Submitted:
16 November 2023
Posted:
17 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. MMR/MMN/LDN in Speech Perception Development
1.2. MMR Time-Frequency Analysis and Speech Perception Development
1.3. The Current Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
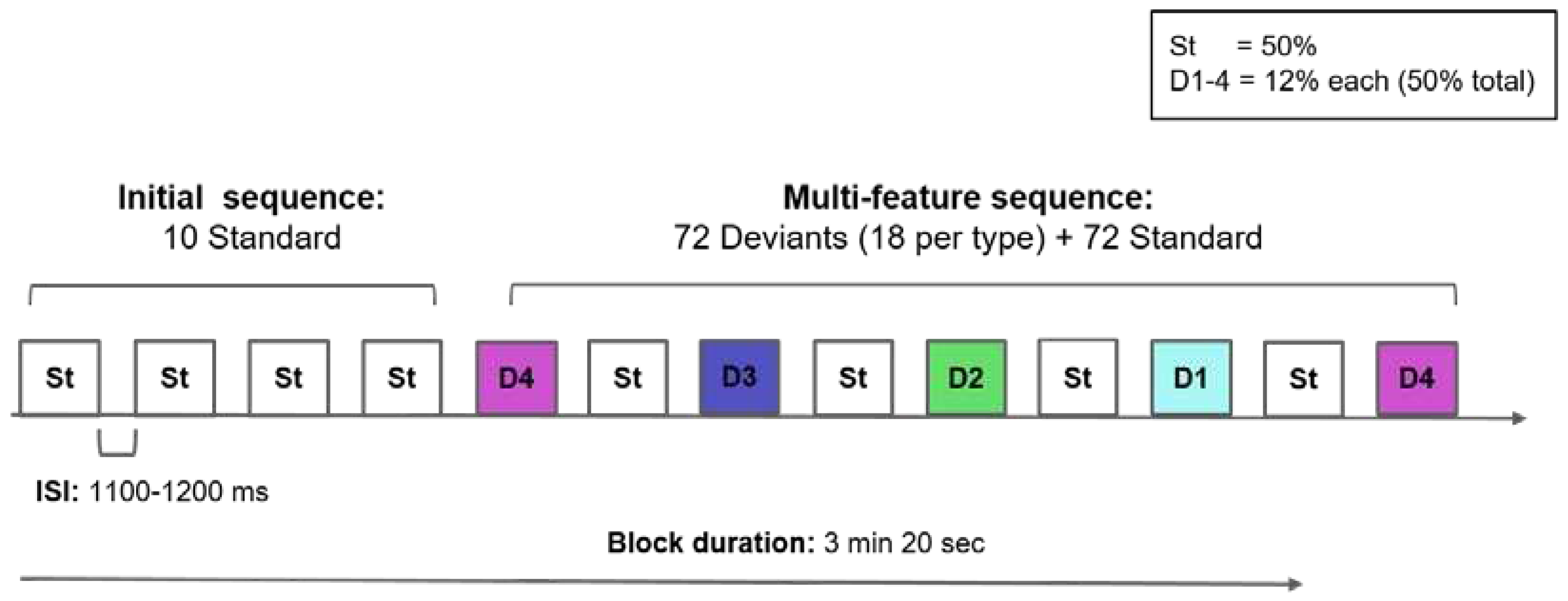
2.2. Stimuli
2.2.1. Phonological Awareness Task
2.2.2. ERP Experiment
2.3. Procedure
2.4. EEG Acquisition and Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioural Results
3.2. EEG Results
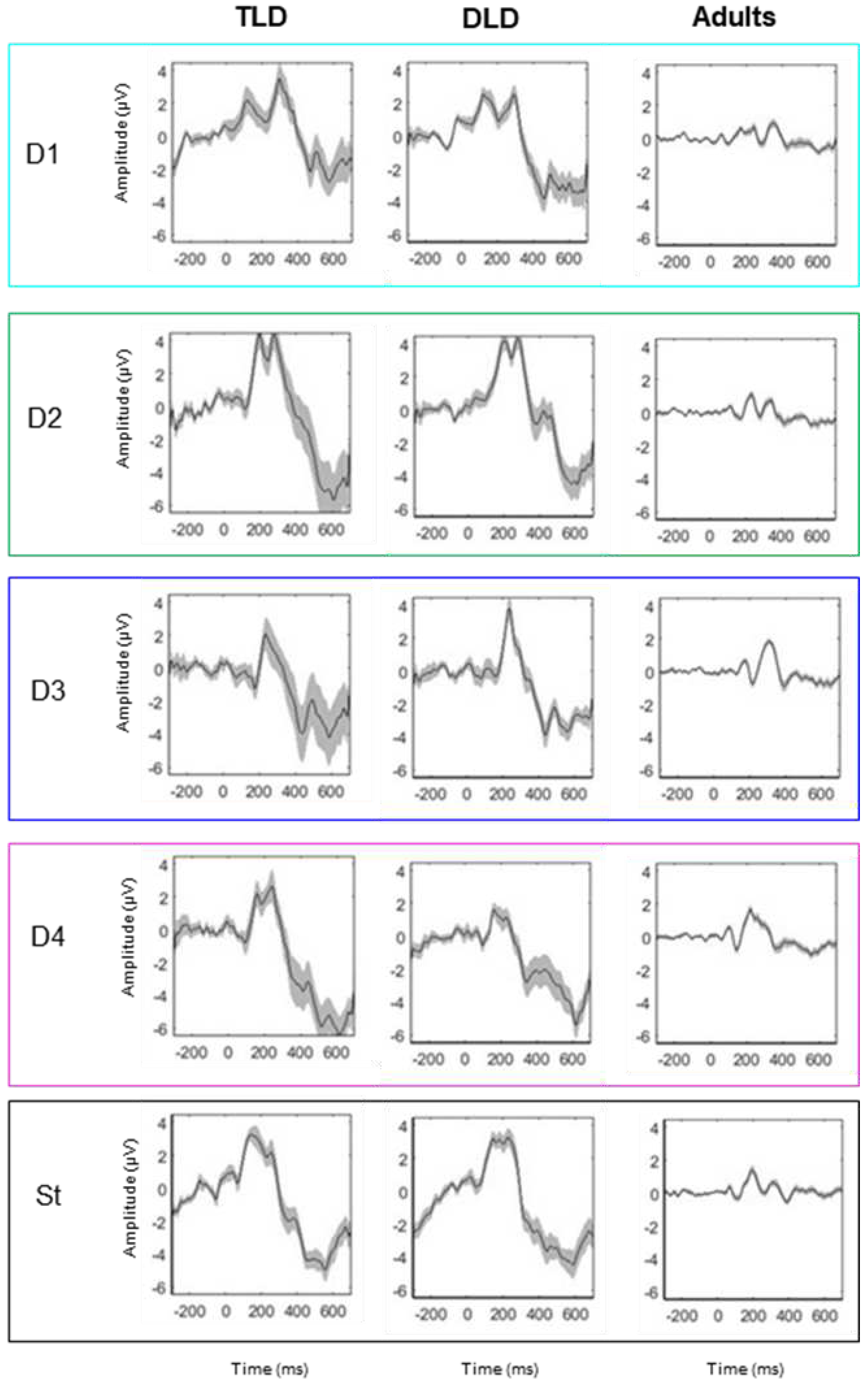
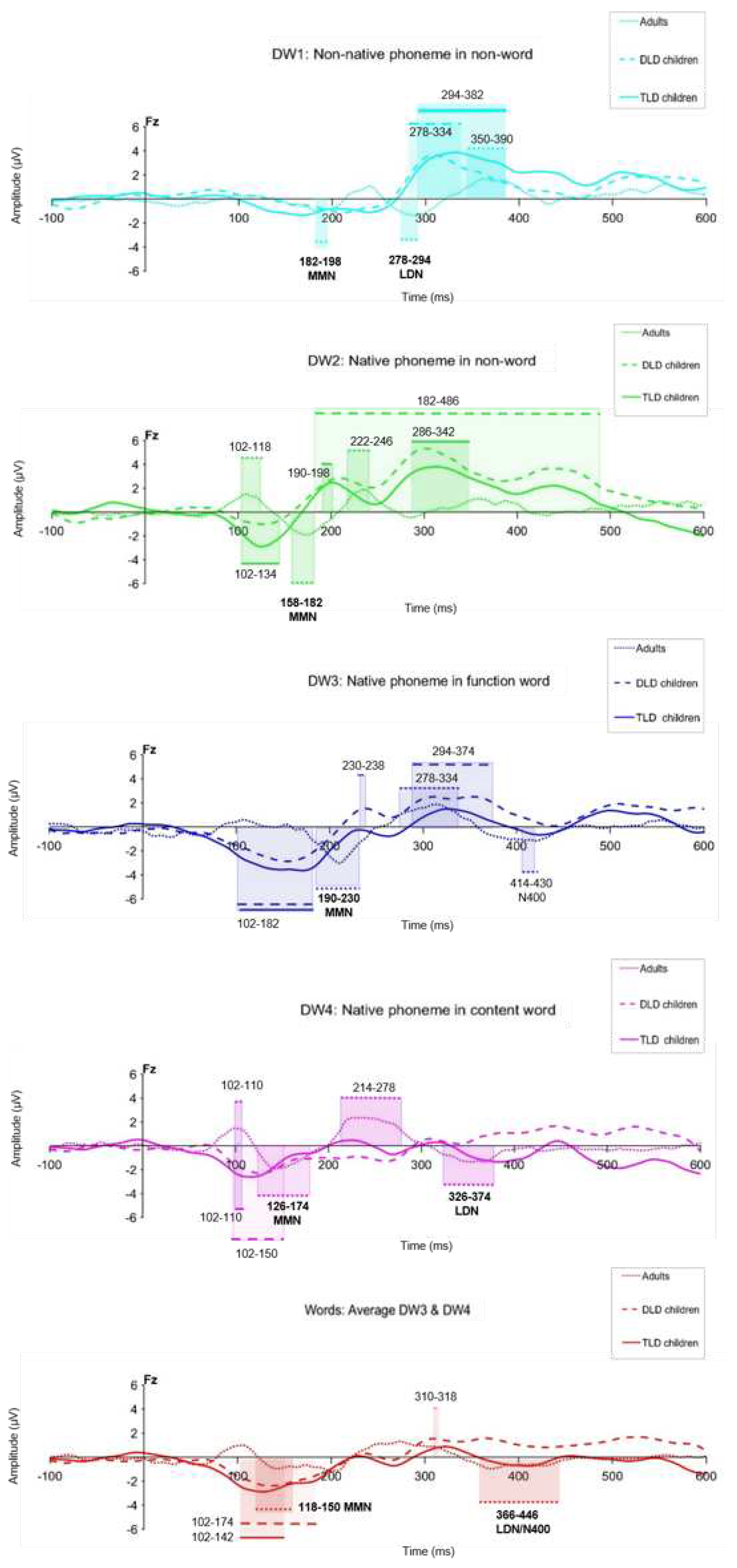
3.2.1. ERP Analysis of MMRs
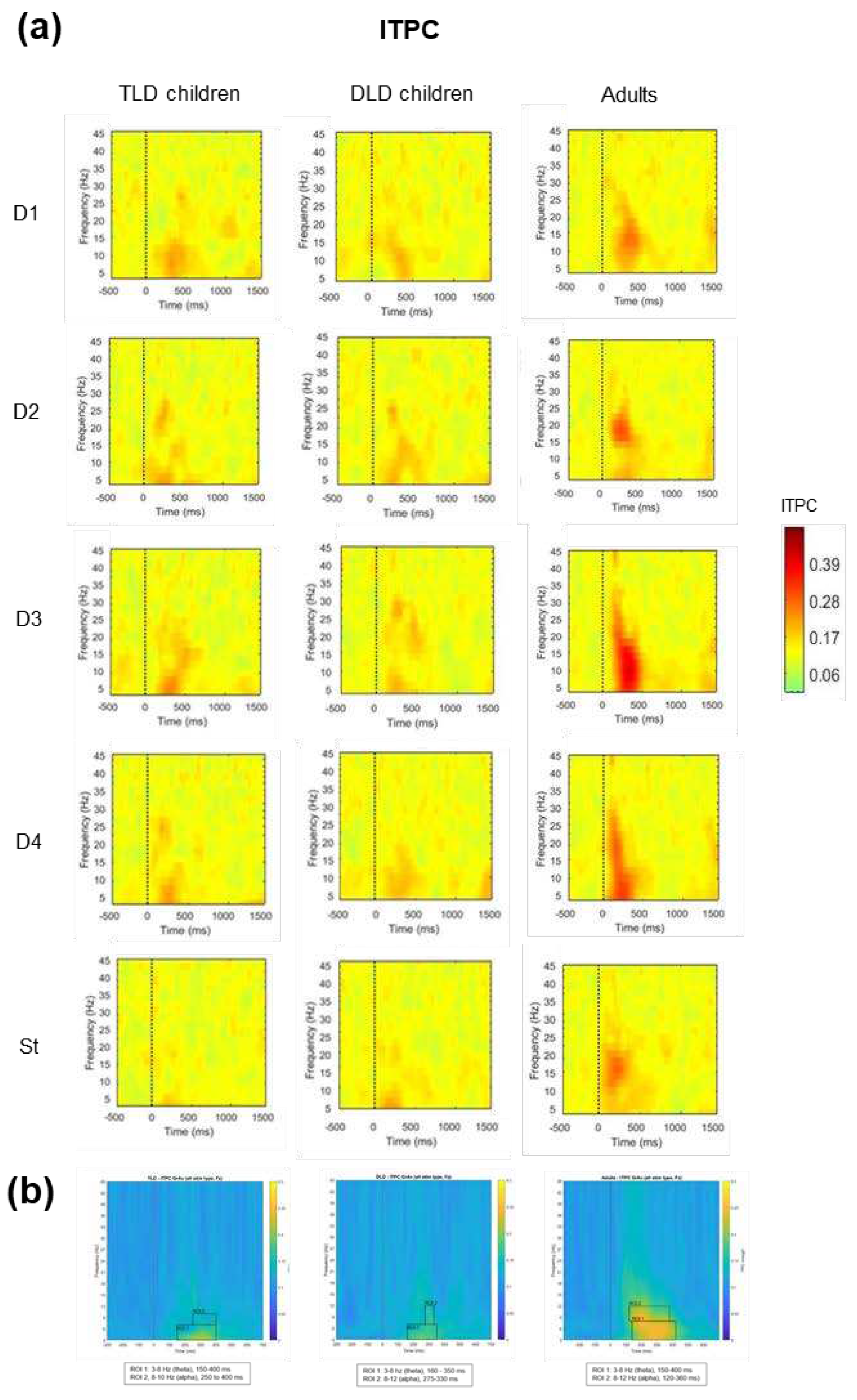
3.2.2. Time-Frequency Analysis of MMRs
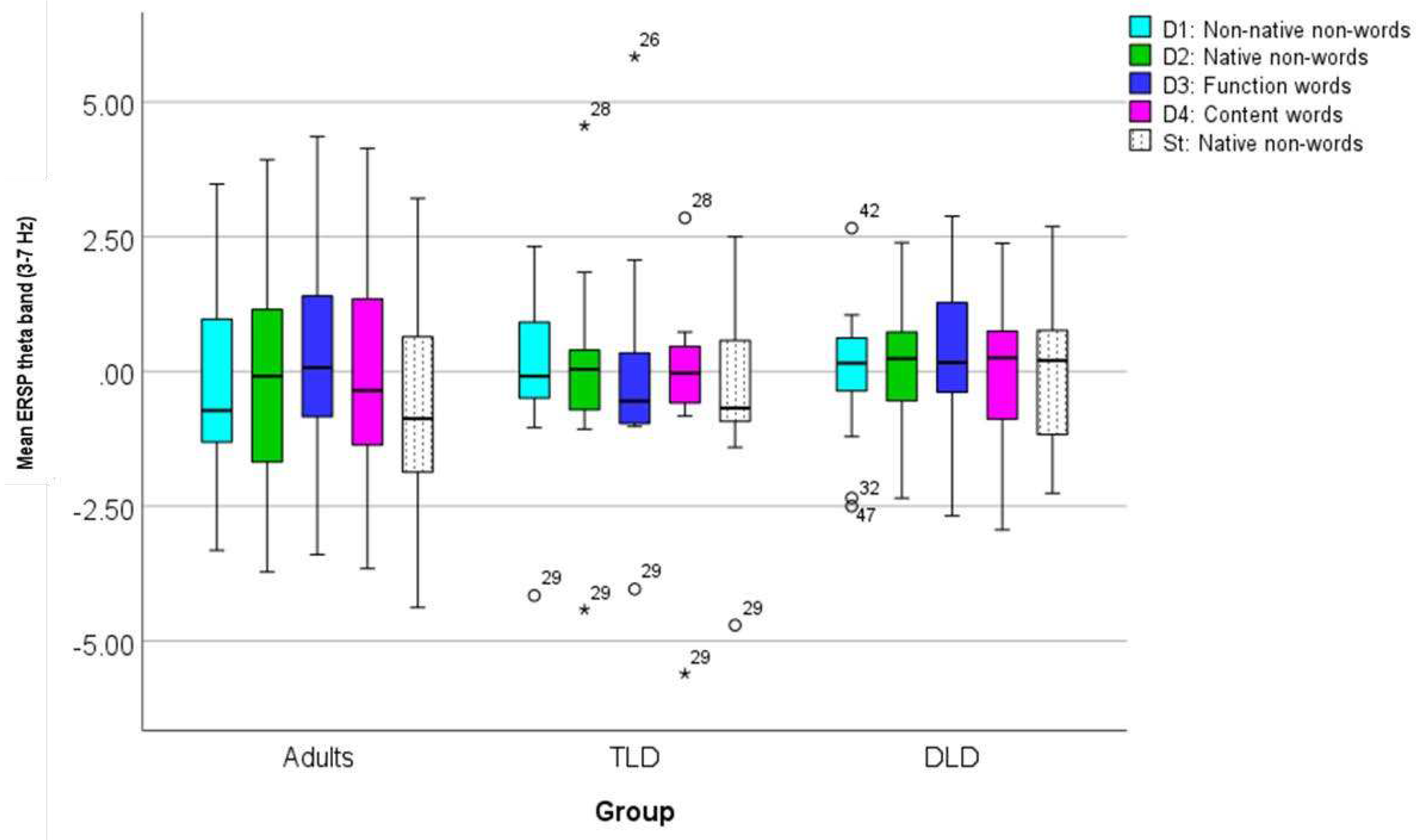
3.2.2. Event-Related Spectral Perturbation (ERSP)
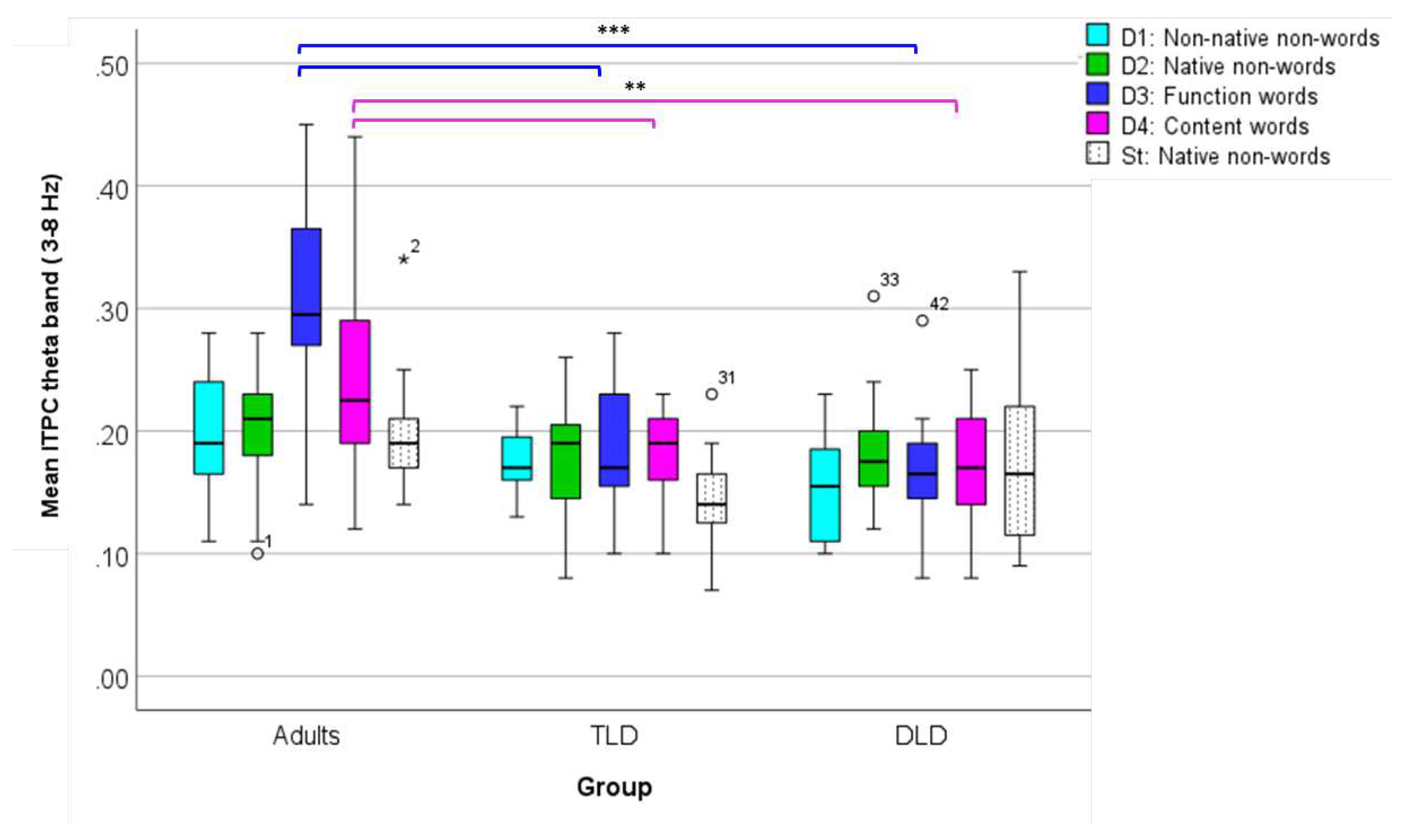
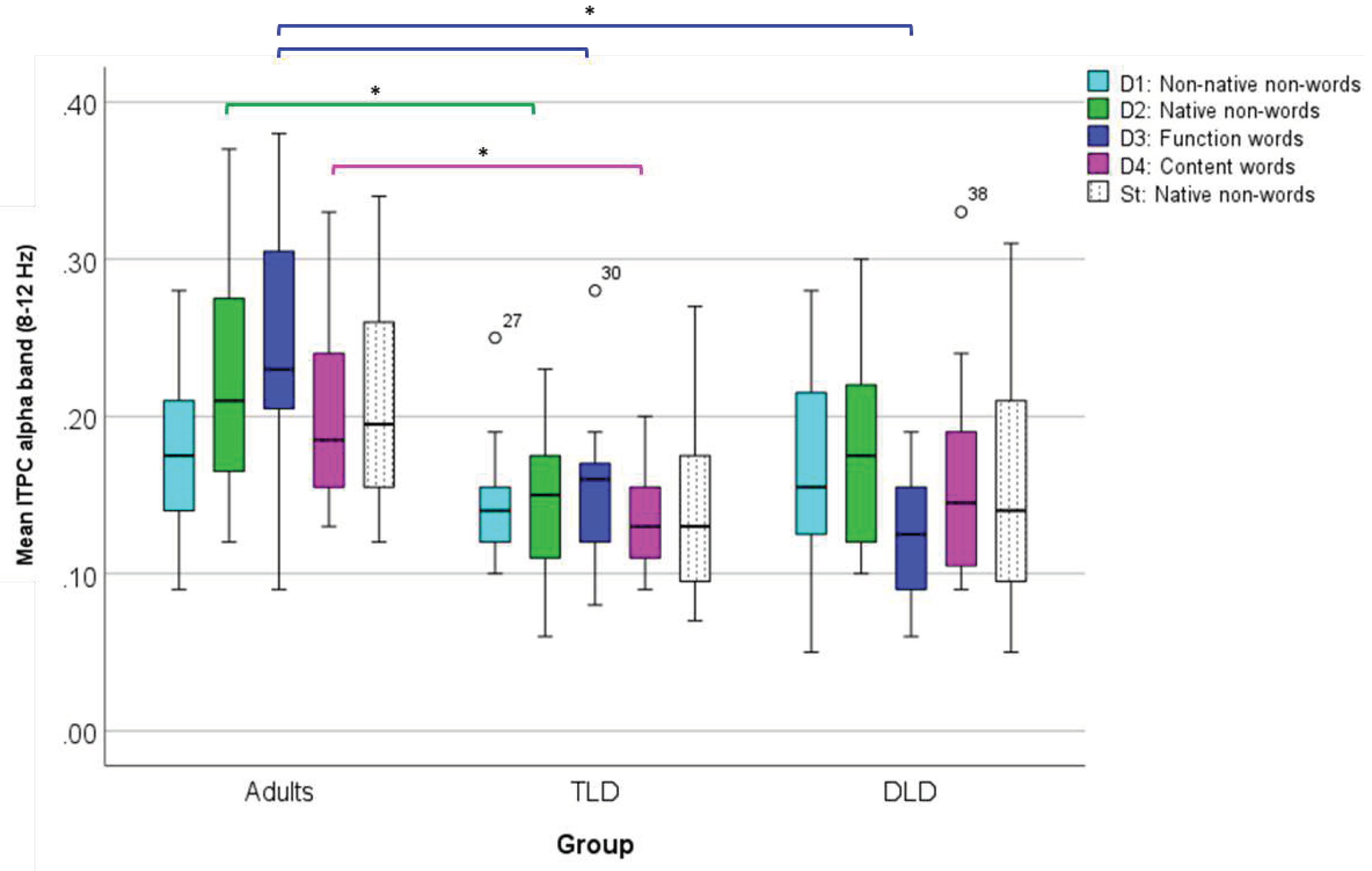
| TLD (n=11) | DLD (n=16) | Adults (n=20) | ||||
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| Non-native non-words | .146 | .043 | .166 | .065 | .175 | .047 |
| Native non-words | .146 | .053 | .176 | .061 | .223 | .075 |
| Function words | .156 | .054 | .127 | .040 | .246 | .082 |
| Content words | .134 | .034 | .159 | .065 | .197 | .052 |
| St (native non-word) | .143 | .065 | .154 | .074 | .205 | .065 |
3.2.4. Correlation between Phonological Awareness and EEG Measures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| TLD | DLD | Adults | |||||||
| Critical t-scores | Test-wise alpha | upper bound FDR | Critical t-scores | Test-wise alpha | Upper bound FDR | Critical t-scores | Test-wise alpha | Upper bound FDR | |
| Non-Nat Non-words |
-3.24 / 3.24 |
0.009 | 0.6 | -3.25 / 3.25 |
0.005 | 0.4 | -2.85 /2.85 | 0.01 | 0.6 |
| Native non-words | -3.07 / 3.07 |
0.012 | 0.7 | -2.78 / 2.78 |
0.014 | 2.0 | -2.80 /2.80 | 0.01 | 0.7 |
| Function Words | -3.19 / 3.19 |
0.010 | 0.6 | -2.81 / 2.81 |
0.013 | 1.1 | -2.69 /2.69 | 0.02 | 0.9 |
| Content Words |
-- | 0.002 | -- | -3.34 / 3.34 |
0.005 | 0.4 | -2.41 /2.41 | 0.03 | 1.4 |
| Words | -3.74 / 3.74 |
0.004 | 0.3 | -2.98 / 2.98 |
0.010 | 0.6 | |||
Appendix B
| Mean Amplitude (100-250 ms, Peak Centred) | ||||||||
| Homogeneity of Varianceᵃ | Normalityᵇ | |||||||
