1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide. Approximately 10% of cancer-related deaths are newly diagnosed and account for 9.4% of all cancer-related deaths [
1]. Despite recent advances in treatment, only 39% of CRC cases are diagnosed at the local stage; the remaining patients are diagnosed at the regional or distant stages, where survival rates are significantly reduced [
2,
3]. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) and doxorubicin (Dox) are primarily prescribed as chemotherapeutic drugs for patients with CRC [
4], the 5-year survival rate is still low because of dose-limiting toxicity and drug resistance when administered for a long time. Therefore, the development of novel and effective adjuvant treatments that minimize the side effects in CRC is urgently required.
c-Myc, a member of the proto-oncogenic transcription factor family, is involved in regulating cell growth and proliferation in normal cells. Uncontrolled c-Myc overexpression contributes to most cancers, including colon cancer [
5,
6]. Controlling the c-Myc signaling pathway within cells can be a treatment strategy for various types of cancer by inducing apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation [
7]. Therefore, reducing c-Myc overexpression can inhibit the progression of colon cancer.
CCR4-NOT transcription complex subunit 2 (CNOT2) plays a crucial role in apoptosis, autophagy, proliferation, and angiogenesis in cancer cells. Previous studies have shown that depletion of CNOT2 can increase apoptosis and decrease metastasis through proliferation and inhibition of angiogenesis [
8,
9]. MID1 Interacting Protein 1 (MID1IP1), also known as MIG12, is highly expressed in various cancer types. A recent study has shown that MID1IP1 acts upstream of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and regulates AMPK phosphorylation in liver cancer cells [
10]. Additionally, MID1IP1 contributes to cancer cell growth and death through co-localization with c-Myc-mediated ribosomal proteins L5, L11, and CNOT2 [
11].
Acetylcorynoline (ACN) is a major alkaloid derived from
C. ambigua Tubers. ACN has been shown to be effective in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD) [
12]. However, the anticancer effects on colon cancer cells and molecular mechanisms of action of ACN have not yet been reported.
Therefore, we investigated the potential anticancer effects of ACN in colon cancer cells.
2. Results
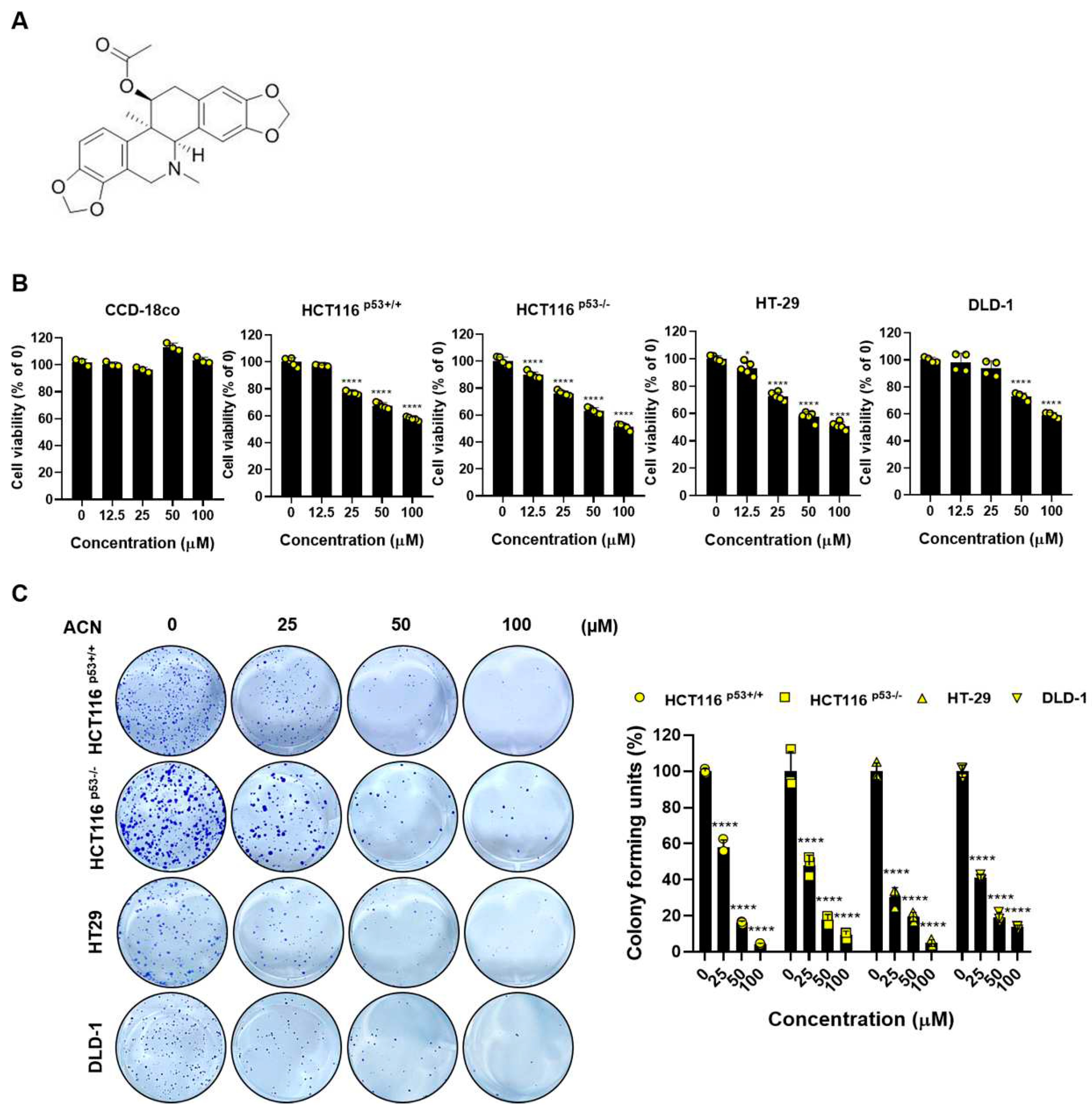
2.1. ACN Inhibits Cell Viability and Proliferation of Colon Cancer Cells
To investigate the effects of ACN, we performed biological assessments on four types of colon cancer cells: HCT116
p53+/+, HCT116
p53-/-, HT-29, and DLD-1. Cell viability was determined using the MTT assay. ACN inhibited the colon cancer cell viability in a dose-dependent manner, whereas the non-cancerous colon cell line CCD-18co was not affected the cell viability when treated with up to 100 µM (
Figure 1B). In addition, the colony formation assay showed that ACN inhibited cell proliferation compared to the untreated group (
Figure 1C). In conclusion, our data indicate that ACN is involved in the viability and proliferation of colon cancer cells.
