1. Introduction
People have used plants that grew in nature in the treatment of various diseases [
1]. The Asteraceae (Compositae) plant is a very large family that has high medicinal and economic value.
Aster, Inula, Xanthium, Eupatorium, Carpesium, Saussurea and
Taraxacum genera belong to this family, and contain active ingredients such as volatile oils, monoterpenes, diterpenes, triterpenes, flavonoids, phenolic acids, steroids, benzofurans, glycolipids, polyacetylenes, and amino acid derivatives that are included in the composition of various drugs [
2,
3].
Inula species have been widely used in traditional medicine as a household remedy and in modern medicine for many years with their various pharmacological activities [
4].
I. helenium,
I. japonica, and
I. racemosa species of the genus
Inula show various pharmacological activities with their phenolic compounds. Among these activities, there are biological activities such as antibacterial, anticancer, antitumor, hepatoprotective, cytotoxic, antifungal, and antioxidant activities can be listed [
5]. Also, it was reported in previous studies that these phenolic compounds cause effective and selective death in cancer cells such as colon, melanoma, ovary, prostate, lung, and leukemia [
6].
I. helenium taxon can be a good source of antioxidant and antimicrobial substance in foods, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetic agents [
7].
Phenolic compounds in the plant have strong antioxidant, anticancer, and antimicrobial activities. The possibility of an alternative to synthetically produced antioxidants, anticancers, and antimicrobials emerged after the discovery of the biological features of plant-derived compounds. In this way, the way was opened for researchers to conduct studies to uncover these features of plants. In the present study, the in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant, antiproliferative, and Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid (DNA) protective activities of leaf ethanol (L-EtOH), leaf pure water (L-PW), root ethanol (R-EtOH), and root pure water (R-PW) extracts of Inula helenium subsp. pseudohelenium plant, and phenolic content were investigated with High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) in the city of Muş, Turkey.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analysis of phenolic compounds with HPLC
The phenolic content of
I. helenium subsp.
pseudohelenium L-EtOH, L-PW, R-EtOH, and R-PW extracts are given in
Table 1. When the analysis amounts of L-EtOH extract were analyzed with the HPLC, the presence of ascorbic acid (27.63±0.82 μg/mL) was detected in the highest amount and caffeic acid (1.15±0.16 μg/mL) was detected in the least amount. The least amount of 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (0.83±0.02 μg/mL), and the highest amount of catechol (32.46±2.24 μg/mL) were determined in L-PW extract. When L-EtOH and L-PW were compared, highly significant differences were detected in ascorbic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, abscisic acid, curcumin, catechol, caffeic acid, and cinnamic acid amounts. It was found that the R-EtOH extract had the highest amount of ascorbic acid (20.69±0.64 μg/mL) and the least amount of quercetin (0.79±0.01 μg/mL). The lowest amount of abscisic acid (0.94±0.01 μg/mL), and the highest amount of apigenin (29.30±1.15 μg/mL) were detected in the R-PW extract. When R-EtOH and R-PW were compared, highly significant differences were detected in ascorbic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, myricetin, catechol and rosmarinic acid amounts. When the leaf EtOH and PW extracts were compared, highly significant differences were detected in quercetin and salicylic acid amounts. Also, when EtOH and PW extracts in the root were compared, highly significant differences were detected in ascorbic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, abscisic acid, kaempferol, and cinnamic acid amounts. No significant differences were detected in the total phenolic content of all extracts.
It was reported in previous studies that the chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, alantolactone, and isoalantolactone substance amounts from the plant of the genus
Inula were very different with the HPLC Method [
8]. Methanol and water extracts that were obtained from the plant of the genus
Inula contained the most campherol. The gallic acid, rutin, rosmarinic acid, quercetin, and coumarin were detected from the extracts [
9]. Caffeic acid and luteolin [
10] were detected in the leaf extract of the same plant, and quercetin [
11] in the flower extract. In the present study, less phenolic content was detected in pure water extract of the roots. Also, the presence of gallic acid was not detected in the extracts, and the presence of curcumin was detected only in ethanol extracts. When previous studies were considered, their results are partially similar to our study, and it is possible that there are some unanalyzed phenolic substances in each plant extract.
2.2. Antimicrobial activity
The antimicrobial activities of
I. helenium subsp.
pseudohelenium L-EtOH, L-PW, R-EtOH and R-PW extracts against
B. subtilis,
S. aureus,
B. megaterium,
E. aerogenes,
E. coli,
P. aeroginosa,
K. pneumonia,
Y. lipolytica,
C. albicans ve
S. cereviciae microorganisms were determined in mm (
Table 2 and
Table 3). The effects of the antibiotics used for control purposes on microorganisms are given in
Table 4.
The L-EtOH extract showed the highest antimicrobial activity against all microorganisms except for B. megaterium, Y. lipolytica and S. cereviciae. It was found that R-EtOH extract showed the best antimicrobial activity by forming the highest inhibition zone against B. megaterium (21.00±0.00) and Y. lipolytica (29.00±0.00). It was found that L-EtOH and L-PW extracts exhibited the best antifungal activity against S. cereviciae. Also, it was observed that the activities of the extracts increased depending on the increased concentration in general. When the activities of the extracts and antibiotics were compared, it was found that L-EtOH and R-EtOH extracts exhibited high significant differences from antibiotics in general (P<0.0001). It was also found that L-PW extract exhibited better activity than Fluconazole.