| DW type | Levene st. | df1 | df2 | p | Group | Shap.-Wilk st. | df | p |
| DW1 | 3.7 | 2 | 44 | .033 | Adults | .943 | 20 | .277 |
| TLD | .975 | 11 | .935 | |||||
| DLD | .92 | 16 | .168 | |||||
| DW2 | 0.429 | 2 | 44 | .654 | Adults | .97 | 20 | .761 |
| TLD | .79 | 11 | .007 | |||||
| DLD | .939 | 16 | .336 | |||||
| Words | 4.659 | 2 | 44 | .015 | Adults | .927 | 20 | .133 |
| TLD | .929 | 11 | .398 | |||||
| DLD | .98 | 16 | .966 | |||||
| DW3 | 5.104 | 2 | 44 | .01 | Adults | .922 | 20 | .109 |
| TLD | .865 | 11 | .066 | |||||
| DLD | .946 | 16 | .436 | |||||
| DW4 | 5.046 | 2 | 44 | .011 | Adults | .981 | 20 | .943 |
| TLD | .922 | 11 | .334 | |||||
| DLD | .933 | 16 | .276 | |||||
| Phonological Awareness Test | ||||||||
| TLD 873 8 .162 DLD .909 14 .151 |
||||||||
| Within Subjects Effect: Stimulus Type | ||||||||
| Equality of Covariance Matricesᶜ | Sphericityᵈ | |||||||
| Box's M | F | df1 | df2 | p | Mauchly's W | Approx. Chi^2 | df | p |
| 93.16 | 2.538 | 30 | 3795 | <.001 | 0.181 | 72.46 | 9 | <.001 |
Appendix C
| Mean Amplitude (250-400 ms, Peak Centred) | ||||||||
| Homogeneity of Varianceᵃ | Normalityᵇ | |||||||
| DW type | Levene st. | df1 | df2 | p | Group | Shap.-Wilk st. | df | p |
| DW1 | 4.087 | 2 | 44 | .024 | Adults | .929 | 20 | .151 |
| TLD | .916 | 11 | .288 | |||||
| DLD | .983 | 16 | .981 | |||||
| DW2 | 4.533 | 2 | 44 | .016 | Adults | .979 | 20 | .920 |
| TLD | .910 | 11 | .242 | |||||
| DLD | .878 | 16 | .036 | |||||
| Words | 1.048 | 2 | 44 | .359 | Adults | .857 | 20 | .007 |
| TLD | .767 | 11 | .003 | |||||
| DLD | .959 | 16 | .645 | |||||
| DW3 | 3.070 | 2 | 44 | .056 | Adults | .961 | 20 | .574 |
| TLD | .970 | 11 | .884 | |||||
| DLD | .939 | 16 | .340 | |||||
| DW4 | 4.675 | 2 | 44 | .014 | Adults | .849 | 20 | .005 |
| TLD | .937 | 11 | .489 | |||||
| DLD | .946 | 16 | .433 | |||||
| Within Subjects Effect: Stimulus Type | ||||||||
| Equality of Covariance Matricesᶜ | Sphericityᵈ | |||||||
| Box's M | F | df1 | df2 | p | Mauchly's W | Approx. Chi^2 | df | p |
| 109.75 | 2.99 | 30 | 3795 | <.001 | .240 | 60.53 | 9 | <.001 |
Appendix D
| 100-250 ms | 250-400 ms | |
| All FDR adjusted p-values ≥ | All FDR adjusted p-values ≥ | |
| Non-native non-words | 0.869 | 0.853 |
| Native non-words | 0.275 | 0.492 |