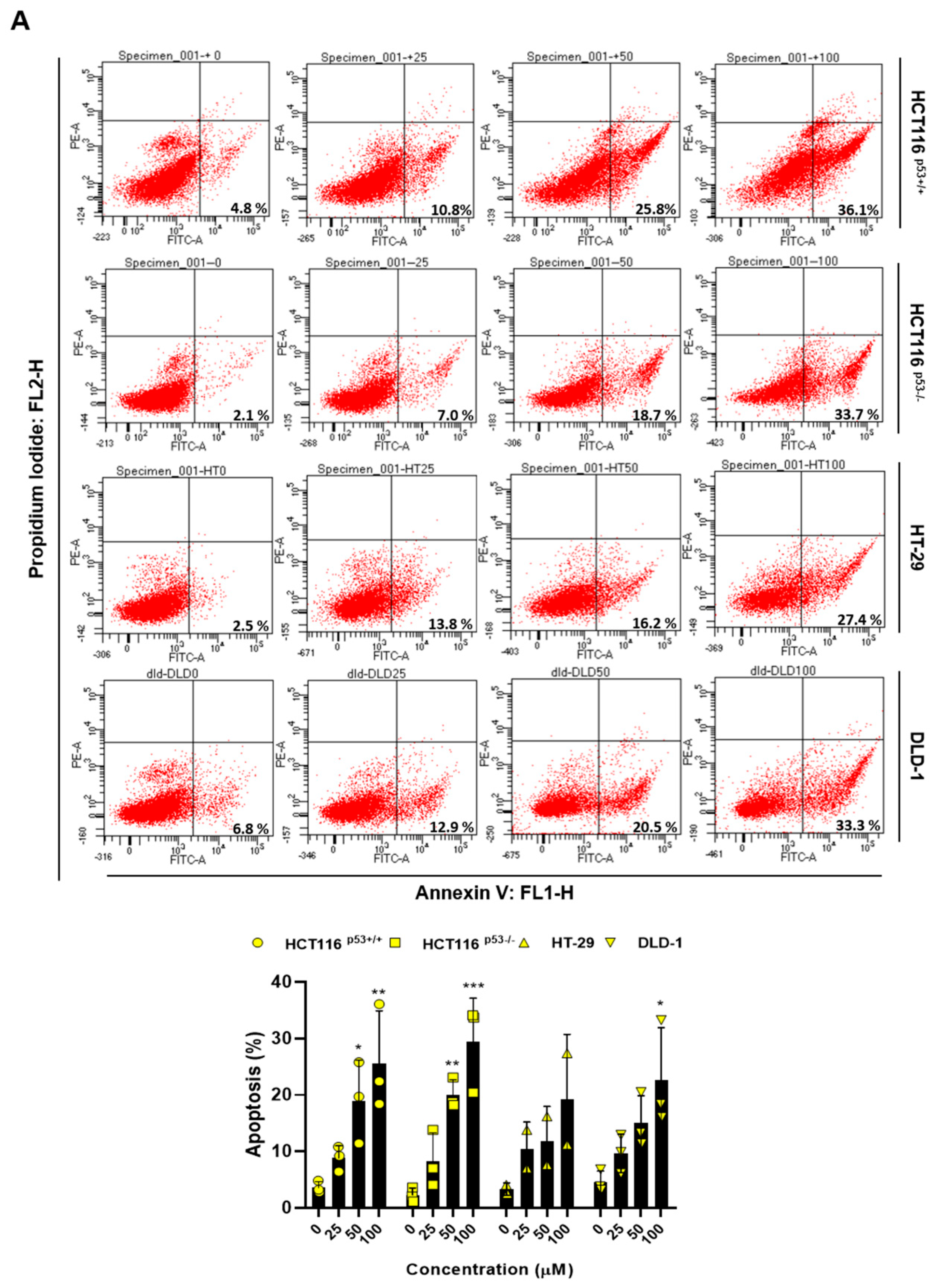
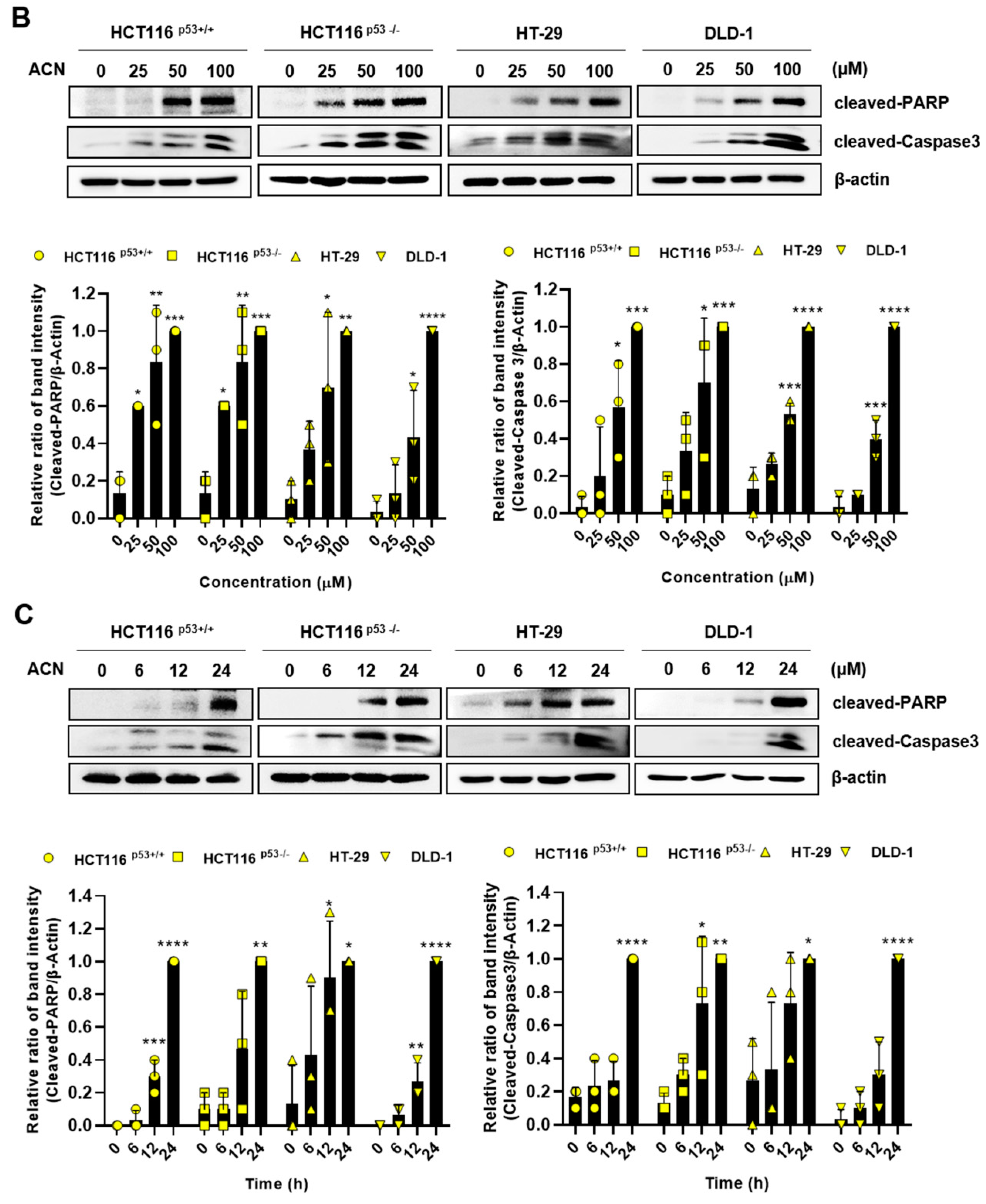
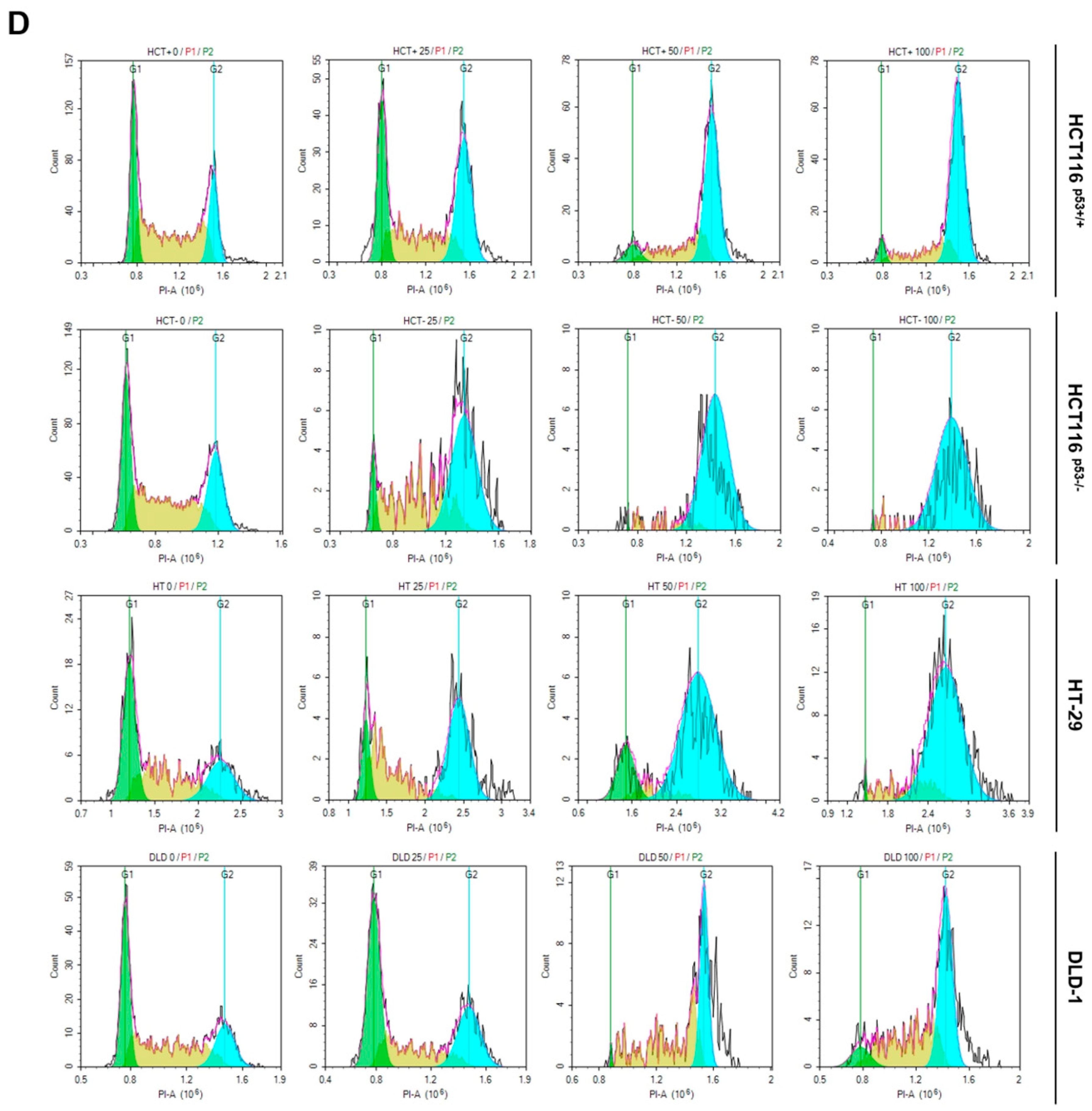
2.2. ACN Regulates Apoptosis and Induces G2/M Phase Arrest
To demonstrate ACN-induced inhibition of colon cancer cell growth, we performed flow cytometry and immunoblotting. Then, we performed Annexin V and PI staining to assess whether ACN induces apoptosis. As shown in
Figure 2A, apoptosis rates were significantly increased in ACN-treated colon cancer cells compared to those in the untreated group. Furthermore, ACN treatment increased the expression of cleaved-PARP and cleaved-caspase3 was increased in a dose- and time-dependent manner (
Figure 2B,C). We also analyzed the cell cycle phase. ACN increased the G2/M phase cell population (
Figure 2D). These result suggested that ACN induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.
