Submitted:
08 November 2023
Posted:
08 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Data and methods
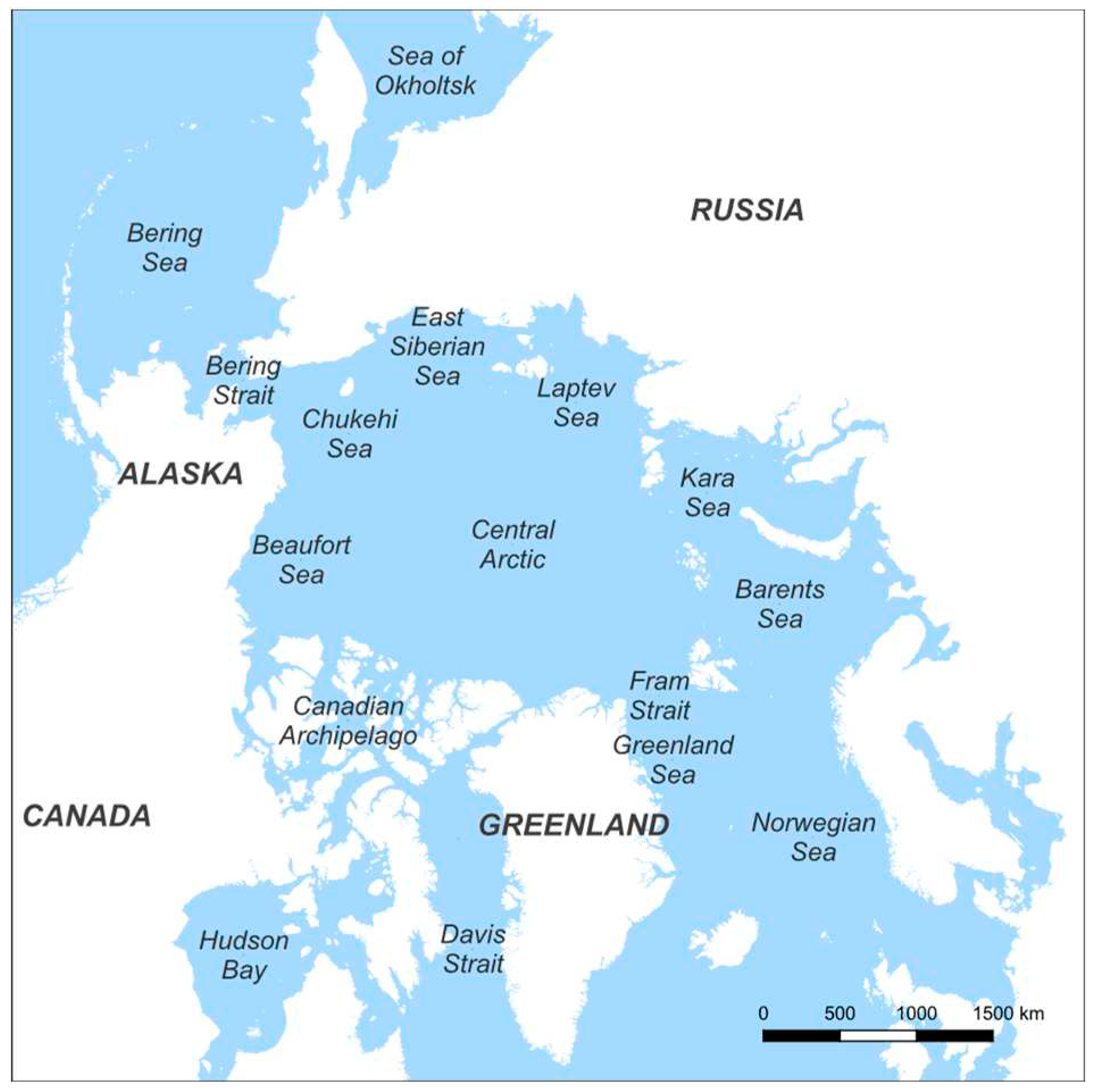
2.1. Data
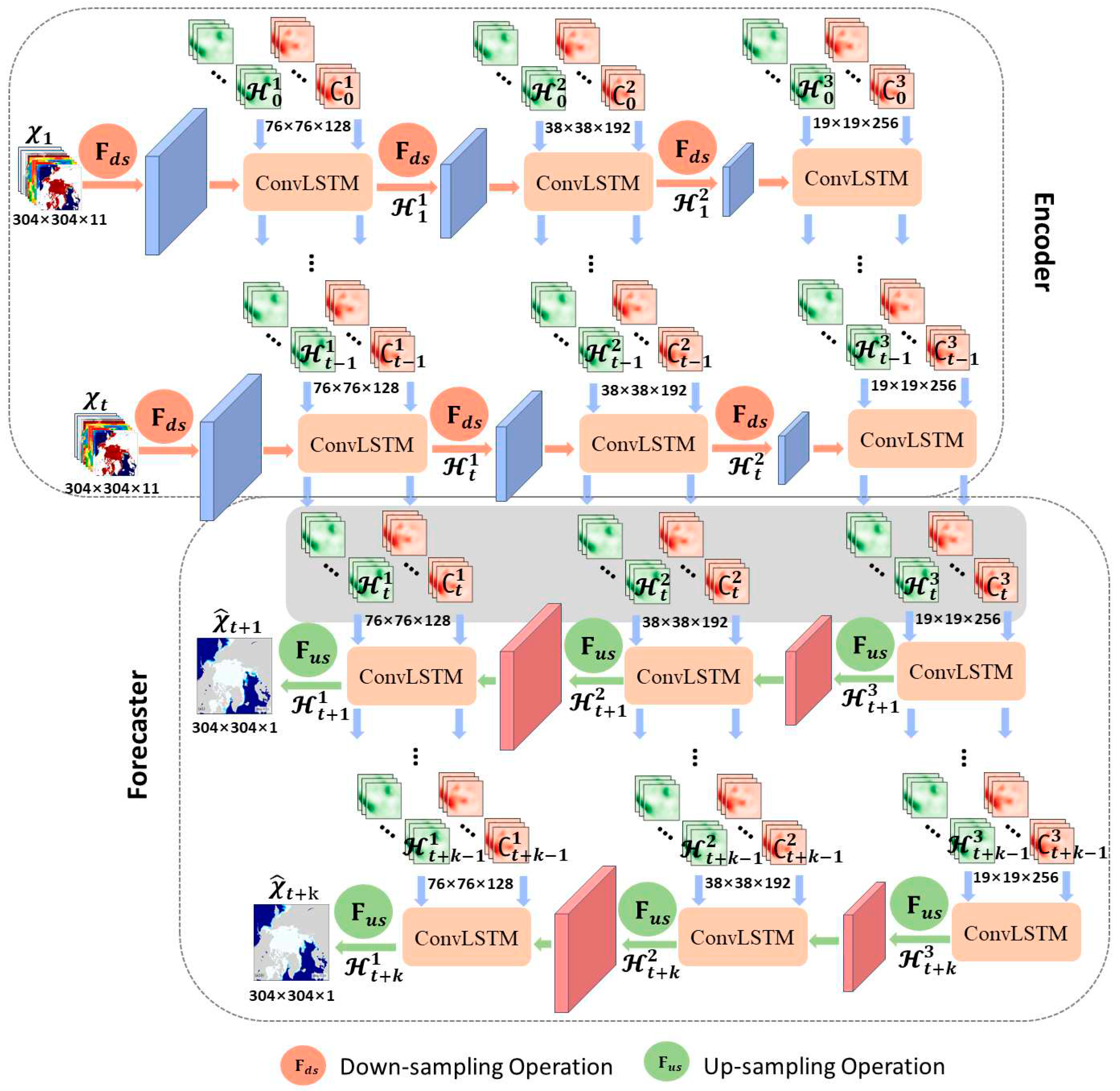
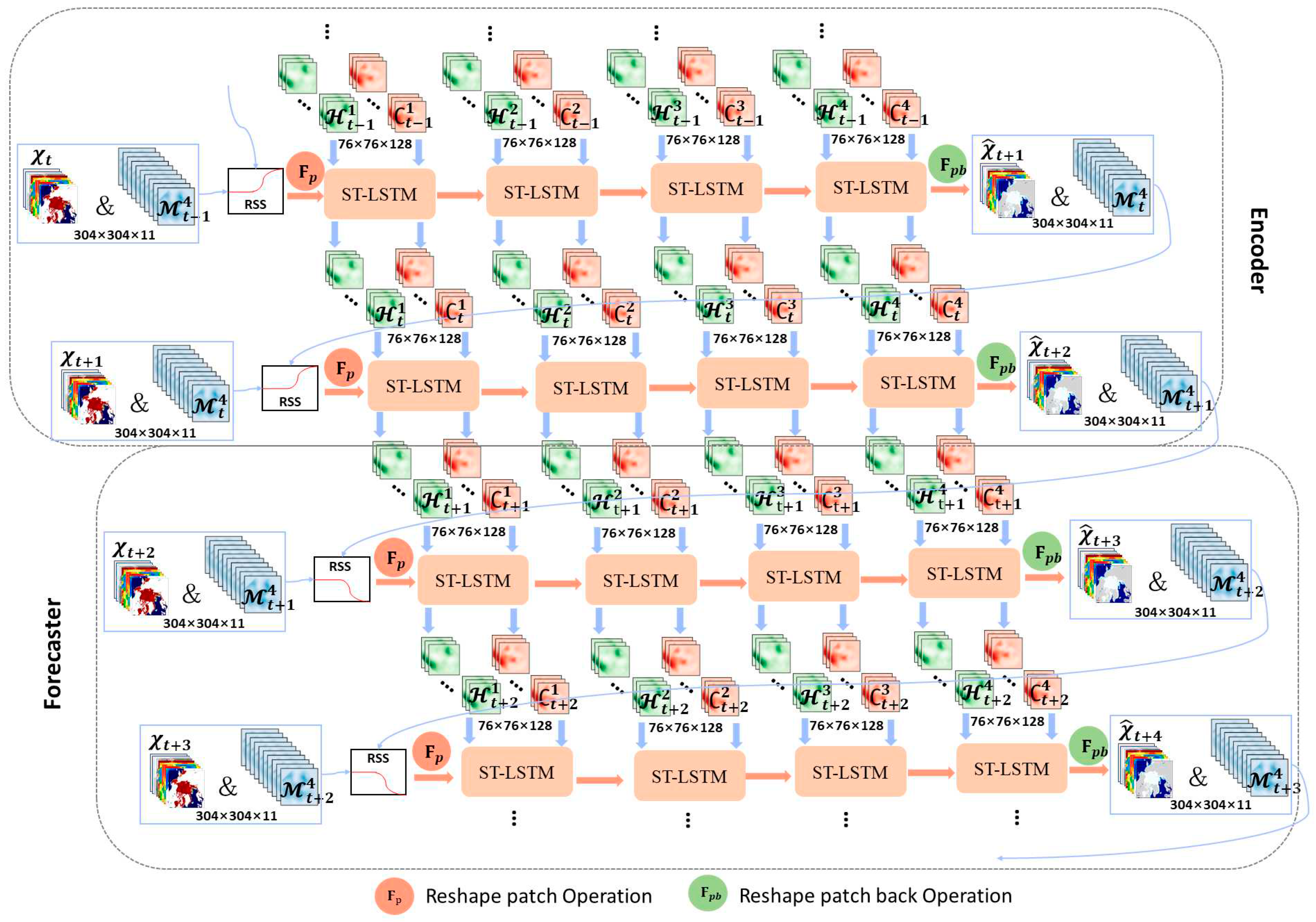
2.2. Model
2.3. Evaluation metrics
3. Results and discussion
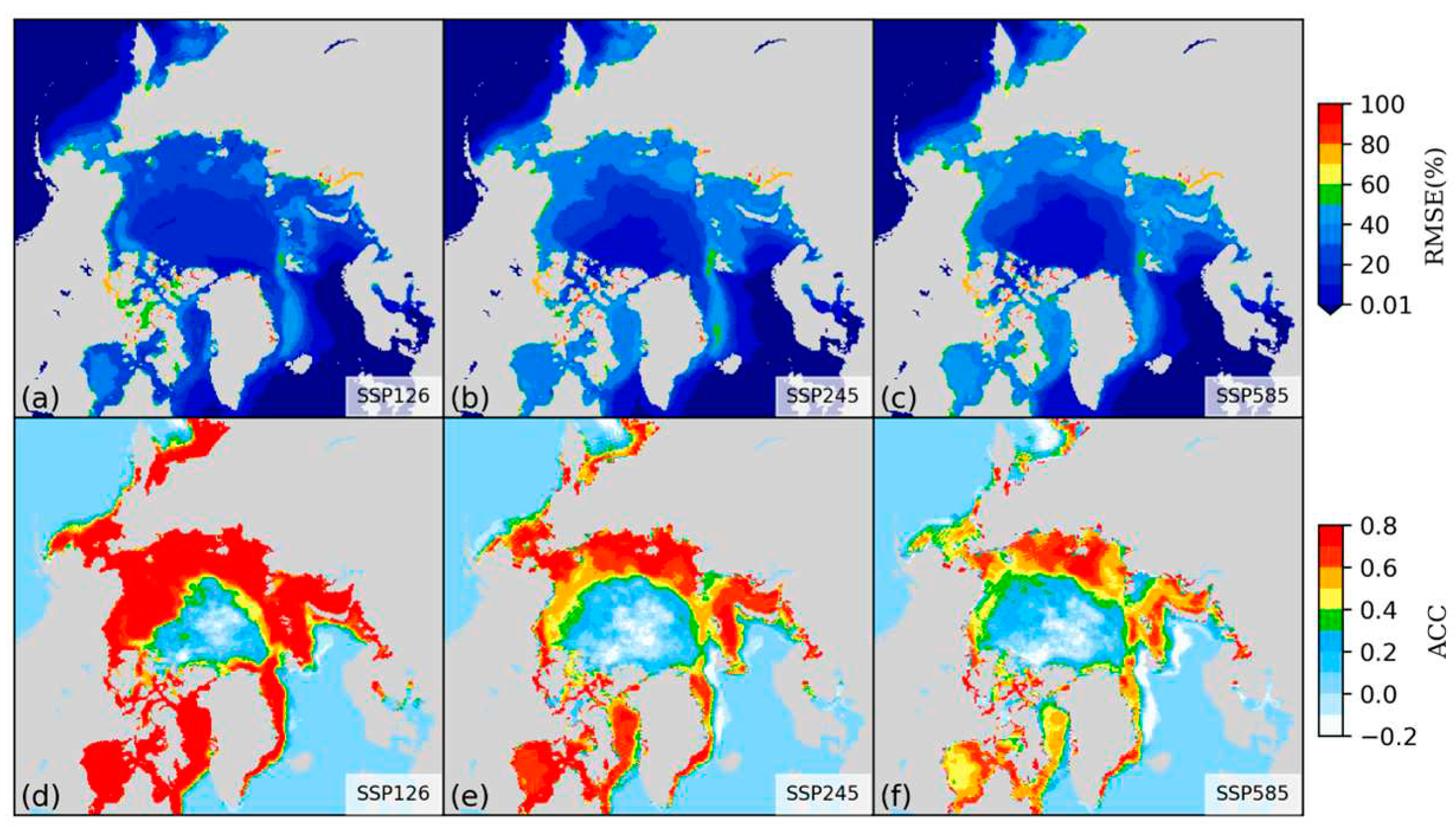
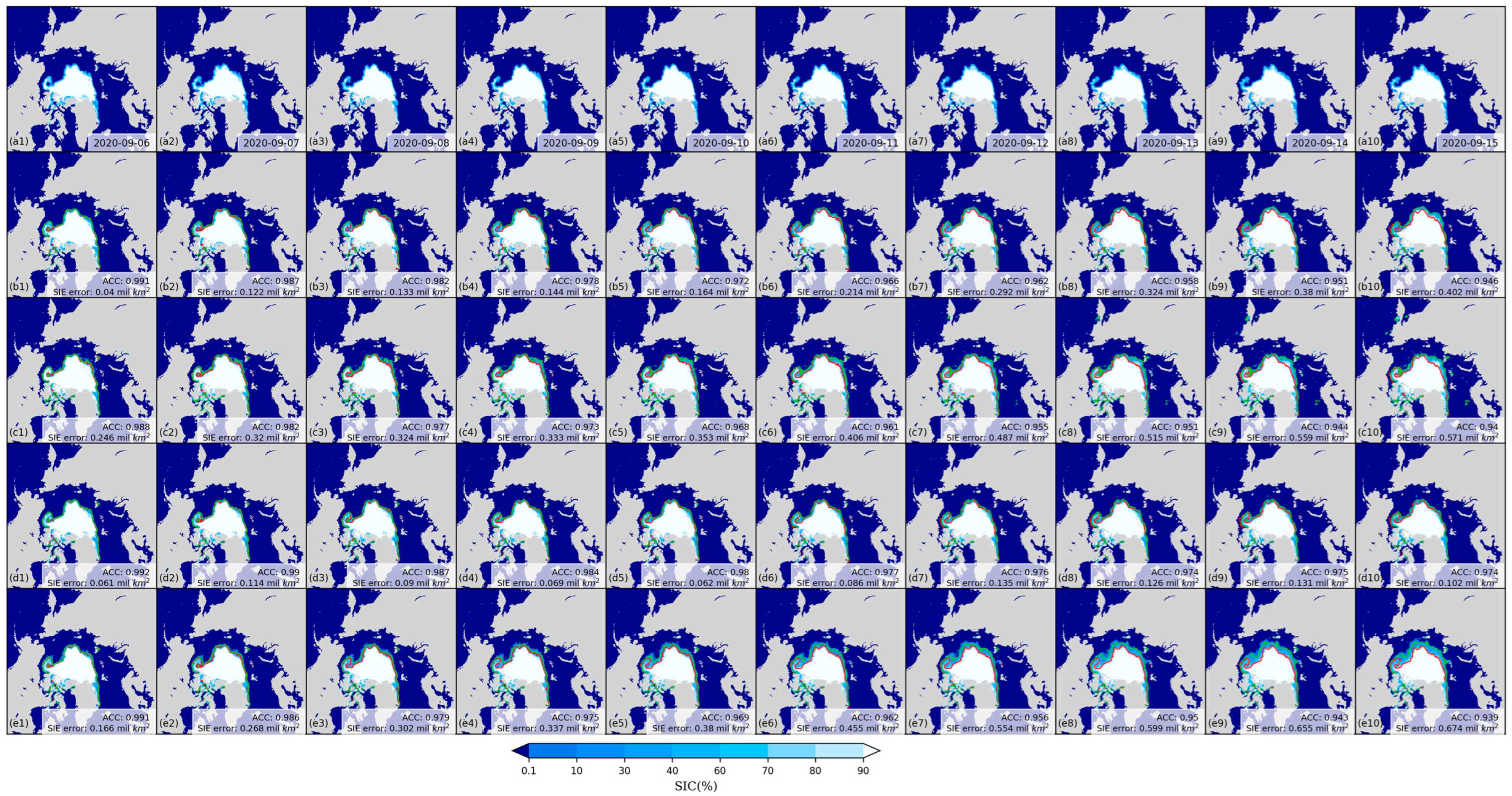
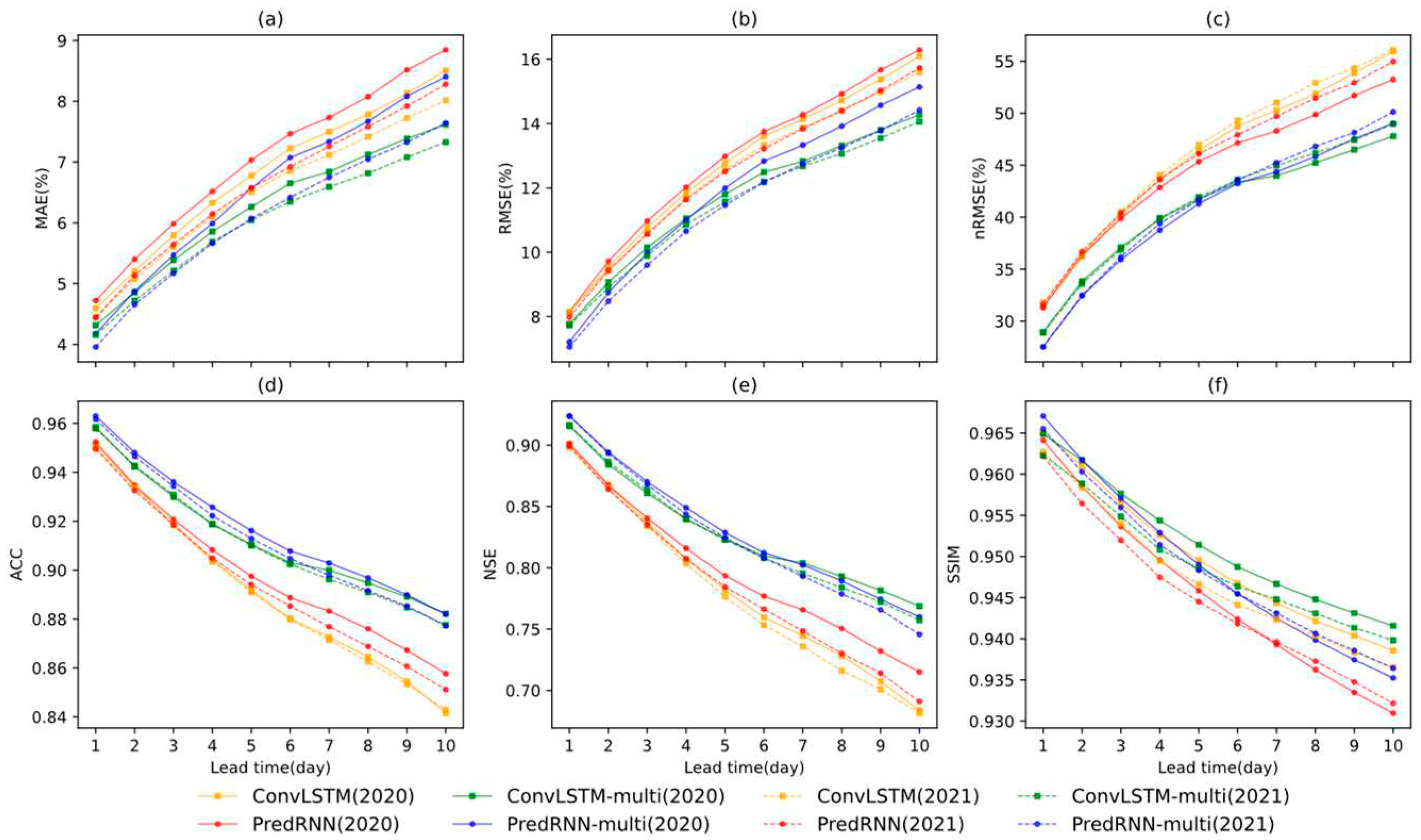
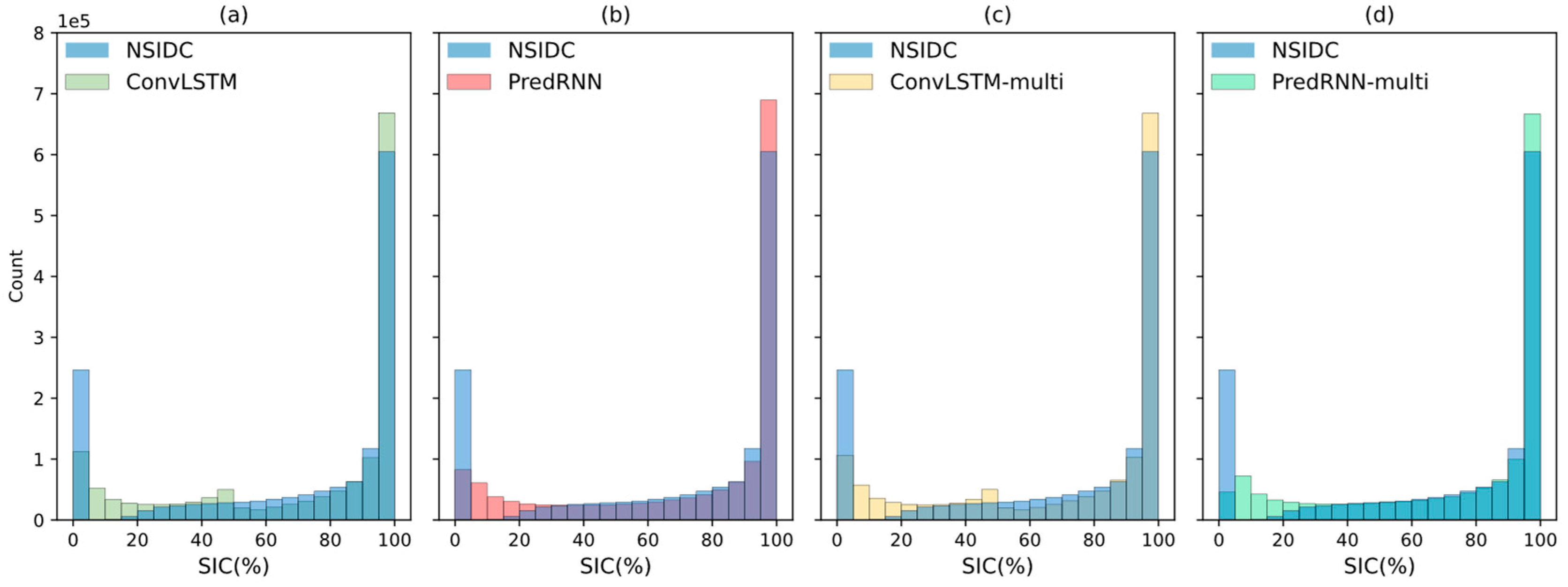
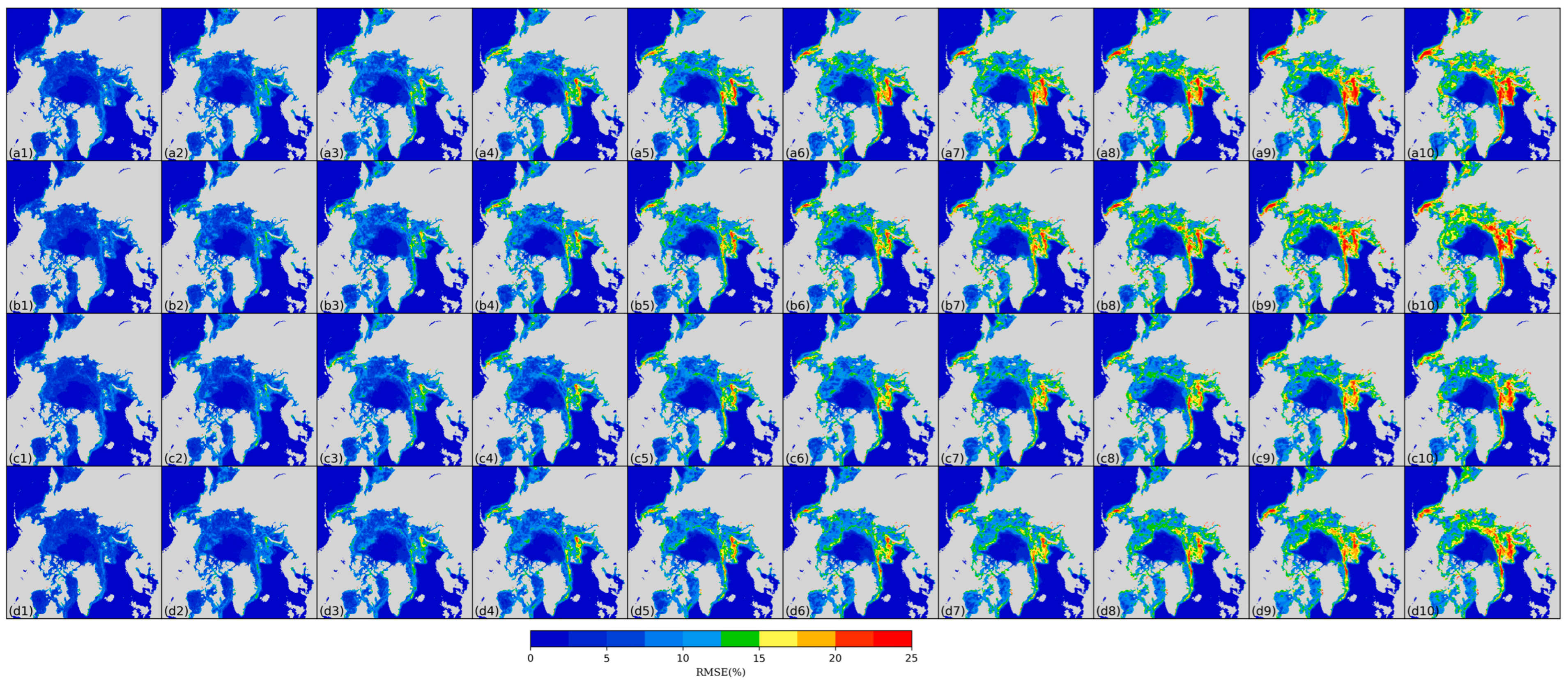
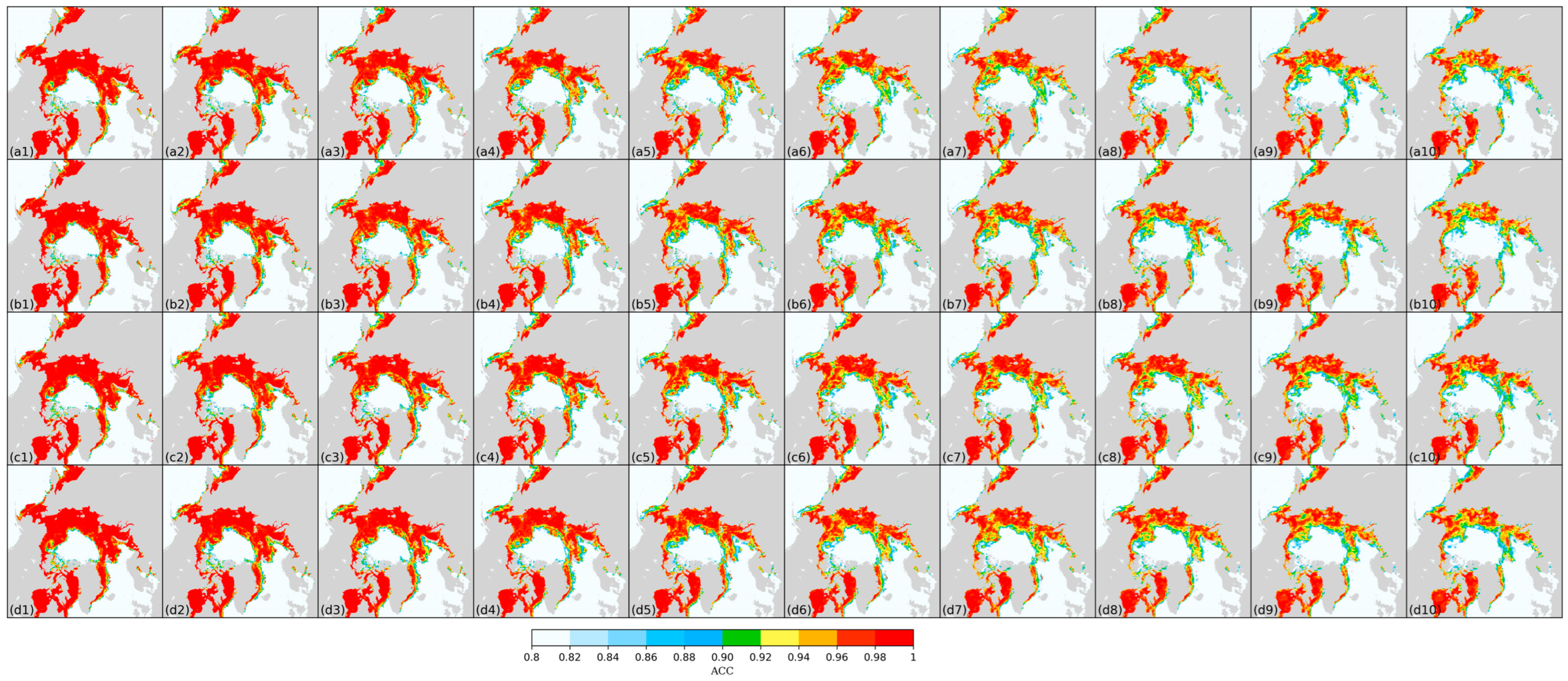
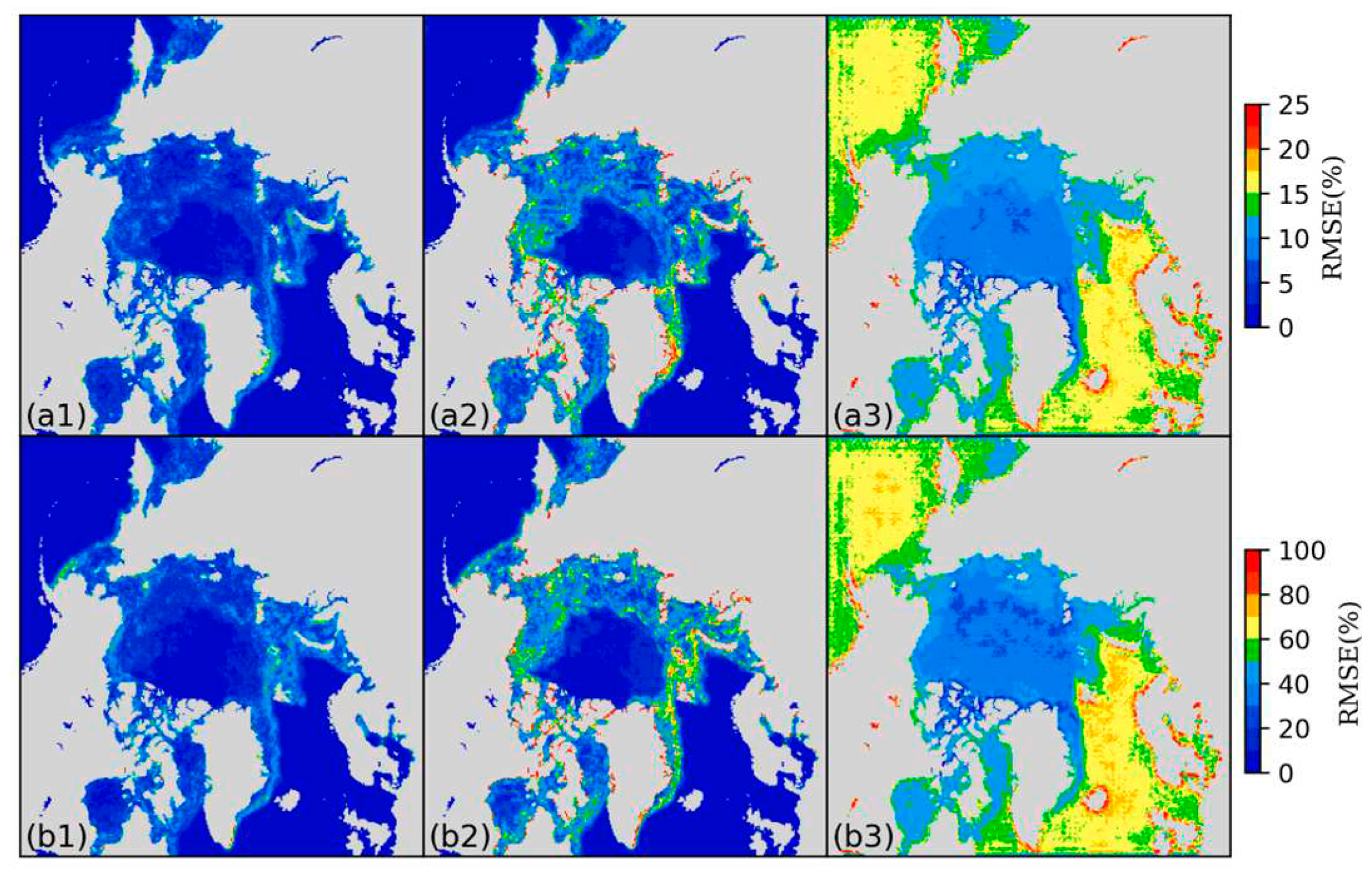
3.1. Daily scale predictions of sea ice concentration
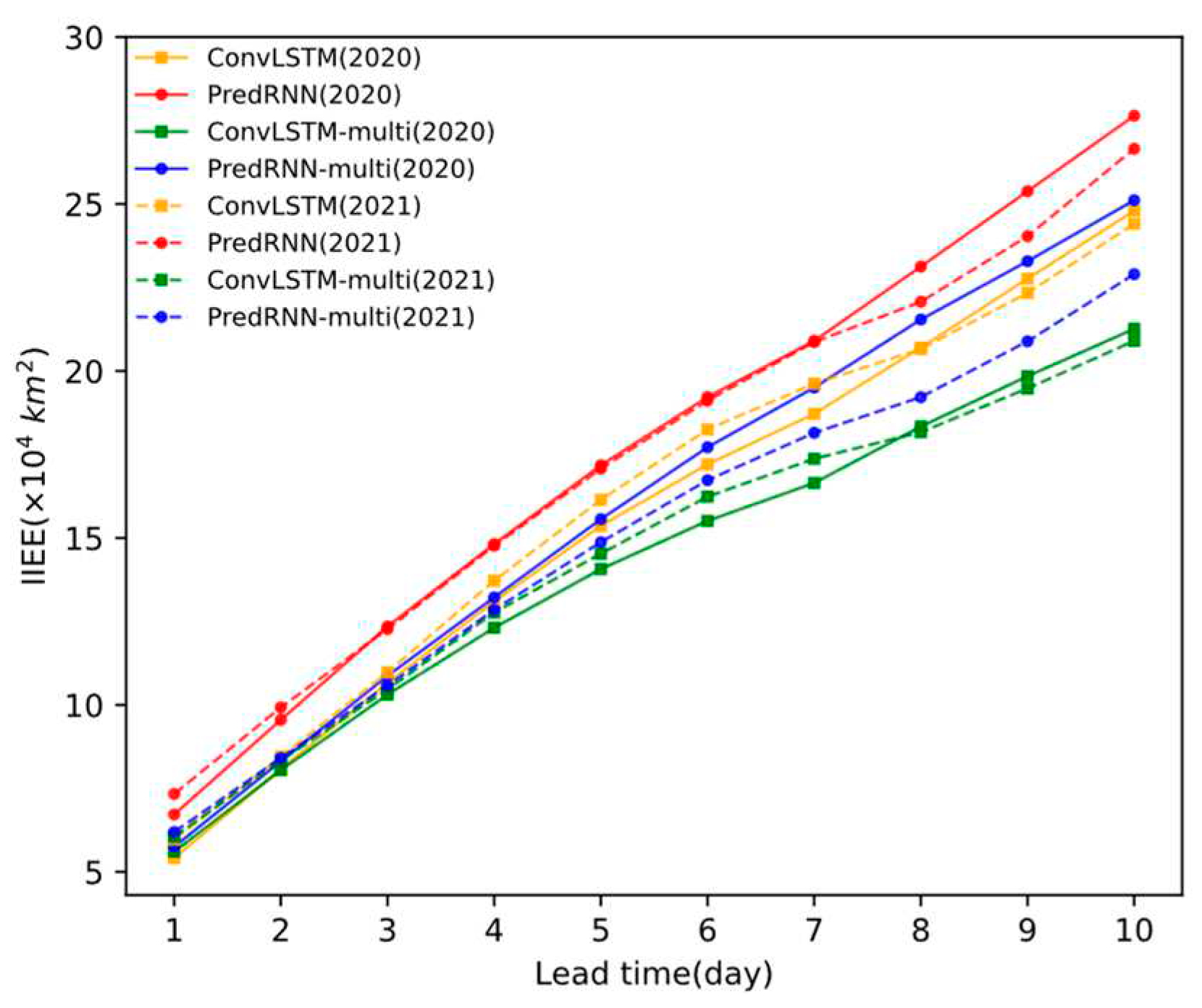