| Function words | 0.558 | 0.404 |
| Content words | 0.725 | 0.618 |
| Words | 0.978 | 0.478 |
Appendix E
| ERSP | |||||||||
| Homogeneity of Varianceᵃ | Normalityᵇ | ||||||||
| Stimulus Type | Levene st. | df1 | df2 | p | Group | Shap.-Wilk st. | df | p | |
| D1 | 2.043 | 2 | 44 | .142 | Adults | .940 | 20 | .235 | |
| TLD | .881 | 11 | .108 | ||||||
| DLD | .919 | 16 | .163 | ||||||
| D2 | 1.657 | 2 | 44 | .202 | Adults | .965 | 20 | .658 | |
| TLD | .894 | 11 | .157 | ||||||
| DLD | .922 | 16 | .180 | ||||||
| D3 | .274 | 2 | 44 | .762 | Adults | .959 | 20 | .519 | |
| TLD | .859 | 11 | .056 | ||||||
| DLD | .955 | 16 | .573 | ||||||
| D4 | 1.033 | 2 | 44 | .364 | Adults | .969 | 20 | .726 | |
| TLD | .788 | 11 | .007 | ||||||
| DLD | .963 | 16 | .711 | ||||||
| St | 1.005 | 2 | 44 | .374 | Adults | .955 | 20 | .441 | |
| TLD | .903 | 11 | .203 | ||||||
| DLD | .960 | 16 | .661 | ||||||
| Within Subjects Effect: Stimulus Type | |||||||||
| Equality of Covariance Matricesᶜ | Sphericityᵈ | ||||||||
| Box's M | F | df1 | df2 | p | Mauchly's W | Approx. Chi^2 | df | p | |
| 69.32 | 1.89 | 30 | 3795 | .002 | .355 | 43.91 | 9 | <.001 | |
Appendix F
| ROI 1 | |||||||||
| Homogeneity of Varianceᵃ | Normalityᵇ | ||||||||
| Stimulus Type | Levene st. | df1 | df2 | p | Group | Shap.-Wilk st | df | p | |
| D1 | 2.806 | 2 | 44 | .071 | Adults | .953 | 20 | .407 | |
| TLD | .967 | 11 | .86 | ||||||
| DLD | .891 | 16 | .059 | ||||||
| D2 | .316 | 2 | 44 | .731 | Adults | .928 | 20 | .141 | |
| TLD | .932 | 11 | .428 | ||||||
| DLD | .879 | 16 | .037 | ||||||
| D3 | 2.198 | 2 | 44 | .123 | Adults | .965 | 20 | .64 | |
| TLD | .928 | 11 | .39 | ||||||
| DLD | .931 | 16 | .25 | ||||||
| D4 | 2.291 | 2 | 44 | .113 | Adults | .944 | 20 | .286 | |
| TLD | .945 | 11 | .583 | ||||||
| DLD | .968 | 16 | .811 | ||||||
| St | 2.746 | 2 | 44 | .075 | Adults | .872 | 20 | .013 | |
| TLD | .983 | 11 | .982 | ||||||
| DLD | .926 | 16 | .211 | ||||||
| ROI2 | |||||||||
| Homogeneity of Varianceᵃ | Normalityᵇ | ||||||||
| Stimulus Type |
Levene st. | df1 | df2 | p | Group | Shap.-Wilk st | df | p | |
| D1 | 1.748 | 2 | 44 | .186 | Adults | .97 | 20 | .761 | |
| TLD | .849 | 11 | .042 | ||||||
| DLD | .981 | 16 | .97 | ||||||
