1. Introduction
Most patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) can be successfully treated with conventional-dose chemotherapy and radiotherapy (RT). Although chemotherapy has a high response rate, 30% of cHL patients will relapse [
1] due to drug resistance, that can be either intrinsic, acquired during drug treatment [
2,
3,
4], promoted by the interactions with the tumor microenvironment (TME) [
5].
Drug-resistant cell lines are used as a tool to find the mechanisms adopted by cancer cells to counteract anticancer therapies, to test novel or alternative treatment strategies, to discover new markers of drug resistance [
6,
7].
The first-line therapies for cHL patients are the multidrug regimen ABVD (adriamycin, bleomycin, vinblastine, dacarbazine) or the BEACOPP (bleomycin, etoposide, adriamycin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, and prednisone) [
1]. Both regimens include doxorubicin (adriamycin), one of the most effective anticancer agents, even though its activity can be reduced by drug resistance and its positive effects compromised by cardiotoxicity [
8]. Therefore, to plan a successful and less toxic use of doxorubicin, it would be worth to investigate the characteristics of doxorubicin-resistant cells. By doing this we could: find prognostic biomarkers to identify doxorubicin-resistant patients; predict therapy responses; avoid the use of ineffective chemotherapy agents; find new/alternative drugs or drug combinations to overcome doxorubicin resistance.
Our aim was to find common markers and mechanisms to predict and overcome doxorubicin resistance in cHL cells. To achieve our goal, we evaluated phenotypic and functional features of two cHL cell lines with acquired resistance to doxorubicin, KM-H2dx and HDLM-2dx [
9], generated in our lab from KM-H2 and HDLM-2 cHL cell lines, respectively.
We analyzed and compared parental cell lines (Hodgkin Reed Sternberg, HRS) with their doxorubicin-resistant counterparts (called HRSdx): survival and cancer stem cells factors; molecules involved in the cross-talk with the TME; immunosuppressive molecules; cytokines/chemokines; immunosuppressive tumor-education of monocytes; cross-resistance to anticancer drugs, including the liposomal formulation of doxorubicin caelyx and γ-radiation; expression of drug transporters; doxorubicin intracellular distribution; DNA damage and resistance to oxidative stress; role of autophagy and extracellular vesicles.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and inhibitors
Doxorubicin (Hikma), PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin caelyx (Jansen Cilag), bleomycin (Sanofi), cisplatin (Accord), dacarbazine (Medac), trabectedin (PharmaMar), bendamustin (Hikma), gemcitabine (Actavis), vinblastine (Velbe) (EG) brentuximab vedotin (BV) (Adcetris, Takeda) were surplus drugs from the clinical pharmacy of CRO Aviano. Prof. Kazuo provided Dehydroxy-methylepoxyquinomicin (DHMEQ) [
10]. Monometil auristatine E (MMAE) and cloroquine were from Sigma-Aldrich, GW4869 from SelleckChem. Antibodies used in flow cytometry and western blot are given in Supplemental
Tables S1 and S2, respectively. Other reagents are described within individual protocols.
2.2. Cell culture and conditioned media
cHL-derived cell lines KM-H2, HDLM-2, and L-428 were from DSMZ (Braunschweig, Germany), human monocytic THP-1 cells from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). KM-H2 cells (CD2/B-like) were established from the pleural effusion of a 37-years old man with mixed cellularity progressing to lymphocyte depletion (stage IV at relapse) [
11]. HDLM-2 cells (T-like), established from pleural effusion of 74 years old man with nodular sclerosis, stage IV in 1982 [
11], are intrinsic resistant to BV [
12,
13]. KM-H2 and HDLM-2 cells were here collectively called “HRS cells” and doxorubicin-resistant cell lines, that we called KM-H2dx and HDLM-2dx, were collectively referred to as “HRSdx cells”. HRSdx cells were generated by continuous exposure of HDLM-2 and KM-H2 cells to increasing concentrations of doxorubicin (10 nM to 100 nM) during sequential passages, for about 12 months. Cell lines were authenticated in our laboratory using PowerPlex 16 HS System (Promega) and GeneMapper ID version 3.2.1 to identify DNA short tandem repeats. They were routinely tested for mycoplasm with negative results. HRS, HRSdx, and THP-1-monocytes were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10 % fetal bovine serum (Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific) (complete medium). To maintain doxorubicin resistance, HRSdx were continuously exposed to doxorubicin: KM-H2dx cells were maintained in 20 ng/mL doxorubicin and HDLM-2dx in 30 ng/mL. HRSdx cells maintained the resistance to doxorubicin for at least two weeks in the absence of the drug.
To obtain the conditioned medium (CM), cells were seeded at 2.0 × 105 cells/mL in complete medium. After 72 h cells were counted and CM was collected to evaluate cytokine levels and used to tumor “educate” monocytes. Cytokine release in CM was quantified using ELISA kits for CCL5, FGF-2, IL-6, IL-13, M-CSF, CCL17/TARC (all from Immunological Sciences, Rome, Italy), TGF-β1 (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific), prostaglandin E2 (Human PGE2) (FineTest), and L-lactate (Cell Biolabs, inc).
2.3. Cellular assays
To determine treatment cytotoxicity and to perform drug combination studies, tumor cells (2.0 × 10
5 cells/mL) were seeded in 24-well plates in complete medium and treated with increasing concentrations of drugs in triplicate for 72 h. Viable cells were counted using the trypan blue dye exclusion assay. Half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC
50) were calculated using CalcuSyn software, v2.1 (Biosoft, Ferguson, MO, USA) [
14]. Resistance factor (RF) was calculated as the ratio of the IC
50 of resistant cell line (KM-H2dx and HDLM-2dx) to that of parental cell line (KM-H2 and HDLM-2). Doubling time (DT) (in days) was calculated using the following formula = h × ln(2)/ln(c2/c1), where c is the number of cells at each time of collection and ln is a neperian logarithm (Roth V, 2006
http://www.doubling-time.com/compute.php) [
15]. To test basal clonogenic growth, tumor cells were suspended at a density of 5.0 x 10
3 cells/mL in RPMI-1640 medium, 15 % FBS, 0.8 % methylcellulose and seeded in 100 µL aliquots (8 replicates) in 96-well flat-bottomed microplates. After 14 days of incubation, plates were observed under phase-contrast microscopy and aggregates with ≥40 cells were scored as colonies [
9].
To compare the effects of conditioned medium from tumor cells on monocyte immunosuppressive differentiation, THP-1-monocytes [
16] (1.0 × 10
5 cells/mL) were cultured in complete medium (RPMI 10% FCS) supplemented with 20 % CM from HRS cells and from HRSdx cells for 6 days (THP-1-monocytes become tumor-educated monocytes, E-monocytes) (CM addition every two days, 3 additions). Flow cytometry was used to assay CD206, PDL-1, and IDO expression in THP-1-monocytes.
2.4. Drug combination studies with chloroquine and GW4869
To evaluate the effects of authophagy and extracellular vesicles (EVs) on doxorubicin activity, tumor cells were cultured with not toxic concentrations of chloroquine (CQ) (inhibitor of authophagy) and of GW4869 (inhibitor of EVs release). To find the not toxic concentrations, tumor cells were cultured with increasing concentrations of CQ (0-10 µM) or GW4869 (0-10 µM) (Supplemental
Figure S1). Then HRS and HRSdx cells (2.0 × 10
5 cells/mL) were cultured with a not toxic concentration of CQ (2.5 µM) or GW4869 (2 µM) alone, or in combination, with different concentrations of doxorubicin. After 72 h viable cells were evaluated with trypan blue dye exclusion assay.