3.2. Sea ice edge prediction accuracy
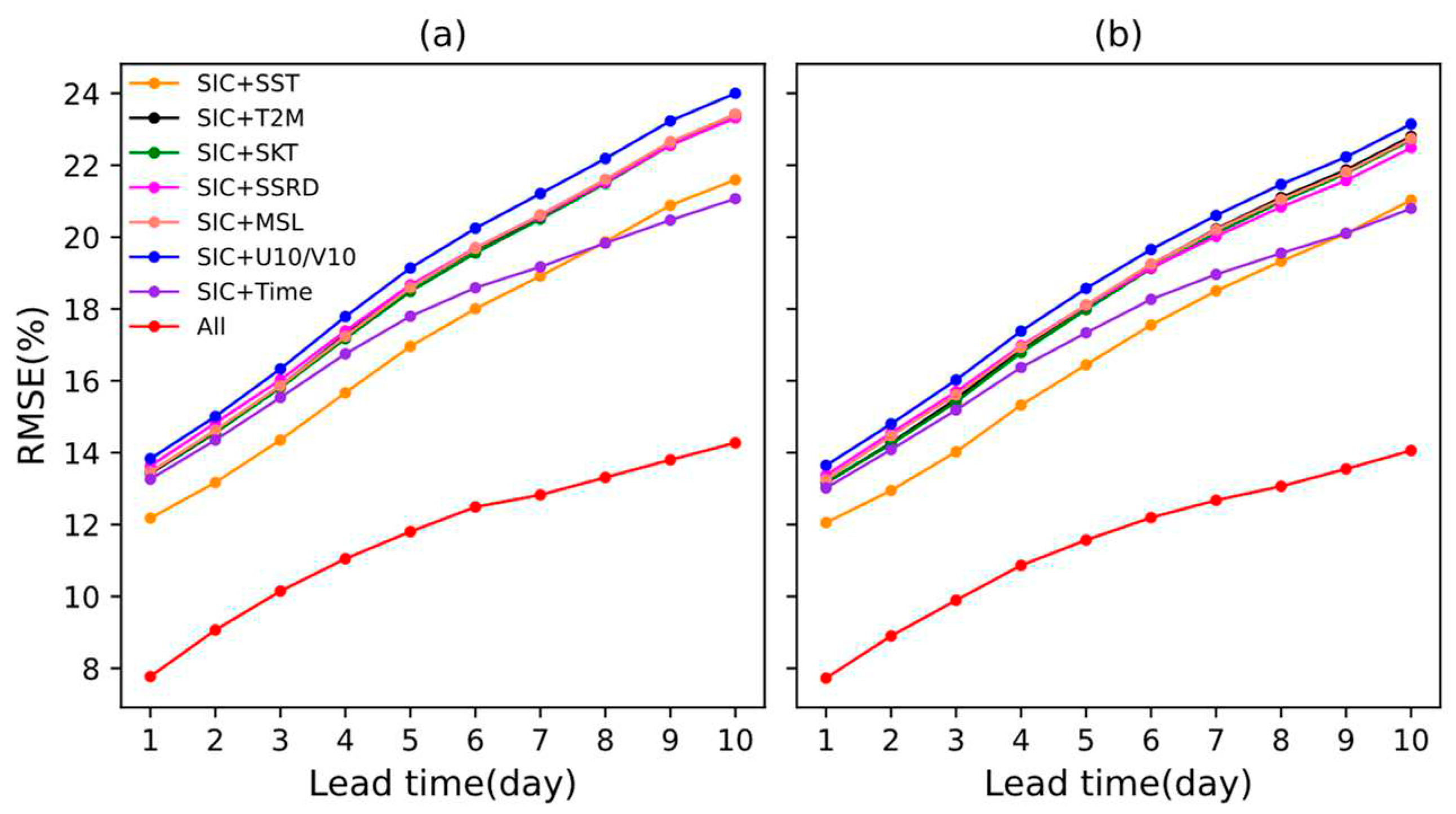
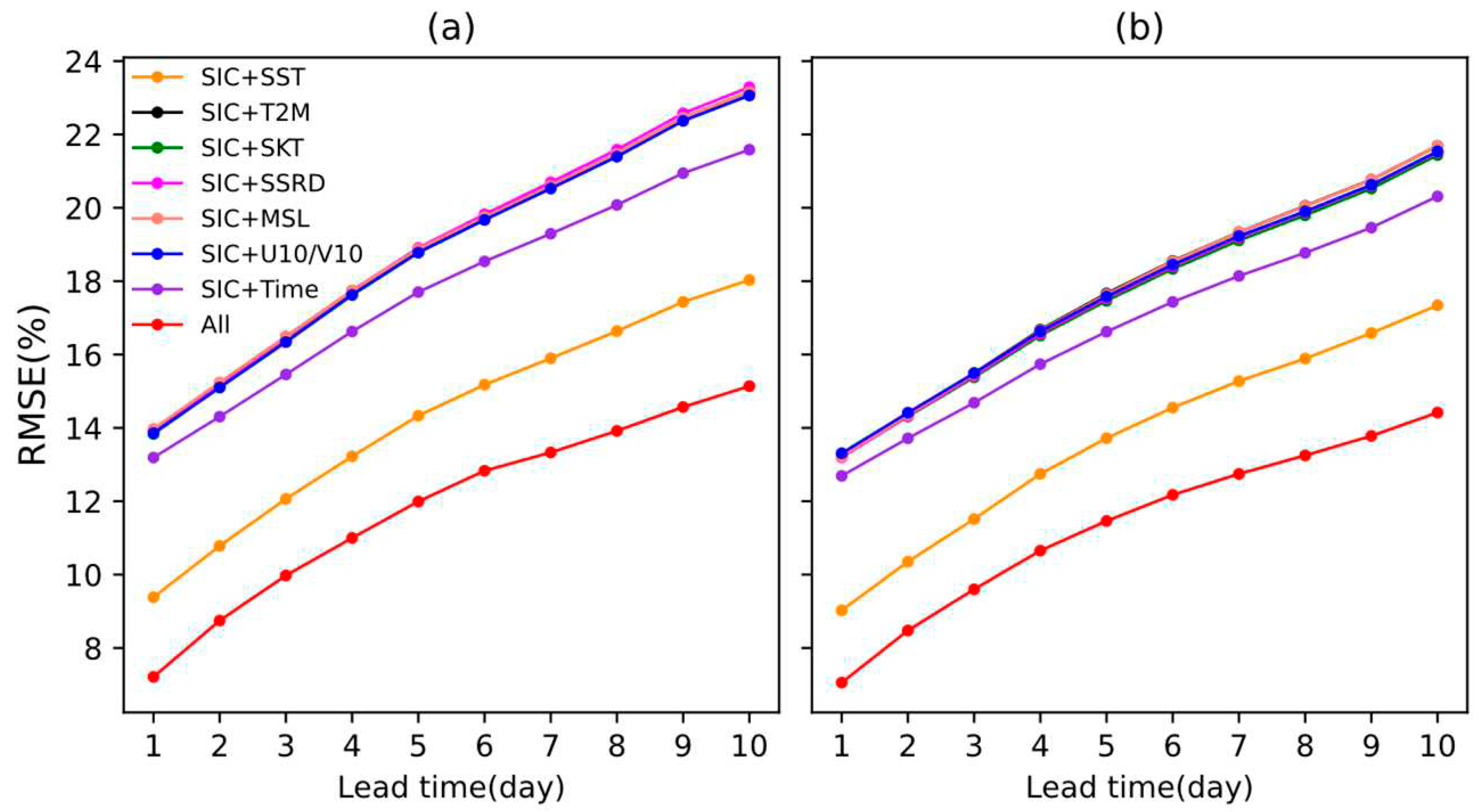
3.3. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
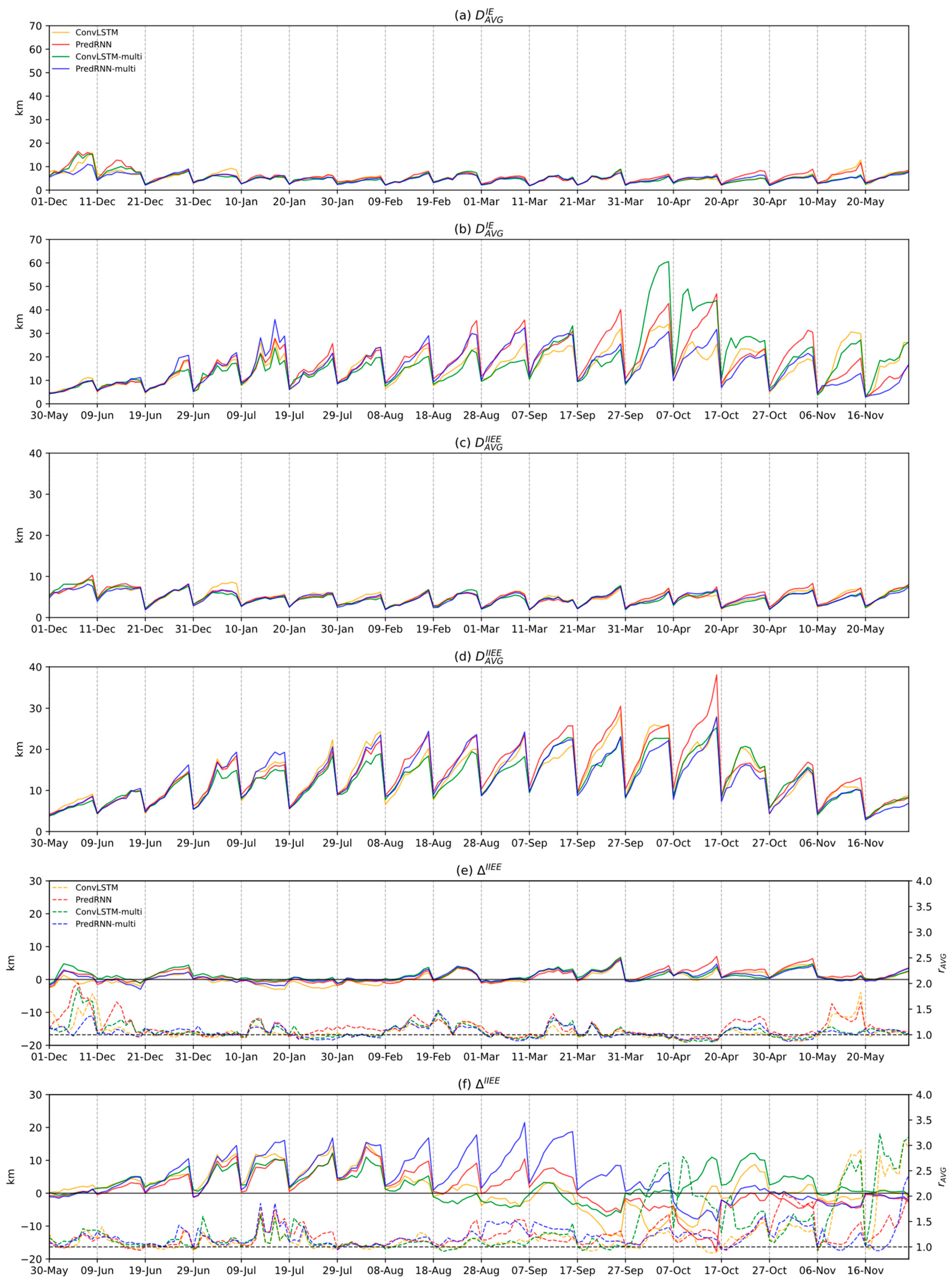
3.4. Prediction ability of the model under extreme conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Model | Spatial resolution | Frequency | Experiment (ensemble members) | |||||
| ACCESS-CM2 | 360×300 | day | SSP126(1) | r1i1p1f1 | SSP245(1) | r1i1p1f1 | SSP585(1) | r1i1p1f1 |
| CESM2-WACCM | 320×384 | day | SSP126(1) | r1i1p1f1 | SSP245(5) | r1i1p1f1 | SSP585(5) | r1i1p1f1 |
| r2i1p1f1 | r2i1p1f1 | |||||||
| r3i1p1f1 | r3i1p1f1 | |||||||
| r4i1p1f1 | r4i1p1f1 | |||||||