| D2 | .980 | 2 | 44 | .383 | Adults | .941 | 20 | .245 | |
| TLD | .972 | 11 | .903 | ||||||
| DLD | .945 | 16 | .419 | ||||||
| D3 | 4.083 | 2 | 44 | .024 | Adults | .961 | 20 | .555 | |
| TLD | .915 | 11 | .278 | ||||||
| DLD | .956 | 16 | .592 | ||||||
| D4 | 1.916 | 2 | 44 | .159 | Adults | .912 | 20 | .069 | |
| TLD | .933 | 11 | .439 | ||||||
| DLD | .877 | 16 | .035 | ||||||
| St | .453 | 2 | 44 | .639 | Adults | .97 | 20 | .761 | |
| TLD | .849 | 11 | .042 | ||||||
| DLD | .981 | 16 | .97 | ||||||
| Equality of Covariance Matricesᶜ | Sphericityᵈ | ||||||||
| ROI | Box's M | F | df1 | df2 | p | Mauchly's W | Approx. Chi^2 | df | p |
| 1 | 35.75 | .974 | 30 | 3795 | .506 | .779 | 10.57 | 9 | .306 |
| 2 | 36.03 | .982 | 30 | 3795 | .495 | .845 | 7.13 | 9 | .624 |
References
- Tomblin, J. B., Records, N. L., Buckwalter, P., Zhang, X., Smith, E., & O’Brien, M. (1997). Prevalence of specific language impairment in kindergarten children. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 40(6), 1245-1260. [CrossRef]
- Sussman JE. Perception of formant transition cues to place of articulation in children with language impairments. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research. 1993;36:1286–1299. [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R. G., Scheffler, F. L., & Lopez, K. (2013). Speech perception and lexical effects in specific language impairment. Clinical linguistics & phonetics, 27(5), 339–354. [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D. V., Hardiman, M., Uwer, R., & von Suchodoletz, W. (2007). Maturation of the long-latency auditory ERP: step function changes at start and end of adolescence. Developmental science, 10(5), 565–575. [CrossRef]
- Kujala, T. (2007). The role of early auditory discrimination deficits in language disorders. Journal of Psychophysiology, 21(3-4), 239-250. [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J. C., Pech-Georgel, C., George, F., Alario, F. X., & Lorenzi, C. (2005). Deficits in speech perception predict language learning impairment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 102(39), 14110-14115. [CrossRef]
- Friederici, A. D. "The neural basis of language development and its impairment." Neuron 52.6 (2006): 941-952.