2.5. Doxorubicin accumulation
Doxorubicin accumulation and distribution were evaluated by confocal microscopy and flow cytometry, thanks to its red fluorescence properties. For confocal microscopy, cells (2.0 × 105 cells/mL) were plated on poly-lysine 35 mm coated wells and treated with 1 µg/mL doxorubicin. Doxorubicin distribution was monitored using confocal microscope in time-lapse xyzt acquisition mode (Leica DM IRE2) for 2 h keeping cells at 37°C and 5% CO2. For flow cytometry assay cells (2.0 × 105 cells/mL) were incubated for 2 h with different concentrations of doxorubicin (0-200 ng/mL). Then, red fluorescence intensity was evaluated on a BD FACSCanto II flow cytometer.
2.6. Flow cytometry
HRS cells were stained with a panel of antibodies (Supplemental
Table S1). To evaluate viability, cells were stained for 15 minutes with FITC Annexin-V (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and 7AAD (BD Pharmingen). For IRF4, DDR1, B-cell lymphoma/leukemia-2 (Bcl-2), and Bcl-2 associated x protein (Bax) evaluation cells were fixed and permeabilized using FIX & PERM Cell Fixation & Cell Permeabilization Kit (Life Technologies). To evaluate mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mit-ROS) generation, cells were stained with 5 μM MitoSOX Red Mitochondrial Superoxide Indicator (Thermo Fisher Scientific) in working solution for 30 min at 37 °C. To detect cytoplasmic ROS (cyt-ROS), the CM-H
2DCFDA (Thermo Fisher) dye has been used. The enzymatic activity of ALDH-1 was measured with ALDEFLUOR™ Kit for ALDH Assays (Stem Cell Technologies, Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA), as previously described [
17]. Results were detected by flow cytometry on a BD FACSCanto II flow cytometer. Data were analyzed using BD FACSDiva v.8.0.1 software (BD Biosciences) unless otherwise indicated.
2.7. Gamma-radiation treatment and cell cycle assay
Cells (2.0 × 105 cells/mL) were seeded in 24-well and irradiated with photon beams of 6 MV energy delivered by radiotherapy linear accelerator (3-6-12 Gy). Clonogenic growth assay was performed immediately after irradiation. Cell cycle analysis was performed after 24 h from irradiation. For cell cycle analysis cells were fixed in cold 70 % ethanol for 15 min, and stained with propidium iodide (PI) solution (50 µg/mL PI, 0.1 % NP-40, 100 µg/mL PureLink RNase A, 0.1 % sodium citrate) for 1 h. The distribution of cells in different cell cycle phases was quantified using ModFit LT 4.0 software (Verity Software House, Topsham, ME, USA). Cell viability was evaluated after 72 h of irradiation with Annexin-V/7AAD staining.
2.8. Real time-PCR
Total RNA was isolated from cells using TriZol reagent (Thermo Fischer) following the manufacturer’s instructions. One µg of total RNA was retro-transcribed using random hexamers and the AMV reverse transcriptase (Promega). One-tenth of the obtained cDNAs was amplified using primers for:
- -
human MDR1 (forward 5′-TAATGCCGAACACATTGGAA-3′ and reverse 5′-TCTTCACCTCCAGGCTCAGT-3′),
- -
human MRP1 (forward 5′-TGCAGAAGGCGGGGAGAACCTC-3′ and reverse 5′-GTCGTCCGTTTCCAGGTCCACG-3′),
- -
human CTR-1 (forward 5′-GGGGATGAGCTATATGGACTCC-3′ and reverse 5′-TCACCAAACCGGAAAACAGTAG-3′),
- -
human GAPDH (forward 5′-GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTC-3′ and reverse 5′-GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC-3′).
The cRNA was then retro-transcribed using the GoScript reverse transcriptase (Promega). Quantitative real-time PCR analyses were performed using the CFX96 TM real-time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA).
2.9. Western blot
Whole-cell lysates were prepared using cold RIPA buffer [150 mM NaCl, 50 mM tris-HCl (pH 8), 0.1% SDS, 1% Igepal, and 0.5% Desoxycholate sodium] containing a protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics S.p.a., Milan, Italy), phosphatase inhibitors 1 mM Na3VO4 and 1 mM NaF (Sigma Aldrich). Protein concentrations were determined using the Protein Assay Dye Reagent Concentrate (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Segrate, Italy). Equal amounts of proteins were mixed with Laemmli buffer, separated in 4-20% SDS-PAGE (Criterion Precast Gel, BioRad) and blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Amersham, GE Healthcare). Membrane strips were blocked with EveryBlot Blocking Buffer (BioRad), and incubated at 4°C overnight with primary antibodies (Supplemental
Table S2), probed with the appropriate secondary antibodies (Supplemental
Table S2), and developed using Immobilon Western Chemioluminiscent HRP Substrate. Images were acquired using a ChemiDoc XRS system (Bio-Rad).
2.10. Migration/invasion assays
These assays were done in Boyden chambers (Corning). Prior to perform migration, the lower side of the chamber was coated with either 20 μg/mL fibronectin (Sigma-Aldrich) (migration) or 50 μg/mL Growth Factor Reduced (GFR) Basement Membrane Matrix (Matrigel, Corning) (Invasion). Cells were labeled with the lipophilic CellTracker CM-DiI dye according to the vendor’s instructions (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Then cells were seeded in 150 μl serum-free medium in the upper side of Boyden chambers. Each insert contained 100,000 tumor cells. The lower side contained 700 μL complete medium. Transmigrated cells were detected using a computer-interfaced GeniusPlus microplate reader (Tecan). Migration was expressed as the percentage of migrated cells at different time points.
2.11. NF-kB p65 transcription factor assays and TrxR
To measure NF-kB p65 active form, tumor cells (5.0 × 106 cells) were collected and nuclear protein was extracted. Briefly, cells were lysed with buffer A (10 mM HEPES [pH 7.9], 10 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol, 0.05 % NP-40, 0.5 mM PMSF, 1 mM Na3VO4, 1 mM NaF) on ice for 30 min. Samples were centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C. Pellets (nuclear fraction) were resuspended in ice-cold extraction buffer B (5 mM HEPES [pH 7.9], 300 mM NaCl, 0.2 M EDTA, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 25% [vol/vol] glycerol, 0.5 mM dithiothreitol, 0.5 mM PMSF, 1 mM Na3VO4, 1 mM NaF) and incubated on ice for 30 min. Samples were centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C, and the supernatant was taken as the nuclear extract. Protein concentration was determined using the Bio-Rad Bradford protein assay. NF-kB DNA binding activity was analyzed using the Transcription Factor Kit for NF-kB p65 (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Data were normalized to that in untreated HRS cells.
To evaluate Thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) activity, cells were lysed in 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.6, 0.1% Triton X-100, 0.9% NaCl. TrxR (EC 1.8.1.9) was assayed using the Thioredoxin Reductase Assay Kit (Sigma-Aldrich). Enzyme activity was determined reading the absorbance at 412 nm using a spectrophotometer (Biomate 3 Thermo Spectronic, Thermo Electonic Corporation, Monza, Italy). The enzymatic activity was normalized to the protein concentration, determined using the Bio-Rad Bradford protein assay.
2.12. Statistical analyses
Statistical analysis was carried out using GraphPad Prism version 6.0 software (GraphPad, La Jolla, USA). Student’s t test was used to compare two groups. One-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni correction was used for multiple comparisons. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test was used to compare each of a number of treatments with a single control. A P-value <0.05 was considered significant.
4. Discussion
For cHL therapy, the main issue is to select patients that could benefit from a standard frontline intensive chemotherapy from those that are poor responder and would take advantage from new alternative therapies.
Drug resistant cHL-derived cell lines could help to find new predictive factors for prognosis and response to drug treatment and novel more active and less toxic therapeutic strategies [47].
Here, we described functional and phenotypic characteristics of KM-H2dx and HDLM-2dx cell lines with acquired resistance to doxorubicin. They were generated in our lab by continuous exposure to doxorubicin of the cHL cell lines KM-H2 and HDLM-2, respectively [11]. To our knowledge this is the first report analyzing the characteristics of HRS cells with acquired resistance to doxorubicin.