It was reported in previous studies that the extracts that were obtained from the roots of
I. helenium show antibacterial activity against
E. coli, B. cereus, S. aureus, E. carotovora, B. subtilis, and
P. aeruginosa bacteria [
12]. It was also reported that water and methanol extracts of
I. viscosa of the genus
Inula show antibacterial activity against Gr positive (Gr+) bacteria, but no activity against Gram negative (Gr-)bacteria [
9]. It was determined that the methanol extracts obtained from the flowers, leaves, and roots of
I. viscosa show antibacterial activity against Gr- bacteria such as
E. coli and
P. aeruginosa [
13]. It was also reported that the ethanol extract obtained from the roots of
I. helenium L. showed significant antimicrobial activities against all tested microorganisms except for
A. niger [
14]. In another study, the ethanol extract of
I. helenium spp.
pseudohelenium showed activity only against
E. coli,
M. morganii and
B. subtilis. Although only methanol extract showed activity against
Y. enterocolitica, water extract showed no antibacterial activity. Also, it was determined that the extracts did not show antifungal activities [
7]. Ethanol (EtOH) extracts obtained in the present study showed the best effect on Gr+ and Gr- bacteria and fungi, while water (PW) extracts showed only antifungal activity. It was also determined that leaf extracts showed better antimicrobial activity compared to root extracts.
Also, it is already known that curcumin exhibits antimicrobial activity against a wide variety of bacteria and fungi [
15]. Gr+ bacteria exhibit a significantly higher susceptibility to curcumin than Gr- ones [
16]. In the present study, only the presence of curcumin was detected in EtOH extracts. In the light of these data, it is considered that the antibacterial activity in EtOH extracts may stem from curcumin. Also, it was found that EtOH extract affected Gr+ more than Gr- ones.
2.3. Antioxidant Results
2.3.1. DPPH. Scavenging Activity
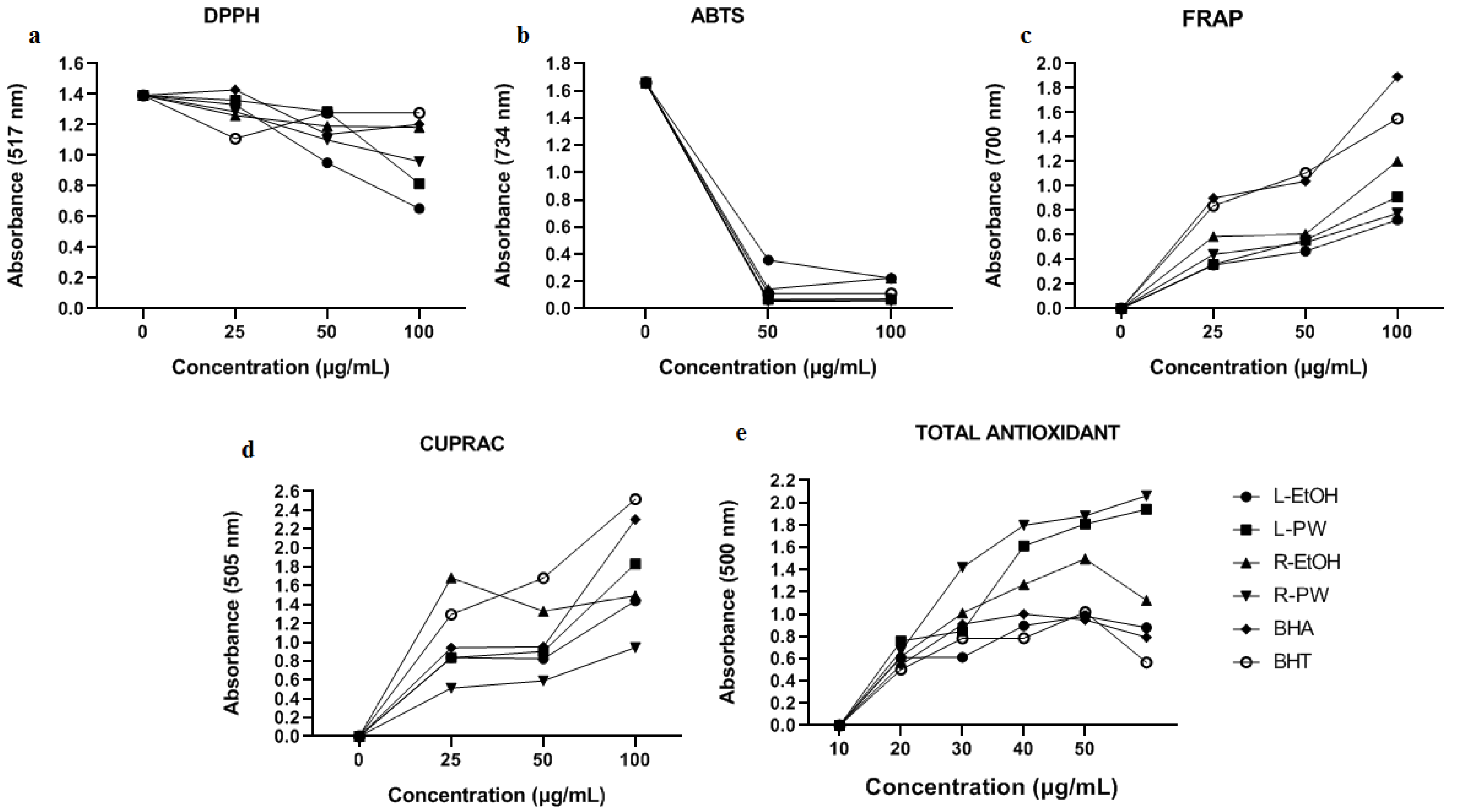
The DPPH radical scavenging activities of L-EtOH, L-PW, R-EtOH, and R-PW extracts were compared with the data of BHA and BHT standard antioxidants. According to our results, it was found that the highest radical scavenging activity was found in the leafs, followed by the roots. Although L-EtOH extract exhibited better activity than L-PW, the opposite was experienced in roots. However, the leaf and root extracts exhibited much higher activity than the standards (
Figure 1a). The DPPH radical scavenging percentages our samples whose activities increased depending on the concentration in 100 µL were listed as follows; L-EtOH: 53.12% ˃ L-PW: 41.49%˃ R-PW: 31.15%˃ R-EtOH: % 15.0˃ BHA: 13.64%˃ RHT: 8.25%.
