Submitted:
01 November 2023
Posted:
09 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Natural active ingredients
3. Skin structure
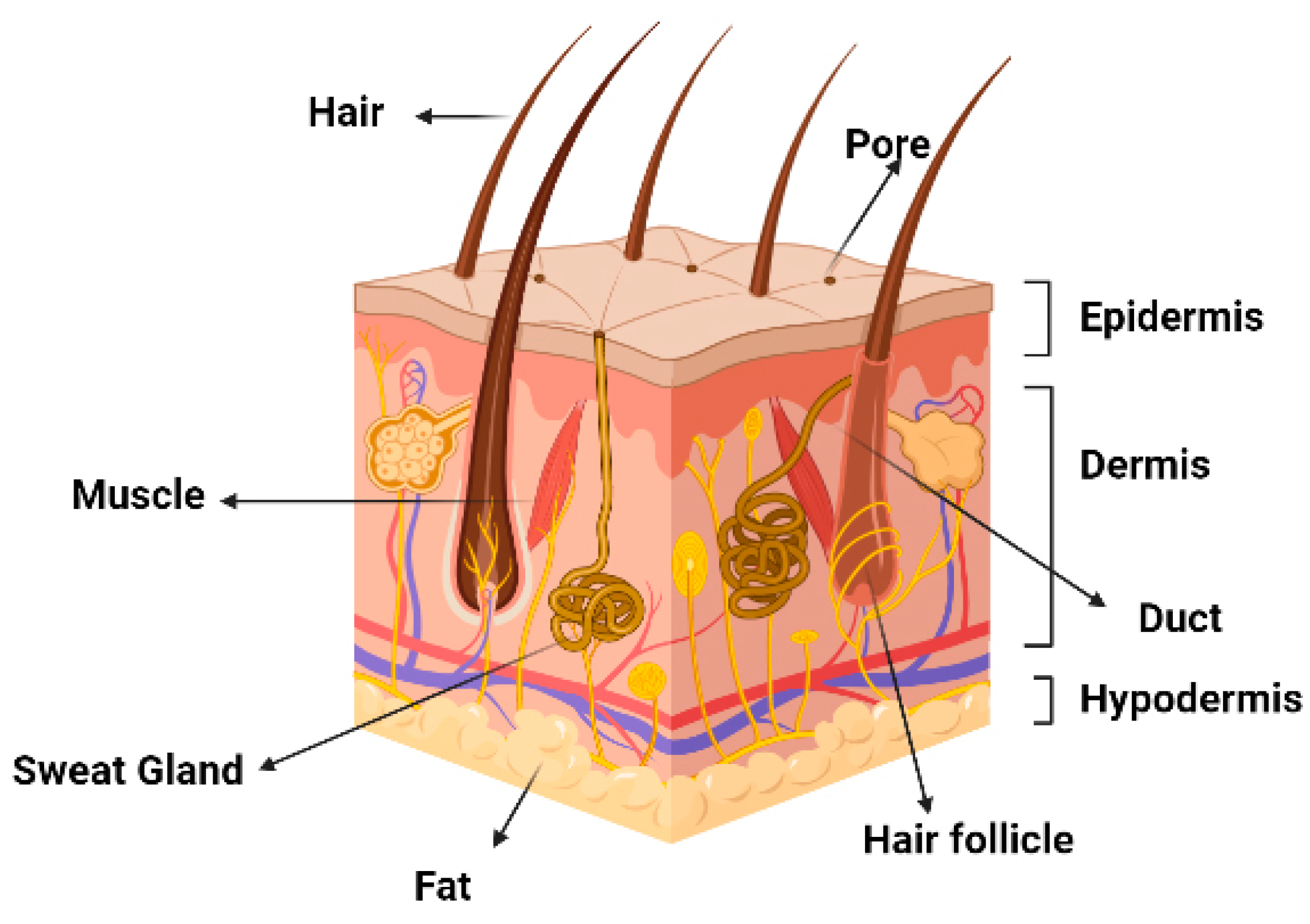
3.1. Keratinocytes
3.2. Fibroblasts
3.2.1. Collagen
3.2.2. Elastin
3.2.3. Hyaluronic Acid
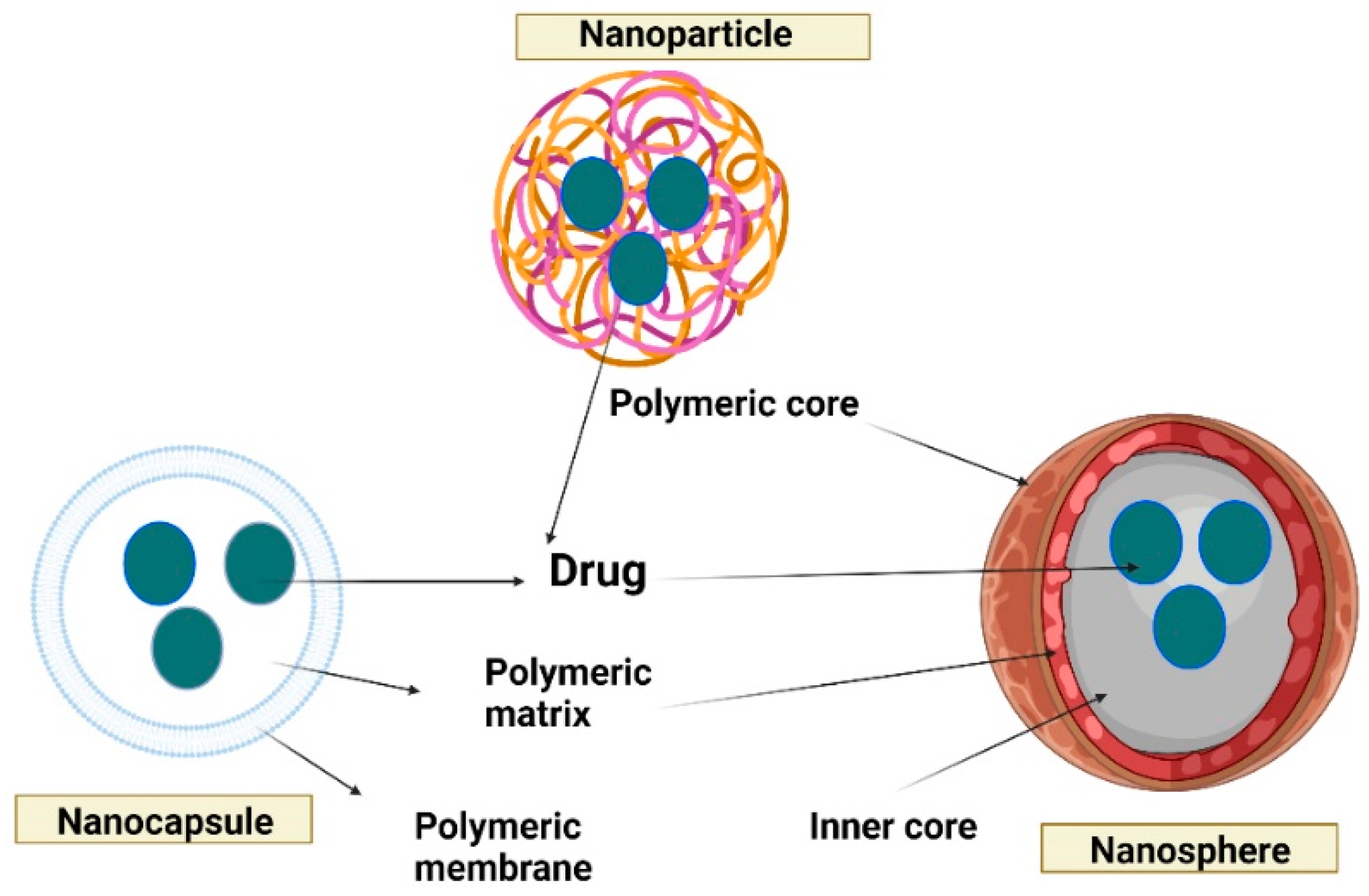
4. Encapsulation methods
5.1. Polymer-based nanoparticles
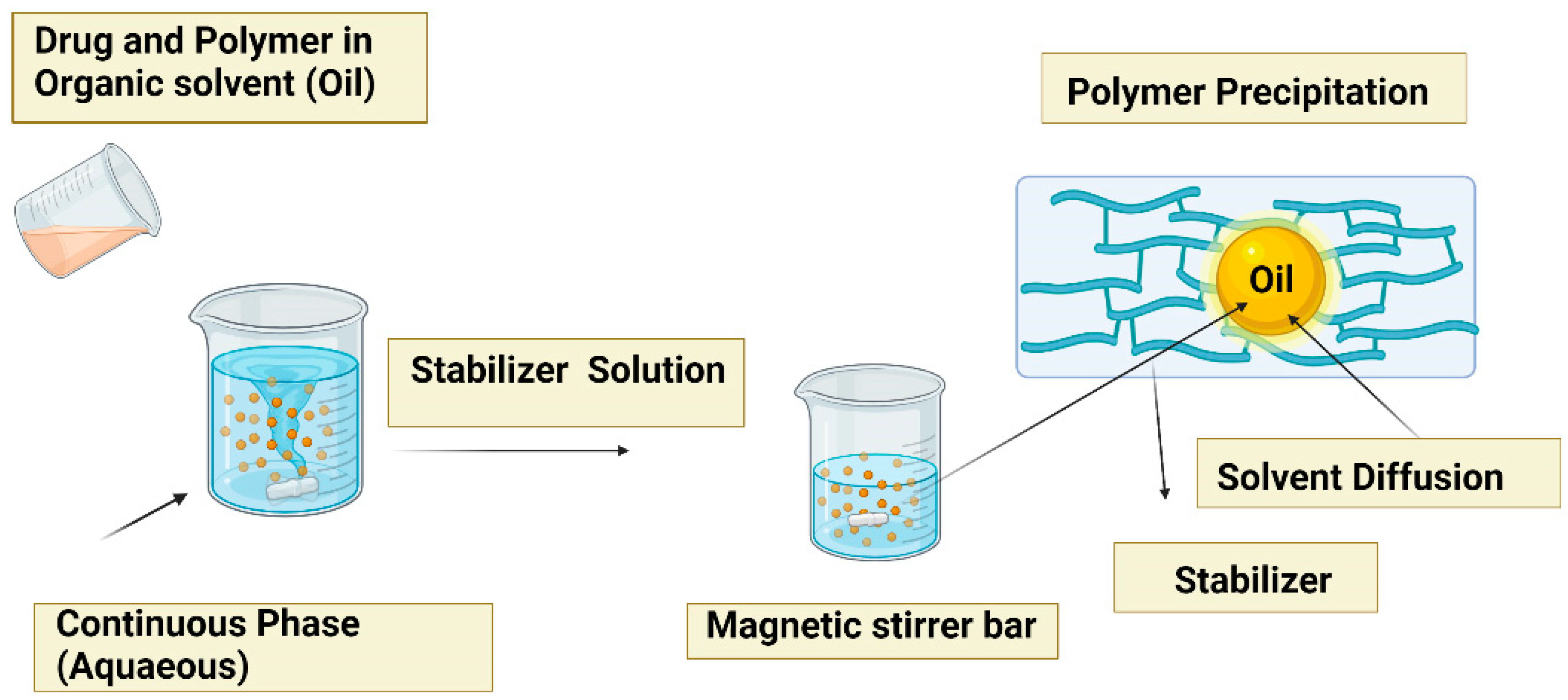
5.2. Nanoprecipitation method
5.3. Simple emulsion evaporation method
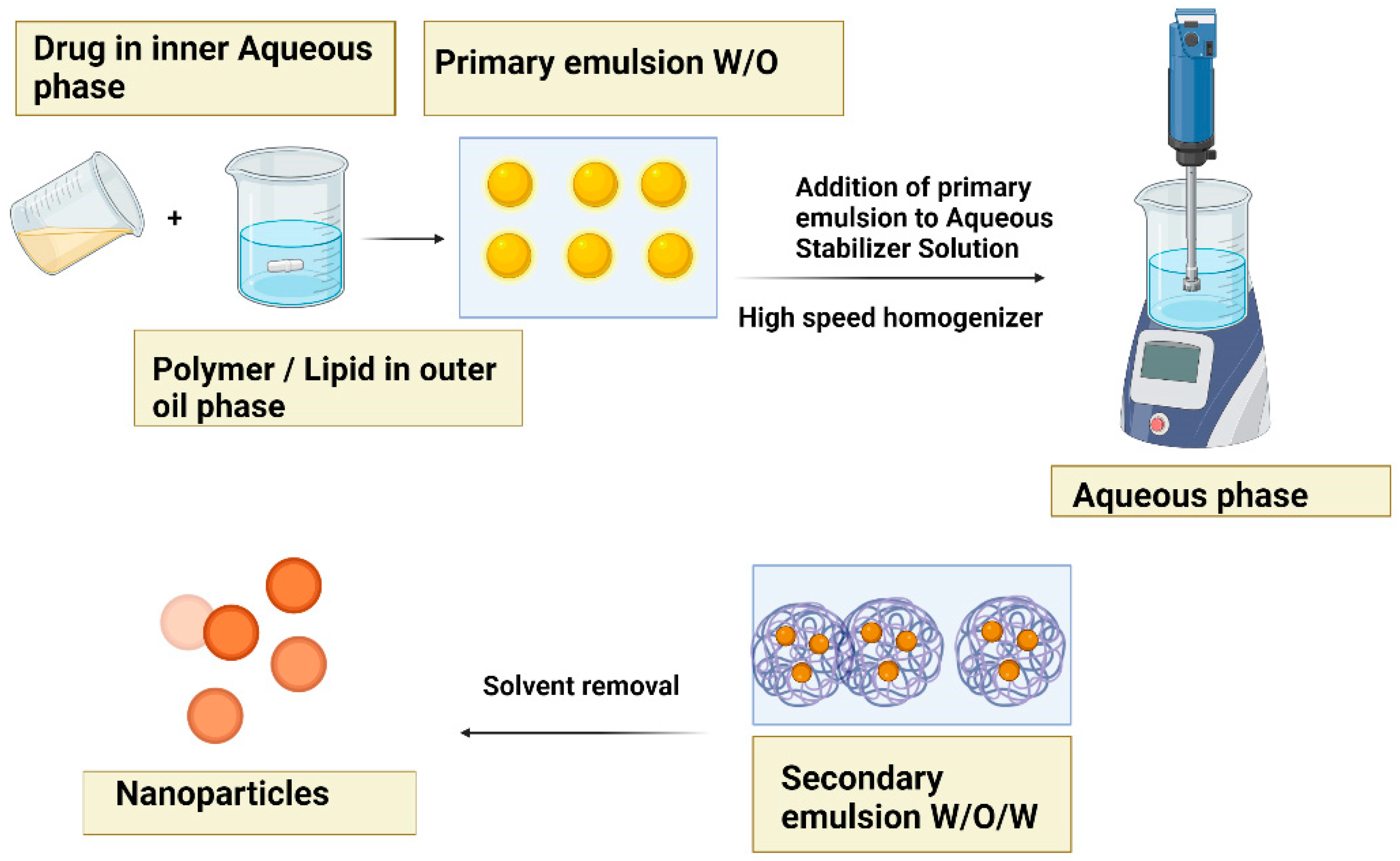
5.4. Double emulsion evaporation method
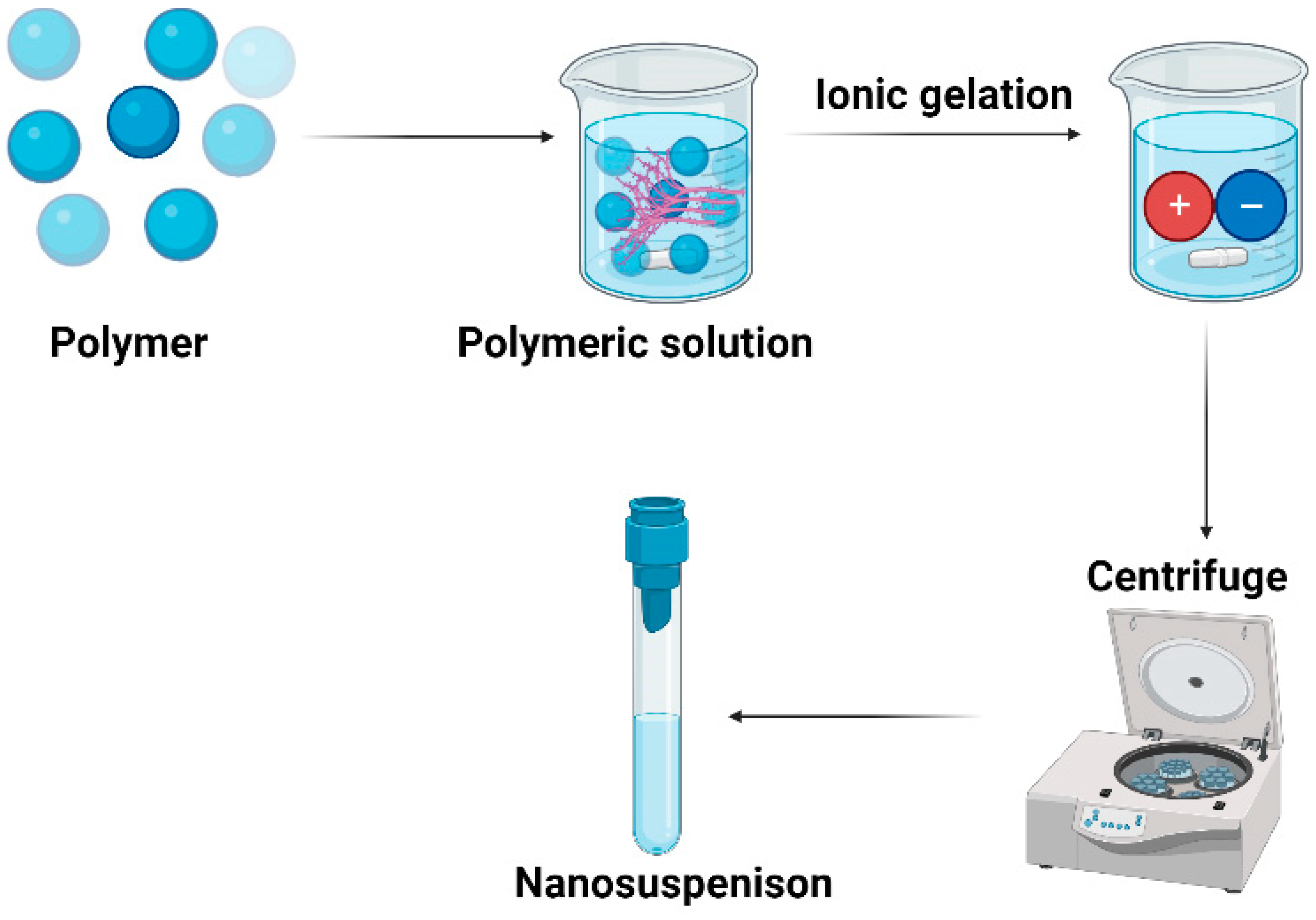
5.5. Ionic gelation
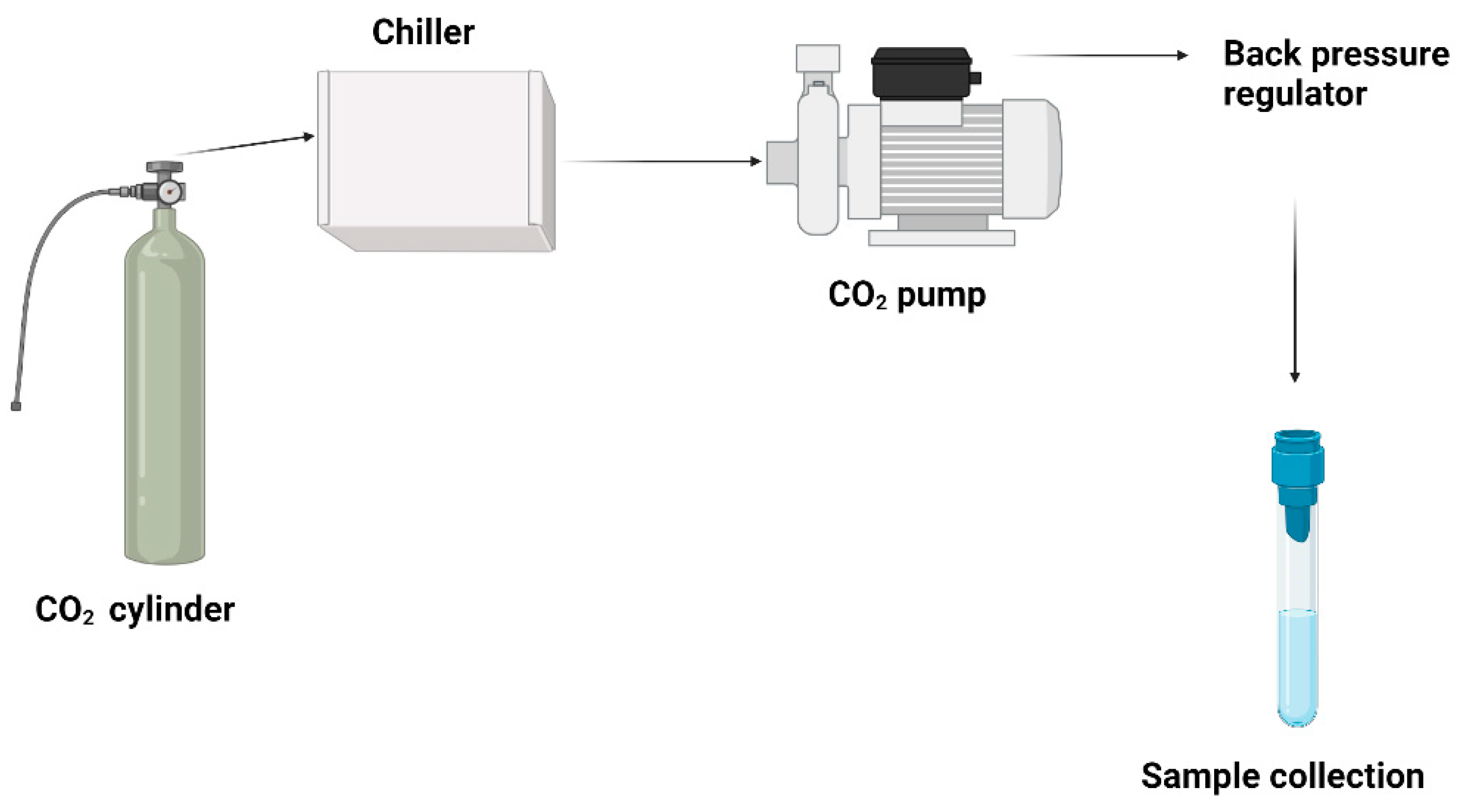
5.6. Supercritical fluid method
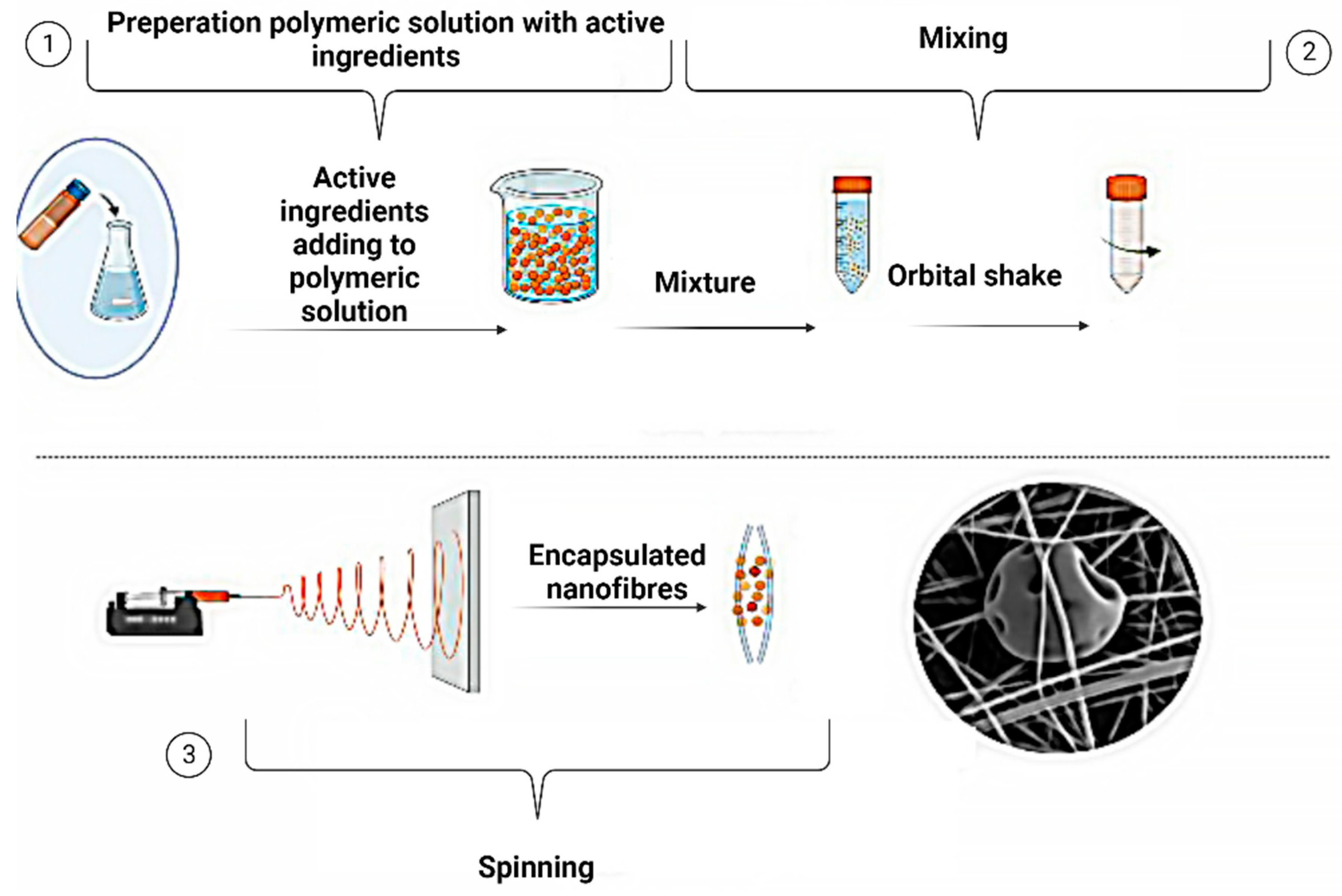
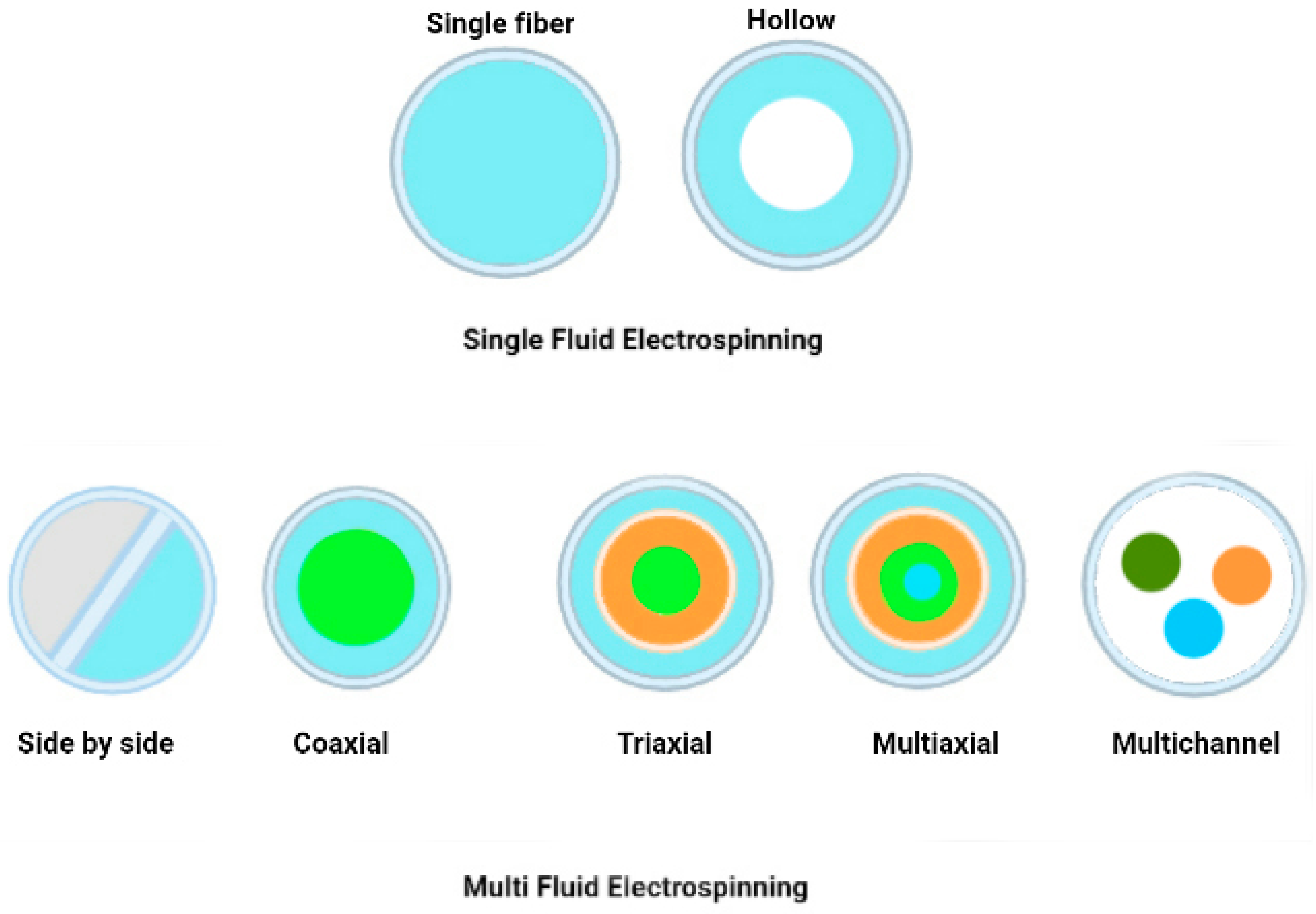
6. Electrospinning for encapsulated active ingredients
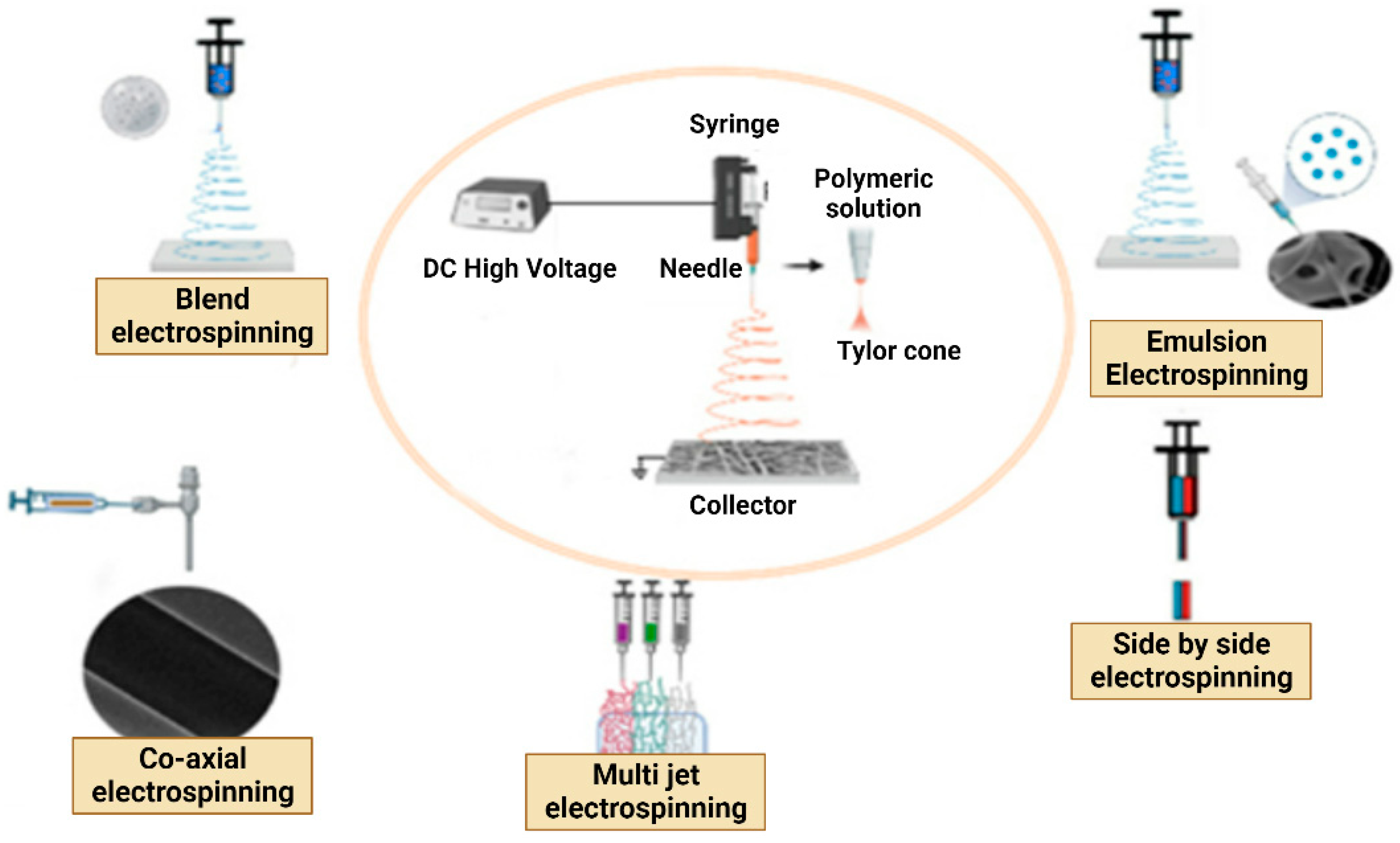
6.1. Electrospinning methods
6.1.1. Single Fluid Electrospinning
- Blend Electrospinning
- Emulsion Electrospinning
6.1.2. Multi-Fluid Electrospinning
- Multi-Jet Electrospinning
- Side-by-Side Electrospinning
6.1.3. Coaxial/Multiaxial Electrospinning
7. Applications of electrospun nanofiber-encapsulated ingredients in the cosmetic industry
8. Conclusions, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Abbreviations
| APIs: | Active pharmaceutical ingredients |
| BCC: | Basal Cell Carcinoma |
| BSTI | Baumann Skin Type Index |
| BSTS | Baumann Skin Type System |
| CIR: | Cosmetic Ingredient Review |
| CMCS: | carboxymethyl chitosan |
| CO2: | Carbon dioxide |
| DRNT | Dry, Resistant, Non-Pigmented, Tight skin |
| DRNW: | Dry-Resistant Non-Pigmented Wrinkled |
| DRPT | Dry, Resistant, Pigmented, Tight skin |
| DRPW: | Dry-Resistant Pigmented Wrinkled |
| DSNT | Dry, Sensitive, Non-Pigmented, Tight skin |
| DSNW | Dry, Sensitive, Non-Pigmented, Wrinkle-Prone skin |
| DSPT | Dry, Sensitive, Pigmented, Wrinkle-Prone/Tight skin |
| DSPW | Dry, Sensitive, Pigmented, Wrinkle-Prone skin |
| EC: | ethyl cellulose |
| FDA: | US Food and Drug Administration |
| HA: | Hyaluronic acid |