HRSdx cells, compared with parental HRS cells, showed: a higher number of giant mostly multinucleated cells; reduced doubling time and clonogenic growth capacity; increased Bcl-2 and CSCs markers; increased migration and invasive capabilities; increased CCR5 expression; decreased levels of molecules involved in the cross-talk with the TME (CD44, DDR1, CD54, CD80, HLA-DR) but increased CD58; increased secretion and expression of molecules involved in the TME formation (CCL5 and TARC) and immunosuppression (PGE, TGF-β, CD26, COX-2); increased capability to induce the M2-TAM phenotype in monocytes; low or moderate cross-resistance to vinblastine, bendamustin, cisplatin, dacarbazine, gemcitabine, BV, MMAE, and γ-radiation; no cross-resistance to bleomycin, trabectedin, and DHMEQ; CTR-1 down-regulation; decreased accumulation of doxorubicin in the nucleus and consequent decreased DNA damage; decreased sensitivity to oxidative stress and increased TrxR enzymatic activity; enhanced sensitivity to doxorubicin used in combination with inhibitors of autophagy and EVs release.
Moreover, only KM-H2dx had an increased expression of ALDH1, Bcl-xL, CXCR4, Jagged1, and CD137; only HDLM-2dx cells acquired a remarkable collateral resistance to caelyx.
HRSdx cells expressed markers of the putative CSCs: low levels of intracellular ROS, increased ALDH1, decreased doubling time [20,48] and cyt-ROS decrease, a higher expression of mit-ROS [22]. We could speculate that doxorubicin treatment selects and expands HRS cells more prone to survive and to be less sensitive to anticancer drugs.
Consistently with the increased migration and invasion capability, HRSdx cells expressed higher levels of ROHA and ROCK [19,49], the chemokine receptors CCR5 and CXCR4 [50], and lower levels of several molecules involved in the interactions with the TME. Genetic alterations could be the reason of the absence of CD49d in HDLM-2 and HDLM-2dx cells [26,51].
In HRSdx cells the decrease of HLA-DR expression could favor the escape from immune system recognition and the increase of CD58, by improving the interactions with CD40L+CD2+ rosetting T cells, could support tumor cell survival [24]. Thus, doxorubicin adapted HRS cells, with increased invasive abilities and reduced expression of molecules involved in the cross-talk with the TME could be more prone to evade from immune system recognition, escape from the lymph node and metastasize.
COX-2 over-expression by tumor cells is an adverse independent prognostic factor in cHL patients treated with ABVD [52]. Indeed, chemotherapy was found to induce COX-2/PGE2 up-regulation in different cancer models and to decrease the effects of the combination of chemotherapy with immunotherapy [53]. COX-2 was up-regulated in both HRSdx cells. Thus, we can speculate that its association with poor prognosis could be related not only to its immunosuppressive activity but also to the development of drug resistance, indicating COX-2 as potential marker of HRS acquired doxorubicin resistance.
The doxorubicin adapted HRS cells secreted increased levels of cytokines/chemokines involved in TME formation (CCL5, TARC, M-CSF, and FGF) and immune-suppression (PGE2, IL-13, TGF-β, and L-lactate) [25]. Consistently, HRSdx-CM was more effective than HRS-CM in inducing an immunosuppressive M2-like TAM phenotype in monocytes. They up-regulated PDL-1, IDO, and especially CD206, known to promote matrix-remodeling and lymphoma dissemination [54]. Thus, HRS with acquired resistance to doxorubicin cells could be more efficient in building an immunosuppressive TME and hijack monocytes [25].
Cross-resistance studies showed that the acquisition of doxorubicin resistance by HRS cells was associated with modest/intermediate collateral resistance to several other chemotherapy agents. However, we found that bleomycin, that is part of ABVD treatment, NF-kB inhibitor DHMEQ [29], and trabectedin had comparable activity in HRS and HRSdx cells [9]. Trabectedin, able to counteract HRS/TME interactions [55] and to enhance the anticancer activity of the inhibitor of telomerase activation BIBR153 in HRS cells [56], could be a promising option in patients with refractory/resistant cHL.
To increase doxorubicin accumulation in tumor cells, and especially to overcome/reduce its cardiac toxicity, the PEGylated liposomal formulation of doxorubicin (caelyx) has been proposed in relapsed or refractory cHL [57]. While in KM-H2dx doxorubicin resistance was partially reverted by caelyx, HDLM-2dx developed a strong resistance to caelyx, that could be attributed to a defective uptake and internalization of liposomes or to the exosome-mediated expelling of the drug, as demonstrated in U937 cells [58]. Chen R and colleagues [3] demonstrated that acquired BV resistance was associated to the overexpression of MDR1 drug efflux transporter. However, we found that HDLM-2 and HDLM-2dx cells, intrinsically resistant to BV but not to MMAE, did not express MDR1, indicating different mechanisms involved in intrinsic or acquired BV resistance and suggesting different approaches to counteract them. Further studies are needed to discover the molecular mechanisms of the cross-resistance to caelyx observed in HDLM-2dx cells and to BV in both, HDLM-2 and HDLM-2dx cells.
HRSdx cells are less sensitive than parental cells to the cytotoxic effects of γ-radiation suggesting that the adaptation of HRS cells to doxorubicin could also decrease the efficacy of radiation therapy in cHL patients [59].
Several mechanisms are involved in the acquired resistance to doxorubicin [33]. One such mechanism is usually associated with an increased expression of the drug efflux transporters [34]. We found only a slightly increase of mRNA levels of MRP1 in HRSdx cells and of MDR1 in KM-H2dx cells [4], outlining the poor role of these drug transporters in the acquired doxorubicin resistance in cHL tumor cells. However, consistently with the cross-resistance to cisplatin, the copper transporter CTR-1, involved in cisplatin influx [42], was down-regulated in HRSdx cells.
The decreased localization of doxorubicin in the nucleus [35], together with the increased expression of anti-apoptotic molecules Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, putative CSCs markers, and detoxifying enzyme TrxR, could explain the reduced sensitivity of HRSdx cells to DNA damage and oxidative stress.