| r5i1p1f1 | r5i1p1f1 | |||||||
| MIROC6 | 360×256 | day | SSP126(3) | r11p1f1 | SSP245(3) | r1i1p1f1 | SSP585(3) | r1i1p1f1 |
| r2i1p1f1 | r2i1p1f1 | r2i1p1f1 | ||||||
| r3i1p1f1 | r3i1p1f1 | r3i1p1f1 | ||||||
| MRI-ESM2-0 | 360×364 | day | SSP126(1) | r1i1p1f1 | SSP245(1) | r1i1p1f1 | SSP585(1) | r1i1p1f1 |

References
- Serreze, M.C.; Meier, W.N. The Arctic's sea ice cover: trends, variability, predictability, and comparisons to the Antarctic. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2019, 1436, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Parkinson, C.L. Arctic sea ice variability and trends, 1979-2010. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.C.; Serreze, M.C.; Holland, M.M.; Kay, J.E.; Malanik, J.; Barrett, A.P. The Arctic’s rapidly shrinking sea ice cover: a research synthesis. Climatic change 2012, 110, 1005–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasthale, A.; Sedlar, J.; Koenigk, T.; Fetzer, E. The thermodynamic state of the Arctic atmosphere observed by AIRS: comparisons during the record minimum sea ice extents of 2007 and 2012. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 2013, 13, 7441–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Bi, H.B.; Huang, H.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, Y.L.; Liang, X.; Fu, M.; Zhang, Z.H. Satellite-observed trends in the Arctic sea ice concentration for the period 1979-2016. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 2019, 37, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witze, A. Arctic sea ice hits second-lowest level on record. Nature 2020. [CrossRef]
- Stephen, K. Societal Impacts of a Rapidly Changing Arctic. Current Climate Change Reports 2018, 4, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard-Wrigglesworth, E.; Armour, K.C.; Bitz, C.M.; DeWeaver, E. Persistence and inherent predictability of Arctic sea ice in a GCM ensemble and observations. Journal of Climate 2011, 24, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krikken, F.; Hazeleger, W. Arctic energy budget in relation to sea ice variability on monthly-to-annual time scales. Journal of Climate 2015, 28, 6335–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guemas, V.; Blanchard-Wrigglesworth, E.; Chevallier, M.; Day, J.J.; Deque, M.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J.; Fuckar, N.S.; Germe, A.; Hawkins, E.; Keeley, S.; et al. A review on Arctic sea-ice predictability and prediction on seasonal to decadal time-scales. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 2016, 142, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Aragh, M.; Goessling, H.; Losch, M.; Hutter, N.; Jung, T. Predictability of Arctic sea ice on weather time scales. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-García, R.; Guemas, V.; Chevallier, M.; Massonnet, F. An assessment of regional sea ice predictability in the Arctic ocean. Climate dynamics 2019, 53, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onarheim, I.H.; Eldevik, T.; Årthun, M.; Ingvaldsen, R.B.; Smedsrud, L.H. Skillful prediction of Barents Sea ice cover. Geophysical Research Letters 2015, 42, 5364–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppäranta, M.; Meleshko, V.P.; Uotila, P.; Pavlova, T. Sea Ice Modelling. In Sea Ice in the Arctic: Past, Present and Future, Johannessen, O.M., Bobylev, L.P., Shalina, E.V., Sandven, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 315-387.