2.3. c-Myc is a Potential Target for the Inhibition of Colon Cancer in ACN
c-Myc is a transcriptional regulator that controls the expression of various genes and regulates proliferation, the cell cycle, and survival of cancer cells [
13,
14]. MID1IP1, which induces apoptosis and is controlled by CNOT2, regulates c-Myc via ribosomal proteins L5 and L11, and is involved in cancer cell growth [
11,
15]. c-Myc is overexpressed in CRC and plays a potential role in colon cancer development [
16]. We hypothesized that the effects of ACN-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest may be related to c-Myc signaling. The protein expression of c-Myc, CNOT2, and MID1IP1 decreased in a dose- and time-dependent manner after ACN treatment of colon cancer cells (
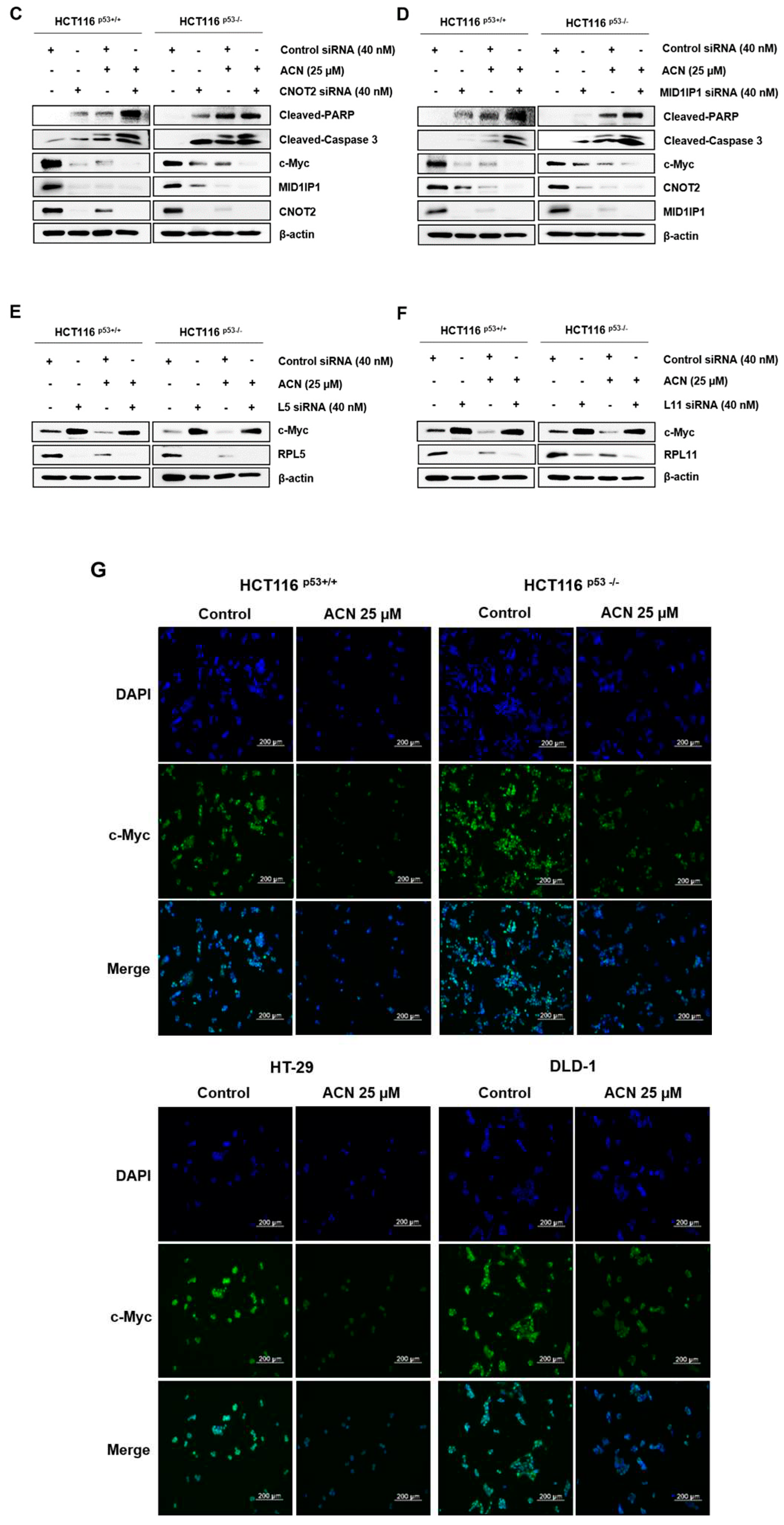
Figure 3A,B). To confirm whether ACN is related to c-Myc through CNOT2 and MID1IP1, we knocked down ACN using siRNA with or without ACN. As shown in
Figure 3C,D, ACN further reduced c-Myc by CNOT2 and MID1IP1 siRNA and strengthened apoptosis by increasing cleaved-PARP and cleaved-caspase3. Additionally, a reduction in MID1IP1 activates L5 and L11, and reduces c-Myc [
11]. ACN inhibits the expression of MID1IP1 and c-Myc, simultaneously, the loss of L5 and L11 reversed the expression of c-Myc reduction to ACN in HCT116
p53+/+ and HCT116
p53-/-, which showed the least expression of c-Myc at 25 µM in four CRC cell lines (
Figure 3E,F). Immunofluorescence staining was performed to confirm the c-Myc expression. The results showed a decrease in c-Myc expression after ACN treatment (
Figure 3G). Collectively, our results demonstrate that c-Myc plays a key role in ACN-induced apoptosis and cell cycle modulation.