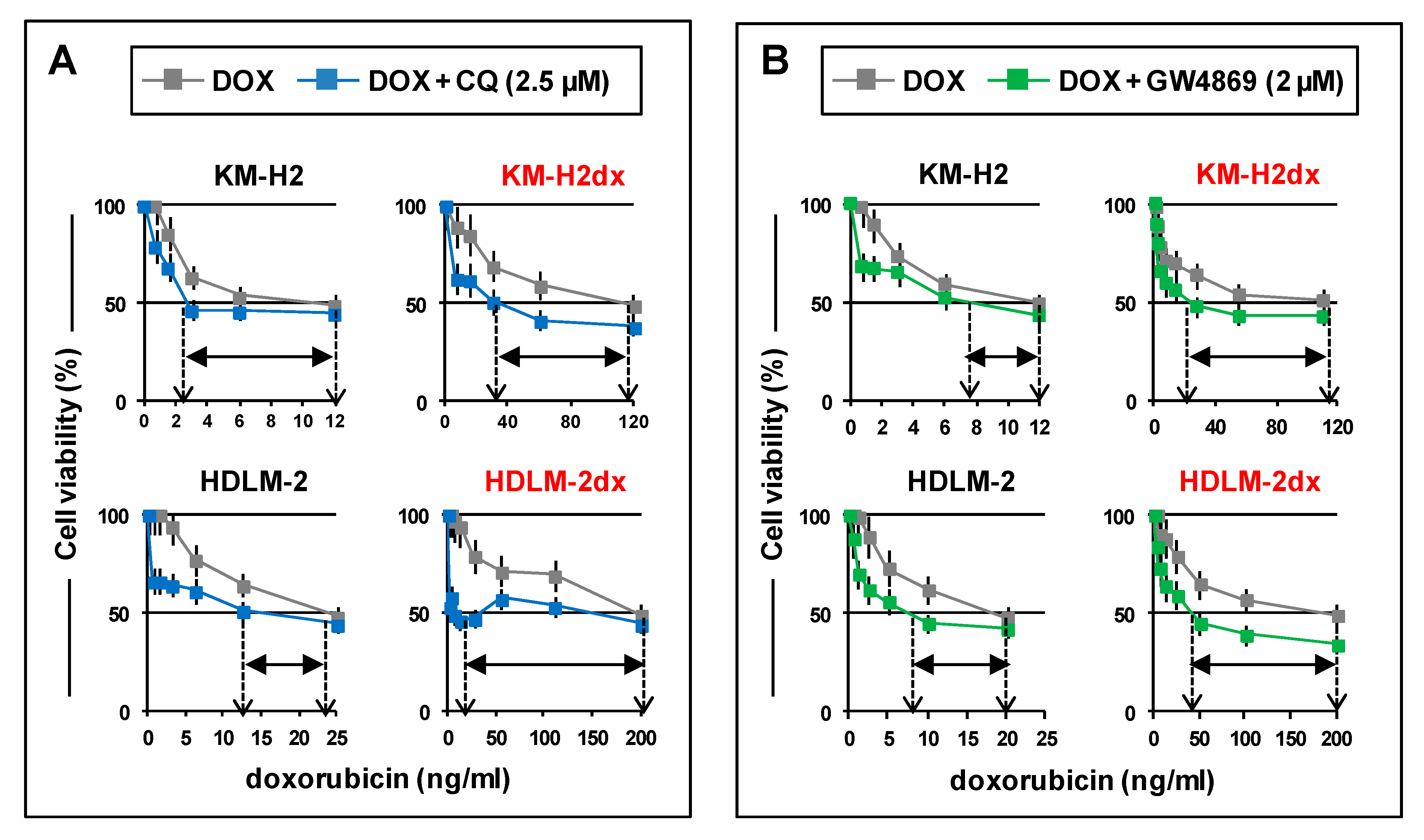
Finally, we found a new role of authophagy and EVs in cHL. Authophagy, required for HRS cell survival [45], could regulate doxorubicin activity by decreasing the accumulation of degraded proteins or by promoting drug sequestration and degradation into lysosomes [60]. Consistently, we found that the autophagy inhibitor CQ enhanced doxorubicin activity and overcame doxorubicin resistance in HRSdx cells.
EVs can reduce drug activity in different cancer models and are used as biomarkers of resistance to therapy [39]. Indeed, we found that EV inhibitor GW4869 enhanced doxorubicin cytotoxicity in HRS cells and counteracted doxorubicin resistance in HRSdx cells, suggesting that drug resistance could be mediated, at least in part, by EVs-mediated expelling of doxorubicin leading to its decreased intracellular accumulation. Given that GW4869 was found to increase the activity of PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin in U937 cells [58], we can speculate that an increased EVs-mediated expelling of caelyx could be the reason of the high cross-resistance to caelyx observed in HDLM-2dx cells.
Figure 1.
Characteristics of HRS and HRSdx cells. (A) Phase contrast photo micrographs of HRS and HRSdx cells. (B) Morphological images of HRS (upper panels) and HRSdx cells (red, lower panels) obtained after May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining (MGG). (Magnification, ×20; scale bar, 10 µm). (C) Growth curves of HRS and HRSdx cells. The number of viable cells were evaluated by trypan blue dye exclusion assay. The calculated doubling times (DT, in days) for each cell line were reported in the figure. (D) Clonogenic growth. Cells were seeded in medium containing 0.8 % methylcellulose. After for 14 days aggregates with ≥40 cells were scored as colonies. Values (total number of colonies) are mean ± SD of 8 replicates of three independent experiments. (E) HRS and HRSdx cells were lysed and NF-kB p65 transcription factor activity was analyzed in nuclear extracts using the Transcription Factor Kit (p65). Results are represented as percent of control (activity HRSdx respect to HRS parental cells) and are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Chemotaxis assays in Boyden chambers. (F) Migration of HRS and HRSdx cells through fibronectin coated (20 µg/ml) chambers towards 20% complete medium. Data are the percentages of cells that migrated from the serum-free upper chamber to the lower complete medium chamber. (G) Invasion. Migration of HRS and HRSdx cells through Matrigel-coated (50 ug/ml) chambers towards 20% complete medium. Data are the percentages of cells that migrated from the matrigel-coated upper chamber to the lower complete medium chamber . (H) Western blot analysis for ROCK, ROHA, and vinculin in HRS and HRSdx cells. Images were acquired using a ChemiDoc XRS system (Bio-Rad). (I) Flow cytometry expression of CCR5 and CXCR4 in HRS and HRSdx cells. Red arrows indicated up-regulated antigens, Results are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P<0.05 HRSdx vs HRS cells.
Figure 1.
Characteristics of HRS and HRSdx cells. (A) Phase contrast photo micrographs of HRS and HRSdx cells. (B) Morphological images of HRS (upper panels) and HRSdx cells (red, lower panels) obtained after May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining (MGG). (Magnification, ×20; scale bar, 10 µm). (C) Growth curves of HRS and HRSdx cells. The number of viable cells were evaluated by trypan blue dye exclusion assay. The calculated doubling times (DT, in days) for each cell line were reported in the figure. (D) Clonogenic growth. Cells were seeded in medium containing 0.8 % methylcellulose. After for 14 days aggregates with ≥40 cells were scored as colonies. Values (total number of colonies) are mean ± SD of 8 replicates of three independent experiments. (E) HRS and HRSdx cells were lysed and NF-kB p65 transcription factor activity was analyzed in nuclear extracts using the Transcription Factor Kit (p65). Results are represented as percent of control (activity HRSdx respect to HRS parental cells) and are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Chemotaxis assays in Boyden chambers. (F) Migration of HRS and HRSdx cells through fibronectin coated (20 µg/ml) chambers towards 20% complete medium. Data are the percentages of cells that migrated from the serum-free upper chamber to the lower complete medium chamber. (G) Invasion. Migration of HRS and HRSdx cells through Matrigel-coated (50 ug/ml) chambers towards 20% complete medium. Data are the percentages of cells that migrated from the matrigel-coated upper chamber to the lower complete medium chamber . (H) Western blot analysis for ROCK, ROHA, and vinculin in HRS and HRSdx cells. Images were acquired using a ChemiDoc XRS system (Bio-Rad). (I) Flow cytometry expression of CCR5 and CXCR4 in HRS and HRSdx cells. Red arrows indicated up-regulated antigens, Results are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P<0.05 HRSdx vs HRS cells.
