Submitted:
27 November 2023
Posted:
27 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Supercritical Antisolvent (SAS) Process
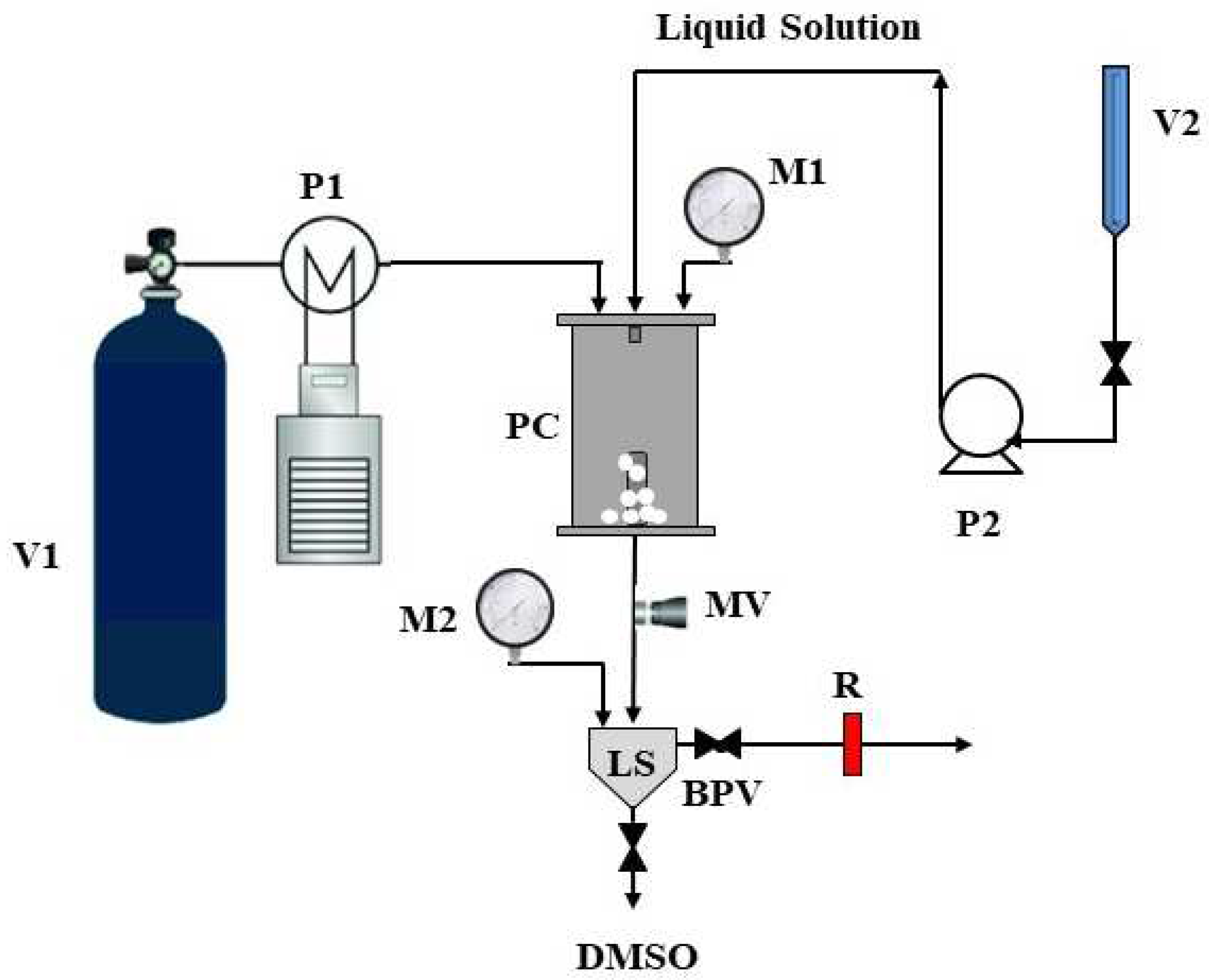
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.3.1. FESEM Characterization and PSDs Evaluation
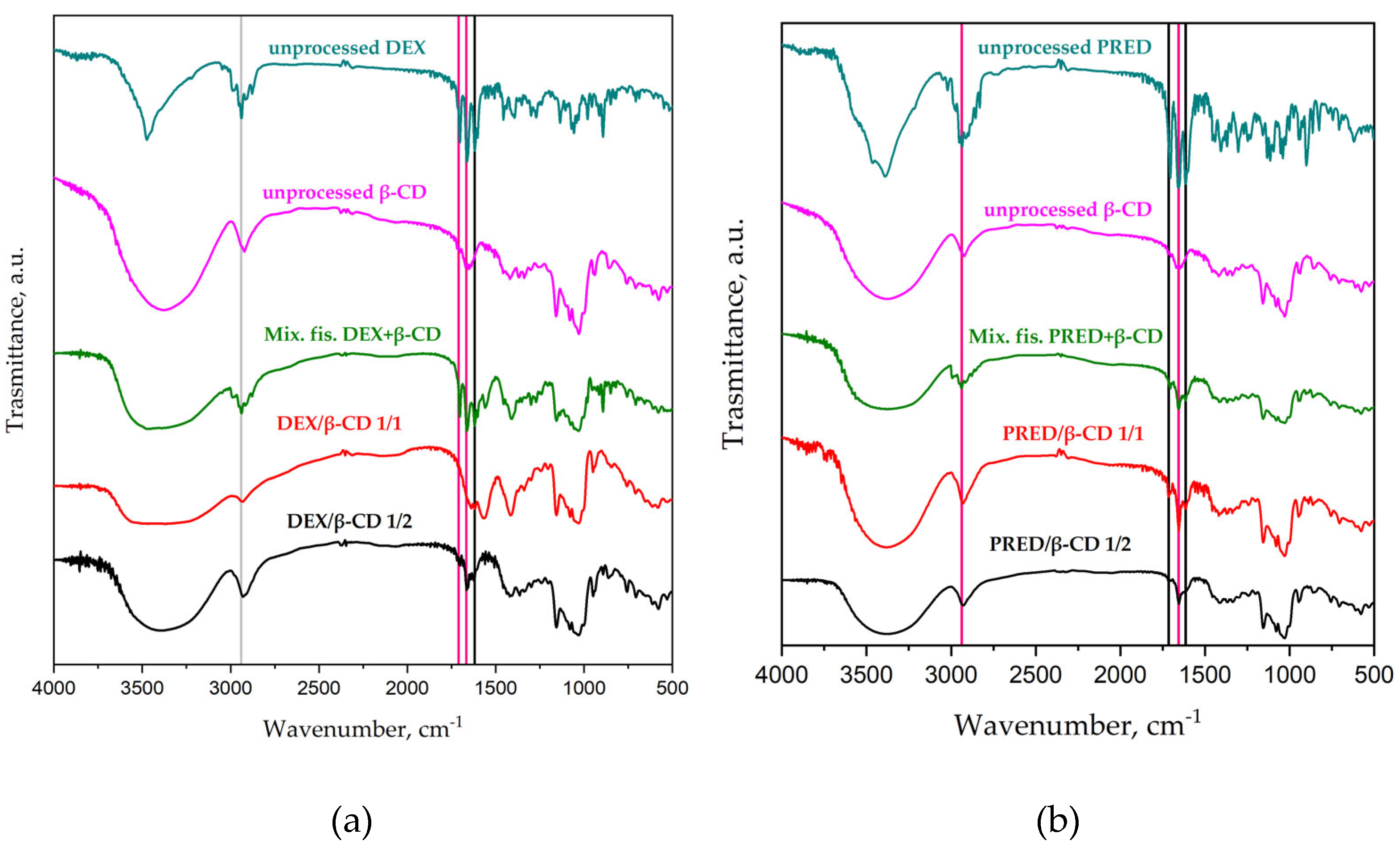
2.3.2 Fourier Transform Infrared Characterization
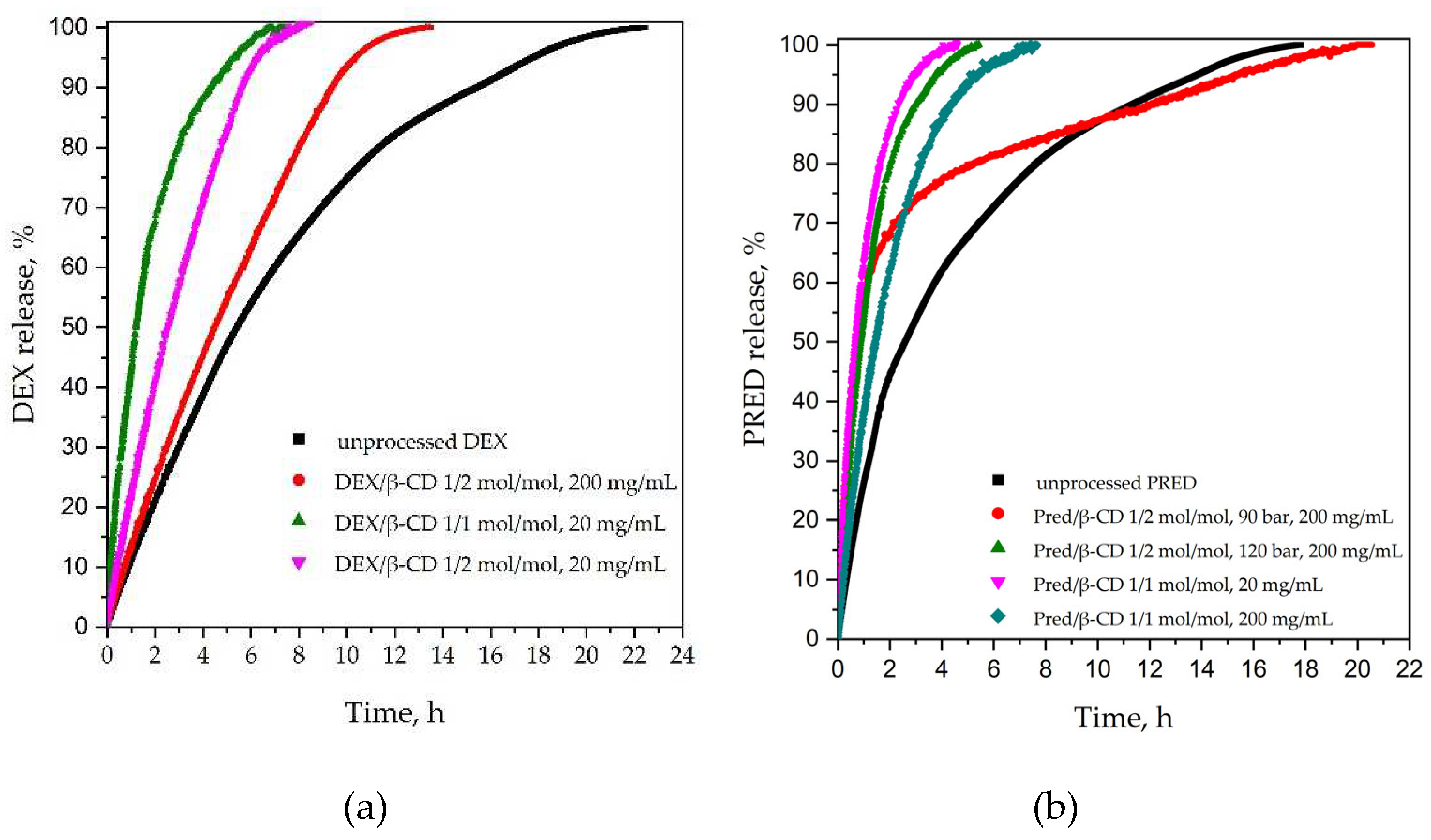
2.3.3 Dissolution Tests
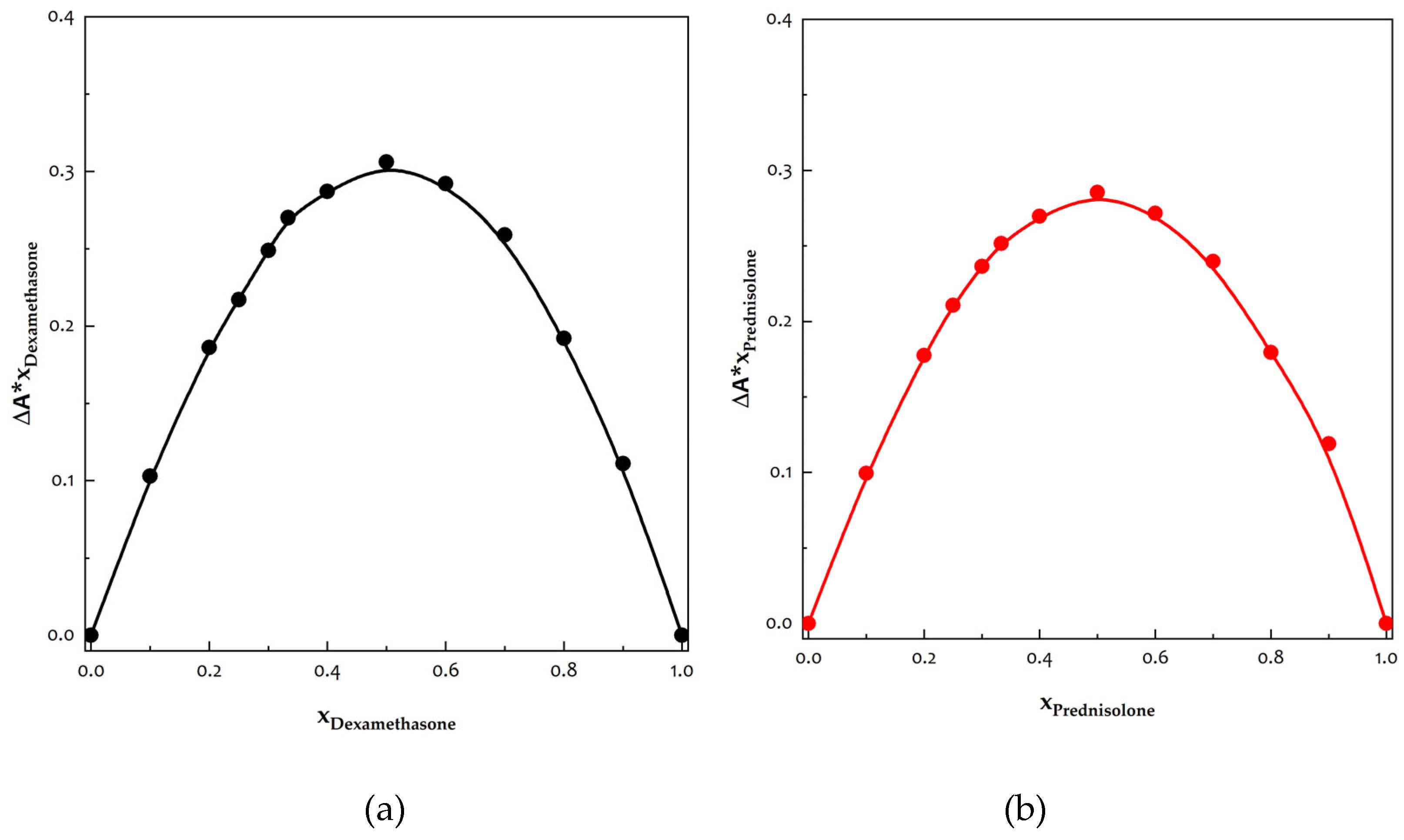
2.3.4. Job’s Method
3. Results and Discussion
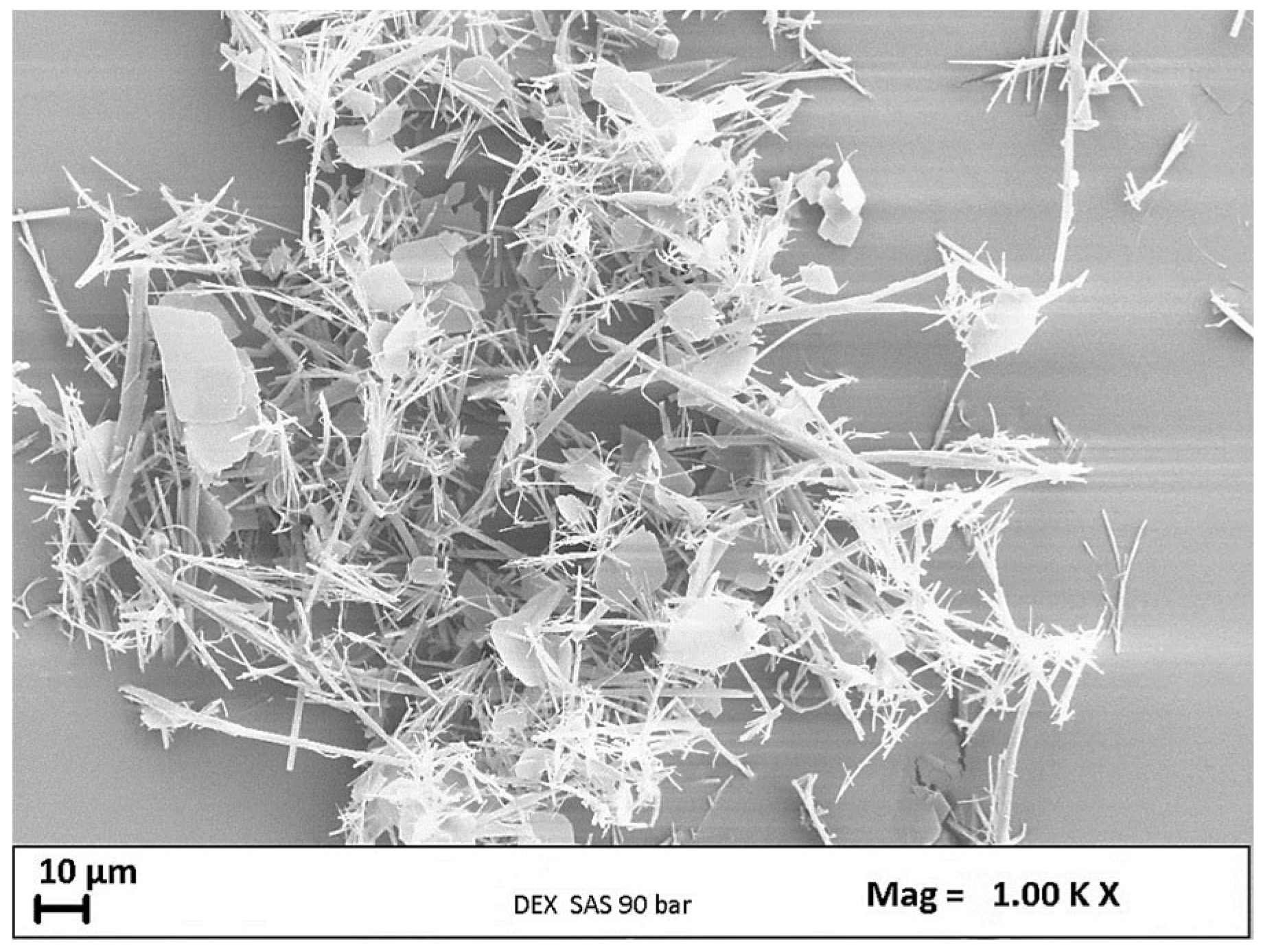
3.1 Preliminary Test for DEX Micronization
3.2 DEX/β-Cyclodextrin
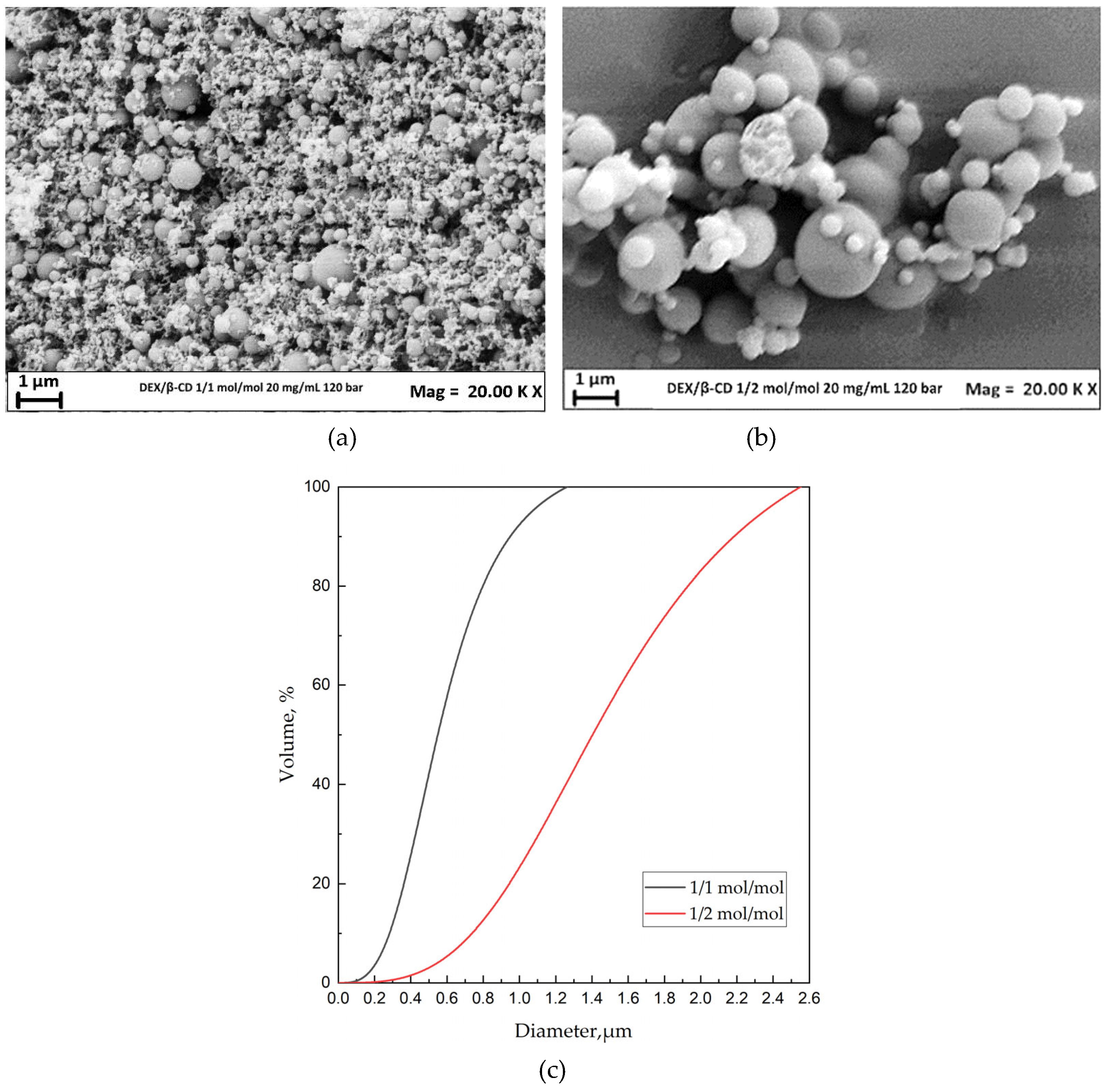
3.2.1 Effect of the DEX/β-CD ratio
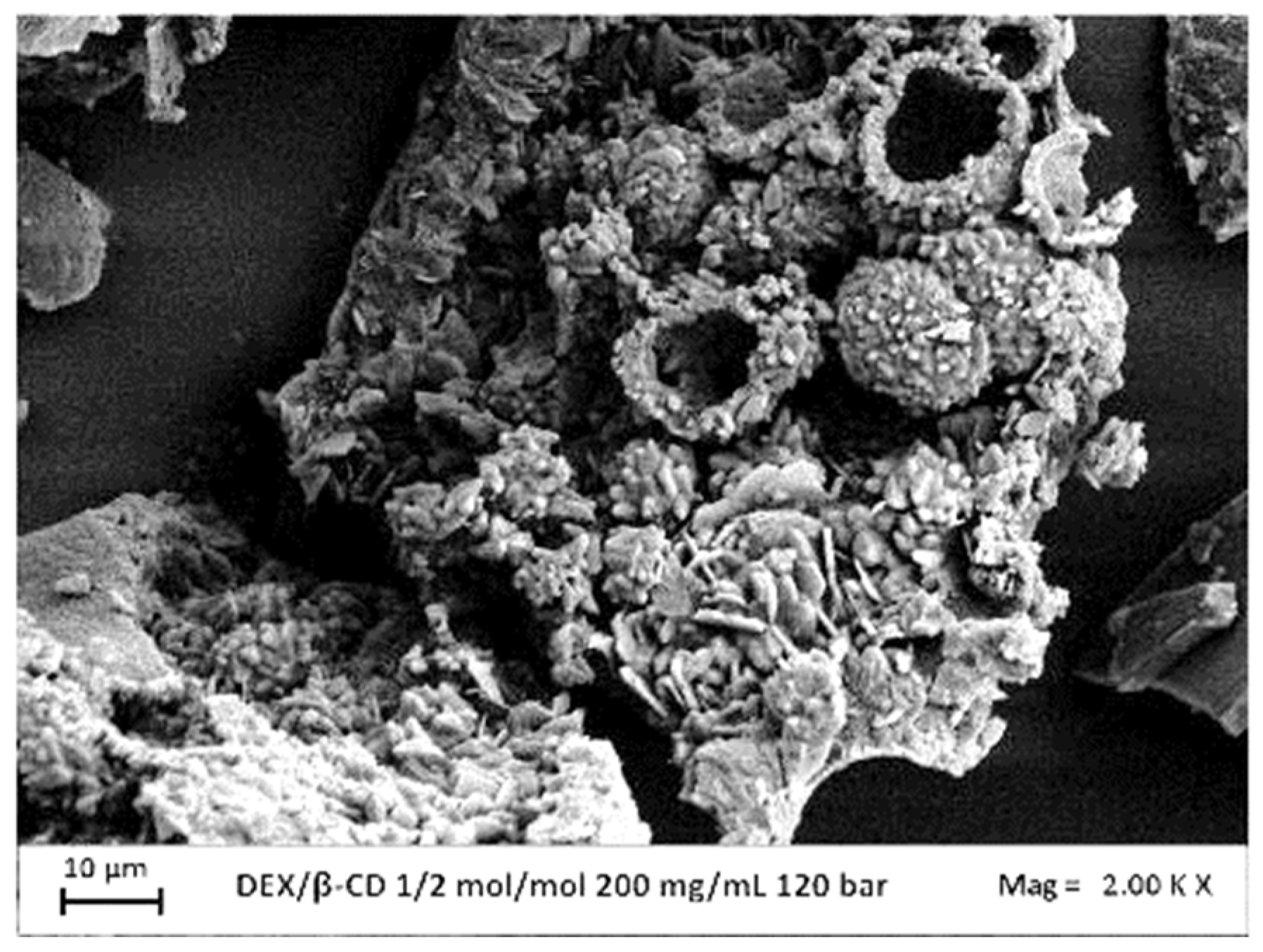
3.2.2 Effect of Concentration
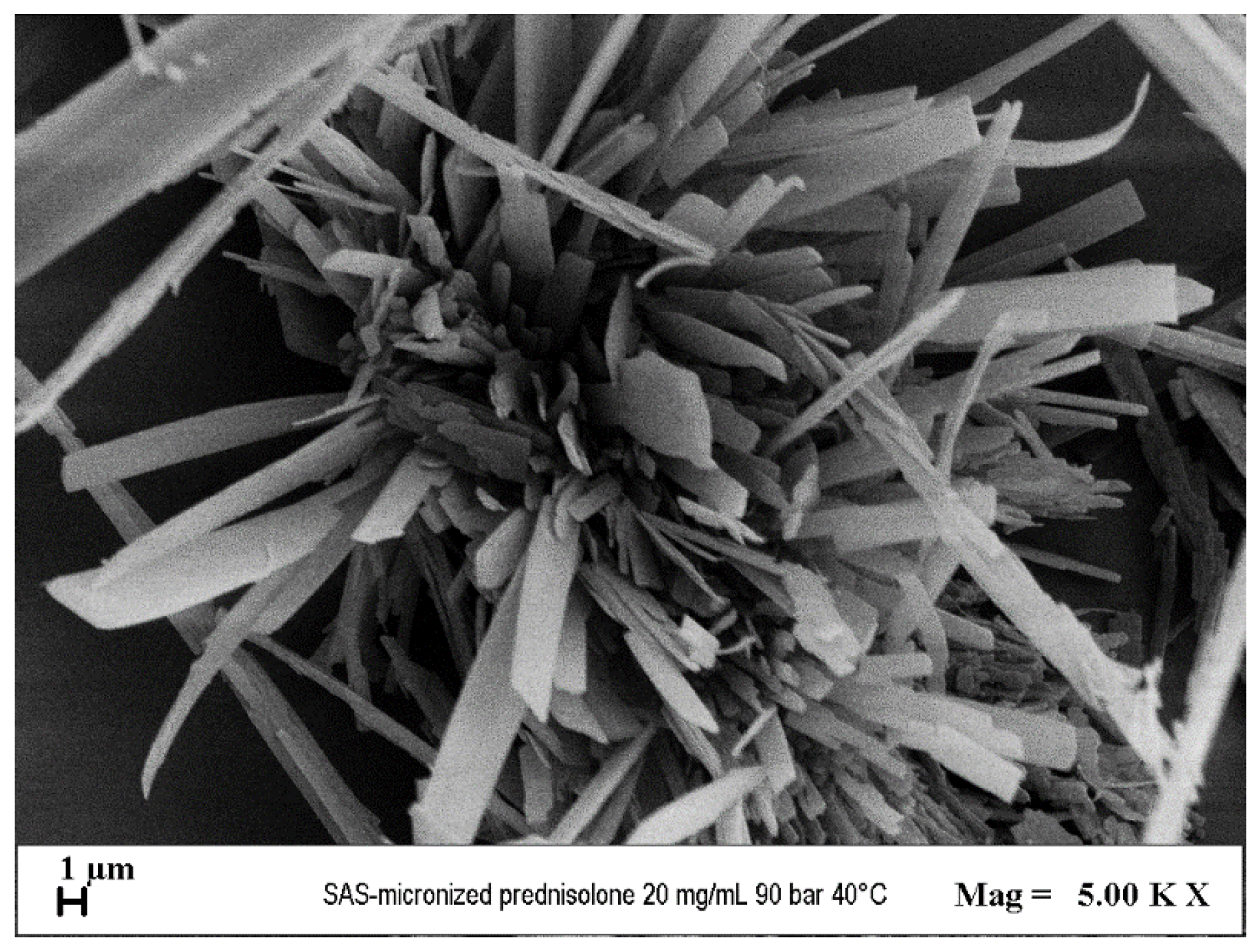
3.3 Preliminary Test for PRED Micronization
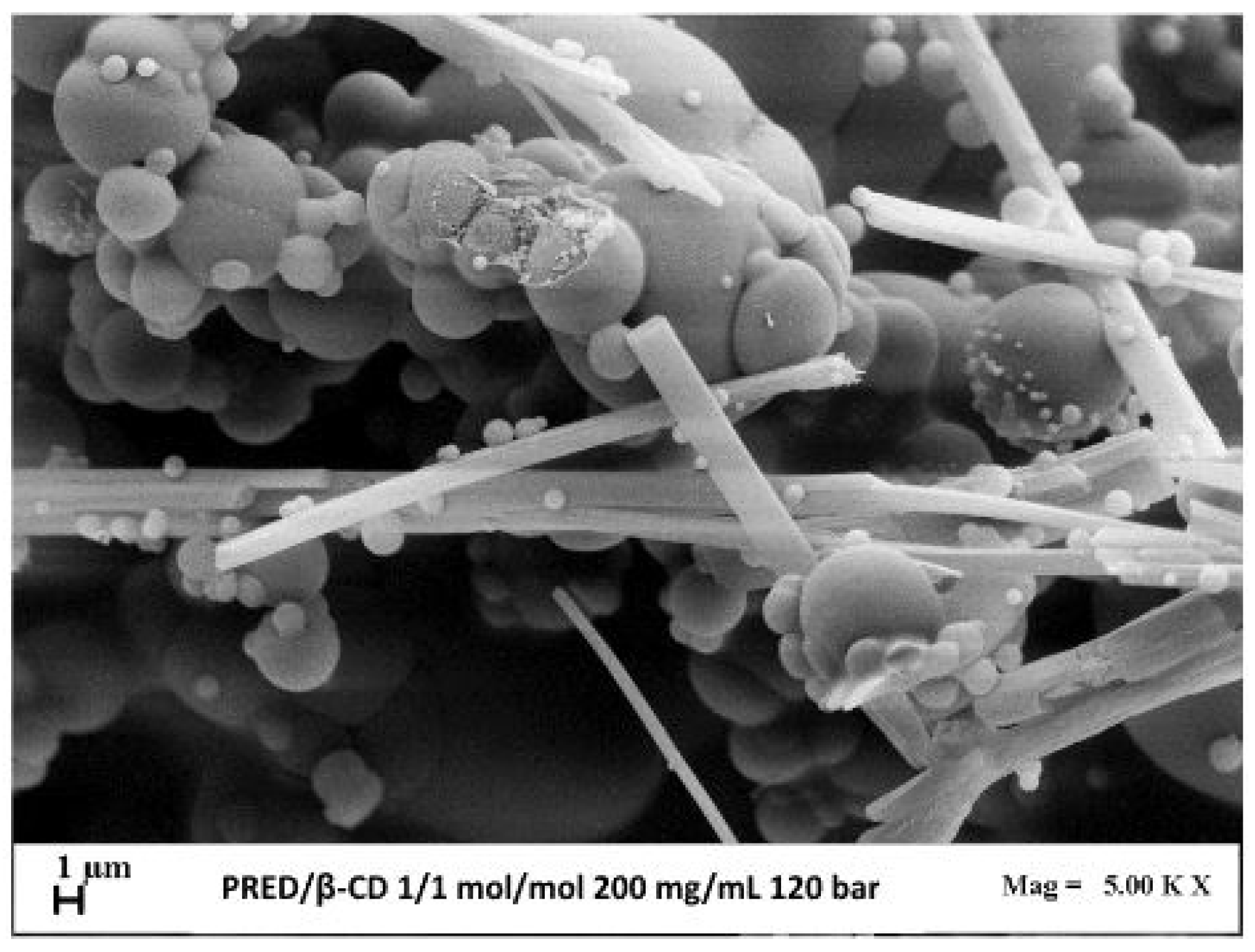
3.4 Micronization of PRED/β-CD Complexes
3.4.1 Effect of Pressure
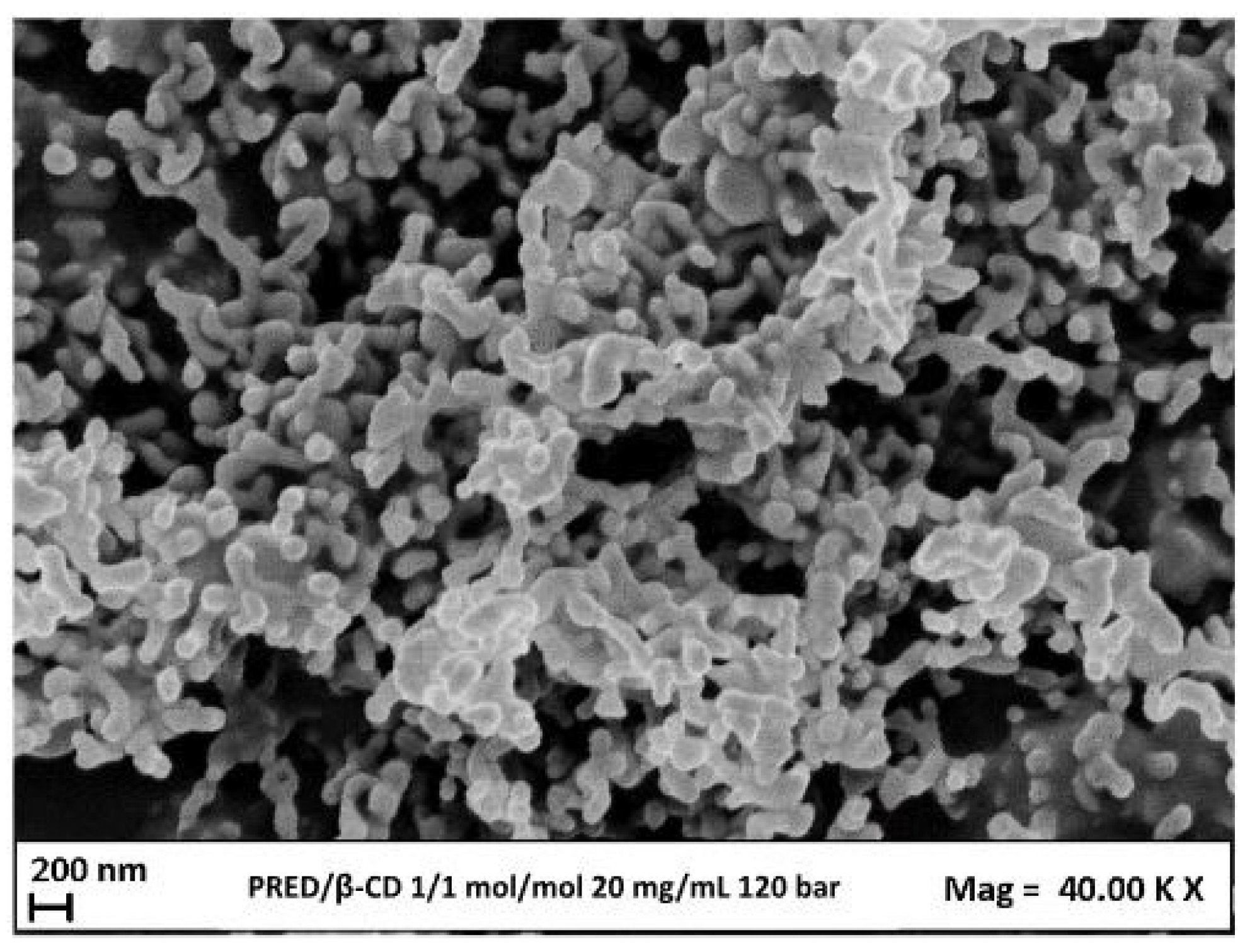
3.4.2 Effect of Molar Ratio PRED:β-CD
3.4.3 Effect of Total Concentration
3.5 Determination of Encapsulation Yield
3.6 Characterization