It is already known that plants that are rich in phenolic compounds have very strong effects in scavenging free radicals. In this context, it was reported that
Inula species that contain secondary metabolites deactivate free radicals by providing hydrogen [
17]. In the literature review, it was found that the results of studies of different taxa of this species and the same genus supported the results of this study. In a previous study [
7] that investigated the antioxidant features of 4 different taxa of
I. helenium species, methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate, and water extracts were used. According to the results of the study, although all the extracts showed performance very close to the standard antioxidant (BHT), it was reported that the ethyl alcohol extract exhibited the highest activity. In the study that was conducted by Berk et al. [
18], according to the results of the DPPH scavenging activity of the water extract of the plant of the genus
Inula, the activity of the extracts increased gradually depending on the concentration. It was reported in another study conducted on
I. helenium [
19] that pure water extract exhibited better activity than ethanol, which is similar to the results of the present study in removing DPPH radicals from the root extract. According to the results of a study that was conducted with different species of
Inula (
I. anatolica,
I. britannica,
I. inuloides,
I. oculus-christi,
I. peacockiana,
I. sechmenii,
I. thapsoides and
I. viscidula), the extracts have strong free radical scavengers [
20]. It was reported in another study that
Inula viscosa has very strong effects on scavenging DPPH radicals [
21].
2.3.2. ABTS+. Scavenging Activity
According to the ABTS radical scavenging activity results, it was found that all extracts showed activity close to or higher than the standards (
Figure 1b). Also, the activity of L-PW and R-PW extracts was found to be higher than that of L-EtOH and R-EtOH extracts. When the fact that ethyl alcohol also partially causes the production of free radicals [
29], it is an expected condition that pure water extracts will have better radical scavenging effects. The percentages of ABTS radical removal in 100 µL of the samples whose activities increase depending on the concentration are listed as follows; R-PW: 96.6% ˃ L-PW: 95.9%≥ BHA: 95.8% ˃BHT: 93.2% ˃ L-EtOH: 86.5%≥ R-EtOH: 86.4%.
Although there are a limited number of studies in the literature on the ABTS radical scavenging activity of this species, the results of some previous studies conducted with different species are similar to the results of the present study. According to the results of the study that was conducted by Petkova et al. [
19], ABTS radical scavenging activity of
I. oculus-christi L. pure water extracts was found to be higher than that of ethanol extract, and it was reported that the activity of the extracts increased in a dose-dependent manner. Also, ABTS radical scavenging activity of the methanol extract of the leaf, root, and flower parts of the plant was evaluated in a thesis for a different species of the genus
Inula [
22]. According to the results, it was found that the root methanol ABTS removal activity was higher than leaf methanol activity. We believe that the reason why the results of this study were not similar to the results of the present study may be because of different species and solvents used.
2.3.3. Ferric Reducing Activity Power (FRAP)
As a result of Fenton Reaction, the free Fe
+3 ions in the medium are transformed into OH, which is the strongest free radical [
23]. For this reason, the FRAP Method was used to measure the conversion of Fe
+3 ion to more stable Fe
+2 ion. According to the results of the study, it is possible to speculate that the iron ion reducing capacities of the samples generally increase depending on the concentration (
Figure 1c). The order of reduction of the extracts and standards at 100 µL concentration was as follows; BHA˃ BHT˃ R-EtOH ˃ L-PW ˃ R-PW˃ L-EtOH.
In their study, Orhan et al. reported that
Inula helenium extract is a strong reducing agent with activity close to ascorbic acid, which is used as a standard [
24]. In a study that was conducted with a plant of the genus
Inula [
18], BHA and BHT were used as standard antioxidants, and it was reported that the reducing power of the extracts increased depending on the concentrations with lower activity rates than the standards. The results of the present study show similarities with the results of this study. Orakcı conducted a study in 2014 on a different species of the
Inula plant in his study [
25]. According to the results of his study, it was reported that the total reducing power of the extracts increased depending on the dose. This is also consistent with the results of our study.
2.3.4. Cupric Reducing Activity Power (CUPRAC)
As seen in
Figure 1d, the copper reducing capacities of the extracts and standards generally increased depending on the concentration. The order of reduction of the extracts and standards at 100 µL concentration was as follows; BHT˃ BHA˃ L-PW ˃ R-EtOH ≥ R-PW˃ L-EtOH. In a study that was conducted with different
Inula species, the Cu
+2 ion reducing capacities of the extracts were examined according to the CUPRAC Method, and it was reported that all of them had very strong reducing capacities [
20]. In the study that was conducted by Petkova et al. [
19], a different species of
Inula plant was examined, and according to the results, it was reported that the pure water extract showed better activity than the ethanol extract, and the reducing power of the extracts increased depending on the concentration. When the results of our study were evaluated, it is possible to argue that they are similar to the results of this study.
2.3.5. Determination of Total Antioxidant Activity
The Thiocyanate Method was used to determine the total antioxidant capacity of the extracts, and the results were compared with the BHA and BHT standards. The absorbance of the samples was taken every 10 hours, and the experiment was ended when the control reached the maximum absorbance at 40th hour (
Figure 1e). The lipid peroxidation destruction percentages of the extracts and standards at 100 µL concentration are listed as follows; BHA: 64.02% L-EtOH: 62.73% ˃BHT: 61.37% ˃ R-EtOH: 43.26% L-PW: % 31.46˃ R-PW: 28.65%.
It was reported previously that the antioxidant potential of I. mentbretiana and I. vicosa extracts was higher than that of Trolox, a standard used for antioxidant potential assays [
24]. According to the results of a study that was conducted with
I. oculus-christi L. the percentage of the lipid peroxidation destruction of the extracts was found to be very close to that of the BHA and BHT standards [
18]. This is similar to the results of the present study.