| INCI: | International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients |
| nm: | Nanometre |
| NMF: | natural moisturising factor |
| NPA: | Natural Products Association |
| O/W/O: | Oil-in-water-in-oil |
| O/W: | Oil-in-water |
| ORNW: | Oily, Resistant, Non-Pigmented, Wrinkle-Prone skin |
| ORPT: | Oily, Resistant, Pigmented, Tight skin |
| ORPW: | Oily, Resistant, Pigmented, Wrinkle-Prone skin |
| OSNT: | Oily, Sensitive, Non-Pigmented, Tight skin |
| OSNW: | Oily, Sensitive, Non-Pigmented, Wrinkle-Prone skin |
| OSPT: | Oily, Sensitive, Pigmented, Tight skin |
| OSPW: | Oily, Sensitive, Pigmented, Wrinkle-Prone skin |
| OTC: | Over-the-counter |
| PAR-2: | Protease-activated receptor-2 |
| PCL: | polycaprolactone |
| PEG: | Polyethylene Glycol |
| pH: | potential of hydrogen |
| PLA: | Poly (lactic acid) |
| PLA: | Polylactic acid |
| PVA: | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PVP: | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| SA: | Sodium alginate |
| SC: | Stratum Corneum |
| SCC: | Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| SLES: | Sodium lauryl ether sulphate |
| SLS: | Sodium lauryl sulphate |
| SPF: | Sun Protection Factor |
| TEWL: | Trans-epidermal Water Loss |
| UV: | Ultraviolet |
| UVA: | Ultraviolet A |
| UVB: | Ultraviolet B |
| VOC: | Volatile Organic CompoundFormun Üstü |
| W/O/W: | Water-in-oil-in-water |
| W/O: | Water-in-oil |
References
- Gupta V, Mohapatra S, Mishra H, Farooq U, Kumar K, Ansari MJ, et al. Nanotechnology in Cosmetics and Cosmeceuticals—A Review of Latest Advancements. Gels 2022;8:173. [CrossRef]
- Bayda S, Adeel M, Tuccinardi T, Cordani M, Rizzolio F. The History of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: From Chemical–Physical Applications to Nanomedicine. Molecules 2019;25:112. [CrossRef]
- Qiao L, Han M, Gao S, Shao X, Wang X, Sun L, et al. Research progress on nanotechnology for delivery of active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicines. J Mater Chem B 2020;8:6333–51. [CrossRef]