- Bishop, D. V. M., Hardiman, M. J., & Barry, J. G. (2012). Auditory deficit as a consequence rather than endophenotype of specific language impairment: electrophysiological evidence. PLoS One, 7(5), e35851. [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.V. M., Carlyon, R. P., Deeks, J. M., & Bishop, S. J. (1999). Auditory temporal processing impairment: Neither necessary nor sufficient for causing language impairment in children. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 42(6), 1295-1310. [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D. V. M., & McArthur, G. M. (2005). Individual differences in auditory processing in specific language impairment: a follow-up study using event-related potentials and behavioural thresholds. Cortex, 41(3), 327-341. [CrossRef]
- Näätänen, R., Kujala, T. & Light, G. (2019). 'The development of MMN', The Mismatch Negativity: A Window to the Brain (Oxford; online edn, Oxford Academic, 23 May 2019). [CrossRef]
- Näätänen, R., Paavilainen, P., Rinne, T., & Alho, K. (2007). The mismatch negativity (MMN) in basic research of central auditory processing: a review. Clinical Neurophysiology, 118(12), 2544-2590. [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D. V. M., Hardiman, M. J., & Barry, J. G. (2010a). Is auditory discrimination mature by middle childhood? A study using time-frequency analysis of mismatch responses from 7 years to adulthood. Developmental Science, 14(2), 402-416. [CrossRef]
- Cheour, M., Korpilahti, P., Martynova, O., & Lang, A. H. (2001). Mismatch negativity and late discriminative negativity in investigating speech perception and learning in children and infants. Audiology and Neurotology, 6(1), 2-11. [CrossRef]
- David, C., Roux, S., Bonnet-Brilhault, F., Ferré, S., & Gomot, M. (2020). Brain responses to change in phonological structures of varying complexity in children and adults. Psychophysiology, 57(9), e13621. [CrossRef]
- Morr, M. L., Shafer, V. L., Kreuzer, J. A., & Kurtzberg, D. (2002). Maturation of mismatch negativity in typically developing infants and preschool children. Ear and Hearing, 23(2), 118–136. [CrossRef]
- Baart, M., & Samuel, A. G. (2015). Early processing of auditory lexical predictions revealed by ERPs. Neuroscience Letters, 585, 98-102. [CrossRef]
- Cutler, A. (2008). The 34th Sir Frederick Bartlett Lecture: The abstract representations in speech processing. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 61(11), 1601-1619. [CrossRef]
- Skeide, M. A., & Friederici, A. D. (2016). The ontogeny of the cortical language network. Nature reviews. Neuroscience, 17(5), 323–332. [CrossRef]
- Kujala, T., & Leminen, M. (2017). Low-level neural auditory discrimination dysfunctions in specific language impairment—A review on mismatch negativity findings. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 28, 65-75. [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D. V. M. (2007). Using mismatch negativity to study central auditory processing in developmental language and literacy impairments: Where are we, and where should we be going? Psychological Bulletin, 133(4), 651–672. [CrossRef]
- Bell, M. A., & Cuevas, K. (2012). Using EEG to study cognitive development: Issues and practices. Journal of Cognition and Development, 13(3), 281-294. [CrossRef]
- Shafer, V. L., Morr, M. L., Kreuzer, J. A., & Kurtzberg, D. (2000). Maturation of mismatch negativity in school-age children. Ear and Hearing, 21(3), 242–251. [CrossRef]
- Makeig, S., Debener, S., Onton, J., & Delorme, A. (2004). Mining event-related brain dynamics. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8(5), 204-210. [CrossRef]
- de Haan, M. (Ed.). (2007). Infant EEG and Event-Related Potentials (1st ed.). Psychology Press. [CrossRef]
- Sussman, E., Kujala, T., Halmetoja, J., Lyytinen, H., Alku, P., & Näätänen, R. (2004). Automatic and controlled processing of acoustic and phonetic contrasts. Hearing Research, 190(1-2), 128-140. [CrossRef]
- Paquette, N., Vannasing, P., Lefrançois, M., Lefebvre, F., Roy, M. S., McKerral, M. ... & Gallagher, A. (2013). Neurophysiological correlates of auditory and language development: a mismatch negativity study. Developmental Neuropsychology, 38(6), 386-401. [CrossRef]
- Maurer, U., Bucher, K., Brem, S., & Brandeis, D. (2003). Development of the automatic mismatch response: from frontal positivity in kindergarten children to the mismatch negativity. Clinical Neurophysiology, 114(5), 808-817. [CrossRef]
- Shafer, V.L., Morr, M.L., Datta, H., Kurtzberg, D., & Schwartz, R.G. (2005). Neurophysiological indexes of speech processing deficits in children with specific language impairment. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17, 1168–1180.
- Cheour, M., Alho, K., Čeponiené, R., Reinikainen, K., Sainio, K., Pohjavuori, M., ... & Näätänen, R. (1998). Maturation of mismatch negativity in infants. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 29(2), 217-226. [CrossRef]
- Cheour, M. (2007). Development of mismatch negativity (MMN) during infancy. In M. de Haan (Ed.), Infant EEG and event-related potentials (pp. 171–198). Psychology Press.
- Cooray, G. K., Garrido, M. I., Brismar, T., & Hyllienmark, L. (2016). The maturation of mismatch negativity networks in normal adolescence. Clinical Neurophysiology, 127(1), 520-529. [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Silva-Pereyra, J., & Kuhl, P. K. (2005). Brain potentials to native and non-native speech contrasts in 7-and 11-month-old American infants. Developmental Science, 8(2), 162-172. [CrossRef]
- Shafer, V. L., Yu, Y. H., & Datta, H. (2010). Maturation of speech discrimination in 4- to 7-yr-old children as indexed by event-related potential mismatch responses. Ear and hearing, 31(6), 735–745. [CrossRef]
- Csépe, V. (1995). On the origin and development of the mismatch negativity. Ear and Hearing, 16(1), 91-104. 16(1): p 91-104, February 1995.
- Kraus, N., McGee, T., Micco, A., Sharma, A., Carrell, T., & Nicol, T. (1993). Mismatch negativity in school-age children to speech stimuli that are just perceptibly different. Electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology, 88(2), 123–130. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y., Tsao, F., & Liu, H. (2016). Developmental changes in brain response to speech perception in late-talking children: A longitudinal MMR study. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 19, 190 - 199. [CrossRef]
- Cheour, M., Leppänen, P. H., & Kraus, N. (2000). Mismatch negativity (MMN) as a tool for investigating auditory discrimination and sensory memory in infants and children. Clinical neurophysiology : official journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology, 111(1), 4–16. [CrossRef]
- Kuuluvainen, S., Alku, P., Makkonen, T., Lipsanen, J., & Kujala, T. (2016). Cortical speech and non-speech discrimination in relation to cognitive measures in preschool children. European Journal of Neuroscience, 43(6), 738-750. [CrossRef]
- Dehaene-Lambertz, G., & Baillet, S. (1998). A phonological representation in the infant brain. Neuroreport, 9(8), 1885-1888. 9(8):p 1885-1888, June 1, 1998.
- Werwach, A., Männel, C., Obrig, H., Friederici, A. D., & Schaadt, G. (2022). Longitudinal trajectories of electrophysiological mismatch responses in infant speech discrimination differ across speech features. Developmental cognitive neuroscience, 56, 101127. [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, T., Bäß, P., Roye, A., Winkler, I., Schröger, E., & Horváth, J. (2021). Word class and word frequency in the MMN looking glass. Brain and Language, 218, 104964. [CrossRef]
- Čeponienė, R., Lepistö, T., Alku, P., Aro, H., & Näätänen, R. (2003). Event-related potential indices of auditory vowel processing in 3-year-old children. Clinical neurophysiology: official journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology, 114(4), 652–661. [CrossRef]
- Strotseva-Feinschmidt, A., Cunitz, K., Friederici, A. D., & Gunter, T. C. (2015). Auditory Discrimination Between Function Words in Children and Adults: A Mismatch Negativity Study. Frontiers in psychology, 6, 1930. [CrossRef]
- Pulvermüller, F., T. Kujala, Y. Shtyrov, J. Simola, H. Tiitinen, P. Alku, K. Alho, S. Martinkauppi, R.J. Ilmoniemi, R. Näätänen, Memory traces for words as revealed by the mismatch negativity, NeuroImage 14 (2001) 607–616.
- Nallet, C. & Gervain, J. (2022) Atypical neural oscillations in response to speech in infants and children with speech and language impairments: a systematic review, Hearing, Balance and Communication, 20:3, 145-154. [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R.G. and Shafer, V.L. (2012). The Neurobiology of Specific Language Impairment. In The Handbook of the Neuropsychology of Language (eds D. Mostofsky and M. Faust). [CrossRef]
- Pihko, E., Kujala, T., Mickos, A., Alku, P., Byring, R., & Korkman, M. (2008). Language impairment is reflected in auditory evoked fields. International journal of psychophysiology, 68(2), 161-169. [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.V. M., Hardiman, M. J., & Barry, J. G. (2010b). Lower-frequency event-related desynchronization: a signature of late mismatch responses to sounds, which is reduced or absent in children with specific language impairment. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(46), 15578-15584. [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, P., & Rivera-Gaxiola, M. (2008). Neural substrates of language acquisition. Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 31, 511-534. [CrossRef]
- Linnavalli, T., Putkinen, V., Huotilainen, M., & Tervaniemi, M. (2017). Phoneme processing skills are reflected in children's MMN responses. Neuropsychologia, 101, 76-84. [CrossRef]
- Norton, E. S., MacNeill, L. A., Harriott, E. M., Allen, N., Krogh-Jespersen, S., Smyser, C. D., ... & Wakschlag, L. (2021). EEG/ERP as a pragmatic method to expand the reach of infant-toddler neuroimaging in HBCD: Promises and challenges. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 51, 100988. [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M., Weber, C., & Friederici, A. D. (2004). Electrophysiological evidence for delayed mismatch response in infants at-risk for specific language impairment. Psychophysiology, 41(5), 772-782. [CrossRef]
- Guttorm, T. K., Leppänen, P. H. T., Hämäläinen, J. A., Eklund, K. M., & Lyytinen, H. J. (2010). Newborn Event-Related Potentials Predict Poorer Pre-Reading Skills in Children at Risk for Dyslexia. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 43(5), 391–401. [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D. V. M., & Hardiman, M. J. (2010). Measurement of mismatch negativity in individuals: a study using single-trial analysis. Psychophysiology, 47(4), 697-705. [CrossRef]
- Maguire, M. J., & Abel, A. D. (2013). What changes in neural oscillations can reveal about developmental cognitive neuroscience: Language development as a case in point. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 6, 125-136. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M. X. (2014). Analyzing neural time series data: theory and practice. MIT press.