Preventing ferric and copper ions accumulating in the organism is very important in preventing oxidative damage. Free ferric and cupric ions transform into highly reactive superoxide and hydroxyl radicals due to Fenton and Haber-Weiss reactions. These radicals, which are very reactive, play a role in the formation of various diseases [
26]. According to the results, it was determined that the extracts were generally effective in reducing iron and copper ions. DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging methods, which are radical removal methods, are among the most preferred methods by researchers because the analysis takes a short time, gives quick results and is reliable [
27]. According to the data results, it was determined that the extracts performed close to or higher than standard antioxidants. Peroxidation, which occurs as a result of the reaction of free radicals with lipids, leads to various diseases [
28]. In this method, where lipid peroxides were removed according to the thiocyanate method, it was determined that L-EtOH extract especially strongly scavenged peroxides.
2.4. DNA Protective Activity
If a strand of the super-helicoid structure (Form I) is broken when a molecule interacts with the super-helicoid plasmid DNA, the DNA transforms into unfolded circular DNA (Form II), which moves more slowly in the gel. If both strands are broken, the linear form DNA structure (Form III) is formed [
29]. The changes caused by the extracts in DNA structure can be determined by observing Form I, Form II, and Form III transformation.
The DNA protective activity of
I. helenium subsp.
pseudohelenium L-EtOH, L-PW, R-EtOH, and R-PW extracts was tested by using pBR322 plasmid DNA. In to this method, the ability of extracts at different concentrations to prevent DNA damage was evaluated in the presence of H
2O
2 and DMSO, which are the factors causing damage to DNA. The image obtained as a result of the test that was done for the extracts in the present study is given in
Figure 2.
According to the obtained gel image, it was found that H2O2 decomposed Form I, and completely destroyed the DNA along with DMSO; and DMSO alone had a partial effect on DNA. It was determined that the L-EtOH extract stabilized the DNA after disrupting the scavenging effect of H2O2+DMSO. It was also determined that only L-EtOH extract did not cause any damage to DNA; and L-PW extract eliminated the scavenging effect of H2O2+DMSO on DNA partially, and stabilized Form II and Form III; and when the L-PW extract was applied alone, it kept the DNA more stable.
It was found that the R-EtOH extract did not make any contribution to the scavenging effect of H2O2+DMSO, and also, only the R-EtOH extract had a scavenging effect when applied on DNA. It was observed that the R-PW extract eliminated the scavenging effect of H2O2+DMSO on DNA and stabilized Form II and Form III. It was also determined that when the R-PW extract was applied alone, it kept the DNA more stable.
In a study that was conducted in Turkey, it was investigated whether the aqueous extract of the aerial parts of the plant of the genus
Inula that was collected from the city of Sivas had protective effects against
in vitro DNA damage. It was reported that the water extract had protective effects on the pBR322 DNA plasmid, which was damaged with H
2O
2 and UV radiation [
18]. There are limited studies conducted on DNA damage of the genus
Inula in the literature. Although the results obtained in the present study were similar to the literature, it was found that the ethanol extract obtained from the roots showed destructive activity on DNA.
2.5. Antiproliferative Activity of The Extracts Against Cell Lines
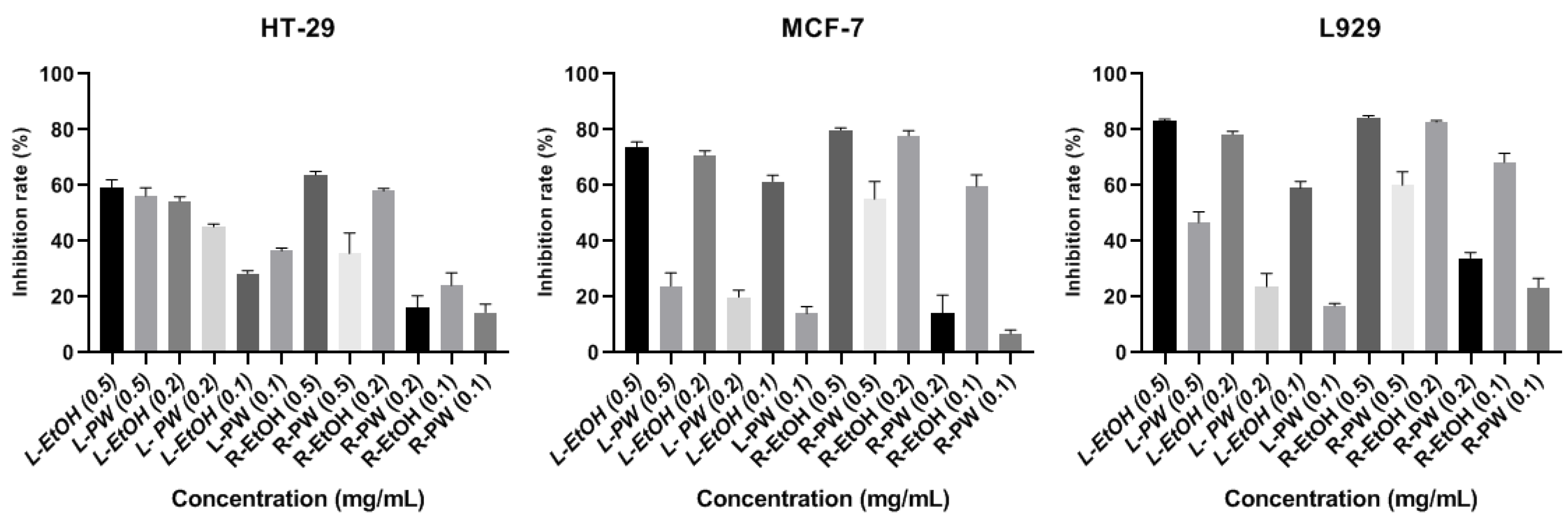
The solutions of the extracts that had three different concentrations (0.1, 0.2 and 0.5 mg/mL) were treated with HT-29, MCF-7, and L-929 cells for 24 hours, and their absorbance was measured spectrophotometrically. The % inhibition values of the cell lines were calculated with the measured absorbances. The inhibition of the cell proliferation was determined with the MTT Test; and % inhibition graphs of the cell lines are given in
Figure 3.