- Salvioni L, Morelli L, Ochoa E, Labra M, Fiandra L, Palugan L, et al. The emerging role of nanotechnology in skincare. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2021;293:102437. [CrossRef]
- Liu J-K. Natural products in cosmetics. Nat Prod Bioprospect 2022;12:40. [CrossRef]
- Chauhan A, Chauhan C. Emerging trends of nanotechnology in beauty solutions: A review. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021. [CrossRef]
- Kaur A, Singh TG, Dhiman S, Arora S, Babbar R. NOVEL HERBS USED IN COSMETICS FOR SKIN AND HAIR CARE : A REVIEW n.d.
- Mohd-Setapar SH, John CP, Mohd-Nasir H, Azim MM, Ahmad A, Alshammari MB. Application of Nanotechnology Incorporated with Natural Ingredients in Natural Cosmetics. Cosmetics 2022;9:110. [CrossRef]
- Bowe WP, Pugliese S. Cosmetic benefits of natural ingredients. J Drugs Dermatol 2014;13:1021–5; quiz 26–7.
- Dini I, Laneri S. The New Challenge of Green Cosmetics: Natural Food Ingredients for Cosmetic Formulations. Molecules 2021;26:3921. [CrossRef]
- Costa EF, Magalhães WV, Di Stasi LC. Recent Advances in Herbal-Derived Products with Skin Anti-Aging Properties and Cosmetic Applications. Molecules 2022;27:7518. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen AV, Soulika AM. The Dynamics of the Skin’s Immune System. Int J Mol Sci 2019;20:1811. [CrossRef]
- Juliano C, Magrini GA. Cosmetic Functional Ingredients from Botanical Sources for Anti-Pollution Skincare Products. Cosmetics 2018;5:19. [CrossRef]
- Rodan K, Fields K, Majewski G, Falla T. Skincare Bootcamp: The Evolving Role of Skincare. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2016;4:e1152. [CrossRef]
- Thibane VS, Ndhlala AR, Abdelgadir HA, Finnie JF, Staden JV. The cosmetic potential of plants from the Eastern Cape Province traditionally used for skincare and beauty. South African Journal of Botany 2019;122:475–83. [CrossRef]
- Hoang HT, Moon J-Y, Lee Y-C. Natural Antioxidants from Plant Extracts in Skincare Cosmetics: Recent Applications, Challenges and Perspectives. Cosmetics 2021;8:106. [CrossRef]