3.7 Determination of Stoichiometries of Inclusion Complexes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samuel, S.; Nguyen, T.; Choi, H.A. Pharmacologic Characteristics of Corticosteroids. J. Neurocrit. Care 2017, 10, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramori, G.; Mumby, S.; Girbino, G.; Chung, K.F.; Adcock, I.M. Corticosteroids. In Nijkamp and Parnham's Principles of Immunopharmacology; Parnham, M.J., Nijkamp, F.P., Rossi, A.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; pp. 661–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramori, G.; Ruggeri, P.; Casolari, P.; Chung, K.F.; Girbino, G.; Adcock, I.M. Fluticasone furoate and vilanterol for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine 2017, 11, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.B.; Nadkarni, N.J.; Patil, S.P.; Godse, K.V.; Gautam, M.; Agarwal, S. Topical corticosteroids in dermatology. Indian journal of dermatology, venereology and leprology 2016, 82, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammers, T.; Sofias, A.M.; van der Meel, R.; Schiffelers, R.; Storm, G.; Tacke, F.; Koschmieder, S.; Brümmendorf, T.H.; Kiessling, F.; Metselaar, J.M. Dexamethasone nanomedicines for COVID-19. Nature Nanotechnology 2020, 15, 622–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Jia, Z.; Foster, K.W.; Wei, X.; Qiao, F.; Jiang, H.; Jin, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, N.; Zhao, G.; et