A highly significant difference was detected against the HT-29 cell line when compared to L-PW extract at 2 mg/mL concentration and L-PW extract at 1 mg/mL concentration when compared to L-EtOH. Also, R-EtOH extract exhibited highly significant differences from R-PW extract at all concentrations. It was also found that L-EtOH extract showed highly significant differences against MCF-7 and L-929 cell lines when compared to L-PW, and R-EtOH extract compared to R-PW at all concentrations. When considered in general terms, it was determined that ethanol extracts had higher antiproliferative features than pure water extracts in all cell lines.
Inula species have widespread medical usage areas, and is known for its biological activities such as anticancer, antitumor, hepatoprotective, and cytotoxic [
5]. Previous studies reported that
Inula extracts exhibit
in vitro cytotoxic effects on various cancer cells (colon, melanoma, ovary, prostate, lung and leukemia) [
30,
31]. In the present study, the
in vitro cytotoxic effects of L-EtOH, L-PW, R-EtOH, and R-PW extracts of
I. helenium subsp.
pseudohelenium of
Inula genus that has anticancer effects on HT-29, MCF-7, and L-929 cell lines were determined.
It was reported that the extracts of
I. helenium had the highest hexane extract against MK-1, HeLa, and B16F10 tumor cells, ethyl acetate and butanol extract exhibited very low inhibitory activity, and the aqueous extract did not show any activity [
32]. It was also reported that the methanol extract of
I. viscosa, which belongs to the genus
Inula, exhibited better antiproliferative activity against MCF-7 and T98-G cells than the aqueous extracts [
9]. The methanol extract of the same plant showed cytotoxic effects against SiHa and HeLa [
33,
34], and the ethanol extract of its flowers showed cytotoxic effects against Vero [
35] cell lines. The variation of the cytotoxic effects of plants of the same genus may be because of the chemical composition of the plants in the harvest area and climate [
36]. Also, it is considered that the solvent used in the extraction process affects the content and biological activity of the extract directly [
35]; and it is already known that different solvents used for plant extraction show different molecules in the extract depending on the solvents used [
37]. In the present study, the antiproliferative activities of
I. helenium extracts grown in different areas obtained from different solvents varied as in the literature. Also, the better activity of the EtOH extract compared to the PW extract may be because of the fact that the solvent releases different molecules in the plant.
Curcumin has shown various anticancer effects by suppressing cell proliferation and metastasis and inducing cell death in various cancer types. Curcumin exhibits protective effects against cancer formation [
38,
39]. Also, it is already known that curcumin supplementation shows therapeutic benefits in clinical trials in patients with colorectal, pancreatic, and breast cancer [
40]. According to the data at hand, EtOH extracts exhibited better anticancer activity than PW extracts especially against MCF-7 cell line. It is considered that this is provided by the curcumin in the EtOH extract.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Collection and Extraction of Plant Samples
I. helenium subsp.
pseudohelenium plant was collected in Çöğürlü village of Muş. The identification of the collected plant samples according to the Flora of Turkey was performed by Murat Kurşat (Bitlis, Turkey). The plant samples were turned into herbarium material, and are now stored in Muş Alparslan University, Central Research Laboratories Application and Research Center. The leaves and roots of the plants were removed and left to dry in shade.
I. helenium subsp.
pseudohelenium leaf ethanol (L-EtOH), leaf pure water (L-PW), root ethanol (R-EtOH), and root pure water (R-PW) extracts were prepared as in the previous study of ours [
41].
3.2. Phenolic Analysis with HPLC
Ascorbic acid, gallic acid, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, trans-p-coumaric acid, myricetin, abscisic acid, quercetin, apigenin, kaempferol, curcumin, catechol, vanillin, caffeic acid, cinnamic acid, rosmarinic acid, and salicylic acid standards were used to determine the phenolic substance amount. The necessary procedure and information to load
I. helenium subsp.
pseudohelenium extracts to HPLC were given in our previous study [
42].
3.3. Determination of Antimicrobial Activity
I. helenium subsp.
pseudohelenium L-EtOH, L-PW, R-EtOH and R-PW extracts were dissolved in 0.2, 0.4, and 0.8 mg/ml in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and the antimicrobial activity investigations were performed by using the Hollow Agar Method [
41].
Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633,
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 and
Bacillus megaterium DSM 32,
Enterobacter aerogenes ATCC 13048,
Eshericha coli ATCC 11229,
Pseudomonas aeroginosa ATCC 9027 and
Klebsiella pneumonia ATCC 13883,
Yarrowia lipolytica,
Candida albicans ATCC 10231 and
Saccharomyces cereviciae were used in the study. These microorganisms were obtained from Muş Alparslan University Central Laboratory. The turbidity of the standard bacteria and yeasts (10
6 CFUs/ml) was adjusted according to the Mc Farland 0.5 standard. Erythromycin (E-15), Ampicillin/Sulbactam (SAM-20), Rifampicin (RD-5), Amikacin (AK-30), and Fluconazole (FCA-25) antibiotic discs were used to compare the antimicrobial effects of the extracts used.