- Dlova NC, Hamed SH, Tsoka-Gwegweni J, Grobler A. Skin lightening practices: an epidemiological study of South African women of African and Indian ancestries. British Journal of Dermatology 2015;173:2–9. [CrossRef]
- Kumar V. Perspective of Natural Products in Skincare. PPIJ 2016;4. [CrossRef]
- He H, Li A, Li S, Tang J, Li L, Xiong L. Natural components in sunscreens: Topical formulations with sun protection factor (SPF). Biomed Pharmacother 2021;134:111161. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed IA, Mikail MA, Zamakshshari N, Abdullah A-SH. Natural anti-aging skincare: role and potential. Biogerontology 2020;21:293–310. [CrossRef]
- Verdier-Sévrain S, Bonté F. Skin hydration: a review on its molecular mechanisms. J Cosmet Dermatol 2007;6:75–82. [CrossRef]
- Hu X, He H. A review of cosmetic skin delivery. J Cosmet Dermatol 2021;20:2020–30. [CrossRef]
- Zeng Q, Qi X, Shi G, Zhang M, Haick H. Wound Dressing: From Nanomaterials to Diagnostic Dressings and Healing Evaluations. ACS Nano 2022;16:1708–33. [CrossRef]
- Antonio JR, Antônio CR, Cardeal ILS, Ballavenuto JMA, Oliveira JR. Nanotechnology in dermatology. An Bras Dermatol 2014;89:126–36. [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Silva M, Martins AM, Sousa-Oliveira I, Ribeiro HM, Veiga F, Marto J, et al. Nanomaterials in hair care and treatment. Acta Biomater 2022;142:14–35. [CrossRef]
- He M, Zhang W, Liu Z, Zhou L, Cai X, Li R, et al. The interfacial interactions of nanomaterials with human serum albumin. Anal Bioanal Chem 2022;414:4677–84. [CrossRef]
- Puglia C, Santonocito D. Cosmeceuticals: Nanotechnology-Based Strategies for the Delivery of Phytocompounds. Curr Pharm Des 2019;25:2314–22. [CrossRef]
- Santos AC, Panchal A, Rahman N, Pereira-Silva M, Pereira I, Veiga F, et al. Evolution of Hair Treatment and Care: Prospects of Nanotube-Based Formulations. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2019;9:903. [CrossRef]
- Ratz-Łyko A, Arct J, Pytkowska K. Moisturizing and Anti-inflammatory Properties of Cosmetic Formulations Containing Centella asiatica Extract. Indian J Pharm Sci 2016;78:27–33.
