Submitted:
22 November 2023
Posted:
30 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
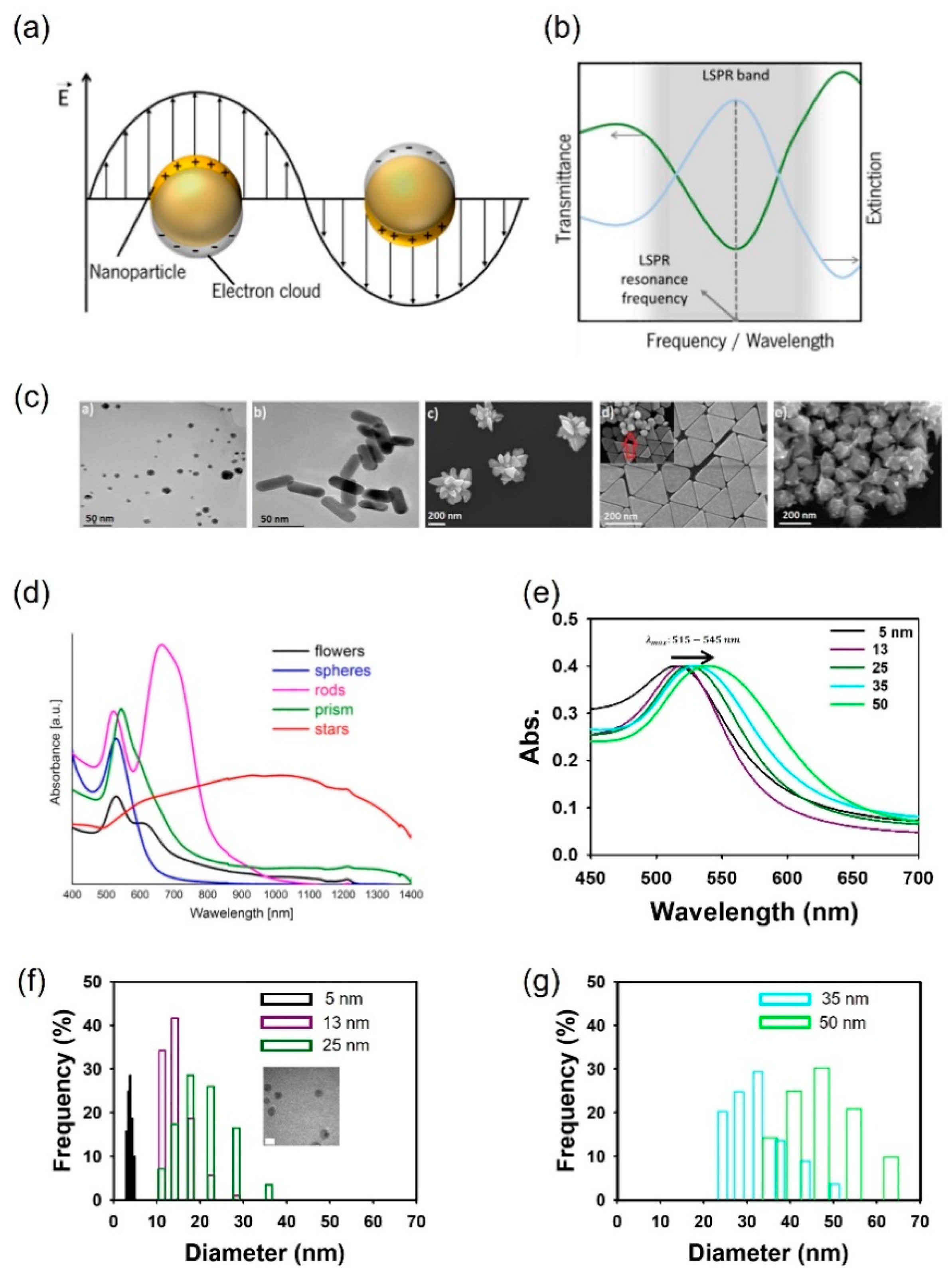
2. Localized surface plasmon resonance principles of the AuNP
3. Visible-signal strategies for ensuring food and agriculture product safety
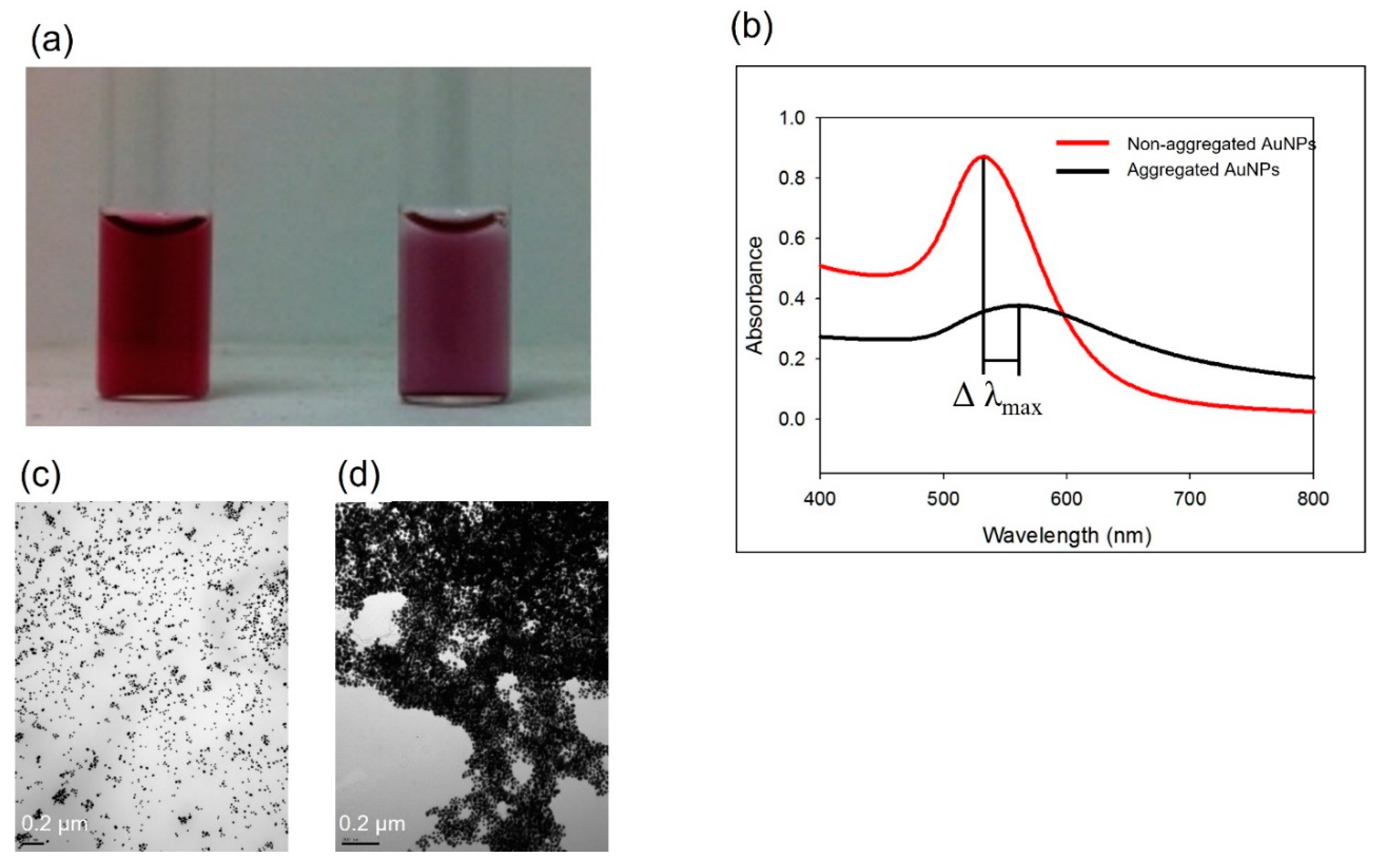
3.1. Non-functionalized AuNPs for pathogen detection
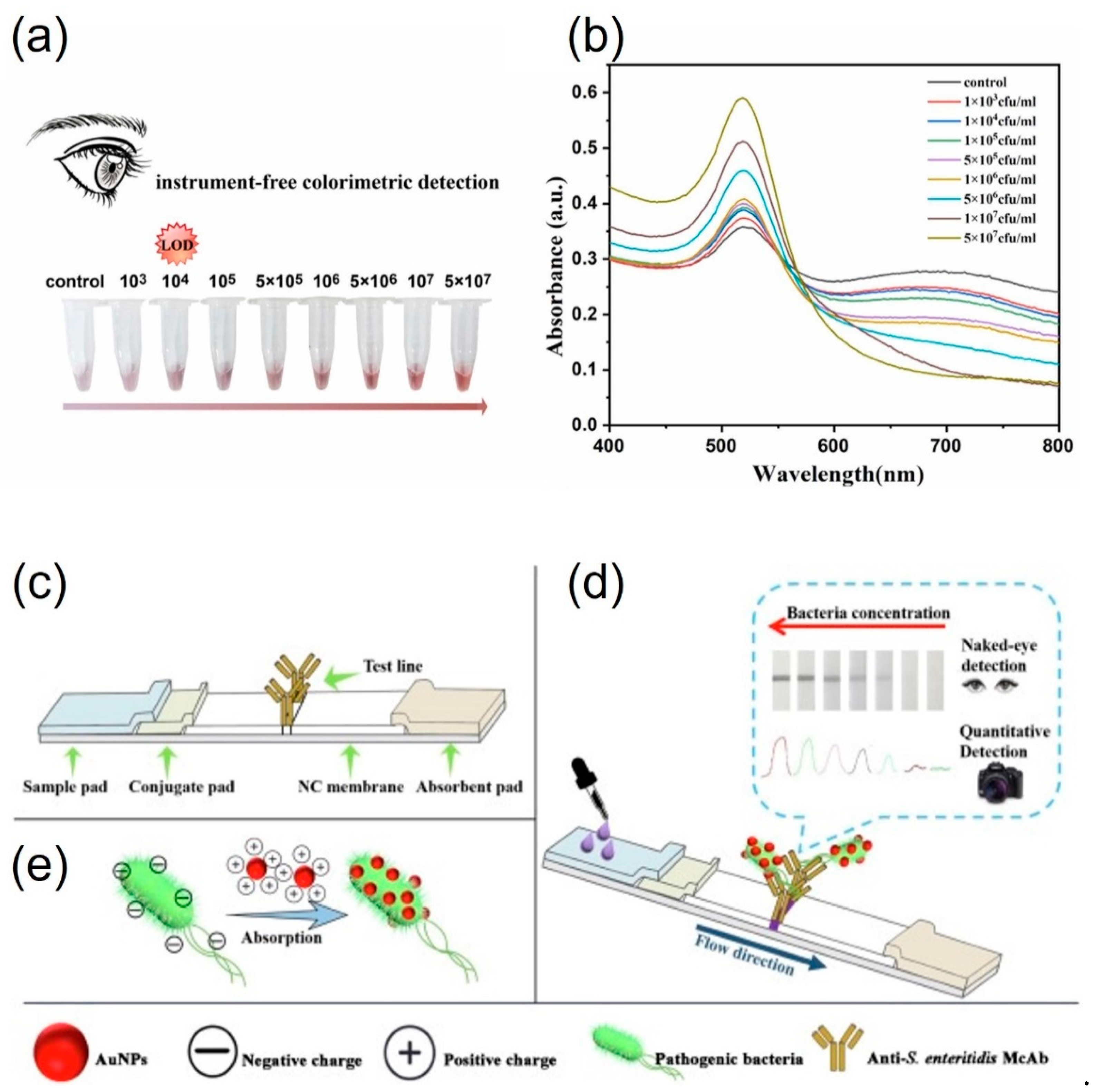
3.2. Protein-functionalized AuNPs for pathogen detection
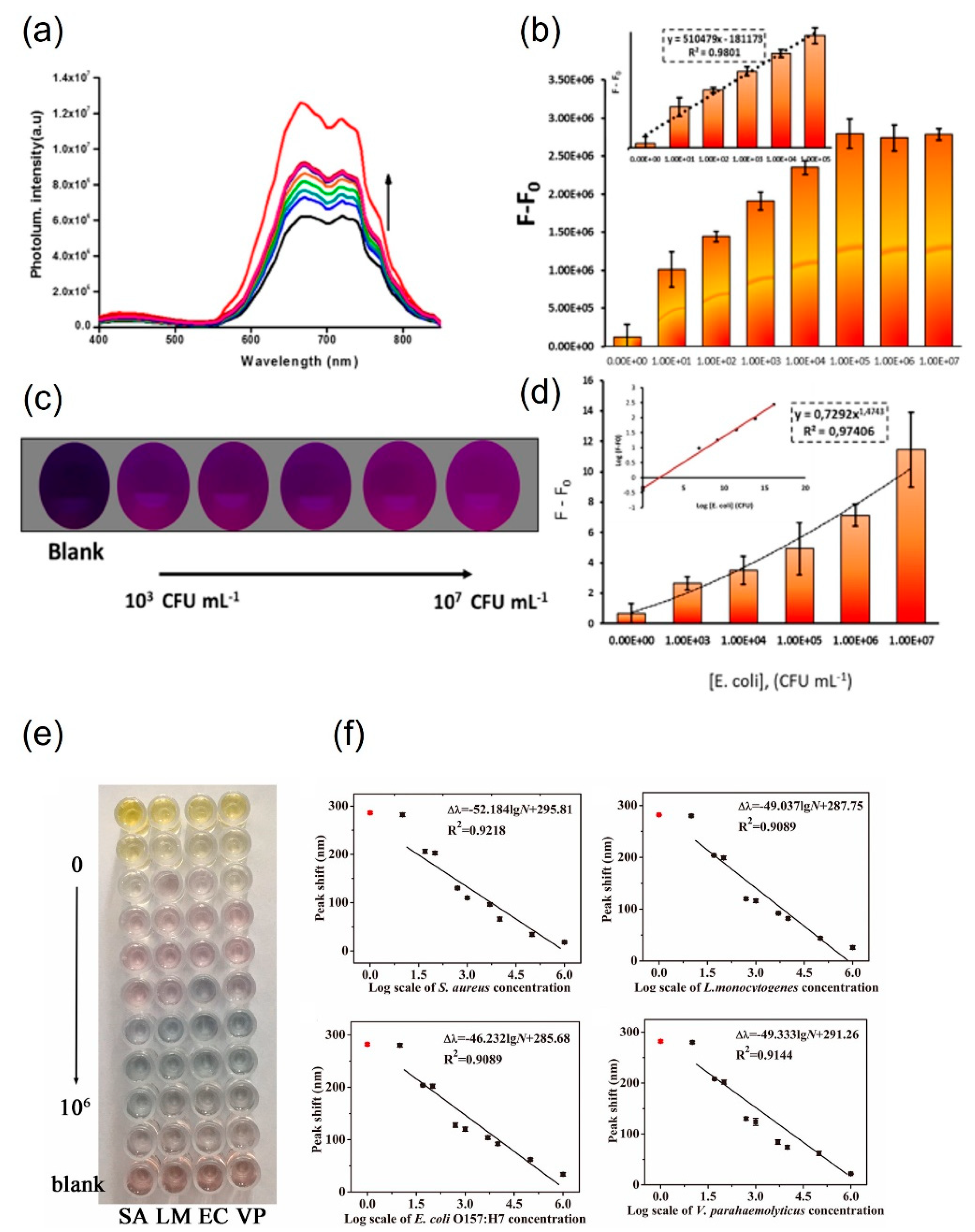
3.3. Small-molecule-functionalized AuNPs for pathogen detection
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Acknowledgements
References
- Zhang, Y.; Simpson, R.B.; Sallade, L.E.; Sanchez, E.; Monahan, K.M.; Naumova, E.N. Evaluating Completeness of Foodborne Outbreak Reporting in the United States, 1998–2019. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiyedun, S.O.; Onarinde, B.A.; Swainson, M.; Dixon, R.A. Foodborne Outbreaks of Microbial Infection from Fresh Produce in Europe and North America: A Systematic Review of Data from This Millennium. Int J Food Sci Technol 2021, 56, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.P.; Shah, H.J.; Weller, D.L.; Ray, L.C.; Smith, K.; McGuire, S.; Trevejo, R.T.; Jervis, R.H.; Vugia, D.J.; Rissman, T. Preliminary Incidence and Trends of Infections Caused by Pathogens Transmitted Commonly through Food—Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network, 10 US Sites, 2016–2021. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2022, 71, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, M.; Simonsen, J.; Mølbak, K. Foodborne Bacterial Infection and Hospitalization: A Registry-Based Study. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2006, 42, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, A.; Ayesha, R.; Gilani, S.A.; Shahbaz, M.; Imran, A.; El-Ghorab, A.; El-Massry, K.F.; Suleman, R.; Gondal, T.A.; Asif, M.; et al. Safety Assessment of Foods at Capital Hospital of Pakistan through the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point System. J Food Prot 2020, 83, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Yoon, Y. Etiological Agents Implicated in Foodborne Illness World Wide. Food Sci Anim Resour 2021, 41, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassarawa, S.S.; Luo, Z.; Lu, Y. Conventional and Emerging Techniques for Detection of Foodborne Pathogens in Horticulture Crops: A Leap to Food Safety. Food Bioproc Tech 2022, 15, 1248–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintela, I.A.; Vasse, T.; Lin, C.