- Fuentemilla, L. L., Marco-Pallarés, J., Münte, T. F., & Grau, C. (2008). Theta EEG oscillatory activity and auditory change detection. Brain Research, 1220, 93-101. [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, F. J., Wu, Z. A., Ho, L. T., & Lin, Y. Y. (2009). Theta oscillation during auditory change detection: an MEG study. Biological Psychology, 81(1), 58-66. [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, F. J., Cheng, C. H., Liao, K. K., & Lin, Y. Y. (2010). Cortico-cortical phase synchrony in auditory mismatch processing. Biological Psychology, 84(2), 336-345. [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.V. M., Anderson, M., Reid, C., & Fox, A. M. (2011). Auditory development between 7 and 11 years: an event-related potential (ERP) study. PLoS One, 6(5), e18993. [CrossRef]
- Müller, V., Gruber, W., Klimesch, W., & Lindenberger, U. (2009). Lifespan differences in cortical dynamics of auditory perception. Developmental Science, 12(6), 839-853. [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, C., Picton, T. W., & Paus, T. (2009). Age-related changes in transient and oscillatory brain responses to auditory stimulation during early adolescence. Developmental Science, 12(2), 220-235. [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, P. K. (2010). Brain mechanisms in early language acquisition. Neuron, 67(5), 713-727. [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Mantilla, S., Hämäläinen, J. A., Musacchia, G., & Benasich, A. A. (2013). Enhancement of gamma oscillations indicates preferential processing of native over foreign phonemic contrasts in infants. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(48), 18746-18754. [CrossRef]
- Giraud, A. L., & Poeppel, D. (2012). Cortical oscillations and speech processing: emerging computational principles and operations. Nature Neuroscience, 15(4), 511-517. [CrossRef]
- Heim, S., Friedman, J. T., Keil, A., & Benasich, A. A. (2011). Reduced sensory oscillatory activity during rapid auditory processing as a correlate of language-learning impairment. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 24(5), 538-555. [CrossRef]
- Heim, S., Keil, A., Choudhury, N., Thomas Friedman, J., & Benasich, A. A. (2013). Early gamma oscillations during rapid auditory processing in children with a language-learning impairment: changes in neural mass activity after training. Neuropsychologia, 51(5), 990–1001. [CrossRef]
- Lovio, R., Pakarinen, S., Huotilainen, M., Alku, P., Silvennoinen, S., Näätänen, R., & Kujala, T. (2009). Auditory discrimination profiles of speech sound changes in 6-year-old children as determined with the multi-feature MMN paradigm. Clinical Neurophysiology, 120(5), 916-921. [CrossRef]
- Näätänen, R., Pakarinen, S., Rinne, T., & Takegata, R. (2004). The Mismatch Negativity (MMN): Towards the optimal paradigm. Clinical Neurophysiology, 115, 140–144.
- Wechsler, D. (2003). The Wechsler intelligence scale for children—fourth edition. London: Pearson.
- Wechsler, D. (2011). Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence–Second Edition. Bloomington, MN: Pearson.
- Varela Moraga, V. M., & Barbieri, Z. D. (2015). PECFO. Prueba de evaluación de conciencia fonológica: manual anual y set de láminas.
- Guardia Gutiérrez, P. A. (2010). The effect of linguistic, phonetic and lexical factors on phonological skills and reading acquisition in Spanish: A longitudinal study (Doctoral dissertation, University of Cambridge). Available on https://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.608697.
- Alonso, M. A., Fernandez, A., & Díez, E. (2015). Subjective age-of-acquisition norms for 7,039 Spanish words. Behavior research methods, 47(1), 268–274.doi.org/10.3758/s13428-014-0454-.
- Corral, S., Ferrero, M. & Goikoetxea, E. LEXIN: A lexical database from Spanish kindergarten and first-grade readers. Behavior Research Methods 41, 1009–1017 (2009). [CrossRef]
- Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134(1):9–21. [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Calderon, J., & Luck, S. J. (2014). ERPLAB: an open-source toolbox for the analysis of event-related potentials. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 213. [CrossRef]
- Luck, S. J. (2014). An introduction to the event-related potential technique. MIT press.
- Groppe, D.M., Urbach, T.P. and Kutas, M. (2011), Mass univariate analysis of event-related brain potentials/fields I: A critical tutorial review. Psychophysiology, 48: 1711-1725. [CrossRef]
- Oostenveld, R., Fries, P., Maris, E. & Schoffelen, JM. FieldTrip: Open Source Software for Advanced Analysis of MEG, EEG, and Invasive Electrophysiological Data. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2011; 2011:156869. [CrossRef]
- Gansonre, C., Højlund, A., Leminen, A., Bailey, C., & Shtyrov, Y. (2018). Task-free auditory EEG paradigm for probing multiple levels of speech processing in the brain. Psychophysiology, 55(11), e13216. [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289-300. [CrossRef]
- Glass, E., Sachse, S., & von Suchodoletz, W. (2008). Development of auditory sensory memory from 2 to 6 years: an MMN study. Journal of Neural Transmission, 115, 1221-1229. [CrossRef]
- Trainor, J. L., Samuel, S. S., Desjardins, N. R., & Sonnadara, R. R. (2001). Measuring temporal resolution in infants using mismatch negativity. NeuroReport, 12(11), 2443–8. [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Mantilla, S., Roesler, C. P., Realpe-Bonilla, T., & Benasich, A. A. (2022). Modulation of Theta Phase Synchrony during Syllable Processing as a Function of Interactive Acoustic Experience in Infancy. Cerebral Cortex (New York, N.Y.: 1991), 32(5), 919–932. [CrossRef]
- Strauß, A., Wöstmann, M., & Obleser, J. (2014). Cortical alpha oscillations as a tool for auditory selective inhibition. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 350. [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.V. M., Snowling, M. J., Thompson, P. A., Greenhalgh, T., & Catalise Consortium. (2016). CATALISE: A multinational and multidisciplinary Delphi consensus study. Identifying language impairments in children. PLOS One, 11(7), e0158753.
- Bishop, D.V. M., Snowling, M. J., Thompson, P. A., Greenhalgh, T., Catalise-2 Consortium, 9Adams, C., ... & House, A. (2017). Phase 2 of CATALISE: A multinational and multidisciplinary Delphi consensus study of problems with language development: Terminology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 58(10), 1068-1080.
- Lee, C. Y., Yen, H. L., Yeh, P. W., Lin, W. H., Cheng, Y. Y., Tzeng, Y. L., & Wu, H. C. (2012). Mismatch responses to lexical tone, initial consonant, and vowel in Mandarin-speaking preschoolers. Neuropsychologia, 50(14), 3228-3239. [CrossRef]
- François, C, Rodriguez-Fornells, A, Teixidó, M, Agut, T, Bosch, L. Attenuated brain responses to speech sounds in moderate preterm infants at term age. Dev Sci. 2021; 24:e12990. [CrossRef]
- van Diepen, R. M., & Mazaheri, A. (2018). The caveats of observing inter-trial phase-coherence in cognitive neuroscience. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 2990. doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20423-z.