- Surjushe A, Vasani R, Saple DG. Aloe vera: a short review. Indian J Dermatol 2008;53:163–6. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava JK, Shankar E, Gupta S. Chamomile: A herbal medicine of the past with bright future. Mol Med Rep 2010;3:895–901. [CrossRef]
- Preethi KC, Kuttan R. Wound healing activity of flower extract of Calendula officinalis. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 2009;20:73–9. [CrossRef]
- Kim HM, Cho SH. Lavender oil inhibits immediate-type allergic reaction in mice and rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 1999;51:221–6. [CrossRef]
- Evangelista MTP, Abad-Casintahan F, Lopez-Villafuerte L. The effect of topical virgin coconut oil on SCORAD index, transepidermal water loss, and skin capacitance in mild to moderate pediatric atopic dermatitis: a randomised, double-blind, clinical trial. Int J Dermatol 2014;53:100–8. [CrossRef]
- Pazyar N, Yaghoobi R, Ghassemi MR, Kazerouni A, Rafeie E, Jamshydian N. Jojoba in dermatology: a succinct review. G Ital Dermatol Venereol 2013;148:687–91.
- Lin T-K, Zhong L, Santiago JL. Anti-Inflammatory and Skin Barrier Repair Effects of Topical Application of Some Plant Oils. Int J Mol Sci 2017;19:70. [CrossRef]
- Villa C, Trucchi B, Gambaro R, Baldassari S. Green procedure for the preparation of scented alcohols from carbonyl compounds. Int J Cosmet Sci 2008;30:139–44. [CrossRef]
- Jose A, Mahey R, Sharma JB, Bhatla N, Saxena R, Kalaivani M, et al. Comparison of ferric Carboxymaltose and iron sucrose complex for treatment of iron deficiency anemia in pregnancy- randomised controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019;19:54. [CrossRef]
- Thring TS, Hili P, Naughton DP. Antioxidant and potential anti-inflammatory activity of extracts and formulations of white tea, rose, and witch hazel on primary human dermal fibroblast cells. J Inflamm (Lond) 2011;8:27. [CrossRef]
- Tang S-C, Yang J-H. Dual Effects of Alpha-Hydroxy Acids on the Skin. Molecules 2018;23:863. [CrossRef]
- Telang PS. Vitamin C in dermatology. Indian Dermatol Online J 2013;4:143–6. [CrossRef]
- Gold MH. Use of hyaluronic acid fillers for the treatment of the aging face. Clin Interv Aging 2007;2:369–76.
- Silverberg JI, Jagdeo J, Patel M, Siegel D, Brody N. Green tea extract protects human skin fibroblasts from reactive oxygen species induced necrosis. J Drugs Dermatol 2011;10:1096–101.
- Mukherjee S, Date A, Patravale V, Korting HC, Roeder A, Weindl G. Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety. Clin Interv Aging 2006;1:327–48.
- Arif T. Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: a comprehensive review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2015;8:455–61. [CrossRef]
- Pazyar N, Yaghoobi R, Bagherani N, Kazerouni A. A review of applications of tea tree oil in dermatology. Int J Dermatol 2013;52:784–90. [CrossRef]
- Lin P-H, Sermersheim M, Li H, Lee PHU, Steinberg SM, Ma J. Zinc in Wound Healing Modulation. Nutrients 2017;10:16. [CrossRef]
- Kohl E, Steinbauer J, Landthaler M, Szeimies R-M. Skin ageing. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2011;25:873–84. [CrossRef]
- Baumann L. Skin ageing and its treatment. J Pathol 2007;211:241–51. [CrossRef]
- Bellu E, Medici S, Coradduzza D, Cruciani S, Amler E, Maioli M. Nanomaterials in Skin Regeneration and Rejuvenation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021;22. [CrossRef]
- Fletcher JR. Anti-aging technoscience & the biologization of cumulative inequality: Affinities in the biopolitics of successful aging. J Aging Stud 2020;55:100899. [CrossRef]
- Arora N, Agarwal S, Rayasa M. Latest Technology Advances in Cosmaceuticals. Int J Pharm Sci Drug Res 2012;4.
- Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Istanbul Altınbaş University, Istanbul, Turkey, Otlatici G, Yegen G, Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Istanbul Altınbaş University, Istanbul, Turkey, Gungor S, Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Istanbul University, 34116, Istanbul, Turkey, et al. Overview on nanotechnology based cosmeceuticals to prevent skin aging. Istanbul J Pharm 2019;48:55–62. [CrossRef]
- Farage MA, Miller KW, Elsner P, Maibach HI. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors in skin ageing: a review. International Journal of Cosmetic Science 2008;30:87–95. [CrossRef]
- Mazur A, Holthoff E, Vadali S, Kelly T, Post SR. Cleavage of Type I Collagen by Fibroblast Activation Protein-α Enhances Class A Scavenger Receptor Mediated Macrophage Adhesion. PLoS One 2016;11:e0150287. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed YH, Moghimi HR, Yousef SA, Chandrasekaran NC, Bibi CR, Sukumar SC, et al. Efficacy, Safety and Targets in Topical and Transdermal Active and Excipient Delivery. Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers Drug Penetration Into/Through the Skin 2017:369–91. [CrossRef]
- Patra JK, Das G, Fraceto LF, Campos EVR, Rodriguez-Torres M del P, Acosta-Torres LS, et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J Nanobiotechnology 2018;16:71. [CrossRef]
- Souto EB, Fernandes AR, Martins-Gomes C, Coutinho TE, Durazzo A, Lucarini M, et al. Nanomaterials for Skin Delivery of Cosmeceuticals and Pharmaceuticals. Applied Sciences 2020;10:1594. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee B. Nanosize drug delivery system. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2013;14:1221. [CrossRef]
- Souto EB, Fangueiro JF, Fernandes AR, Cano A, Sanchez-Lopez E, Garcia ML, et al. Physicochemical and biopharmaceutical aspects influencing skin permeation and role of SLN and NLC for skin drug delivery. Heliyon 2022;8:e08938. [CrossRef]
- Ganceviciene R, Liakou AI, Theodoridis A, Makrantonaki E, Zouboulis CC. Skin anti-aging strategies. Dermatoendocrinol 2012;4:308–19. [CrossRef]
- Rajpoot K. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: A Promising Nanomaterial in Drug Delivery. Curr Pharm Des 2019;25:3943–59. [CrossRef]
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P. Epidermis and Its Renewal by Stem Cells. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th edition, Garland Science; 2002.
- Eckhart L, Lippens S, Tschachler E, Declercq W. Cell death by cornification. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 2013;1833:3471–80. [CrossRef]
- Brenner M, Hearing VJ. The Protective Role of Melanin Against UV Damage in Human Skin. Photochem Photobiol 2008;84:539–49. [CrossRef]
- Baker LB. Physiology of sweat gland function: The roles of sweating and sweat composition in human health. Temperature (Austin) 2019;6:211–59. [CrossRef]
- Romanovsky AA. Skin temperature: its role in thermoregulation. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2014;210:498–507. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim AAE, Bagherani N, Smoller BR, Reyes-Baron C, Bagherani N. Functions of the Skin. In: Smoller B, Bagherani N, editors. Atlas of Dermatology, Dermatopathology and Venereology, Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2020, p. 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Carro E, Angenent M, Gracia-Cazaña T, Gilaberte Y, Alcaine C, Ciriza J. Modeling an Optimal 3D Skin-on-Chip within Microfluidic Devices for Pharmacological Studies. Pharmaceutics 2022;14:1417. [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre-Utile A, Braun C, Haftek M, Aubin F. Five Functional Aspects of the Epidermal Barrier. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:11676. [CrossRef]
- Coulombe1 PA, Lee C-H. Defining keratin protein function in skin epithelia: Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex and its aftermath. J Invest Dermatol 2012;132:763–75. [CrossRef]
- Layers of the Skin | SEER Training n.d. Available online: https://training.seer.cancer.gov/melanoma/anatomy/layers.html (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Nakashima T, Yasumatsu R, Kuratomi Y, Masuda M, Kuwano T, Toh S, et al. Role of squamous cell carcinoma antigen 1 expression in the invasive potential of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head & Neck 2006;28:24–30. [CrossRef]
- Sander CS, Chang H, Hamm F, Elsner P, Thiele JJ. Role of oxidative stress and the antioxidant network in cutaneous carcinogenesis. International Journal of Dermatology 2004;43:326–35. [CrossRef]
- De Graaf YGL, Euvrard S, Bouwes Bavinck JN. Systemic and topical retinoids in the management of skin cancer in organ transplant recipients. Dermatol Surg 2004;30:656–61. [CrossRef]
- Plikus MV, Wang X, Sinha S, Forte E, Thompson SM, Herzog EL, et al. Fibroblasts: origins, definitions, and functions in health and disease. Cell 2021;184:3852–72. [CrossRef]
- Schultz GS, Wysocki A. Interactions between extracellular matrix and growth factors in wound healing. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2009;17:153–62. [CrossRef]
- Sorrell JM, Caplan AI. Fibroblast heterogeneity: more than skin deep. Journal of Cell Science 2004;117:667–75. [CrossRef]
- Shoulders MD, Raines RT. COLLAGEN STRUCTURE AND STABILITY. Annu Rev Biochem 2009;78:929–58. [CrossRef]
- P B, H S. Structurally distinct collagen types. Annual Review of Biochemistry 1980;49. [CrossRef]
- Di Lullo GA, Sweeney SM, Körkkö J, Ala-Kokko L, San Antonio JD. Mapping the Ligand-binding Sites and Disease-associated Mutations on the Most Abundant Protein in the Human, Type I Collagen*. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2002;277:4223–31. [CrossRef]
- Nelson BR, Majmudar G, Griffiths CE, Gillard MO, Dixon AE, Tavakkol A, et al. Clinical improvement following dermabrasion of photoaged skin correlates with synthesis of collagen I. Arch Dermatol 1994;130:1136–42.
- Skinner SM, Gage JP, Wilce PA, Shaw RM. A preliminary study of the effects of laser radiation on collagen metabolism in cell culture. Aust Dent J 1996;41:188–92. [CrossRef]
- Orringer JS, Kang S, Johnson TM, Karimipour DJ, Hamilton T, Hammerberg C, et al. Connective tissue remodeling induced by carbon dioxide laser resurfacing of photodamaged human skin. Arch Dermatol 2004;140:1326–32. [CrossRef]
- Weiss RA, Weiss MA, Beasley KL. Rejuvenation of photoaged skin: 5 years results with intense pulsed light of the face, neck, and chest. Dermatol Surg 2002;28:1115–9. [CrossRef]
- Wang F, Garza LA, Kang S, Varani J, Orringer JS, Fisher GJ, et al. In vivo stimulation of de novo collagen production caused by crosslinked hyaluronic acid dermal filler injections in photodamaged human skin. Arch Dermatol 2007;143:155–63. [CrossRef]
- Wilcox WR. Connective Tissue and Its Heritable Disorders: Molecular, Genetic, and Medical Aspects,. Am J Hum Genet 2003;72:503–4.