- Chi, J.; Kim, H.C. Prediction of Arctic Sea Ice Concentration Using a Fully Data Driven Deep Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; De Silva, L.W.A.; Yamaguchi, H. Artificial Neural Network for the Short-Term Prediction of Arctic Sea Ice Concentration. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Cho, J.; Kang, Y.Q.; Yoon, H.J.; Lee, Y.W. Satellite-Based Prediction of Arctic Sea Ice Concentration Using a Deep Neural Network with Multi-Model Ensemble. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzner, S.; Graversen, R.; Christensen, K.H. Assessment of High-Resolution Dynamical and Machine Learning Models for Prediction of Sea Ice Concentration in a Regional Application. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2020, 125. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.C.; Han, D.; Lee, S.; Im, J. Prediction of monthly Arctic sea ice concentrations using satellite and reanalysis data based on convolutional neural networks. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 1083–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, T.R.; Hosking, J.S.; Perez-Ortiz, M.; Paige, B.; Elliott, A.; Russell, C.; Law, S.; Jones, D.C.; Wilkinson, J.; Phillips, T.; et al. Seasonal Arctic sea ice forecasting with probabilistic deep learning. Nature Communications 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Bogaardt, L.; Attema, J.; Hazeleger, W. Extended-Range Arctic Sea Ice Forecast with Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Networks. Mon. Weather Rev. 2021, 149, 1673–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C. Bootstrap Sea Ice Concentrations from Nimbus-7 SMMR and DMSP SSM/I-SSMIS, Version 3. Available online: https://nsidc.org/data/NSIDC-0079/versions/3 (accessed on 6 5 2023).
- Hersbach, H., Bell, B., Berrisford, P., Biavati, G., Horányi, A., Muñoz Sabater, J., Nicolas, J., Peubey, C., Radu, R., Rozum, I., Schepers, D., Simmons, A., Soci, C., Dee, D., Thépaut, J-N. ERA5 hourly data on single levels from 1940 to present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/10.24381/cds.adbb2d47?tab=form (accessed on 6 5 2023).
- Arctic sea ice minimum is 2nd lowest on record. Available online: https://public.wmo.int/en/media/news/arctic-sea-ice-minimum-2nd-lowest-record (accessed on 6 7 2023).
- Notz, D.; Community, S. Arctic sea ice in CMIP6. Geophysical Research Letters 2020, 47, e2019GL086749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.J.; Chen, Z.R.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.Y.; Wong, W.K.; Woo, W.C. Convolutional LSTM Network: A Machine Learning Approach for Precipitation Nowcasting. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montreal, CANADA, Dec 07-12, 2015.
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Yu, P.; Long, M. PredRNN: A Recurrent Neural Network for Spatiotemporal Predictive Learning. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2022, PP.
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. Advances in neural information processing systems 2014, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, S.; Vinyals, O.; Jaitly, N.; Shazeer, N. Scheduled Sampling for Sequence Prediction with Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montreal, CANADA, Dec 07-12, 2015.
- Melsom, A.; Palerme, C.; Müller, M. Validation metrics for ice edge position forecasts. Ocean Sci. 2019, 15, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goessling, H.F.; Tietsche, S.; Day, J.J.; Hawkins, E.; Jung, T. Predictability of the Arctic sea ice edge. Geophysical Research Letters 2016, 43, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, U.; Loeng, H.; Rudels, B.; Ozhigin, V.K.; Dieck, W. Atlantic water flow through the Barents and Kara Seas. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 2002, 49, 2281–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Årthun, M.; Eldevik, T.; Smedsrud, L.; Skagseth, Ø.; Ingvaldsen, R. Quantifying the influence of Atlantic heat on Barents Sea ice variability and retreat. Journal of Climate 2012, 25, 4736–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.C.; Serreze, M.C.; Holland, M.M.; Kay, J.E.; Malanik, J.; Barrett, A.P. The Arctic's rapidly shrinking sea ice cover: a research synthesis. Climatic change 2012, 110, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfirman, S.; Colony, R.; Nürnberg, D.; Eicken, H.; Rigor, I. Reconstructing the origin and trajectory of drifting Arctic sea ice. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 1997, 102, 12575–12586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, V.; Pavlova, O.; Korsnes, R. Sea ice fluxes and drift trajectories from potential pollution sources, computed with a statistical sea ice model of the Arctic Ocean. Journal of marine Systems 2004, 48, 133–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Source | Unit | Temporal resolution | Spatial resolution | Value range | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sea ice concentration | NSIDC | % | Daily | 25 km | [0,1] | |
| Sea surface temperature | ECMWF ERA5 | K | Hourly | 0.25° | [0,1] | |
| 2m temperature | ECMWF ERA5 | K | Hourly | 0.25° | [0,1] | |
| Skin temperature | ECMWF ERA5 | K | Hourly | 0.25° | [0,1] | |
| Surface solar radiation downwards | ECMWF ERA5 | J m-2 | Hourly | 0.25° | [0,1] | |
| Mean sea level pressure | ECMWF ERA5 | Pa | Hourly | 0.25° | [0,1] | |
| 10m u-component of wind | ECMWF ERA5 | m s-1 | Hourly | 0.25° | [0,1] | |
| 10m v-component of wind | ECMWF ERA5 | m s-1 | Hourly | 0.25° | [0,1] | |
| Land mask | # | # | Daily | 25 km | 0/1 | |
| Cosine of initialization day index | # | # | Daily | 25 km | [–1,1] | |
| Sine of initialization day index | # | # | Daily | 25 km | [-1,1] | |
| Year | Scenarios | MAE | RMSE | nRMSE | ACC | NSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | SSP126 | 19.67% | 29.13% | 69% | 0.76 | 0.53 |
| SSP245 | 23.57% | 32.94% | 78% | 0.74 | 0.47 | |
| SSP585 | 25.44% | 35.2% | 85% | 0.71 | 0.41 | |
| 2021 | SSP126 | 20.08% | 29.22% | 70% | 0.76 | 0.53 |
| SSP245 | 23.32% | 32.11% | 76% | 0.75 | 0.49 | |
| SSP585 | 24.58% | 33.95% | 80% | 0.73 | 0.45 |
| ConvLSTM | PredRNN | ConvLSTM-multi | PredRNN-multi | SSP126 | SSP245 | SSP585 | ||||||||
| 5.44 | 14.97 | 6.28 | 18.10 | 5.45 | 15.51 | 5.05 | 16.86 | 30.50 | 127.46 | 28.74 | 203.26 | 30.85 | 217.10 | |
| 5.03 | 12.51 | 5.15 | 13.72 | 4.87 | 11.74 | 4.79 | 13.52 | 25.18 | 90.62 | 23.32 | 124.80 | 23.36 | 132.34 | |
| 1.42 | 4.70 | 1.68 | 5.68 | 1.55 | 4.39 | 1.36 | 7.73 | 6.92 | 66.94 | 2.62 | 111.80 | 3.54 | 118.79 | |
| 1.07 | 1.22 | 1.19 | 1.27 | 1.10 | 1.31 | 1.05 | 1.23 | 1.22 | 1.4 | 1.24 | 1.54 | 1.33 | 1.56 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