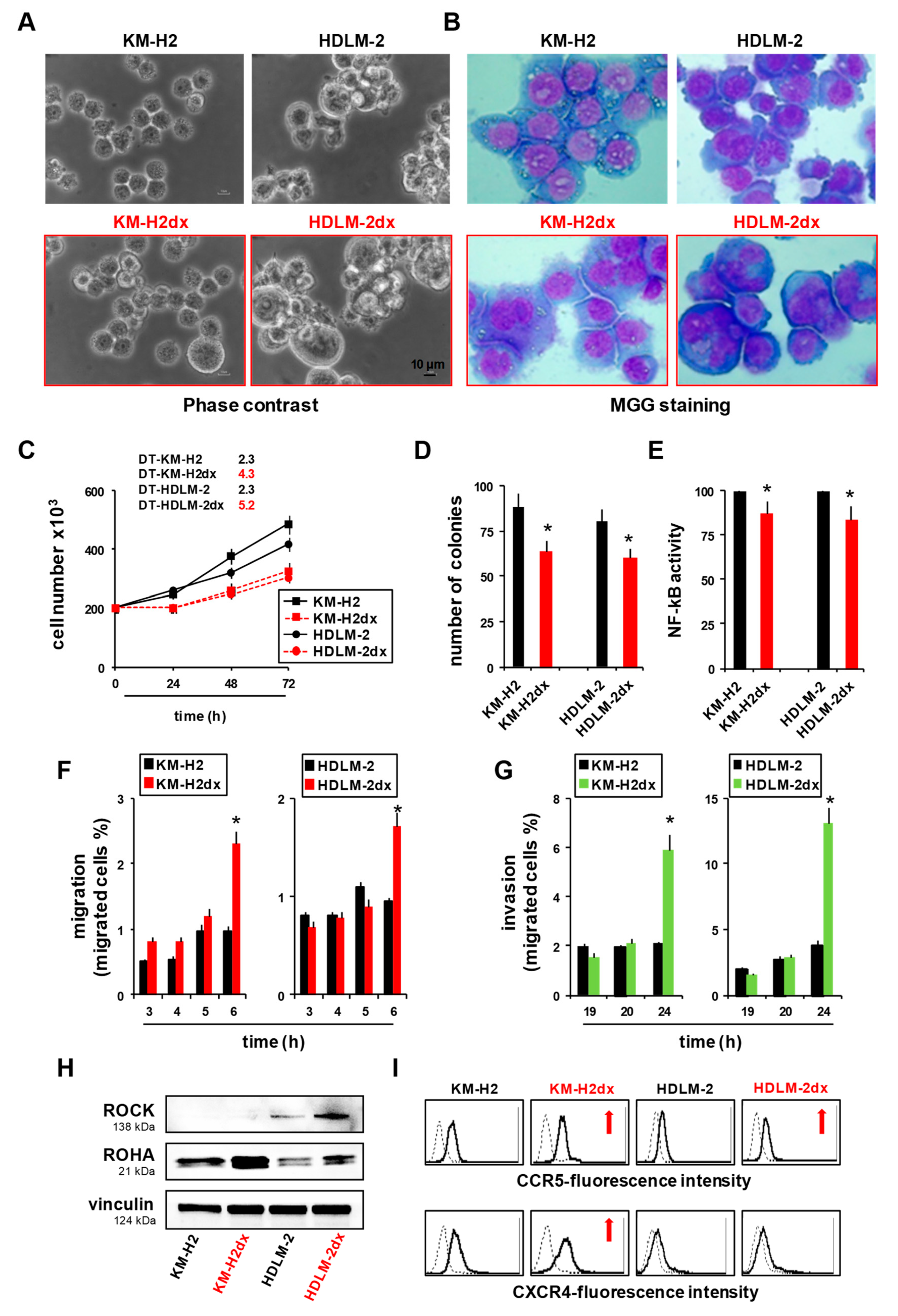
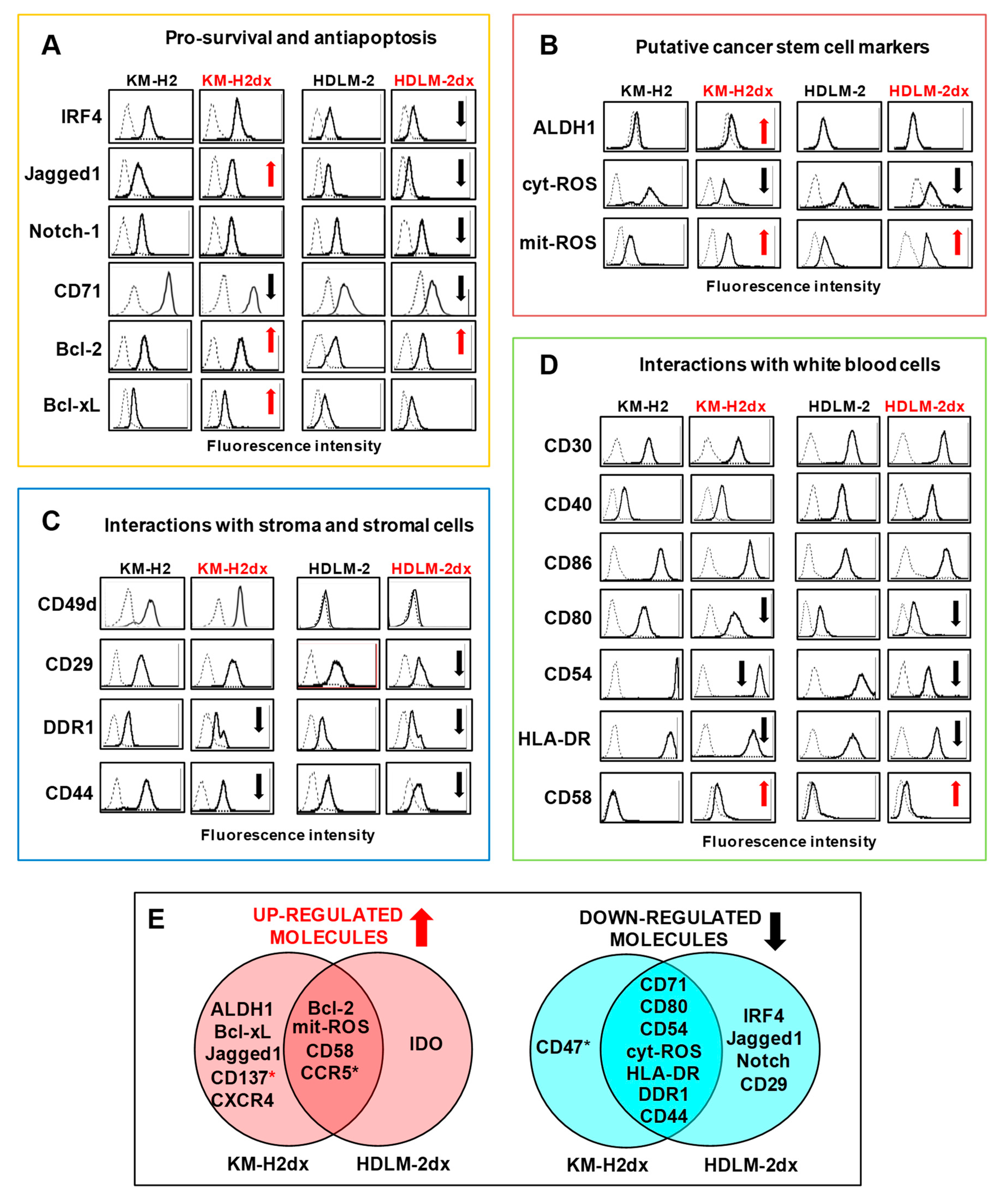
Figure 2.
Phenotypes of HRS and HRSdx cells. Flow cytometry assay of molecules expressed by HRS and HRSdx cells. Representative flow cytometry histograms showing the expression of (A) survival factors and antiapoptotic molecules, (B) markers of the putative cancer stem cells, (C) molecules involved in the interactions with collagen and stromal cells, (D) or with white blood cells (lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and mast cells). Red arrows indicate up-regulated antigens, black arrows down-modulated antigens in doxorubicin resistant HRSdx respect to parental HRS cells. (E) Venn diagrams showing the molecules modulated in both HRSdx, and those specifically up-regulated or down-regulated in KM-H2dx and HDLM-2dx.
Figure 2.
Phenotypes of HRS and HRSdx cells. Flow cytometry assay of molecules expressed by HRS and HRSdx cells. Representative flow cytometry histograms showing the expression of (A) survival factors and antiapoptotic molecules, (B) markers of the putative cancer stem cells, (C) molecules involved in the interactions with collagen and stromal cells, (D) or with white blood cells (lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and mast cells). Red arrows indicate up-regulated antigens, black arrows down-modulated antigens in doxorubicin resistant HRSdx respect to parental HRS cells. (E) Venn diagrams showing the molecules modulated in both HRSdx, and those specifically up-regulated or down-regulated in KM-H2dx and HDLM-2dx.
Figure 3.