-S.; Wu, V.C.H. Advances, Applications, and Limitations of Portable and Rapid Detection Technologies for Routinely Encountered Foodborne Pathogens. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 1054782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, V. Advances in Biosensor Development for the Screening of Antibiotic Residues in Food Products of Animal Origin–A Comprehensive Review. Biosens Bioelectron 2017, 90, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Bhardwaj, A. Biosensor Technology for Pesticides—a Review. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2015, 175, 3093–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, J.A.; Rushworth, J.V.H.; Millner, P.A. Biosensor Regeneration: A Review of Common Techniques and Outcomes. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6267–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Kumari, M.; Arun, R.K. Development and Implementation of Portable Biosensors in Microfluidic Point-of-Care Devices for Pathogen Detection. In Miniaturized Biosensing Devices: Fabrication and Applications; Springer, 2022; pp. 99–122. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Bai, X.; Bhunia, A.K. Current State of Development of Biosensors and Their Application in Foodborne Pathogen Detection. J Food Prot 2021, 84, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hsieh, K.; Wong, P.K.; Mach, K.E.; Liao, J.C.; Wang, T.-H. Single-Cell Pathogen Diagnostics for Combating Antibiotic Resistance. Nature Reviews Methods Primers 2023, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Hejji, L.; Kim, K.-H.; Kukkar, D.; Souhail, B.; Bhardwaj, N.; Brown, R.J.C.; Zhang, W. Advances in Surface Plasmon Resonance–Based Biosensor Technologies for Cancer Biomarker Detection. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 197, 113767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pissuwan, D.; Gazzana, C.; Mongkolsuk, S.; Cortie, M.B. Single and Multiple Detections of Foodborne Pathogens by Gold Nanoparticle Assays. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 2020, 12, e1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, S.; Song, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Jin, M. One-Step Colorimetric Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus Based on Target-Induced Shielding against the Peroxidase Mimicking Activity of Aptamer-Functionalized Gold-Coated Iron Oxide Nanocomposites. Talanta 2021, 232, 122448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanoff Jr, D.D.; Chumanov, G. Synthesis and Optical Properties of Silver Nanoparticles and Arrays. ChemPhysChem 2005, 6, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.L.; Coronado, E.; Zhao, L.L.; Schatz, G.C. The Optical Properties of Metal Nanoparticles: The Influence of Size, Shape, and Dielectric Environment. J Phys Chem B 2003, 107, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiqa, A.R.; Abdul Aziz, A.; Mehrdel, B. Nanoparticle Optical Properties: Size Dependence of a Single Gold Spherical Nanoparticle. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing, 2018; Vol. 1083; p. 012040. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Nonlinear Optical Properties of Metal Nanoparticles: A Review. RSC Adv 2017, 7, 45129–45144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechberger, W.; Hohenau, A.; Leitner, A.; Krenn, J.R.; Lamprecht, B.; Aussenegg, F.R. Optical Properties of Two Interacting Gold Nanoparticles. Opt Commun 2003, 220, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, C.M.; McCusker, C.D.; Yilmaz, T.; Rotello, V.M. Toxicity of Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized with Cationic and Anionic Side Chains. Bioconjug Chem 2004, 15, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, K.; Jin, S.; Liu, J.; Wei, T.; Cao, W.; Zou, G.; Liang, X.-J. Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized with Therapeutic and Targeted Peptides for Cancer Treatment. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.G.; Kamat, P. V Chromophore-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. Acc Chem Res 2003, 36, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, P.M.; Vig, K.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2011, 1, 31–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Yong, K.-T.; Roy, I.; Dinh, X.-Q.; Yu, X.; Luan, F. A Review on Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Biosensing Applications. Plasmonics 2011, 6, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, S.; Mascini, M.; Turner, A.P.F.; Minunni, M. Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging for Affinity-Based Biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 2010, 25, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P. SPR Biosensors: Historical Perspectives and Current Challenges. Sens Actuators B Chem 2016, 229, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedberg, B.; Nylander, C.; Lundström, I. Biosensing with Surface Plasmon Resonance—How It All Started. Biosens Bioelectron 1995, 10, i–ix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Park, J.; Kang, S.; Kim, M. Surface Plasmon Resonance: A Versatile Technique for Biosensor Applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 10481–10510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, E.; Fendler, J.H. Exploitation of Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance. Advanced materials 2004, 16, 1685–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unser, S.; Bruzas, I.; He, J.; Sagle, L. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensing: Current Challenges and Approaches. Sensors 2015, 15, 15684–15716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T. V Gold Nanorod-Based Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors: A Review. Sens Actuators B Chem 2014, 195, 332–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.S.; Borges, J.; Lopes, C.; Pereira, R.M.S.; Vasilevskiy, M.I.; Vaz, F. Gas Sensors Based on Localized Surface Plasmon Resonances: Synthesis of Oxide Films with Embedded Metal Nanoparticles, Theory and Simulation, and Sensitivity Enhancement Strategies. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherry, L.J.; Jin, R.; Mirkin, C.A.; Schatz, G.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy of Single Silver Triangular Nanoprisms. Nano Lett 2006, 6, 2060–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Cho, S.H.; Zandi, O.; Ghosh, S.; Johns, R.W.; Milliron, D.J. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance in Semiconductor Nanocrystals. Chem Rev 2018, 118, 3121–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willets, K.A.; Van Duyne, R.P. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy and Sensing. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2007, 58, 267–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haes, A.J.; Van Duyne, R.P. A Unified View of Propagating and Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors. Anal Bioanal Chem 2004, 379, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonzon, C.R.; Jeoung, E.; Zou, S.; Schatz, G.C.; Mrksich, M.; Van Duyne, R.P. A Comparative Analysis of Localized and Propagating Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors: The Binding of Concanavalin A to a Monosaccharide Functionalized Self-Assembled Monolayer. J Am Chem Soc 2004, 126, 12669–12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.