3.4. Antioxidant Assays
3.4.1. DPPH Scavenging Activity
The free radical scavenging activities of the extracts were performed according to the previous study of ours [
42]. The extract and standard antioxidants at 25, 50, and 100 μg/mL concentrations were diluted with 3 mL ethanol, and 1 mL 0.1 mM DPPH radical solution was added. After the samples were vortexed, they were left for incubation for 30 minutes. Finally, their absorbances were taken at 517 nm in a spectrophotometer (Schimadzu, 1800). The DPPH radical scavenging percentages of the extracts and standards were calculated with the help of the following equation:
3.4.2. ABTS.+ Scavenging Activity
The ABTS radical cation (ABTS
•+) was produced after reacting a 7 mM stock solution of ABTS with 2.45 mM potassium persulfate and incubating the mixture in the dark at room temperature for 12 hours before using. The ABTS
•+ solution was diluted with methanol to yield an absorbance of 0.7 ± 0.01 at 734 nm. The plant extracts and fractions (1 mL) were allowed to react with 2 ml ABTS
.+ solution, and the absorbance was measured at 734 nm after 1 min [
43].
3.4.3. Ferric Reducing Activity Power (FRAP)
The FRAP Analysis was performed after modifying the method that was applied by Oyaizu [
44]. The plant extracts and standards at different concentrations were made up to 1 mL with pure water, and 0.2 M phosphate buffer (pH 6.6) was added along with 2.5 mL potassium ferric cyanide [K
3Fe(CN)
6] solution (1%). This mixture was kept at 50˚C for 20 minutes. Following these procedures, 2.5 ml 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) was added to the reaction mixture, and 2.5 ml supernatant of the solution was taken, and after 2.5 ml of pure water, 0.5 ml FeCl
3 were added, and the absorbance was read at 700 nm against the blind.
3.4.4. Cupric Reducing Activity Power (CUPRAC)
A total of 0.1 mL of sample solution was taken, and the volume was made up to 1 mL with methanol, and 1 mL CuCl
2 (0.01 M), neocuprine (7.5x10
-3 M), and ammonium acetate solutions were added and mixed with vortex. After 30 minutes at room temperature, the absorbance value was read at 450 nm in the spectrophotometer [
45].
3.4.5. Determination of Total Antioxidant Activity
Total antioxidant activity was determined according to the Thiocyanate Method [
46]. The volume of the samples at 25, 50, and 100 μg/mL concentrations was made up to 2.5 ml with buffer solution, and 2.5 ml linoleic acid was added to the tubes. For control, 2.5 ml buffer solution of linoleic acid was used. Incubation was performed at 37
oC, and 100 μl was taken from these tubes every ten hours, placed in test tubes that contained 4.7 ml ethanol, and 100 μl of Fe
2+ and 100 μl SCN
- solution were added. The absorbances of the samples at 500 nm were read against the blind.
3.5. Effects of Extracts on DNA
The effect of plant extracts on pBR322 plasmid DNA was determined with the Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Method. The plant extracts were prepared with DMSO at 100, 50, and 25 mg/ml concentrations. The procedure for mixing, incubation, and imaging of the samples by loading on agarose gel was performed according to the previous study of ours [
41,
42].
3.6. Antiproliferative Activity of Extracts
In the present study, human colon cancer cell line (HT-29), human breast cancer cell line (MCF-7), and healthy mouse fibroblast (L-929) cell lines were used. Cell lines were obtained from Muş Alparslan University Central Research Laboratories Application and Research Center. Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) was used as the broth medium for these cell lines.
I. helenium subsp.
pseudohelenium extracts were prepared in DMEM at 1, 2, and 5 mg/ml concentrations, and 3-(4,5-dimethyl-thiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) test was applied to determine the cytotoxicity levels [
47]. For the MTT test, 5x10
3 cells in 100 μL medium in each well of 96-well plate were counted with a cell count device, and were then inoculated. The inoculated cells were incubated for 24-48 hours in a 5% CO
2 incubator; and 100 μl of the diluted extracts were added to the cell lines. Only 100 μl of medium was added to the cells in the control wells. Samples were incubated for 24 hours, after which the broth medium in the wells was removed with the help of a vacuum pump; and 10 µl of MTT solution and 90 µl of broth medium were added to each well, and left in an incubator that had 5% CO
2 at 37
oC for 4 hours. The broth medium that had MTT was removed from the medium after 4 hours; and 100 µl Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) was added to each well, and their Optical Density (OD) was measured with a microplate reader (Thermo scientific MULTISKAN GO, Finland) at 540 nm wavelength. A cell line broth medium without sample was used as the control group. The average of the absorbance values that were obtained by reading the control wells was taken, and this value was accepted as 100% viable cells. The % inhibition rates of the cells were calculated with the help of the following formula.
3.7. Statistical Analysis
The results were given as %, mean, and standard error of mean (Mean +- SEM). The phenolic substance amount was compared between themselves, and antimicrobial activity was compared with the results of the standard antibiotics (Erythromycin, Ampicillin/Sulbactam, Rifampicin, Amikacin, and Fluconazole) by using Tukey’s Multiple Comparison and t test after One-Way ANOVA. Those with p<0.05 were considered to be statistically significant, and statistical significance level was indicated with the symbol “*”. In this respect, P<0.05 (significant); *, P<0.01 (very significant); **, P<0.001*** and P<0.0001**** (extremely significant) and P>0.05 (not significant) ns.