Tumor cell expression and secretion of immunosuppressive molecules and monocyte immunosuppressive education by tumor cell conditioned medium (CM). (A) Flow cytometry assay of immunosuppressive molecules expressed by HRS and HRSdx cells. Red arrows indicate up-regulated antigens, black arrows down-modulated antigens in HRSdx respect to HRS cells. (B) Cytokines secreted by HRS and HRSdx cells cultured for 72 h in complete medium. Their concentrations were evaluated by ELISA assay and reported as pg × 106 cells, excluding L-lactate (*, ng/106 cells). Values for KM-H2 and HDLM-2 are shown in the respective insert. Bar charts report the fold increase of the concentration of each chemokine secreted by HRSdx respect to HRS cells. (C) Monocytic THP-1 cells were cultured with HRS-CM and HRSdx-CM, then CD206, PDL-1, and IDO expression was evaluated by flow cytometry. Red arrows indicate antigens up-regulated by HRSdx-CM respect to HRS-CM. (D) Immunosuppression (IS). Schematic representation of common HRSdx modifications cells leading to immunosuppression (antigens, cytokines, monocytes, tumor education). Red arrow indicates up-regulated antigens, black arrow down-modulated antigens (HRSdx respect to HRS cells).
Figure 3.
Tumor cell expression and secretion of immunosuppressive molecules and monocyte immunosuppressive education by tumor cell conditioned medium (CM). (A) Flow cytometry assay of immunosuppressive molecules expressed by HRS and HRSdx cells. Red arrows indicate up-regulated antigens, black arrows down-modulated antigens in HRSdx respect to HRS cells. (B) Cytokines secreted by HRS and HRSdx cells cultured for 72 h in complete medium. Their concentrations were evaluated by ELISA assay and reported as pg × 106 cells, excluding L-lactate (*, ng/106 cells). Values for KM-H2 and HDLM-2 are shown in the respective insert. Bar charts report the fold increase of the concentration of each chemokine secreted by HRSdx respect to HRS cells. (C) Monocytic THP-1 cells were cultured with HRS-CM and HRSdx-CM, then CD206, PDL-1, and IDO expression was evaluated by flow cytometry. Red arrows indicate antigens up-regulated by HRSdx-CM respect to HRS-CM. (D) Immunosuppression (IS). Schematic representation of common HRSdx modifications cells leading to immunosuppression (antigens, cytokines, monocytes, tumor education). Red arrow indicates up-regulated antigens, black arrow down-modulated antigens (HRSdx respect to HRS cells).
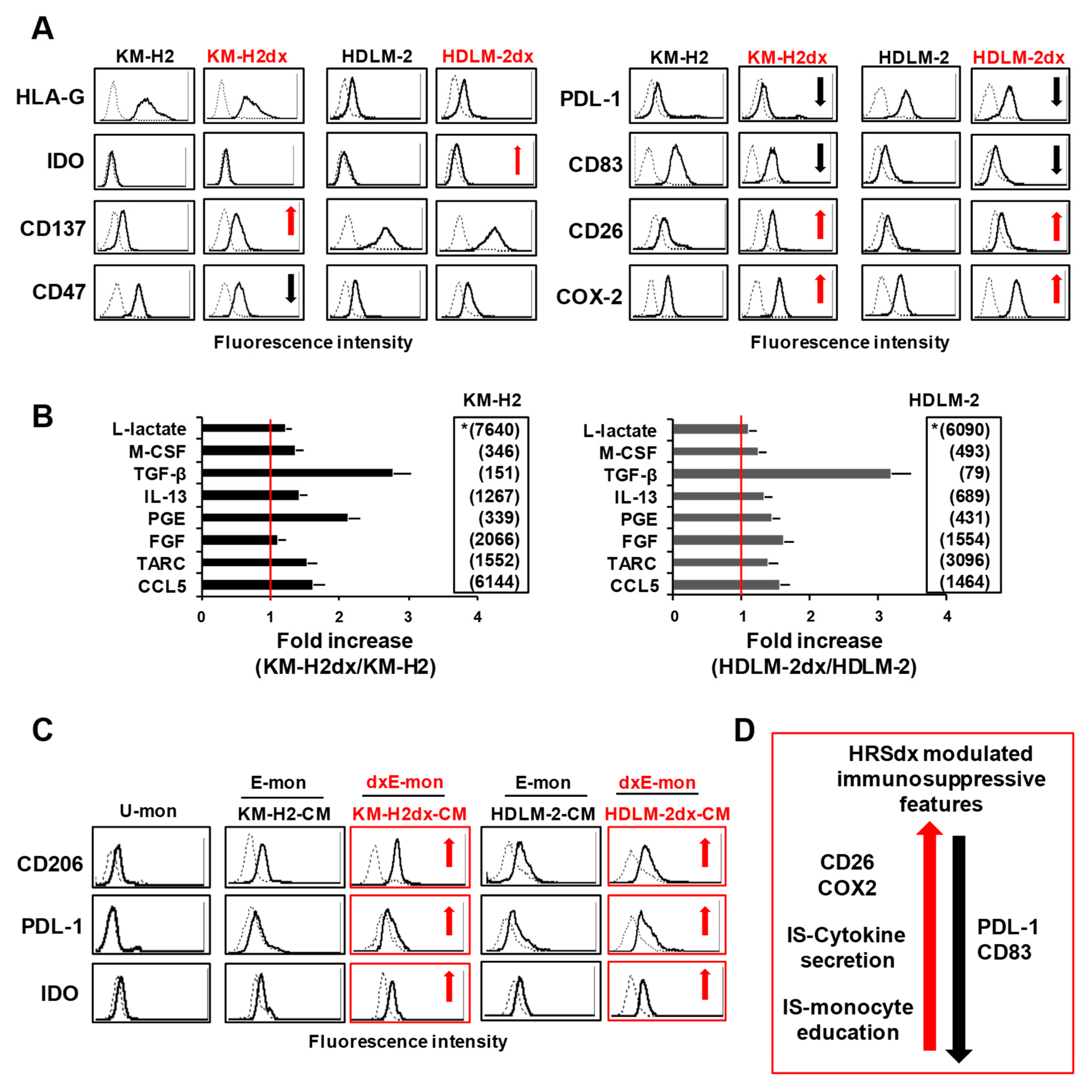
Figure 4.
Cross-resistance pattern and γ-radiation activity in HRS and HRSdx cells. (A) Resistance factor (RF) value is the ratio of HRSdx IC50 (KM-H2dx and HDLM-2dx) over HRS IC50 (KM-H2 and HDLM-2). RFs are reported in ascending order. RF < 1 indicates cross-sensitivity (CS), RF ≥1 indicates cross-resistance (CR). RF ranging from 1 to 2 indicates low CR, RF from 2 to 5 indicates moderate CR, RF ≥ 5 indicates high CR. (B-D) Tumor cells were treated with γ-radiation (0-12 Gy). Then, cell viability, clonogenic growth, and cell cycle distribution were evaluated. (B) Cells were double stained with Annexin-V-FITC and 7AAD and analyzed by flow cytometry. Bar charts show the percentage of viable cells (Annexin-V and 7AAD negative cells). (C) Clonogenic growth assay. Untreated and γ-radiation treated cells were seeded in medium containing 0.8 % methylcellulose and cultured for 14 days; aggregates with ≥40 cells were scored as colonies. Values (total number of colonies) are mean ± SD of 8 replicates. (D) Bar charts show the percentage of cells in each cell cycle phase, evaluated after propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry analysis. (E) Representative cytofluorimetric histograms of the cell cycle progression after γ-radiation treatment. Results are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 HRSdx vs parental HRS cells.
Figure 4.
