watanabe, N.; Wu Mu, J.; Kohzuki, M.; Endo, M.; Fujii, E.; Kanzaki, T.; Murata, Y. Post-ischemic hypothermia blocks caspase-3 activation in the newborn rat brain after hypoxia-ischemia. Brain Res. 2001, 910, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penman, M.; Shah, P. Time to adopt cooling for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: Response to a previous commentary. Pediatrics 2008, 121, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanavati, T.; Seemaladinne, N.; Regier, M.; Yossuck, P.; Pergami, P. Can We Predict Functional Outcome in Neonates with Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy by the Combination of Neuroimaging and Electroencephalography? Pediatr. Neonatol. 2015, 56, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shellhaas, R.A.; Kushwaha, J.S.; Plegue, M.A.; Selewski, D.T.; Barks, J.D.E. An evaluation of cerebral and systemic predictors of 18-month outcomes for neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. J. Child Neurol. 2015, 30, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.A.; Cascio, M.A.; Ferrand, A.; Shevell, M.; Racine, E. The complexity of physicians’ understanding and management of prognostic uncertainty in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J. Perinatol. 2019, 39, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Jia, X.; Xu, H.; Gao, L.; Wei, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Wei, L. Blood Plasma Metabolic Profile of Newborns with Hypoxic-Ischaemic Encephalopathy by GC-MS. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6677271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, H.Q.; Sun, Y.F.; Chen, L.; Xiao, Q.X.; Luo, B.Y.; Zhou, H.S.; Zhou, D.; Chang, Q.Y.; Xiong, L.L. Current analysis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy research issues and future treatment modalities. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCandless, S.E.; Wright, E.J. Mandatory newborn screening in the United States: History, current status, and existential challenges. Birth Defects Res. 2020, 112, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordfalk, F.; Ekstrøm, C.T. Newborn dried blood spot samples in Denmark: the hidden figures of secondary use and research participation. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 27, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tann, C.J.; Martinello, K.A.; Sadoo, S.; Lawn, J.E.; Seale, A.C.; Vega-Poblete, M.; Russell, N.J.; Baker, C.J.; Bartlett, L.; Cutland, C.; et al. Neonatal Encephalopathy with Group B Streptococcal Disease Worldwide: Systematic Review, Investigator Group Datasets, and Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, S173–S189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starodubtseva, N.L.; Eldarov, C.M.; Kirtbaya, A.R.; Balashova, E.N.; Gryzunova, A.S.; Ionov, O.V.; Zubkov, V.V.; Silachev, D.N. Recent Advances in Diagnostics of Neonatal Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy. Bull. Russ. State Med. Univ. 2022, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevtsova, Y.; Eldarov, C.; Starodubtseva, N.; Goryunov, K.; Chagovets, V.; Ionov, O.; Plotnikov, E.; Silachev, D. Identification of Metabolomic Signatures for Ischemic Hypoxic Encephalopathy Using a Neonatal Rat Model. Children 2023, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuligowski, J.; Solberg, R.; Sánchez-Illana, Á.; Pankratov, L.; Parra-Llorca, A.; Quintás, G.; Saugstad, O.D.; Vento, M. Plasma metabolite score correlates with Hypoxia time in a newly born piglet model for asphyxia. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, N.; Pardo, A.C. Challenges in neurologic prognostication after neonatal brain injury. Semin. Perinatol. 2017, 41, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, C.; O’Boyle, D.; Finder, M.; Hallberg, B.; Walsh, B.H.; Henshall, D.C.; Boylan, G.B.; Murray, D.M. Predictive modelling of hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy risk following perinatal asphyxia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polat, M.; Şimşek, A.; Tansuǧ, N.; Sezer, R.G.; Özkol, M.; Başpinar, P.; Tekgül, H. Prediction of neurodevelopmental outcome in term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2013, 17, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, D.M.; Boylan, G.B.; Ali, I.; Ryan, C.A.; Murphy, B.P.; Connolly, S. Defining the gap between electrographic seizure burden, clinical expression and staff recognition of neonatal seizures. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2008, 93, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.K.; Kaiser, J.R.; Guffey, D.; Minard, C.G.; Guillet, R.; Gunn, A.J. Hypoglycaemia and hyperglycaemia are associated with unfavourable outcome in infants with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: A post hoc analysis of the CoolCap Study. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2016, 101, F149–F155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osredkar, D.; Thoresen, M.; Maes, E.; Flatebø, T.; Elstad, M.; Sabir, H. Hypothermia is not neuroprotective after infection-sensitized neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Resuscitation 2014, 85, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falck, M.; Osredkar, D.; Maes, E.; Flatebø, T.; Wood, T.R.; Sabir, H.; Thoresen, M. Hypothermic Neuronal Rescue from Infection-Sensitised Hypoxic-Ischaemic Brain Injury Is Pathogen Dependent. Dev. Neurosci. 