- Volpert-Esmond, H. I., Page-Gould, E., & Bartholow, B. D. (2021). Using multilevel models for the analysis of event-related potentials. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 162, 145-156. [CrossRef]
- Petit, S., Badcock, N. A., Grootswagers, T., & Woolgar, A. (2020). Unconstrained multivariate EEG decoding can help detect lexical-semantic processing in individual children. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 10849. [CrossRef]
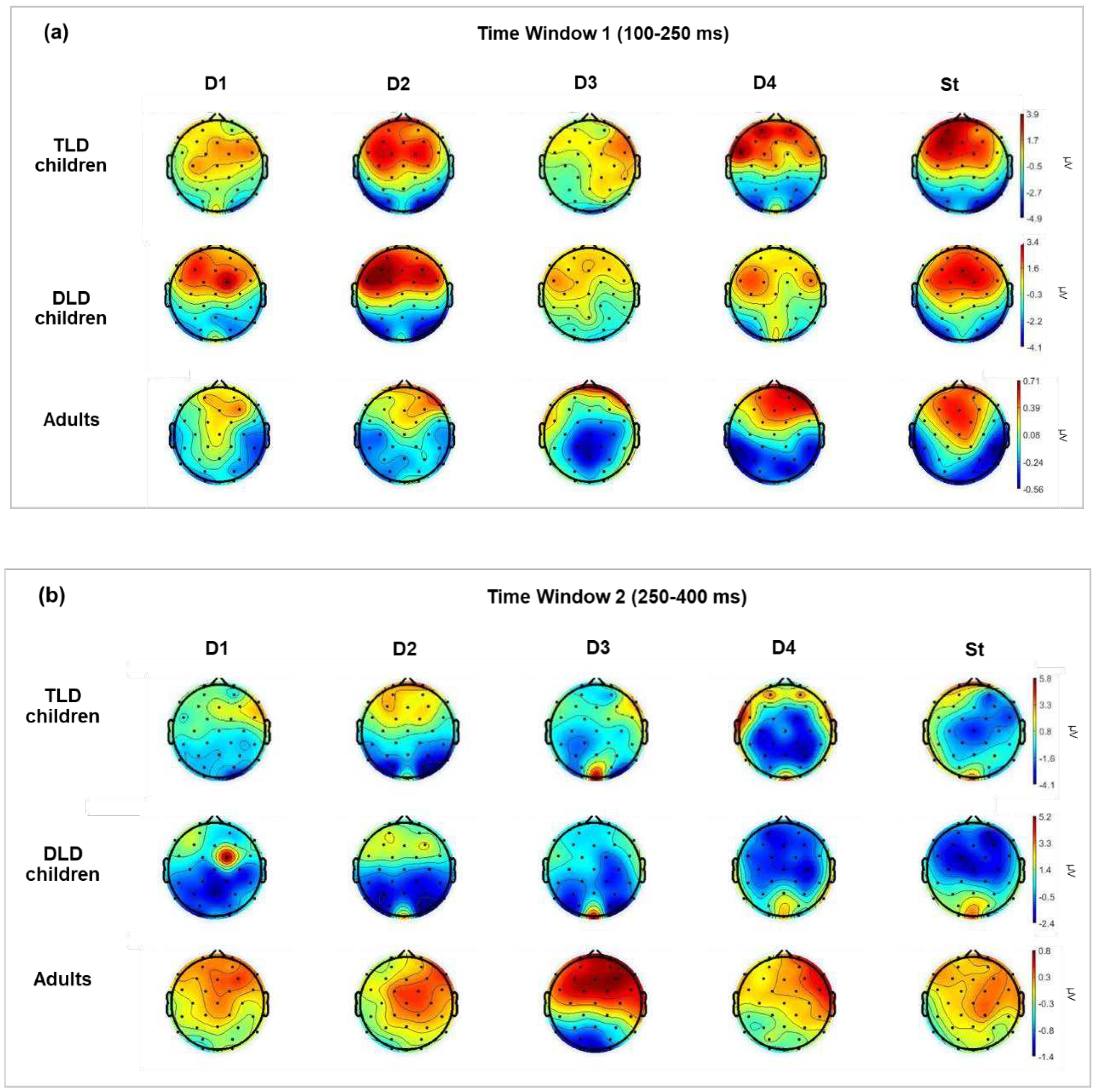
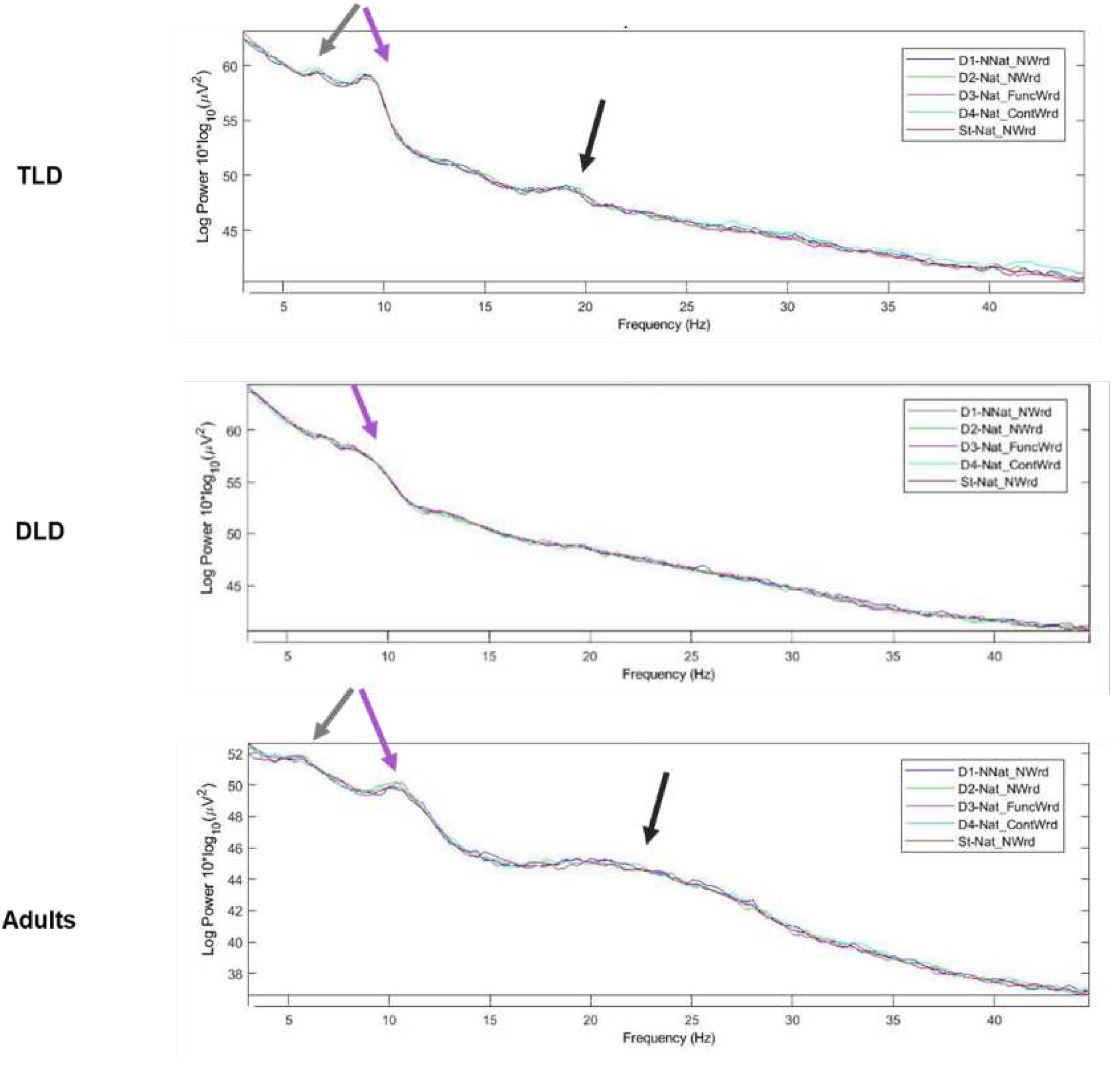
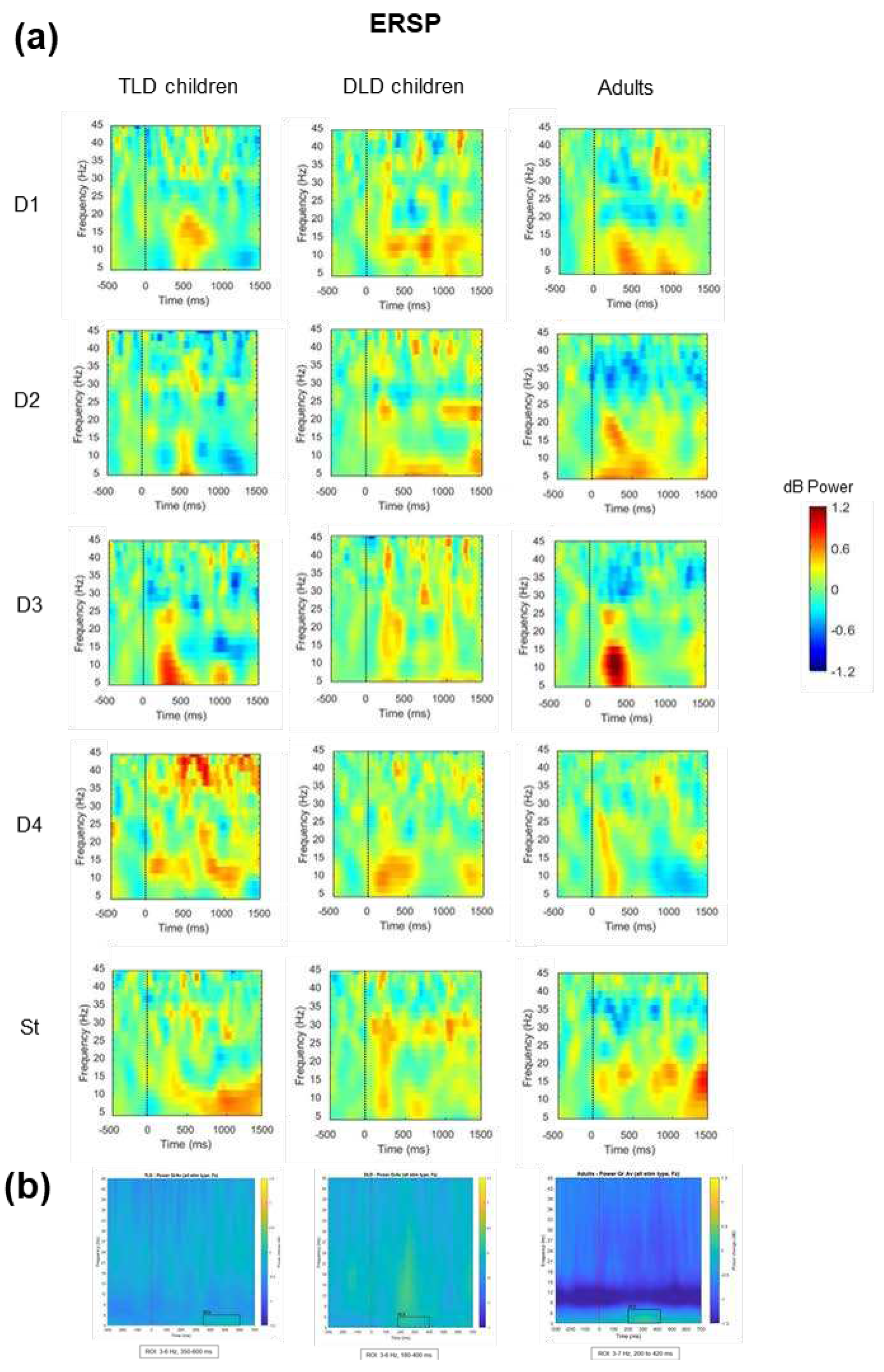
| Measure | TLD (n=11) | DLD (n=16) | Adults (n=20) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | min-max | M | SD | min-max | M | SD | min-max | |
| Age (years.months) |
5.2 | 0.23 | 4.10-5.6 | 5.2 | 0.33 | 4.9-5.7 | 34.2 | 4.8 | 24.9-44.11 |
| PTA left ear (dB HL) |
20.9 | 1.69 | 20-25 | 20.6 | .91 | 20-22.5 | 6.9 | 3.6 | 0-13 |
| PTA right ear (dB HL) |
21.3 | 1.58 | 20-25 | 20.6 | 1.12 | 20-23.8 | 6.2 | 3.7 | 0-13 |
| Block Design (Z score) |
18.1 | 1.58 | 15-19 | 15.7 | 2.98 | 10-19 | 60.7 | 7.8 | 44 - 79 |
| Type | Class | Initial Consonant |
Vowel | Final Consonant | Age of Acquisition a | Oral Frequencyb |
| St | non-word | /f/ Native, labiodental, unvoiced fricative |
/u/ | /s/ | -- | -- |
| D1 | non-word | /ʃ/ Non-Native, postalveolar, unvoiced fricative |
/u/ | /s/ | -- | -- |
| D2 | non-word | /x/ Native, velar, unvoiced fricative |
/u/ | /s/ | -- | -- |
| D3 | function word (determiner) | /t/ Native, dental, unvoiced, alveolar |
/u/ | /s/ | 4.24 ª | 2.63 ᵇ |
| D4 | content word (noun) |
/l/ Native, alveolar, voiced, lateral |
/u/ | /s/ | 3.18 ª |
2.53 ᵇ |
| Group | TLD | DLD | Adults | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DW Type | Significant responses (ms) | Duration (ms) | Polarity | Significant responses (ms) | Duration (ms) | Polarity | Significant responses (ms) | Duration (ms) | Polarity |
| Non-native non-word |
-- -- 294-382 |
-- -- 88 |
-- -- Pos. |
-- -- 278-334 |
-- -- 56 |
-- -- Pos. |
182-198 278-294 350-390 |
24 16 40 |
Neg. Neg. Pos. |
| Native non-word |
102-134 -- 190-198 286-342 |
32 -- 8 56 |
Neg. -- Pos. Pos |
-- -- 182- 486 -- |
-- -- 164 -- |
-- -- Pos. -- |
102-118 158-182 222-246 -- |
16 24 24 -- |
Pos. Neg. Pos. -- |
| Function word | 102-182 -- -- -- |
80 -- -- -- |
Neg. -- -- -- |
102-182 230-238 294-374 -- |
80 8 80 -- |
Neg. Pos. Pos. -- |
-- 190-230 278-334 414-430 |
-- 40 56 16 |
-- Neg. Pos. Neg. |
| Content word | 102-110 -- -- -- |
8 -- -- -- |
Neg. -- -- -- |
102-150 -- -- -- |
48 -- -- -- |
Neg. -- -- -- |
102-110 126-174 214-278 326-374 |
8 48 64 48 |
Pos. Neg. Pos. Neg. |
| Words (function + content) |
102-142 -- -- |
40 -- -- |
Neg. -- -- |
102-174 310-318 -- |
72 8 -- |
Neg. Pos. -- |
118-150 -- 366-446 |
32 -- 80 |
Neg -- Neg |
| TW1 | ||||||
| TLD | DLD | Adults | ||||
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| Non-native non-words | 184.6 | 50.71 | 197.1 | 37.9 | 178.5 | 29.8 |
| Native non-words | 136.6 | 38.5 | 127.9 | 22.2 | 167.4 | 22.5 |
| Function words | 145.1 | 23.2 | 160.1 | 28.5 | 202.5 | 23.2 |
| Content words | 137.1 | 38.9 | 161.3 | 51.0 | 157.0 | 21.3 |
| Words | 131.8 | 21.7 | 160.0 | 38.0 | 154.4 | 35.7 |
| TW2 | ||||||
| TLD | DLD | Adults | ||||