Cross-resistance pattern and γ-radiation activity in HRS and HRSdx cells. (A) Resistance factor (RF) value is the ratio of HRSdx IC50 (KM-H2dx and HDLM-2dx) over HRS IC50 (KM-H2 and HDLM-2). RFs are reported in ascending order. RF < 1 indicates cross-sensitivity (CS), RF ≥1 indicates cross-resistance (CR). RF ranging from 1 to 2 indicates low CR, RF from 2 to 5 indicates moderate CR, RF ≥ 5 indicates high CR. (B-D) Tumor cells were treated with γ-radiation (0-12 Gy). Then, cell viability, clonogenic growth, and cell cycle distribution were evaluated. (B) Cells were double stained with Annexin-V-FITC and 7AAD and analyzed by flow cytometry. Bar charts show the percentage of viable cells (Annexin-V and 7AAD negative cells). (C) Clonogenic growth assay. Untreated and γ-radiation treated cells were seeded in medium containing 0.8 % methylcellulose and cultured for 14 days; aggregates with ≥40 cells were scored as colonies. Values (total number of colonies) are mean ± SD of 8 replicates. (D) Bar charts show the percentage of cells in each cell cycle phase, evaluated after propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry analysis. (E) Representative cytofluorimetric histograms of the cell cycle progression after γ-radiation treatment. Results are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 HRSdx vs parental HRS cells.
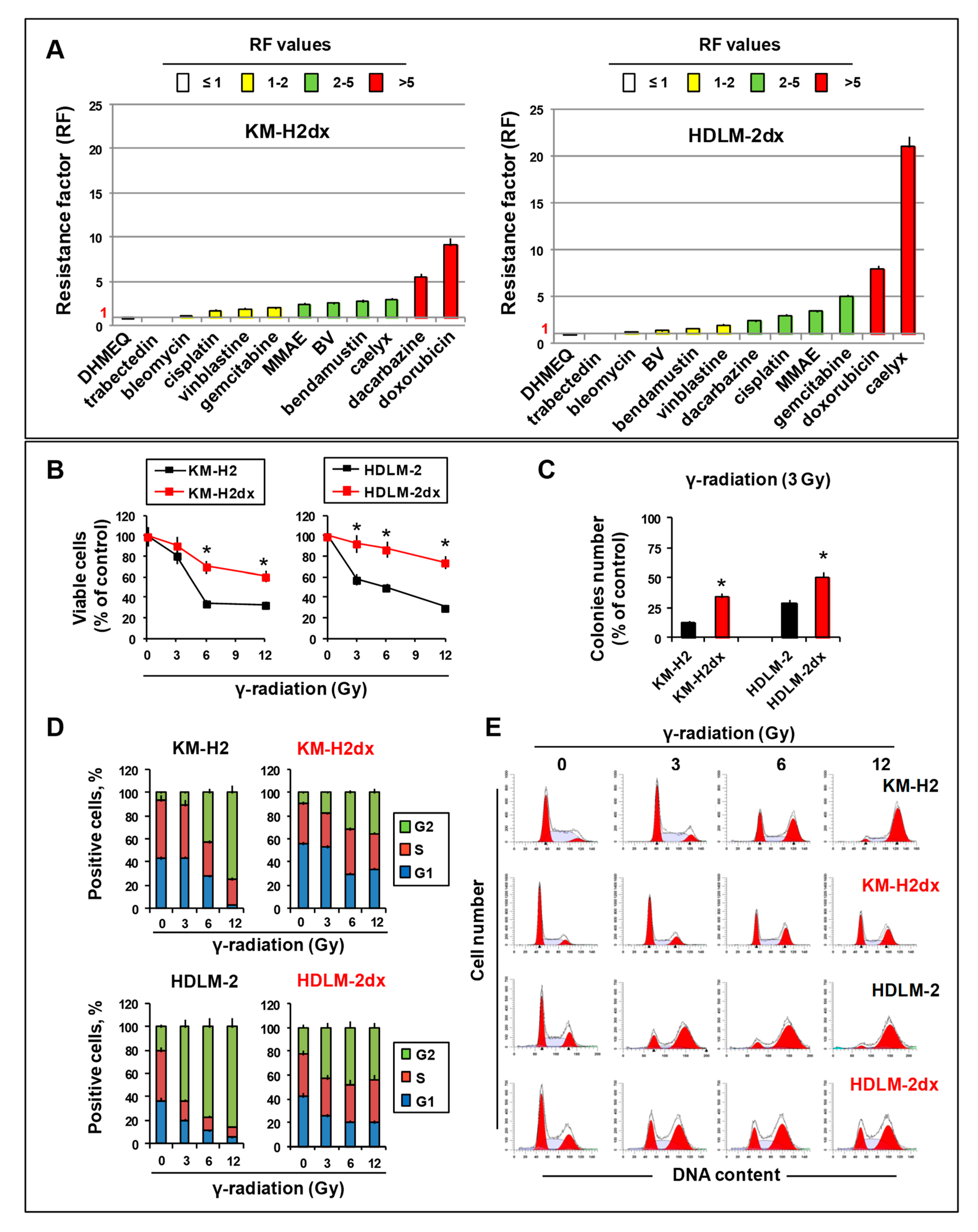
Figure 5.
Expression of drug transporters, uptake, distribution, and DNA damage by doxorubicin in HRS and HRSdx cells. (A) Relative mRNA expression of MDR1/ABCB1 and MRP1/ABCC1 in HRS and HRSdx cells using GAPDH gene expression as internal control. (B) Western blot for MDR1, MRP1, and α-tubulin expression. (C) Flow cytometry-based doxorubicin accumulation assay. HRS and HRSdx cells were incubated with doxorubicin (0-200 ng/ml) for 2 h. Then the percentage of red fluorescence positive cells was evaluated by flow cytometry. (D) Cells were incubated with doxorubicin (DOX, 1 µg/ml). After 2 h, doxorubicin internalization and distribution were evaluated by confocal microscopy. (E) HRS and HRSdx cells were incubated for 24 h with doxorubicin (KM-H2 IC90 = 100 ng/ml and HDLM-2 IC90 = 175 ng/ml). Then γ-H2AX expression was evaluated by flow cytometry. (F) KM-H2dx and HDLM-2dx cells were incubated for 24 h with doxorubicin (KM-H2dx IC90 = 300 ng/ml and HDLM-2dx IC90 = 450 ng/ml). γ-H2AX expression was evaluated by flow cytometry. Results are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 HRSdx vs parental HRS cells.
Figure 5.
Expression of drug transporters, uptake, distribution, and DNA damage by doxorubicin in HRS and HRSdx cells. (A) Relative mRNA expression of MDR1/ABCB1 and MRP1/ABCC1 in HRS and HRSdx cells using GAPDH gene expression as internal control. (B) Western blot for MDR1, MRP1, and α-tubulin expression. (C) Flow cytometry-based doxorubicin accumulation assay. HRS and HRSdx cells were incubated with doxorubicin (0-200 ng/ml) for 2 h. Then the percentage of red fluorescence positive cells was evaluated by flow cytometry. (D) Cells were incubated with doxorubicin (DOX, 1 µg/ml). After 2 h, doxorubicin internalization and distribution were evaluated by confocal microscopy. (E) HRS and HRSdx cells were incubated for 24 h with doxorubicin (KM-H2 IC90 = 100 ng/ml and HDLM-2 IC90 = 175 ng/ml). Then γ-H2AX expression was evaluated by flow cytometry. (F) KM-H2dx and HDLM-2dx cells were incubated for 24 h with doxorubicin (KM-H2dx IC90 = 300 ng/ml and HDLM-2dx IC90 = 450 ng/ml). γ-H2AX expression was evaluated by flow cytometry. Results are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 HRSdx vs parental HRS cells.