- Baumann L, Bernstein EF, Weiss AS, Bates D, Humphrey S, Silberberg M, et al. Clinical Relevance of Elastin in the Structure and Function of Skin. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum 2021;3:ojab019. [CrossRef]
- Cosmeceuticals and Cosmetic Ingredients | AccessDermatologyDxRx | McGraw Hill Medical n.d. Available online: https://dermatology.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookID=2812 (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Simionescu DT, Lu Q, Song Y, Lee J, Rosenbalm TN, Kelley C, et al. Biocompatibility and remodeling potential of pure arterial elastin and collagen scaffolds. Biomaterials 2006;27:702–13. [CrossRef]
- Lierova A, Kasparova J, Filipova A, Cizkova J, Pekarova L, Korecka L, et al. Hyaluronic Acid: Known for Almost a Century, but Still in Vogue. Pharmaceutics 2022;14:838. [CrossRef]
- Dovedytis M, Liu ZJ, Bartlett S. Hyaluronic acid and its biomedical applications: A review. Engineered Regeneration 2020;1:102–13. [CrossRef]
- Jegasothy SM, Zabolotniaia V, Bielfeldt S. Efficacy of a New Topical Nano-hyaluronic Acid in Humans. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 2014;7:27–9.
- Ehlers E-M, Behrens P, Wünsch L, Kühnel W, Russlies M. Effects of hyaluronic acid on the morphology and proliferation of human chondrocytes in primary cell culture. Annals of Anatomy - Anatomischer Anzeiger 2001;183:13–7. [CrossRef]
- Casanova F, Santos L. Encapsulation of cosmetic active ingredients for topical application--a review. J Microencapsul 2016;33:1–17. [CrossRef]
- Begines B, Ortiz T, Pérez-Aranda M, Martínez G, Merinero M, Argüelles-Arias F, et al. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Recent Developments and Future Prospects. Nanomaterials 2020;10:1403. [CrossRef]
- Bahamonde-Norambuena D, Molina-Pereira A, Muñoz M, Zepeda K, Vilos C. Polymeric Nanoparticles in Dermocosmetic. International Journal of Morphology 2015;33:1563–8. [CrossRef]
- Fytianos G, Rahdar A, Kyzas GZ. Nanomaterials in Cosmetics: Recent Updates. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2020;10:979. [CrossRef]
- Martínez Rivas CJ, Tarhini M, Badri W, Miladi K, Greige-Gerges H, Nazari QA, et al. Nanoprecipitation process: From encapsulation to drug delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2017;532:66–81. [CrossRef]
- Salatin S, Barar J, Barzegar-Jalali M, Adibkia K, Kiafar F, Jelvehgari M. Development of a nanoprecipitation method for the entrapment of a very water soluble drug into Eudragit RL nanoparticles. Res Pharm Sci 2017;12:1–14. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Chan HF, Leong KW. Advanced Materials and Processing for Drug Delivery: The Past and the Future. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2013;65:104–20. [CrossRef]
- Pulingam T, Foroozandeh P, Chuah J-A, Sudesh K. Exploring Various Techniques for the Chemical and Biological Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022;12:576. [CrossRef]
- Morán D, Gutiérrez G, Blanco-López MC, Marefati A, Rayner M, Matos M. Synthesis of Starch Nanoparticles and Their Applications for Bioactive Compound Encapsulation. Applied Sciences 2021;11:4547. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz E, Orozco VH, Hoyos LM, Giraldo LF. Study of sonication parameters on PLA nanoparticles preparation by simple emulsion-evaporation solvent technique. European Polymer Journal 2022;173:111307. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal M, Valour J-P, Fessi H, Elaissari A. Preparation of biodegradable PCL particles via double emulsion evaporation method using ultrasound technique. Colloid and Polymer Science 2015;3:861–73. [CrossRef]
- Merino D, Casalongué C, Alvarez V. Polysaccharides as Eco-Nanomaterials for Agricultural Applications. Handbook of Ecomaterials, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Lee H, An S, Kim S, Jeon B, Kim M, Kim IS. Readily Functionalizable and Stabilizable Polymeric Particles with Controlled Size and Morphology by Electrospray. Sci Rep 2018;8:15725. [CrossRef]
- Giri TK. Nanoarchitectonics for Smart Delivery and Drug Targeting. William Andrew 2016:119–41.
- Reverchon E, Adami R. Nanomaterials and supercritical fluids. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids 2006;37:1–22.
- Byrappa K, Ohara S, Adschiri T. Nanoparticles synthesis using supercritical fluid technology - towards biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2008;60:299–327. [CrossRef]
- Girotra P, Singh S, Nagpal K. Supercritical fluid technology: A promising approach in pharmaceutical research. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology 2012;18. [CrossRef]
- Liu G, Li J, Deng S. Applications of Supercritical Anti-Solvent Process in Preparation of Solid Multi-component Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021;13:475. [CrossRef]
- Barhoum A, Bechelany M, Hamdy Makhlouf AS. Handbook of Nanofibers. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Cui W, Zhou Y, Chang J. Electrospun nanofibrous materials for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Sci Technol Adv Mater 2010;11:014108. [CrossRef]
- Garg K, Bowlin G. Electrospinning Jets and Nanofibrous Structures. Biomicrofluidics 2011;5:13403. [CrossRef]
- Zaid Alkilani A, McCrudden MTC, Donnelly RF. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015;7:438–70. [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazeem NZA, Al-Hazeem NZA. Nanofibers and Electrospinning Method. IntechOpen; 2018. [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan BA, Krishnaswamy M, Xu H, Hoque ME. Electrospinning of Biomedical Nanofibers/Nanomembranes: Effects of Process Parameters. Polymers (Basel) 2022;14:3719. [CrossRef]
- Yarin A, Koombhongse S, Reneker D. Taylor Cone and Jetting from Liquid Droplets in Electrospinning of Nanofibers. Journal of Applied Physics 2001;90:4836–46. [CrossRef]
- Barhoum A, Pal K, Rahier H, Uludag H, Kim IS, Bechelany M. Nanofibers as new-generation materials: From spinning and nano-spinning fabrication techniques to emerging applications. Applied Materials Today 2019;17:1–35. [CrossRef]
- Nayl AA, Abd-Elhamid AI, Awwad NS, Abdelgawad MA, Wu J, Mo X, et al. Review of the Recent Advances in Electrospun Nanofibers Applications in Water Purification. Polymers (Basel) 2022;14:1594. [CrossRef]
- Dokuchaeva AA, Timchenko TP, Karpova EV, Vladimirov SV, Soynov IA, Zhuravleva IY. Effects of Electrospinning Parameter Adjustment on the Mechanical Behavior of Poly-ε-caprolactone Vascular Scaffolds. Polymers (Basel) 2022;14:349. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Chen X, Lu W, Wang J, Xu Y, Guo Y. Application of Electrospinning in Antibacterial Field. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2021;11:1822. [CrossRef]
- Luraghi A, Peri F, Moroni L. Electrospinning for drug delivery applications: A review. J Control Release 2021;334:463–84. [CrossRef]
- Xue J, Wu T, Dai Y, Xia Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem Rev 2019;119:5298–415. [CrossRef]
- Sun G, Sun L, Xie H, Liu J. Electrospinning of Nanofibers for Energy Applications. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2016;6:129. [CrossRef]
- Zhang C, Feng F, Zhang H. Emulsion electrospinning: Fundamentals, food applications and prospects. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2018;80:175–86. [CrossRef]
- Tian Y, Zhou J, He C, He L, Li X, Sui H. The Formation, Stabilization and Separation of Oil–Water Emulsions: A Review. Processes 2022;10:738. [CrossRef]
- Wu Y-K, Wang L, Fan J, Shou W, Zhou B-M, Liu Y. Multi-Jet Electrospinning with Auxiliary Electrode: The Influence of Solution Properties. Polymers (Basel) 2018;10:572. [CrossRef]
- Varesano A, Carletto RA, Mazzuchetti G. Experimental investigations on the multi-jet electrospinning process. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2009;209:5178–85. [CrossRef]
- Mohammadalizadeh Z, Bahremandi-Toloue E, Karbasi S. Recent advances in modification strategies of pre- and post-electrospinning of nanofiber scaffolds in tissue engineering. Reactive and Functional Polymers 2022;172:105202. [CrossRef]
- Ding B, Kimura E, Sato T, Fujita S, Shiratori S. Fabrication of blend biodegradable nanofibrous nonwoven mats via multi-jet electrospinning. Polymer 2004;45:1895–902. [CrossRef]
- Xue J, Xie J, Liu W, Xia Y. Electrospun Nanofibers: New Concepts, Materials, and Applications. Acc Chem Res 2017;50:1976–87. [CrossRef]
- Li D, Yue G, Li S, Liu J, Li H, Gao Y, et al. Fabrication and Applications of Multi-Fluidic Electrospinning Multi-Structure Hollow and Core–Shell Nanofibers. Engineering 2022;13:116–27. [CrossRef]
- Yu D-G, Li J-J, Zhang M, Williams GR. High-quality Janus nanofibers prepared using three-fluid electrospinning. Chem Commun (Camb) 2017;53:4542–5. [CrossRef]
- Yu D-G, Yang C, Jin M, Williams GR, Zou H, Wang X, et al. Medicated Janus fibers fabricated using a Teflon-coated side-by-side spinneret. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2016;138:110–6. [CrossRef]
- Zheng X, Kang S, Wang K, Yang Y, Yu D-G, Wan F, et al. Combination of structure-performance and shape-performance relationships for better biphasic release in electrospun Janus fibers. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2021;596:120203. [CrossRef]
- Lu Y, Huang J, Yu G, Cardenas R, Wei S, Wujcik EK, et al. Coaxial electrospun fibers: applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 2016;8:654–77. [CrossRef]
- Pant B, Park M, Park S-J. Drug Delivery Applications of Core-Sheath Nanofibers Prepared by Coaxial Electrospinning: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2019;11:305. [CrossRef]
- Rathore P, Schiffman JD. Beyond the Single-Nozzle: Coaxial Electrospinning Enables Innovative Nanofiber Chemistries, Geometries, and Applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021;13:48–66. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Chen X, Liu Y, Gao Y, Liu P. Electrospun Coaxial Fibers to Optimise the Release of Poorly Water-Soluble Drug. Polymers 2022;14:469. [CrossRef]
- Baykara T, Taylan G. Coaxial electrospinning of PVA/Nigella seed oil nanofibers: Processing and morphological characterisation. Materials Science and Engineering: B 2021;265:115012. [CrossRef]
- Liu W, Ni C, Chase D, Rabolt J. Preparation of Multilayer Biodegradable Nanofibers by Triaxial Electrospinning. ACS Macro Letters 2013;2:466–8. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Yang Y, Yu D-G, Zhu M-J, Zhao M, Williams GR. Tunable zero-order drug delivery systems created by modified triaxial electrospinning. Chemical Engineering Journal 2019;356:886–94. [CrossRef]
- Yu D, Wang M, Xiaoyan L, Liu X, Zhu L-M, Bligh S. Multifluid electrospinning for the generation of complex nanostructures. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology 2019;12:e1601. [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli MZA, Nordin D, Shaari N, Kamarudin SK. Overview of Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2023;15:2418. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Chi C, Chen J, Zhang X, Gong M, Wang X, et al. Electrospun quad-axial nanofibers for controlled and sustained drug delivery. Materials & Design 2021;206:109732. [CrossRef]
- Miletić A, Pavlić B, Ristić I, Zeković Z, Pilić B. Encapsulation of Fatty Oils into Electrospun Nanofibers for Cosmetic Products with Antioxidant Activity. Applied Sciences 2019;9:2955. [CrossRef]
- Wilk S, Benko A. Advances in Fabricating the Electrospun Biopolymer-Based Biomaterials. J Funct Biomater 2021;12:26. [CrossRef]
- White-Chu EF, Reddy M. Dry skin in the elderly: complexities of a common problem. Clin Dermatol 2011;29:37–42. [CrossRef]
- Clark EW. A brief history of lanolin. Pharm Hist (Lond) 1980;10:5–6.