2.4. ACN Attenuates c-Myc Stability
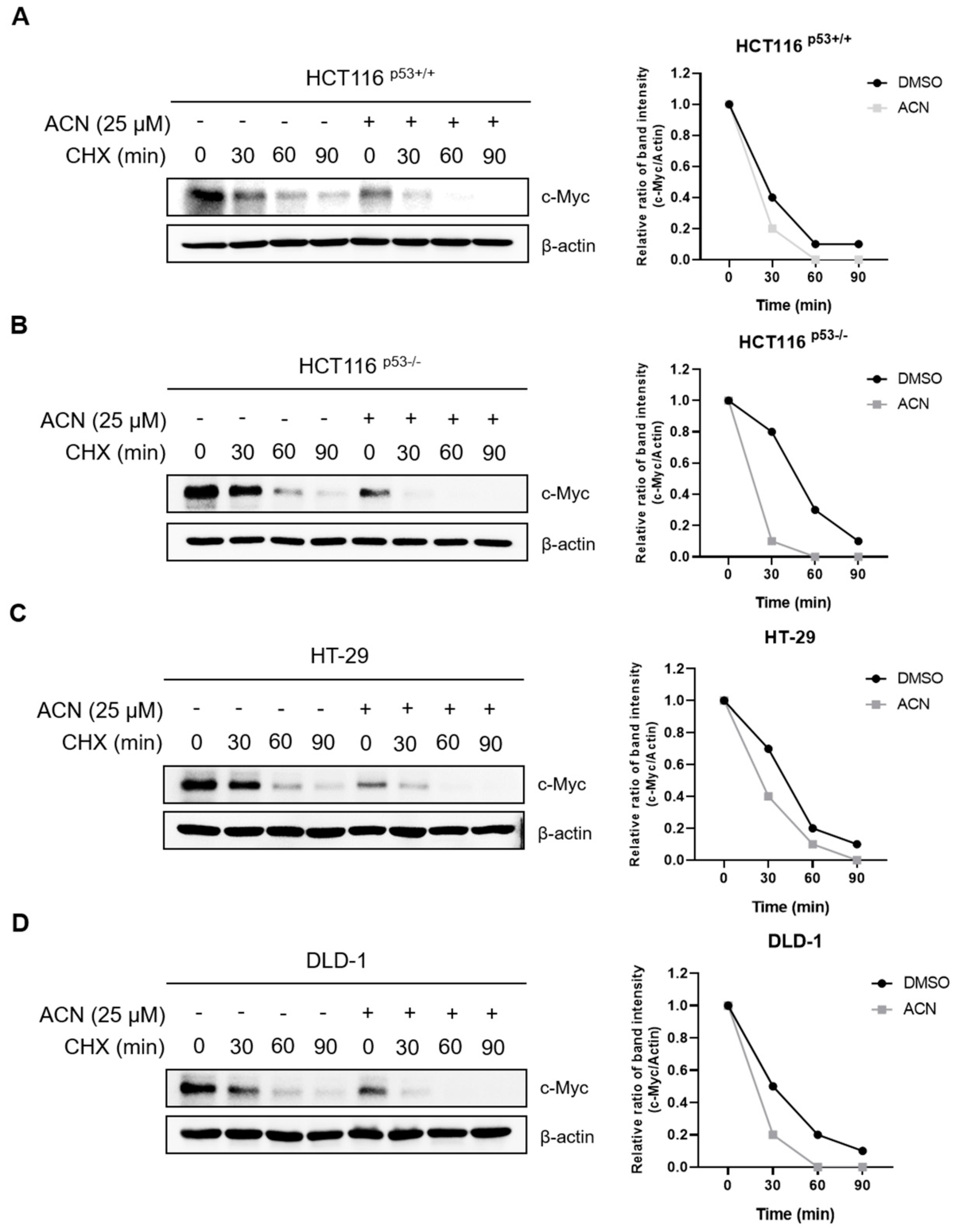
To investigate the effect of ACN on c-Myc stability, a CHX chase analysis was performed. ACN decreased the half-life of c-Myc compared with that in the control group (
Figure 4). These results indicate that ACN regulates the half-life of c-Myc and reduces its expression.
2.5. ACN Regulates Serum Induced c-Myc Stimulation
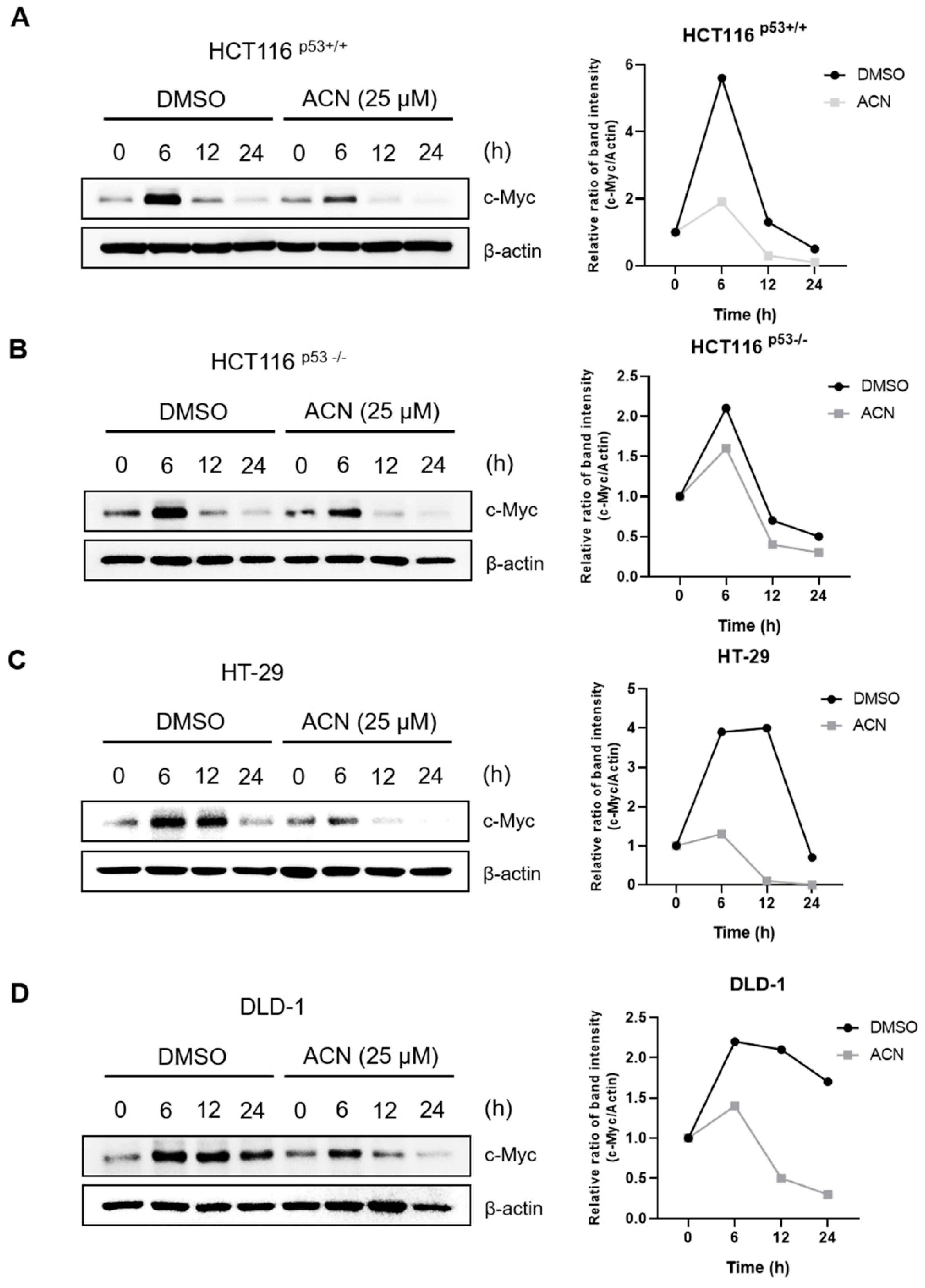
c-Myc expression changes rapidly during serum stimulation. To determine whether ACN affected serum-induced c-Myc stimulation, we compared c-Myc expression after treatment with ACN or DMSO through serum stimulation (
Figure 5). This suggests that ACN rapidly regulates c-Myc expression following serum stimulation.