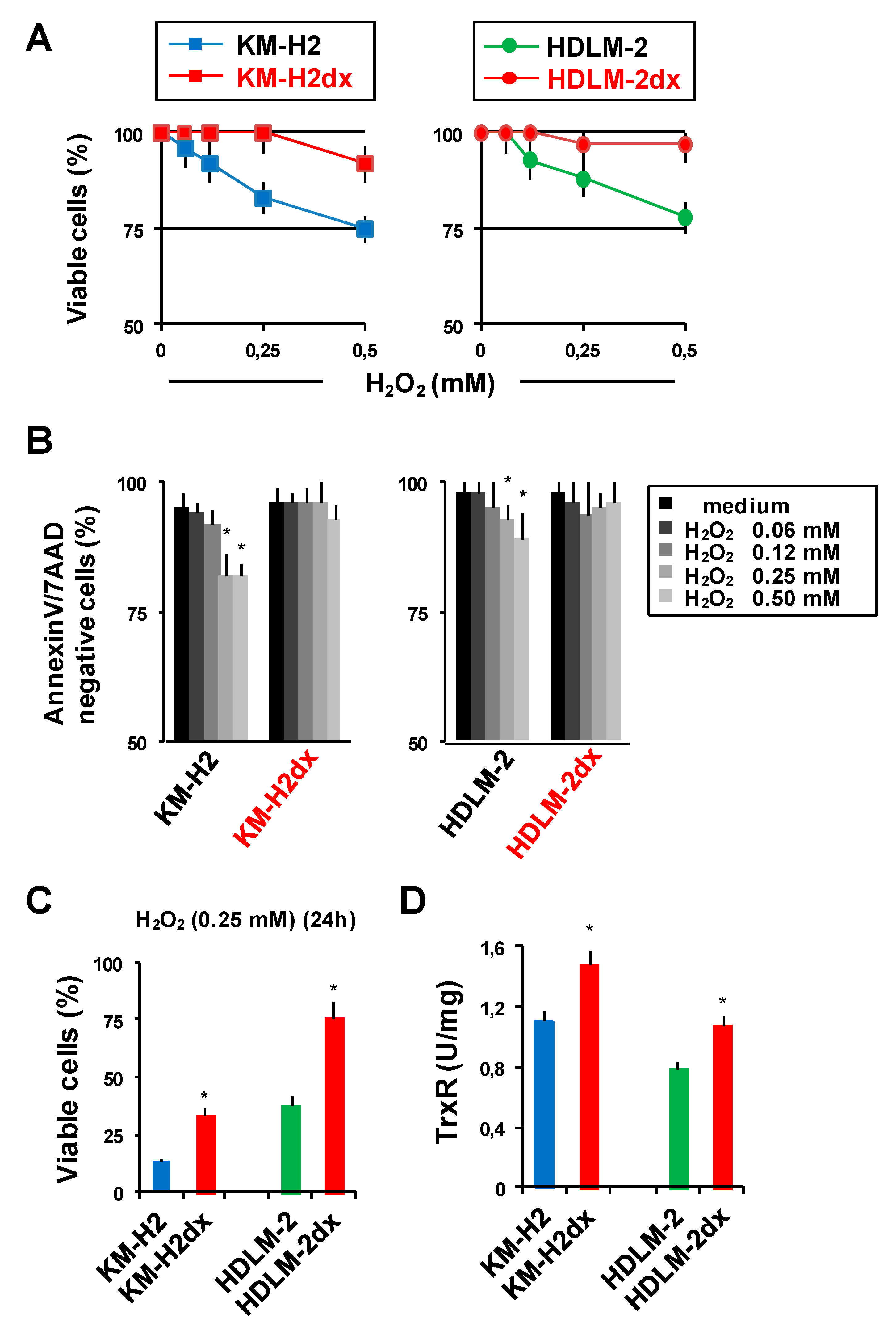
Figure 6.
Sensitivity of HRS and HRSdx to oxidative stress. HRS and HRSdx cells were treated with H2O2 (0-0.5 mM). (A) After 1 h cell viability was evaluated with trypan blue dye exclusion assay. (B) Alternatively, cells were double stained with Annexin-V-FITC and 7AAD and analyzed by flow cytometry. Bar charts show the percentage of viable cells (Annexin-V- and 7AAD-negative cells). (C) HRS and HRSdx cells were treated for 24 h with H2O2 (0.25 mM). After 24 h cell viability was evaluated with trypan blue dye exclusion assay. (D) TrxR enzymatic activity was evaluated using TrxR assay kit and expressed as U/mg of protein. Results are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 HRSdx vs parental HRS cells.
Figure 6.
Sensitivity of HRS and HRSdx to oxidative stress. HRS and HRSdx cells were treated with H2O2 (0-0.5 mM). (A) After 1 h cell viability was evaluated with trypan blue dye exclusion assay. (B) Alternatively, cells were double stained with Annexin-V-FITC and 7AAD and analyzed by flow cytometry. Bar charts show the percentage of viable cells (Annexin-V- and 7AAD-negative cells). (C) HRS and HRSdx cells were treated for 24 h with H2O2 (0.25 mM). After 24 h cell viability was evaluated with trypan blue dye exclusion assay. (D) TrxR enzymatic activity was evaluated using TrxR assay kit and expressed as U/mg of protein. Results are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 HRSdx vs parental HRS cells.
Figure 7.
Chloroquine and GW4869 enhance cell death induced by doxorubicin. HRS and HRSdx cells were cultured with doxorubicin (DOX) in the presence or not of (A) a non-toxic concentration of chloroquine (CQ) (2.5 µM) or (B) GW4869 (2 µM). After 72 h cell viability was evaluated by trypan blue dye exclusion assay. Results are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 DOX vsDOX plus CQ or DOX plus GW4869. Arrows indicate the IC50 of doxorubicin, in the presence or not of CQ or GW4869. Difference in IC50 is shown by the horizontal black double-headed arrow.
Figure 7.
Chloroquine and GW4869 enhance cell death induced by doxorubicin. HRS and HRSdx cells were cultured with doxorubicin (DOX) in the presence or not of (A) a non-toxic concentration of chloroquine (CQ) (2.5 µM) or (B) GW4869 (2 µM). After 72 h cell viability was evaluated by trypan blue dye exclusion assay. Results are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 DOX vsDOX plus CQ or DOX plus GW4869. Arrows indicate the IC50 of doxorubicin, in the presence or not of CQ or GW4869. Difference in IC50 is shown by the horizontal black double-headed arrow.
Table 1.
Cross-resistance pattern of doxorubicin resistant HRS cells. Half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of chemotherapy agents in KM-H2, KM-H2dx, HDLM-2, and HDLM-2dx. Mean ± standard deviation (SD).
Table 1.
Cross-resistance pattern of doxorubicin resistant HRS cells. Half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of chemotherapy agents in KM-H2, KM-H2dx, HDLM-2, and HDLM-2dx. Mean ± standard deviation (SD).
Chemotherapy
agent (IC50) |
Cell line |
| KM-H2 |
KM-H2dx
|
HDLM-2 |
HDLM-2dx |
doxorubicin (ng/ml)
caelyx (ng/ml)
bleomycin (µg/ml)
binblastine (nM)
dacarbazine (µg/ml)
bendamustin (µM)
gemcitabine (nM)
cisplatin (µM)
brentuximabv. (µg/ml)
MMAE (pg/ml)
trabectedin (pM)
DHMEQ (µM)
|
12 ± 0.9
408 ± 38
2.5 ± 0.4
0.25 ± 0.03
47.5 ± 5.1
7.25 ± 0.06
0.53 ± 0.04
0.48 ± 0.005
10 ± 1.1
75 ± 7.9
140 ± 13.5
5.1 ± 0.6 |
110 ± 10.9
1280 ± 115
2.6 ± 0.3
0.49 ± 0.03
265 ± 24
20.2 ± 1.8
1.1 ± 0.15
0.83 ± 0.07
25 ± 2.3
182 ± 16
150 ± 14
4.7 ± 0.05 |
25 ± 1.9
480 ± 42
10 ± 0.09
0.31 ± 0.02
115 ± 10
10.8 ± 1.7
3.1 ± 0.4
1.3 ± 0.04
250 ± 28
53 ± 5.03
185 ± 16
4.8 ± 0.5 |
200 ± 19
10,333 ± 1091
12 ± 0.15
0.67 ± 0.07
280 ± 25
17.4 ± 1.5
18 ± 1.6
4 ± 0.38
350 ± 33
183 ± 17
187 ± 16
4.1 ± 0.35 |