Submitted:
08 November 2023
Posted:
09 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
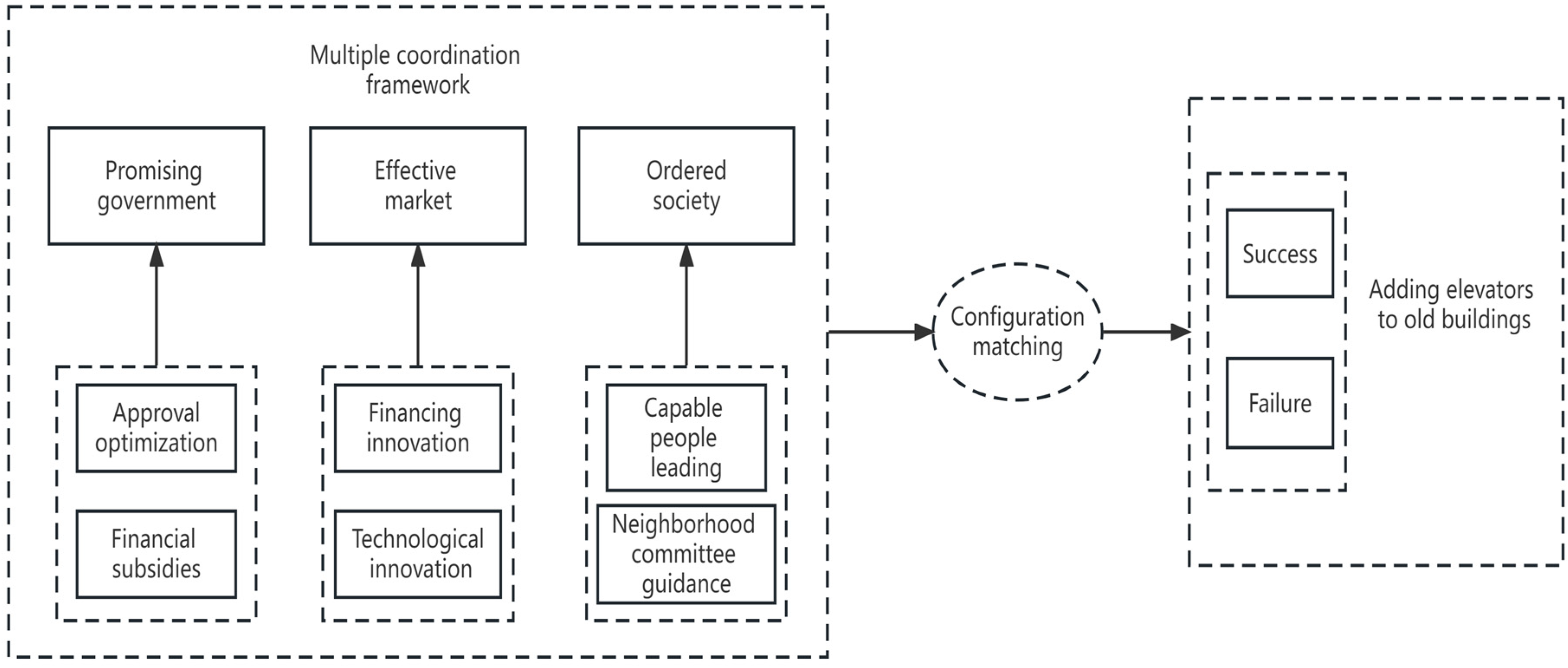
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Research methods and ideas
2.2. Sample selection and data sources
2.3. Variable setting and assignment
2. Results
2.1. Construct a truth table
| Number of cases | Conditional variable | Outcome variable |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approval optimization | Financial subsidies | Financing innovation | Technological innovation | Capable people leading | Neighborhood committee guidance | ||
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
2.2. Necessity analysis of individual variables
2.3. Analysis of successful combination of conditions
2.4. Analysis of failed combination of conditions
2.5. Typical case presentation of success
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, S.L.; Yin, L. The Evolution and Logical Implications of the Policy for Installing Elevators in Old Communities: A Quantitative Analysis Based on 67 Policy Texts. Administrative Tribune 2021, 28, 82–91. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.W.; Yang, Z.Y. From Destructive Conflict to Constructive Conflict: The Way to Break Through the Installation of Elevators in Old Communities. Journal of Tianjin Administration Institute 2020, 22, 60–69. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Song, Y. The Mode Transition of Local Governments in Urban Governance: A Case Study on Elevators Installation on Stocked Housing in Hangzhou City. Urban Development Studies 2021, 28, 127–134. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.S.; Bai, Y.F. Analysis of the Financial Subsidy Effect on the Renovation of Old Residential Areas. Sub National Fiscal Research 2022, 215, 57–68. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ning, C.Q. Theoretical Analysis of the Compensation Method for Sharing the Cost of Installing Elevators in Existing Residential Buildings. Urban Problems 2014, 226, 44–48. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, P. Research on the Operation Management of Old Urban Community Renovation Fund. Construction Economy 2022, 43, 70–75. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Han, H.Y. He driving mechanism of long term governance of the old Community by Interest sharing Social Enterprise: Reshaping the roles and reallocating the resources. Journal of Beijing Administration Institute 2021, 133, 34–41. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.B.; Li, D.B.; Li, W.L. Research on the Problems and Counter Measures of Adding Elevators to Existing residential Buildings in China. Construction Economy 2019, 40, 11–14. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.P. Renovation of Old Residential Community in Towns and Cities: New Impetus of Economic Growth in the Recovery of Covid-19 Panel. Administration Reform 2020, 5, 41–46. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Li, F.Q.; Huang, H. Research on Planning Approaches to Existing Residential Settlements from the Perspective of the Actor Network: Case of Community Micro Renewable of Shanghai. Urban Development Studies 2021, 28, 13–18. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Li, Y. Resolving Conflicts in Installing Elevators for Existing Residential Buildings: Policy Analysis with Deliverable Role playing. Journal of Tianjin Administration Institute 2020, 22, 70–78+87. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, B. Research on the Key Factors Affecting the Demand for Residential Buildings Renovation Catering for the elder people. Reformation & Strategy 2012, 28, 175–178. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.X.; Chen, H. The multiple Streams Approach to Understand Policy Agenda Setting in Community: A Case Study of Elevators Retrofitting on Old Communities in H District of Fuzhou. Urban Development Studies 2021, 28, 11–15. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Wu, L.F. Appeals Promote Publicity: The Rationale of Participating in Community Governance Based on the Field Research of Installing New Elevators in the Long Established Condominium Communities of City H. Zhejiang Social Sciences 2019, 9, 88–95+158. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.F. Interpretation of the “Guiding Opinions of the General Office of the State Council on Comprehensively Promoting the Renovation of Old Urban Residential Areas”. Urban and Rural Development 2020, 14–17. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.Z.; Jia, L.D. Configuration Perspective and Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA): A New Path in Management Research. Journal of Management World 2017, 6, 155–167. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Z.W. Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA) and Research in Journalism and Communication. Chinese Journal of Journalism & Communication 2016, 38, 6–25. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, W.H.; Lan, H.L. Why do Chinese enterprises Completely Acquire High tech Enterprises: A Fuzzy yet Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsqca) Based on 94 Cases. China Industrial Economics 2019, 4, 117–135. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Wang, B.H. Research on the Influence Factors of Internet Public Opinion on University Image: Qualitative Comparative Analysis(qca) based on 30 Public Opinion cases. Journal of National Academy of Education Administration 2020, 8, 77–85. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ran, A.B.; Liu, J.Y. Policy System of China old Residential Community Renovation from the Perspective Policy Tool. Urban Development Studies 2021, 28, 57–63. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xiahou, M.E.; Liu, W.C.; Li, Z.R.; et al. Research on the Policy Text of Old Residential Area Reconstruction from the Perspective of Policy Tools: A Case Study of Nanjing. Modern Urban Research 2023, 3, 15–20. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.P. Public Service Co Production and its Mechanisms Driven by Grassroots: A Case Study of PPP Regeneration of Micro Infrastructure in Y Sub District in S City. Chinese Public Administration 2022, 4, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.X. Research on the Financing Model of the Old Residential Community Renewal under the New Situation. Modern Urban Research 2021, 11, 115–120. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Shan, S.; Li, J.X. Market Oriented Exploration on the Profit Model of the Old Community Reconstruction: Take J Community in Beijing as an Example. Construction Economy 2021, 42, 88–91. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- An, J.M.; Guo, L.; Xu, Y.; et al. Discussion on Micro-fit Sustainable Business Model of Old Residential District Reconstruction from the Perspective of Micro-renewal. Urban Development Studies 2022, 29, 70–76. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Song, F.X.; Kang, S.Y. The Difficult Position and Path of the Reformation of Old Community Under the Background of the Aging Population. Hebei Academic Journal 2020, 40, 191–197. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.L.; Chen, D.L.; Zhang, W.J.; et al. Suitability Evaluation and Integrated Application of Comprehensive Technology for Renovation of old Community based on System Theory. Urban Development Studies 2023, 30, 18–24. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Zhuang, T.; Jiang, L.D.; et al. Research on Type Identification and Renewal Strategy of Old Urban Residential Areas from the Perspective of Evolutionary Resilience. Urban Development Studies 2023, 30, 130–140. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ru, P.; Shen, Y.Y.; Su, J. Do smart renovations increase neighborhood attachment: Evidence from field surveys in two old neighborhoods in Beijing. China Soft Science 2023, 66–75. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.Q.; Wang, Y. Research on the effect of the “Invisible Presence” of Danwei on Community Collective Action: Case Studies of Elevator Installation Projects for Old Residential Districts in Guangzhou. Journal of Public Management 2021, 18, 93–104+172. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.G.; Xiang, F. “Influencing emotion with Informal Norms” and “Influencing emotion with emotion”: Re-understanding of Community Emotional Governance. Chinese Public Administration 2021, 432, 11–18. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.J.; Liao, Q.J.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Research on Collaboration Mode of Regeneration of Old Residential District Dominated by Neighborhood Committee: A Case Study of Yangzhong Community in Guangzhou. Shanghai Urban Planning Review 2021, 160, 16–22. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y. Innovative Ways and Internal Logic of Old Community Governance: A Case Study of HC Community Governance in Beijing. Study & Exploration 2021, 316, 43–50. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Fu, G.W. Governance of Old Urban Neighborhoods: Realistic Obstruction and Future Direction. Tribune of Study 2023, 447, 93–100. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ragin, C.C.; Fiss, P.C. Net Effects Analysis versus Configurational Analysis: An Empirical Demonstration. In Redesigning Social Inquiry: Fuzzy Sets and Beyond; Ragin, C.C., Ed.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2008; pp. 190–212. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Tang, C. The Rationales of the Supply of Communal Public Goods: a Case Study of Installing New Elevators in the Long-established Condominium Communities. Chinese Public Administration 2019, 9, 62–66. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
| 1 | Due to space limitations, it will not be displayed temporarily. Interested readers can request it from the author at email: jinguofu@stu.ynu.edu.cn
|
| Variable category | Variable | Judgment explanation | Reference source | Weight | Assignment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome variable |
Result | Success | / | 51.5% | 1 | |
| Failure | 48.5% | 0 | ||||
| Conditional variable | Promising government | Approval optimization | Introduce relevant policies to assist in approval or optimize approval procedures | Wang [11] ; Guo [1] ; Ran [20] ; Xiahou [21] |
41.2% | 1 |
| Not optimized for approval | 58.8% | 0 | ||||