- Ertas IF, Uzun M, Altan E, Kabir MH, Gurboga M, Ozakpinar OB, et al. Investigation of silk fibroin-lanolin blended nanofibrous structures. Materials Letters 2023;330:133263. [CrossRef]
- Thau P. Glycerin (glycerol): Current insights into the functional properties of a classic cosmetic raw material. J Cosmet Sci 2002;53:229–36.
- Fluhr JW, Gloor M, Lehmann L, Lazzerini S, Distante F, Berardesca E. Glycerol accelerates recovery of barrier function in vivo. Acta Derm Venereol 1999;79:418–21. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves MM, Lobsinger KL, Carneiro J, Picheth GF, Pires C, Saul CK, et al. Morphological study of electrospun chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol)/glycerol nanofibres for skin care applications. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2022;194:172–8. [CrossRef]
- Movahedi M, Asefnejad A, Rafienia M, Khorasani MT. Potential of novel electrospun core-shell structured polyurethane/starch (hyaluronic acid) nanofibers for skin tissue engineering: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2020;146:627–37. [CrossRef]
- Fan L, Cai Z, Zhang K, Han F, Li J, He C, et al. Green electrospun pantothenic acid/silk fibroin composite nanofibers: fabrication, characterisation and biological activity. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2014;117:14–20. [CrossRef]
- Gehring W, Gloor M. Effect of topically applied dexpanthenol on epidermal barrier function and stratum corneum hydration. Results of a human in vivo study. Arzneimittelforschung 2000;50:659–63. [CrossRef]
- Biro K, Thaçi D, Ochsendorf FR, Kaufmann R, Boehncke W-H. Efficacy of dexpanthenol in skin protection against irritation: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Contact Dermatitis 2003;49:80–4. [CrossRef]
- Kazsoki A, Palcsó B, Alpár A, Snoeck R, Andrei G, Zelkó R. Formulation of acyclovir (core)-dexpanthenol (sheath) nanofibrous patches for the treatment of herpes labialis. Int J Pharm 2022;611:121354. [CrossRef]
- Kligman AM. Dermatologic uses of urea. Acta Derm Venereol 1957;37:155–9.
- Krysiak Z, Stachewicz U. Urea-Based Patches with Controlled Release for Potential Atopic Dermatitis Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2022;14. [CrossRef]
- Jin YH, Lee SJ, Chung MH, Park JH, Park YI, Cho TH, et al. Aloesin and arbutin inhibit tyrosinase activity in a synergistic manner via a different action mechanism. Arch Pharm Res 1999;22:232–6. [CrossRef]
- Wahedi HM, Jeong M, Chae JK, Do SG, Yoon H, Kim SY. Aloesin from Aloe vera accelerates skin wound healing by modulating MAPK/Rho and Smad signaling pathways in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine 2017;28:19–26. [CrossRef]
- Draelos ZD. Skin lightening preparations and the hydroquinone controversy. Dermatol Ther 2007;20:308–13. [CrossRef]
- Kumar L, Verma S, Joshi K, Utreja P, Sharma S. Nanofiber as a novel vehicle for transdermal delivery of therapeutic agents: challenges and opportunities. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2021;7:175. [CrossRef]
- Hazra B, Sarkar R, Biswas S, Mandal N. Comparative study of the antioxidant and reactive oxygen species scavenging properties in the extracts of the fruits of Terminalia chebula, Terminalia belerica and Emblica officinalis. BMC Complement Altern Med 2010;10:20. [CrossRef]
- Sancheti G, Jindal A, Kumari R, Goyal PK. Chemo-preventive action of emblica officinalis on skin carcinogenesis in mice. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2005;6:197–201.
- Lin J-H, Shiu B-C, Hsu P-W, Lou C-W, Lin J-H. PVP/CS/Phyllanthus emblica Nanofiber Membranes for Dry Facial Masks: Manufacturing Process and Evaluations. Polymers 2022;14:4470. [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai N, Edmondson D, Veiseh O, Matsen F, Zhang M. Electrospun chitosan-based nanofibers and their cellular compatibility. Biomaterials 2005;26:6176–84. [CrossRef]
- Zhu W, Gao J. The use of botanical extracts as topical skin-lightening agents for the improvement of skin pigmentation disorders. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 2008;13:20–4. [CrossRef]
- Gupta S, Dutta P, Acharya V, Prasad P, Roy A, Bit A. Accelerating skin barrier repair using novel bioactive magnesium-doped nanofibers of non-mulberry silk fibroin during wound healing. Journal of Bioactive and Compatible Polymers 2022;37:38–52. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Qin Y, Bai R, Zhang X, Yuan L, Liu J. Preparation of pH-sensitive and antioxidant packaging films based on κ-carrageenan and mulberry polyphenolic extract. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2019;134:993–1001. [CrossRef]
- Shindo Y, Witt E, Han D, Epstein W, Packer L. Enzymic and non-enzymic antioxidants in epidermis and dermis of human skin. J Invest Dermatol 1994;102:122–4. [CrossRef]
- Pullar JM, Carr AC, Vissers MCM. The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients 2017;9:866. [CrossRef]
- Fathi-Azarbayjani A, Qun L, Chan YW, Chan SY. Novel vitamin and gold-loaded nanofiber facial mask for topical delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010;11:1164–70. [CrossRef]
- Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, Chhoa M, Matsubara A, Miyamoto K, et al. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. Br J Dermatol 2002;147:20–31. [CrossRef]
- Nada A, Hassabo A, Mohamed A, Zaghloul S. Encapsulation of Nicotinamide into Cellulose Based Electrospun Fibers. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science 2016;6:013–21. [CrossRef]
- Katiyar SK, Ahmad N, Mukhtar H. Green tea and skin. Arch Dermatol 2000;136:989–94. [CrossRef]
- Sadri.Minoo, Arab-Sorkhi S, Vatani H, Bagheri Pebdeni A. New wound dressing polymeric nanofiber containing green tea extract prepared by electrospinning method. Fibers and Polymers 2015;16:1742–50. [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy S, Boşgelmez-Tinaz G, Seçilmiş-Canbay H. Tocopherol, carotene, phenolic contents and antibacterial properties of rose essential oil, hydrosol and absolute. Curr Microbiol 2009;59:554–8. [CrossRef]
- Zarshenas MM, Moein M, Zomorodian K, Almasi M, Pakshir K. Preparation and Analysis of Rosa damascena Essential Oil Composition and Antimicrobial Activity Assessment of Related Fractions. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology (Sciences) 2017;41. [CrossRef]
- Lin Y-C, Hu S, Huang P-H, Lin T-C, Yen F-L. Electrospun Resveratrol-Loaded Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Cyclodextrin Nanofibers and Their Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2020;12:552. [CrossRef]
- Torras MAC, Faura CA, Schönlau F, Rohdewald P. Antimicrobial activity of Pycnogenol. Phytother Res 2005;19:647–8. [CrossRef]
- Wang A, Pope SD, Weinstein JS, Yu S, Zhang C, Booth CJ, et al. Specific sequences of infectious challenge lead to secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-like disease in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019;116:2200–9. [CrossRef]
- Baxter RA. Anti-aging properties of resveratrol: review and report of a potent new antioxidant skin care formulation. J Cosmet Dermatol 2008;7:2–7. [CrossRef]
- De Spirt S, Stahl W, Tronnier H, Sies H, Bejot M, Maurette J-M, et al. Intervention with flaxseed and borage oil supplements modulates skin condition in women. Br J Nutr 2009;101:440–5. [CrossRef]
- Hadad S, Goli S. Improving Oxidative Stability of Flaxseed Oil by Encapsulation in Electrospun Flaxseed Mucilage Nanofiber. Food and Bioprocess Technology 2019;12. [CrossRef]
- Hadad S, Goli S. Fabrication and characterisation of electrospun nanofibers using flaxseed ( Linum usitatissimum ) mucilage. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2018;114. [CrossRef]
- Staniforth V, Chiu L-T, Yang N-S. Caffeic acid suppresses UVB radiation-induced expression of interleukin-10 and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in mouse. Carcinogenesis 2006;27:1803–11. [CrossRef]
- Saija A, Tomaino A, Trombetta D, De Pasquale A, Uccella N, Barbuzzi T, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of caffeic and ferulic acids as topical photoprotective agents. Int J Pharm 2000;199:39–47. [CrossRef]
- Vilchez A, Acevedo F, Cea M, Seeger M, Navia R. Applications of Electrospun Nanofibers with Antioxidant Properties: A Review. Nanomaterials 2020;10:175. [CrossRef]
- Kaya S, Yilmaz DE, Akmayan I, Egri O, Arasoglu T, Derman S. Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester Loaded Electrospun Nanofibers for Wound Dressing Application. J Pharm Sci 2022;111:734–42. [CrossRef]
- Wang Q-J, Gao X, Gong H, Lin X-R, Saint-Leger D, Senee J. Chemical stability and degradation mechanisms of ferulic acid (F.A) within various cosmetic formulations. J Cosmet Sci 2011;62:483–503.