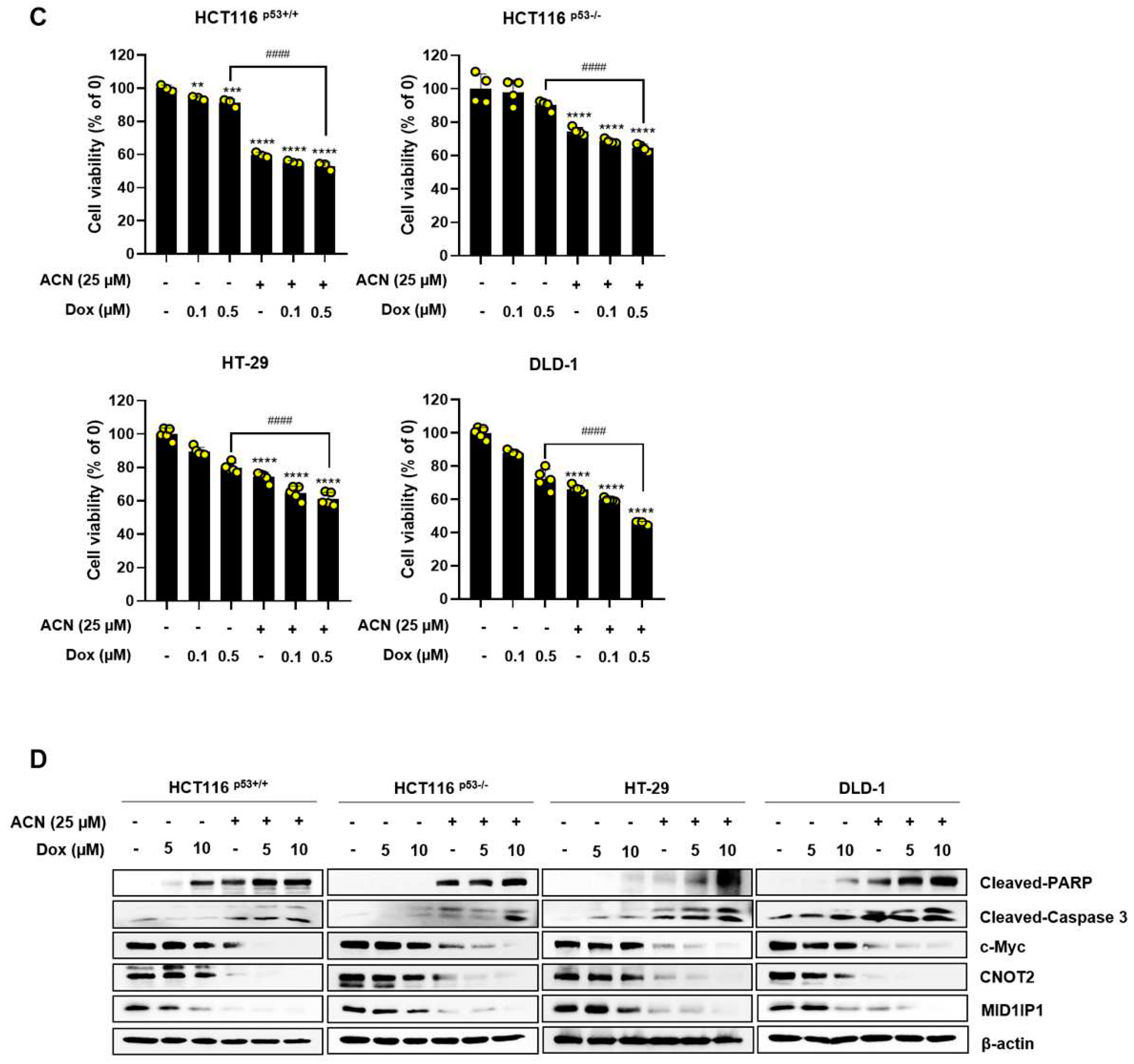
2.6. Potential Effect of ACN with 5-FU or Dox in Colon Cancer Cells
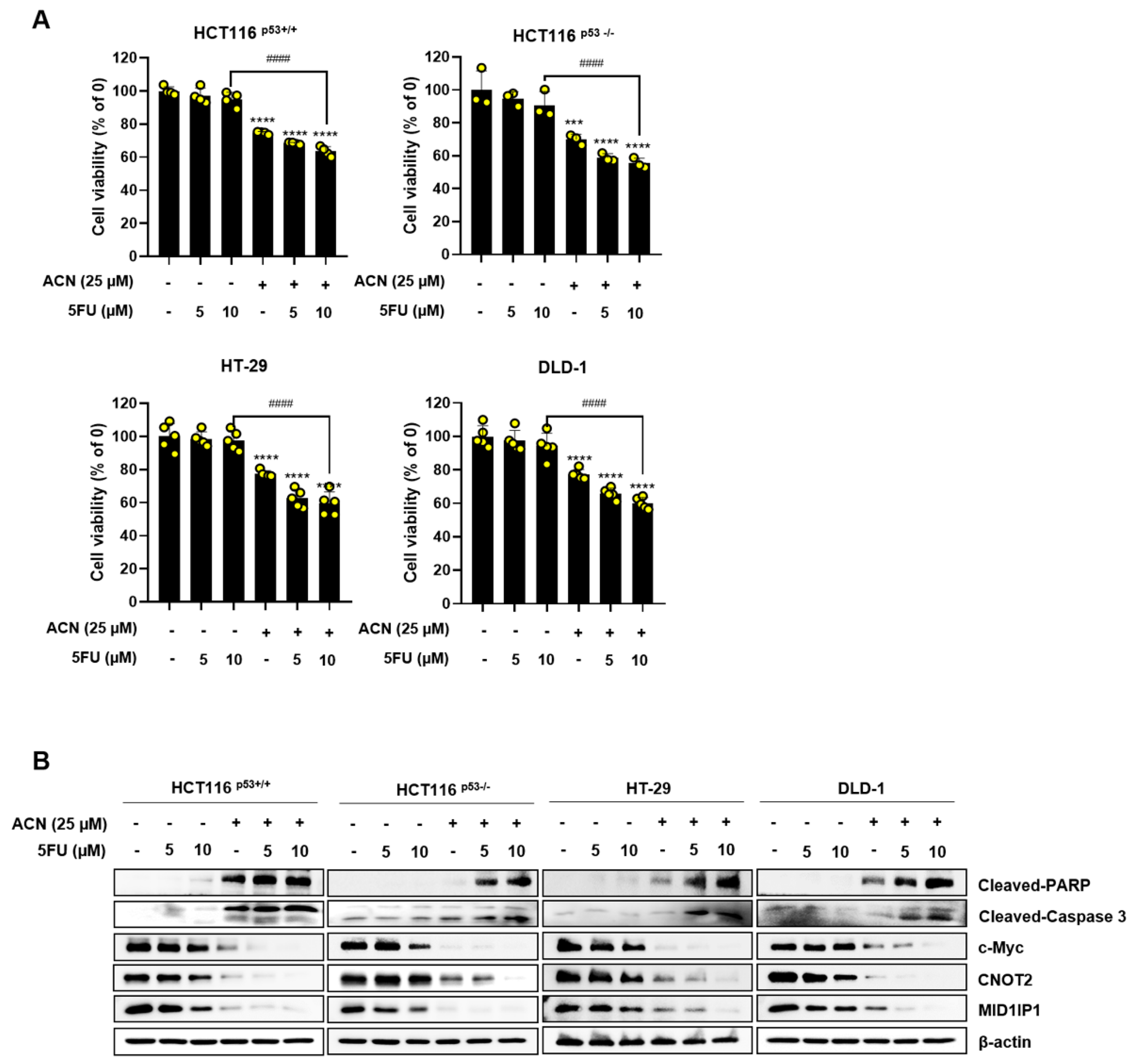
Minimizing side effects by reducing the dose of the anticancer drugs 5-FU and Dox is important. Therefore, we investigated whether the combined effect of ACN could maximize its efficacy using low-dose 5-FU and Dox. The combined treatment significantly reduced cell viability compared to that in the control group (
Figure 6A,C). The combination of anticancer drugs and ACN alleviated c-Myc, MID1IP1, and CNOT2 expression and increased the expression of cleaved-PARP and cleaved-caspase3 compared to the control group (
Figure 6B,D). In conclusion, ACN enhances the combined effect of anticancer drugs in colon cancer cells.
3. Discussion
Despite the development of new treatments for CRC, side effects and drug resistance continue to emerge. Therefore, identifying novel treatments is important. In the present study, we analyzed the anticancer activity of ACN derived from the tubers of C. ambigua in colon cancer cells.
We demonstrated that ACN inhibited cell viability and proliferation in a dose-dependent manner in the human colon cancer cells HCT116+/+, HCT-/-, HT-29, and DLD-1. Our study showed that ACN induces apoptosis by increasing cleaved-PARP and cleaved-caspase3, and inhibits the protein expression of cyclin D1, CDK4, and CDK2, which play a role in regulating cell cycle progression. Downregulation of cell cycle-related proteins suggests the possibility of cell cycle arrest, further contributing to the inhibitory effect of ACN on colon cancer cell growth. In addition, we observed an increase in the cell population in the G2/M phase. In this study, ACN induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in colon cancer cells.
c-Myc is deregulated and highly expressed in human cancers, including colon cancer [
17]. Therefore, the use of c-Myc as a therapeutic strategy is attractive for cancer therapy [
18]. MID1IP1 is regulated by the co-localization of c-Myc, which is mediated by the ribosomal proteins L5, L11, and CNOT2 [
11]. In this study, we observed that ACN is a potential target for anticancer activity via c-Myc regulation. Interestingly, ACN reduced the expression of MID1IP1 and CNOT2 and further increased the expression of cleaved-PARP and cleaved-caspase3, which are related to apoptosis in colon cancer cells when knocked down respectively with ACN. Additionally, ACN quickly regulated the expression of c-Myc induced by serum stimulation.
The commonly used chemotherapeutic drugs, 5-FU and Dox, have dose-limiting toxicity and drug resistance; therefore, a new adjuvant treatment must be developed to overcome these limitations. We observed a significant decrease in cell viability when ACN was used in combination with low doses of 5-FU and Dox. Combination treatment also increased apoptosis and further reduced the expression of the oncogenes c-Myc, CNOT2, and MID1IP1 in colon cancer cells. This suggests that ACN can be used in combination with low-dose 5-FU and Dox to minimize the side effects of chemotherapy and maximize its therapeutic effect.