-C.; Astruc, D. Gold Nanoparticles: Assembly, Supramolecular Chemistry, Quantum-Size-Related Properties, and Applications toward Biology, Catalysis, and Nanotechnology. Chem Rev 2004, 104, 293–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, A.; Malankowska, A.; Nowaczyk, G.; Grześkowiak, B.F.; Tuśnio, K.; Słomski, R.; Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Jurga, S. Size and Shape-Dependent Cytotoxicity Profile of Gold Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med 2017, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Chattopadhyay, N. Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Based Superquenching of Fluorescence: A Review. J Lumin 2015, 160, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Ma, Z.; Su, Z. Biorecognition-Driven Self-Assembly of Gold Nanorods: A Rapid and Sensitive Approach toward Antibody Sensing. Chemistry of Materials 2007, 19, 5809–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanromán-Iglesias, M.; Zhang, K.A.I.; Chuvilin, A.; Lawrie, C.H.; Grzelczak, M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Conjugated Polymers as Molecular Gates for Light-Controlled Release of Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2015, 7, 15692–15695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Yu, G.; Wei, J.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; et al. A Single Thiolated-Phage Displayed Nanobody-Based Biosensor for Label-Free Detection of Foodborne Pathogen. J Hazard Mater 2023, 443, 130157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, T.; Jia, P.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Diversely Positive-Charged Gold Nanoparticles Based Biosensor: A Label-Free and Sensitive Tool for Foodborne Pathogen Detection. Food Chem X 2019, 3, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Song, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C. Label-Free Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus Based on Bacteria-Imprinted Polymer and Turn-on Fluorescence Probes. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2021, 4, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.J.; Suk, H.-J.; Sung, H.Y.; Li, T.; Poo, H.; Kim, M.