al. Dexamethasone prodrug nanomedicine (ZSJ-0228) treatment significantly reduces lupus nephritis in mice without measurable side effects — A 5-month study. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine 2021, 31, 102302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Crielaard, B.J.; Dusad, A.; Lele, S.M.; Rijcken, C.J.F.; Metselaar, J.M.; Kostková, H.; Etrych, T.; Ulbrich, K.; et al. Nanomedicines for Inflammatory Arthritis: Head-to-Head Comparison of Glucocorticoid-Containing Polymers, Micelles, and Liposomes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, I.; Sen, A. In silico screening predicts common cold drug Dextromethorphan along with Prednisolone and Dexamethasone can be effective against novel Coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics 2022, 40, 3706–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqurshi, A.; Hanafy, A.F.; Abdalla, A.M.; Guda, T.K.; Gabr, K.E.; Royall, P.G. Ocular anti-inflammatory activity of prednisolone acetate loaded chitosan-deoxycholate self-assembled nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 3679–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusini, R.; Varna, M.; Couvreur, P. Advanced nanomedicines for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2020, 157, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchero, M. Supercritical Carbon Dioxide as a Green Alternative to Achieve Drug Complexation with Cyclodextrins. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 562–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansook, P.; Ogawa, N.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins: structure, physicochemical properties and pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeoye, O.; Cabral-Marques, H. Cyclodextrin nanosystems in oral drug delivery: A mini review. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeber, A.W.; Bakker, H. Amorphization by ball milling. A review. Physica B: Condensed Matter 1988, 153, 93–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, A.R.d.V.; Alencar, É.d.N.; Xavier Júnior, F.H.; Oliveira, C.M.d.; Marcelino, H.R.; Barratt, G.; Fessi, H.; Egito, E.S.T.d.; Elaissari, A. Freeze-drying of emulsified systems: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 503, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vehring, R. Pharmaceutical particle engineering via spray drying. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 999–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louey, M.D.; Van Oort, M.; Hickey, A.J. Aerosol dispersion of respirable particles in narrow size distributions produced by jet-milling and spray-drying techniques. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottola, S.; Mancuso, A.; Sacco, O.; Vaiano, V.; De Marco, I. Photocatalytic Systems Based on ZnO Produced by Supercritical Antisolvent for Ceftriaxone Degradation. Catalysts 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwineza, P.A.; Waśkiewicz, A. Recent Advances in Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Natural Bioactive Compounds from Natural Plant Materials. Molecules 2020, 25, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottola, S.; Viscusi, G.; Iannone, G.; Belvedere, R.; Petrella, A.; De Marco, I.; Gorrasi, G. Supercritical Impregnation of Mesoglycan and Lactoferrin on Polyurethane Electrospun Fibers for Wound Healing Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9269–9283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldino, L.; Cardea, S.; Reverchon, E. A supercritical CO2 assisted electrohydrodynamic process used to produce microparticles and microfibers of a model polymer. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 33, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverchon, E.; Schiavo Rappo, E.; Cardea, S. Flexible supercritical CO2-assisted process for poly(methyl methacrylate) structure formation. Polymer Engineering and Science 2006, 46, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, Ž.; Markočič, E.; Leitgeb, M.; Primožič, M.; Knez Hrnčič, M.; Škerget, M. Industrial applications of supercritical fluids: A review. Energy 2014, 77, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, P.; De Marco, I. Preparation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes by supercritical antisolvent process. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 44, 101397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, M.D.; Piqueras, C.M.; Piva, G.K.; Ramírez-Rigo, M.V.; Filho, L.C.; Bucalá, V. Simultaneous formation of inclusion complex and microparticles containing Albendazole and β-Cyclodextrin by supercritical antisolvent co-precipitation. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Ji, M.; Sun, Y.; Yan, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Preparation and characterization of baicalein/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex for enhancement of solubility, antioxidant activity and antibacterial activity using supercritical antisolvent technology. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2020, 96, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosapio, V.; Reverchon, E.; De Marco, I. Coprecipitation of Polyvinylpyrrolidone/β-Carotene by Supercritical Antisolvent Processing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 11568–11575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, P.M.J. Formation and stability of inorganic complexes in solution. Annales de Chimie 1928, 9, 113–203. [Google Scholar]
- Campardelli, R.; Reverchon, E.; De Marco, I. Dependence of SAS particle morphologies on the ternary phase equilibria. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 130, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-L.; Lin, J.-C.; Hai, W.; Tan, H.-W.; Luo, Y.-W.; Xie, X.-L.; Cao, Y.; He, F.-A. A novel crosslinked β-cyclodextrin-based polymer for removing methylene blue from water with high efficiency. Colloids Surf., A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 560, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosapio, V.; De Marco, I.; Reverchon, E. PVP/corticosteroid microspheres produced by supercritical antisolvent coprecipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 292, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, S.; Yasmeen, K.; Hanif, M.; Khaliq, O.; Muhammad, H.; Hafsa; Tahiri, I.A.; Jahangir, S.; Ali, S.T. Electrochemical Methodology for NSAID's Determination and its Interaction with Steroid Dexamethasone. International Journal of Electrochemical Science 2019, 14, 5748–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Roy, A.; Roy, K.; Roy, M.N. Study to explore the mechanism to form inclusion complexes of β-cyclodextrin with vitamin molecules. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| API | API/β-CD [mol/mol] |
P [bar] |
Ctot [mg/mL] |
Morphology | MD±SD [μm] |
| DEX | 1/0 | 120 | 10 | C | - |
| 1/1 | 120 | 20 | MP | 0.197±0.18 | |
| 1/2 | 120 | 20 | MP+cMP | 0.609±0.42 | |
| 120 | 200 | C+AGG | - | ||
| PRED | 1/0 | 90 | 20 | C | - |
| 1/1 | 120 | 20 | cMP | 0.131±0.07 | |
| 120 | 200 | cMP+C | 4.19±4.03 | ||
| 1/2 | 90 | 200 | cMP+C | 0.435±0.30 | |
| 120 | 200 | cMP+MP | 2.14±1.43 |
| API | API:β-CD [mol:mol] |
P [bar] |
Ctot [mg/mL] |
Encapsulation yield [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEX | 1/1 | 120 | 200 | 93 |
| 1/2 | 120 | 20 | 87 | |
| 200 | 57 | |||
| PRED | 1/1 | 120 | 20 | 89 |
| 200 | 78 | |||
| 1/2 | 90 | 200 | 55 | |
| 120 | 200 | 68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