In conclusion, this study demonstrated the anticancer activity of ACN in colon cancer cells. ACN induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest to inhibit cancer cell growth by inhibiting the c-Myc signaling pathway. These results suggest that ACN can be used for chemotherapy with low-dose 5-FU and Dox.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
ACN was purchased from Chemfaces (Wuhan Chemfaces Biochemical CO., Ltd., China), 5-FU was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), and Dox was purchased from Selleck Chem (Munich, Germany).
4.2. Cell Culture
CCD-18co, HCT116p53+/+, HCT116p53-/-, HT-29, and DLD-1 cells were purchased from the Korean Cell Line Bank (KCLB; Seoul, Republic of Korea). The cell lines were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI)-1640 and supplemented with 1% antibiotics and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C.
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
Cells were distributed in 96-well plates (1 × 104 cells/well) and treated with different concentrations of ACN for 24 h. Cytotoxicity was assessed using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT; Sigma Aldrich Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) assay, and formazan was detected at 570 nm using a microplate reader (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
4.4. Colony Formation Assay
Cells were treated with ACN and each concentration was distributed in six-well plates (1 × 103 cells/well), which were cultivated for 1 week at 5% CO2 and 37 °C. After colony formation, the cells were fixed for 10 min and stained using the Diff-Quick Kit (Sysmex Corporation, Kobe, Hyogo, Japan).
4.5. Western Blotting
Immunoblotting was performed as described previously [
19]. Briefly, ACN-treated cells (1 × 10
4 cells/well) were lysed in lysis buffer (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA, USA). Protein samples were separated using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The antibodies used were as follows: cleaved-PARP, cleaved-caspase 3, CNOT2 (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA, USA), MID1IP1 (ProteinTech Antibody Group, Chicago, IL, USA), c-Myc (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), and β-actin (Cat No. sc-47778). These antibodies were diluted in tris-buffered saline + 0.1% Tween 20 (TBST; 1:1000) and incubated at 4 °C overnight. The horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies (cat. sc-516102 and sc-2004) was incubated for 1 h and detected using an ImageQuant LAS 500 (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Sydney, Australia).