-G. Novel Antibody/Gold Nanoparticle/Magnetic Nanoparticle Nanocomposites for Immunomagnetic Separation and Rapid Colorimetric Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus in Milk. Biosens Bioelectron 2013, 43, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, N.; Torralba, A.S.; Álvarez-Diduk, R.; Afkhami, A.; Merkoçi, A. Lab in a Tube: Point-of-Care Detection of Escherichia Coli. Anal Chem 2020, 92, 4209–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byzova, N.A.; Zherdev, A. V; Gorbatov, A.A.; Shevyakov, A.G.; Biketov, S.F.; Dzantiev, B.B. Rapid Detection of Lipopolysaccharide and Whole Cells of Francisella Tularensis Based on Agglutination of Antibody-Coated Gold Nanoparticles and Colorimetric Registration. Micromachines (Basel) 2022, 13, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yao, S.; Shang, M.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Wang, J. A Multicolor Sensing System for Simultaneous Detection of Four Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria Based on Fe3O4/MnO2 Nanocomposites and the Etching of Gold Nanorods. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2021, 149, 112035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Liu, D.; Han, D.; Wang, Z. Phenylboronic Acid Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Highly Sensitive Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín, M.J.; Rashid, A.; Rejzek, M.; Fairhurst, S.A.; Wharton, S.A.; Martin, S.R.; McCauley, J.W.; Wileman, T.; Field, R.A.; Russell, D.A. Glyconanoparticles for the Plasmonic Detection and Discrimination between Human and Avian Influenza Virus. Org Biomol Chem 2013, 11, 7101–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, R.; Huang, X.; Feng, H.; Teo, W.; Xing, B. Colorimetric Screening of Bacterial Enzyme Activity and Inhibition Based on the Aggregation of Gold Nanoparticles. Chemical communications 2009, 1972–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Cao, Y.; Meng, Q.; Lu, J. Aptasensors for Rapid Detection of Escherichia Coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium. Nanoscale Res Lett 2012, 7, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, M.S.; Chen, P.Z.; Jones, L.; Gu, F.X. Branching and Size of CTAB-Coated Gold Nanostars Control the Colorimetric Detection of Bacteria. RSC Adv 2014, 4, 10660–10668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, S.M.; Bald, D.; Azzazy, H.M.E. Direct Detection of Unamplified Hepatitis C Virus RNA Using