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| Non-native non-words | 340.9 | 35.6 | 316.9 | 28.6 | 323.3 | 62.4 |
| Native non-words | 310.0 | 21.7 | 314.0 | 28.5 | 335.4 | 64.2 |
| Function words | 337.3 | 32.7 | 329.4 | 32.0 | 364.9 | 65.1 |
| Content words | 321.6 | 42.3 | 338.6 | 42.0 | 371.2 | 41.4 |
| Words | 326.6 | 32.9 | 330.4 | 34.2 | 400.1 | 24.1 |
| TW1 | ||||||
| TLD | DLD | Adults | ||||
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| Non-native non-words | -2.35 | 2.73 | -1.57 | 2.16 | -0.76 | 1.13 |
| Native non-words | -2.45 | 2.55 | -1.19 | 2.02 | -1.59 | 1.51 |
| Function words | -3.97 | 3.22 | -3.16 | 2.55 | -2.08 | 0.92 |
| Content words | -2.72 | 2.62 | -2.60 | 1.68 | -1.58 | 1.11 |
| Words | -3.06 | 2.26 | -2.63 | 1.78 | -0.95 | 0.92 |
| TW2 | ||||||
| TLD | DLD | Adults | ||||
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| Non-native non-words | -0.81 | 2.80 | -0.29 | 2.77 | -1.45 | 1.48 |
| Native non-words | 0.85 | 3.56 | 1.78 | 3.08 | - 0.81 | 1.01 |
| Function words | -1.66 | 3.55 | -0.03 | 2.17 | -1.85 | 1.88 |
| Content words | -2.27 | 3.07 | -1.67 | 2.30 | -1.56 | 1.55 |
| Words | -1.58 | 2.50 | -0.43 | 1.67 | -1.72 | 1.68 |
| TW1 | F | p | η2 |
| Non-native non-words | 2.441 | .099 | .100 |
| Native non-words | 1.368 | .265 | .059 |
| Function words | 2.277 | .115 | .094 |
| Content words | 2.139 | .130 | .089 |
| Words | 7.855 | .001 (*) | .263 |
| TW2 | F | p | η2 |
| Non-native non-words | 1.141 | .329 | .049 |
| Native non-words | 4.701 | .014 (*) | .176 |
| Function words | 2.727 | .076 | .110 |
| Content words | .382 | .685 | .017 |
| Words | 2.275 | .115 | .094 |
| TLD | DLD | Adults | ||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Non-native non-words | -.109 | 1.65 | .001 | 1.25 | -.125 | 1.88 |
| Native non-words | .039 | 2.15 | .008 | 1.27 | -.072 | 2.16 |
| Function words | .032 | 2.43 | .257 | 1.63 | .267 | 2.01 |
| Content words | -.326 | 2.03 | -.021 | 1.39 | -.063 | 2.07 |
| St (native non-word) | -.428 | 1.81 | -.041 | 1.34 | -.471 | 1.97 |
| TLD | DLD | Adults | ||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Non-native non-words | .174 | .027 | .154 | .047 | .196 | .049 |
| Native non-words | .175 | .052 | .180 | .046 | .200 | .050 |
| Function words | .186 | .062 | .167 | .046 | .308 | .082 |
| Content words | .181 | .040 | .170 | .051 | .241 | .076 |
| St (native non-word) | .147 | .043 | .172 | .067 | .196 | .046 |
| ERP measures | ||||||
| Non-native non-words | Native non-words |
Function words | Content words | Words | ||
| Mean amplitude TW1 | ||||||
| PECFO | r | - .299 | - .185 | - .229 | - .034 | - .167 |
| p | .176 | .409 | .305 | .879 | .458 | |
| Mean amplitude TW2 | ||||||
| r | -.194 | - .043 | - .305 | - .169 | - .353 | |
| p | .388 | .851 | .167 | .451 | .107 | |
| Time-frequency measures | ||||||
| Non-native non-words | Native non-words |
Function words | Content words | Standard (native non-word) |
||
| PECFO | ERSP theta | |||||
| r | .082 | - .321 | - .271 | - .283 | - .319 | |
| p | .716 | .145 | .223 | .201 | .147 | |
| ITPC theta (ROI 1) | ||||||
| r | .206 | - .183 | - .112 | .32 | - .467 | |
| p | .358 | .415 | .619 | .146 | .028 | |
| ITPC alpha (ROI 2) | ||||||
| r | .039 | - .368 | .206 | - .052 | - .31 | |
| p | .863 | .092 | .357 | .818 | .16 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