4.6. Cell Cycle Analysis by Flow Cytometry
Cells were distributed in six-well plates (2 × 105 cells/well) and treated with or without ACN. After being treated for 24 h, cells were washed twice with PBS, and fixed in 70% precooled ethanol for 3 h. Then, cells were resuspended in RNase A (100 µg/mL) and PI (50 µg/mL) for 20 min. The samples were analyzed using NovoCyte flow cytometery (ACEA Biosciences, San Diego, CA, USA).
4.7. Annexin V/propidium Iodide (PI) Assay
The drug-treated cells (2 × 105 cells/well) were harvested using trypsin and washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Subsequently, the cells were suspended in binding buffer containing fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-tagged annexin V and PI for 15 min. A FACSCanto II flow cytometery (BD Biosciences, Becton-Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) was used to analyze apoptosis.
4.8. Cycloheximide (CHX) Chase Assay for c-Myc Stability
Cells were distributed in six-well plates (2 × 105 cells/well) and exposed to 25 µM of ACN. Then, the protein synthesis inhibitor CHX (50 µg/mL) was added for 0, 30, 60, and 90 min. Western blotting was performed to confirm the expression of c-Myc and β-actin.
4.9. Serum Stimulation for c-Myc Induction
Cells were distributed in six-well plates (2 × 105 cells/well) and starved in serum-free medium for 24 h. Subsequently, 25 µM of ACN diluted 20% FBS was incubated and cells were harvested at 0, 6, 12, and 24 h. c-Myc and β-actin protein expression levels were measured using western blotting.
4.10. Immunofluorescence Assay
Cells were distributed in two-well culture slides (1 × 105 cells/well) and treated with or without ACN for 24 h. Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min and permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 at room temperature. A antibody against c-Myc (1:200; Abcam Cambridge, UK) was incubated overnight at 4 °C, then incubated with Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit IgG antibody (1:500; Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) for 1 h. Next, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was used for staining nuclei and observed using CELENATM S Digital Imaging System (Logos Biosystems, Inc. Anyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, South Korea).
4.11. Gene Silencing Using Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)
Cells were seeded in six-well plates (7 × 104 cells/well) and transfected with control, CNOT2, MID1IP1, RPL5, or RPL11 siRNAs (Bioneer, Daejeon, Korea) using INTERFERin (Polyplus-transfection SA, France), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After 48 h, the protein levels were detected using western blotting.
4.12. Statistical Analysis
All data were repeated at least thrice and expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). The Student’s t-test was performed to compare two groups, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Dunnett’s test was performed for multiple groups. GraphPad Prism software (version 8.0; San Diego, CA, USA) was used to determine the statistical significance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Y.-R.P. and H.-J.J.; methodology: Y.-R.P.; data curation: Y.-R.P., W.J., J.H.J. and H.-J.J.; original draft preparation: Y.-R.P.; and writing—review and editing: Y.-R.P., W.J., S.-M.P., S.W.K., H.B., J.H.J. and H.-J.J. All authors have read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea, funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2021R1F1A1058698).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the members of the Jang Laboratory for their active discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.J.; Pigula, M.; Baglo, Y.; Najafali, D.; Hasan, T.; Huang, H.-C. Breaking the selectivity-uptake trade-off of photoimmunoconjugates with nanoliposomal irinotecan for synergistic multi-tier cancer targeting. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Rabou, A.A.; Ahmed, H.H.; Shalby, A.B. Selenium Overcomes Doxorubicin Resistance in Their Nano-platforms Against Breast and Colon Cancers. Biological Trace Element Research 2020, 193, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, T.R.; Sabò, A.; Amati, B. MYC: connecting selective transcriptional control to global RNA production. Nature Reviews Cancer 2015, 15, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, B.; Liebermann, D.A. , Apoptotic signaling by c-MYC. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6462–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, C.V. c-Myc target genes involved in cell growth, apoptosis, and metabolism. Molecular and cellular biology 1999, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, E.J.; Jung, D.-B.; Lee, H.; Han, I.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.-H. CNOT2 promotes proliferation and angiogenesis via VEGF signaling in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Letters 2018, 412, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jung, J.H.; Hwang, J.; Park, J.E.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, W.Y.; Suh, J.Y.; Kim, S.-H. CNOT2 Is Critically Involved in Atorvastatin Induced Apoptotic and Autophagic Cell Death in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. Cancers 2019, 11, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Sim, D.Y.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, S.-H. Hypolipogenic Effect of Shikimic Acid Via Inhibition of MID1IP1 and Phosphorylation of AMPK/ACC. International journal of molecular sciences 2019, 20, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Sim, D.Y.; Im, E.; Kim, S.; Chang, S.; Kim, S.-H. Colocalization of MID1IP1 and c-Myc is Critically Involved in Liver Cancer Growth via Regulation of Ribosomal Protein L5 and L11 and CNOT2. Cells 2020, 9, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.-H.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-S.; Tsai, R.-T.; Liu, S.-P.; Chang, W.-L.; Lin, H.-L.; Lu, C.-H.; Wei, J.-R.; Wang, Z.-W.; Shyu, W.-C.; Lin, S.-Z. Acetylcorynoline attenuates dopaminergic neuron degeneration and α-synuclein aggregation in animal models of Parkinson's disease. Neuropharmacology 2014, 82, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Liao, J.-M.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, S.; Nguyen, D.; Hao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Cao, B.; Kim, S.-H.; Lu, H. Inauhzin(c) Inactivates c-Myc Independently of p53. Cancer Biology & Therapy 2015, 16, 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Stine, Z.E.; Walton, Z.E.; Altman, B.J.; Hsieh, A.L.; Dang, C.V. MYC, Metabolism, and Cancer. Cancer Discovery 2015, 5, 1024–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, D.; Ko, H.M.; Jang, H.-J. Inhibition of CNOT2 Induces Apoptosis via MID1IP1 in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Activating p53. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xianjun, F.; Xirui, X.; Jie, T.; Huiwen, M.; Shaojun, Z.; Qiaoyun, L.; Yunxin, L.; Xuqun, S. Momordin Ic induces G0/1 phase arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cells by suppressing SENP1/c-MYC signaling pathway. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2021, 146, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, C.V. MYC on the Path to Cancer. Cell 2012, 149, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J.; O'Grady, S.; Tang, M.; Crown, J. MYC as a target for cancer treatment. Cancer Treatment Reviews 2021, 94, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codenotti, S.; Poli, M.; Asperti, M.; Zizioli, D.; Marampon, F.; Fanzani, A. Cell growth potential drives ferroptosis susceptibility in rhabdomyosarcoma and myoblast cell lines. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology 2018, 144, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).