4. Conclusions
It has great importance to determine the biological activities of medicinal plants that are used in traditional medicine as household remedy and to use these in modern medicine. The antimicrobial, antioxidant, anticancer, DNA-protective activities and phenolic content of pure water and ethanol extracts obtained from the leaves and roots of Inula helenium subsp. pseudohelenium plant were investigated in the study. According to the HPLC Analysis results, although all of the extracts did not contain gallic acid, it was found that only EtOH extracts contained curcumin. EtOH extracts exhibited antibacterial and antifungal activity, and PW extract exhibited only antifungal activity, and L-EtOH showed the best antimicrobial activity. According to the antioxidant results, it was found that L-EtOH extract scavenged DPPH radicals more than standard antioxidants, and exhibited activity close to the standards in removing ABTS radicals. It was also found that the strongest extract in inhibiting lipid peroxides was L-EtOH. However, according to the FRAP and CUPRAC Test results, it was determined that the L-EtOH extract had a more moderate effect. It can be argued that the reason for this is related to the fact that the chelating feature of the extract is higher than its reducing feature. Only the L-EtOH extract stabilized the DNA after disrupting the scavenging effect of H2O2+DMSO. According to the anticancer activity results of the extracts, EtOH extracts exhibited the strongest effects especially against MCF7. When the results were evaluated in general, it was found that L-EtOH extract showed better activity than other extracts. In future studies, our purpose is especially to isolate and purify the active components of the L-EtOH extract, and to investigate their effects on more different cancer cells. However, more in vivo and in vitro studies are required to explore the full mode of action of the active ingredients of extracts such as L-EtOH.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C. and Y.A.; methodology, M.C. and Y.A.; investigation, M.C.; Y.A. and N.Y.; resources, Y.A. and N.Y.; data curation, N.Y. and Y.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C. and Y.A.; writing—review and editing, M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data of the study are available from the authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank GREENERING COST Action CA18224 supported by COST (European Cooperation Science and Technology).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References
- Njume, C.; Afolayan, A.J.; Ndip, R.N. An overview of antimicrobial resistance and the future of medicinal plants in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infections. Afr. J. Pharmacy Pharmaco.l 2009, 3, 685–699. [Google Scholar]
- Manez, S.; Hernandez, V.; Gıner, R.M.; Rıos, J.L.; et al. Inhibition of pro-inflammatory enzymes by inuviscolide, a sesquiterpene lactone from Inula viscosa. Fitoterapia, 2007, 78, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.J.; Jin, H.Z.; Fu, J.J.; Hu, X.J.; et al. Antranilic acid derivatives from Inula japonic. Chinese Chem Lett., 2008, 19, 556–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Değerli, S.; Berk, S.; Malatyalı, E.; Tepe, B. Screening of the in vitro amoebicidal activities of Pastinaca armenea (Fisch. & C.A.Mey.) and Inula oculus-christi (L.) on Acanthamoeba castellanii cysts and trophozoites. Parasitol Res, 2012, 110, 565–570. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Gao, K. Antimicrobial activities of some thymol derivatives from the roots of Inula hupehensis. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, A.; Khan, M.; Ali, M.; Li, J.; et al. Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer with alantolactone and ısoalantolactone. Sci. World J., 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albayrak, S.; Korkmaz, C.A.E.; Paksoy, M.Y.; Aksoy, A. An investigation on antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of four Inula helenium L. Taxa. Iran J. Sci. Technol., 2015, 39, 473–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Q. Simultaneous determination of chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, alantolactone and ısoalantolactone in Inula helenium by HPLC. J. Chromatogr. Sci., 2014, 53, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkan, E.; Karakaş, F.P.; Yıldırım, A.B.; Taş, İ.; et al. Promising medicinal plant Inula viscosa L.: Antiproliferative, antioxidant, antibacterial and phenolic profiles. Prog. Nutr. 2019, 21, 652–661. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi, H.; Hosni, K.; Zaouali, W.; Amri, I.; et al. Comprehensive phytochemical analysis, antioxidant and antifungal activities of Inula viscosa aiton leaves. J. Food Saf., 2016, 36, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimech, I.; Weiss, E.K.; Chedea, V.S.; Marin, D.; et al. Evaluation of anti-oxidant and acetylcholinesterase activity and identification of polyphenolics of the invasive weed Dittrichia viscosa. Phytochem Anal, 2014, 25, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.L. , Chen, J., Jin, X.J., Yang, J.L. et al. Sesquiterpenoids, alantolactone analogues, and seco-guaiene from the roots of Inula helenium. Tetrahedron, 2011, 67, 9193–9198. [Google Scholar]
- Gökbulut, A.; Ozhan, O.; Satılmış, B.; Batcıoglu, K.; et al. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities and phenolic compounds of selected Inula species from Turkey. Nat Prod Com, 2013, 8, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diguță, C.; Cornea, C.P.; Ioniță, L. ; Brîndușe. G. et al. Studies on antimicrobial activity of Inula helenium L Romanian cultivar. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 19, 9699. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Kadir, H.A.; Hassandarvish, P.; Tajik, H.; et al. A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 186864. [Google Scholar]
- Lutomski, J.; Kedzia, B.; Debska, W. Wirkung des äthanolextraktes und aktiver substanzen aus curcuma longa auf bakterien und pilze. Planta Med, 1974, 26, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trendafilova, A.; Ivanova, V.; Rangelov, M.; Todorova, H.; et al. Caffeoylquinic acids, cytotoxic, antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase and tyrosinase enzyme inhibitory activities of six Inula species from Bulgaria. Chem Biodivers 2020, 17, 2000051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, Ş.; Bektaş, B.; Arslan, S. Screening of the antioxidant, antimicrobial and DNA damage protection potentials of the aqueous extract of Inula oculus-christi. Afr. J. Pharmacy Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Petkova, N.; Vrancheva, R.; Mihaylova, D.; Ivanov, I.; et al. Antioxidant activity and fructan content in root extracts from elecampane (Inula helenium L.). J. Bio. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 4, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ceylan, R.; Zengin, G.; Mahomoodally, M.; Fawzi, S.K.; et al. Enzyme inhibition and antioxidant functionality of eleven Inula species based on chemical components and chemometric insights. Biochem. Syst. Ecol., 2021, 95, 104–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheyar-Kraouche, N.; Silva, A.B.; Serra, A.T.; Bedjou, F.; et al. Characterization by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and antioxidant activity of an ethanolic extract of Inula viscosa leaves. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal, 2018, 156, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köken, T.; Serteser, M.; Kahraman, A.; Biyokimya. In: Dilek O.N. (ed) Karaciğer, Afyon Kocatepe Üniversitesi Klinik Tıp Kitapları Serisi, (Ankara), 2003, p.58.