Unmodified Gold Nanoparticles. Clin Biochem 2010, 43, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Teo, W.; Tan, S.; Feng, H.; Padmanabhan, P.; Xing, B. Metallic Nanoparticles Bioassay for Enterobacter Cloacae P99 β-Lactamase Activity and Inhibitor Screening. Analyst 2010, 135, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.K.; Suri, C.R.; Chaudhry, M.; Tiwari, R.P.; Rishi, P. A Gold Nanoparticles Based Immuno-Bioprobe for Detection of Vi Capsular Polysaccharide of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhi. Mol Biosyst 2012, 8, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Gontard, L.C.; Tram, T.; Ly, L.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. Dual Enlargement of Gold Nanoparticles: From Mechanism to Scanometric Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria. Small 2011, 7, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Cao, C.; Han, S.J.; Sim, S.J. Detection of Pathogen Based on the Catalytic Growth of Gold Nanocrystals. Water Res 2009, 43, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ge, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Lee, S.-T. A Facile Assay for Direct Colorimetric Visualization of Lipopolysaccharides at Low Nanomolar Level. Nano Res 2012, 5, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhao, H.; Qiao, F.; Chen, L.; Duan, R.; Ai, S. Colorimetric Detection of Escherichia Coli O157:H7 Using Functionalized Au@Pt Nanoparticles as Peroxidase Mimetics. Analyst 2013, 138, 3026–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Ma, Q.; Shang, K.; Liu, T.; Yin, H.; Ai, S. Gold Nanoparticles as Colorimetric Sensor: A Case Study on E. Coli O157:H7 as a Model for Gram-Negative Bacteria. Sens Actuators B Chem 2012, 161, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Gaston, M.A.; Weiss, A.A.; Zhang, P. Colorimetric Viral Detection Based on Sialic Acid Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 2013, 42, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, O.R.; Li, X.; Garcia-Gonzalez, L.; Zhu, Z.-J.; Yan, B.; Bunz, U.H.F.; Rotello, V.M. Colorimetric Bacteria Sensing Using a Supramolecular Enzyme–Nanoparticle Biosensor. J Am Chem Soc 2011, 133, 9650–9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Types | Pathogens | Analysis time | Detection limit | Working range | Sample type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-functionalized AuNPs |
E. coli and B. cereus |