| Financial subsidies | With financial subsidies | Huang [8] ; Gao [10]; Chen [4] ; Wang [22] |
38.2% | 1 | ||
| No financial subsidies | 61.8% | 0 | ||||
| Effective market | Financing innovation | With financing innovation | Yang [7] ; Li [23] ; Shan [24] ; An [25] |
26.5% | 1 | |
| No financing innovation | 73.5% | 0 | ||||
| Technological innovation | With technological innovation | Song [26] ; Zhang [27] ; Zhang [28] ; Ru [29] |
48.5% | 1 | ||
| No technological innovation | 51.5% | 0 | ||||
| Ordered society | Capable people leading | With capable people leading | Yan [2] ; Li [30] ; Liu [31] ; Shi [13] |
86.8% | 1 | |
| No capable people leading | 13.2% | 0 | ||||
| Neighborhood committee guidance | With neighborhood committee guidance | Zhou [14] ; Tan [32] ; Song [33] ; Feng [34] |
79.4% | 1 | ||
| No neighborhood committee guidance |
20.6% | 0 | ||||
| 条件变量 | Outcome variable | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success | Failure | |||
| Consistency | Coverage | Consistency | Coverage | |
| Approval optimization | 0.800000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| ~Approval optimization | 0.200000 | 0.175000 | 1.000000 | 0.825000 |
| Financial subsidies | 0.457143 | 0.615385 | 0.303030 | 0.384615 |
| ~Financial subsidies | 0.542857 | 0.452381 | 0.696970 | 0.547619 |
| Financing innovation | 0.485714 | 0.944444 | 0.030303 | 0.055556 |
| ~Financing innovation | 0.514286 | 0.360000 | 0.969697 | 0.640000 |
| Technological innovation | 0.571429 | 0.606061 | 0.393939 | 0.393939 |
| ~Technological innovation | 0.428571 | 0.428571 | 0.606061 | 0.571429 |
| Capable people leading | 0.742857 | 0.440678 | 1.000000 | 0.559322 |
| ~Capable people leading | 0.257143 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| Neighborhood committee guidance | 0.885714 | 0.574074 | 0.696970 | 0.425926 |
| ~Neighborhood committee guidance | 0.114286 | 0.285714 | 0.303030 | 0.714286 |
| Political and social dual-drive type | Market and social dual-drive type | Ternary co-drive type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conditional configuration | Path 1 | Path 2 | Path 3 | Path 4 | Path 5 | Path 6 |
| Approval optimization | ● | ● | ⨂ | ● | ● | |
| Financial subsidies | ⨂ | ● | ⨂ | |||
| Financing innovation | ● | ● | ⨂ | ● | ||
| Technological innovation | ● | ⨂ | ● | ⨂ | ||
| Capable people leading | ● | ● | ● | |||
| Neighborhood committee guidance | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| Consistency | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Raw coverage | 0.429 | 0.543 | 0.143 | 0.143 | 0.314 | 0.057 |
| Unique coverage | 0.114 | 0.086 | 0.143 | 0.114 | 0.029 | 0.029 |
| Solution consistency | 1 | |||||
| Solution coverage | 1 | |||||
| Government and market double failure type |
Market failure type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conditional configuration | Path 1 | Path 2 | Path 3 | Path 4 |
| Approval optimization | ⨂ | ⨂ | ⨂ | ⨂ |
| Financial subsidies | ● | ● | ||
| Financing innovation | ⨂ | ⨂ | ⨂ | |
| Technological innovation | ⨂ | ⨂ | ||
| Capable people leading | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Neighborhood committee guidance | ● | ⨂ | ||
| Consistency | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Raw coverage | 0.576 | 0.697 | 0.273 | 0.121 |
| Unique coverage | 0.152 | 0.273 | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Solution consistency | 1 | |||
| Solution coverage | 1 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