- Famurewa, A.C.; Asogwa, N.T.; Aja, P.M.; Akunna, G.G.; et al. Moringa oleifera seed oil modulates redox imbalance and iNOS/NF-κB/caspase-3 signaling pathway to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic mechanisms against anticancer drug 5-fluorouracil-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. S. Afr. J. Bot., 2019, 127, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, N.; Gökbulut, A.; Orhan, D. Antioxidant potential and carbohydrate digestive enzyme inhibitory effects of five Inula species and their major compounds. S. Afr. J. Bot., 2017, 111, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orakcı, M. Ebenus laguroides Boiss. Var. laguroides, Inula thapsoides Subsp. thapsoides ve Onosma sericeum Bitkilerinin in vitro Antioksidan Aktivitelerinin Belirlenmesi, Yüksek Lisans Tezi, (Sivas), 2014, p.38.
- Bayarsaikhan, G.; Avan, A.N.; Demirci Çekiç, S.; Apak, R. Use of modified CUPRAC and dinitrophenylhydrazine colorimetric methods for simultaneous measurement of oxidative protein damage and antioxidant defense against oxidation. Talanta 2019, 204, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savci, A. Biological active compounds and biological activities of the foam used in the traditional kerebiç dessert. International Food Research Journal 2022, 29, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.W.; Cha, H.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; et al. NOX4 promotes ferroptosis of astrocytes by oxidative stress-induced lipid peroxidation via the impairment of mitochondrial metabolism in Alzheimer's diseases. Redox Biology 2021, 4, 101947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Barcelo, J.M.; Lee, B.; Kohlhagen, G.; et al. Human Mitochondrial Topoisomerase I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2001, 98, 10608–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seca, A.M.; Grigore, A.; Pinto, D.C.; Silva, A.M. The genus Inula and their metabolites:From ethnopharmacological to medicinal uses. J Ethnopharmacol 2014, 154-2, 286–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belayachi, L.; Aceves-Luquero, C.; Merghoub, N.; Bakri, Y.; et al. Screening of north african medicinal plant extracts for cytotoxic activity against tumor cell lines. European J. Med. Plants 2013, 3-3, 310–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, T.; Shimada, Y.; Nagao, T.; Okabe, H.; et al. , Antiproliferative sesquiterpene lactones from the roots of Inula helenium. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2002, 25, 1370–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merghoub, N.; El Btaouri, H. , Benbacer, L., Gmouh, S. et al. Inula viscosa extracts ınduces telomere shortening and apoptosis in cancer cells and overcome drug resistance. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbacer, L.; Merghoub, N.; El Btaouri, H.; Gmouh, S. et al. Antiproliferative effect and induction of apoptosis by Inula viscosa L. and Retama monosperma L. extracts in human cervical cancer cells, in: Rajamanickam, R. (Ed.), Topics on Cervical Cancer with an Advocacy for Prevention, (InTech, Rijeka, Croatia), 2012, p.267.
- Talib, W.H.; Mahasneh, A.M. Antiproliferative activity of plant extracts used against cancer in traditional medicine. Sci. Pharm., 2010, 78, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, M.; Chahmi, N.; El Mzibri, M.; Gmouh, S.; et al. Cytotoxic effect and chemical composition of Inula viscosa from three different regions of Morocco. European J. Medm. Plants 2016, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 37. Bar-Shalom, R,; Bergman, M.; Grossman, S. et al. Inula viscosa extract inhibits growth of colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through ınduction of apoptosis. Front. Oncol. 2019, 10, 2–27.
- Liu, H.T.; Ho, Y.S. Anticancer effect of curcumin on breast cancer and stem cells. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness, 2018, 7, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Duan, D.; Yao, J.; et al. Inhibition of thioredoxin reductase by alantolactone prompts oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis of HeLa cells. Biochem. Pharmacol., 2016, 102, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Patchva, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Therapeutic roles of curcumin: Lessons learned from clinical trials. AAPS J., 2013, 15, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alan, Y.; Yılmaz, N. Phenolic Substance Contents and Biological Activities of Verbascum Insulare Boıss. & Heldr. Extracts. Farmacıa 2019, 67, 641–647. [Google Scholar]
- Savci, A.; Kocpinar, E.F.; Alan, Y.; Kursat, M. Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and DNA protection activities of some Tanacetum species and phenolic richness in their ethanolic extracts. Int. Food Res. J. 2020, 27, 160–170. [Google Scholar]
- Re, R.V.E. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical decolorization assay. Free Radic. Bio. Med. 1999, 29, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyaizu, M. Studies on products of browning reaction antioxidative activities of products of browning reaction prepared from glucosamine. Jpn. J. Nutr. Diet. 1986, 44, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, A.; Savci, A.; Alan, Y.; Birsen, H. Synthesis and spectroscopic properties of 4,4′-bipyridine linker bioactive macrocycle boronate esters: photophysical properties and antimicrobial with antioxidant studies. J. Organomet. Chem., 2021, 941, 121807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, N.; Buldurun, K.; Alan, Y.; Savci, A.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, antioxidant, antimicrobial and DNA binding properties of ruthenium(II), cobalt(II) and nickel(II) complexes of Schiff base containing o vanillin. Res. Chem. Intermed., 2019, 45, 3525–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkış, E.; Keleştemür, Ü.; Alan, Y.; Turan, N.; et al. Cobalt and ruthenium complexes with pyrimidine based schiffbase: Synthesis, characterization, anticancer activities and electrochemotherapy efficiency. J. Mol. Struct., 2021, 1226, 129402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).