~1 h | ~108 CFU·mL-1 | NDa | Culture | [55] |
|
E. coli O157:H7 and S. enterica |
20 min | 105 CFU·mL-1 | 105-108 CFU/mL | Culture | [56] | |
|
S. aureus, Achromobacter xylosoxidans, Delftia acidovorans, and Stenophomonas maltophilia |
~ 5 min | ~1.5×106 CFU·mL-1 | NDa | Culture | [57] | |
| Hepatitis C virus | ~30 min | 2.5 copies·μL-1 RNA | ~2.5-100 copies·μL-1 | Serum | [58] | |
| Enterobacter cloacae | ~35 min | 16 fmol/mL of P99 β-lactamase | 15-80 fmol·mL-1 | β-lactamase | [59] | |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | 100 min | 103 cfu·mL-1 | 103-107 CFU·mL-1 | Spiked shrimp | [46] | |
| Salmonella enteritidis | n.d.a | 103 cfu·mL-1 | 103-108 CFU·mL-1 | Spiked lettuce and pork | [47,48] | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 135 min | 102 cfu·mL-1 | 102-104 CFU·mL-1 | Spiked pork | [48] | |
| Protein functionalized AuNPs | Staphylococcus aureus | 40 min | 1.5×107 CFU·mL-1 (milk) 1.5×105 CFU·mL-1 (PBS) |
1.5×107-1.5×108 CFU·mL-1 | Spiked milk | [49] |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | ~ 3 min | 5×102 CFU·mL-1 | 1.5×105- 1.5×108 CFU·mL-1 | NDa | [60] |
| Types | Pathogens | Analysis time | Detection limit | Working range | Sample type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein functionalized AuNPs | C. jejuni | Overnight | 106 CFU·mL-1 | 106-109 CFU·mL-1 | Culture | [61] |
| G. lambliacysts | NDa | 1×103 cells·mL-1 | 103-104 cells·mL-1 | Culture | [62] | |
| S. enterica serovar | < 5min | 103 CFU·mL-1 | 103- 104 CFU·mL-1 | Culture | [60] | |
| E. coli O157:H7 | 20 min | 103 cfu/mL 100 cfu·mL-1 (with smartphone) |
103 to 107 cfu·mL-1 | River and tap water | [50] | |
| Francisella tularensis | 20 min | 103 cfu·mL-1 | 103 to 109 cfu·mL-1 | Natural and tap water | [51] | |
| Small molecule functionalized AuNPs | S. aureus | ~2 h | 50 CFU·mL-1 | 5×102 – 5×106 CFU·mL-1 | Spiked milk, urine, lung fluid | [53] |
| E. coli 055:B5 LPS | ~5 min | 330 fmol/mL lipopolysaccharides | 5-90 pmol·mL-1 | NDa | [63] |
|
| E. coli O157:H7 | < 40 min | 7 CFU·mL-1 | 7-6×106 CFU·mL-1 | Culture | [64,65] | |
| Influenza B/Victoria and Influenza B/Yamagata | ~10 min | 0.15 vol% dilution of Hemagglutinati-on assay titer 512 virus | 0.15 -1.25 vol% | Culture | [66] | |
| E. coli XL1 | ~10 min | 102 CFU·mL-1 (solution) 104 CFU/mL (test strip) |
102 – 107 CFU·mL-1 (solution) 104 – 108 CFU·mL-1 (test strip) |
Culture | [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