- Vashisth P, Kumar N, Sharma M, Pruthi V. Biomedical applications of ferulic acid encapsulated electrospun nanofibers. Biotechnol Rep (Amst) 2015;8:36–44. [CrossRef]
- Charurin P, Ames JM, del Castillo MD. Antioxidant activity of coffee model systems. J Agric Food Chem 2002;50:3751–6. [CrossRef]
- Sheng X, Fan L, He C, Zhang K, Mo X, Wang H. Vitamin E-loaded silk fibroin nanofibrous mats fabricated by green process for skin care application. Int J Biol Macromol 2013;56:49–56. [CrossRef]
- Taepaiboon P, Rungsardthong U, Supaphol P. Vitamin-loaded electrospun cellulose acetate nanofiber mats as transdermal and dermal therapeutic agents of vitamin A acid and vitamin E. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2007;67:387–97. [CrossRef]
- Bhagavathula N, Warner RL, DaSilva M, McClintock SD, Barron A, Aslam MN, et al. A combination of curcumin and ginger extract improves abrasion wound healing in corticosteroid-impaired hairless rat skin. Wound Repair Regen 2009;17:360–6. [CrossRef]
- Jacob J, Haponiuk J, Thomas S, Peter G, Gopi S. Use of Ginger Nanofibers for the Preparation of Cellulose Nanocomposites and Their Antimicrobial Activities. Fibers 2018;6:79. [CrossRef]
- Jacob J, Peter G, Thomas S, Haponiuk JT, Gopi S. Chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposites with cellulose nanofibers from ginger rhizomes and its antimicrobial activities. Int J Biol Macromol 2019;129:370–6. [CrossRef]
- Israili ZH. Antimicrobial properties of honey. Am J Ther 2014;21:304–23. [CrossRef]
- Ediriweera ERHSS, Premarathna NYS. Medicinal and cosmetic uses of Bee’s Honey - A review. Ayu 2012;33:178–82. [CrossRef]
- Pakolpakçıl A, Draczynski Z. Green Approach to Develop Bee Pollen-Loaded Alginate Based Nanofibrous Mat. Materials 2021;14:2775. [CrossRef]
- Ionescu OM, Mignon A, Iacob AT, Simionescu N, Confederat LG, Tuchilus C, et al. New Hyaluronic Acid/Polyethylene Oxide-Based Electrospun Nanofibers: Design, Characterisation and In Vitro Biological Evaluation. Polymers (Basel) 2021;13:1291. [CrossRef]
- Pugazhenthi K, Kapoor M, Clarkson AN, Hall I, Appleton I. Melatonin accelerates the process of wound repair in full-thickness incisional wounds. J Pineal Res 2008;44:387–96. [CrossRef]
- Morganti P. Melatonin and immunostimulating substance-based compositions. EP1991222B1, 2016.
- Mirmajidi T, Chogan F, Rezayan AH, Sharifi AM. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a nanofiber wound dressing loaded with melatonin. Int J Pharm 2021;596:120213. [CrossRef]
- Rahman S, Carter P, Bhattarai N. Aloe Vera for Tissue Engineering Applications. JFB 2017;8:6. [CrossRef]
- Barbosa R, Villarreal A, Rodriguez C, De Leon H, Gilkerson R, Lozano K. Aloe Vera extract-based composite nanofibers for wound dressing applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 2021;124:112061. [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh HMA, Wilkinson JM. Biological activities of lavender essential oil. Phytother Res 2002;16:301–8. [CrossRef]
- Wells R, Truong F, Adal AM, Sarker LS, Mahmoud SS. Lavandula Essential Oils: A Current Review of Applications in Medicinal, Food, and Cosmetic Industries of Lavender. Natural Product Communications 2018;13:1934578X1801301038. [CrossRef]
- Sofi HS, Akram T, Tamboli AH, Majeed A, Shabir N, Sheikh FA. Novel lavender oil and silver nanoparticles simultaneously loaded onto polyurethane nanofibers for wound-healing applications. Int J Pharm 2019;569:118590. [CrossRef]
- Uhlířová R, Langová D, Bendová A, Gross M, Skoumalová P, Márová I. Antimicrobial Activity of Gelatin Nanofibers Enriched by Essential Oils against Cutibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nanomaterials 2023;13:844. [CrossRef]
- Liu H, Yu H, Xia J, Liu L, Liu GJ, Sang H, et al. Topical azelaic acid, salicylic acid, nicotinamide, sulphur, zinc and fruit acid (alpha-hydroxy acid) for acne. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2020;5:CD011368. [CrossRef]
- Yaru W, Lan X, Jianhua S, Chenxu F. Preparation, Characterization and Drug Release of Salicylic Acid Loaded Porous Electrospun Nanofibers. Recent Patents on Nanotechnology 2018;12. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves S. Use of enzymes in cosmetics: proposed enzymatic peel procedure 2021;1:29–35.
- Bié J, Sepodes B, Fernandes PCB, Ribeiro MHL. Enzyme Immobilisation and Co-Immobilization: Main Framework, Advances and Some Applications. Processes 2022;10:494. [CrossRef]
- Basso A, Serban S. Overview of Immobilized Enzymes’ Applications in Pharmaceutical, Chemical, and Food Industry. Methods Mol Biol 2020;2100:27–63. [CrossRef]
| Skin Type | Active Ingredient | Benefits | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry skin | Aloe vera | Moisturises and soothes dry skin and helps restore the natural skin moisture barrier. | [30] |
| Chamomile | It has anti-inflammatory properties and soothes dry, irritated skin. | [31] | |
| Calendula | Helps to hydrate and heal dry, damaged skin. | [32] | |
| Lavender | Has calming properties and soothes dry, itchy skin. | [33] | |
| Coconut oil | Has moisturising properties and helps to soothe and hydrate dry skin. | [34] | |
| Jojoba oil | Helps to moisturise dry skin without leaving a greasy residue | [35] | |
| Shea butter | Has deeply moisturising properties, helps to soothe and nourish dry skin | [36] | |
| Olive oil | Contains antioxidants and moisturising properties, helps to hydrate and protect dry skin | [37] | |
| Rosehip oil | Contains essential fatty acids and vitamin A, helps to hydrate and rejuvenate dry skin | [38] | |
| Witch hazel | Has astringent properties, helps to tighten and tone dry, ageing skin | [39] | |
| Normal skin | Niacinamide | Helps improve skin texture and tone, reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and strengthens the skin barrier | [40] |
| Vitamin C | Helps brighten and even out skin tone, promotes collagen synthesis, and protects against environmental damage | [41] | |
| Hyaluronic acid | Provides deep hydration and helps retain moisture in the skin, improving skin elasticity and firmness. | [42] | |
| Green tea extract | Has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, helps protect against UV damage, and promotes healthy skin ageing | [43] | |
| Retinoids | Helps stimulate collagen production, improves skin texture and tone, and reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles | [44] | |
| Oily skin | Salicylic acid | Helps unclog pores, reduces oiliness, and prevents breakouts | [45] |
| Tea tree oil | Has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, helps reduce acne and oiliness | [46] | |
| Zinc | Helps regulate sebum production, has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, and promotes wound healing. | [47] | |
| Witch hazel | Has astringent properties that can help tighten and tone oily skin, reduces inflammation and irritation | [39] | |
| Combination | Niacinamide | Helps regulate sebum production, improves skin texture and tone, and strengthens the skin barrier. | [40] |
| Hyaluronic acid | Provides deep hydration to dry areas while being lightweight enough not to exacerbate oiliness in the T-zone | [42] | |
| Vitamin C | Helps brighten and even out skin tone, promotes collagen synthesis, and protects against environmental damage | [41] | |
| Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) | Help exfoliate dead skin cells, improve skin texture and tone, and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. | [40] | |
| Jojoba oil | A similar structure to the natural skin sebum helps regulate oil production and hydrates dry areas. | [35] |
| Electrospun polymers | Ingredients | Benefits for skin | Personal Care Category | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silk fibroin | Lanolin | Occlusive, emollient | Lipophilic | [150,151,152] |
| Chitosan, PVA | Glycerine | Anti-inflammatory, barrier recovery | Humectant, moisturiser | [153,154,155] |
| Chitosan, Gelatin, and PVA | Hyaluronic Acid | Humectant, anti-aging | Humectant, moisturiser | [42,156] |
| Silk fibroin | Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid/Dexpanthenol) | Hydration, barrier protection, reduction of trans-epidermal water loss (TEWL), fibroblast stimulation, and re-epithelialisation. | Humectant, emollient, antiinflammatory | [157,158,159,160] |
| PVA, Gelatin | Urea | Anti-inflammatory, hydrating, keratolytic | Humectant, emollient | [161,162] |
| Chitosan,Gelatin, and PVA | Aloesin | Tyrosinase inhibition, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory | Depigmenting, sun protective (UVB) | [163,164] |
| PVA | Hydroquinone | Tyrosinase inhibition | Depigmenting, brightening, lightening | [165,166] |
| Chitosan | Emblica Extract | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antitumor, chemo-preventive, hepatoprotective, analgesic, antibacterial | Depigmenting, anti-ageing, sunscreen | [167,168,169,170] |
| PVA, PCL, Chitosan | Mulberry Extract | Antityrosinase, antihyperglycemic, antitumorigenic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antioxidant, anti-atherogenic, antimicrobial chemo-preventive, neuro-protective | Depigmenting | [171,172,173] |
| PVA | Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photo-protectant, depigmenting | Depigmenting | [174,175,176] |
| PVA | Niacinamide | PAR-2 inhibition, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-ageing, photoprotective | Depigmenting, exfoliant | [171,177,178] |
| PVA, Chitosan | Green Tea | Antioxidant, anti-ageing, antiacne, antiangiogenic, anticarcinogenic, anticarcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, chemo-preventive, immunomodulatory,2photoprotective | Anti-ageing, moisturising, antiacne, anogenital wart treatment | [43,179,180] |
| PVA.Chitosan | Rosa Damascena | Antioxidant, antibacterial, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, and anxiolytic | Antioxidant | [181,182] |
| PVA, PLGA | Pycnogenol | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticarcinogenic, photoprotective, antimicrobial | Anti-inflammatory, hydrating | [183,184,185] |
| PVA, PLGA | Resveratrol | Antioxidant, antibacterial, anticancer, antiinflammatory, antitumorigenic, anti-tyrosinase, cardioprotective | Anti-ageing, anticancer | [186] |
| PVA, PLGA.Chitosan | Flaxseed Oil | Antioxidant, anti-ageing, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic | Antioxidant, anti-ageing | [187,188,189] |
| PVA, PLGA | Caffeic Acid | Antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, immunostimulatory, neuroprotective, photoprotective | Antioxidant, anti-ageing | [190,191,192,193] |
| PLGA.PEO | Ferulic Acid | Antioxidant, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, cardioprotective, neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, photoprotective, skin lightening | Antioxidant, anti-ageing, photoprotection | [192,194,195] |
| Cellulose acetate | Tocopherol (Vitamin E) | Antioxidant, photoprotection, wound healing | Antioxidant, moisturising, anti-ageing | [196,197,198] |
| Chitosan, PVA | Ginger | Antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, antinausea, wound healing | Antioxidant, analgesic, photo-protectant | [199,200,201] |
| Hyaluronic acid, PEO | Honey/Propolis/Royal Jelly | Analgesic, antioxidant, antiinflammatory, antimicrobial, antitumor, antiseptic, antipyretic, antiulcer, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory |
Antioxidant, anti-ageing, photoprotection, antiseptic, wound healing | [202,203,204,205] |
| Chitosan, Polycaprolactone,PVA | Melatonin | Antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, anti-ageing, anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, immunomodulatory | Antioxidant, anti-ageing | [206,207,208] |
| Pullulan | Aloe Vera | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, laxative, wound healing | Moisturising, soothing, cooling, burning and wound healing | [30,209,210] |
| Polyurethane, Gelatin | Lavandula | Anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antiseptic, anti-colic, antispasmodic, antidepressant, sedative | Soothing, sedating, anti-inflammatory, analgesic | [211,212,213,214] |
| PLA | Salicylic Acid | Anti-inflammatory, pore cleansing | Cleansing, antiacne, pore minimising, exfoliating | [215,216] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