2017, 39, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uziel, G.; Ghezzi, D.; Zeviani, M. Infantile mitochondrial encephalopathy. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 16, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saudubray, J.M.; Garcia-Cazorla, A. An overview of inborn errors of metabolism affecting the brain: From neurodevelopment to neurodegenerative disorders. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussap, M.; Antonucci, R.; Noto, A.; Fanos, V. The role of metabolomics in neonatal and pediatric laboratory medicine. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 426, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennet, L.; Booth, L.; Gunn, A.J. Potential biomarkers for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010, 15, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiou, N.; Theodoridis, G.; Sarafidis, K. Understanding neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy with metabolomics. Hippokratia 2017, 21, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.-R. Screening newborns for metabolic disorders based on targeted metabolomics using tandem mass spectrometry. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Song, J. Non-derivatizing Tandem Mass Spectrometry Assay for Expanded Newborn Screening and Cutoffs for Preterm Neonates. Ann. Lab. Med. 2023, 43, 133–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra-González, I.; Cruz-Bautista, I.; Bello-Chavolla, O.Y.; Vela-Amieva, M.; Pallares-Méndez, R.; Ruiz de Santiago Y Nevarez, D.; Salas-Tapia, M.F.; Rosas-Flota, X.; González-Acevedo, M.; Palacios-Peñaloza, A.; et al. Optimization of kidney dysfunction prediction in diabetic kidney disease using targeted metabolomics. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fabritiis, S.; Valentinuzzi, S.; Piras, G.; Cicalini, I.; Pieragostino, D.; Pagotto, S.; Perconti, S.; Zucchelli, M.; Schena, A.; Taschin, E.; et al. Targeted metabolomics detects a putatively diagnostic signature in plasma and dried blood spots from head and neck paraganglioma patients. Oncogenesis 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Cicalini, I.; Cufaro, M.C.; Agnifili, L.; Mastropasqua, L.; Lanuti, P.; Marchisio, M.; De Laurenzi, V.; Del Boccio, P.; Pieragostino, D. Multi-omics approach for studying tears in treatment-naïve glaucoma patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulman, A.; Prentice, P.; Wong, M.C.Y.; Matthews, L.; Bond, N.J.; Eiden, M.; Griffin, J.L.; Dunger, D.B. The development and validation of a fast and robust dried blood spot based lipid profiling method to study infant metabolism. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannucci, S.J.; Back, S.A. The Vannucci Model of Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury in the Neonatal Rodent: 40 years Later. Dev. Neurosci. 2022, 44, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotnikov, E.Y.; Brezgunova, A.A.; Pevzner, I.B.; Zorova, L.D.; Manskikh, V.N.; Popkov, V.A.; Silachev, D.N.; Zorov, D.B. Mechanisms of LPS-induced acute kidney injury in neonatal and adult rats. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Suárez, O.; Concheiro-Guisán, A.; Sánchez-Pintos, P.; Cocho, J.A.; Fernández Lorenzo, J.R.; Couce, M.L. Acylcarnitine profile in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Med. (United States) 2019, 98, e15221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, B.H.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Mandal, R.; Wishart, D.S.; Boylan, G.B.; Kenny, L.C.; Murray, D.M. The Metabolomic Profile of Umbilical Cord Blood in Neonatal Hypoxic Ischaemic Encephalopathy. PLoS One 2012, 7, e50520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyburg, J.; Schulze, A.; Kohlmueller, D.; Linderkamp, O.; Mayatepek, E. Postnatal changes in neonatal acylcarnitine profile. Pediatr. Res. 2001, 49, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, A.M.; Genaro-Mattos, T.C.; Korade, Z.; Peeples, E.S. Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury Alters Brain Acylcarnitine Levels in a Mouse Model. Metabolites 2022, 12, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famularo, G.; De Simone, C.; Trinchieri, V.; Mosca, L. Carnitines and its congeners: A metabolic pathway to the regulation of immune response and inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1033, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassink, G.; Davidson, J.O.; Dhillon, S.K.; Zhou, K.; Bennet, L.; Thoresen, M.; Gunn, A.J. Therapeutic Hypothermia in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, R.C.; Procianoy, R.S. Hipotermia terapêutica para recém-nascidos com encefalopatia hipóxico isquêmica. J. Pediatr. (Rio. J). 2015, 91, S78–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldán, A.; Figueras-Aloy, J.; Deulofeu, R.; Jiménez, R. Glycine and other neurotransmitter amino acids in cerebrospinal fluid in perinatal asphyxia and neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 1999, 88, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, S.A.; Peeters-Scholte, C.M.P.C.D.; De Barse, M.M.J.; Roeleveld, M.W.; Klomp, L.W.J.; Berger, R.; De Koning, T.J. Increased concentrations of both NMDA receptor co-agonists d-serine and glycine in global ischemia: A potential novel treatment target for perinatal asphyxia. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.J.; Zornow, M.H.; Grafe, M.R.; Scheller, M.S.; Skilling, S.R.; Smullin, D.H.; Larson, A.A. Hypothermia prevents ischemia-induced increases in hippocampal glycine concentrations in rabbits. Stroke 1991, 22, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillis, J.W.; Walter, G.A. Effect of a brief hypoxic/hypotensive episode on the in vivo release of cerebral cortical γ-aminobutyric acid and glycine. Brain Res. 1989, 504, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.; Dávalos, A.; Naveiro, J.; Noya, M. Neuroexcitatory amino acids and their relation to infarct size and neurological deficit in ischemic stroke. Stroke 1996, 27, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ni, X.; Dong, W.; Qin, W.; Xu, L.; Jiang, Y. Accurately quantified plasma free glycine concentration as a biomarker in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Amino Acids 2023, 55, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Garcia Canaveras, J.C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Liang, L.; Jang, C.; Mayr, J.A.; Zhang, Z.; Ghergurovich, J.M.; Zhan, L.; et al. Serine Catabolism Feeds NADH when Respiration Is Impaired. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 809–821.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, M.; Kure, S.; Sugawara, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kojima, K.; Shinka, T.; Sato, K.; Narisawa, A.; Aoki, Y.; Matsubara, Y.; et al. Direct correlation between ischemic injury and extracellular glycine concentration in mice with genetically altered activities of the glycine cleavage multienzyme system. Stroke 2007, 38, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramelo, I.; Coelho, M.; Rosado, M.; Cardoso, C.M.P.; Dinis, A.; Duarte, C.B.; Grãos, M.; Manadas, B. Biomarkers of hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy: a systematic review; Springer Nature Singapore, 2023; Vol. 19; ISBN 0123456789.
- Johnston, M. V Excitotoxicity in perinatal brain injury. Brain Pathol. 2005, 15, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Boyle, D.S.; Dunn, W.B.; O’Neill, D.; Kirwan, J.A.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Hallberg, B.; Boylan, G.B.; Murray, D.M. Improvement in the Prediction of Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy with the Integration of Umbilical Cord Metabolites and Current Clinical Makers. J. Pediatr. 2021, 229, 175–181.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Farghali, O.G.; El-Chimi, M.S.; El-Abd, H.S.; El-Desouky, E. Amino acid and acylcarnitine profiles in perinatal asphyxia: a case-control study. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinke, S.N.; Walsh, B.H.; Boylan, G.B.; Sykes, B.D.; Kenny, L.C.; Murray, D.M.; Broadhurst, D.I. 1H NMR derived metabolomic profile of neonatal asphyxia in umbilical cord serum: Implications for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 4230–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, E.L. 2.1 The Support of Energy Metabolism in the Central Nervous System with Substrates Other than Glucose. In Handbook of Neurochemistry and Molecular Neurobiology: Brain Energetics. Integration of Molecular and Cellular Processes; Lajtha, A., Gibson, G.E., Dienel, G.A., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, 2007; pp. 137–179. ISBN 978-0-387-30411-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, X.; Chen, W.; Lin, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, W. A verification of the application of the non-derivatized mass spectrometry method in newborns screening of metabolic disorders. Med. (United States) 2019, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Heo, W.Y.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, H.S.; Hwang, N.; Park, H.D.; Sung, S.I.; Chang, Y.S.; Park, W.S.; Lee, S.Y. Comprehensive Evaluation of the NeoBase 2 Non-derivatized MSMS Assay and Exploration of Analytes With Significantly Different Concentrations Between Term and Preterm Neonates. Ann. Lab. Med. 2023, 43, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartog, N.; Hershfield, M.; Michniacki, T.; Moloney, S.; Holsworth, A.; Hurden, I.; Fredrickson, M.; Kleyn, M.; Walkovich, K.; Secord, E. Newborn tandem mass spectroscopy screening for adenosine deaminase deficiency. Ann. allergy, asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy, Asthma, Immunol. 2022, 129, 776–783.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perko, D.; Groselj, U.; Cuk, V.; Iztok Remec, Z.; Zerjav Tansek, M.; Drole Torkar, A.; Krhin, B.; Bicek, A.; Oblak, A.; Battelino, T.; et al. Comparison of Tandem Mass Spectrometry and the Fluorometric Method—Parallel Phenylalanine Measurement on a Large Fresh Sample Series and Implications for Newborn Screening for Phenylketonuria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicalini, I.; Valentinuzzi, S.; Pieragostino, D.; Consalvo, A.; Zucchelli, M.; Donzelli, S.; Ambrogi, D.; Brown, H.A.; Calton, L.J.; Stuppia, L.; et al. Analytical evaluation of the ideal strategy for high-throughput flow injection analysis by tandem mass spectrometry in routine newborn screening. Metabolites 2021, 11, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




